How to Download, Install, and Configure OpenSSH for Windows
Download
To get started with OpenSSH for Windows, select the appropriate file from the list on the right. Choose the version that matches your system’s architecture:
- ARM: For ARM-based Windows devices
- ARM64: For 64-bit ARM architecture
- Win32: For 32-bit Windows systems
- Win64: For 64-bit Windows systems
Download the corresponding installer (.msi) or zip file for your platform. Symbol files are also available for debugging purposes if needed.
Install
For MSI Installers:
- Run the downloaded .msi file.
- Follow the on-screen instructions in the installation wizard.
- The default installation location is usually
C:\Program Files\OpenSSH, but you can choose a different path if desired. - After installation, OpenSSH server and client tools will be available on your system.
For Zip Files:
- Download the zip file for your platform.
- Extract the contents to your preferred location, such as
C:\OpenSSH. - Add the OpenSSH binaries to your system’s PATH environment variable to make the command-line tools accessible.
Configure
Server Configuration:
- Go to the OpenSSH installation directory.
- Locate the
sshd_configfile. This file allows you to customize settings such as:- Permitted users
- Authentication methods (password or key-based)
- Port and address configurations
- Edit the configuration file with a text editor to meet your security requirements.
- Save the changes and restart the OpenSSH server service.
Client Configuration:
OpenSSH client tools, including ssh and scp, are included. Use these tools to securely connect to remote systems. For example, use the ssh command to connect to a remote server.
Verify Installation
After installation, verify that OpenSSH is properly installed by checking the version information through the command line.
- OpenSSH for Windows allows you to securely access remote computers with Windows-native tools using the command line interface.
- To install OpenSSH Client and Server on Windows, go to Settings > System > Optional features > View features, search for “OpenSSH“, and continue to install the components.
Windows users normally use the Remote Desktop Protocol to access other Windows devices remotely. As RDP offers a remote graphical user interface (GUI), it is a convenient method for remote access. However, it offers limited functionality, especially if you are a sysadmin. For that purpose, some people prefer to use the Secure Socket Shell (SSH) protocol.
SSH provides a command-line interface to remote computers and servers, and therefore, a more granular control over them. Previously, we used third-party apps like “PuTTY” and “MobaXterm” to develop an SSH connection with the remote devices. However, Microsoft has made a Windows-native SSH client available which can be used instead.
OpenSSH for Windows is a Feature on Demand (FoD) add-on for the Windows operating system. This means that although it is free, it is not installed by default, and needs to be installed manually. If you install it, you can use the SSH protocol through the native command line to access and control the remote computers, provided that your user account has the required privileges.
This guide will show you how to install and use OpenSSH for Windows. These will work on both Windows 11 and Windows 10 (version 1809 and above). Using this guide, you can install both OpenSSH Client and OpenSSH Server in a few easy steps.
Table of Contents
What is OpenSSH
The Secure Socket Shell, or Secure Shell is a networking protocol that allows a remote connection with another device securely. SSH uses a client-server model to communicate with remote computers and ensures data integrity through encryption. It uses multiple layers of the OSI reference model to make sure that the communicated data between the devices is secure.
Originally, OpenSSH was a tool used for remote connection with other devices which comes preinstalled in Linux-based operating systems. Since it is an open-source utility, it has been modified for other platforms, including Windows.
Microsoft has now made “OpenSSH for Windows” available that you can install with a small update package.
Before installing OpenSSH, your system needs to meet a few requirements.
Requirements for OpenSSH for Windows
Before proceeding to install either OpenSSH Client or Server, you must make sure that your PC satisfies the prerequisites, which are:
- OS should be Windows 10 version 1809 or later.
- The PowerShell version should be 5.1 or above
- The user account must be a member of the Administrators group.
To check the OS version, run the following command in the Run Command box:
WinVerTo check the PowerShell version, run the following command in PowerShell:
$PSVersionTable.PSVersionTo check if your user is a member of the Administrators group, run the following command in PowerShell. If it returns “True“, it means that you are a member of the Administrator group.
(New-Object Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal([Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent())).IsInRole([Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole]::Administrator)Once you have made sure that your PC satisfies these requirements, you may continue to install OpenSSH Client, OpenSSH Server, or both.
Install OpenSSH on Windows
Implement the following steps to install OpenSSH on your Windows computer to access it remotely. Optionally, you can also install “OpenSSH Server” to access this device from another PC using the SSH protocol.
-
Press the Windows key + i to open the Settings app.
-
Click System.
-
Go to “Optional Features“.
Open the optional features settings page -
Click “View features“.
View optional features -
Search for “OpenSSH“.
-
Select “OpenSSH Client” and optionally, “OpenSSH Server“, and then click Next.
Select OpenSSH Client and Server -
Click Install.
Install OpenSSH Client and Server on Windows
After performing these steps, OpenSSH Client (and Server) will be installed on your computer.
Note: These features can take some time to install.
Alternative to the steps above, you can also run the following command in an elevated PowerShell instance to install OpenSSH for Windows:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like 'OpenSSH*'This command will install both OpenSSH Client and OpenSSH Server.
Using OpenSSH Client for Windows
Once OpenSSH Client for Windows has been installed, you can begin using it to connect with remote PCs on the network. Of course, OpenSSH has to be configured on the remote PC first, the method for which has been given below in this post.
First, confirm that it has been installed successfully by running the following command in Command Prompt:
ssh
Once confirmed, you can access a remote PC on the network which has SSH configured using this command:
ssh [Username]@[ServerName]
Note: You may be asked for user credentials if connecting for the first time.
Note that the command above will try to connect to the remote device using the default port, which is 22. If you want to use a different port, then you will need to use this command instead:
ssh [Username]@[ServerName] -p [PortNumber]
Configuring OpenSSH Server for Windows
If you have installed the OpenSSH Server on your Windows PC, you will need to configure it before you can connect to this PC using the SSH protocol.
Configuring the OpenSSH server can be a bit thicker. You need to make sure that it is allowed through the firewall and the proper ports. Therefore, it involves a few steps. Here is what you need to do:
-
First, run the following command in an elevated PowerShell to run the “sshd” service automatically.
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic' -
Now start the service with this command:
Start-Service sshd -
Now use the following command to ensure that the SSH server is running and waiting for the connections on port 22:
netstat -na| find ":22" -
Now ensure that the Windows Defender Firewall allows inbound connections to Windows through the TCP port 22 with this command:
Get-NetFirewallRule -Name *OpenSSH-Server* |select Name, DisplayName, Description, EnabledConfirm rules for SSH server connection -
[Conditional] If you find that the rule is missing or disabled, run the following command to create a new inbound rule:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22 -
To change the default rules for the SSH connection, run the following command in PowerShell which will open the respective OpenSSH file in Notepad:
start-process notepad C:\Programdata\ssh\sshd_config -
Make the necessary changes in the file to manage the permissions, and then save the file using the CTRL + S shortcut keys.
Here are a few examples of the rules:
- Deny domain user:
DenyUsers itt\administrator@192.168.10.10 - Allow a domain group:
AllowGroups itt\sshadmins - Allow local groups:
AllowGroups Administrators
Manage SSH permissions - Deny domain user:
-
After making the changes, run the following command in PowerShell:
restart-service sshd
After performing the steps above, you should be able to connect to this PC using the SSH protocol. For that purpose, use the command ssh [Username]@[ServerName] as discussed above.
Conclusion
With SSH, you do not need to perform a long string of operations to perform a simple task. Instead, you can access it with Windows-native OpenSSH and continue to manage the remote PC using commands. This makes OpenSSH for Windows an excellent utility for network and system administrators.
В современных версиях Windows уже есть встроенный SSH сервер на базе пакета OpenSSH. В этой статье мы покажем, как установить и настроить OpenSSH сервер в Windows 10/11 и Windows Server 2022/2019 и подключиться к нему удаленно по защищенному SSH протоколу (как к Linux).
Содержание:
- Установка сервера OpenSSH в Windows
- Настройка SSH сервера в Windows
- Sshd_config: Конфигурационный файл сервера OpenSSH
- Подключение по SSH к Windows компьютеру
- Логи SSH подключений в Windows
Установка сервера OpenSSH в Windows
Пакет OpenSSH Server включен в современные версии Windows 10 (начиная с 1803), Windows 11 и Windows Server 2022/2019 в виде Feature on Demand (FoD). Для установки сервера OpenSSH достаточно выполнить PowerShell команду:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like ‘OpenSSH.Server*’ | Add-WindowsCapability –Online
Или при помощи команды DISM:
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
Если ваш компьютер подключен к интернету, пакет OpenSSH.Server будет скачан и установлен в Windows.
Также вы можете установить сервер OpenSSH в Windows через современную панель Параметры (Settings -> Apps and features -> Optional features -> Add a feature, Приложения -> Управление дополнительными компонентами -> Добавить компонент. Найдите в списке OpenSSH Server и нажмите кнопку Install).
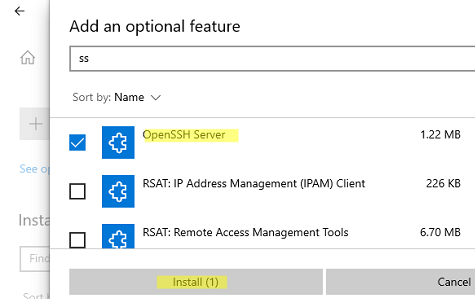
На изолированных от интернета компьютерах вы можете установить компонент с ISO образа Features On Demand (доступен в личном кабинете на сайте Microsoft: MSDN или my.visualstudio.com). Скачайте диск, извлеките его содержимое в папку c:\FOD (достаточно распаковать извлечь файл
OpenSSH-Server-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~.cab
), выполните установку из локального репозитория:
Add-WindowsCapability -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0 -Online -Source c:\FOD
Также доступен MSI установщик OpenSSH для Windows в официальном репозитории Microsoft на GitHub (https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/). Например, для Windows 10 x64 нужно скачать и установить пакет OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi. Следующая PowerShell команда скачает MSI файл и установит клиент и сервер OpenSSH:
Invoke-WebRequest https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/download/v8.9.1.0p1-Beta/OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -OutFile $HOME\Downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -UseBasicParsing
msiexec /i c:\users\root\downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi
Также вы можете вручную установить OpenSSH сервер в предыдущих версиях Windows (Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2016/2012R2). Пример установки Win32-OpenSSH есть в статье “Настройка SFTP сервера (SSH FTP) в Windows”.
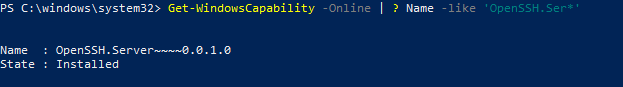
Чтобы проверить, что OpenSSH сервер установлен, выполните:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like 'OpenSSH.Ser*'
State : Installed
Настройка SSH сервера в Windows
После установки сервера OpenSSH в Windows добавляются две службы:
- ssh-agent (OpenSSH Authentication Agent) – можно использовать для управления закрытыми ключами если вы настроили SSH аутентификацию по ключам;
- sshd (OpenSSH SSH Server) – собственно сам SSH сервер.
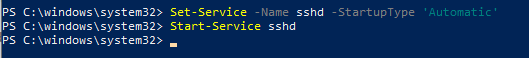
Вам нужно изменить тип запуска службы sshd на автоматический и запустить службу с помощью PowerShell:
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Start-Service sshd
С помощью nestat убедитесь, что теперь в системе запущен SSH сервер и ждет подключений на порту TCP:22 :
netstat -na| find ":22"
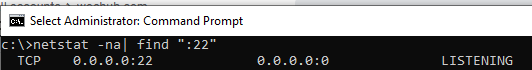
Проверьте, что включено правило брандмауэра (Windows Defender Firewall), разрешающее входящие подключения к Windows по порту TCP/22.
Get-NetFirewallRule -Name *OpenSSH-Server* |select Name, DisplayName, Description, Enabled
Name DisplayName Description Enabled ---- ----------- ----------- ------- OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) Inbound rule for OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) True
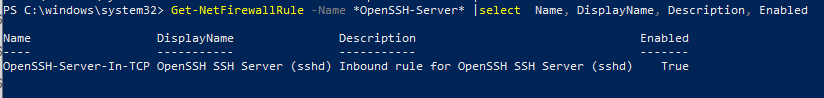
Если правило отключено (состоянии Enabled=False) или отсутствует, вы можете создать новое входящее правило командой New-NetFirewallRule:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
Рассмотрим, где храниться основные компоненты OpenSSH:
- Исполняемые файлы OpenSSH Server находятся в каталоге
C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\
(sshd.exe, ssh.exe, ssh-keygen.exe, sftp.exe и т.д.) - Конфигурационный файл sshd_config (создается после первого запуска службы):
C:\ProgramData\ssh - Файлы authorized_keys и ssh ключи можно хранить в профиле пользователей:
%USERPROFILE%\.ssh\
Sshd_config: Конфигурационный файл сервера OpenSSH
Настройки сервере OpenSSH хранятся в конфигурационном файле %programdata%\ssh\sshd_config. Это обычный текстовый файл с набором директив. Для редактирования можно использовать любой текстовый редактор (я предпочитаю notepad++). Можно открыть с помощью обычного блокнота:
start-process notepad C:\Programdata\ssh\sshd_config
Например, чтобы запретить SSH подключение для определенного доменного пользователя (и всех пользователей указанного домена), добавьте в конце файле директивы:
DenyUsers winitpro\[email protected] DenyUsers corp\*
Чтобы разрешить подключение только для определенной доменной группы:
AllowGroups winitpro\sshadmins
Либо можете разрешить доступ для локальной группы:
AllowGroups sshadmins
По умолчанию могут к openssh могут подключаться все пользователи Windows. Директивы обрабатываются в следующем порядке: DenyUsers, AllowUsers, DenyGroups,AllowGroups.
Можно запретить вход под учетными записями с правами администратора, в этом случае для выполнения привилегированных действий в SSH сессии нужно делать runas.
DenyGroups Administrators
Следующие директивы разрешают SSH доступ по ключам (SSH аутентификации в Windows с помощью ключей описана в отдельной статье) и по паролю:
PubkeyAuthentication yes PasswordAuthentication yes
Вы можете изменить стандартный SSH порт TCP/22, на котором принимает подключения OpenSSH в конфигурационном файле sshd_config в директиве Port.
После любых изменений в конфигурационном файле sshd_config нужно перезапускать службу sshd:
restart-service sshd
Подключение по SSH к Windows компьютеру
Теперь вы можете попробовать подключиться к своей Windows 10 через SSH клиент (в этом примере я использую putty).
Вы можете использовать встроенный SSH клиентом Windows для подключения к удаленному хосту. Для этого нужно в командной строке выполнить команду:
ssh [email protected]
В этом примере
alexbel
– имя пользователя на удаленном Windows компьютере, и 192.168.31.102 – IP адрес или DNS имя компьютера.
Обратите внимание что можно использовать следующие форматы имен пользователей Windows при подключении через SSH:
-
alex@server1
– локальный пользователь Windows -
[email protected]@server1
–пользователь Active Directory (в виде UPN) или аккаунт Microsoft/ Azure(Microsoft 365) -
winitpro\alex@server1
– NetBIOS формат имени
В домене Active Directory можно использовать Kerberos аутентификацию в SSH. Для этого в sshd_config нужно включить параметр:
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
После этого можно прозрачно подключать к SSH сервер с Windows компьютера в домене из сессии доменного подключается. В этом случае пароль пользователя не указывается и выполняется SSO аутентификация через Kerberos:
ssh -K server1
При первом подключении появится стандартный запрос на добавление узла в список известных SSH хостов.
Нажимаем Да, и в открывшееся окне авторизуемся под пользователем Windows.
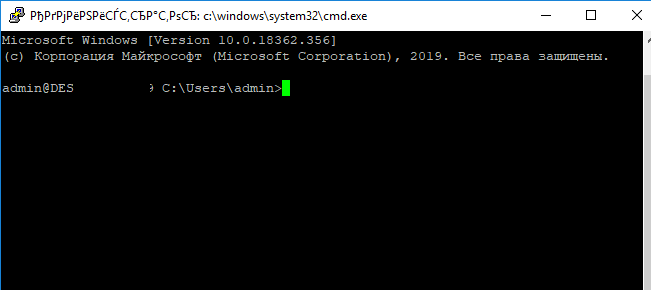
При успешном подключении запускается командная оболочка cmd.exe со строкой-приглашением.
admin@win10tst C:\Users\admin>
В командной строке вы можете выполнять различные команды, запускать скрипты и программы.
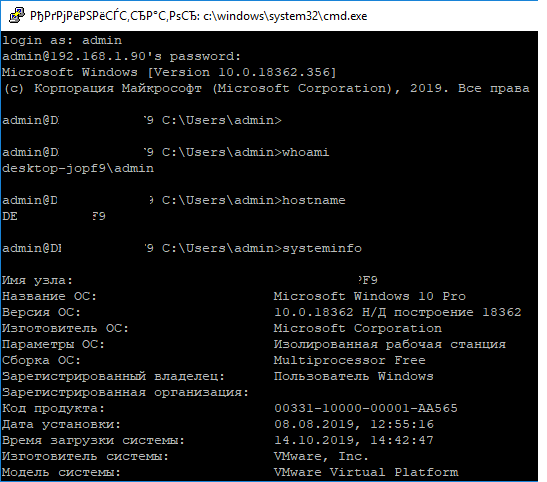
Я предпочитаю работать в командной строке PowerShell. Чтобы запустить интерпретатор PowerShell, выполните:
powershell.exe
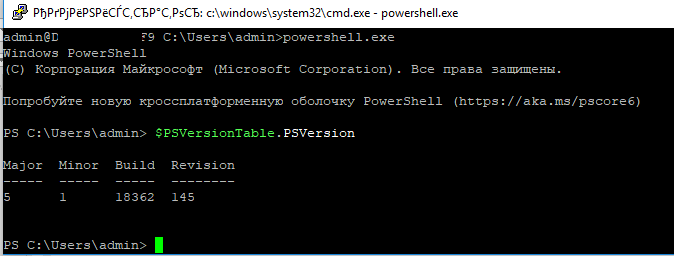
Чтобы изменить командную оболочку (Shell) по умолчанию в OpenSSH с cmd.exe на PowerShell, внесите изменение в реестр такой командой:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\OpenSSH" -Name DefaultShell -Value "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -PropertyType String –Force
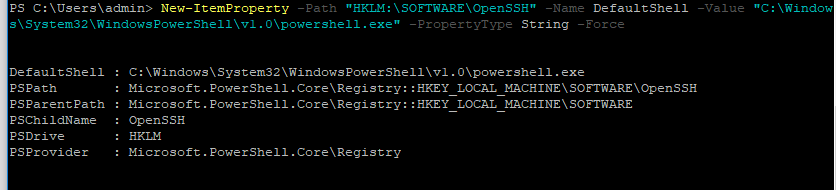
Осталось перезапустить SSH подключение и убедиться, что при подключении используется командный интерпретатор PowerShell (об этом свидетельствует приглашение
PS C:\Users\admin>
).
В SSH сессии запустилась командная строка PowerShell, в которой работают привычные функции: авто дополнение, раскраска модулем PSReadLine, история команд и т.д. Если текущий пользователь входит в группу локальных администраторов, то все команды в его сессии выполняются с повышенными правами даже при включенном UAC.
Логи SSH подключений в Windows
В Windows логи подключений к SSH серверу по-умолчанию пишутся не в текстовые файлы, а в отдельный журнал событий через Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). Откройте консоль Event Viewer (
eventvwr.msc
>) и перейдите в раздел Application and services logs -> OpenSSH -> Operational.
При успешном подключении с помощью к SSH серверу с помощью пароля в журнале появится событие:
EventID: 4 sshd: Accepted password for root from 192.168.31.53 port 65479 ssh2
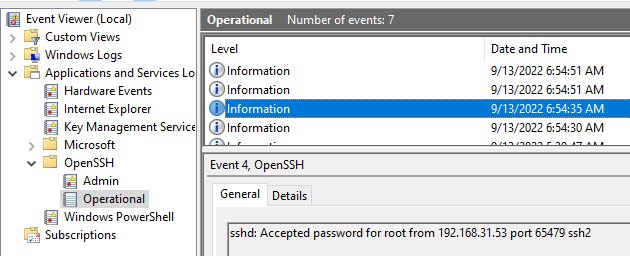
Если была выполнена аутентификация с помощью SSH ключа, событие будет выглядеть так:
sshd: Accepted publickey for locadm from 192.168.31.53 port 55772 ssh2: ED25519 SHA256:FEHDEC/J72Fb2zC2oJNb45678967kghH43h3bBl31ldPs
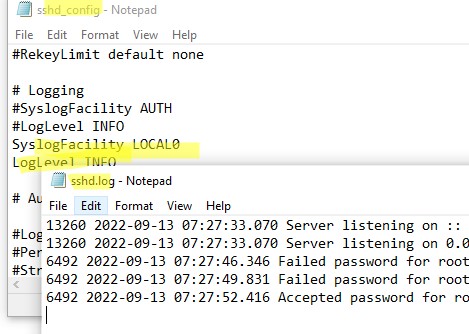
Если вы хотите, чтобы логи писались в локальный текстовый файл, нужно в файле sshd_config включить параметры:
SyslogFacility LOCAL0 LogLevel INFO
Перезапустите службу sshd и провеьте, что теперь логи SSH сервера пишутся в файл C:\ProgramData\ssh\logs\sshd.log
Install using WinGet
Starting with GitHub Release 8.9.1.0, OpenSSH Beta releases are available through WinGet.
With WinGet installed on the machine, use the following commands:
- Search:
winget search "openssh beta" - Install:
winget install "openssh beta" - Uninstall:
winget uninstall "openssh beta"
note: to install/uninstall only the OpenSSH client or OpenSSH server, see https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/wiki/Install-Win32-OpenSSH-Using-MSI for args that can be passed to winget via --override (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/package-manager/winget/install).
Install Win32 OpenSSH (test release)
-
Win32-OpenSSH Github releases can be installed on Windows 7 and up.
-
Note these considerations and project scope first.
-
Download the latest build of OpenSSH.
To get links to latest downloads this wiki page. -
Extract contents of the latest build to
C:\Program Files\OpenSSH(Make sure binary location has the Write permissions to just to SYSTEM, Administrator groups. Authenticated users should and only have Read and Execute.) -
In an elevated Powershell console, run the following
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File install-sshd.ps1
-
Open the firewall for sshd.exe to allow inbound SSH connections
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
Note:
New-NetFirewallRuleis for Windows 2012 and above servers only. If you’re on a client desktop machine (like Windows 10) or Windows 2008 R2 and below, try:netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=sshd dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=22 -
Start
sshd(this will automatically generate host keys under %programdata%\ssh if they don’t already exist)net start sshd
-
Optional
- To configure a default shell, see here
- To setup
sshdservice to auto-startSet-Service sshd -StartupType Automatic
- To migrate sshd configuration from older versions (0.0.X.X), see here
Uninstall Win32 OpenSSH
- Start Windows Powershell as Administrator
- Navigate to the OpenSSH directory
cd 'C:\Program Files\OpenSSH'
- Run the uninstall script
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File uninstall-sshd.ps1
Установка
Для работы с удаленными папками на windows сервере по ssh из VSCode плагином Remote-SSH на стороне windows сервера требуется служба ssh-сервера. Давайте его установим.
- Скачиваем последнюю версию дистрибутива OpenSSH
Сейчас доступна версия v8.0.0.0p1-Beta. Скачиваем OpenSSH-Win64.zip.
- Создаем каталог C:\Program Files\OpenSSH и распаковываем в неё содержимое архива.
- Запускаем powershell от имени администратора.
- Выполняем скрипт установки:
cd "\Program Files\OpenSSH"
.\install-sshd.ps1
sshd and ssh-agent services successfully installed
Если произошла ошибка политики безопасности, то можно выполнить установку так:
powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File .\install-sshd.ps1
- Генерируем серверные ключи:
Если при этом появляется ошибка
Нужно в папке C:\ProgramData создать вручную директорию ssh
- Снова пытаемся сгенерировать серверные ключи:
На этот раз процедура выполняется успешно.
- Настраиваем владельца и права доступа на файлы ключей и каталоги сервера :
PowerShell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File .\FixHostFilePermissions.ps1
На каждый вопрос отвечаем “A”.
- Открываем 22 порт
OpenSSH работает по порту TCP 22. Откроем доступ в Firewall:
New-NetFirewallRule -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 22 -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -DisplayName SSH
Эта команда сработает на Windows Server 12 и моложе. На более старых серверах порт можно открыть через GUI в оснастке Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
- Запуск службы OpenSSH
Открываем список служб:
Находим службу “OpenSSH SSH Server”. В свойствах службы устанавливаем автоматический запуск и запускаем её.
Проверим что 22 порт работает:
22 порт слушается.
- Проверка OpenSSH
Проверим с помощью WinSCP. Для доменного пользователя используется логин вида domain\username.
При первом входе появится окно:
Yes.
Установка завершена.
в тексте 356 слов






