This repository was archived by the owner on Feb 4, 2025. It is now read-only.
v2.1.7740.35837
Version 2.1.7740
Beta Release
Fix :
- Fixed a string length error for the German language (this problem should also exist with other languages but only if the strings were long enough) — related to issue #74
Changed
- Redesign of the connection functions to the Nut server
- Creation of a DLL containing functions not essential to the GUI in order to prepare for the upcoming arrival of service mode
- Modification of the instantaneous power calculation method in the case of inverters not supporting the variables previously used — in conjunction with issue #68 (thanks to faugusztin)
v2.0.7722.30975
Version 2.0.7721
Fix :
- Fix an error when checking for an update to the latest version.
This error causes the detection of an update that does not exist. (issue #70) - Also fixes incorrect version number detection (build version number was truncated)
Changed :
- Improvements to the code managing the «ups.status» variable to take into account all possible values
v2.0.7721.35955
Version 2.0.7721
Fix :
- Fixed an error preventing WinNUT from starting on a new installation (crash in the encryption function due to a string = Nothing)
Related to issue #62 - Since the logging was improved, the view / delete functions of the current log file no longer pointed to the correct files.
Added :
- Addition of a small signage icon indicating if the battery is in Charge / Discharge / Charged state.
When the status is unknown (Connection not established or lost), no status is displayed. - Added Russian translation (ru-RU) (thanks to NoGood — #65)
- Addition of the possibility of creating a Bug Report when WinNUT encounters a critical error in order to retrieve the information necessary to resolve this bug.
Changed :
- Password is now hidden in TextBox (#63)
- Windows Title Modified to «Windows NUT Client», like older versions (#61) and is now a translatable string
- Settings Poll Delay are now Expressed In seconds (#64), also renaming «Delay» parameters to «Polling Interval»
- The translations have been modified accordingly for these 3 fixes
- Change the way the program version is displayed in notifications
Only major and minor versions are displayed due to limitations on the number of characters that can be displayed in notifications - Toast Popup : Use Short Program Version Instead of complete Program Version
- Some improvements on Preferences Gui
- Improved logging when entering or exiting Windows from sleep.
- The required .Net Framework version is now 4.7.2 (instead of 4.5.2) (Windows 7 sp1, 8, 8.1, 10)
- Addition of a daily rotation of the logs (previously required a deletion of the journal file when it exceeded 5000KB or else no longer journaling new elements)
- Translations Improvements
v2.0.7710.35866
Version 2.0.7710
WARNING
Due to a bug not discovered during the publication and preventing the startup after a new installation, it is recommended to first install version 2.0.4.0 to be able to configure and test the connection of WinNUT and then perform a manual update to take advantage of this version.
Consequently, this version has been requalified as «pre-release» and should therefore no longer be considered as a stable version.
This problem will be fixed in the next version.
Fix :
- Fixed an error generating a bad loading of the default parameters during the first launch following a new installation (without any version previously installed)
- Fix an error preventing the detection of certain updates if the name of the release does not include the revision version number
Added :
- Username and password are now stored in an encrypted way in registry. (issue #37)
The conversion of old authentification data is automaticThe conversion of old authentication data is automatic at first launch of WinNUTs new version. - Added FSD support that can be provided by NUT server.
If the NUT server informs that it is initiating a Forced Shutdown, WinNUT will take this into account and initiate the shutdown process in the same way as if it determines that the conditions are required to do so.
The option must be activated in the settings of WinNUT so that it takes into account the FSD signal (Follow FSD signal).
Changed :
- WinNUT is now distributed under the GNU GPL v3 license (and later).
- When an update is present, the Changelog window will indicate the Changelog content of each version (both stable and development) present between the currently installed version and the new version.
In this way, it is easier to take into account all the evolutions / corrections applied from the installed version.
v2.0.7706 beta
Fix :
- App crash when disconnecting with null streams (Thanks to tgp1994) (Issue #48)
- Correction of a bad state of the Notify Icon Text when the return value of ups status is not only «OL» (Issue #45)
- Add -f parameter to force shutdown (Issue #46)
- Some modifications provided by tgp1994
- Fixed a bug that could occur when using a value of «0» for the grace period (thanks to jcsmook — pull requests #55)
- Fixed a bug generating an infinite connection / reconnection loop when the load value is retrieved to «0» during connection (thanks to jcsmook, pull requests #55)
- Correction of a code error causing the event time not to be updated in the logs.
- Fixed an error causing an unhandled exception when you do not want to apply the update immediately and the installation file already exists at the location specified for saving.
- In the case of a left click on the systray icon, WinNUT was restored to its original size and the context menu was opened at the same time.
This behavior has been corrected and only the context menu opens.
Restoring the WinNUT window to its original size is caused by a single or double click only.
Added :
- Addition of a directory containing the translations at the repository level.
Makes it easier to submit a new translation (or correction) via a fork / pull request (nonPointer idea — issue #35) - Translation of the «List UPS Variable’s» interface (translation forgot during v2.0)
Changed :
- Some changes on how logs work (Thanks to tgp1994)
- Modification of the code to recover the power supply frequency of the UPS when it only provides the output frequency (modification made in response to an unsuccessful commit of pull requests #55 — problem encountered by jcsmook)
- Modification of the generated installer:
— Addition of a custom image banner
— Removal of the dependent Windows libraries installed in the WinNUT directory - The update process is no longer based on the «changelog.txt» of the repository but on the list of releases via the GitHub APIs.
This modification has been implemented to avoid reproducing issue #53.
This modification also brings the possibility of receiving both stable and development updates for those who choose to follow the development channel (the more recent of the two being the proposed update). - The changes made to the update process allow the implementation of a more suitable versioning of the type
[Major Version].[Minor Version].[Automatic Build Version].[Automatic Revision Version] - Complete syntax review of Changelog.txt file
v2.0.4.0
Added: EXPERIMENTAL — Connection function to the nut server with identification and password.
Fix : When the «Minimize to tray» option is disabled but the «Start Minimized» and «close to tray» options are active,
reducing or closing sends the application to the systray without the possibility of having access to the icon notification
Fix : When the name of the UPS in the parameters is incorrect, it is no longer possible to display the UPS variable information window.
Fix : Fixed a typo preventing shutdown at the end of the timeout
Fix/Added : When the name of the UPS in the parameters is incorrect, the connection is not established and a notification is displayed for 10 seconds.
Added : When the application is minimized in the systray and a change of connection state to the Nut server or a change of state of the UPS
occurs, a notification popup is displayed for 10 seconds.
Added : When the application is minimized without being sent to the systray (in task bar), the connection and battery status is displayed
in the text of the window in order to be quickly visualized when the application icon is hovered in the task bar.
Changed : The application icon has been modified to add an outline to the white shape in order to be visible when it is on a white background
Changed : The arrows of the icon displayed during reconnection are now in yellow to be more visible due to their small size.
Changed : The import of an old Ini file has been modified. The function is no longer automatic due to a problem with access rights to the
default installation directory. The import is now started manually from the File menu
Changed : The behavior of the extinction count progress bar has been corrected and behaves in a more fluid and consistent way
Changed : Restoring the main window from the notification icon only requires a single click (double click previously required)
v2.0.4.0_beta
Added: EXPERIMENTAL — Connection function to the nut server with identification and password.
Fix : When the «Minimize to tray» option is disabled but the «Start Minimized» and «close to tray» options are active,
reducing or closing sends the application to the systray without the possibility of having access to the icon notification
Fix : When the name of the UPS in the parameters is incorrect, it is no longer possible to display the UPS variable information window.
Fix : Fixed a typo preventing shutdown at the end of the timeout
Fix/Added : When the name of the UPS in the parameters is incorrect, the connection is not established and a notification is displayed for 10 seconds.
Added : When the application is minimized in the systray and a change of connection state to the Nut server or a change of state of the UPS
occurs, a notification popup is displayed for 10 seconds.
Added : When the application is minimized without being sent to the systray (in task bar), the connection and battery status is displayed
in the text of the window in order to be quickly visualized when the application icon is hovered in the task bar.
Changed : The application icon has been modified to add an outline to the white shape in order to be visible when it is on a white background
Changed : The arrows of the icon displayed during reconnection are now in yellow to be more visible due to their small size.
Changed : The import of an old Ini file has been modified. The function is no longer automatic due to a problem with access rights to the
default installation directory. The import is now started manually from the File menu
Changed : The behavior of the extinction count progress bar has been corrected and behaves in a more fluid and consistent way
Changed : Restoring the main window from the notification icon only requires a single click (double click previously required)
v2.0.3.0_beta
Version 2.0.3.0
Fix : Application crash when opening the ‘UPS Variable’ window
Fix : No feedback when checking for update (manual or automatic)
v2.0.2.0_beta
Version 2.0.2.0
Fix : All hard-coded translations are translated
Fix : The log file is now correctly created
Added : Some Translations
WinNUT v1.8.0.3
Version 1.8.0.3
Change : WinNUT is ready to update to version 2
Всем известно, что для защиты от сбоев электропитания нужно купить бесперебойник. Но сам по себе источник бесперебойного питания не решает проблему, а только отсрочивает негативные последствия. Действительно, если питание пропадет надолго, то после разрядки батарей ИБП ваши системы аварийно завершат работу. Избежать этого позволяют модели, имеющие обратную связь, но, чтобы использовать эти возможности нам потребуется система управления электропитанием и сегодня мы расскажем об открытом и бесплатном продукте — NUT (Network UPS Tools).
Онлайн-курс по устройству компьютерных сетей
На углубленном курсе «Архитектура современных компьютерных сетей» вы с нуля научитесь работать с Wireshark и «под микроскопом» изучите работу сетевых протоколов. На протяжении курса надо будет выполнить более пятидесяти лабораторных работ в Wireshark.
Почему именно NUT? Ведь многие производители ИБП предлагают собственные утилиты, в т.ч. и под Linux, при этом они явно лучше знают свою продукцию. В теории это так, но практика вовсе не так радужна. Во-первых, качество «родного» ПО очень сильно отличается от вендора к вендору. Где-то это вполне неплохие решения, а где-то лютая мешанина скриптов, бинарников и устаревших технологий.
Кроме того, ИБП у вас может быть не один, причем разных производителей и устраивать зоопарк проприетарного ПО — не самый лучший вариант. Что касается второго аргумента, то существует UPS management protocol — RFC 9271, если бесперебойник его поддерживает, то все равно какое ПО мы будем использовать для работы с ним.
NUT — это открытое программное обеспечение, поддерживающее большое количество источников бесперебойного питания и предоставляющее единый интерфейс работы с ними, кроме того оно работает в клиент-серверном режиме что позволяет организовать сетевое управление электропитанием, это удобно, когда к одному бесперебойнику подключено несколько компьютеров. С полным списком поддерживаемых устройств вы можете ознакомиться на официальном сайте: https://networkupstools.org/stable-hcl.html
Структурно NUT состоит из трех основных частей:
- Драйвер — используется для связи с ИБП.
- Сервер (upsd) — при помощи драйвера связывается с ИБП и получает сообщения об его состоянии.
- Служба мониторинга (upsmon) — контролирует сервер и выполняет действия на основе полученной от сервера информации.
Важный момент! Сервер NUT никак не связывается с клиентами и не передает им никаких команд, все решения принимает клиент, который при помощи службы мониторинга получает с сервера состояние выбранного ИБП и сообщения от него, на основании которых затем предпринимаются некоторые действия.
Таким образом один сервер NUT может контролировать сразу несколько физически подключенных к нему через интерфейс обратной связи ИБП и предоставлять информацию об их состоянии клиентам через локальную сеть. Это позволяет реализовывать достаточно сложные схемы управления электропитанием, наподобие приведенной ниже:
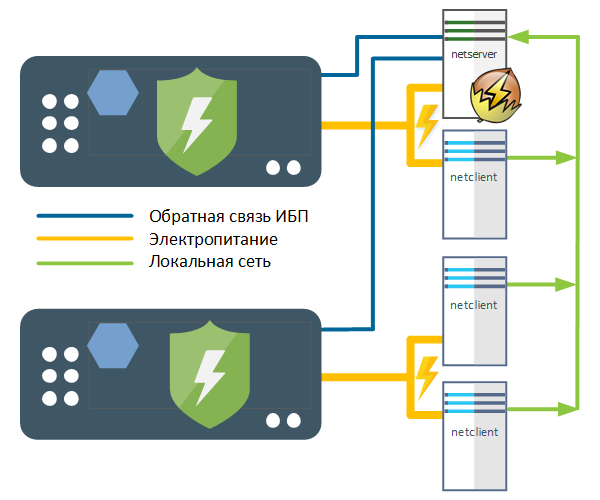
Таким образом имея единственный сервер NUT мы получаем централизованную систему управления питанием, которая обеспечит корректное выключение всех подключенных к ИБП компьютеров, а затем самого ИБП. При возобновлении электропитания сначала включатся ИБП, а затем все подключенные к ним устройства (для этого они должны иметь соответствующие настройки в BIOS).
Установка NUT и настройка драйвера ИБП
Установка NUT проста, в Debian / Ubuntu существует одноименный метапакет, который устанавливает сразу и сервер, и клиент. В других системах обратитесь к документации по доступным пакетам.
apt install nutТеперь подключим к серверу ИБП и перезагрузим систему, после чего попробуем автоматически определить его настройки при помощи служебного пакета nut-scanner:
nut-scannerУтилита просканирует все доступные интерфейсы и выведет готовые параметры подключения для обнаруженных устройств, в нашем случае был найдет ИБП серии PowerCom Smart King Pro+ подключенный через USB.
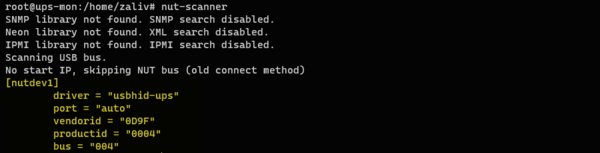
Фактически это готовые опции для настройки драйвера, советуем сохранить их для использования в дальнейшем. Теперь откроем файл /etc/nut/ups.conf и в самый конец добавим секцию, аналогичную указанной выше. В квадратных скобках указываем желаемое имя, ниже следуют опции подключения. В минимальной конфигурации будет достаточно первых двух: driver и port. Если предполагается использовать несколько ИБП, то мы можем уточнить производителя и модель: vendorid и productid, а вот опцию bus — лучше не использовать, при переключении ИБП в другой разъем она изменится. В случае использования нескольких ИБП одной модели лучше использовать другую опцию — serial с указанием серийного номера устройства.
Также мы советуем изучить документацию производителя, многие из них указывают рекомендуемые конфигурации драйвера для работы с NUT, например, для PowerCom у нас вышло следующее:
[powercom1]
driver = usbhid-ups
port = auto
vendorid = 0d9f
productid = 0004
serial = AAA-BBBB-CCC
pollonlyПоследняя опция как раз взята из рекомендаций производителя, без нее ИБП работал с NUT нестабильно, периодически отваливаясь, что требовало либо его переподключения, либо перезагрузки компьютера.
Теперь проверим работу драйвера:
upsdrvctl startЕсли все сделано правильно, то вы увидите что-то подобное:
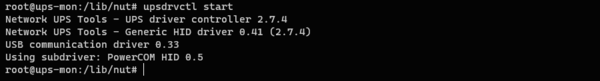
Как видим, драйвер запустился нормально и увидел наш ИБП, теперь остановим его, чтобы избежать конфликтов при дальнейшей настройке.
upsdrvctl stopЕсли же драйвер запускается с ошибками попробуйте переключить ИБП в другой разъем или перезагрузить компьютер.
Настройка сервера NUT
Прежде всего откроем /etc/nut/nut.conf и установим режим работы:
MODE=netserverДля сервера доступны режимы:
- standalone — сервер запущен локально и принимает соединения только на localhost, используется для управления локально подключенным ИБП, который не питает других ПК,
- netserver — сетевой режим, сервер принимает соединения по локальной сети, подходит для построения сетевой системы управления питанием.
Мы сразу будем настраивать сетевой режим, большинство настроек при этом не будут отличаться от локальных, поэтому вы также можете настроить и локальный режим по этой инструкции.
Теперь перейдем в /etc/nut/upsd.conf, в нем нам потребуется указать сетевые опции, а именно адрес и порт, на котором будет принимать подключения сервер:
LISTEN 127.0.0.1 3493
LISTEN 192.168.99.120 3493Обратите внимание на регистр написания, название опции должно быть обязательно в верхнем регистре, для локального режима достаточно будет только указания первой строки.
Следующим шагом заведем пользователей в файле /etc/nut/upsd.users. Мы рекомендуем, как минимум, завести административного пользователя, который будет иметь права менять настройки UPS и пользователей для чтения данных состояния бесперебойника. Вы можете завести разные учетные данные для разных ПК или одну на всех — выбор остается за вами. В нашем случае содержимое файла выглядит так:
[upsadmin]
password = Pa$$word_1
actions = SET
instcmds = ALL[upsmon-m]
password = 123456789
upsmon master[upsmon-s]
password = 987654321
upsmon slave
В нашем случае мы завели трех пользователей: административного, пользователя локального клиента (master) и удаленных клиентов (slave).
Сохраним все изменения и попробуем запустить службу сервера и сразу проконтролируем ее статус:
systemctl start nut-server
systemctl status nut-server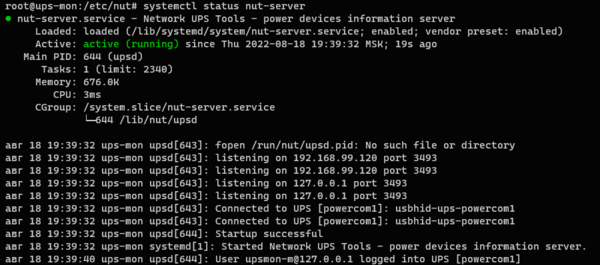
Теперь можем получить данные о состоянии ИБП командой:
upsc powercom1@localhostГде мы указываем имя нашего драйвера и имя или адрес узла, на котором запущена серверная часть NUT.
В выводе мы можем увидеть частоту и напряжение на входе и на выходе устройства, текущую нагрузку в процентах (ups.load) и статус бесперебойника, который может иметь следующие значения:
- OL — On Line — работа от сети
- OB — On Battery — работа от батареи
- LB — Low Battery — низкий заряд батареи
Как мы уже говорили, сам сервер не предпринимает никаких действий, а только получает данные от ИБП и предоставляет их клиентам, но именно состояние LB служит триггером для службы мониторинга инициирующим выключение устройств.
Настройка службы мониторинга в Linux
Начнем с локального сервера, клиентская часть здесь уже установлена, поэтому просто откроем файл /etc/nut/upsmon.conf и добавим в него строку:
MONITOR powercom1@localhost 1 upsmon-m 123456789 masterРазберем указанные опции: powercom1@localhost — указывают имя драйвера и сервер NUT, следующая за ними единица говорит о том, что питание устройства следует отключить, для отладки можно временно указать там ноль, в этом случае будут генерироваться все события и записи в логах, но отключение питания производиться не будет. Затем указываем имя пользователя и пароль, а также тип устройства — master, это говорит о том, что перед нами головное устройство и оно будет выключено только после того, как выключатся все подчиненные компьютеры.
Запустим службу мониторинга:
systemctl start nut-monitorОстальные параметры можно оставить по умолчанию. Но следует обратить внимание на опции NOTIFYFLAG, которые описывают реакцию службы на те или иные события. По умолчанию, когда опция закомментирована, применяются действия SYSLOG и WALL, т.е. пишется событие в системный лог и отправляется сообщение всем залогиненым пользователям.
Дополнительно можно включить выполнение скрипта действием EXEC, сам скрипт общий для всех событий и указывается в опции NOTIFYCMD, само событие и реакцию на него следует определять в самом скрипте, но это уже выходит за рамки данной статьи, поэтому рекомендуем обратиться к документации.
На удаленных устройствах нам нет необходимости устанавливать все пакеты, достаточно только клиентского:
apt install nut-clientПосле чего откроем /etc/nut/nut.conf и укажем режим работы:
MODE=netclientЗатем в /etc/nut/upsmon.conf внесем строку:
MONITOR powercom1@192.168.99.120 1 upsmon-s 987654321 slaveМы не будем подробно разбирать синтаксис, так как это сделали выше, отметим изменения. При указании драйвера и узла мы использовали IP-адрес сервера NUT (можно также его FQDN), а в конце строки указали slave, что обозначает подчиненный мониторинг, кроме состояния ИБП он отслеживает также команды от головного мониторинга (master). Понятно, что в качестве драйвера следует указывать именно тот ИБП, к которому физически подключен данный узел.
После чего точно также запускаем службу:
systemctl start nut-monitorДля проверки получим сведения об ИБП:
upsc powercom1@192.168.99.120Для просмотра подключенных клиентов выполните команду:
upsc -с powercom1@192.168.99.120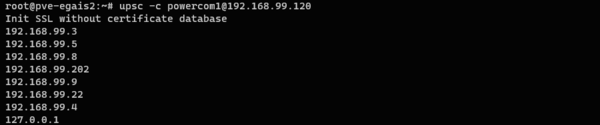
А теперь как это все работает, мы не будем углубляться в подробности, а представим максимально упрощенную схему, достаточную для понимания происходящих событий.
- Батареи ИБП разряжаются, и он переходит в состояние LB
- Мониторинг master-узла получает этот статус и выставляет флаг FSD (forced shutdown)
- Мониторинг slave-узлов видит этот флаг и инициирует выключение
- Master-узел ждет отключения подчиненных узлов и выставляет флаг POWERDOWNFLAG
- При необходимости master завершает свою работу и выключает ИБП
Последний момент очень важен, потому что если после того, как slave-узлы будут выключены, подача питания возобновится, то ИБП не выключится и повторного запуска подключенных устройств не произойдет. Поэтому master узел в обязательном порядке выключает ИБП, чтобы при его последующем включении произошел запуск всех подключенных к нему устройств.
Настройка службы мониторинга в Windows
Сервер NUT может управлять и Windows-клиентами, для этого нужно установить один из клиентов NUT, мы используем WinNUT-Client, он поставляется в виде MSI-пакета и проблем с его установкой возникнуть не должно. Настройки его также просты: указываем адрес и порт сервера, имя драйвера, логин и пароль.
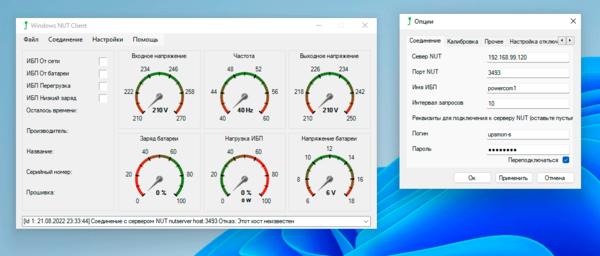
Также советуем пробежаться по прочим вкладкам и настроить автозапуск приложения и выполнить, при желании, более тонкую подстройку. Кроме выполнения своей основной функции приложение также показывает основные параметры ИБП в виде графических индикаторов.
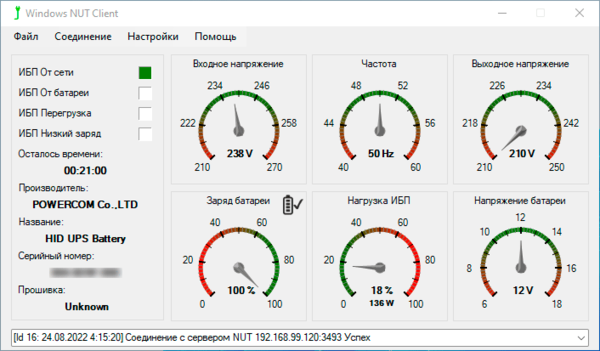
Как видим, настроить NUT просто, но данная статья и близко не затронула всех возможностей этой системы. Пока что мы организовали базовую систему централизованного управления электропитанием, но при желании ее можно бесконечно улучшать и дополнять, благо проект прекрасно документирован.
Онлайн-курс по устройству компьютерных сетей
На углубленном курсе «Архитектура современных компьютерных сетей» вы с нуля научитесь работать с Wireshark и «под микроскопом» изучите работу сетевых протоколов. На протяжении курса надо будет выполнить более пятидесяти лабораторных работ в Wireshark.
ups
power
monitoring
network
An open-source Windows software for monitoring devices on a network via NUT protocol, checking UPS status and receiving notifications.
What is WinNUT-Client?
WinNUT-Client is a free, open-source Windows application that interfaces with uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs) and other power devices using the Network UPS Tools (NUT) monitoring protocol. It provides a graphical user interface to check the status of UPSs and other NUT-compatible hardware on a local network.
Some of the key features of WinNUT-Client include:
- Real-time monitoring of UPS voltage, load level, temperature, battery capacity, and more
- Logging of power events and automatic shutdown configuration during power failures
- Notifications via popup alerts, email, and execution of custom scripts
- Support for a wide variety of UPS models from various manufacturers
- Customizable interface and data graphs
- Secured monitoring utilizing SSL/TLS encryption
WinNUT-Client must connect to a NUT server daemon running on either the local or remote networked machine. It is commonly used along with NUT server implementations like NUTRS, WinNUT, or nut for managing multiple UPS devices in a centralized location. The application runs on Windows platforms.
Overall, WinNUT-Client offers an efficient way for IT staff to visually track critical power infrastructure across a business’s network. With real-time status information and robust notification options, it enables the early detection of potential power issues and outages.
WinNUT-Client Features
Features
- Monitor devices on a network via the Network UPS Tools (NUT) protocol
- Check the status of uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs)
- Receive notifications for UPS-related issues
Pros
Open-source software
Allows monitoring of UPS devices on a network
Provides notifications for UPS-related issues
Cons
Limited to Windows operating system
May require additional configuration for complex network setups
Lacks some advanced features compared to commercial UPS monitoring software
Official Links
The Best WinNUT-Client Alternatives
Top
System & Hardware
and
Device Monitoring
and other similar apps like WinNUT-Client
PowerChute
PowerChute is an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) management software developed by APC. It is designed to work in conjunction with APC UPS hardware to protect IT equipment from power surges, outages, and other electrical anomalies.Some key features of PowerChute include:Power event notifications — Provides early warnings of impending power issues…
UPS Assistant
UPS Assistant is a desktop application developed by United Parcel Service to help streamline the shipping process for high volume shippers. Some key features of UPS Assistant include:Shipment Preparation — Enter shipment details like ship to/from addresses, package weight and dimensions, and declared value. Print shipping and return labels.Tracking -…
Winpower
Winpower is an electrical engineering software suite developed by CIMTEC Automation specifically for the design, simulation, and analysis of industrial electrical control systems. It integrates tools for schematic design, PLC programming, HMI development, and system simulation into a single intuitive platform.Key features of Winpower include:Intuitive schematic editing tools for drawing…
Когда возникает задача мониторить бесперебойники у рабочих станций? Запищал – заменил, конец. Чинить ИБП – дело неблагодарное, менять аккумуляторы – не все хотят возиться (или даже моветон).
Так думал и я, особенно после череды ИБП с отказавшей электроникой. Ситуацию усугублял софт от производителей. Он, как бы это помягче выразиться, барахло. Причем у всех – APC, Ippon, Powercom, TrippLite. Что серверный, что для рабочих станций. Пробовать платные версии после опыта с бесплатными – желания не возникло. А совсем весело, когда ИБП от разных производителей.
Но мониторить всё же надо. Плюсы очевидны: 1) можно поменять ИБП ДО того, как он издаст прощальный писк; 2) можно сразу увидеть, где сдохла батарея, а где электроника.
Минус же прост, как всегда: стоимость решения, в деньгах или человеко-часах.
Вот эту проблему и будем решать.
Если имеем зоопарк, то самый адекватный способ – это Network UPS Tools.
По нему мало информации про Windows, а ещё нет GUI. Но это мы решим.
Справедливости ради нужно отметить, что есть похожий проект на Python. Но мне лично кажется совершенно излишним использование Python (и подобные технические решения) там, где можно обойтись парой строк нативного скриптинга.
Disclaimer
- Это не «готовое решение».
- Это не предложение, а рассказ.
- Да, есть Zabbix, Cacti, etc, и это тяжеловесные решения для больших компаний, требующие выделенного сервера и всё равно какого-то промежуточного слоя для поддержки соответствующего протокола UPS.
- При всём вышеперечисленном, решение достаточно простое, достаточно лёгкое и стоит 0 валюты.
Разумеется, для сбора информации понадобятся UPS с инфо-портом. У меня возникли проблемы с COM-портом IPPON, всё остальное работает на ура.
Обычно для рабочих станций используется подключение ИБП по USB, этот случай и рассмотрим. Нужно установить NUT на все рабочие станции с ИБП.
Возможные проблемы при этом:
- > Драйвер libusb лучше ставить отдельно. Те, что в комплекте, понимает не все ИБП;
- Если libusb предлагает стандартное имя HID UPS Battery, нужно его изменить – со стандартным именем некоторые системы почему-то не видят UPS;
- если процессе установки появилось сообщение «Драйвер без цифровой подписи«, то его нужно повторно переустановить руками, иначе он слетает;
- если libusb не распознал модель UPS, то с первого раза драйвер ставится НЕКОРРЕКТНО! Об этом говорит ошибка «upsmon ERROR ACCESS DENIED», или драйвер просто слетает. Нужно: остановить службу NUT, удалить драйвер libusb, подождать, пока установится «USB устройство ввода», выбрать для него вручную драйвер libusb заново;
- Для NUT нужны сторонние библиотеки, которых в комплекте установки нет. Setup об этом говорит, но кто ж его читает
Плюс часто в системах уже есть софт с этими библиотеками. Точно нужны: libeay32.dll, ssleay32.dll, libgcc_s_dw2-1.dll (есть в папке NUT-bin), libusb.dll (есть в дистрибутиве libusb), msvcr71.dll (в составе Net Framework 1.1). Все эти файлы должны быть в папке Windows\System32;
- иногда нужно указать bus=«bus-0» для USB UPS в ups.conf;
- на быстрых машинах и на некоторых сетевых картах служба NUT стартует раньше, чем драйвер и/или сетевой интерфейс. При этом тип запуска «Автозагрузка (отложенный запуск)» приводит к ошибке «upsc ERROR DATA STALE». Решение: создать задачу, которая будет проверять наличие процесса upsd при появлении события с кодом 1 из источника «Network UPS Tools» и перезапускать службу Network UPS Tools скачать xml-файл задачи скачать скрипт (должен быть в папке NUT\others).
Примерный скрипт полуавтоматической установки NUT на клиенты:
N:\NUT-Installer-2.6.5-6.msi /qn
copy N:\dll\ssleay32.dll C:\Windows\System32 /Y
copy N:\dll\libeay32.dll C:\Windows\System32 /Y
copy N:\dll\libgcc_s_dw2-1.dll C:\Windows\System32 /Y
copy N:\dll\libusb.dll C:\Windows\System32 /Y
copy N:\etc\* "%programfiles%\NUT\etc"
rem добавляем IP-адрес клиента в конфиг NUT автоматически
SET IP=192.168.100.10
set ip_address_string="IP Address"
rem Uncomment the following line when using Windows 7 (with removing "rem")!
set ip_address_string="IPv4-адрес"
REM echo Network Connection Test
for /f "usebackq tokens=2 delims=:" %%f in (`ipconfig ^| findstr /c:%ip_address_string%`) do SET IP=%%f
ECHO LISTEN %IP% 3493 >> "%programfiles%\NUT\etc\upsd.conf"
rem Ставим драйвер libusb отдельно
N:\libusb-win32-bin-1.2.6.0\bin\inf-wizard.exe
rem Правим конфиги, там буквально две строки
notepad "%programfiles%\NUT\etc\ups.conf"
notepad "%programfiles%\NUT\etc\upsmon.conf"
pause
net use N: /delete /YКак понять, почему не работает NUT под Windows:
- проверяем, есть ли в процессах nut.exe
- если есть, то проверяем upsd.exe и upsmon.exe
- если upsd нет в процессах, идём в nut\sbin и запускаем руками:
- «upsd не может быть запущен, так как отсутствует dll» – проверяем dll в system32, перезагружаемся на всякий случай;
- «upsd error creating named pipe» – upsd уже запущен
- запускается и сразу закрывается – проверить ip-адрес в upsd.conf в секции LISTEN, особенно актуально, если на машине DHCP ;
- upsd запустился, но не видит UPS – установить или переустановить libusb, проверить libusb.dll в system32, переименовать устройство из HID UPS Battery;
- если upsd стартовал, идём в bin и выполняем upsc our_ups@localhost
- «upsc не может быть запущен, так как отсутствует dll» – проверяем библиотеки ;
- «upsc failed connection unknown error» – проверяем, запущен ли upsd и upsmon, внимательно проверяем секцию MONITOR в upsmon.conf, ещё раз проверяем библиотеки dll;
- «upsc error data stale» – либо UPS один раз запускался и больше не работает, тогда переустанавливаем драйвер libusb и переименовываем HID UPS Battery, либо служба NUT поднялась быстрее, чем стал виден сетевой интерфейс или USB UPS, перезапускаем службу;
- «upsmon error ACCESS DENIED» – переустанавливаем драйвер, как описано выше.
Для сервера мониторинга нужны:
- NUT в режиме standalone;
- любой web-сервер с php и mysql. Я использую Uniform Server
- MySQL-база и папка www из репозитория, и пара batch-скриптов оттуда же.
Базу SQL и www кладём в соответствующие каталоги веб-севера. Скрипты из batch_scripts копируем в папку установки NUT. Запускаем веб-сервер, переходим на localhost/index_ups.php. Добавляем любой из клиентских UPS в формате UPS_name@host. Запускаем скрипт get_ups_list_mysql.cmd. Проверяем. Enjoy.
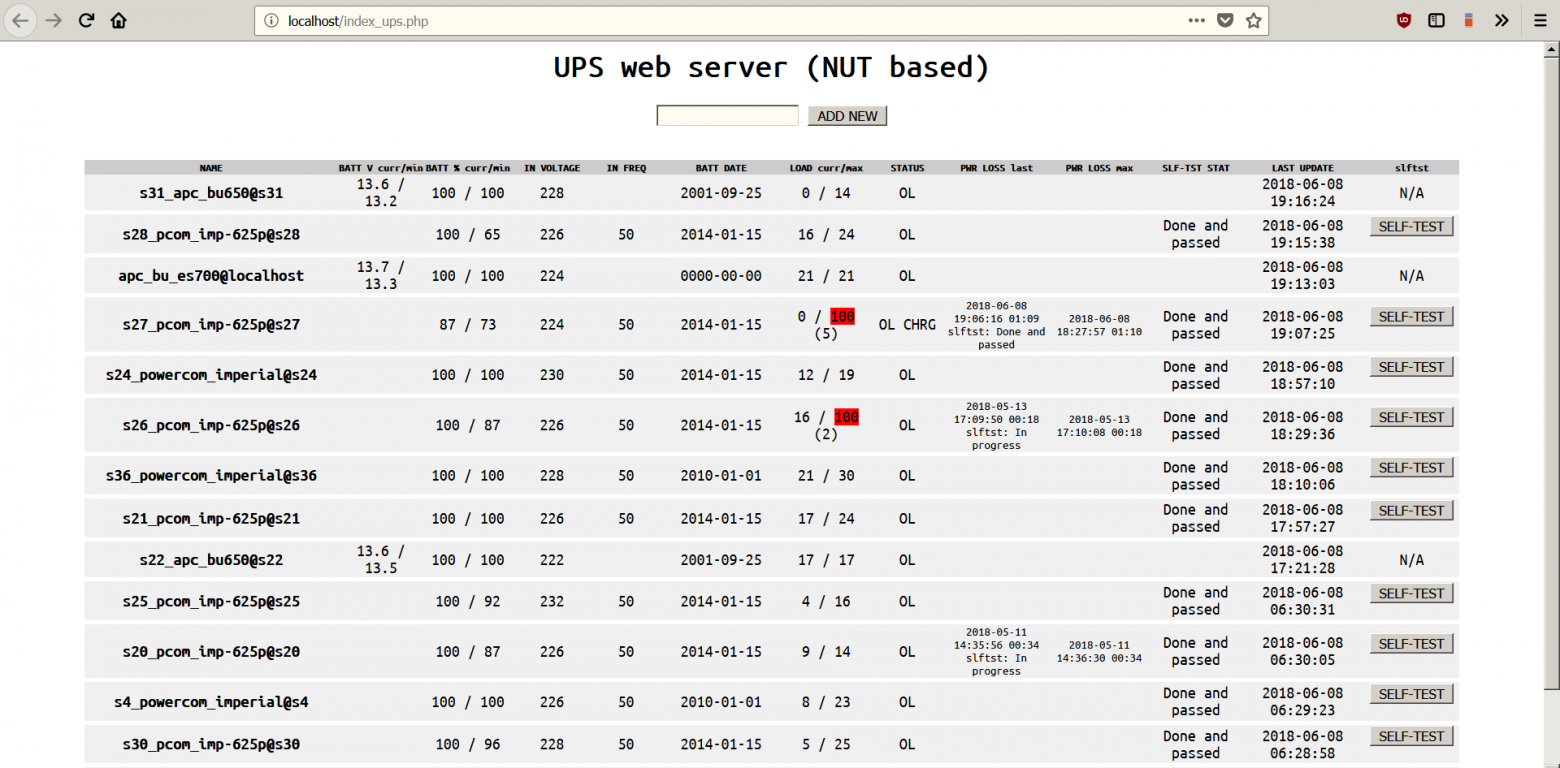
Что мы можем увидеть полезного, помимо текущего состояния? Например:
- если минимальный вольтаж батареи приближается к 10 – лучше заменить её заранее;
- при нормальных значениях вольтажа отказ ИБП будет связан скорее всего, с отказом электроники (ваш, К.О.);
- нагрузка более 70 процентов нежелательна, 100 не нормальна, если не связана с событием self-test;
- минимальный заряд батареи менее 30% говорит о неисправности батареи либо о неверных настройках автоотключения при разряде на клиенте.
Несколько моментов:
- столбцы можно сортировать нажатием на заголовок;
- максимальные/минимальные значения выводятся через слеш к текущим, критические отмечаются красным;
- осторожнее с кнопкой «self-test».
Если у кого-то проблемы с установкой/работой NUT под Windows – пишите, разберёмся вместе.
Спасибо за внимание!
Только зарегистрированные пользователи могут участвовать в опросе. Войдите, пожалуйста.
Какой софт вы используете для мониторинга ИБП рабочих станций?
18.8% Софт от производителя22
29.06% Zabbix / Cacti / подобное34
24.79% Не использую, но после прочтения статьи решил, что надо бы29
4.27% Другое, рассказал в комментариях5
Проголосовали 117 пользователей. Воздержались 24 пользователя.
42ITy™
42ITy™ is a next generation platform for data center
service optimization that aims to bridge the gap between the traditional silos
of IT and facility management.
42ITy™ promotes an open, community based approach, to
ensure broad and vendor agnostic support, while leveraging and giving back to
leading open source software components including NUT (Network UPS Tools),
0MQ/Malamute & MariaDB, among others.
Network UPS Tools Services for Windows
Network UPS Tools Services for Windows provides tools and services to run an
upsd-compatible server to report the status of UPS devices connected to a
system or server in primary (aka «master») mode. It allows other systems,
e.g. Network UPS Tools secondary (aka «slave») daemons and monitoring clients,
access to UPS information using standard Windows programming interfaces for
easier setup.
nut-snmpagent
nut-snmpagent is an SNMP wrapper to expose the upsc output into Net-SNMP.
NUT.Net
A .Net implementation of NUT client and server state machinery.
Used in the nearby WinNUT-Client (.Net) project.
jNut
A Java module to talk to an UPS via NUT (Network UPS Tools) upsd.
This originated in NUT codebase, but was externalized into a sibling project.
UPS::Nut
A Perl module to talk to an UPS via NUT (Network UPS Tools) upsd.
PyNUT
PyNUT is an abstraction class written in Python to access NUT (Network UPS
Tools) server and execute commands without needing to know the communication
protocol.
ups_control
A developing Python wrapper to upsc which can generate email and shutdown
the machine.
Nutify
Nutify is a comprehensive monitoring system designed to track the health
and performance of your Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) devices.
It provides real-time insights into critical UPS metrics, allowing you to
ensure the continuous operation and protection of your valuable equipment.
Nutify collects data, generates detailed reports, and visualizes key parameters
through interactive charts, all accessible via a user-friendly web interface.
NUT can be configured via web interface, data stored into SQLite, and
notifications sent to mobile, Discord and other targets.
go.nut
A Golang library for interacting with NUT.
Node-NUT
A NodeJS module that implements a NUT (Network UPS Tools) client.
NUT HTTP API
An API wrapper that outputs the upsc command as a JSON output. This is a
small HTTP server written in JavaScript which relays HTTP request parameters
to upsc command line arguments, and neatly wraps the result as JSON.
PeaNUT
A tiny dashboard for Network UPS Tools.
Written in NodeJS, can serve as a Docker container or as a Homepage widget,
includes Web-UI and a REST API for queries.
NUTService and C# NUTClient
A Windows service to communicate with NUT server and initiate safe shutdown
when UPS forced shutdown or low battery happens, depending on your settings.
-
The
NUTClient.cs(along with other files) in project sources provides
a C# implementation of the NUT protocol for the client side.

 Плюс часто в системах уже есть софт с этими библиотеками. Точно нужны: libeay32.dll, ssleay32.dll, libgcc_s_dw2-1.dll (есть в папке NUT-bin), libusb.dll (есть в дистрибутиве libusb), msvcr71.dll (в составе Net Framework 1.1). Все эти файлы должны быть в папке Windows\System32;
Плюс часто в системах уже есть софт с этими библиотеками. Точно нужны: libeay32.dll, ssleay32.dll, libgcc_s_dw2-1.dll (есть в папке NUT-bin), libusb.dll (есть в дистрибутиве libusb), msvcr71.dll (в составе Net Framework 1.1). Все эти файлы должны быть в папке Windows\System32;