Item Preview

symantec-norton-desktop-3.0-for-windows-disk1.png
symantec-norton-desktop-3.0-for-windows-disk2.png
symantec-norton-desktop-3.0-for-windows-disk3.png
symantec-norton-desktop-3.0-for-windows-disk4.png
symantec-norton-desktop-3.0-for-windows-disk5.png
symantec-norton-desktop-3.0-for-windows-disk6.png
symantec-norton-desktop-3.0-for-windows-disk7.png
1,707
Views
11
Favorites
2
Reviews
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
Uploaded by
wossman
on
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
Norton Desktop for Windows 3.1 3.0
| Category: | Utility |
| Year: | 1993 |
| Description: | Rather good File/Program Manager replacement for Windows 3.1 Among other things, every drive on your system appears on the desktop, and right-click support is added. |
| Manufacturer: | Norton Computing |
| Localization: | EN |
| OS: | Windows 3.x |
Files to download
| #5796 | norton1.vfd.7z | 1.2 MB | 0xFB30BBCB | ||
| #5797 | norton2.vfd.7z | 1.4 MB | 0x9980E5D8 | ||
| #5798 | norton3.vfd.7z | 1.4 MB | 0x5A374C3A | ||
| #5799 | norton4.vfd.7z | 1.4 MB | 0xA7CC8883 | ||
| #5800 | norton5.vfd.7z | 862.8 KB | 0xF310B5BE | Fake? | |
| #5801 | norton6.vfd.7z | 1.3 MB | 0x2AE8572A | ||
| #5802 | norton7.vfd.7z | 686.3 KB | 0x7E2279B6 |
Scroll down for comments. Register to leave your one.
Comments
Peter Norton Computing / Symantec
Peter Norton Computing was Peter Norton’s own company that he started in 1985. His first product, The Norton Utilities, became ubiquitous during the DOS era. Offering power that simply didn’t come with the standard DOS commands, these provided undelete, file find, wipedisk and wipefile commands to name but a few — they were considered essential both for security and convenience.

Symantec had started out even earlier, in 1982, in the field of artificial intelligence. Through a series of acqusitions and mergers, Symantec released their first product in 1985: a database management system called Q&A. It was unique in that it used a natural-language query based on a 600-word dictionary. This allowed users to request data by typing in English sentences, hence the product name, Q&A.
Despite its modest success at selling Q&A, Symantec had difficulty in gaining market share over other database companies such as Ashton Tate with their dBase product and even from Lotus, with their spreadsheet with data capabilities, Lotus 1-2-3. They made just $8m in their first two years of sales — far short of expectations — though it would go on to be a big seller for them! The board soon realised they could not be a single-product company like WordPerfect or Ashton-Tate.
This led Symantec to enter into a period of acquiring other software companies in 1987 that had niche products outside of their database specialty. As part of these acquisitions, it was important they not only gained the products, but also the development staff.
In 1987, they released a word processor, Q&A Write. Similar to WordPerfect, typical operations are accessed via the function keys in combination with Shift, Ctrl and Alt. It was designed to be fun and easy to use. There were numerous features not found in bigger word processing packages at the time, including the ability to perform mathematical functions directly in the document, extract data from a Lotus 1-2-3 .WK1 file and incorporate it into your document, built-in spell checker, and box drawing. It sold for $199.
Peter Norton Computing was bought by Symantec in August 1990, but they retained the famous «Norton» branding across numerous product lines well into the 2000s. At the time of the acquisition, the DOS utilities market was estimated to be worth $410m, of which Peter Norton Computing had about a 34% share. The acquired company became a division of Symantec and was renamed Peter Norton Computing Group. Most of Peter Norton Computing’s 115 employees were retained. The merger also helped Norton Computing regain the market share it was losing to competitors, especially Central Point Software.
Norton Utilities
As mentioned, The Norton Utilities was first released in 1985. Offering a suite of DOS utilities that either didn’t come with any version of DOS, or bettered the functionality they provided.
Norton Utilities 7.0 [for Windows] arrived in 1993. Now designed to work with hard disks that used DoubleSpace or Stacker, it came with a suite of data recovery tools including Disk Editor, The Norton Disk Doctor, and Unerase. Disk Editor could restore files that weren’t even visible by DOS 6.0, The Norton Disk Doctor could automate more kinds of disk repair than any other utility on the market at the time. Unerase could be used to rebuild files that DOS 6’s Undelete couldn’t even recognise. Norton Utilities 7.0 also came with Speedisk that was able to defragment DoubleSpace drives, The Norton Cache, was their equivalent to DOS 6’s SmartDrive, but was smaller and faster. In the package it also came with an emergency disk to allow you to boot into and recover a system that wouldn’t boot itself.
Norton AntiVirus / Symantec AntiVirus
Building on the success of The Norton Utilities, a number of other products including Norton Commander and Norton Backup followed. Jumping on the anti-virus bandwagon, Norton AntiVirus was first launched in 1990.
Just like other anti-virus tools that it competed against, it had several key utilities including:
- Virus Intercept — A memory resident program that protected against
infected files entering your system. Virus Intercept required as
little as 1K RAM, and could load in high memory. - Virus Clinic — A program that scanned your system for the presence
of known viruses and file irregularities, and repair infections
caused by most known viruses. It had flexible scanning features such as quickly checking your entire computer system for virus
infection, or check executable files only. Scanning could be set to
occur every time you start your computer, or only on demand.
Version 1.0.0 was launched in December 1990. Out of the box, the virus definitions (the 32 KB-sized NAV.DEF file dated 6th December 1990) could detect and remove 142 viruses. The main program was called Virus Clinic. The installer provides you with the option to install Virus Intercept on startup, which is the memory-resident virus portion of Norton AntiVirus.
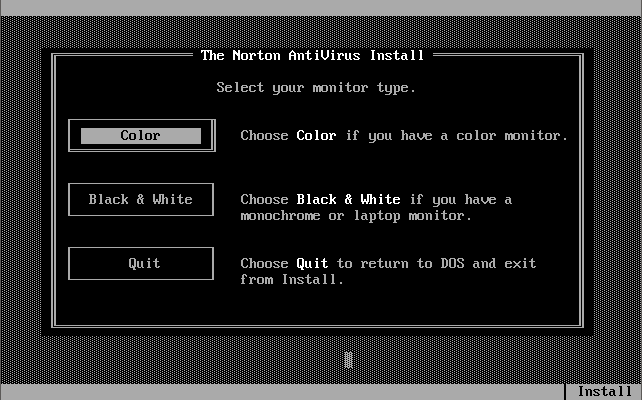
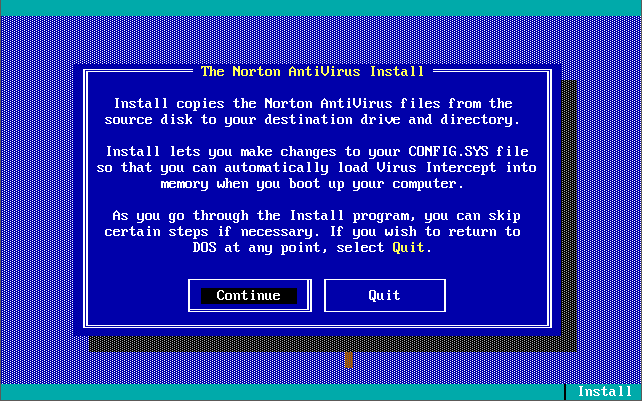
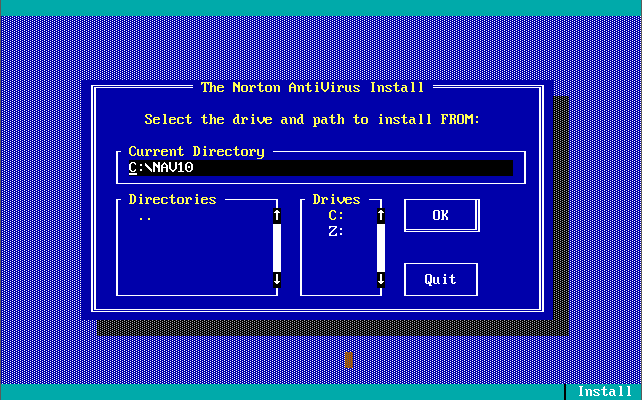
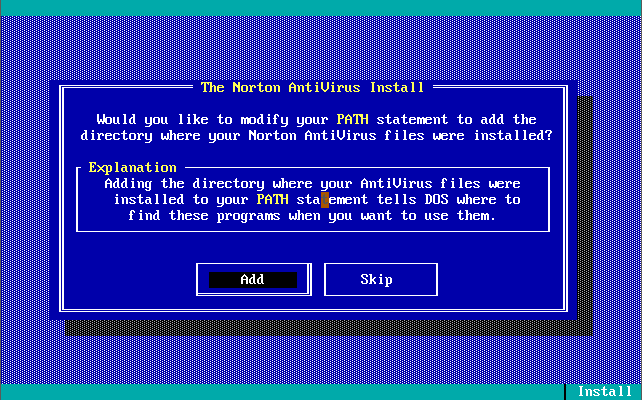
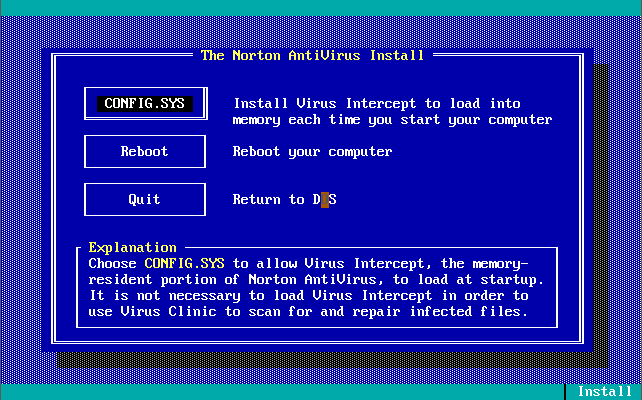
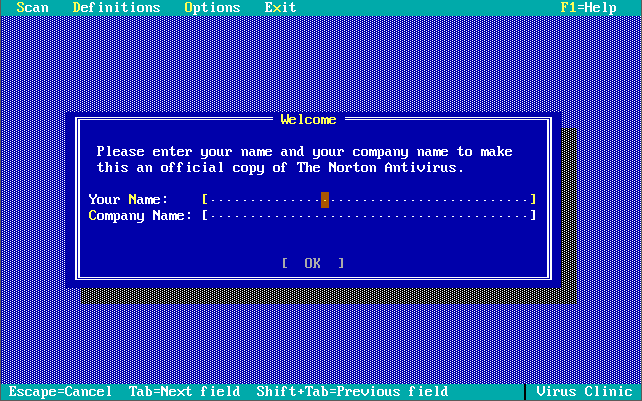
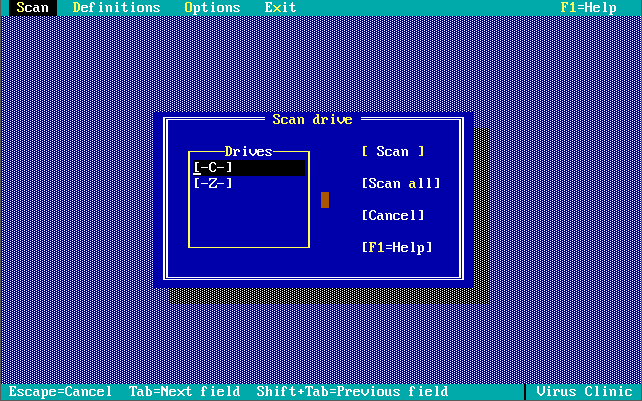
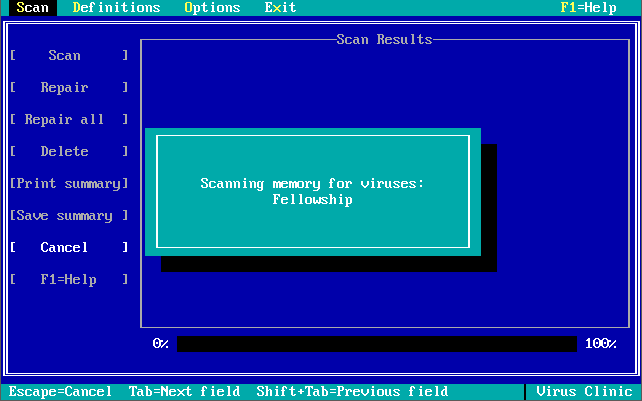
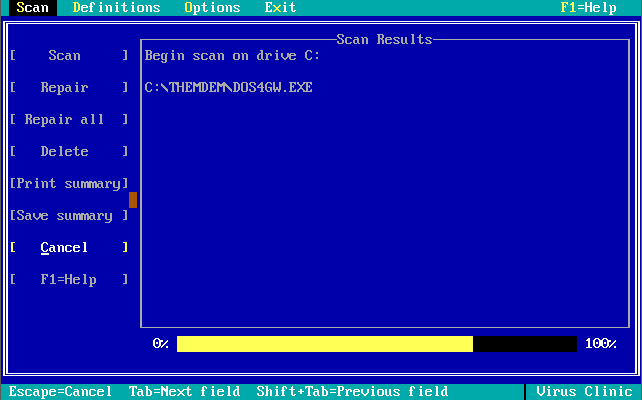
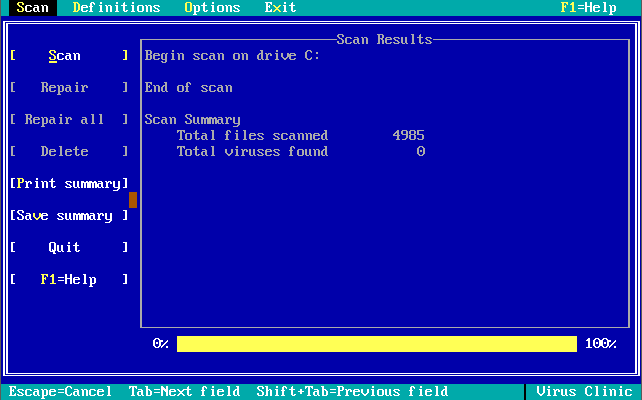
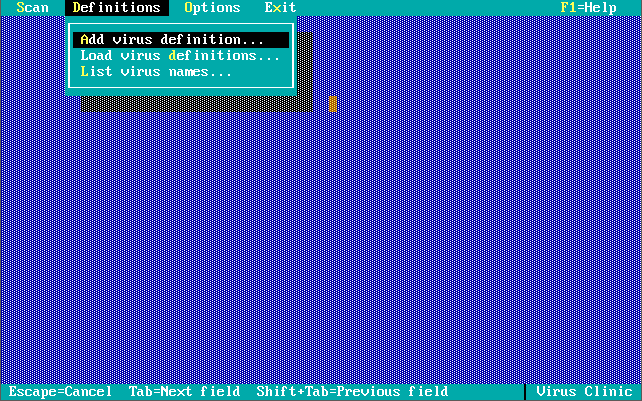
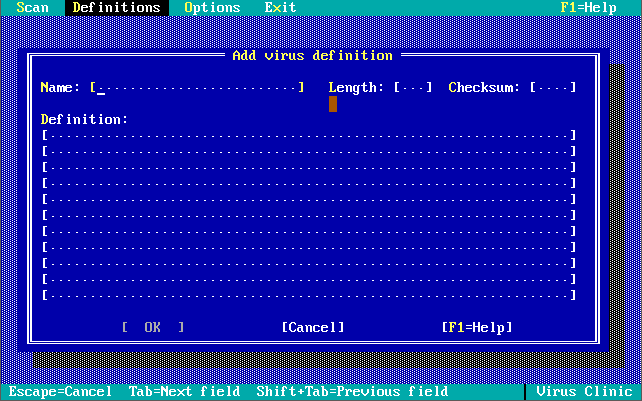
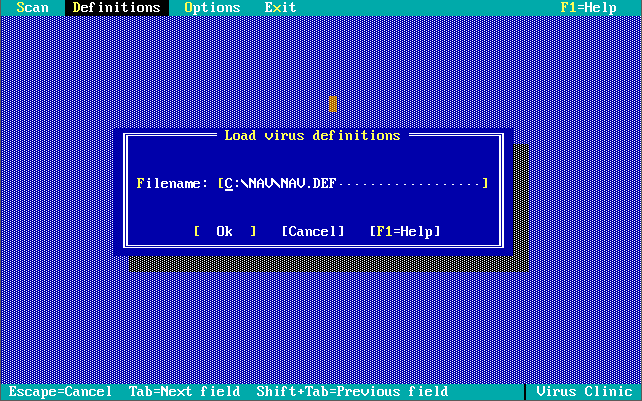
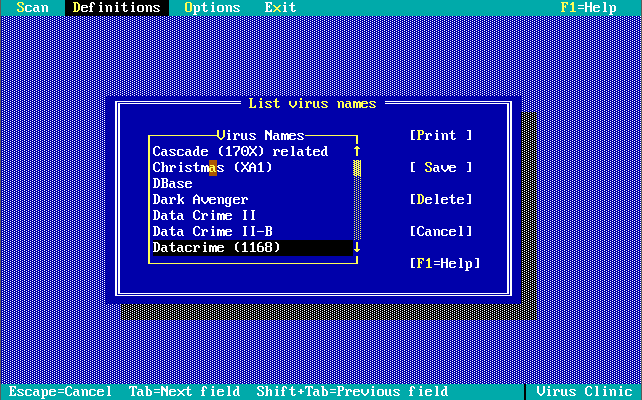
Note in these last 3 screenshots the somewhat unique ability to input your own virus definitions, or signatures directly!
Version 1.5 arrived on 5th August 1991, 8 months after the first release. It was much the same as v1.0.0 to install, except for the added option of the level of scanning on startup that Virus Intercept would perform. It could detect and remove 321 viruses. No other features differed from v1.0.0.
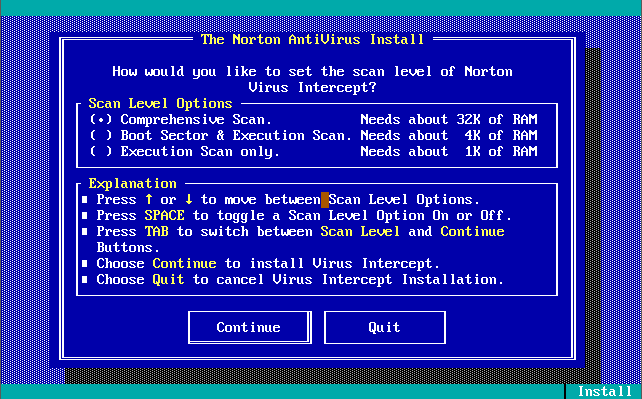
Virus Intercept v1.5’s startup settings
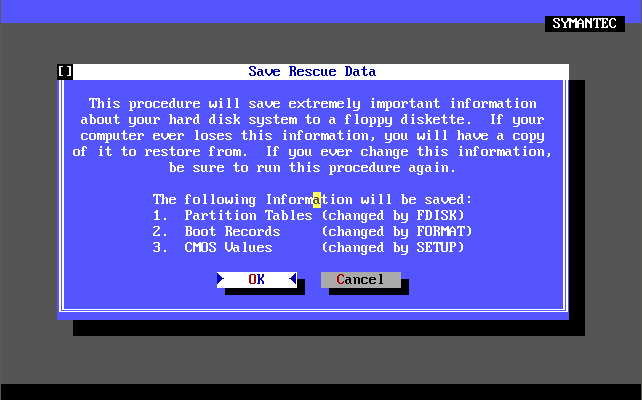
Version 2.0 was released in 1992, supporting both DOS and Windows. It’s virus definition file (dated 7th April 1992 and weighing in at 31 KB) detected 340 known viruses and 1,005 strains. This version added the concept of creating a ‘Rescue Disk’ that you could use to boot virus-free and run a scan. You could still add your own virus definition manually via the Definitions->Modify List menu option.
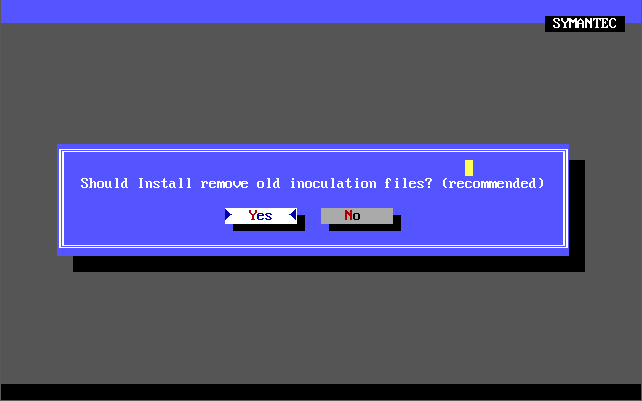
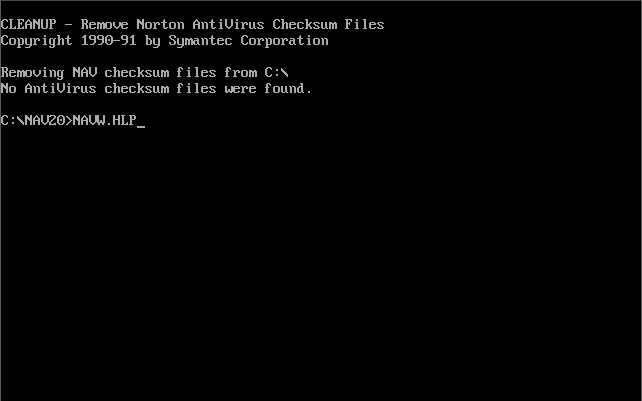
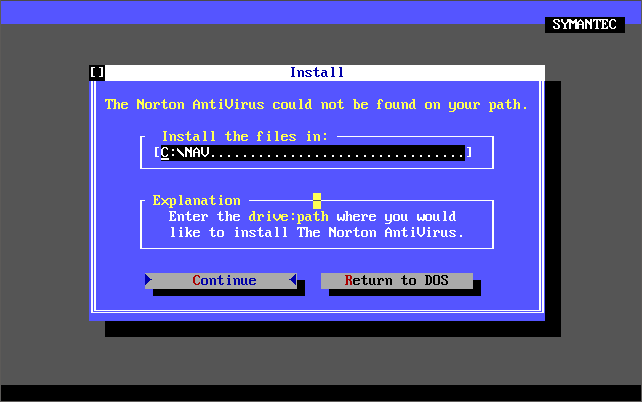
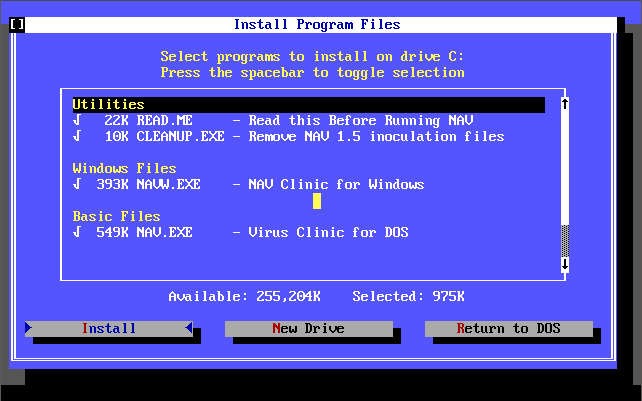
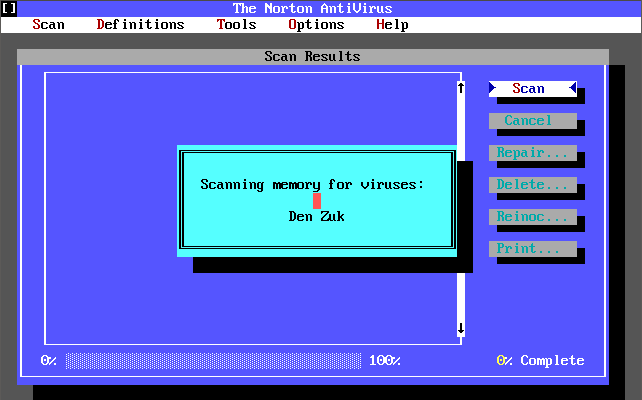
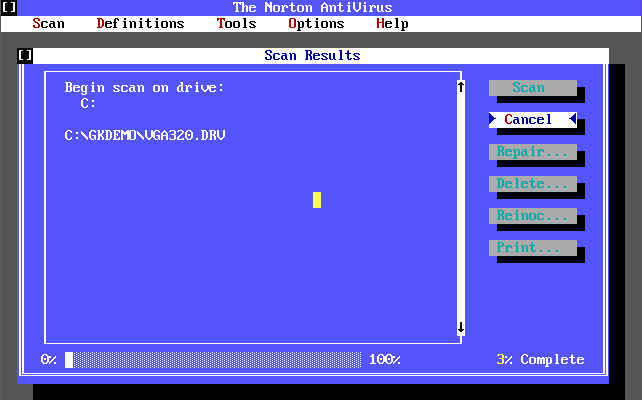
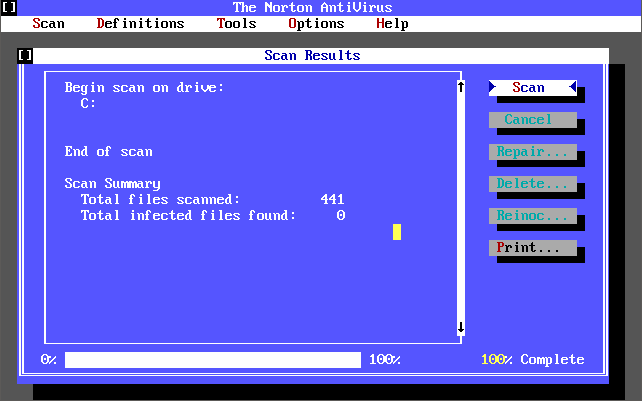
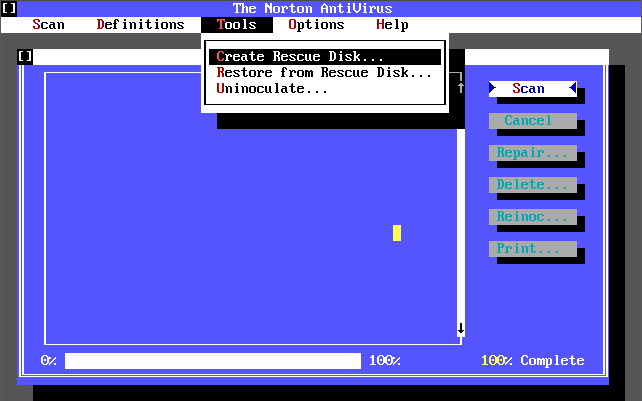
There was also a ‘Michelangelo Edition’ which was a free cut-down version of Norton AntiVirus 2.0 for DOS that came out on 15th February 1992 in time for when the Michelangelo virus was due to activate on 6th March 1992. Upon activation the virus would begin formatting the infected computer’s hard disk. Symantec released this version which detects and removes the Michelangelo virus.





Version 2.1:

Version 3.0:



Version 5.0:



The last virus definition updates for DOS were around September 2001, which was 0907i16.exe.
Norton Commander
The Norton Commander was a file manager, editor, viewer and terminal emulator, first launched in 1986. It was designed to make those difficult or impossible tasks in the DOS command line possible and easy to do. With two ‘panels’ you could view two directories side-by-side and perform operations between them.
Version 4.0 arrived in July 1993, adding these new features:
- over 30 new file viewers including Lotus 1-2-3, RBase, dBase, Reflex, Paradox, Q&A, compressed files (.ZIP, .ZOO, .ARJ, .ARC, .LZH, .ARC and .PAK) and images (both bitmap and vector)
- compressed file handling
- new editor features
- a new cloning feature
- advanced features for Power Users
- new shortcut keys
- filter/attribute improvements
Version 5.0 was released in February 1995, and added the following new features:
- drag & drop capability to copy or move files between the left and right panels
- more advanced filters for selecting files based on date/time, size, and attributes
- a sync feature to keep directories the same between two or more computers or network volumes
- compressed file viewing
- more disk utilities including format disk, label disk and copy disk
- network utilities (for Novell Netware 3.x and 4.x) including attach/detach network, map drive, send message, and server info
- file split/merge
- disk cleanup
- file search — a completely rewritten File Finder with regular expression support, duplicate file search, multiple search locations and much more
- modified terminal emulation program
- 20 screen savers (both text and graphics)
Version 5.51 was the last release for DOS, arriving on 1st July 1998. It was almost the same as version 5.0 in terms of functionality, but added support for long filenames (LFNs), though in DOS real mode this did require a TSR to be loaded first, otherwise filenames would be truncated.
Norton Desktop
The Norton Desktop for Windows was launched in 1991, combining the features of Symantec’s three most popular DOS utility programs: The Norton Utilities, The Norton Commander, and The Norton Backup. At $149, it was designed to be an enhanced replacement to the standard Windows File Manager and Program Manager.
«Symantec’s Norton Desktop for Windows has established itself as the leading replacement for Windows’ Program and File Managers. Competing packages either define themselves in terms of Norton Desktop or make sure they work with it. Version 2.0 of the $149 package is a successful upgrade.
Most of the components of the product have been enhanced, and there are several new modules including an editor, virus protection, a macro recorder, and a financial calculator.
The central element of the collection is the Norton Desktop itself, a combined file-launcher, and manipulator. Symantec has addressed the most frequent complaint about this module: slow loading times. While our tests didn’t match the ‘up to six times faster’ claims of Symantec, the effect was still dramatic. On our 25-MHz 386 test system, Norton Desktop 1.0 took 20 seconds to load under Windows 3.0 and 15 seconds under Windows 3.1. Loading Version 2.0 running under Windows 3.1 took only 7 seconds. The time Windows takes to load is not included in these results.
Norton’s Quick Access, part of the Desktop, had the look of Program Manager in Version 1.0 but included enhancements such as subfolders. Version 2.0 lets you choose one of
three looks: the Program Manager look, a scrolling text list, or an icon-only toolbox.
Also new to the basic desktop are drag-and-drop capabilities, and not just for the few Norton-specific programs supported in Version 1.0.
There are also several improvements
to the file manipulator. The side-by-side directory tree and file lists are still there, but now you can easily get the total size of all the files in a directory — a capability that was lacking in Version 1.0.
A popular feature of the file view is the button bar, which lets you call up file actions from text buttons. Version 1.0 allowed
only six buttons. Version 2.0 can have up to 14 (depending on your display type).
Improved File Viewing
The file viewers have also been improved. Support has been added for almost 20 new file types including .DRW, 24-bit TIFF, and Lotus 1-2-3, Release 3.0, files. Most graphics, word processor, database, and spreadsheet file types are included (two exceptions are .PIF and Targa). The ZIP viewer shows only the zip directory, not the files within. Lotus’s Magellan, a DOS product, as been doing this for years, but no Windows program has this feature.
The file viewers worked well, with two exceptions. Some Microsoft Word for Windows 2.0 files we tried to view generated error messages, and the .PCX viewer failed on 24-bit color .PCXs and a few 8-bit .PCX files.
Sleeper, the included screen saver, has been improved. It will use the screen savers that come with Windows 3.1 as well as those that ship with Intermission and with AfterDark 1.0.
Batch Runner, the batch language that Symantec licenses from Wilson Windoware, has several enhancements in this version. Network-specific commands have been added, the batch editor has been improved, and, most significantly, there is now a Macro Builder to record batch files. But there is still no dialog editor.
Missing from the initial shipment of Version 2.0 is support for tape drives in the included Norton Backup for Windows.
This is promised, and a coupon is provided to get the tape backup module for a nominal shipping charge when it becomes available.
New Editor
Of the new modules, the best is Desktop Editor, a vast improvement over Notepad. It will edit multiple files using the Windows MDI, has a powerful search feature including pattern matching, and offers multilevel undo. It also includes a great file-comparison feature.
A financial calculator to supplement the tape and scientific calculators is also new. Using reverse Polish notation, it will do cash flow analysis and statistics on entered data. In addition, there are fill-in-the-blank forms for simple interest, mortgage amortization, bond yield, and date/time arithmetic.
Also new with this version is virus protection that includes everything
in the standalone Norton Anti-Virus program: a DOS device driver and both Windows- and DOS-based scanners.
There is an uninstall module, something we wish other Windows programs provided. And the incompatibility with Turbo Pascal for Windows programs has been resolved.
Any regular user of Norton Desktop for Windows will want to upgrade, for the faster loading and the useful editor if nothing else. What was already a good alternative to the basic Windows interface has become even more attractive.»
PC Magazine, 16 June 1992

An advert for Norton Desktop 1.0 for Windows (1991)
In 1992, Version 2.0 was released at the same price as Version 1.0: $149, or $49 for the upgrade version. Also released
the same year was Norton Desktop for DOS Version 1.0.
In 1993, Norton Desktop 3.0 for Windows was released.
(Redirected from Norton Desktop)
Norton Commander (NC) is a discontinued prototypical orthodox file manager (OFM), written by John Socha and released by Peter Norton Computing (later acquired in 1990 by the Symantec corporation). NC provides a text-based user interface for managing files on top of MS-DOS. It was officially produced between 1986 and 1998. The last MS-DOS version of Norton Commander, 5.51, was released on July 1, 1998.
Norton Commander
|
Norton Commander v.5.51 for DOS. Note the long file names present when running on Windows. |
|
| Original author(s) | John Socha |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1986; 39 years ago |
| Final release |
5.51 |
| Operating system | MS-DOS |
| Type | File manager |
| License | Commercial proprietary software |
A related product, Norton Desktop, a graphical shell for MS-DOS and Windows, succeeded Norton Commander. It came in two variants, Norton Desktop for DOS and Norton Desktop for Windows.
John Socha started work on Norton Commander in 1984; at the time, he called it «Visual DOS» or «VDOS».[1]
Norton Commander was easy to use because it had a constant view of two file manipulation objects at once. After starting the program the user sees two panels with file lists. Each panel can be easily configured to show information about the other panel, a directory tree, or a number of other options. At the bottom of the screen, Norton Commander displays a list of commands that are extended on demand by the CTRL and ALT keys. Thus, without heavy use of the mouse (although mouse functionality was integrated around version 3.0), the user is able to perform many file manipulation actions quickly and efficiently. Additionally, it also includes a built-in text file viewer (invoked with F3 key) and text file editor (invoked with F4 key).
Norton Commander was very popular during the DOS era and it has been extensively cloned. For example, the IntelliJ IDE used to include a «Commander» plugin that performed file manipulation using the same shortcut keys as Norton Commander[2] but the plugin is now obsolete.[3]
Windows 95 included a new graphical shell called Windows Explorer and supported long filenames (LFN). Symantec released Norton Commander 5.51 to support long filenames using the standard Windows APIs. In order to preserve LFNs while working in real mode, Norton Commander 5.51 required the use of a terminate-and-stay-resident (TSR) utility. Norton Commander did not have native support for LFNs in real mode and would truncate them.
According to former Peter Norton Group developer Mark Lawler, after Symantec had acquired Peter Norton Computing, Symantec had speculated Microsoft Windows would be a success, so the key PNC resources had been diverted, while new programmers for the Windows platform were hired. Enrique Salem (who eventually became Symantec’s CEO) led the development of a Windows shell replacement for Windows File Manager and Program Manager released as Norton Desktop for Windows.
Norton Commander for Windows
edit
Norton Commander for Windows was a Windows 95 variant of the classical DOS file manager.
Version 1.0 was first released in 1996. It supported both Windows 95 and Windows NT.
This version fully integrated with Windows features such as the Recycle Bin and Quick View. Quick View feature was supported via the included basic Quick View Plus.
Version 1.02 added Windows 98 support.
Version 2.0 was released in 2000. It supports Windows 2000 and functions under Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7. Installer included Network Utilities, Norton Commander Scheduler, and the Norton Commander.
Network Utilities allows for viewing devices and systems on network, connecting to remote systems, mapping network drives, network monitoring, and more.
Norton Commander is little changed from previous versions, and includes file compression/de-compression of various formats, network utilities access, disk cleanup, files and folder compare, FTP connection management, and more.
The last Windows version of Norton Commander was 2.01.
Norton Commander for OS/2
edit
Version 1.0 was released in December 1992. It supports OS/2 2.0 with HPFS or FAT file system.
It does not include the command prompt found in other versions of Norton Commander.
In June 1993, Symantec lowered the price of Norton Commander for OS/2 to $49, and soon ceased sales.
BYTE in 1989 listed Norton Commander 2.0 for DOS as among the «Distinction» winners of the BYTE Awards, stating that «navigating through a crowded hard disk is a breeze».[4]
Norton Commander-inspired software
edit
There are many programs that follow the style of Norton Commander as created by John Socha. Examples are:
- ACE Archiver for DOS in the first versions had a NC-inspired interactive interface
- Altap Salamander for Windows
- BeFAR[5] for BeOS
- Commander One for macOS
- Demos Commander for Unix and Linux
- Directory Opus for Amiga (1990) and Windows (2001)
- DOS Command Center (DCC) DOS and Win95 versions
- DOS Navigator for DOS
- Double Commander for Windows and Linux
- FAR Manager for Windows, OSX and Linux
- fman[6] for Windows, Mac and Linux
- Ghost Commander[7] for Android systems
- GNOME Commander for Unix-like systems
- HiFile[8] for Windows, Mac and Linux
- Krusader for Unix-like systems
- Midnight Commander for Unix-like systems (including macOS) and Windows
- muCommander for Java platform
- Music on Console for Unix-like systems; actually a music player
- PowerDesk by Avanquest, of which an evaluation version of Version 4 is included in Microsoft’s Windows NT 4.0 Resource Kits
- Stereo Shell for DOS
- The DOS Controller by Søren Kragh
- Total Commander for Windows
- Volkov Commander for DOS
- WinNC[9] for Windows 10
- RAR archive manager used to have Norton Commander-like interface, the last version with that interactive file manager interface look-alike was DOS version 2.50
- Xfolders for OS X
References in popular culture
edit
- Norton Commander is a song released by the Montreal indie group, Men I Trust. While the song contains no literal references to the Norton Commander file manager, it is speculated that the song’s subject matter of comfort and familiarity relate to the familiarity and reliability of the software.[10]
- A mobile game called Progressbar95 features an unlockable gamemode called «Progress Commander» based on the software.
- Comparison of file managers
- ^ Bezroukov, Nikolai (2005). «The History of Development of Norton Commander». Softpanorama.
As John Socha recollected the events (personal communication): ‘I started work on what became known as the Norton Commander in the fall of 1984 … At the time I called it Visual DOS, with the abbreviation of VDOS instead of the usual two-letter abbreviations used at the time.’
- ^ «Commander Tool Window». Retrieved 9 August 2012.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Commander». Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- ^ «The BYTE Awards». BYTE. January 1989. p. 327.
- ^ BeFAR
- ^ fman
- ^ Ghost Commander
- ^ HiFile
- ^ WinNC
- ^ Men I Trust – Norton Commander (All We Need), retrieved 2021-05-18
- The History of Development of Norton Commander (Softpanorama)
- 21st Century Nostalgia A Tribute to Norton Commander 5.0
- Norton Desktop for Windows 1.0 A graphical review in the GUI Gallery
