Аннотация: 16-разрядные Windows. Windows 9x. Windows NT. Windows CE. Windows Mobile и Windows Phone.
Microsoft Windows – операционные системы корпорации Microsoft, различные версии которых предназначены для широкого класса устройств – от суперкомпьютеров до встроенных систем. В настоящее время Microsoft Windows установлена на большинстве персональных компьютеров: по данным сайта анализа веб трафика StatCounter (http://gs.statcounter.com) операционные системы Windows (версий XP, Vista, 7) в августе 2012 года были установлены на 88% компьютеров в мире; в то же время по данным компании веб-аналитики Net Applications (http://marketshare.hitslink.com) Windows занимает 92% рынка настольных компьютеров и ноутбуков.
В настоящее время существует несколько семейств (family) операционных систем Windows, предназначенных для использования на разных типах компьютеров:
- семейство клиентских операционных систем Windows NT (Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 и др.);
- семейство серверных операционных систем Windows NT Server (Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008 и др.);
- семейство мобильных операционных систем Windows Mobile и Windows Phone (Windows Mobile 6, Windows Phone 7 и др.);
- семейство встроенных операционных систем реального времени Windows CE (Windows CE 7.0 и др.).
Кроме того, в прошлом выпускались 16 разрядные операционные системы (Windows 1.0, Windows 2.х, Windows 3.х) и семейство операционных систем Windows 9x (Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows Me).
В данной лекции представлен краткий обзор семейств операционных систем Microsoft Windows (рис.2.1).
16 разрядные Windows
Первой Windows была Windows 1.0, выпущенная в ноябре 1985 года. Это была не полноценная операционная система, а надстройка над операционной системой MS-DOS. Windows 1.0 предоставляла пользователю графический оконный интерфейс и возможность запускать несколько приложений одновременно (и то и другое отсутствовало в MS DOS). Сначала эту программу хотели назвать Interface Manager, но затем склонились к названию Windows («окна»), как более точно отражающему суть работы с новой программой [7]. Минимальные системные требования к памяти ограничивались 256 КБ.
В Windows 2.0 (декабрь 1987 года) были введены некоторые улучшения графического интерфейса (в частности поддержка перекрывающихся окон) и работы с памятью. Также для большего удобства стали использоваться комбинации клавиш. В мае 1988 года и в марте 1989 года появляются соответственно Windows 2.10 и Windows 2.11, поддерживающие новые на то время процессоры Intel 80286 и Intel 80386 [16].
В мае 1990 года выходит Windows 3.0 с улучшенной графикой и поддержкой виртуальной памяти. В 1992 1993 гг. появляются версии Windows for Workgroups 3.1 и 3.11, в которых имеется поддержка работы в одноранговых сетях и сетях под управлением сервера. Это были последние версии 16 разрядных Windows.
Windows 9x
В августе 1995 года выпускается Windows 95 – 32 разрядная клиентская операционная система, в которой была встроенная поддержка работы с Интернетом (браузер Internet Explorer) и модемными сетями, а также технология Plug-and-Play («подключи и работай»), позволяющая быстро подключать к компьютеру различные устройства. Впервые появилась кнопка Пуск (Start) и Панель задач (Taskbar). Windows 95 требовала минимум 4 МБ оперативной памяти [7].
На смену Windows 95 в июне 1998 года приходит Windows 98 с множеством программ для работы с Интернетом (Internet Explorer 4, Outlook Express и др.), поддержкой DVD и USB, первым появлением Панели быстрого запуска программ (Quick Launch bar). Windows 98 была последней операционной системой, основанной на MS DOS [7].
Последней версией в семействе 9x стала Windows Me (Millennium Edition, сентябрь 2000 года). Эта система была нацелена на домашних пользователей, и, следовательно, имела широкую поддержку работы с мультимедиа (Windows Media Player 7, Windows Movie Maker), Интернетом и домашними сетями.
Другим направлением развития операционных систем Windows в 90 е годы стало семейство NT.
Windows NT
В июле 1993 года была выпущена первая операционная система семейства NT – Windows NT 3.1. Есть разные варианты объяснения названия NT, самый распространенный вариант – это аббревиатура от New Technology («новая технология»).
Разработка системы, основанной на новом ядре (не MS DOS), началась в 1989 году. К новой операционной системе предъявлялись следующие основные требования [5]:
- 32 разрядность;
- поддержка многопроцессорных систем;
- поддержка вытесняющей многозадачности и виртуальной памяти;
- высокая производительность;
- возможность работы в качестве сервера и клиента;
- переносимость;
- совместимость с другими версиями Windows и MS DOS, а также частичная совместимость с UNIX;
- безопасность;
- надежность;
- поддержка Unicode.
Windows NT 3.1 соответствовала всем этим требованиям, а на ядре этой системы (конечно, с изменениями) основаны все современные версии Windows, включая Windows 8.
Windows NT 3.1 поддерживала процессоры Intel 80386, Intel 80486, MIPS R4000 и DEC Alpha [5]. Существовали клиентская и серверная версии системы – Windows NT и Windows NT Advanced Server. Windows NT, помимо других файловых систем, поддерживала специально разработанную в Microsoft файловую систему NTFS (New Technology File System).
В 1994 1996 годах последовательно выходят операционные системы Windows NT 3.5, Windows NT 3.51 и Windows NT 4.0. Целями разработки Windows NT 3.5 были повышение производительности и надежности, а также уменьшение размера системы. В Windows NT 3.51 была включена поддержка процессора IBM PowerPC. Windows NT 4.0 обладала таким же графическим интерфейсом как и система Windows 95 [5].
Windows 2000, вышедшая в декабре 1999 года, разрабатывалась в качестве системы для профессиональных пользователей, объединяющей два направления – Windows 9x и Windows NT [7]. Система Windows 2000 включала Active Directory (служба и базу данных ресурсов для управления большими сетями) и поддержку значительного числа Plug-and Play устройств, в том числе беспроводных сетей, USB, IEEE 1394 и др. Существовало 4 версии Windows 2000 – одна клиентская (Professional) и три серверных (Server, Advanced Server и Datacenter Server). Windows 2000 была последней системой, для которой выпускались одновременно клиентские и серверные версии.
Следующим шагом стало объединение обоих направлений клиентских систем: и систем для профессиональных пользователей (Windows 2000 Professional), и систем для домашних пользователей (Windows Me). Результатом такого объединения стала операционная система Windows XP (август 2001 года). Благодаря своей стабильности, скорости и удобному интерфейсу, Windows XP стала (и до сих пор является) одной из самых распространенных операционных систем в мире. Важным шагом явилось появление 64 разрядных версий Windows XP (Windows XP 64-bit Edition). Количество строк кода в Windows XP – 45 миллионов [7].
В марте 2003 года выходит серверная операционная система Windows Server 2003, имеющая большую производительность и поддерживающая более мощное оборудование, чем Windows 2000. Система имеет 4 основные версии: Web, Standard, Enterprise и Datacenter. Например, версия Datacenter поддерживает 64 процессора и до 64 ГБ оперативной памяти (до 512 ГБ на 64 разрядных платформах).
Клиентская операционная система Windows Vista вышла в ноябре 2006 года. Акцент при разработке этой системы был сделан на безопасность – контроль учетных записей пользователей (User Account Control), шифрование дисков (BitLocker Drive Encryption), антишпионское программное обеспечение (Windows Defender) и др. В Windows Vista был также изменен пользовательский интерфейс, в частности поменяла вид кнопка Пуск (Start).
В феврале 2008 года появилась операционная система Windows Server 2008, основанная на коде Windows Vista – поэтому большая часть нововведений Windows Vista перешла и в Windows Server 2008.
В июле 2009 года выходит Windows 7, отличающаяся расширенной поддержкой ноутбуков и планшетов. Основные особенности Windows 7 – новые приемы работы с окнами, мгновенный поиск информации на компьютере, поддержка сенсорных экранов (Windows Touch), большие возможности по настройке оформления рабочей среды.
В 2012 году Microsoft выпускает новейшие версии операционных систем – клиентскую Windows 8 (октябрь 2012 года) и серверную Windows Server 2012 (сентябрь 2012 года). Windows 8 – операционная система, одинаково рассчитанная как на обычные настольные компьютеры и ноутбуки, так и на планшетные компьютеры, завоевавшие в последнее время существенную долю всего рынка персональных компьютеров (см. лекцию 3 «Windows 8»).
Windows CE
Windows CE – операционная система реального времени для встраиваемых систем. Символы «CE», по утверждению Microsoft, обозначают «Compact, Connectable, Compatible, Companion, Efficient»1http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;Q166915 . В настоящее время эта система имеет официальное название Windows Embedded Compact (http://www.microsoft.com/windowsembedded).
Windows CE поставляется разработчикам устройств в виде набора компонентов, из которых можно создать операционную систему для конкретного устройства. Например, операционные системы Windows Mobile построены на основе Windows CE.
Первая версия Windows CE 1.0 появилась в 1996 году и была разработана как урезанная версия Windows 95. В дальнейшем команда разработчиков Windows CE сотрудничала с командой Windows 2000, затем Windows CE развивалась как независимая система.
На сентябрь 2012 года последней версией является Windows CE 7.0.
Windows Mobile и Windows Phone
Windows Mobile – операционная система для смартфонов и карманных персональных компьютеров (КПК, Personal Digital Assistant – PDA), основанная на Windows CE.
Первые версии операционных систем этого семейства назывались Pocket PC (2000 год). С 2003 года утвердилось наименование Windows Mobile – были выпущены операционные системы Windows Mobile 2003, Windows Mobile 5, Windows Mobile 6. Последней версией с таким названием стала система Windows Mobile 6.5 (2009 год).
С октября 2010 года Microsoft выпустила новую операционную систему для мобильных устройств – Windows Phone 7, несовместимую с Windows Mobile, хотя и основанную также на Windows CE. В Windows Phone 7 появился новый пользовательский интерфейс, в настоящее время называемый Modern UI.
В октябре 2012 года ожидается выход Windows Phone 8, основанной на ядре Windows NT.
Резюме
В лекции представлен обзор операционных систем Windows с 1985 года до 2012 года. Рассмотрены основные семейства и их ключевые представители – 16 разрядные Windows, Windows 9x, Windows NT, Windows NT Server, Windows Mobile/Windows Phone и Windows CE.
В следующей лекции приводится обзор новейшей операционной системы от Microsoft – Windows 8.
Контрольные вопросы
- Перечислите основные семейства операционных систем Windows и дайте их краткую характеристику.
- Назовите основных представителей 16 разрядных Windows.
- Перечислите основные отличия операционных систем Windows NT от Windows 9x.
- Чем отличаются клиентские и серверные версии Windows NT?
- Охарактеризуйте операционные системы семейства Windows CE.
- Охарактеризуйте операционные системы семейства Windows Mobile/Windows Phone.
Windows is a Microsoft product that began as an operating environment that slowly evolved into a full-fledged operating system and has since become the most popular operating system for home computers. By the early 1990s Windows began to overtake DOS because of its more friendly graphical user interface. Games have been made for Windows all through it’s history, but they didn’t start to become mainstream until after Windows 95 was released.
Because Windows is an evolving platform games tend to work on multiple versions of the software. In general, Windows exists in three blocks, 16-bit, 32-bit, and 64-bit, and games targeted to a block tends to work in each block. However, due to the nature of drivers, DLLs, etc., games are sometimes fickle even within a block. When documenting a Windows game, try to include which versions of Windows the game will work with.
Contents
- 1 Versions
- 1.1 Early Windows
- 1.2 Windows 16-bit
- 1.3 Windows 32-bit
- 1.4 Windows XP
- 1.5 Windows 64-bit
- 2 Music and Sound
- 3 Links
Versions
Over the years, Windows has been released in a large variety of versions and flavors, however in order to simplify things, the Video Game Music Preservation Foundation has grouped them into smaller categories.
Early Windows
|
Windows 1, 2 |
|
| Released: | 1985-11-20 |
| Discontinued: | 2001-12-31 |
| Developer: | Microsoft |
| Type: | Software |
This early block of Windows included versions 1 and 2; both were operating environments that ran from DOS. There are no known games that were released for these platforms that include music.
Windows 16-bit
|
Windows 3, 3.1, 3.11 |
|
| Released: | 1990-05-22 |
| Discontinued: | 2001-12-31 |
| Developer: | Microsoft |
| Type: | Software |
The 16-bit block of Windows included versions 3.0, 3.1, and 3.11. It was the first popular version of Windows and was sold on the majority of PCs in the early 1990s. Windows 3.x featured stronger multimedia support than the previous versions of Windows allowing for various types of music and sound effects to be played. Unfortunately, Windows 3.x had poor graphic support and most users experienced it with a mere 16 colors and a fixed 640×480 screen resolution. Some of the later updates of Windows 3.11 included higher resolution graphics and more colors, though not many games took advantage of this.
After random boots, a MIDI mapper shows up in the Control Panel, where you can map every MIDI channel (out of all 16) to another driver. Windows 3.x came with two items:
- «Base» and «Extended» configurations. Games came either with Base MIDI files, Extended MIDI files, MIDI files that combine both, or two sets of MIDI files.
- An «Ad Lib» driver. Some MIDI files sound only good there, whereas on everything else, you hear unrealistic instruments and unequalized volumes. Games include Dare to Dream and probably Dracula In London (W16).
- Games released for Windows 16.
Windows 32-bit
|
Windows 95, 98, ME |
|
| Released: | 1995-08-24 |
| Discontinued: | 2001-12-31 |
| Developer: | Microsoft |
| Type: | Software |
The 32-bit Windows block included the versions 95, 98, and ME. These versions of Windows were full-fledged operating systems and only used DOS as a bootstrapper. With this block of Windows, multimedia was vastly improved thanks to APIs like DirectX. Support for 32 bit color was added, high-resolution graphics became the norm, and network capabilities were vastly improved. The 32-bit era of Windows saw the death of DOS gaming, as every major development company switched off of DOS during this era.
The MIDI mapper has been replaced by a list of MIDI music playback devices, of which you can select a default. VGMPF currently does not remember any available devices as of 1995. In 1996, Microsoft added the now-infamous Microsoft GS Wavetable SW Synth to DirectX and all subsequent Windows versions.
- Games released for Windows 32.
Windows XP
|
Windows NT, 2000, XP |
|
| Released: | 2001-10-25 |
| Discontinued: | 2014-04-08 |
| Developer: | Microsoft |
| Type: | Software |
The most popular released of Windows has been Windows XP which was based on the earlier incarnations NT and 2000. However, while NT and 2000 were targeted more for business use, Windows XP was targeted for home users as well. The version featured a major upgrade to the kernel, including a 64-bit version, and several improvements to multimedia capabilities, networking, and security. Windows XP is a self-contained OS that didn’t use DOS for bootstrapping. However, these added improvements came at a price which prevented certain older Windows games from running in XP. Those games for the 32-bit platform that didn’t require complicated graphics tend to work on the XP platform as well.
The Windows 3.x way of playing MIDI files has changed, more notably for the worse. At least in early Windows XP installations, each song is delayed by about one second. When started from a specific position, notes get skipped or switched to piano.
Windows 64-bit
|
Windows Vista, 7, 8, 8.1, 10, 11 |
|
| Released: | 2006-11-30 |
| Developer: | Microsoft |
| Type: | Software |
This block features Vista, 7, 8, 8.1, 10, and 11. Windows Vista flopped into the market disappointing many people. While it added several improvements to gaming, it also broke backward compatibility with numerous Windows XP games, and hogged all the system resources, causing games to run slower. Thankfully, Windows 7 fixed most of those problems and added a richer gaming experience overall. However, there are still several XP games that cannot run on Windows 7, and more new games that will run on Windows 7, but not XP, are appearing. Windows 8 is essentially Windows 7 with an overhauled interface to make it more friendly on touchscreen displays. Little was changed that affects the gaming or multimedia experience, and nearly every game that worked in Windows 7 will work in 8. Windows 10 is mostly back-ward compatible with Windows 7 and 8. Windows 11 has been the latest current release.
While first Windows system build as 64-bit appeared in 2006, the ultimate success of Windows XP has lead developers to continue making 32-bit games so they could be played both on 32-bit and 64-bit platforms. In 2014-2015, when the end of Windows XP support has forced users to move onto 64-bit platforms, and few years after that, professional games have aborted 32-bit compatibility in favor of utilizing more RAM. However, as of 2023 it’s still common to make games and programs that don’t require too much RAM to be compatible with 32-bit architecture.
Unfortunately, the default MIDI music playback device selection has become hidden from the user.
- Games released for Windows 64.
Music and Sound
Since Windows is a software platform, it doesn’t have any audio capabilities, however, most audio devices manufactured since the early 1990s have been made to be compatible with Windows. Here is a list of some of the more popular ones from the early 1990s:
- Roland: MT-32, LAPC-I
- Media Vision: Pro AudioSpectrum, Pro AudioSpectrum 16
- Creative: Sound Blaster, Sound Blaster Pro, Sound Blaster 16, Sound Blaster AWE 32
- Gravis: UltraSound
- Disney: Sound Source
- Ad Lib: AdLib
- Tandy 1000: Tandy 3 Voice, Tandy DAC,
In the late 1990s and beyond, most motherboards were being manufacturer with built-in audio devices capable of playing fully digital music and sound.
Links
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microsoft_Windows — Wikipedia.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Microsoft Windows is the name of several families of computer software operating systems created by Microsoft. Microsoft first introduced an operating environment named Windows in November 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs).
All versions of Microsoft Windows are commercial proprietary software.
General information
[edit]
Basic general information about Windows.
| Name | Release date | Latest version | Support status | Codename | OS required | Architecture | Editions | Target market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0 | 1985-11-20 | 1.04 (1987-04-08) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Interface Manager | DOS 2.0 or higher | 16-bit | Desktops | |
| Windows 2.0 | 1987-09-08 | 2.03 (1987-12-09) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
DOS 3.0 or higher | 16-bit | Desktops | ||
| Windows 2.1x | 1988-05-27 | 2.11 (1989-03-13) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
DOS 3.0 or higher | 16-bit | Desktops | ||
| Windows 3.0 | 1990-05-22 | 3.0a with Multimedia Extensions (1991-10-20) |
Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
DOS 3.1 or higher | 16-bit | Windows 3.0 Windows 3.0a Windows 3.0a with Multimedia Extensions |
Desktops | |
| Windows 3.1x | 1992-04-06 | 3.11 (1993-12-31) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Janus
|
DOS 3.3 or higher | 16-bit* | Windows 3.1 Windows for Workgroups 3.1 Windows 3.11 Windows for Workgroups 3.11 Windows 3.2 (Simplified Chinese only) |
Desktops |
- * Has partial 32-bit compatibility with Win32s
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Latest version | Support status | Codename | MS-DOS version | Kernel type | Architecture | Editions | Target market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | 1995-07-14 | 950 | 4.00.950C OSR2.5 (1997-11-26) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Chicago | MS-DOS 7.0, MS-DOS 7.1 (OSR2.x) | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Retail, OSR1, OSR2, OSR2.1, OSR2.5 | Desktops |
| Windows 98 | 1998-05-15 | 1998 | 4.10.1998 | Unsupported (2006-07-11) |
Memphis | MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Desktops | |
| Windows 98 SE | 1999-05-05 | 2222 | 4.10.2222A (2000-02-25) | Unsupported (2006-07-11) |
MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Desktops | ||
| Windows Me | 2000-06-19 | 3000 | 4.90.3000 (2000-09-14) | Unsupported (2006-07-11) |
Millennium | MS-DOS 8.0 | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Desktops |
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Latest build | Support status | Codename, working name | Supported architectures | Editions | OS type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | 1993-07-27 | 3.1 | 528 | 528 (SP3) (1994-11-10) |
Unsupported (2000-12-31)[1] |
New Technology OS/2 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS |
Workstation, Advanced Server |
Workstation, Server |
|
| Windows NT 3.5 | 1994-09-21 | 3.5 | 807 | 807 (SP3) (1995-06-21) |
Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Daytona | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC[2] |
Workstation, Server |
Workstation, Server |
|
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-30 | 3.51 | 1057 | 1057 (SP5) (1996-09-19) |
Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
— | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC |
Workstation, Server |
Workstation, Server |
|
| Windows NT 4.0 | 1996-07-31 | 4.0 | 1381 | 1381 (SP6a) (1999-11-30) |
Unsupported (2004-06-30) Extended Security Updates were released until 2006. |
Cairo/Shell Update Release Hydra (Terminal Server) Impala (Embedded) |
IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC |
Workstation, Server, Server Enterprise Edition, Terminal Server, Embedded |
Workstation, Server, Embedded PCs |
|
| Windows 2000 | 1999-12-15 | 5.0 | 2195 | SP4 Rollup 1 v2 (2005-09-13) |
Unsupported (2010-07-13) |
Windows NT 5.0
|
IA-32 | Professional, Server, Advanced Server, Datacenter Server, Powered (Embedded) |
Desktop, Workstation, Server, Embedded PCs |
|
| Windows XP | 2001-08-24 | 5.1 | 2600 | 2600 (SP3) (2008-04-21) |
Unsupported (2014-04-08) |
Whistler | IA-32, IA-64, x86-64 | HomeK, ProfessionalKx64, Media Center, Tablet PC, Starter, Embedded |
Desktop, Workstation, Embedded PCs |
|
| Windows Server 2003 | 2003-04-24 | 5.2 | 3790 | 3790 (SP2) (2007-03-13) |
Unsupported (2015-07-14) |
Whistler Server, Windows.NET Server | IA-32, IA-64, x86-64 | Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, Web, Storage, Small Business Server, Compute Cluster |
Server, Network Appliance, Embedded PCs, HPC |
|
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005 | 5.2 | 3790 | ? | Unsupported (2015-07-14) |
? | IA-32, x86-64 | Server, Network Appliance, Embedded PCs, HPC |
||
| Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | 2006-07-08 | 5.1 | 2600 | — | Unsupported (2014-04-08) |
Eiger, Mönch | IA-32 | Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | Desktop | |
| Windows Vista | 2006-11-30 | 6.0 | 6000 | 6002 (SP2) (2009-04-28) |
Unsupported (2017-04-11) |
Longhorn | IA-32, x86-64 | Starter, Home BasicK, Home PremiumK, BusinessK, EnterpriseK, UltimateK |
Desktop, Workstation |
|
| Windows Home Server | 2007-11-04 | 5.2 | 3790 | — | Unsupported (2013-01-08) |
Q, Quattro | IA-32, x86-64 | Home Server | Server | |
| Windows Server 2008 | 2008-02-04 | 6.0 | 6001 | 6002 (SP2) (2009-04-28) |
Out of extended support (2020-01-14); Grandfathered paid Premium Assurance (limited to some critical security issues) security update support until January 13, 2026. |
Longhorn Server | x86-64, IA-64, IA-32 | WebCore, StandardCorewHVCwHV, EnterpriseCorewHVCwHV, Small Business Server, DatacenterCorewHVCwHV, HPC, HyperV Core, Foundation, Storage |
Server | |
| Windows 7 | 2009-07-22 | 6.1 | 7600 | 7601 (SP1) (2011-02-22) |
Unsupported (2020-01-14) |
7 | IA-32, x86-64 | StarterK, Home BasicK, Home PremiumK, ProfessionalK, UltimateK, EnterpriseK |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009-07-22 | 6.1 | 7600 | 7601 (SP1) (2011-02-22) |
Out of extended support (2020-01-14); Grandfathered paid Premium Assurance (limited to some critical security issues) security update support until January 13, 2026. |
7 Server | x86-64, IA-64 | StandardCore, EnterpriseCore, DatacenterCore, WebCore |
Server | |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | 2011-04-06 | 6.1 | 8400 | — | Unsupported (2016-04-12) |
Vail | x86-64 | Home Server | Server | |
| Windows Server 2012 | 2012-08-01 | 6.2 | 9200 | — | Unsupported (2023-10-10) |
8 Server | x86-64 | Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup |
Server | |
| Windows 8 | 2012-08-01 | 6.2 | 9200 | — | (RTM only) Unsupported (2016-01-12) |
8 | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7 | Windows 8, Pro, EnterpriseK, Windows RT |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
|
| Windows 8.1 | 2013-08-27 | 6.3 | 9600 | — | Unsupported (2023-01-10) |
Blue | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7 | Windows 8.1, Pro, EnterpriseK, Windows RT 8.1 |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
|
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013-10-18 | 6.3 | 9600 | — | Out of extended support (2023-10-10); Paid support via the Extended Security Updates (ESU) program until October 13, 2026. |
Blue Server | x86-64 | Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Storage Essentials, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup |
Server | |
| Windows 10 | Original Release | 2015-07-29 | 10.0 | 10240 | — | Unsupported (2017-05-09) |
Threshold | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
| On extended support (2025-10-14) |
Enterprise LTSB | |||||||||
| November Update | 2015-11-12 | 10586 | — | Unsupported (2017-10-10) |
Threshold 2 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise |
||||
| Anniversary Update | 2016-08-02 | 14393 | — | Unsupported (2018-04-10) |
Redstone | Home, Pro, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2019-04-09) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| On extended support (2026-10-13) |
Enterprise LTSB | |||||||||
| Creators Update | 2017-04-11 | 15063 | — | Unsupported (2018-10-09) |
Redstone 2 | Home, Pro, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2019-10-08) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Fall Creators Update | 2017-10-17 | 16299 | — | Unsupported (2019-04-09) |
Redstone 3 | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7, ARM64 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
|||
| Unsupported (2020-10-13) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| April 2018 Update | 2018-04-30 | 17134 | — | Unsupported (2019-11-12) |
Redstone 4 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2021-05-11) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| October 2018 Update | 2018-10-02 | 17763 | — | Unsupported (2020-11-10) |
Redstone 5 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2021-05-11) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| On extended support (2029-01-09) |
Enterprise LTSC | |||||||||
| May 2019 Update | 2019-05-21 | 18362 | — | Unsupported (2020-12-08) |
19H1 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, Education, Enterprise |
||||
| November 2019 Update | 2019-11-12 | 18363 | — | Unsupported (2021-05-11) |
19H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2022-05-10) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| May 2020 Update | 2020-05-27 | 19041 | — | Unsupported (2021-12-14) |
20H1 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, Education, Enterprise |
||||
| October 2020 Update | 2020-10-20 | 19042 | — | Unsupported (2022-05-10) |
20H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2023-05-09) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| May 2021 Update | 2021-05-18 | 19043 | — | Unsupported (2022-12-13) |
21H1 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, Education, Enterprise |
||||
| November 2021 Update | 2021-10-16 | 19044 | — | Unsupported (2023-06-13) |
21H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2024-06-11) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Mainstream supported (2027-01-12) |
Enterprise LTSC | |||||||||
| 2022 Update | 2022-10-18 | 19045 | — | Supported (2025-10-14); paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program, which offers continued security updates until October 13, 2026 for consumers, or at most October 10, 2028 for businesses and schools. |
22H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education Education, Enterprise |
||||
| Windows Server 2016 | 2016-09-26 | 10.0 | 14393 | — | On extended support (2027-01-12) |
Redstone Server | x86-64 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, MultiPoint Premium, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup |
Server | |
| Windows Server 2019 | 2018-10-02 | 10.0 | 17763 | — | On extended support (2029-01-09) |
Redstone 5 Server | x86-64 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter |
Server | |
| Windows Server 2022 | 2021-08-18 | 10.0 | 20348 | — | Mainstream support (2026-10-13) Extended support (2031-10-14) |
21H2 Server | x86-64 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Datacenter for Azure |
Server | |
| Windows 11 | Original Release | 2021-10-05 | 10.0 | 22000 | — | Unsupported (2023-10-10) |
Sunvalley (21H2) | x86-64, ARM64 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, SE |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
| Unsupported (2024-10-08) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| 2022 Update | 2022-09-20 | 22621 | 22H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, SE |
||||||
| Supported (2025-10-14) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| 2023 Update | 2023-10-31 | 22631 | Supported (2025-11-11) |
23H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, SE |
|||||
| Supported (2026-11-10) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| 2024 Update | 2024-10-01 | 26100 | Supported (2026-10-13) |
24H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, SE |
|||||
| Supported (2027-10-12) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Windows Server 2025 | 2024-11-01 | 10.0 | 26100 | — | Mainstream support (2029-10-09) Extended support (2034-10-10) |
24H2 | x86-64, ARM64 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Datacenter for Azure |
Server | |
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Latest build | Support status | Codename, working name | Supported architectures | Editions | OS type |
- ^N has also an N-edition
- ^K has also an N-edition
- ^KN has also an N-edition
- ^x64 has a separate x64-edition
- ^Core has also a Core-edition
- ^wHV has also an edition without HyperV
- ^CwHV has also a Core-edition without HyperV
Windows Embedded Compact
[edit]
Windows Embedded Compact (Windows CE) is a discontinued variation of Microsoft’s Windows operating system for minimalistic computers and embedded systems. Windows CE was a distinctly different kernel, rather than a trimmed-down version of desktop Windows. It is supported on Intel x86 and is compatible on MIPS, ARM, and Hitachi SuperH processors.
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Current version | Support status | Codename | Based on (kernel) | Kernel type | Operating environments | Editions | Purpose | Short description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows CE 1.0 | 1996-11-16 | Unsupported | Pegasus, Alder | CE 1.0 | Embedded | First release of Microsoft’s Windows CE line for minimalistic computers and embedded systems | |||||
| Windows CE 2.0 | 1997-11-29 | Unsupported | Mercury, Apollo | CE 2.0 | 2.1, 2.11 | Embedded | |||||
| Windows CE 3.0 | 2000-06-15 | Unsupported (2007-10-09) |
Cedar, Galileo, Rapier, Merlin, Stinger | CE 3.0 | Embedded kernel | Embedded | |||||
| Windows CE 4.0 | 2002-01-07 | Unsupported | Talisker | CE 4.0 | 4.1, 4.2 | Embedded | |||||
| Windows CE 5.0 | 2004-07-09 | 5.0 (2004-07-09) |
Unsupported (2014-10-14) |
Macallan | CE 5.0 | Embedded kernel | Embedded | ||||
| Windows Embedded CE 6.0 | 2006-11-01 | Unsupported (2018-04-10) |
Yamazaki | CE 6.0 | Hybrid kernel | ||||||
| Windows Embedded Compact 7 | 2011-03-01 | ? | ? | Unsupported (2021-04-13) |
Chelan | CE 7.0 | Hybrid | ? Standard, POSReady |
|||
| Windows Embedded Compact 2013 | 2013-08-11 | Update 17 (2017-11-15) |
Unsupported (2023-10-10) |
— | CE 8.0 | Standard Industry (8.0, 8.1) Handheld |
Embedded |
The Windows IoT family is the successor to the now-discontinued Windows Embedded family.
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Editions | License | OS type | Support status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 IoT | Anniversary Update | 2016-08-02 | NT 10.0 | 14393 | Core | OEM | IoT | Unsupported (2018-04-10)[3] |
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2019-04-09)[4] |
|||||||
| Enterprise LTSB | On extended support (2026-10-13)[5] |
|||||||
| Creators Update | 2017-04-11 | 15063 | Core | Unsupported (2018-10-09)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2019-10-08)[4] |
|||||||
| Fall Creators Update | 2017-10-17 | 16299 | Core | Unsupported (2019-04-09)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2020-10-13)[4] |
|||||||
| April 2018 Update | 2018-04-30 | 17134 | Core | Unsupported (2019-11-12)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2021-05-11)[4] |
|||||||
| October 2018 Update | 2018-10-02 | 17763 | Core | Unsupported (2020-11-10)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2021-05-11)[4] |
|||||||
| Core LTSC, Enterprise LTSC | On extended support (2029-01-09)[6][7] |
|||||||
| May 2019 Update | 2019-08-29 | 18362 | Enterprise | Unsupported (2020-12-08)[4] |
||||
| November 2019 Update | 2019-11-12 | 18363 | Unsupported (2022-05-10)[4] |
|||||
| May 2020 Update | 2020-05-27 | 19041 | Unsupported (2021-12-14)[4] |
|||||
| October 2020 Update | 2020-10-20 | 19042 | Unsupported (2023-05-09)[4] |
|||||
| May 2021 Update | 2021-05-18 | 19043 | Unsupported (2022-12-13)[4] |
|||||
| November 2021 Update | 2021-11-16 | 19044 | Enterprise | Unsupported (2024-06-11)[4] |
||||
| Enterprise LTSC | On extended support (2032-01-13)[8] | |||||||
| 2022 Update | 2022-10-18 | 19045 | Enterprise | Supported (2025-10-14)[4] |
||||
| Windows Server IoT 2019 | 2019-02-26[9] | NT 10.0 | 17763 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup, Telecommunications |
OEM | IoT, Server | On extented support (2029-01-09)[10][11] |
|
| Windows Server IoT 2022 | 2021-08-18[12][better source needed][dubious – discuss] | NT 10.0 | 20348 | Standard, Datacenter, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup, Telecommunications |
OEM | IoT, Server | Supported (2031-10-14)[13] |
|
| Windows 11 IoT | Original Release | 2021-10-04 | NT 10.0 | 22000 | Enterprise | OEM | IoT | Unsupported (2024-10-08)[14] |
| 2022 Update | 2022-09-20 | 22621 | Supported (2025-10-14)[15] |
|||||
| 2023 Update | 2023-10-31 | 22631 | On extended support (2026-11-10)[16] |
|||||
| 2024 Update | 2024-10-01 | 26100 | Supported (2027-10-12) |
|||||
| Windows Server IoT 2025 | 2024-11-01[17] | NT 10.0 | 26100 | Standard, Datacenter | OEM | IoT, Server | Supported (2034-10-10)[18] |
|
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Editions | License | OS type | Support status |
Windows Mobile is Microsoft’s discontinued line of operating systems for smartphones.
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Current version | Support status | Codename | Based on (kernel) | Supported architectures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Pocket PC 2000 | 2000-04-19 | Unsupported (2007-10-09) |
Rapier | CE 3.0 | |||
| Windows Pocket PC 2002 | 2001-10-04 | Unsupported (2008-10-14) |
Merlin | CE 3.0 | |||
| Windows Mobile 2003 | 2003-06-23 | Unsupported (2014-07-08) |
Ozone | CE 4.20 | |||
| Windows Mobile 5.0 | 2005-05-9/12 | Unsupported (2015-10-13) |
Magneto | CE 5.0 | |||
| Windows Mobile 6.0 | 2007-02-12 | Unsupported (2013-01-08) |
Crossbow | CE 5.2 | |||
| Windows Mobile 6.1 | 2008-04-01 | ||||||
| Windows Mobile 6.5 | 2009-05-11 |
Windows Phone is Microsoft’s discontinued line of operating systems for smartphones.
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Current version | Support status | Codename | Based on (kernel) | Supported architectures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Phone 7 | 2010-11-08 | 7004 | 7.10.8862 | Unsupported | Photon | CE 6.0 | ARM |
| Windows Phone 7.5 | 2011-09-27 | 7720 | Unsupported | Mango | CE 6.1 | ARM | |
| Windows Phone 7.8 | 2013-02-01 | 8858 | Unsupported (2014-10-14) |
Tango | CE 6.1 | ARM | |
| Windows Phone 8 | 2012-10-29 | 10211 | 10.0.10586 | Unsupported (2014-07-08) |
Apollo, Portico | NT 6.2 | ARM[citation needed] |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | 2014-04-14 | 12359 | Unsupported (2017-07-11) |
Blue | NT 6.3 | ARM | |
| Windows 10 Mobile | 2015-11-08 | 10586–16299 | Unsupported | Threshold, Redstone | NT 10.0 | ARM |
Technical information
[edit]
| Name | Architecture | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | LFN support | Update management | APIs | Safe Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0 | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 2.0 | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 2.1x | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 3.0 | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 3.1x | x86 16-bit (partial 32-bit compatibility through Win32s) | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16, Win32s | No |
| Name | Kernel | Kernel type | Architecture | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | LFN support | Update management | APIs | DDIs | Safe Mode | DirectX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | MS-DOS 7.0 (Win95, Win95A), MS-DOS 7.1 (Win95B, Win95C) | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Partial (OSR 2.1/2.5 only)[19] | Partial (OSR 2.x only)[20] | Yes | Partial(OSR 2.5 only, Windows Update only supports Internet Explorer 4) | Win16, Win32 | DOS, DLL, VxD, WDM (USB-only), direct-access | Yes | N/A (RTM/OSR1) 2.0a (OSR2/2.1) 5.0 (OSR2.5) 8.0a (optional) |
| Windows 98 | MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DOS, DLL, VxD, WDM (partial), direct-access | Yes | 5.2 9.0c (Oct 2006) (optional) |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DOS, DLL, VxD, WDM (partial), direct-access | Yes | 6.1a 9.0c (Oct 2006) (optional) |
| Windows Me | MS-DOS 8.0 | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DLL, VxD, WDM (partial), direct-access | Yes | 7.1 9.0c (Oct 2006) (optional) |
It is possible to install the MS-DOS variants 7.0 and 7.1 without the graphics user interface of Windows. If an independent installation of both, DOS and Windows is desired, DOS ought to be installed prior to Windows, at the start of a small partition. The system must be transferred by the (dangerous) «SYSTEM» DOS-command, while the other files constituting DOS can simply be copied (the files located in the DOS-root and the entire COMMAND directory). Such a stand-alone installation of MS-DOS 8 is not possible, as it is designed to work as real mode for Windows Me and nothing else.
The Windows NT kernel powers all recent Windows operating systems. It has run on IA-32, x64, DEC Alpha, MIPS architecture, PowerPC, Itanium, ARMv7, and ARM64 processors, but currently supported versions run on IA-32, x64, ARMv7, and ARM64.
| Name | Architecture | Store |
Integrated |
SMP support | USB support |
UDMA |
Long filename support | Package management | Update management | APIs | DDIs |
Safe Mode |
Data Execution Prevention | DirectX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS | — | No | Yes | No | ? | Yes (NTFS and HPFS volumes only) | — | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | No | |
| Windows NT 3.5 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS | — | No | Yes | No | ? | Yes (except on CDFS volumes) | — | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | No | |
| Windows NT 3.51 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | — | No | Yes | No | ? | Yes (except on CDFS volumes) | — | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | No | |
| Windows NT 4.0 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | — | No | Yes | Partial (with third-party device drivers)[21] | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update (if Internet Explorer 5 or later is installed) | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | Yes 3.0a, 5.0 (unofficial) |
| Windows 2000 | IA-32 | — | No | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0 with update or SP4)[22] | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF | Yes | No | Yes 7.0, 9.0c (Feb 2010) (optional) |
| Windows XP | IA-32 (NT5.1), Itanium (NT5.1/5.2), x64 (NT5.2) | — | Yes | Yes (Professional Edition only) | Yes (USB 2.0 with update or SP1+)[23] | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes (in SP2) | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows Server 2003 | IA-32, Itanium, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0)[24] | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes (with SP1) | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | IA-32 | — | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows Vista | IA-32, x64 | Windows Marketplace | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET, POSIX (only Enterprise and Ultimate) | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 10.1 11.0 (optional) |
| Windows Server 2008 | IA-32, Itanium, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 10.1 11.0 (optional) |
| Windows Home Server | IA-32 | — | ? | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | ? | Yes | — | Windows Update | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | ? | ? | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows 7 | IA-32, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.0 11.1 (optional) |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Itanium, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.0 11.1 (optional) |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | x64 | — | ? | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | ? | Yes | — | Windows Update | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | ? | ? | Yes 11.0 11.1 (optional) |
| Windows Server 2012 | x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.1 |
| Windows 8 | IA-32, x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.1 |
| Windows 8.1 | IA-32, x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store, PowerShell | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.2 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.2 |
| Windows 10 | IA-32, x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.1 and Thunderbolt 3) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store, PowerShell | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT, Linux | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 12 |
| Windows Server 2016 | x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.1 and Thunderbolt 3) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 12 |
| Name | Architecture | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | Package management | APIs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Phone 8 | ARMv7 | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | Yes | Windows Phone Store | Silverlight |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | ARMv7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Phone Store | Silverlight WinRT |
| Windows 10 Mobile | ARMv7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Microsoft Store |
Supported file systems
[edit]
Various versions of Windows support various file systems, including:FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, HPFS, or NTFS, along with network file systems shared from other computers, and the ISO 9660 and UDF file systems used for CDs, DVDs, and other optical disc drives such as Blu-ray. Each file system is usually limited in application to certain media, for example CDs must use ISO 9660 or UDF, and as of Windows Vista, NTFS is the only file system which the operating system can be installed on. Windows Embedded CE 6.0, Windows Vista Service Pack 1, and Windows Server 2008 onwards support exFAT, a file system more suitable for USB flash drives.
| FAT12 | FAT16 | FAT32 | HPFS | ISO 9660 | NTFS | UDF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | Yes | Yes | Yes (OSR2 or above) | Network Drive | Yes | Network Drive | No |
| Windows 98 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Network Drive | Yes | Network Drive | Yes (1.5, read) |
| Windows Me | Yes | Yes | Yes | Network Drive | Yes | Network Drive | Yes (1.5, read) |
| FAT12 | FAT16 | FAT32 | HPFS | ISO 9660 | NTFS | exFAT | UDF | ReFS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1, 3.5, 3.51 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes v1.0/v1.1 | No | ? | No |
| Windows NT 4.0 | Yes | Yes | No | Partial | Yes | Yes v1.2 | No | ? | No |
| Windows 2000 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v3.0 | No | Yes | No |
| Windows XP | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v3.1 | Optional | Yes (2.01) | No |
| Windows Server 2003 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v3.1 | Optional | Yes | No |
| Windows Vista | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | No |
| Windows Server 2008 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2012 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows 8 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | No |
| Windows 8.1 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows 10 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2016 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| FAT12 | FAT16 | FAT32 | HPFS | ISO 9660 | NTFS | UDF (More Info) | ReFS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Phone 8 | ? | Yes | Yes | No | ? | Yes v5 | ? | No |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | ? | Yes | Yes | No | ? | Yes v5 | ? | No |
| Windows 10 Mobile | ? | Yes | Yes | No | ? | Yes v5 | ? | ? |
Hardware requirements
[edit]
Installing Windows requires an internal or external optical drive, or a USB flash drive. A keyboard and mouse are the recommended input devices, though some versions support a touchscreen. For operating systems prior to Vista, an optical drive must be capable of reading CD media, while in Windows Vista onwards, such a drive must be DVD-compatible. The drive may be detached after installing Windows.
| CPU | RAM | Free disk space | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | 386 | 4 MB | 120 MB |
| Windows 98 | 486 DX2 66 MHz | 16 MB | 300 MB |
| Windows Me (Millennium Edition) | Pentium 150 MHz | 32 MB | 400 MB |
| Version | CPU | RAM | Free disk space | Video adapter and monitor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Recommended | ||||
| Windows NT 3.51 Workstation | 386, 25 MHz | 8 MB | 16 MB | 90 MB | VGA (640×480) |
| Windows NT 4.0 Workstation | 486, 33 MHz | 12 MB | ? | 110 MB | |
| Windows 2000 Professional | 133 MHz | 32 MB | 128 MB | 650 MB | |
| Windows XP | 233 MHz | 64 MB | 128 MB | 1.5 GB | Super VGA (800×600) |
| Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | 500 MB | ||||
| Windows XP 64-Bit Edition | 700 MHz Itanium[25] | 1 GB[25] | ? | 6 GB[25] | |
| Windows Server 2003 | 1 GHz (x86) or 1.4 GHz (x64) | 128 MB | 256 MB | 2 GB (x86) 4 GB (x64) |
|
| Windows Vista | 800 MHz | 384 MB (Starter) 512 MB (others)[26][dubious – discuss] |
2 GB | 15 GB (~6.5 GB for OS) |
Super VGA (800×600) WDDM & DirectX 9 for Aero |
| Windows Server 2008 | 1 GHz (x86) or 1.4 GHz (x64) | 2 GB | 10 GB | ||
| Windows 7 | 1 GHz | 1 GB (x86) 2 GB (x64) |
4 GB | 16 GB (x86) 20 GB (x64) (~6.5 GB for OS) |
|
| Windows Server 2012 | 1.4 GHz (x86-64) | 512 MB | 1 GB | 10 GB | Super VGA (800×600), 32-bit color |
| Windows 8 | 1 GHz | 1 GB (x86) 2 GB (x64) |
4 GB | 16 GB (x86) 20 GB (x64) (~6.5 GB for OS) |
Super VGA (800×600), 32-bit color 1024 x 768 for Windows Store apps 1366 x 768 to snap apps |
| Windows 8.1 | |||||
| Windows 10 | 1 GHz or faster processor or SoC | 1 GB (x86) 2 GB (x64) |
4 GB | 16 GB (x86) 20 GB (x64) |
Super VGA (800×600), 32-bit color |
| Windows Server 2016 | 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor | 512 MB ECC memory 2 GB with Desktop Experience installed[27] |
depends on role | 32 GB (~10 GB for OS) |
XGA (1024 x 768) |
| Windows Server 2019 | 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor | 512 MB ECC memory 2 GB with Desktop Experience installed[27] |
depends on role | 32 GB | XGA (1024 x 768) |
| Windows Server 2022 | 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor | 512 MB ECC memory 2 GB with Desktop Experience installed[28] |
depends on role | 32 GB | XGA (1024 x 768) |
| Windows Server 2025 | 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor | 512 MB ECC memory 2 GB with Desktop Experience installed[28] |
4 GB with Desktop Experience installed | 32 GB | XGA (1024 x 768) |
| Windows 11 | 64-bit 1 GHz or faster processor or SoC with two or more cores | 4 GB | — | 64 GB (~10 GB for OS) |
720p greater than 9″ diagonally, 32-bit color |
| Version | CPU | RAM | Free disk space | Video adapter and monitor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Recommended | ||||
| Windows Phone 7 | 0.8 GHz | 256 MB | — | 4 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
| Windows Phone 8 | 1 GHz | 512 MB | — | 8 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | 1 GHz | 512 MB | — | 4 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
| Windows 10 Mobile | 1 GHz | 1 GB | 2 GB | 8 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
Physical memory limits
[edit]
Maximum limits on physical memory (RAM) that Windows can address vary depending on both the Windows version and between IA-32 and x64 versions.[29][30]
| Operating system | Limit on Real Mode | Limit on Standard Mode | Limit on Enhanced Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0x | 640 KB | — | — |
| Windows 2.0x | 640 KB | — | 16MB |
| Windows 2.1x | 640 + 64 KB | — | 16MB |
| Windows 3.0x | 640 + 64 KB | 16MB | 16MB |
| Windows 3.1x | — | 256MB[31] | 256MB[31] |
| Windows 95 | — | — | 944MB[32] |
| Windows 98 | — | — | 1GB |
| Windows ME | — | — | 1.5GB |
| Operating system | Limit on IA-32 | Limit in IA-64 | Limit on x64 | Limit on ARM32 | Limit on ARM64 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows NT 3.5 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows NT 4.0 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2000 Professional/Server | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2000 Advanced Server | 8 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2000 Datacenter | 32 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows XP Starter | 512 MB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows XP Home | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows XP Professional | 4 GB | 128 GB | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 RTM Web | 2 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 RTM Standard/Small Business | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 RTM Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | 512 GB | — | — | — |
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | — | 32 GB | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP1 Standard | 4 GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP1 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | 1 TB | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP2 Standard | 4GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP2 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | 2 TB | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R2/SP1 Standard | 4 GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R2/SP1 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | — | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Vista Starter | 1 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Vista Home Basic | 4 GB | — | 8 GB | — | — |
| Windows Vista Home Premium | 4 GB | — | 16 GB | — | — |
| Windows Vista Business/Enterprise/Ultimate | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Home Server | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 Web Server/Standard/Small Business | 4 GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 | — | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | — | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 for Itanium–Based Systems | — | 2 TB | — | — | — |
| Windows 7 Starter | 2 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 7 Home Basic | 4 GB | — | 8 GB | — | — |
| Windows 7 Home Premium | 4 GB | — | 16 GB | — | — |
| Windows 7 Professional/Enterprise/Ultimate | 4 GB | — | 192 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | — | — | 8 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Web Server/Standard | — | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 | — | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise/Datacenter | — | — | 2 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium–Based Systems | — | 2 TB | — | — | — |
| Windows 8 (Core) | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows 8 Pro/Enterprise | 4 GB | — | 512 GB | — | — |
| Windows RT | — | — | — | 4 GB | — |
| Windows Server 2012 Standard/Datacenter | — | — | 4 TB | — | — |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard | — | — | 4 TB | — | — |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Workgroup | — | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Hyper-V Server 2012 | — | — | 4 TB | — | — |
| Windows 8.1 (Core) | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows 8.1 Pro/Enterprise | 4 GB | — | 512 GB | — | — |
| Windows RT 8.1 | — | — | — | 4 GB | — |
| Windows 10 Mobile | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 10 Home | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Windows 10 Pro | 4 GB | — | 2 TB | 4 GB | 2 TB |
| Windows 10 Pro for Workstations | 4 GB | — | 6 TB | 4 GB | 6 TB |
| Windows 10 Education | 4 GB | — | 2 TB | 4 GB | 2 TB |
| Windows 10 Enterprise | 4 GB | — | 6 TB | 4 GB | 6 TB |
| Windows Server 2016 Essentials | — | — | 64 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2016 Standard | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2016 Datacenter | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2019 Essentials | — | — | 64 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2019 Standard | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2019 Datacenter | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2022 Essentials | — | — | 64 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2022 Standard | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2022 Datacenter | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows 11 Home | — | — | 128 GB | — | 128 GB |
| Windows 11 Pro | — | — | 2 TB | — | 2 TB |
| Windows 11 Pro for Workstations | — | — | 6 TB | — | 6 TB |
| Windows 11 Education | — | — | 2 TB | — | 2 TB |
| Windows 11 Enterprise | — | — | 6 TB | — | 6 TB |
| Resource access control | Subsystem isolation mechanisms | Integrated firewall | Encrypted file systems | Defender | Windows Hello | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 2000 | ACLs | TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes (NTFS only) | No | No | |
| Windows XP | ACLs | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall (from SP2), TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes (NTFS only) | Optional | No |
| Windows Server 2003 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Optional | No |
| Windows Vista | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows Server 2008 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 7 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows Server 2012 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 8 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 8.1 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 10 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Windows Server 2016 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 Windowstation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Version | Shell | Visual styles | Browser | Web server | Windows Media Player | Command-line interpreter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0 | MS-DOS executive | (Unnamed) | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2.0 | MS-DOS executive | (Unnamed) | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 3.0 | Program Manager | (Unnamed) | — | — | 3.0 (Multimedia Extension edition only) | — |
| Windows 3.1x | Program Manager | (Unnamed) | — | — | 3.1 | — |
| Windows 95 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 1 in OEM RTM Internet Explorer 2 in OSR1 Internet Explorer 3 in OSR2 and OSR2.1 Internet Explorer 4 in OSR2.5 |
— | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows NT 4.0 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 2 Internet Explorer 3 (in some localized editions) |
PWS | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe |
| Windows 98 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 4.01 | PWS | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows 98 SE | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 5 | PWS | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows 2000 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 5.01 | IIS 5.0 | 5.0 and 6.4 (side by side) | COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe |
| Windows Me | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 5.5 | — | 6.4 and 7.0 (side by side) | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows XP | Windows shell | Luna (default), Classic | Internet Explorer 6 | IIS 5.1 | 5.1, 6.4 and 8 (in RTM) 5.1, 6.4 and 9 (in SP2) |
COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows Server 2003 | Windows shell | Classic (default), Luna | Internet Explorer 6 | IIS 6.0 | 9 (in RTM), 10 (in SP1) | COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows Vista | Windows shell | Aero (default), Classic | Internet Explorer 7 | IIS 7 | 11 | COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows Server 2008 | Windows shell, Server Core | Classic (default), Aero (via «Desktop Experience») | Internet Explorer 7 | IIS 7 | 11 (enabled by installing «Desktop Experience») | COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows 7 | Windows shell | Aero (default), Classic | Internet Explorer 8 | IIS 7.5 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, PowerShell 2.0 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Windows shell, Server Core | Classic (default), Aero (via «Desktop Experience») | Internet Explorer 8 | IIS 7.5 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | cmd.exe, PowerShell 2.0 |
| Windows Server 2012 | Windows shell, Server Core | Metro | Internet Explorer 10 | IIS 8 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | cmd.exe, PowerShell 3.0 |
| Windows 8 | Windows shell | Metro | Internet Explorer 10 | IIS 8 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, PowerShell 3.0 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Windows shell, Windows server core | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 | IIS 8.5 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | cmd.exe, PowerShell 4.0 |
| Windows 8.1 | Windows shell | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 | IIS 8.5 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, PowerShell 4.0 |
| Windows 10 | Windows shell | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 Microsoft Edge |
IIS 10.0 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, PowerShell 5.0 |
| Windows Server 2016 | Windows shell, Windows server core | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 Microsoft Edge |
IIS 10.0 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | cmd.exe, PowerShell 5.1 |
| Windows Server 2019 | Windows shell, Windows server core | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 Microsoft Edge |
IIS 10.0 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | cmd.exe, PowerShell 5.1 |
| Windows Server 2022 | Windows shell, Windows server core | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 Microsoft Edge |
IIS 10.0 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | cmd.exe, PowerShell 5.1 |
| Windows 11 | Windows shell | Mica | Internet Explorer 11(Hidden) Microsoft Edge |
IIS 10.0 | 12 (2022) | COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, PowerShell v.1 |
Timeline of Windows versions
|
|---|

|
- List of Microsoft Windows versions
- List of operating systems
- Comparison of operating systems
- Comparison of operating system kernels
- Comparison of Windows Vista and Windows XP
- Microsoft Windows version history
- Comparison of DOS operating systems
- Architecture of Windows NT
- List of Microsoft codenames
Windows clones and emulators
[edit]
- Freedows OS–Windows clone
- ReactOS–project to develop an operating system that is binary compatible with application software and device drivers for Microsoft Windows NT version 5.x
- Wine (software)–compatibility layer which allows to execute programs that were originally written for Microsoft Windows
- ^ «Product Lifecycle Dates-Windows Product Family». Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 11, 2004. Retrieved August 24, 2021.
- ^ «Windows NT 3.5 for PowerPC». November 9, 1994. Archived from the original on August 12, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e «Windows 10 IoT Core — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on November 18, 2020. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise — Microsoft Lifecycle». Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSB 2016 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 23, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core LTSC — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 10, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSC 2019 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on November 16, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSC 2021 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on November 16, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Microsoft announces latest Windows IoT innovations for intelligent edge devices at Embedded World». February 26, 2019. Archived from the original on February 26, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2019 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 23, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2019 for Storage — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 23, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Announcing the GA of Windows Server IoT 2022». Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2022 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 11 IoT Enterprise (Version 21H2) — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on October 5, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 11 IoT Enterprise — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved September 22, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 11 IoT Enterprise — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on November 1, 2023. Retrieved November 1, 2023.
- ^ «Announcing the General Availability of Windows Server IoT 2025!». Retrieved November 30, 2024.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2025 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Retrieved November 30, 2024.
- ^ «Availability of Universal Serial Bus Support in Windows 95». Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on December 10, 2005.
- ^ «How to Enable Direct Memory Access (DMA)». Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on June 27, 2006.
- ^ «Windows NT 4.0 does not support Universal Serial Bus». Microsoft Support. November 2004. Archived from the original on September 6, 2005.
- ^ «Updated USB 2.0 Drivers Are Available in Windows 2000 Service Pack 4 (SP4)». Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on October 29, 2006. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ Jones, Don (August 5, 2002). «USB 2.0 Support in Windows XP:High Speed at Last». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 31, 2004. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ «USB 2.0 and Windows Operating Systems». Windows Hardware Development. May 11, 2007. Archived from the original on March 3, 2011. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ a b c «Release Notes for Windows XP 64-Bit Edition Setup». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 10, 2007. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
- ^ «Windows Vista Starter Fact Sheet». Microsoft. January 2007. Archived from the original on March 7, 2007.
- ^ a b «System Requirements». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on June 27, 2017. Retrieved May 24, 2018.
- ^ a b «Hardware requirements for Windows Server». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on August 21, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM the Windows operating system can handle?». Crucial. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ «Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases». Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 5, 2008. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ a b «Q84388: Windows 3.1 Memory Limits». December 15, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 95/98 error «Insufficient memory to initialize Windows» — IBM IntelliStation M Pro (Type 6889)». IBM. December 15, 2022.
- Official website
- Time line from Microsoft
Источник статьи
Автор24
— учеба по твоим правилам
Общие понятия об операционных системах
Ресурсы компьютера, такие как процессор, оперативная память, периферийные устройства, могут эффективно работать только в том случае, если их совместную работу координируют специальные программы. Иначе устройства будут работать несогласованно или вообще не смогут приносить пользу. Поэтому на любом компьютере используется операционная система. Операционной системой (ОС) – называется комплекс управляющих программ, предназначенных для управления вычислительным процессом и наиболее эффективного использования всех ресурсов вычислительной системы. Операционная система осуществляет планирование вычислительного процесса и управление его ходом. Все программы, которые мы устанавливаем на компьютер, работают под управлением и контролем операционной системы. Все устройства, которые мы подключаем к компьютеру, «общаются» с операционной системой через специальные программы – драйверы устройств. Кроме того, операционная система предоставляет пользователю интерфейс для взаимодействия с ресурсами компьютера.
Операционные системы в зависимости от их назначения могут обладать или не обладать следующим рядом свойств:
- Многозадачность — возможность запускать и выполнять одновременно более одной программы.
- Работа в режиме реального времени. ОС с этим свойством используются чаще всего для управления автоматическими комплексами. Их главная черта – это способность быстро реагировать на непредсказуемый поток внешних событий;
- Многопользовательский режим. Специальный режим, который позволяет работать нескольким пользователям за несколькими терминалами, разделяя при этом ресурсы одного и того же компьютера;
- Распределенность. При распределенном режиме работы пользователь , может обращаться к ресурсам разных компьютеров. ОС так управляет этими ресурсами, что у пользователя создается впечатление работы за одним единственным компьютером.
- Встроенность. Встроенные ОС работают на компьютере, который встроен в какое-то устройство и управляет этим устройством. Других функций такой компьютер не выполняет. Встроенная ОС поставляется только вместе с устройством и не распространяется отдельно от него.
- Интерактивность. Интерактивные системы рассчитаны на пользователя, который сидит за терминалом и ожидает отклика системы на свои действия.
«Операционная система Windows» 👇
Противоположностью интерактивным ОС являются ОС с пакетной обработкой, которые вообще не предполагают наличия пользователя.
Интерактивные системы могут иметь текстовый интерфейс, а могут иметь графический интерфейс.
Операционные системы семейства Windows
Современные ОС семейства Windows – это графические, интерактивные, многозадачные ОС корпорации Microsoft. Семейство ОС Windows состоит из двух групп:
- Windows 9x. Группа ОС для $16$ и $32$ –разрядных процессоров. Производились с $1995$ по $2000$ год. В настоящее время ОС этой группы являются устаревшими;
- Windows NT. Это группа современных ОС. Все ОС этой группы бывают $32$ и $64$-разрядными и работают соответственно на $32$ и $64$-разрядных процессорах. Именно к этой группе относятся популярные системы Windows XP, Windows $7$, Windows $8$. Имеются ОС, предназначенные для управления серверными компьютерами ;
- Windows для смартфонов. К этой группе относятся ОС Windows CE, Windows mobile, Windows Phone, Windows $10$ Mobile. Системы этой группы можно приобрести исключительно в составе готовых смартфонов.;
- Windows Embedded. Группа встраиваемых ОС реального времени применяемых для различных специализированных устройств. Например, для информационных и платежных терминалов, систем видеонаблюдения.
Далее работа операционной системы будет проиллюстрирована на примере Windows $7$.
Файловая система
Одним из основных понятий неразрывно связанных с понятием операционной системы является файловая система. Файловой системой называется целый сложный механизм, который ответственен за сохранение данных на жестком диске и других внешних носителях. Этот механизм работает следующим образом. Для того чтобы пользователь мог обращаться к данным, которые он сохранил на диске, эти данные должны быть как-то поименованы естественным для пользователя образом. Такая поименованная часть диска называется файлом. Размер файла может быть любым – пользователь сохраняет под единым именем столько данных, сколько он считает целесообразным. Область данных (винчестер, флешку, съемный винчестер и т.д.) разбивается на так называемые секторы размером по $512$ байт. А секторы объединяются в кластеры. Кластер является минимальной адресуемой единицей дисковой памяти, которая выделяется под хранение файла. Один кластер может хранить данные только одного файла. Размер кластера фиксирован и является различным для разных файловых систем. Процесс разметки области хранения данных называется форматированием.
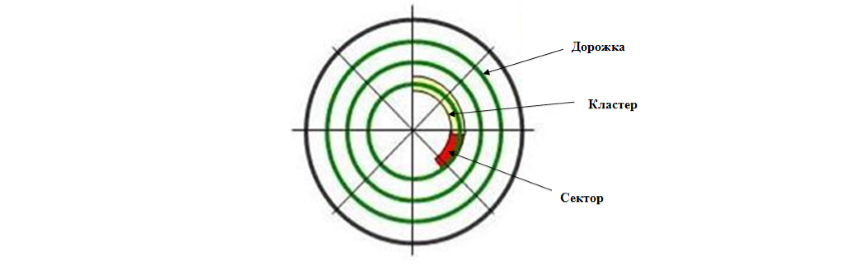
Рисунок 1.
ОС Windows $7$ поддерживает четыре типа файловых систем:
- FAT16. Это довольно старая файловая система, предназначенная для дисков размером менее $512$ Мб. Максимальный объем, который поддерживает FAT $16$, равен $2$ Гб.
- FAT32. Используется для флеш-памяти размером больше $2$ Гб.
- exFAT. Была разработана как улучшенная версия FAT$32$ для флеш-памяти.
- NTFS. Эта файловая система является базовой для Windows $7$. Она была создана, чтобы полностью вытеснить FAT$16$ и FAT$32$. NTFS быстрее и надежнее своих предшественниц, имеет средства для шифрования данных. ОС Windows $7$ может быть установлена только на диск, который отформатирован в файловой системе NTFS, но при этом Windows может работать с другими областями хранения данных, которые отформатированы в FAT$16$, FAT$32$ и exFAT.
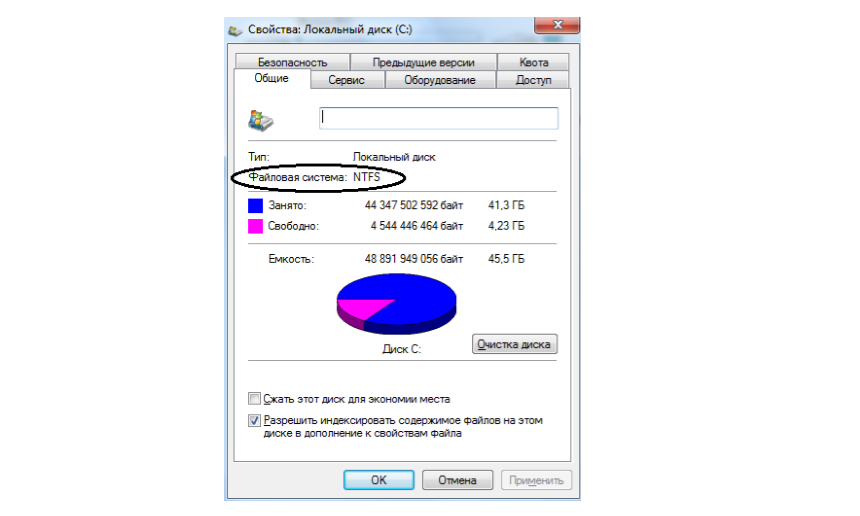
Рисунок 2.
Для операционных систем других семейств используются совершенно другие файловые системы. Например, для ОС Linux жесткий диск форматируется в файловой системе ext$3$. Можно на одном и том же компьютере один раздел диска отформатировать в NTFS и установить там Windows $7$, а другой раздел отформатировать в ext$3$ и установить на нем Linux. В этом случае работая под Windows пользователь вообще не будет видеть раздел отформатированный в ext$3$ и никак не сможет получать из него данные.
Для того чтобы узнать, какая файловая система (из доступныx для Windows) выбрана на определенном разделе жесткого диска нужно нажать правой кнопкой мыши на пиктограмме диска и выбрать в контекстном меню пункт «свойства». В открывшемся окне можно прочитать информацию о размере диска, количестве свободного места и файловой системе.
Microsoft Windows is a group of several graphical operating system families, all of which are developed, marketed, and sold by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Windows families include Windows NT and Windows Embedded; these may encompass subfamilies, e.g. Windows Embedded Compact (Windows CE) or Windows Server. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile and Windows Phone.
Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for their text-based operating system, MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs).[1] Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world’s personal computer (PC) market with over 90% market share, overtaking Mac OS, which had been introduced in 1984. Apple came to see Windows as an unfair encroachment on their innovation in GUI development as implemented on products such as the Lisa and Macintosh (eventually settled in court in Microsoft’s favor in 1993). On PCs, Windows is still the most popular operating system. However, in 2014, Microsoft admitted losing the majority of the overall operating system market to Android,[2] because of the massive growth in sales of Android smartphones. In 2014, the number of Windows devices sold was less than 25% that of Android devices sold. This comparison however may not be fully relevant, as the two operating systems traditionally target different platforms. Still, numbers for server use of Windows (that are comparable to competitors) show one third market share, similar to for end-user use.
As of October 2021, the most recent version of Windows for PCs and tablets is Windows 11. The most recent versions for server computers is Windows Server 2022. The last version available for smartphones and embedded devices was Windows 10. A specialized version of Windows runs on the Xbox One and Xbox Series X/Xbox Series S video game consoles.[3] Microsoft rolled out its first release of Windows 11 on October 5, 2021.[4]
Versions[]
There have been many versions of Windows since its introduction in 1985, ranging from 16-bit to 64-bit, for both client and server applications.
Major releases of the consumer operating system[]
- Windows 1.0 (1985)
- Windows 2.0 (1987)
- Windows 2.1 (1988)
- Windows 3.0 (1990)
- Windows 3.1 (1992)
- Windows 95 (1995)
- Windows 98 (1998)
- Windows 2000 (2000)
- Windows Me (2000)
- Windows XP (2001)
- Windows Vista (2006)
- Windows 7 (2009)
- Windows 8 (2012)
- Windows RT (2012)
- Windows 8.1 (2013)
- Windows 10 (2015)
- Windows 11 (2021)
Major releases of the business / server operating system[]
- Windows NT 3.1 (1993)
- Windows NT 3.5 (1994)
- Windows NT 3.51 (1995)
- Windows NT 4.0 (1996)
- Windows 2000 Server (2000)
- Windows Server 2003 (2003)
- Windows Server 2003 R2 (2005)
- Windows Server 2008 (2008)
- Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009)
- Windows Server 2012 (2012)
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (2013)
- Windows Server 2016 (2016)
- Windows Server 2019 (2018)
- Windows Server 2022 (2021)
- Windows Server 2025 (2024)
History[]
Windows was first originated as an add-on to MS-DOS to provide a graphical user interface to the traditional command-line system.
Windows 1.0[]
A typical Windows 1.0 desktop.
The first independent version of Microsoft Windows, version 1.0, released in November 1985, lacked a degree of functionality and achieved little popularity.
Windows 2.0[]
Windows 2.0 was released in November 1987 and was slightly more popular than its predecessor. Windows 2.03 (release date January 1988) had introduced overlapping windows, which led to Apple Computer filing a suit against Microsoft alleging copyright infringement.
Windows 3.0[]
A Windows 3.11 Workgroup desktop.
Windows 3.0, released in 1990, was the first Windows version to achieve broad commercial success, selling 2 million copies in the first six months. It featured improvements to the user interface and to multitasking capabilities. It was updated to version 3.1 in 1992.
Windows NT 3.1[]
In July 1993, Microsoft released Windows NT based on IBM OS/2 technology (which Microsoft had been co-developing for several years prior). NT was targeted at businesses rather than home users, although these separate lines would later be combined.
Windows 95[]
On August 24, 1995, Microsoft released Windows 95, which introduced support for native 32-bit applications and long file names of up to 255 characters. The most significant addition, however, was the Start Menu – a graphical menu which provides a central launching point for programs and performing other tasks.
Windows 98[]
The next in line was Microsoft Windows 98 released in June 1998. Substantially criticized for its slowness compared with Windows 95, many of its basic problems were later rectified with the release of Windows 98 Second Edition in 1999.
Windows 2000/Me[]
As part of its business line, Microsoft released the NT-based Windows 2000 in February 2000, which was used for servers and workstations alike. The consumer version was the 9x-based Windows Me (Millennium Edition), released in September 2000. Windows Me attempted to implement a number of new technologies for Microsoft, most notably Universal Plug and Play, however, the OS was substantially criticized for its lack of compatibility and stability.
Windows XP[]
A typical Windows XP desktop.
In October 2001, Microsoft released Windows XP, a version built on the Windows NT kernel that also retained the consumer-oriented usability of Windows 95 and its successors. It shipped in two distinct editions, «Home» and «Professional», the former lacking many of the superior security and networking features of the Professional edition. Additionally, the «Media Center» edition was released in 2003, with an emphasis on support for DVD and TV functionality including program recording and a remote control.
Windows Server 2003[]
Windows Server 2003 was introduced in April 2003, replacing the Windows 2000 line of server products with a number of new features and a strong focus on security; this was followed in December 2005 by Windows Server 2003 R2 (Release 2).
Windows Vista[]
The long-awaited Windows Vista, codenamed Longhorn, was released in 2007 with 5 editions. Vista was built on the more recent and more stable platform of Server 2003. Windows Server 2008 was introduced in February 2008.
Windows 7[]
In October 2009, Windows 7 was launched as the successor to Vista, and is considered to be a lot more stable and usable than its predecessor. At the same time, Windows Server 2008 R2 was launched as an update to the server line.
Windows 8[]
In October 26, 2012, Windows 8 was launched as the successor to Windows 7 and introduced major changes to the OS’s platform and user interface to improve experience on mobile devices, because Windows was now competing with mobile OS’s. Windows Server 2012 was also released.
Windows 8.1[]
Windows 8.1 was released on October 17, 2013 to address complaints of Windows 8. It included visual enhancements, new apps, and support for new technologies. It received more acceptance than Windows 8. Windows Server 2012 R2 was released at that time.
Windows 10[]
Windows 10 was released on July 29, 2015 as the successor to Windows 8.1, and addresses shortcomings in the user interface first introduced with Windows 8. Changes include the return of the Start menu, a virtual desktop system, and the ability to run Windows Store apps within windows on the desktop instead of in full-screen mode. The user interface is designed to handle changes between mouse and touchscreen interfaces. The server equivalents for Windows 10 are Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019. The current version of Windows 10 is version 21H1, released in May 2021.
Windows 11[]
Windows 11, codenamed «Sun Valley«, was leaked on June 15, 2021 and was formally announced on June 24 as the successor to Windows 10 during a livestream. Preview builds began being released through the Windows Insider Program on June 28, demonstrating the return of a rounded user interface and a Start Menu and Taskbar that are centered by default.[5] Windows 11 was released as a free upgrade to eligible customers on October 5, 2021.[4][6] A phased rollout of the Windows 11 2022 Update (22H2) began on September 20, 2022.[7] The next annual update is codenamed «Copper» (23H2) and is scheduled for release in 2023. New features in development include the ability to expand the view of Widgets, an improved Xbox Game Pass Widget, redesigned «Rename this PC» and date/time picker UI.[8]
Future[]
Microsoft announced that major new versions of Windows are being scheduled for release every 3 years, placing the next such version in 2024.[9] Upcoming features from a prototype build that was demonstrated at Microsoft Ignite 2022 included a rounded floating Taskbar, weather information and system icons at the top corners, an elongated pill-shaped search bar at the top center, and a working codename of «Next Valley«.[10] In December 2022, Microsoft began the Zinc (24H2) development semester.[11] On March 8, 2023, the Windows Insider Program initiated the Canary Channel to begin separate testing of experimental features believed to be intended for Windows 12.[12]
Interface[]
Microsoft Office apps in Windows 11.
The most obvious feature of Windows is a window or a container for other graphical objects. A Window in Microsoft Windows typically contains a status bar, title bar, minimize and maximize buttons, close button, and system menu (also called the windows menu or control menu). Another prominent feature since Windows 95 and NT 4.0 is the desktop, which holds various icons that the user can double-click to open. The Start Button and Start Menu, attached to the taskbar and typically below the desktop, gives users access to installed programs and many of the other features of the operating system.
Due to these and features, Windows makes it possible to perform most common tasks, some quite complex, with very little computer knowledge. Windows also comes with features to help the disabled through its accessibility options. Under Windows XP, these features include the Narrator, Magnifier, and contrast display mode.
Logo timeline[]
1985-2001 as Microsoft Windows 1.0x-2.x
1988-2001 as Microsoft Windows 3.0
1991-2010 as Microsoft Windows 3.1-2000
1995-2006 as Microsoft Windows 9x
2001-2014 as Windows XP
2006-2012 as Windows Vista-7
2012-2015 as Windows 8 and Windows 8.1
2015-2021 as Windows 10
2021-present as Windows 11
Widespread usage[]
Microsoft Windows is installed on the vast majority of personal computers. A July 2005 poll of Network Computing magazine readers found that 90% of their organizations used Microsoft’s desktop operating systems. It has achieved enormous market penetration due to the domination of MS-DOS in the early days of PC compatible computers (IBM PC clones). It is also the primary platform for Microsoft Office and most non-console computer games.
The widespread use of Microsoft’s operating system has benefited from not being tied to the success of one hardware manufacturer and from Microsoft’s willingness to license the operating system to manufacturers. This is in contrast with Apple Computer, which does not license Mac OS X to other manufacturers, and Sun Microsystems, which did not license Solaris before it was made free and open-source. However, the wide spectrum of possible hardware permutations with Microsoft Windows is also a major source of computer problems because of hardware-software incompatibilities for consumers.
In the past, companies who wanted to be in the computer business had to create their own operating systems (such as the Amiga, BBC Micro or ZX Spectrum) or choose another OS; even an exclusive license with one vendor was significantly cheaper than developing and supporting a new operating system and software base.
Due to Microsoft’s extensive licensing agreements with many computer vendors, Windows presently comes pre-installed on most computers as a bundled OEM version, making it the default or only choice for most of the market.
For some consumers, Windows is the only valid option for a computing environment, or it is mandated by their workplace; additionally, an unfamiliarity with other operating systems results in a lack of desire to switch to other operating systems. A significant percentage of computer users simply lack the technical knowledge needed to install an operating system.
Finally, the large base of software available exclusively for the Windows family of operating systems has become the single largest self-perpetuating reason for the popularity of Windows. In recent years, many companies have been started with the sole intention of releasing Windows software; the fact that there is already a large customer base in place is reason enough for such companies to spend their resources solely on Windows software development. As a result, the fact that many companies are supporting Windows exclusively is a self-reinforcing reason for customers to choose Windows.
Maintaining compatibility in a new release of Windows with this large collection of software designed to run on older flavors of Windows consumes a large part of the resources of the Windows development team.
Security[]
The Windows XP Security Center supplied in Service Pack 2.
Security has been a major weakness of Windows for many years, and even Microsoft itself has been the victim of cracks and hacks. Due to the widespread usage of Windows on personal computers, many crackers (also known as black hat hackers) have targeted Windows rather than the lesser-used operating systems such as Linux, Unix, Mac OS X, and FreeBSD. Some believe that due to being designed for security in a multi-user and/or networked environment some other operating systems have a relatively small number of security issues. Windows was originally designed for ease-of-use on a single-user PC without a network connection and did not have security features built-in from the outset. Combined with occasionally flawed code (such as buffer overflows), Windows is a continuous target of worms and virus writers. Furthermore, until Service Pack 2 of Windows XP most versions of Windows were shipped with important security features disabled by default, and vulnerable albeit useful system services enabled by default. In June 2005, Bruce Schneier’s Counterpane Internet Security reported that it had seen over 1,000 new viruses and worms in the previous six months.
Microsoft publicly admitted their ongoing security problems shortly after the turn of the century and now claims to regard security as their number one priority. As a result, Service Pack 2 for Windows XP greatly increased the security of the operating system. Microsoft releases security patches through its Windows Update service approximately once a month (usually the second Tuesday of the month), although critical updates are made available at shorter intervals when necessary. In Windows 2000 (Service Pack 3 and later), Windows Me, and Windows XP, updates can be automatically downloaded and installed if the user selects to do so.
As another step in their focus on security, Microsoft has released Windows Defender (formerly Windows AntiSpyware and Giant AntiSpyware) a free program designed to protect against spyware and other unwanted software.
A study conducted by Kevin Mitnick and marketing communications firm Avantgarde found that an unprotected and unpatched Windows XP system lasted only 4 minutes on the Internet before it was compromised. The AOL/National Cyber Security Alliance Online Safety Study of October 2004 determined that 80% of Windows users were infected by at least one spyware/adware product. Much documentation is available describing how to increase the security of Microsoft Windows products. Typical suggestions include deploying Microsoft Windows behind a hardware or software firewall, running anti-virus and anti-spyware software, and installing patches as they become available through Windows Update.
See also[]
- General
- Microsoft
- Further reading
- Architecture of the Windows NT operating system line
- History of Microsoft Windows
- List of Microsoft Windows components
- Microsoft Windows topics
- Windows Explorer
- Windows Genuine Advantage
- Windows Media
References[]
- ↑ «The Unusual History of Microsoft Windows». Retrieved April 22, 2007.
- ↑ Keizer, Gregg (July 14, 2014). «Microsoft gets real, admits its device share is just 14%». IDG. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. «[Microsoft’s chief operating officer] Turner’s 14% came from a new forecast released last week by Gartner, which estimated Windows’ share of the shipped device market last year was 14%, and would decrease slightly to 13.7% in 2014. [..] Android will dominate, Gartner said, with a 48% share this year»
- ↑ «Xbox One Architecture Finally Explained — Runs OS ‘Virtually Indistinguishable’ from Windows 8». WCCFtech. Archived from the original on September 6, 2015.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Windows 11 available on October 5 by Aaron Woodman, Microsoft. 2021-08-31.
- ↑ Microsoft releases Windows 11 preview, available to download now by Tom Warren, The Verge. 2021-06-28.
- ↑ Windows 11 release date is October 5 by George Cox, The Spectrum. 2021-09-13.
- ↑ Windows 11, version 22H2 known issues and notifications, Microsoft. 2022-09-22.
- ↑ Windows 11 25201 gets new ‘Rename this PC’ and date/time picker UI, here is how to enable it, by Taras Buria, NeoWin. 2022-09-15.
- ↑ Microsoft moves to new Windows development cycle with major release every three years, feature drops in between by Zac Bowden, Windows Central. 2022-07-15.
- ↑ Microsoft accidentally revealed a UI design prototype for the next version of Windows at Ignite 2022 by Zac Bowden, Windows Central. 2022-10-13.
- ↑ Microsoft quietly stomps into Windows 11 Zinc development semester by Sayan Sen, Neowin. 2022-12-13.
- ↑ Microsoft releases Windows 11 Build 23403 on the rebooted Dev Channel by Wayne Williams, BetaNews. 2023-03-08.
External links[]
Official[]
- Microsoft’s Official Windows Website
- Official Promotional Website (Windows.com)
- Windows history time line from Microsoft
- Windows official Twitter
- Windows official YouTube channel
Tips and documentation[]
- How to run multiple versions of Windows on one PC
- Tech-Recipes Windows Guide – listing of almost 500 Windows Tutorials
- The Windows Documentation Project (wiki)
- Securing Microsoft Windows (for Home and Small Business Users)
- Symantec Anti-Virus Research Center – excellent informational security resource, and Symantec are makers of Norton Anti-Virus (third party software sold separately).
- dotwhat? — File Extension Listing – a huge listing of file extensions and the programs that use them
- Windows – tips and tricks for Windows 98, ME, NT, 2000 and XP
- Windows Support Script
- The Windows Wiki
- Vernalex’s Windows Services Utility – an unofficial list of most Windows services with detailed descriptions and recommended run states
Programming Microsoft Windows[]
- Microsoft Development Network for programming Microsoft Windows
- Windows API tutorial in C++
Libraries[]
- RSWL – free Reliable Software C++ Windows API library.
Reviews and evaluation[]
- Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows – an exhaustive evaluation of Microsoft’s products and technologies
- «Time to Live on the Network» – a security study by Kevin Mitnick and AvantGarde (PDF)
- Windows XP: rough around the edges – an UI review of Windows XP
- Frank Mahler’s Interface Hall Of Shame (in German)
- AOL/National Cyber Security Alliance Online Safety Study (October 2004) (PDF)
- Interface Hall of Shame – an analysis of user interfaces with a focus on Windows
Other[]
- Windows history – a Windows history time line graph by Éric Lévénez (detailed, continually updated)
- GUIdebook: Windows Gallery – a website dedicated to preserving and showcasing graphical user interfaces
- Windows 20th Birthday
|
Microsoft Windows family |
|---|
| Versions • Components • History |
| Original |
| DOS-based |
| Windows 1.0 • Windows 2.0 • Windows 2.1 (Windows/286 • Windows/386) • Windows 3.0 • Windows 3.1 |
| Windows 9x |
| Windows 95 • Windows 98 • Windows Me |
| Windows NT |
| Early versions |
| Windows NT 3.1 • Windows NT 3.5 • Windows NT 3.51 • Windows NT 4.0 • Windows 2000 |
| Client |
| Windows XP (development) • Windows Vista (editions • development) • Windows 7 (editions • development) • Windows 8 • Windows 10 • Windows 11 |
| Windows Server |
| Server 2003 • Server 2008 (2008 R2) • HPC Server 2008 • Home Server • Small Business Server • Essential Business Server • Windows Server 2012 • Windows Server 2016 • Windows Server 2019 • Windows Server 2022 |
| Specialized |
| Windows Embedded • Windows PE • Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs |
| Mobile |
| Windows Mobile • Windows Phone |
| Cancelled |
| Cairo • Nashville • Neptune • Odyssey • Windows 10X |
| Related |
| Metro • Midori • OS/2 • Windows Aero • Windows Setup • Windows XP themes • Microsoft Plus! |
