Setting up an NFS (Network File System) server on Windows 7 can be a useful way to share files and resources across a network. NFS allows multiple computers to access the same files simultaneously, making it convenient for collaboration and file sharing. In this tutorial, we will guide you through the steps to set up an NFS server on Windows 7.
Step 1: Install the NFS Server Feature:
Windows 7 does not natively support NFS, so you will need to install the «Services for NFS» feature. Here’s how to do it:
1. Click on the Start menu and open the Control Panel.
2. Navigate to «Programs» > «Programs and Features.«
3. In the left sidebar, click on «Turn Windows features on or off.«
4. Scroll down and locate «Services for NFS» in the list. Check the box next to it.
5. Click «OK» and wait for the feature to be installed.
Step 2: Configure the NFS Server:
Once the NFS Server feature is installed, you need to configure it to share the desired folders. Follow these steps:
1. Open the Control Panel again and go to «Administrative Tools.«
2. Double-click on «Services for Network File System» to open the NFS server configuration panel.
3. In the «Server» tab, click on the «Add» button to select the folder you want to share.
4. Browse and choose the folder you want to share, then click «OK.«
5. By default, the NFS server allows read-only access. If you want to enable write access, click on the «Permissions» button and adjust the settings as needed.
6. Click «OK» to apply the changes.
Step 3: Adjust the NFS Server Settings (Optional):
If you want to fine-tune the NFS server settings, you can modify certain parameters such as port numbers and cache settings. Here’s how:
1. In the NFS server configuration panel, click on the «Mappings» tab.
2. From here, you can change the server’s port numbers, cache size, and other settings according to your requirements.
3. Make the desired changes and click «OK» to save the settings.
Step 4: Start the NFS Server Service:
Once you have configured the NFS server, you need to start the NFS server service for it to become active. Here’s how:
1. Open the «Services for Network File System» window again.
2. In the «Server» tab, click on the «Start» button next to «Server Status.«
3. Wait for the service to start, and you will see the status change to «Running.«
4. Close the NFS server configuration panel.
Step 5: Access the NFS Share from Client Computers:
After setting up the NFS server, you can now access the shared folder from other computers on the network. Here’s how to do it:
1. On the client computer, open File Explorer.
2. In the address bar, type the IP address or hostname of the NFS server followed by the shared folder name (e.g., \\192.168.1.100\SharedFolder).
3. Press Enter, and the shared folder should appear in File Explorer.
4. You can now browse, open, and modify files within the NFS share.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. Enables easy file sharing and collaboration across a network. | 1. Requires the installation of additional software on Windows 7. |
| 2. Allows multiple computers to access the same files simultaneously. | 2. NFS is not as widely supported on Windows compared to other operating systems. |
| 3. Provides flexibility and scalability for storing and accessing shared files. | 3. Requires proper network configuration and security measures to prevent unauthorized access. |
Setting up an NFS server on Windows 7 can be a great way to streamline file sharing and collaboration among multiple computers on a network. By following the steps outlined in this tutorial, you can easily configure an NFS server and start sharing files seamlessly. Keep in mind the pros and cons associated with NFS to ensure it aligns with your specific requirements and network setup.
Video Tutorial: What ports are needed for NFS?
Setting up an NFS (Network File System) file server can be a useful solution for sharing and accessing files across a network. Here are the steps to set up an NFS file server:
1. Choose a suitable server: Select a server machine with enough storage capacity, processing power, and memory to meet your requirements. Ensure that the server is running a suitable operating system, such as Linux or Unix, which typically have native support for NFS.
2. Install NFS packages: Depending on your server’s operating system, you may need to install the necessary NFS packages. For example, on a Linux distribution like Ubuntu, you can install the NFS server and related utilities using the package manager, such as Apt or Yum.
3. Configure exports: The next step is to configure the NFS exports file. This file specifies the directories you want to share with NFS clients. Edit the exports file (typically found at /etc/exports or /etc/exportfs) and add an entry for each directory you want to share. Define the access permissions (read-only or read-write) and specify the IP addresses or network ranges that are allowed to access the shares.
4. Start NFS services: After configuring the exports file, start the NFS services on the server. Depending on your operating system, the command may vary. For instance, on Ubuntu, you can start the NFS server using the command «sudo service nfs-kernel-server start«.
5. Configure NFS clients: On the machines that want to access the NFS shares, you need to configure the client-side settings. Install the NFS client packages (if not already present) and ensure that they are up-to-date.
6. Mount the NFS shares: Once the client-side configuration is complete, you can mount the NFS shares. Use the mount command along with the server’s IP or hostname, followed by the shared directory’s path on the server. For example, «sudo mount server_ip:/shared_directory /local_mount_point«.
7. Test and verify: After mounting the NFS shares, verify that the clients can access the shared files and directories as intended. Create, modify, or delete files to check if the changes are reflected across the network.
Remember that these steps are general guidelines, and the exact commands and processes may vary depending on your specific operating system and its version. It’s always recommended to refer to the documentation of your operating system and NFS implementation for detailed instructions.
What specs do I need for NFS server?
When setting up an NFS (Network File System) server, there are several important specifications to consider. Here are the key factors to take into account:
1. Hardware requirements:
– CPU: A modern multi-core CPU with sufficient processing power to handle the expected workload is important. More cores can help handle concurrent requests efficiently.
– Memory (RAM): Sufficient RAM is essential to accommodate the operating system, NFS service, and the concurrent client connections. The exact amount primarily depends on the anticipated workload and the number of clients.
– Storage: NFS servers need reliable storage with adequate capacity to store the shared files. Depending on the desired level of redundancy and performance, one can choose between options like hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs), using a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configuration if necessary.
2. Network considerations:
– Network Interface Cards (NICs): High-performance NICs, preferably with support for gigabit or higher speeds, are recommended to ensure efficient data transfer between the NFS server and clients.
– Network Bandwidth: Sufficient network bandwidth is critical to handle the expected demand from the clients. It depends on the number of clients, the size of files being transferred, and the intensity of concurrent operations.
– Network Security: Implementing appropriate network security measures, such as firewalls and encryption protocols, is crucial to protect the NFS server and its data from unauthorized access.
3. Operating System and Software:
– Choose a stable and robust operating system with good support for NFS. Popular choices include Linux distributions like CentOS or Ubuntu Server, which offer NFS functionality out-of-the-box.
– Install the latest stable release of the NFS server software to benefit from bug fixes, performance improvements, and new features. Ensure compatibility with the chosen operating system and validate its support for NFSv4, which is more secure and feature-rich than previous versions.
4. Configuration and Optimization:
– Fine-tune NFS server configuration settings to meet your specific requirements, such as adjusting the number of allowed concurrent connections, specifying the shared directories, and setting up access controls.
– Consider implementing caching mechanisms on the server-side, like NFS caching, to improve overall performance and reduce network bandwidth consumption.
– Regularly monitor and assess the NFS server’s performance to identify any bottlenecks or areas that may need optimization, adjusting settings and hardware as necessary.
Remember, the actual hardware and software requirements of an NFS server can vary depending on the specific use case, anticipated workload, and the number of clients. It is therefore important to analyze your requirements thoroughly and plan accordingly to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
How to setup NFS server on Windows?
Setting up an NFS server on Windows involves several steps:
1. Verify your Windows version: NFS is not natively supported on all versions of Windows. Ensure that you have a compatible version, such as Windows Server editions or some specialized Windows 10 variants like Enterprise or Education.
2. Enable the NFS server feature: Open the Control Panel and navigate to the «Programs» section. Then click on «Turn Windows features on or off.» Find «Services for NFS» and check the box next to it. Click «OK» and let Windows install the necessary components.
3. Configure the NFS server: After enabling the NFS server feature, open the «Services for NFS» administration tool. You can access it by searching for «NFS» or locating it in the Administrative Tools folder. In the tool, click on «Server Manager» and then select «Manage NFS Sharing.» Here, you can set the default NFS server settings, such as choosing the NFS version, enabling user mapping, configuring access permissions, and defining exported directories.
4. Export directories: To share directories via NFS, you need to export them on the NFS server. In the «Manage NFS Sharing» window, click the «Add» button and browse to select the directories you want to share. Define the NFS share name, set the permissions, and configure any additional options required.
5. Configure firewall rules: By default, Windows Firewall may block NFS traffic. Ensure that the necessary port and protocol exceptions are in place to allow NFS communication. The standard NFS port is UDP/TCP 2049.
6. Test and verify: Once the NFS server is set up, test the NFS shares from a client device running an NFS client. Verify that you can mount and access the exported directories correctly.
Remember, NFS (Network File System) is commonly used in Unix-like environments, and Windows compatibility can sometimes present challenges. Additionally, consider security aspects, such as authentication methods and network configurations, to ensure the NFS server setup meets your specific requirements.
How to install NFS Client on Windows 7?
To install an NFS (Network File System) client on Windows 7, you can follow the steps below:
1. Open the Control Panel: Click on the «Start» button in the bottom-left corner of the desktop, then select «Control Panel» from the menu.
2. Go to «Programs«: In the Control Panel window, locate and click on the «Programs» or «Programs and Features» option.
3. Enable Windows Features: Within the Programs section, you will find an option called «Turn Windows features on or off.» Click on it to open the Windows Features window.
4. Find NFS Client: In the Windows Features window, scroll down and look for «Services for NFS.» Check the checkbox beside it.
5. Install the NFS Client: After selecting the «Services for NFS» option, click on the «OK» button to begin the installation process. Windows will then install the necessary components and enable the NFS client on your system.
6. Reboot the computer: Once the installation is complete, it is recommended to restart your computer to ensure the changes are applied.
After following these steps, the NFS client will be installed on your Windows 7 machine, allowing you to connect and access NFS shares on remote servers.
It’s worth noting that NFS is typically used in Unix-like environments, and Windows 7’s built-in NFS client may not support advanced features and performance optimizations compared to dedicated NFS clients available for Windows. If you require advanced NFS functionality, you may want to consider using third-party NFS clients like «NFS Manager» or «DiskAccess.«
Remember to always verify the authenticity and security of any third-party software you choose to install on your Windows 7 system.
How do I know if NFS server is installed?
To verify if the NFS (Network File System) server is installed on your system, you can follow these steps:
1. Open a terminal or command prompt on your device.
2. Type the following command and press Enter:
«`bash
systemctl status nfs-server
«`
This command checks the status of the NFS server service and whether it is running or not.
– If the service is installed, active, and running, it will show you a status message indicating that it is active and running.
– If the service is not installed or not running, it will display a message indicating that the service is inactive or not found.
Alternatively, you can also use the following command to check if the NFS server package is installed on your system:
«`bash
dpkg -l | grep nfs-server
«`
This command lists all installed packages and filters out the ones related to the NFS server. If the package is installed, it will display the relevant details. If the package is not found, it won’t display any output, indicating that it is not installed.
Please note that these commands assume you are using a Linux-based operating system. If you are using a different operating system, the steps to check for NFS server installation may vary.
Let’s start with the basic. So, what is a NFS server ?
Network File System (NFS) is a protocol developed by Sun Microsystems, which enables a user to access files on a different system as if the file is locally available over the network. It lets user to modify/copy files resided on a remote system. So its basically a protocol for a network drive. The create NFS server then can be accessed via another Windows or a Linux system.
As you might have already known that NFS server feature is not available on non-server versions of Windows and that’s the main reason you are here. But with the help of right tools we should be able to setup NFS server on non-server Windows.
We will be creating a NFS server on a Windows system using a free tool and accessing the server from a Linux system. I will be using Windows 10 Pro and a Arch Linux (Xfce) system in this article.
Read also: Fix Requested NFS version or transport protocol is not supported
So, without any further ado let’s jump into it.
Setuping NFS Server On Non-Server Windows System
First of all head to the below link and download winNFSd, our free NFS server program.
winNFSd GithHub (Source code if you need)
winNFSd (Binary)
Extract the downloaded WinNFSd.exe on C:/nfs (or where ever you like).
Now we will create two files namely paths.txt and start_server.bat within the winnfsd executable folder.
Contents of paths.txt
Open paths.txt using any text editor and write down any path that you want to share one per line, including an alias.
For example, my paths.txt looks like this.
C:\Users > /c D:\ > /d
In the first line C:\Users would be the path that i want to share and /c would be the alias for it, so i can access the path using alias from Linux system.
Contents of start_server.bat
This file is optional, but its really handy. We will run this bat file to run our winNFSd executable with all the needed parameters. We wont need to write that long arguments every time we run it. Below is what it looks like in my start_service.bat.
c:\nfs\WinNFSd.exe -addr 192.168.1.64 -pathFile "c:\nfs\paths.txt"
Where,
in place of 192.168.1.64, put your own local IP address. You can get your local IP address using cmd by entering ipconfig command.
And you know about the paths.txt file.
Now create a shortcut of start_service.bat (if you want) on your desktop. You are ready to run your NFS server on your non-server Windows system.
After running the start_server.bat, you should get a window like below.
Now we have a working NFS server running from a non server Windows. You can connect to this server via any NFS client that supports NFS v2 or v3.
winNFSd doesn’t support NFS v4.
Mount NFS Drive on Linux Using Terminal (nfs-utils)
We have already setup NFS server on non server Windows now lets mount the remote drive and access the files from our Linux system. I am using Arch Linux with Xfce desktop environment but it should apply to any distribution out there.
First of all we will need the nfs-utils package, install it if not already.
To install the package on Arch Linux issue the following command as root, if any other Linux distro, search on respective sites.
sudo pacman -S nfs-utils
After that we will need to edit nfsmount.conf file.
By default it will try to connect using nfs v4 protocol. We will set the default version to 3 because as i have already told you, WinNFSd does not support nfs v4.
Use your favourite text editor to edit the file, i am using nano here.
sudo nano /etc/nfsmount.conf
Find the line with #Defaultvers=4 and instead of 4 or anything else write 3 and also remove the # to uncomment the line and save the file. Control + S will save the file on nano.
Lets create a folder on our root directory where we will mount our network drive. I have create a folder named mountc on my root dir ie: /mountc. To create the dir,
cd / sudo mkdir mountc
Now that we are all set, lets mount the nfs drive. Issue the following command,
sudo mount -t nfs 192.168.1.64:/c /mountc -v
Where,
Put the nfs server IP instead of 192.168.1.64 and instead of /c put your own alias that you have assigned on your paths.txt file. And /mountc is the path where /c will be mounted.
Now you can access the nfs drive by navigating to /mountc from your file manager.
After you have issued the following command you will get something like below.
On NFS server terminal,
On NFS client terminal,
To unmount the mounted drive issue the following command,
sudo umount /mountc -lf
Where /mountc is the mount point. And i am using -f just to force the unmounting.
Note: I am not using any kind of firewall. You might need to disable or create rules on your firewall. Good luck.
And this is how you setup nfs server on non-server windows 10, 7 and mount it on a Linux system.
If you faced any issue or want to appreciate just comment below. I will try to be helpful.
How to Configure NFS Server on Windows 7
on
November 06, 2017
in
Video
|
Usually we configure NFS Server on Linux/Unix Machine for File sharing in Network between Unix Machines,But here in this tutorial we learn how to configure a Windows 7 machine as NFS Server.
I have used third party software named hanewin nfs package to install nfs package on windows and configure NFS Server on Windows7 machine.
If you want to configure NFS Server on Linux you can easily configure NFS server.
Usually people know that NFS Server is configured on Linux Machine only for sharing files with Linux clients. But that’s half truth. In real world today we can easily configure NFS on windows Machine also.
If you want to configure NFS Server with NIS Server and Autofs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux you can watch this video.
First we need to configure NIS SERVER.We set NIS DOMAIN NAME and then we will configure NFS Server and after that we will configure Autofs Server for automation process.Not forget to configure Firewall and Selinux otherwise your configuration will not work.
Practical Implementation of NIS NFS and Autofs Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
You can submit this project in your Engineering Major Project.This is very helpful for computer science students.
Cisco Packet Tracer on Apple Silicon (M1, M2, M3, or M4) in 2025
Cisco Packet Tracer on Apple Silicon (M1, M2, M3, or M4) in 2025 Want to practice networking and prepare for Cisco certifications like CC…
We can use the haneWIN NFS tool to make any physical or virtual Windows computer as an NFS share. This guide shows how to configure and set up NFS share on Windows 7 and connect it to VMware ESX server as storage. Here I explain the steps I followed in my test lab to create and connect storage to the VMware ESXi server. Network File System (NFS) developed by Sun Microsystems (Solaris) to use in UNIX based systems.
Update:
Though this post was originally published for Windows 7 host OS, it might work with Windows 10 and 11 as long as Hanewin NFS works on the latest Windows OS with proper firewall settings.
To set up NFS share on earlier Microsoft Operating systems, you need a component called ‘Windows Services for UNIX (WSFU)’ which can be downloaded from the Microsoft website. But WSFU is not available for Windows 7. So, creating an NFS share on Windows 7 and allowing other UNIX based Operating Systems to access the share is not straightforward without third-party utilities. As mentioned earlier, this case is applicable for Windows 10/11 and 8.1 Operating Systems also.
haneWIN NFS Server works nicely with Windows 7 to create and share Network File Systems. Download 30 days trial version of hanWIN NFS here. If you are happy with the product, get the registered version for permanent use.
Steps to Configure NFS Share on Windows 7/10/11
1) Download and install the haneWIN product.
2) I suggest switching off the Windows firewall in the Windows client.
3) Right Click and Run as administrator to open it.
4) Go to the Server tab and make sure below both checkboxes are ticked.
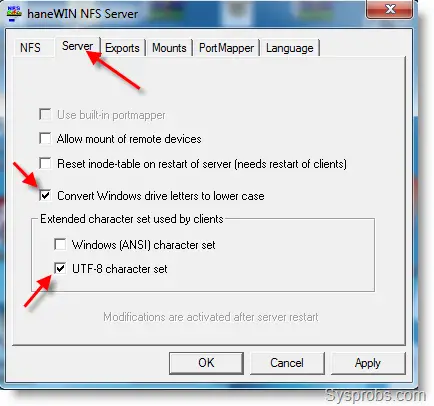
5) Navigate to the Exports tab; here we can define which drive or folder will be shared. The best part is, that it doesn’t require any Windows permissions to configure. I’m going to share a folder created for ESXi storage at this location.
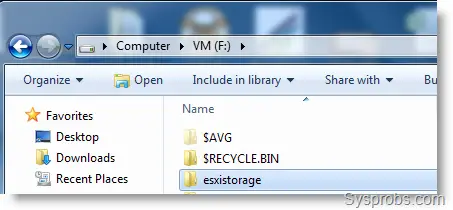
Click on the ‘Edit exports file’ button, remove the example shares and add your share location. I added the following line in the opened text file.
-public to enable web-based NFS share access. More details are available under help.
Note – You can’t save this file if you started the program without selecting the run as administrator option.
See Also
Configure iSCSI disks on Windows computer with VMware
How to connect FreeNAS iSCSI disks to VMware ESX Server
6) Press Restart Server to take effect from the changes in the export file.
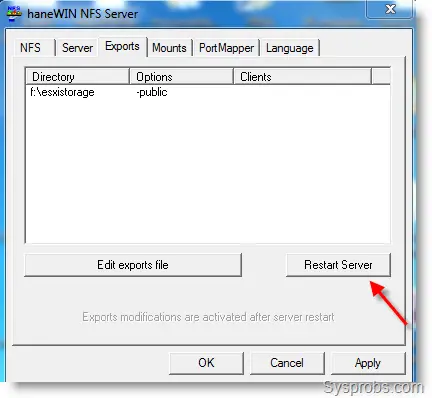
7) That’s it. Now we set up the Windows 7 as an NFS server with a share that can be accessed by UNIX based Operating systems and programs.
To view connected clients and mount points, click on the Mounts tab. I managed to connect this share from the VMware ESXi server. Here is the IP address of the connected client.
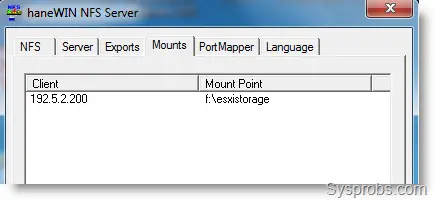
Connect Windows Share with haneWIN NFS to VMware ESXi Server Storage
As described earlier, you can easily use Windows OS partitions and folders with haneWIN NFS as network storage for VMware ESX or ESXi servers without any hardware devices. It is a very simple and easy way to extend data store with Windows shares in a testing environment or for home use.
Before continuing further steps in connecting the NFS share with VMware vSphere, make sure to meet the following requirements.
a) Network connectivity between VMware ESXi server and Windows host
b) Windows firewall is switched off or an exception is given for NFS/storage services.
Here is the recap of the NFS share setup for VMware storage in this example.
My F drive properties as shown below.
1) Open the vSphere client, go to the Configuration tab and click Storage.
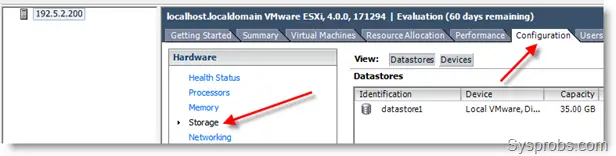
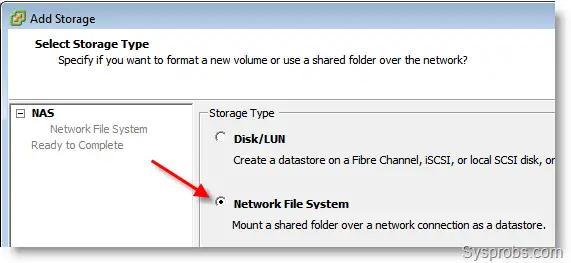
2) Click on ‘Add storage’ at the top right. Select the second option Network File System.
3) My Windows 7 host computer which has a haneWIN NFS server IP is 192.5.2.100.
So, type the IP address in the server location.
The folder name (Shared directory) should be typed as shown below.
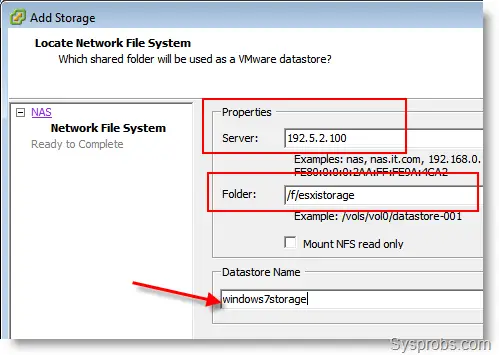
4) Click Next and OK. That’s it. The added Windows OS NFS will appear under VMware ESXi storage. It will detect the Windows partition capacity and free space.
If you don’t mount this storage as ‘Read only’, then you can use this as a full-fledged disk to install Operating Systems and save files.
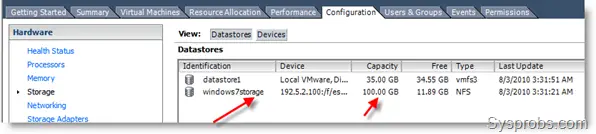
The good thing is, that the same storage (Windows folder) can be accessed in Windows explorer like a normal folder too. So, it’s easy to transfer data.
I hope this guide is useful in setting up and using the Windows OS folder/partition as storage for VMware vSphere by using the haneWIN NFS utility.
NFS Server Windows
Иногда NFS — единственный вариант что-то расшарить или примонтировать.
Но Microsoft, начиная c Windows 7 включительно, выпилила NFS Server в НЕ серверных системах.
Текущее ( 2023 год ) состояние можно посмотреть здесь: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/nfs/nfs-overview
Поэтому, поднять NFS Server на Windows 7, Windows 10 и т.д. — воспользоваться сторонними программами.
Мы рассмотрим winNFSd. Ссылка на гит — https://github.com/winnfsd/winnfsd
По причине его простоты — это один .exe-шник. Который можно запустить с параметрами через .bat-ник.
Поддерживает NFS v2 и v3 протоколы.
Весь процесс состоит из двух команд:
1. Качаем: https://github.com/winnfsd/winnfsd/releases/download/2.4.0/WinNFSd.exe
2. Запускаем: WinNFSd.exe с:\share_folder
Всё)
Рассмотрим теперь более подробные варианты.
Вариант 1 — одной командой.
В данном примере расшарена будет папка с:\share_folder
И по сети она будет видится именно так — /с/share_folder, то есть с указанием корневого диска.
А если запустить следующим образом:
WinNFSd.exe с:\share_folder /share
то по сети будет шариться имя share.
Пример с расшариванием каталога на определенный сетевой адрес:
WinNFSd.exe -addr 192.168.1.20 c:\share_folder /share
Если использовать точку «.» вместо расшариваемого ресурса экспортироваться будет текущий каталог:
WinNFSd.exe . /exports
Вариант 2 — c использованием конфиг-файла и .bat-ника.
1. Создаем какую-нибудь папку на диске (опционально )
Пусть будет c:\winNFSd
2. Копируем туда наш скачанный WinNFSd.exe
Создаем еще два файла в этой же папке: paths.txt и nfsd.bat
3. Пишем в созданные файлы следующее:
— в paths.txt
d:\some_folder_share_1
d:\some_folder_share_2
...
— в nfsd.bat
c:\winNFSd\WinNFSd.exe -addr 192.168.1.64 -pathFile "c:\winNFSd\paths.txt"
4. Запускаем наш батник: nfsd.bat
Плюс такого метода — можно разные папки указывать и запускать батника, например, через шедулер, или из скрипта — мало как 
P.S.
Это не единственная программа такого рода.
Есть еще более продвинутый вариант NFS Server на Windows, называется — haneWIN NFS Server
Официальный сайт — https://hanewin.net/nfs-e.htm
Поддерживает протоколы NFS 3, NFS 2, WebNFS и NLM; Символические ссылки, жесткие ссылки Unix на NTFS томах; Запускается как служба в Windows и много чего еще. Штука мощная и полезная.
Рассматривать его мы не будем (Как минимум, сейчас;)
Но знать про нее стоит.
