Blue Screen error is completely destructive to the windows 10 system and almost irrecoverable in most cases. PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED is one such issue that appears and leads the computer to start bug checking. Just after that Windows 10 restart and then again repeat the same process. Bug check value for this BSOD is 0x0000006B. The problem occurs mainly due to corrupted Bootcat.cache file or often when this file is resized at the time of booting.
The initial problem you may encounter after being affected by stop error PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED is a frequent restart and bug checking. There might be irregular flashing on the screen and freezing of the desktop area temporarily. Things will get complicated much when the Windows will start rebooting frequently leaving no option to take any action. You know well stop error or BSOD is a critical system crash leading the system resources to go missing. However, Microsoft indicated Bootcat.cache file related issues are the main reason behind this BSOD error, you have got more common causes. Driver problems mostly outdated ones, missing dll files; bad areas in hard disk, using an old edition of OS can also cause the same issue. Before the error causes much noxiousness in your Windows 10 system, let’s resolve it from today’s discussion. Starting with the Method list –
PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED
Here is how to fix PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error in Windows 10 –
1] Disable Automatic Restarting feature
PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED blue screen error forces Windows to a very critical system crash. Necessary resources tend to go missing and the Windows shuts down immediately in order to minimize the extent of the loss. Therefore, the error message will appear on display with bug code 0x0000006B and you cannot take any action to save an ongoing task. The entire system will be unstable and definitely, no can detect the cause of the issue as well as apply fix accordingly.
Automatic Restarting is a built-in feature in Windows computer and it can be disabled tweaking Startup settings. Once disabled, you can approach for deploying the workarounds and get fixed BSOD error. Here is how to disable the feature –
- Click on Start, type System properties and then press Enter.
- Select “System info” from the right pane.
- Choose Advanced system settings from the left column of the next Window.
- When the System Properties will open, jump into the Advanced tab.
- On the Startup and Recovery area, perform a hit on the Settings button.
- In the next pop up, move out for the System failure field.
- Uncheck the box that is set for “Automatically restart”.
- Finally, click the OK button at the bottom and save these changes.
2] Delete the Bootcat.Cache to fix PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD
Windows 10 encounters PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD once the Bootcat.Cache file becomes corrupted or resized at the startup. This is a component of CodeIntegrity and its location in Windows is “C:\Windows\System32\Codeintegrity”. In order to fix the drawback, we have to delete this file and boot the system to fully functional OS.
Here are the steps you have to follow –
- Press Windows logo key and I.
- Click Update & Security.
- From the next page, select Recovery located at the left pane.
- Move on to adjacent right side pane and reach to Advanced startup.
- Click Restart now.
- When the blue screen shows up next, choose to Troubleshoot => Advanced options => Command Prompt.
- In the Elevated Command Prompt window, insert below text –
C:
cd windows/system32/codeintegrity
del bootcat.cache
- Press Enter.
- Once deleting is done, exit Command Prompt and Restart Windows 10.
- The system will recreate the Bootcat.cache file again automatically and PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED error will be fixed.
See if you need – Fix: bootrec /fixboot access denied in Windows 10.
3] Copy Bootcat.cache files from another computer
In case deleting the Bootcat.cache file from your computer doesn’t resolve the PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error, you can apply another hotfix. The idea is to copy this file from a full function and error-free computer running the identical version of Windows 10.
- Copy C:\Windows\System32\Codeintegrity, Press WIN+R, and paste the same.
- Hit Enter.
- Copy all the items from this location and place in a USB drive by pasting.
- Insert the device through a port in the system getting the error and copy all the items in the same location.
4] Disable Secure Boot
Secure Boot in Windows 10 keeps the system protected from virus attack and this is another advanced technology support working on top of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). The utility is intended for ensuring the computer boot up using only trusted firmware supplied by the manufacturer.
Some users have come up with a fact that having Secured Boot enabled in Windows 10 can be dangerous as it often causes PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error. Usually, that might happen due to some hardware misconfiguration and in that case, you have to disable it. The guidelines are as following –
- Boot Windows 10 to Automatic Repair using guidelines from the 2nd method above.
- When the blue screen floats up, select Troubleshoot > Advanced Options.
- From the next screen, select UEFI Firmware Settings to enter into BIOS.
- Though Every OEM has its own way of showing options, Secure Boot is usually residing under Security / Boot / Authentication Tab.
- Set the Secure Boot to Disabled.
- Press F10 in order to Save and Exit.
- Restart Windows and changes will be effective immediately.
5] Install the latest patches
Outdated Windows 10 is very much likely to be affected by PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error especially if a released package is left uninstalled for long time. The update patches released by Microsoft always come with something new, advanced technologies, security modification, and moreover the big fixes. You might have missed out some important change and end up encountering blue screen error.
Updating the latest patches in Windows 10 is one easy task and automatic when the device is connected with an active unmetered internet connection. But often the system is out to install automatically and you need to check for updates time and again manually. Here are the steps to install latest patches to update OS –
- Press Windows key to open the Start menu and click Gear icon from there.
- From the UI opening next, select the Update & Security tile.
- After additional setting page unrolls, select Windows Update from the left pane.
- Jump to the adjacent right side and click on Check for updates link.
- After all, patches being available, click Download button.
- Installation will begins automatically upon accomplishing the downloading.
- Attend Restarting as guided to complete the updating process successfully.
6] Run a full system scan for malware
Malware is strongly coded programs staying in disguise like a usual file in the system. As the computes nowadays are always connected to the internet, the chances to get affected by spyware are a lot more. These bugs are always on the move through links in webpages, spam mails, and often via USB drives too. Though the Primary intention of a virus is to steal sensitive data and cause harm to the owner, they are responsible for corrupt system files too. Some DLL files will also go missing leading the system to undergo PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error.
While surfing the internet, you need to be more cautious about worms, Trojans, spyware and must not click any suspicious links. Anti-virus programs keep the system secured by eliminating malware and strengthening the shield. Windows Security is the latest inclusion by Microsoft with robust architecture to provide maximum security to the system. A full system scan with this tool will help you stay out of malicious programs both online and offline. Here are the steps to run a full system scan in Windows Security –
- Open the Start menu and scroll down in the app list alphabetically.
- Click Windows Security to launch it.
- From the following window, select “Virus & threat protection” located at the left pane.
- Click on Scan options link from the right side pane.
- Choose the radio button set for Full scan and click Scan now button.
- If the tool detects some vulnerability, click Clean Threat option to get rid of them.
- On the following page, click Remove followed by clicking Start actions to clean up all the threats.
- When the process ends, Restart Windows 10 to make changes effective.
7] Copy and register ntdll.dll file
Not only Bootcat.cache file, missing some DLL files such as ntdll.dll is equally responsible for the PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD. In order to fix the error, we can copy the same file from a secured computer and paste it to the System32 folder of affected computer.
The process is almost similar to copying the Bootcat.cache file as discussed before but you need to register after pasting it. The prerequisite is safe to use USB drive and the computer from which you will be copying must have the same edition of Windows 10. Follow the below instructions to accomplish the task –
- Insert the USB drive to the identical and healthy computer from where you choose to copy the DLL files.
- Go to C:\Windows\System32 and copy all the files having .dll extension.
- Paste the items to the USB drive.
- Take out the drive and insert to the affected computer.
- Copy and Paste all the .dll files to C:\Windows\System32.
- Now, launch the elevated Command Prompt and enter below commands –
regsvr32 (name of DLL file)
Note – Replace name of DLL file with ntdll.dll, wintrust.dll, vbscript.dll, oleaut32.dll, cryptdlg.dll, softpub.dll, jscript.dll, initpki.dll, msxml.dll successively.
- Press Enter key after each.
- Finally, Restart.
- Hopefully, the PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error will resolve once this change is effective.
8] Run Startup repair
Startup Repair is an advanced recovery tool in Windows that fixes issues restricting Windows 10 from starting at all. The tool will run a few diagnostics and try to fix the problem so that you can boot up Windows 10. PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD leads the windows to a very critical system crash and that may affect the startup of it. Therefore, carrying out the repair might be a good option to fix the error and many users have got successful results.
The guidelines are as follows –
- Insert the Installation media drive like CD/DVD/USB to the Windows 10 computer.
- Restart the Windows and press any key while booting.
- Select Language Preference.
- Hit the Next button there.
- Do a click on Repair your Computer.
- Choose the OS edition that you opt to.
- Hit the Next button.
- Choose “Startup Repair” option from the next display. Now the system will carry out some scans and fix if the device has some booting related issues automatically.
- In order to check, click on the ‘View Diagnostic & Repair Details.’
- Hit the Finish button from here to restart Windows 10.
- Once it starts again, check if the PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error is fixed.
9] Run System File Checker
System files have fixed components and structure that make it executable when necessary to run the Windows. These files can be corrupted due to power surge, malware infection, and updating issues as well. Corrupted system file appears unreadable after losing the components and structure from them. The last result of this problem is PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED Blue Screen error too.
You have the ability to solve these broken system files and recover some missing DLL components using System File Checker utility. Follow the below guidelines –
- Hold down Winkey and press R.
- In the empty text box of Run, type cmd.
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Enter keys together at once.
- Click Yes when UAC floats up to open Elevated Command Prompt.
- In the succeeding black window, type below command and press Enter –.
sfc /scannow
- Now, System File Checker will detect and resolve unsettled components and rectify them furthermore missing DLL files will be recovered accordingly.
- Once done, Restart Windows 10 and make all the changes effective.
10] Update the drivers to re-gain stability
Drivers provide stability in the system as well as maintain interaction between computer bus and the hardware accessories. They are key components and every function needs minimum one “driver” to perform its function and establish the relationship. When they remain outdated, the system will lose the integrity, functionality, and will be unstable as well. In order to make the system up and running, there is no alternative to updating these components. The easiest way to update all the drivers simultaneously is Windows upgrade but you often customize this setting as of saving time.
Most of the Blue Screen errors like PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED are the upshot of Driver related issues. You may get such trouble occurs because of outdated or a defective update is installed in the system. Windows Device Manager is a complete utility to update the drivers and more driver related upper hands like Uninstalling and rolling back them to default. Moreover, you can easily detect and outdated one as they will be shown with identifying sign. Here are the steps to update a driver using Windows Device Manager –
- Invoke Run dialog and type devmgmt.msc in the text box.
- Click Ok button on the box to open up Windows Device Manager.
- When the console loads completely, look closely for any mark of exclamation.
- Split the driver list of that device by double-clicking.
- Make a right-click on the outdated driver having a yellow indication on it.
- Select Update Driver option from context.
- From the appearing popup, click “Search automatically for updated driver software” option.
- In the end, restart and make all these changes working.
11] Uninstall or disable third party anti-malware program
Anti-malware programs strengthen the security layer in a system and keep it protected from potential threats. We have told earlier how Windows Security maintains the utmost protection to Windows and of course, it’s a default tool. Using a third-party anti-virus application may often be a little unsafe as not all can be trustworthy. PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED error might be a consequence of this reason.
Since Windows Security is the best ever utility to eliminate malware, you can rely on it completely. It is legit to uninstall all third party anti-malware programs to keep the system out of additional trouble. You can uninstall them using the below steps –
- Press Windows key and X and select Apps and Features option from the list.
- Move to the right pane, locate a third-party anti-malware program, and do a click on it.
- Hit Uninstall option from expanded pane.
- If any confirmation message shows up, click “Uninstall”.
- Follow the next guidelines to complete this task.
- Finally, restart Windows and check if the error appears again.
12] Perform System Restore and undo recent changes
Recent changes in Windows might have a contradiction with Windows Registry resulting in PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED error. You often install new programs from various unknown sources where some of this may seem buggy. Forcibly canceling any task like uninstalling programs can also be risky to have negative changes in the system.
In order to fix the Blue Screen error evolved after any such changes; you can simply undo it by loading back previous state. One of the easiest ways to bypass any critical issues and process is System Restore. The tool will reverse Windows to an earlier saved Point of time in Windows 10 where you were not experiencing an error. To run the utility, follow the below guidelines –
- Press Windows key and type recovery in the text area.
- Select the same “Recovery” under Best match.
- When a new window opens from Control Panel, select Open System Restore link.
- From the wizard coming up, click Next from the bottom end.
- From the succeeding page, put a checkmark to the box says Show more restore points.
- After the system shows all the points, choose the most recent where you prefer to revert Windows.
- Select Next to proceed ahead.
- After the following page unrolls, click the Finish button.
- Click Yes from the warning message popup to continue restoring.
13] Repair Windows image file using DISM tool
Windows image file can cause PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error got corrupted. These are the components of a major upgrade of Windows that come in ISO- format. The usual task with these snapshots is to make identical CD-R or DVD-R drive for upgrading Windows.
The installation image, after getting corrupted by third-party tools, malware attacks, causes BSOD or blue screen error in Windows 10. Running Deployment Image Servicing and Management tool is the best way to fix the defective image files. Here are the instructions to run this tool –
- Open the Start menu pressing Windows key once.
- Click Power icon and select Restart option keep holding Shift button down at the same time.
- Window, after completing Rebooting, will boot to Automatic Repair.
- From the subsequent blue screen, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Command Prompt.
- When the black screen will show up, type following command at blinking cursor –.
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
- Press the Enter key to activate DISM tool.
- Upon finishing the task, Restart the computer.
- Check if the BSOD error has resolved already.
14] Try booting Windows 10 in Safe Mode
Booting in the Safe Mode is a startup method allowing the least number of programs and tools to be loaded for running the system. The target is to cut off third-party applications and unnecessary programs so that system runs with minimum resources. This will make troubleshooting for PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error a lot easier. If any third party application causes this mess up, it will then resolve as no such application is available in Safe Mode on Windows 10. In case the error stays, you can then go for necessary troubleshooting using tools accordingly.
Safe Mode has been a great utility to resolve most of the critical issues that are evolved in Windows over the years. Follow the below guidelines to accomplish this task –
- Invoke Run dialog pressing Win+R.
- Type msconfig in the search box and press Enter.
- Enter the Boot tab when System Configuration window opens.
- Scroll down to the second half and reach to “Boot options” area.
- Check the box that reads Safe boot followed by selecting radio button set for Minimal.
- Click Apply button and then Ok.
- Open Start menu and click Power icon.
- Select Restart and System Will Boot to Safe Mode once power On.
- If you want to disable Safe Mode, uncheck the box set for Safe Mode in the System Configuration like before.
15] Fix bad sectors in Hard Disk in Elevated Command Prompt
Bad sectors in the hard disk can be formed due to forcibly pulling cables from CPU, external damage to the CPU, and undetermined power outage issues. Hard Disk is the soul of a device but usually, we don’t maintain it properly.
Bad areas in the disk are very much likely to cause PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error in Windows 10. Well, there is an ingenious utility to fix these areas formed namely disk checking tool. It will activate after executinG CHKDSK command in the Elevated CMD.EXE. The instructions to run this tool are as following –
- Open the Taskbar Search pressing Win and S together.
- Type cmd.exe and right-click Command Prompt when shows up in the result.
- Select Run as Administrator followed by clicking Yes when UAC prompts.
- When in the Elevated Command Prompt window, enter below command –.
chkdsk /f /r C:
- Execute the entered command by pressing Enter key.
- Subsequent to the Disk checking tool finishes detecting bad areas, fixing will commence automatically.
- After the task ends, restart Windows 10 and check if PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED BSOD error is resolved.
Methods:
1] Disable Automatic Restarting feature
2] Delete the Bootcat.Cache
3] Copy Bootcat.cache files
4] Disable Secure Boot
5] Install the latest patches
6] Run a full system scan for malware
7] Copy and register ntdll.dll file
8] Run Startup repair
9] Run System File Checker
10] Update the drivers to re-gain stability
11] Uninstall or disable third party anti-virus program
12] Perform System Restore
13] Repair Windows image file
15] Fix bad sectors in Hard Disk
That’s all!!
When Windows detects hardware or software problem, Windows generate error code which identifies what is happening on your computer, notebook, tablet or smartphone. One of these errors is named Blue Screen Of Death (BSOD). End users do not like BSOD because BSOD is stopping our daily work. Every BSOD includes error name and an error code which help us to identify the possible issue. One of the BSOD which will be the topic of this article is PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED, error code 0x0000006B. What Microsoft said about error code 0x0000006B? Microsoft said: “This issue occurs because of the Bootcat.cache file is corrupted or because of the size of the Bootcat.cache file is changed since the last successful start.” We can confirm this problem with Bootcat.cache, and add another reasons including corrupted files, bad hardware, bad or incorrect cables and others. BSOD 0x0000006B occurs on operating system from Windows 2000 to Windows 10, and Windows Server 2008, too.
This is error code:
STOP: 0x0000006B (Parameter1, Parameter2, Parameter3, Parameter4)
PROCESS1_INITIALIZATION_FAILED
NOTE: The four parameters in the Stop error message may vary, depending on the configuration of the computer.
This error occurs on client and server machines, and on smartphones, too. In 16 methods we will show you how to solve issues on client and server machines, and the last one method will show you how to solve issues on your Windows Phone smartphone.

So what is the best solution for this problem? We will show you all solutions through 17 methods.
Method 1: Delete Bootcat.cache file
As Microsoft said, the first solution is to delete Bootcat.cache file from a CodeIntegrity folder, so, we will start with deleting this file from CodeIntegrity . Bootcat.cache file is a file located at following location C:\Windows\Ssystem32\Codeintegrity. By default, Windows is installed on C: partition and default name is a Local Disk (C:). We will show you how to delete Bootcat.cache file on Windows 7 Enterprise x64. If you are using another operating system, from Windows 2000 to Windows 10, you can follow the same procedure to solve issues with BSOD 0x0000006B. You will need to boot your computer to proper Windows operating system. You can boot your computer using DVD or USB flash drive. You should burn Windows ISO file to DVD or USB Flash drive. If you do not know how to burn ISO file to your USB flash drive, please read instructions on this LINK.
- Insert the Windows 7 installation DVD disk or USB flash drive
- Restart your Windows
- Boot your computer from the DVD drive or USB flash drive
- Enter your language and other preferences and click Next to continue
- Click Repair your computer
- Under System Recovery Options click Windows 7 and then click Next
- Click Command Prompt
- Type diskpart. Diskpart is a command line disk partitioning utility integrated into Windows. Diskpart will provide more information about available volumes on our computer.
- Type list volume and press Enter.
- Type Exit to leave Diskpart
- Type D: to open our system partition, because Windows is installed on D: partition
- Type cd windows\system32\codeintegrity and press Enter
- Type del bootcat.cache and press Enter
- Close Command prompt
- Restart your computer
- Test your computer
Method 2: Copy Bootcat.cache file from another computer
If the first method did not solve your problem, you should try this method, which includes copying Bootcat.cache file from another operating system which is working without any problems. If you have a problem with Windows 7 x64, you need to copy Bootcat.cache file from the same Windows, but a different computer. For this method, you will need USB flash disk with minimal capacity because Bootcat.cache is approximately 5 MB. Also, you will need Windows 7 x64 installation disk, which can be burned to DVD or USB flash disk. We will show you how to copy Bootcat.cache on Windows 7 x64. The first step is copying Bootcat.cache file to USB flash drive, and second step is to paste copied Bootcat.cache file to CodeIntegrity folder.
- Log on another machine
- Insert USB flash drive to working computer
- Hold Windows logo and press E to open Windows Explorer or File Explorer
- Navigate to following location C:\Windows\System32\Codeintegrity
- Right click on Bootcat.cache file and choose Copy
- Open your USB flash disk
- Right click and select Paste
- Eject USB flash drive from machine
- Insert USB flash drive into machine with BSOD issue
- Insert the Windows 7 installation DVD disk or USB flash disk
- Restart your Windows
- Boot your computer from the DVD drive or USB flash disk
- Enter your language and other preferences and click Next to continue
- Click Repair your computer
- Under System Recovery Options click Windows 7 and then click Next
- Click Command Prompt
- Type diskpart. Diskpart is a command line disk partitioning utility integrated into Windows. Diskpart will provide more information about available volumes on our computer.
- Type list volume and press Enter.
- Type Exit to leave Diskpart
- Type D: to open our system partition, because Windows is installed on D: partition
- Type cd windows\system32\codeintegrity and press Enter
- Type copy E:\bootcat.cache and press Enter, because E: is USB flash disk
- Close Command prompt
- Restart your computer
- Test your computer
Method 3: Copy ntdll.dll file from another computer
If the first two methods did not solve your problem, you will need to copy another file, named ntdll.dll, from one to another machine. If you have a problem with Windows 10 x64, you should copy ntdll.dll from the computer which uses the same operating system edition. Again, we will show you how to do it on Windows 7 x64. The procedure is simple as copying Bootcat.cache file. Regardless, we will show you the whole procedure. For this method, you will need USB flash disk with minimal capacity because ntdll.dll is approximately 1.6 MB. Also, you will need Windows 7 x64 installation disk, which can be burned to DVD or USB flash disk. We will show you how to copy ntdll.dll on Windows 7 x64. The first step is copying ntdll.dll file to USB flash drive, and second step is to paste copied ntdll.dll file to a System32 folder.
- Log on another machine
- Insert USB flash drive to working computer
- Hold Windows logo and press E to open Windows Explorer or File Explorer
- Navigate to following location C:\Windows\System32
- Right click on ntdll.dll file and choose Copy
- Open your USB flash disk
- Right click and select Paste
- Eject USB flash drive from machine
- Insert USB flash drive into machine with BSOD issues
- Insert the Windows 7 installation DVD disk or USB flash disk
- Restart your Windows
- Boot your computer from the DVD drive or USB flash disk
- Enter your language and other preferences and click Next to continue
- Click Repair your computer
- Under System Recovery Options click Windows 7 and then click Next
- Click Command Prompt
-
Type diskpart. Diskpart is a command line disk partitioning utility integrated into Windows. Diskpart will provide more information about available volumes on our computer.
- Type list volume and press Enter.
- Type Exit to leave Diskpart
- Type D: to open our system partition, because Windows is installed on D: partition
- Type cd windows\system32 and press Enter
- Type copy E:\ntdll.dll and press Enter, because E: is USB flash disk
- Close Command prompt
- Restart your computer
- Test your computer
Method 4: Delete file COMPONENTS
If deleting and copying Bootcat.cache and ntdll.dll did not solve your problem, next method will include working with file named COMPONENTS. You need to delete file COMPONENTS through Command Prompt. We will show you how to do it on Windows 7 x64. You will need Windows 7 x64 installation disk, which can be burned to DVD or USB flash disk.
- Insert the Windows 7 installation DVD disk or USB flash disk
- Restart your Windows
- Boot your computer from the DVD drive or USB flash disk
- Enter your language and other preferences and click Next to continue
- Click Repair your computer
- Under System Recovery Options click Windows 7 and then click Next
- Click Command Prompt
- Type diskpart. Diskpart is a command line disk partitioning utility integrated in Diskpart will provide more information about available volumes on our computer.
- Type list volume and press Enter.
- Type Exit to leave Diskpart
- Type D: to open our system partition, because Windows is installed on D: partition
- Type cd windows\system32\config and press Enter
- Type del components and press Enter
- Close Command prompt
- Restart your computer
- Test your computer
Method 5: Install Windows 7 SP1
If you are using Windows 7 without SP1, you will need to download SP1 for your Windows 7. If you are using Windows 7 x86, you will need to download and install Windows 7 SP1 x86, if you are using Windows 7 x64, you will need to download and install Windows 7 SP1 x64. Windows 7 SP1 is available on Microsoft Download Center.
- Open Internet browser (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Edge or other)
- Open web site on this LINK
- Download proper architecture version of Windows 7 SP1
- Install Windows 7 SP1
- Restart your Windows
- Test your computer
Method 6: Uninstall Roxio GoBack
If you are using Roxio GoBack software, you will need to uninstall software and enjoy working on your computer, without boring BSOD error. So, what is Roxio? Roxio GoBack is disk utility developed by Norton which provides recording up to 8 GB of disk changes. If you are not using Roxio GoBack software, then you need to read another method. We will show you how to remove Roxio GoBack software from your computer. We are using Windows 7 x64 and Roxio GoBack Deluxe Edition.
- Hold Windows logo and press R
- Type appwiz.cpl and press Enter
- Select Roxio GoBack Deluxe Edition software
- Right click on Roxio GoBack Deluxe Edition software and choose Uninstall
- Follow the procedure to uninstall Roxio GoBack Deluxe Edition software
- Restart your Windows
- Test your computer
Method 7: Repair a Windows Image using DISM
For this method, we will need to use a tool named DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management). The DISM is command line tool which allows you to mount Windows image file (install.wim) and do image servicing including installing, uninstalling, configuring and Windows update. DISM is a part of Windows ADK (Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit) which you can download on this LINK. The procedure of repairing Windows image is the same for operating systems Windows 7 to Windows 10.
- Open Internet browser (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Edge or other)
- Open website on this LINK to download Windows ADK
- Run Windows ADK
- Choose DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) and click Install
- Click Start menu and type Deployment Image Servicing and Management
- Right click on Deployment Image Servicing and Management and choose Run as Administrator
- Click Yes to accept running DISM as Administrator
- Type DISM /image:D:\ /cleanup-image /revertpendingactions and press Enter
- Restart your Windows
- Test your computer
Method 8: Exclude a folder from scans
The cause of the BSOD problem can be Antivirus, too. To alleviate the problems, you should exclude CodeIntegrity and catroot folders from antivirus scanning. We will show you how to exclude both folders on Windows Defender which is by default integrated into Windows 10. If you are using another antivirus, you should exclude CodeIntegrity and catroot from the scan. If you do not have experience with configuration of antiviruses, please read user manual of antivirus you are using. Terminology is the same, only user experience could be different.
- Click on Start menu and type Windows Defender
- Right click on Windows Defender and choose Run as Administrator
- Click Yes to confirm running Windows Defender as Administrator
- Click Settings at the top right corner
- Click Add and exclusion under Exclusions
- Click Exclude a folder
- Navigate to folder CodeIntegrity on following location C:\Windows\System32\CodeIntegrity
- Click Exclude this folder
- Click Exclude a folder, again
- Navigate to folder catroot on following location C:\Windows\System32\catroot
- Click Exclude this folder
- Check are folders added well
- Test your computer
Method 9: Remove malware
You should be careful when you are browsing the Internet. There are a lot of malware which will try to attack your computer, destroy your operating system, application or your data. BSOD occurs because malware infects your computer and make some damage. The first step you should do is scan your hard disk with Antivirus. If you are home users, you can download freeware antivirus including Avira, Avast, AVG, and others. In case you are using Windows 8 and Window 10, you can use Windows Defender, which is integrated into your operating system. After you remove all malware, you need to restart your Windows. If malware infected some files and your antivirus can not remove malware from file, files will be moved to quarantine or delete from your hard disk. If malware infects Bootcat.cache or ntdll.dll, you should remove that files and copy the same files from another computer. How you will do it? Please read first four methods. To be more secure, we are recommending you to update your operating system, applications and drivers.
Method 10: Restore your operating system from backup
A lot of users are ignoring doing a backup and restore. One of the most important steps in business, and in your home environment is to implement backup and restore strategies. There are few backup tasks you can do including creating a system image, turning on system restore and backup of your data. In the case of failure, you can revert your operating system to the previous state when everything worked without any problems. Few users solved problem with BSOD by doing system image restore.
Method 11: System restore
Sometimes after Windows update or some system changes, computer stops to work. The solution for this to revert your Windows to the previous state, before that update or system changes. One of the steps end users are ignoring is creating a system restore checkpoints. If you are not one of the users who ignored this, we are recommending you to restore your Windows to the previous state using System Restore. If you know when computer worked without problems, revert your Windows to that date. If System Restore is not enabled on your computer, then you need to read Method 9. We are recommending you to enable System Restore, by reading this LINK.
- Hold Windows logo and press Enter
- Type rstrui.exe and press Enter
- Click Choose a different restore point and click Next
- Choose proper checkpoint and click Next
- Click Finish
- Restart your Windows and wait until Windows finished system restore
- Test your computer
Method 12: Disconnect UPS devices
Microsoft said: “If you have an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) connected to your destination computer, disconnect the serial cable before installing the Service Pack. Setup automatically attempts to detect devices that are connected to serial ports, and UPS equipment can cause issues with the detection process. You can leave your computer connected to a UPS for power as long as the UPS itself is plugged in. However, you should make sure that you have enough power for the entire installation, which can take a long time.”
Based on that we are recommending you to disconnect UPS device from your server machine or client machines, install SP1 (method 5) and eliminate BSOD issue. Few users solved issue on their server by using this method.
Method 13: Change CD or DVD
Sometimes, you can not install an operating system from CD or DVD, because you are using scratched CD or DVD. We are recommending you to burn another CD or DVD, or to burn operating system to USB flash drive. If this did not solve the problem, next step is to change cables and CD or DVD disk. If you are using ATA drive (old computers) you should buy ATA CD or DVD drive, and if you are using SATA drive, you should buy SATA CD or DVD drive. Please note that you can not install ATA CD or DVD drive to SATA port, and vice versa.
Method 14: CHKDSK /R
When your HDD is not working good because of file corruption or bad sectors, you should do a check disk. Check disk is a utility which will help you to find bad sectors, and fix them in case there are fixable. You will do it through Command prompt.
- Click on Start menu and type Command prompt
- Right click on Command prompt and choose Run as Administration
- Click Yes to confirm running Command prompt as Administrator
- Type chdksk /r and press Enter. Because you want to check system partition you will need to restart your computer.
- Type Y and press Enter to accept resetting your computer
- Restart your Windows
- Please wait until Windows finished repairing file system on computer. There are 5 stages which should be finished.
- Test your computer
Method 15. Change HDD or SSD
When there is no problem with software, next step will be changing hardware components. HDDs are SSDs are storing our operating systems, drivers, application, and data. When software troubleshooting is not giving a good result, next step should be changing hardware components. You will need to change your HDD or SSD. Be careful when purchasing HDD. There are two different types of HDDs, ATA and SATA. You can not install SATA HDD to ATA port, and vice versa. Also, there are different SATA standards, including SATA I, SATA II, SATA III and SATA 3.1. Different standards provide different transfer rates. If you are using motherboard which supports only SATA I, you do not need to buy HDD SATA III, because HDD SATA III will work as SATA I HDD, because of port limitation. All SSDs are using SATA connectors. Some of HDD’s and SSD’s manufacturer are WD, Seagate, Samsung, Kingston, Adata, and others.
Method 16: Change RAM module
Sometimes because of faulty RAM, Windows’s or application’s instructions can not be stored in RAM address pool, and because of that, you will see BSOD on your monitor. Few users solved their problem by changing RAM module. How will you do it? If you are using more RAM modules, you should try to unplug one by one and test is there a problem with RAM module. Also, if you are planning to purchase another RAM module, you should check which generation of RAM memory is using your motherboard. As always, we are recommending you to check the technical documentation of your motherboard and based on that you can purchase proper RAM module for your computer or notebook. We will show you how to check which RAM module is using notebook HP 2000-2b09WM.
- Open Internet browser (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Edge or other)
- Open HP’s website on this LINK. We will open HP Support site because we are using HP notebook
- Navigate to Memory section. In our example. HP 2000 is using DDR3 RAM, and there are 2 memory slots available, for maximum 8 GB RAM.
- Purchase RAM module
- Install RAM module
- Test your computer
SOLUTION FOR SMARTPHONES
Method 1: Reset Windows Phone
If you are using Windows Phone, you can see PROCESS1 INITIALIZATION FAILED. It is not weird, because Windows Phone is using Windows 8, Windows 8.1 or Windows 10 operating system. You tried to update your Windows Phone, and update process stopped because of BSOD. What should you do?
- Shutdown your phone
- Hold Volume down and Power button
- Finish updating your smartphone
,
The blue screen error «Process1 Initialization Failed STOP 0x0000006B» may appear on Windows 10 or 8-based computers because of a damage in Windows system files.
The Windows 10 error «Process1 Initialization Failed» can usually occur after a power failure or after updating Windows and in rare cases, the error may be due to a virus attack or to a memory (RAM) problem.
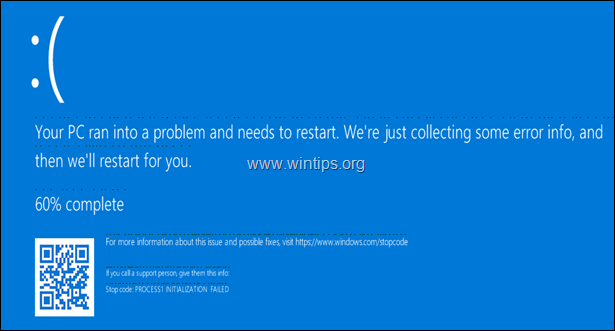
This tutorial contains instructions to resolve the BSOD Error 0x0000006B: «Process1 Initialization Failed» in Windows 10 OS.
How to fix Error 0x0000006B: Process1 Initialization Failed in Windows 10.
Suggestions: Before you continue to the methods below, try the following…
1. Continually press the Power button for 5-6 seconds, to fully power off your PC. Power on it again and try to boot to Windows.
2. Disconnect all the peripheral devices that you don’t need (e.g. USB Drives, SD Cards, USB Wireless Mouse or Keyboard Receiver, USB Wireless Network Card, Printer etc.), and try to boot to Windows.
3. Check the Memory (RAM) for problems.
Requirements: A Windows Installation USB or DVD media.
In order to fix the «Process1 Initialization Failed» problem on Windows 10 you need a Windows 10 USB or DVD Installation Media. If you don’t own a Windows 10 Installation Media, then (from another computer) you can create one, by following the instructions mentioned on these articles:
- How to create a Windows 10 USB boot media.
- How to create a Windows 10 DVD boot media.
Method 1: Perform a Windows Startup Repair.
Method 2. Check Disk and File System for Errors.
Method 3. Delete the «bootcat.cache» file.
Method 4. Rename the NTDLL.DLL File.
Method 5. Replace the NTDLL.DLL from Another Working Computer.
Method 6. Reinstall Windows 10.
Method 1: Perform a Windows Startup Repair
The first method to resolve the «Process1 Initialization Failed (0x0000006B)» error, is to perform a «startup repair» from a Windows Installation Media. TO do that:
1. Boot your computer from the Windows installation media (USB or DVD).
2. At the first setup screen click Next.
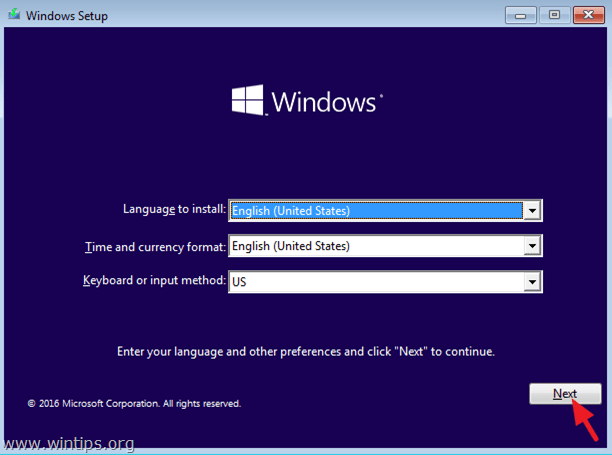
3. At the next screen select Repair your computer.
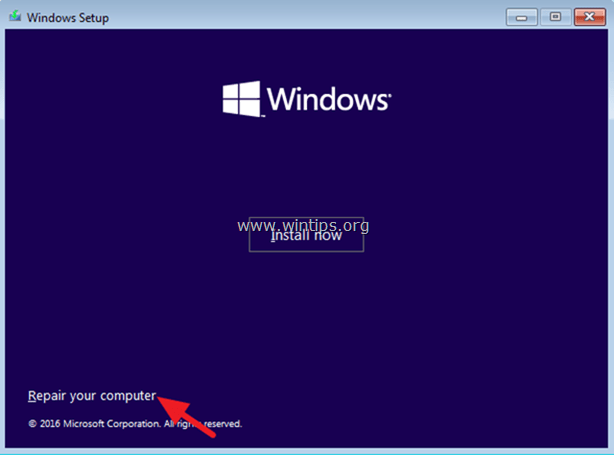
4. Then click Troubleshoot –> Advanced options –> Startup Repair.

5. Wait while Windows diagnosing and fix problems.
6. When the Startup Repair is completed try to boot in Windows normally. If your still receive the «Process1 Initialization Failed » error or if the Startup Repair couldn’t repair your PC, continue to the next method.
Method 2. Check Disk and File System for Errors.
The next method to fix the «Stop 0x0000006B: Process1 Initialization Failed» error, is to repair the hard disk and the file system. To do that:
1. Boot from the Windows installation media.
2. At the Windows Setup screen press SHIFT + F10 to access the Command Prompt. *
* Or choose: NEXT –> REPAIR YOUR COMPUTER -> TROUBLESHOOT -> ADVANCED OPTIONS -> COMMAND PROMPT)
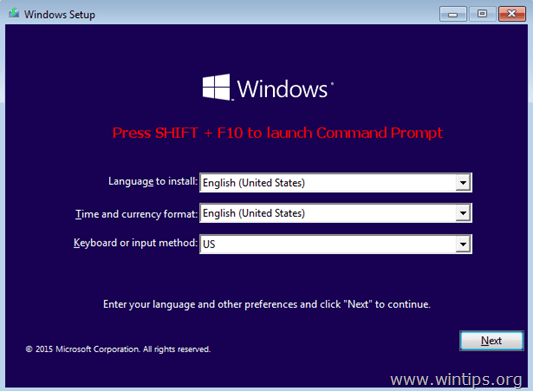
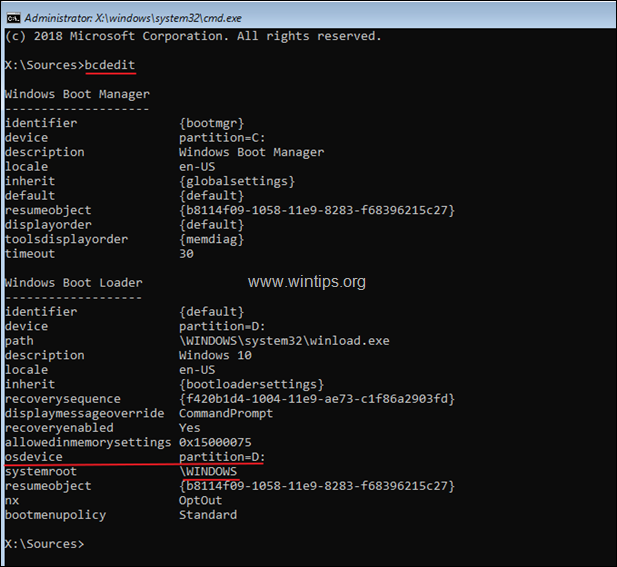
3. In command prompt, give the following command and press Enter, to find out the Windows drive:
- bcdedit
4. Notice the drive letter at «osdevice . . . . . partition=X:» line.
* Info: The «OSDEVICE» is the drive which contains the Windows Operating System (aka: «Windows drive»).
e.g. As you can see at the screenshot below the Windows drive is the drive D:
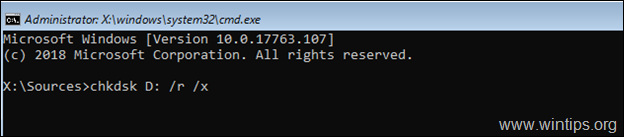
5. Now proceed and check the Windows drive for problems, by typing this command:
- chkdsk X: /r /x
* Note: Replace the letter «X» according to your case. e.g.:
chkdsk D: /r /x
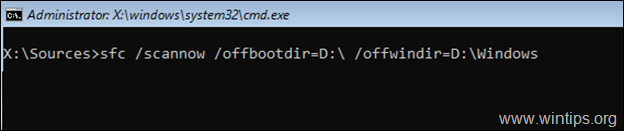
6. When the CHKDSK process is completed, check the Windows System files, by typing this command: *
- sfc /SCANNOW /OFFBOOTDIR=X:\ /OFFWINDIR=X:\windows
* Notes:
1. Replace the letter ‘X‘ according to your case.
sfc /SCANNOW /OFFBOOTDIR=D:\ /OFFWINDIR=D:\windows
2. If after typing the above command, you receive the error «Windows Resource Protection could not start the repair service», the following may be responsible:
a. You ‘re using a Windows Installation Media, that is incompatible with the installed Windows version & architecture (64 or 32 bit).
b. The Windows Installation Media is damaged. At this case, proceed to recreate the Windows Installation Media.
7. When the SFC repair is completed, type exit to close the command prompt window.
8. Remove the Windows Installation media and close all open windows.
8. Reboot your computer and see if Windows can start normally,
Method 3. Delete the «BOOTCAT.CACHE» file.
The «Process1 Initialization Failed» problem, can be caused because the «BOOTCAT.CACHE» file is corrupted. At that case, proceed and delete the «BOOTCAT.CACHE» file, by following the instructions below:
1. Boot from the Windows 10 installation media and launch command prompt.
2. By using the BCDEDIT command (see the Steps 2 & 3 in the above method), find the Windows Drive Letter.
3. Navigate to the Windows drive, by typing: «Drive_Letter:» (without quotes & press Enter). *
* Note: Replace the Drive_Letter according to your case. In this example the Windows are located at drive «D», so we type:
- D:
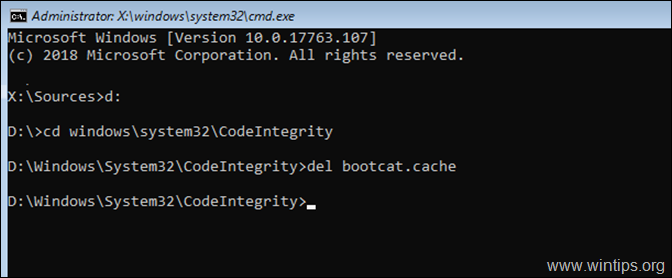
4. Now type the following command and press Enter:
- cd windows\system32\CodeIntegrity
5. Then give the following command and press Enter: *
- del bootcat.cache
* Note: If you receive «The file cannot be found» error, after executing the last command, then the «NTDLL.DLL» file is corrupted. (To fix the problem see the next methods…)
6. Remove the installation media and try to boot to Windows normally.
Method 4. RENAME the NTDLL.DLL File.
The BSOD «Process1 Initialization Failed» commonly appears because the NTDLL.DLL (C:\Windows\System3ntdll.dll) file is damaged. The NTDLL.DLL file is used to create the BOOTCAT.CACHE file which is needed from Windows to boot normally.
To fix the damaged NTDLL.DLL file, proceed as follows:
1. Boot from the Windows 10 installation media and launch command prompt.
2. By using the BCDEDIT command (see the Steps 2 & 3 in the above method), find the Windows Drive Letter.
3. Navigate to the Windows drive, by typing: «Drive_Letter:» (without quotes & press Enter). *
* Note: Replace the Drive_Letter according to your case. In this example the Windows are located at drive «D», so we type:
- D:
4. Now type the following commands in order, to rename the «NTDLL.DLL» file:
- cd windows\system32
- ren ntdll.dll ntdll.BAK
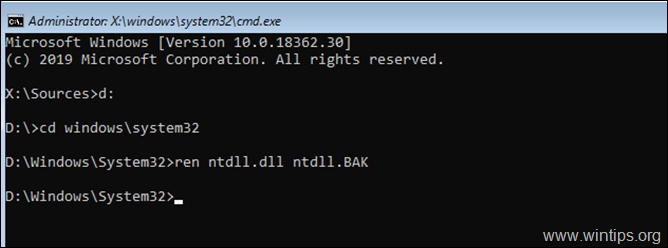
5. Remove the installation media and close all open windows to restart your PC.
6. After restart, Windows will display again the «Process1 Initialization Failed» error screen, but after 2 or 3 automatically restarts, it should start the «Automatic Repair» process.

7. Let Windows fix the issues, and when it’s done, Windows will start normally. *
* Note: If Windows still not start, see the next solution.
Method 5. Replace the NTDLL.DLL from Another Working Computer
Another method, to resolve the blue screen error «0x0000006B: Process1 Initialization Failed» in all Windows versions, is to copy the «NTDLL.DLL» file from another working PC. To do that: *
* Important: In order to apply the steps in this method, you must have access to another working computer, with the same Windows Version and Architecture as the installed Windows version and architecture (e.g. Windows 10 Home 64bit).
1. From another working computer, (with the same Windows version/architecture), copy the «NTDLL.DLL» file from the «C:\Windows\System32\» directory to the root folder of the USB Windows installation media.
2. Boot the PC with the «Process1 Initialization Failed» error, from the Windows Installation media and launch command prompt.
3. At command prompt, list all drive letters (drives), with this command:
- wmic logicaldisk get name
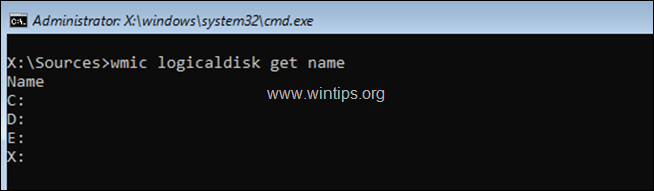
4. Now, by using the «DIR <Drive_Letter>:« command (e.g. «DIR C:», «DIR D:», «DIR E:», etc.), examine the contents of all the listed drives (except the drive X:), and find out which drive contains the ntdll.dll file and which drive contains the Windows folder.
e.g. As you can see in the screenshot below the ‘NTDLL.DLL’ file is located at drive E:\ and the ‘Windows’ folder at drive D:\
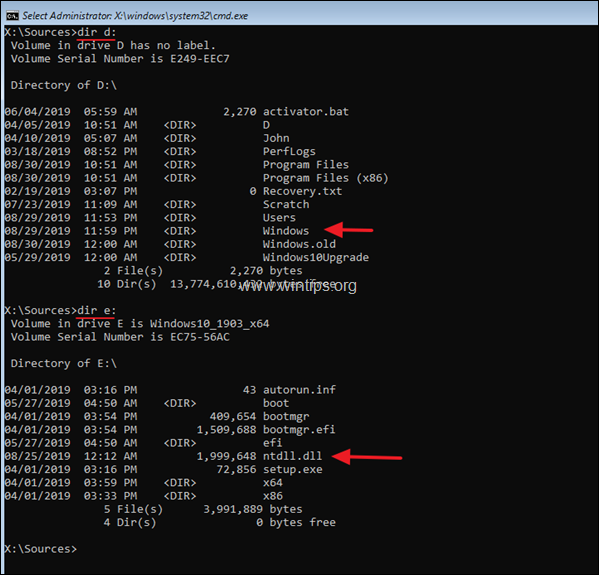
5. Once you locate which drive contains the ‘NTDLL.DLL’ file, type its drive letter and : and press Enter. *
* e.g. At this example the ‘NTDLL.DLL’ file is on drive «E:», so we have to type:
- E:
6. Now give the following command to copy the «NTDLL.DLL» file from the USB to the «\windows\system32» folder of the Windows drive («D:» in this example). *
- copy ntdll.dll D:\windows\system32
* Note: Replace the Windows drive letter according your case.
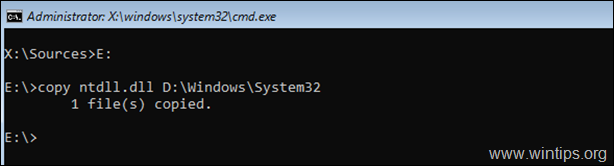
7. When the file is copied, remove the installation media and close all the open windows to restart your PC.
Method 6. Reinstall Windows 10.
If none of the above methods solved your problem, I suggest to backup your files and to RESET your PC to its default state, or to perform a clean Windows 10 installation.
That’s it! Which method worked for you?
Let me know if this guide has helped you by leaving your comment about your experience. Please like and share this guide to help others.
If this article was useful for you, please consider supporting us by making a donation. Even $1 can a make a huge difference for us in our effort to continue to help others while keeping this site free:
- Author
- Recent Posts
Konstantinos is the founder and administrator of Wintips.org. Since 1995 he works and provides IT support as a computer and network expert to individuals and large companies. He is specialized in solving problems related to Windows or other Microsoft products (Windows Server, Office, Microsoft 365, etc.).

» Process1 Initialization Failed » is a bug checking error which occurs when the boot files get corrupted. Most often this error is experienced after a software or hardware installation.
Similar to other BSOD errors, this too can lead to the loss of important files. Whenever these types of blue screen errors appear, your PC usually restarts. Thus, the users will not be able to take any actions since the PC boots frequently.
However, your troubleshooting steps should be easier depending on the cause. Al though this BSOD looks complicated to diagnose, there are general methods and solutions which will help you eradicate this error from your PC permanently.
In this article, let’s look at the 12 Ways to Fix Process1 Initialization Failed in Windows. This post contains all the instructions on how to solve this error.
Let’s get started,
1. Check RAM
A faulty RAM can bring many BSOD errors onto your PC. Hence, there is also a possibility to fix this error by replacing the RAM memory. If you suspect the RAM to be defective, make sure to check them. And be sure to replace the RAM module according to the generation the PC uses. If you aren’t sure which RAM is causing the problem, you can try testing them one by one.
2. Perform CHKDSK
In some instances, your hard drive may fail to work properly if it is with bad sectors. Similar to system files, bad sectors are most likely to cause Process1 initialization failed error. The command CHKDSK scans and corrects bad sectors on the hard drive. Scanning in essence is not just one partition. Each partition in the hard drive must be scanned individually.
To run CHKDSK,
- Insert the installation media
- Restart the PC
- Boot from the installation media
- Choose your language
- Press Shift + F10
- Type and press Enter after the command
CHKDSK x : / f / r (x stands for the respective drive)
3. Perform SFC Scan
System files are essential components for running the operating system. There are various reasons for them to get corrupted. Once it becomes corrupted, no more it can be readable. As a result, you will encounter Process1 initialization failed and other errors. However, damaged system files can be corrected using a tool known as System File Checker (SFC).
To run SFC Scan,
- Insert the installation media
- Restart the PC
- Boot from the installation media
- Choose your language
- Press Shift + F10
- Type and press Enter after the command
» SFC/Scannow »
4. Perform DISM
Image files are nothing but ISO format files that replaces tradional DVD-R or CD-R. If these files get corrupted, it can cause several BSOD errors. Deployment Image Serving and Management (DISM) is a tool used to fix damaged image files. Besides that, it can be used to mount images as well. This tool can help you diagnose Process1 initialization failed error.
To perform DISM,
- Insert the installation media
- Restart the PC
- Boot from the installation media
- Choose your language
- Press Shift + F10
- Type and press Enter after the command
dism/online/cleanup-image/scanhealth
dism/online/cleanup-image/restorehealth
After each command press Enter
7. Again type,
dism/online/cleanup- image/restorehealth/source:wim:X:sourcesinstall.wim:1/Limitaccess
( X refers to the drive mounted )
After each command press Enter
5. Update Windows
Windows require updates for its continuous improvements. They provide new features as well as various fixes for the PC related problems. If one of those updates goes missing, your system is most likely to get Process1 initialization failed error. Therefore, it is essential to download all the missing updates.
Your computer will most often search for updates automatically when its connected to the internet. Otherwise, you need to follow the manual method.
6. Uninstall Antivirus
Not all the Antivirus programs are trustworthy. Some third party Antivirus programs are known to be incompatible with the system. The consequence of this is the Process1 initialization failed error. Therefore, depending on the priority uninstall or disable the Antivirus program.
If that fixes the Process1 initialization failed error, try to use an Antivirus program different from that you previously used.
7. Disable Secure Boot
Secure boot is a process which makes sure that your PC only boots up using authorized softwares. This mechanism prevents virus and other forms of dangerous attacks.
Sometimes due to hardware misconfigurations and other reasons, the functioning of secure boot can be hindered. As a result, you may end up getting Process1 initialization failed error. So you can temporarily get rid of this error by disabling secure boot in the BIOS.
8. Perform Startup Repair
Startup repair is a tool which allows you to fix most boot related problems. Since Process1 initialization failed is also a startup error this tool can be used to repair it. However, to use this tool successfully you will be needing a windows installation media.
To perform Startup repair,
- Insert the installation media
- Restart the PC
- Boot from the installation media
- Choose your language
- Select troubleshoot
- Select Automatic Repair
This process will repair your operating system.
9. Update Drivers
There are also chances for the new hardware devices connected to your computer to cause this problem. The reason of the problem may be the incompatible drivers of the newly connected device. Most often this happens if the driver installed is not from the official manufacturer. So to prevent this error, you need to update all the existing drivers.
10. Perform System Restore
Recent changes in the system can also trigger Process1 initialization failed error. Especially, if the windows registry gets corrupted. Such changes can be reverted easily using the system restore feature. System restore reverts your operating system back to a point where there was no error. In fact this method has proved to be effective even against some critical issues. For that reason, it is worth trying it in these types of failures.
To Restore System,
- Insert the installation media
- Restart the PC
- Boot from the installation media
- Choose your language
- Select troubleshoot
- Select » System Restore »
11. Delete BOOTCAT.CACHE File
Several users of Windows 7 with outdated service packs have reported to experience Process1 initialization failed error. Bootcat.cache file is usually located in the code integrity folder. There exists possibility for this error to occur if the Bootcat.cache file gets corrupted. Thus, you need to find a way to delete this file manually.
To delete Bootcat.cache file,
- Insert the installation media
- Restart the PC
- Boot from the installation media
- Choose your language
- Press Shift + F10
- Type » Diskpart »
- Type » Exit »
- Type » C » ( C refers to the system partition )
- Type » cd windows\system32\codeintegrity »
- Type » del bootcat.cache »
Type and Press Enter after each command.
12. Reinstall Windows
- Insert the installation media
- Restart the PC
- Boot from the installation media
- Choose your language
- Press Shift + F10
- Type » Diskpart »
- Type » Exit »
- Type » C » ( C refers to the system partition )
- Type » cd windows\system32\codeintegrity »
- Type » del bootcat.cache »
Type and Press Enter after each command.
If you still cannot get rid of Process1 initialization failed error, then I would suggest you to perform a clean installation of windows. Once the installation procedure is over, you will be getting a new operating system without any errors. However, for this process of windows installation you will be requiring an installation media with the setup of current operating system.
Be aware that reinstalling windows will make you loose files. Hence, before you start make sure that a back up is made.

























