In this article, we will learn the steps on How to Setup L2TP/IPsec VPN with a Pre-Shared key on Windows Server 2019.
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a secure network tunnel that allows you to connect to your private network from internet locations. So, you can access and use your internal resources based on assign permission.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP):
L2TP is the industry standard when setting up secure VPN tunnels. L2TP supports either computer certificates or a Pre-shared key as the authentication method for IPsec. L2TP/IPsec VPN connections provide data confidentiality, data integrity, and data authentication.
Understanding the SSTP Test Lab:
- WS2K19-DC01: Domain Controller and DNS.
- WS2K19-VPN01: Member Server.
- WS10-CLI01: Windows 10 Client Machine.
Step:1 Install Remote Access Server role on Windows Server 2019:
1. The first step is the installation of the Remote Access Server role. Open Server Manager Console and start role and feature installation wizard. Select the Remote Access Server role.
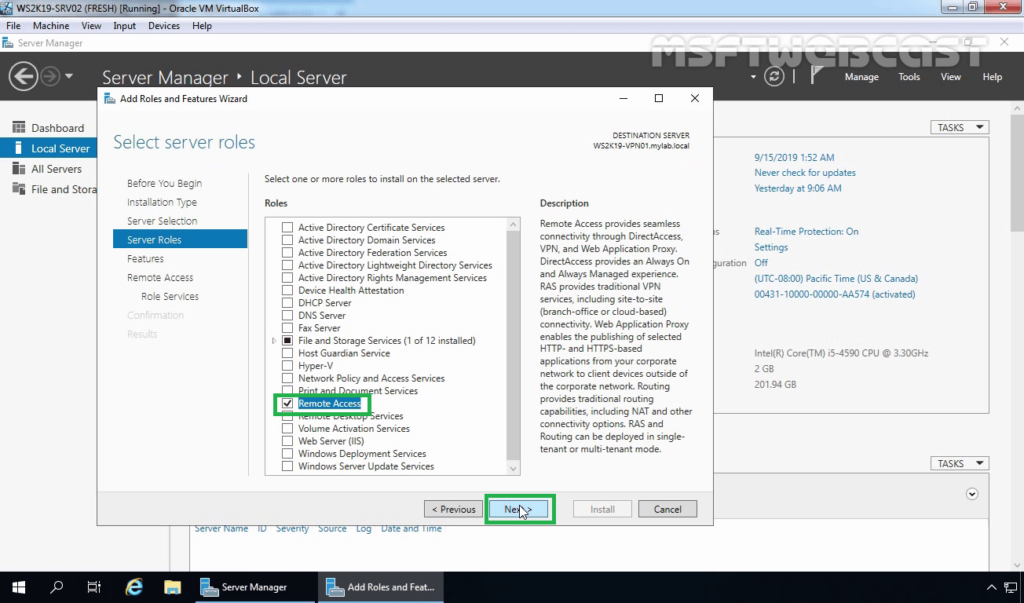
2. On select role services, select DirectAccess and VPN (RAS) role service. Click Next and finish the installation.
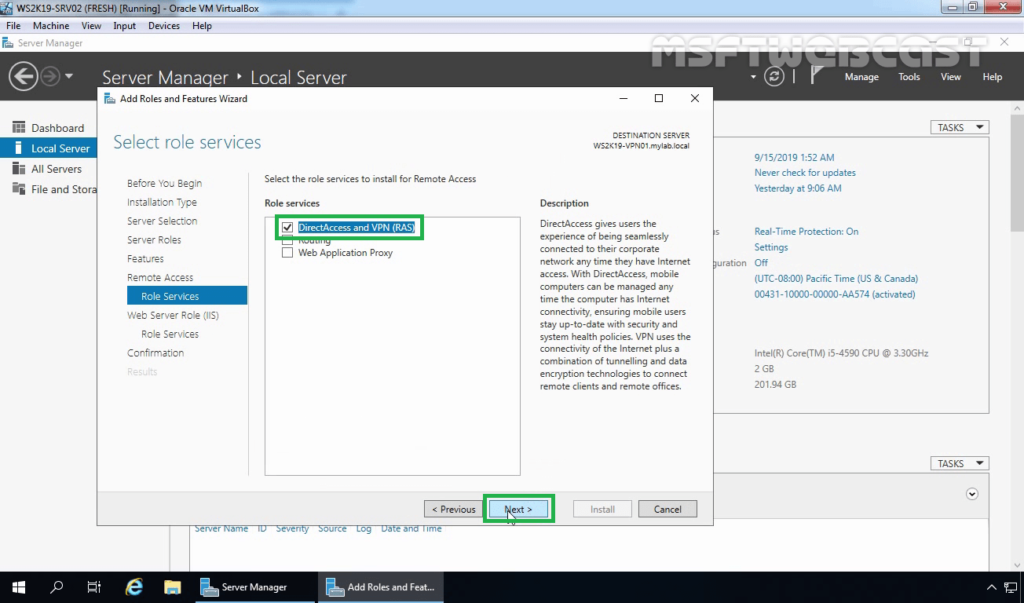
3. When the installation finished, click on close.
Step:2 Configure L2TP/IPsec VPN on Windows Server 2019:
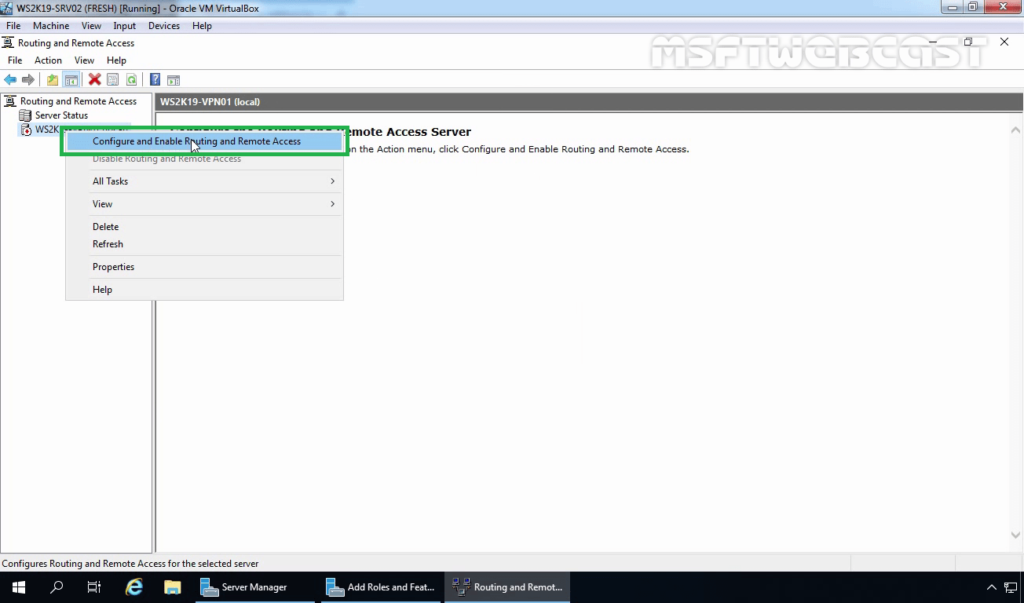
4. On Member Server, Open Server Manager. Click on Tools and select Routing and Remote Access Console.
5. Right-click on the Server name and select Configure and Enable Routing and Remote Access.
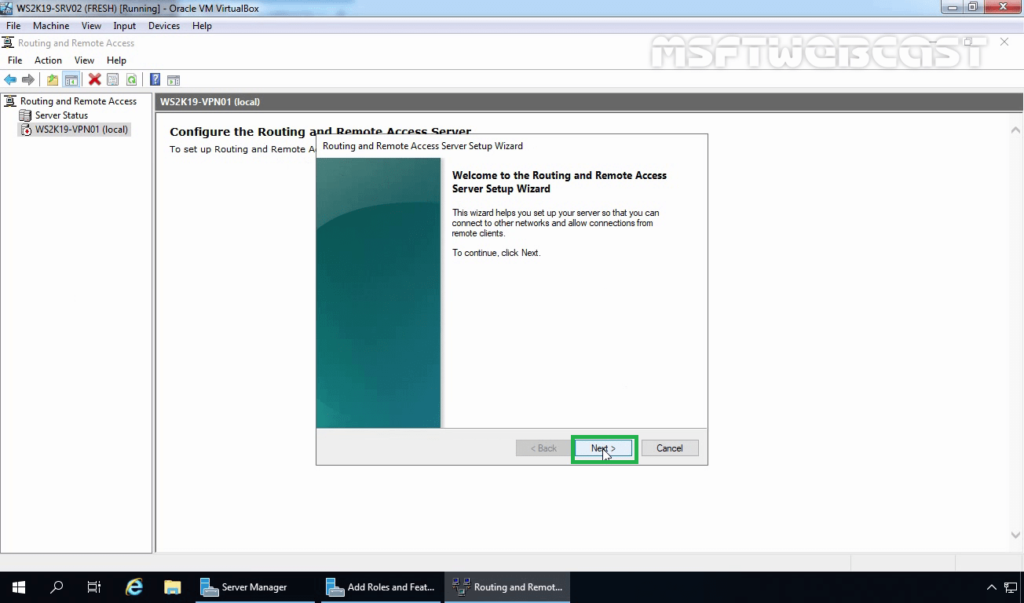
6. On Welcome screen, click Next.
7. On the Configuration page, select the Custom configuration radio button. Click Next.
8. On select the service page, select VPN Access. Click Next.
9. After clicking on the Finish, it will ask you to start the service. Click on Start service.
10. Now you will see a green up arrow beside your server name.
Step:3 Configure Pre-Shared Key for IPsec Authentication.
To configure the Pre-shared Key for L2TP/IPsec VPN, we need to set up specific settings in the VPN server’s properties section.
11. Right-click on the server name and click on Properties.
12. On the Security tab, select the checkbox Allow Custom IPsec Policy for L2TP/IKEv2 Connection. Specify a strong Pre-Shared Key for L2TP/IPsec VPN connection.
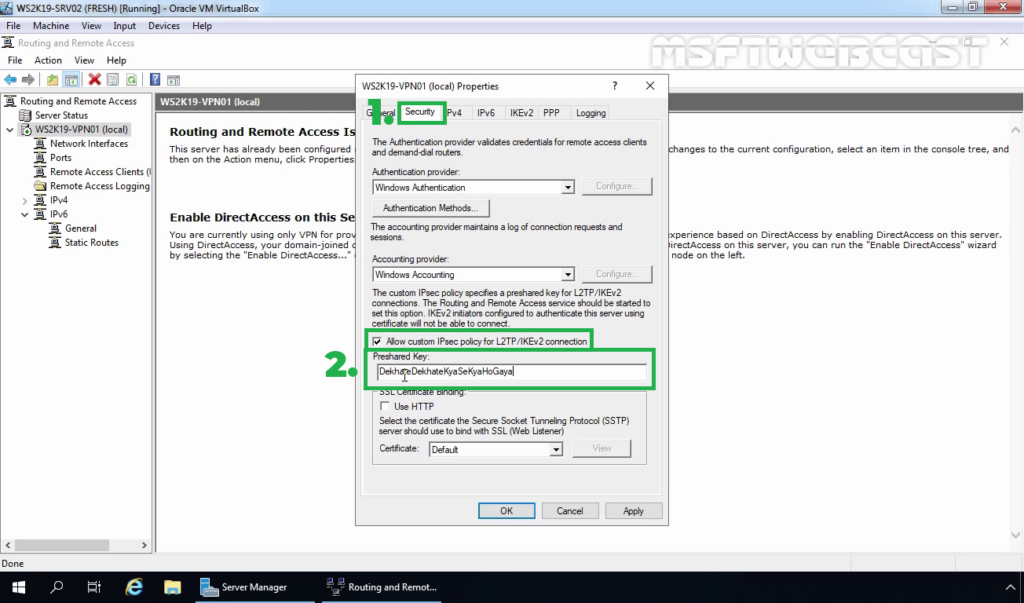
13. Click on IPv4 Tab. Select the Static Address Pool radio button. Click on Add button.
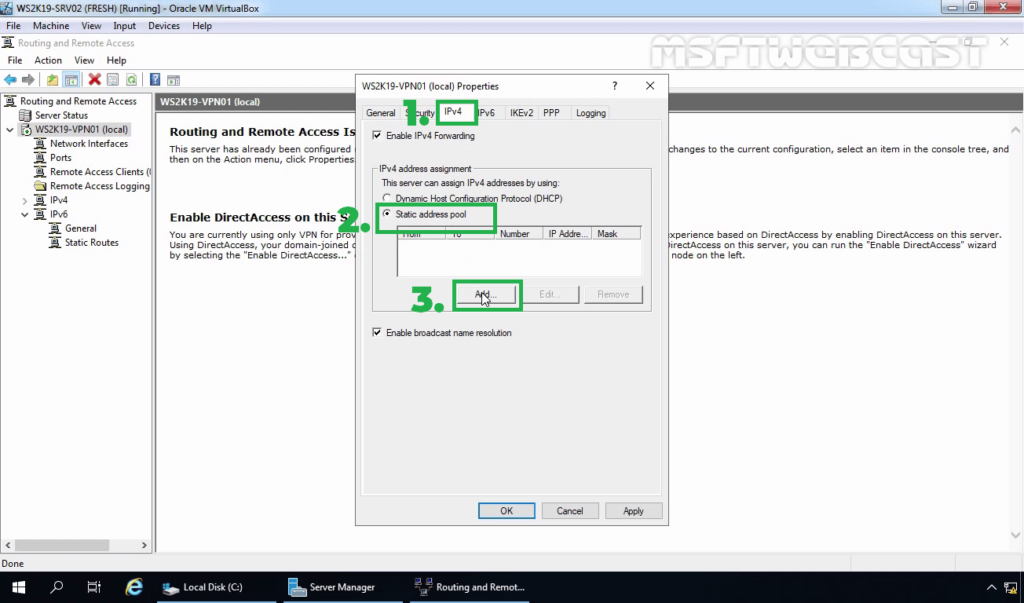
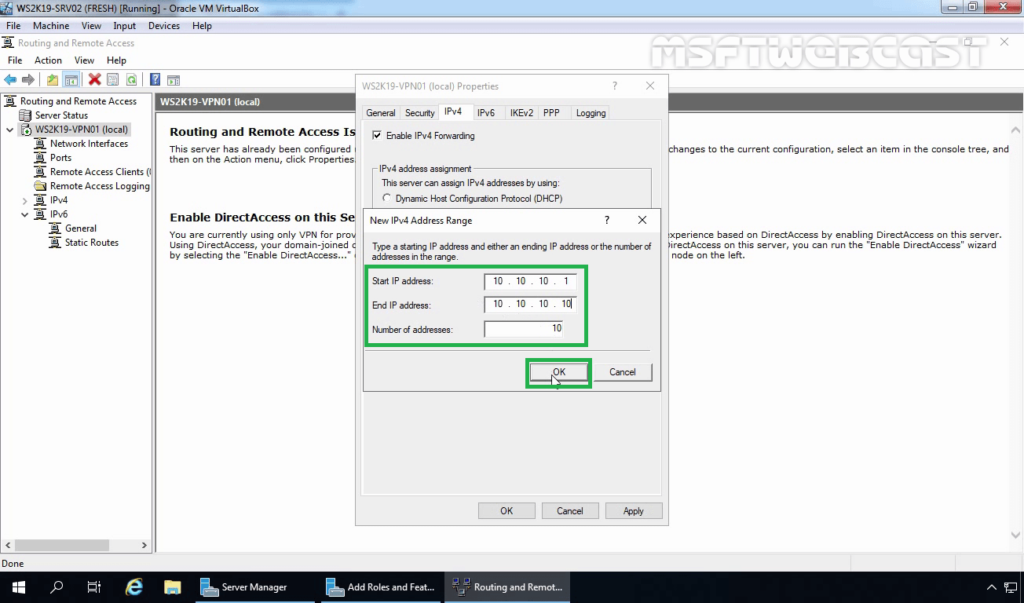
14. Specify the IP address range. Click on OK.
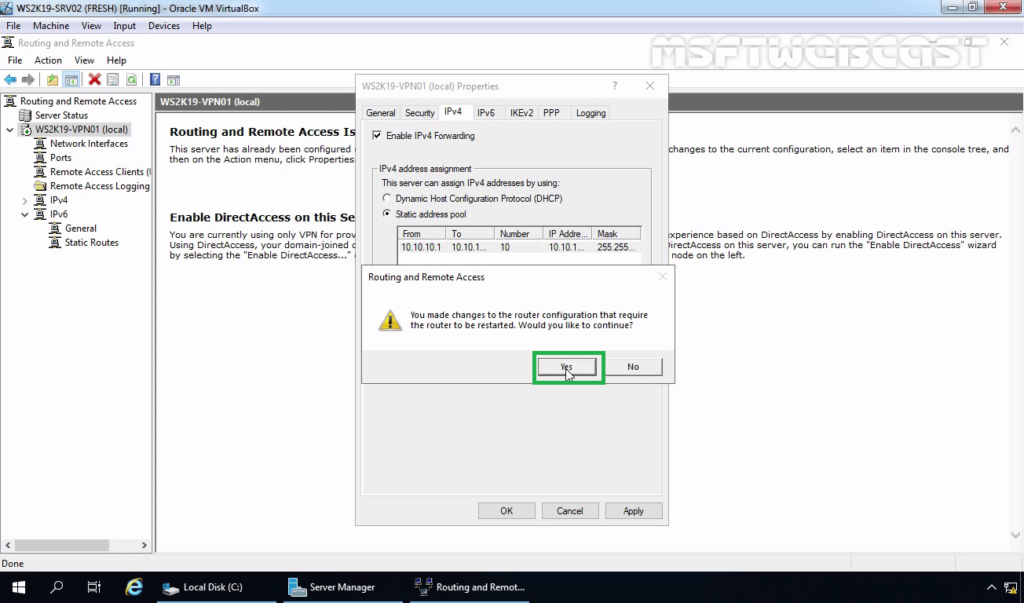
15. Click on Apply to save the changes to the VPN server. It will ask to restart the Routing and Remote Access service. Click on yes to do so.
Step:4 Create AD User and allow dial-in access:
16. On Domain Controller, Open Active Directory Users and Computers snap-ins. Create AD users name Test User1 and Test User2.
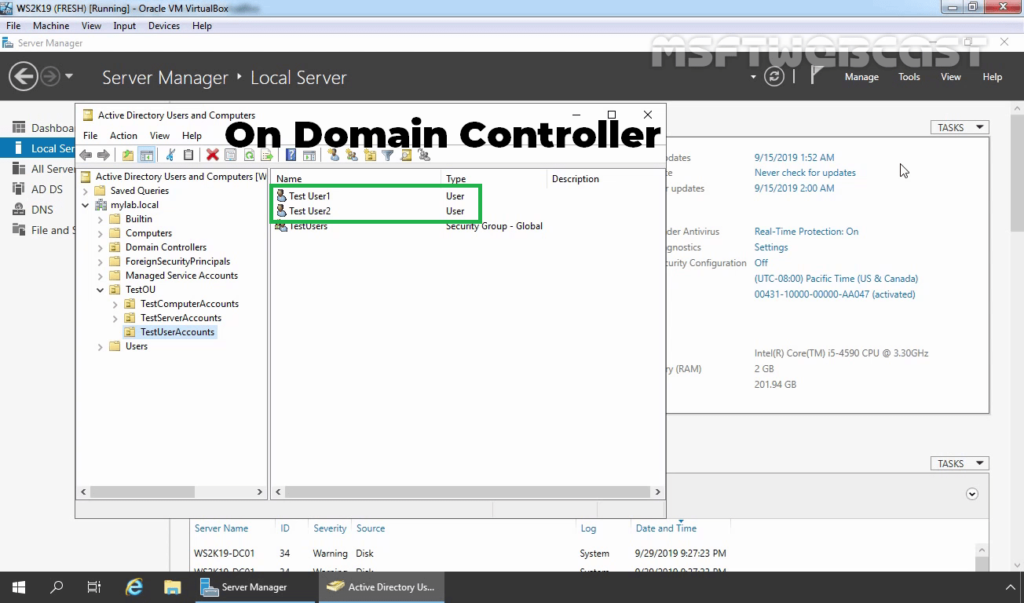
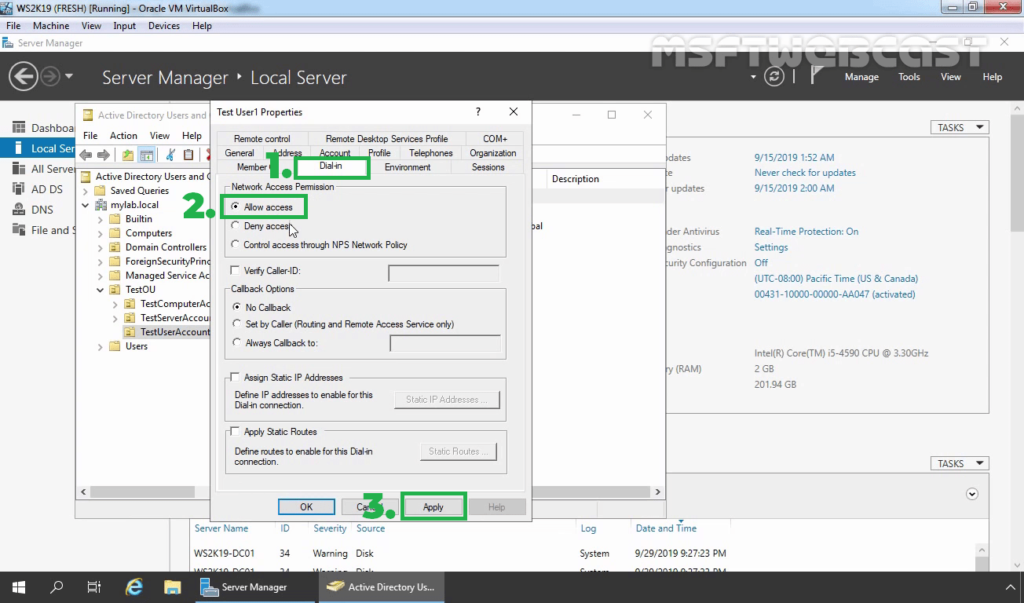
17. Enable dial-in access for selected VPN users by opening the user properties and selecting Allow access on the tab Dial-in.
Note: If you want, you can configure Network Policy Server to allow VPN users to connect to the VPN server running on Windows Server 2019.
Step:5 Setup a VPN Connection for L2TP/IPsec VPN:
On Windows 10 client machine, we need to create a new VPN connection.
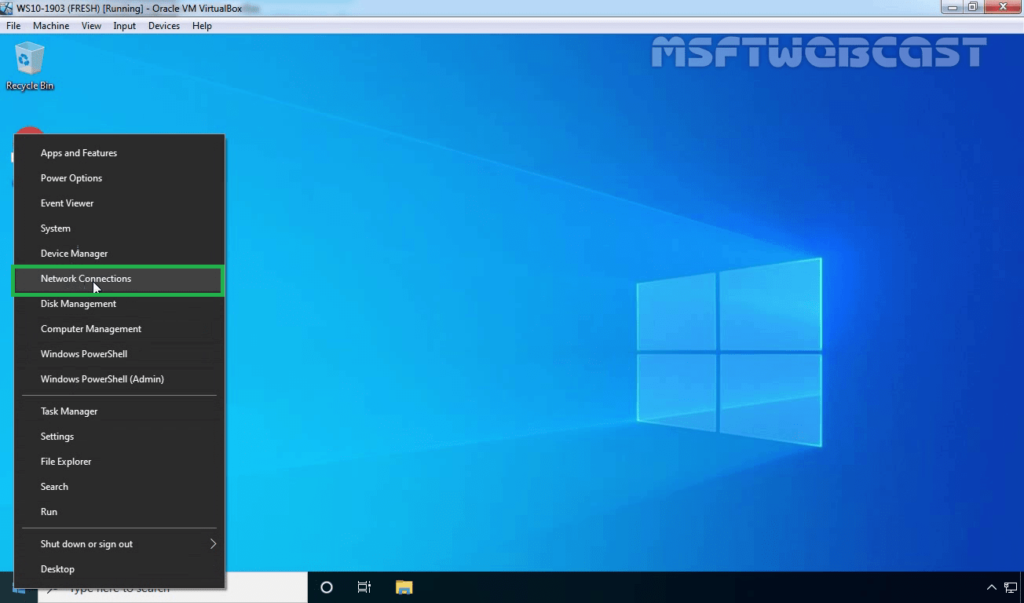
18. Right-click on the Start button and select Network Connections.
19. On left-pane, click on VPN.
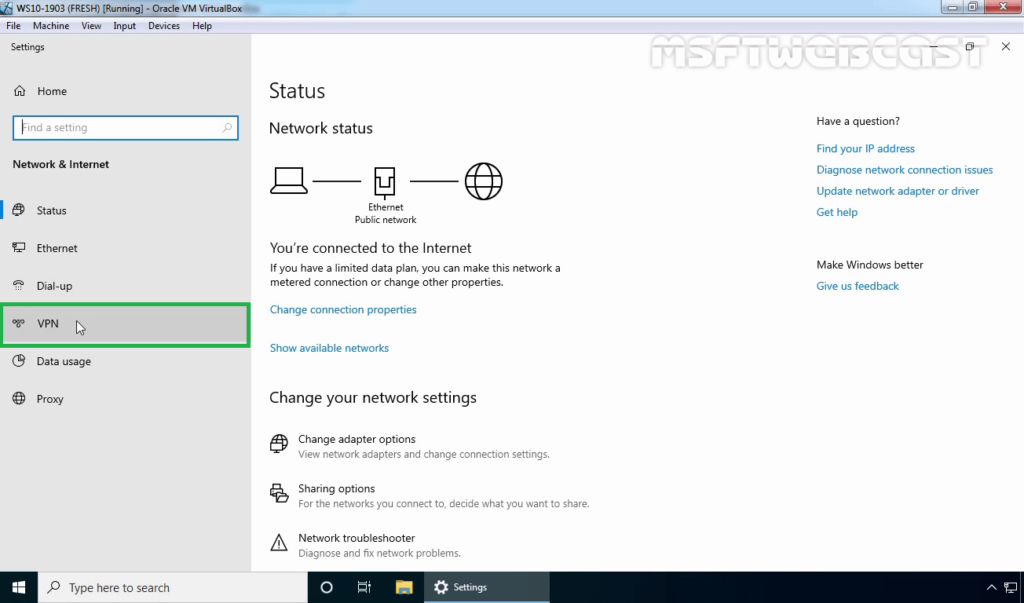
20. Click on add a new VPN connection.
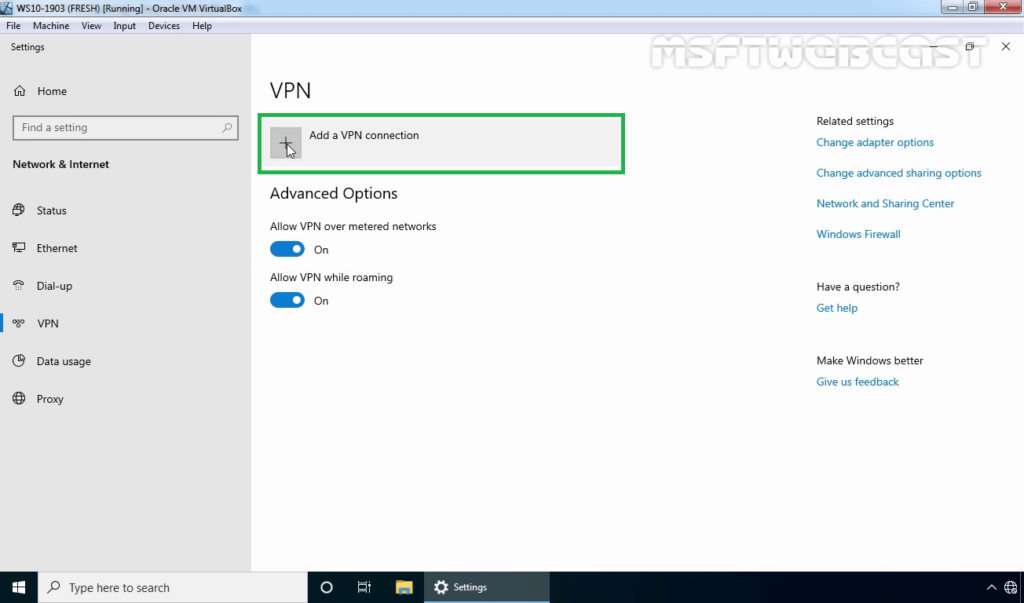
21. Specify the required information for the VPN connection.
- VPN Provider: Windows (Built-in)
- Connection Name: Name of your choice
- Server Name or IP Address: Public IP Address of VPN server
- VPN Type: L2TP/IPsec with Pre-shared key
- Pre-Shared Key: Specify the key which we had assign on VPN Server.
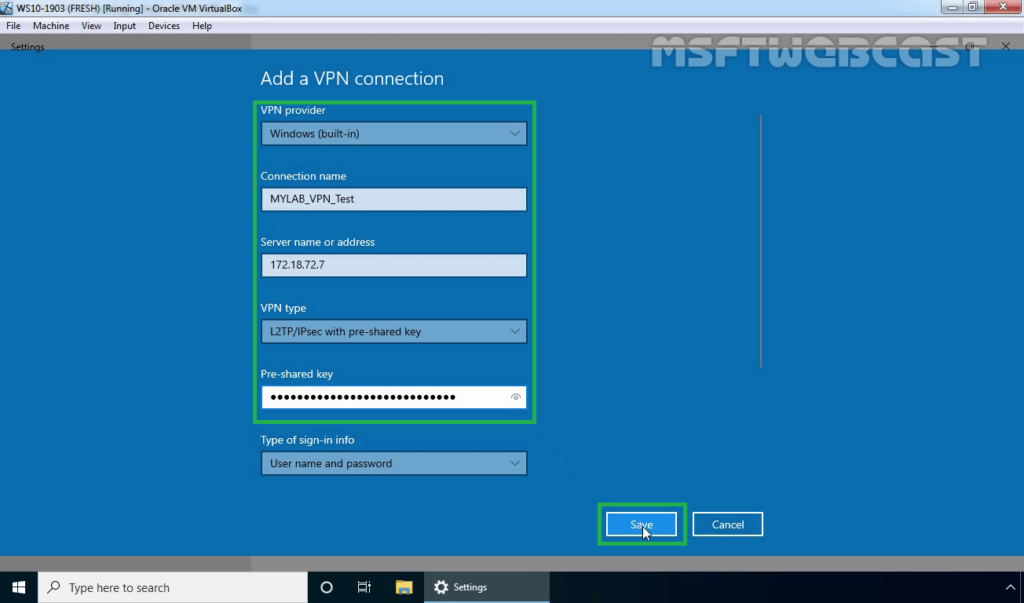
22. Click on Save.
Step:6 Test L2TP/IPsec VPN Connection:
23. Click on VPN connection and select Connect.
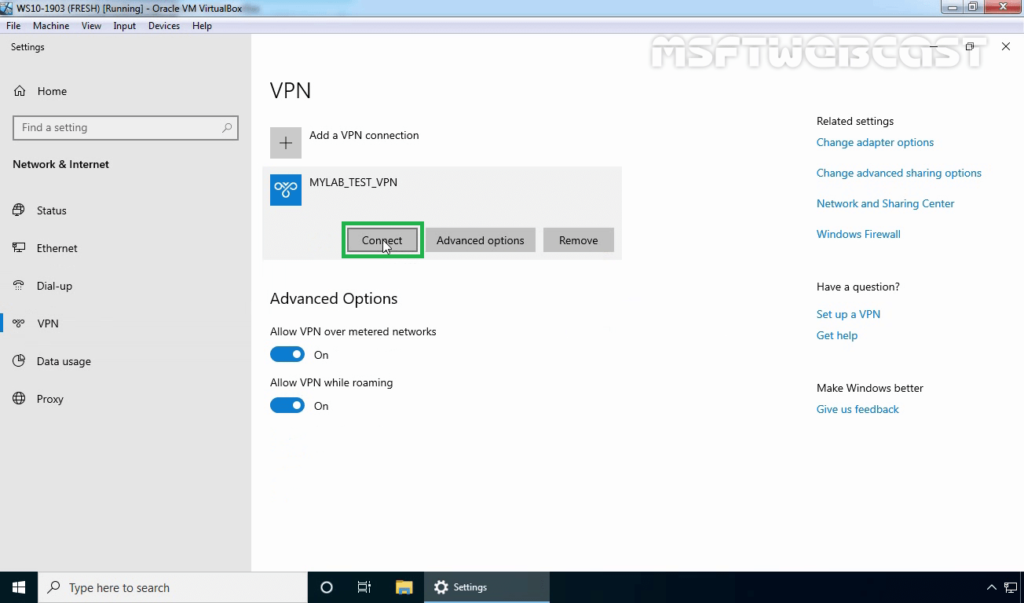
24. Specify a username and password to connect the VPN server. Click OK to connect.
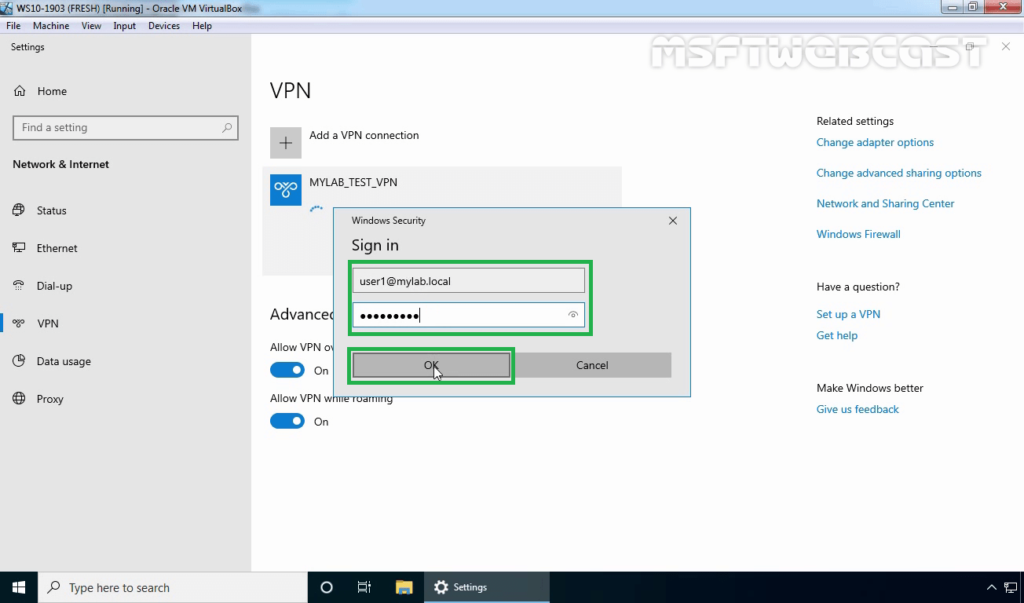
25. Verify the VPN connection is successfully connected with the VPN server using the L2TP/IPsec protocol.
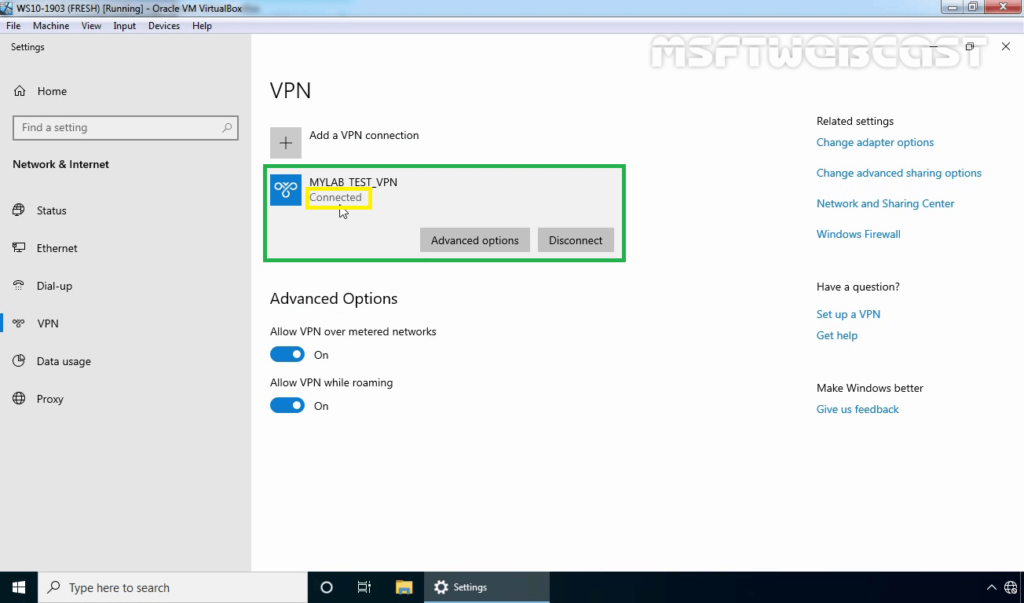
Step:7 Monitor L2TP/IPsec VPN Connection:
On Windows 10 Client Machine:
26. Press Windows Key and R key together. At Run menu type ncpa.cpl and press enter to open Network Connection console.
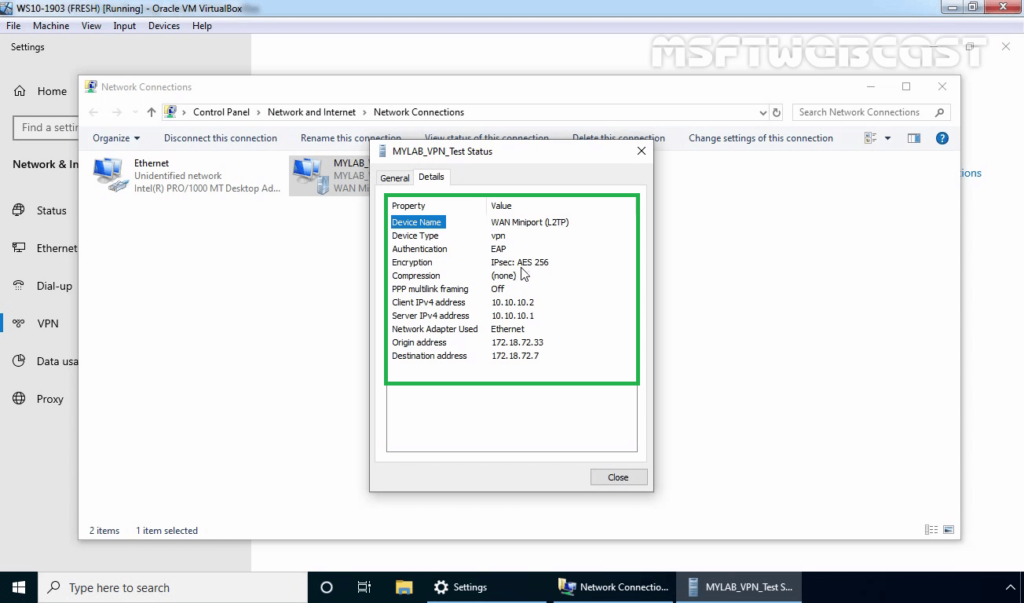
27. Right-click on VPN connection and click on the Status button.
28. Click on details to see information about VPN connection like Authentication Method, Encryption Mod, etc.
On VPN Server:
29. Press Windows Key and R key together. At Run menu type wf.msc and press enter to open Windows Defender Firewall and Advanced Security console.
30. Expand Monitoring, Expand Security Associations. Expand and Click on Main Mode.
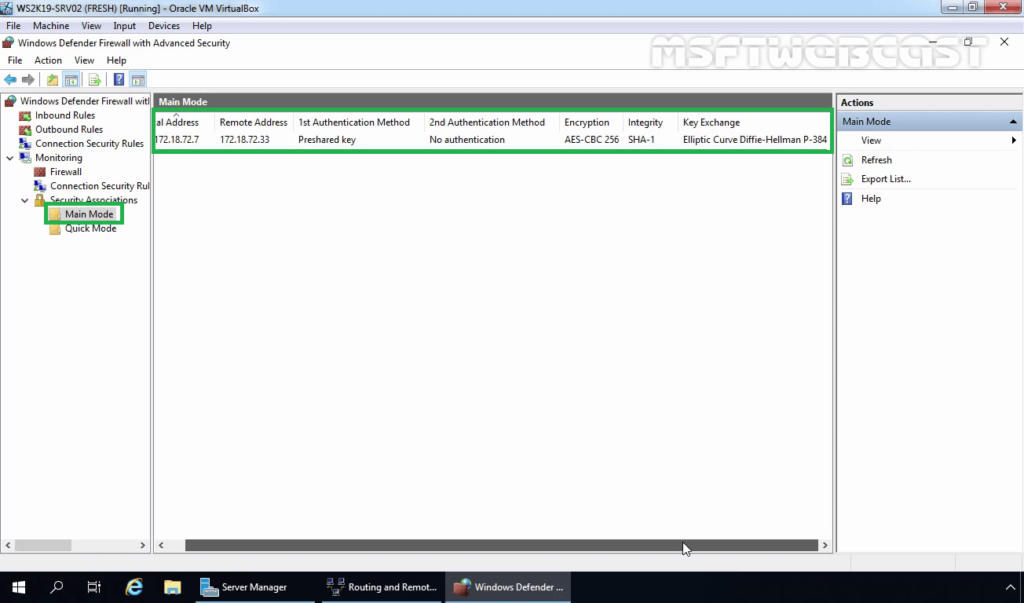
You can verify the authentication method and Encryption Standard for IPsec main mode connection.
- Authentication Method: Pre-Shared Key.
- Encryption Standard: AES-CBC 256 Bit
- Integrity Algorithm: SHA-1
- Key-Exchange Mode: Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman P-384.
31. Also, check Quick Mode Tunnel Information.
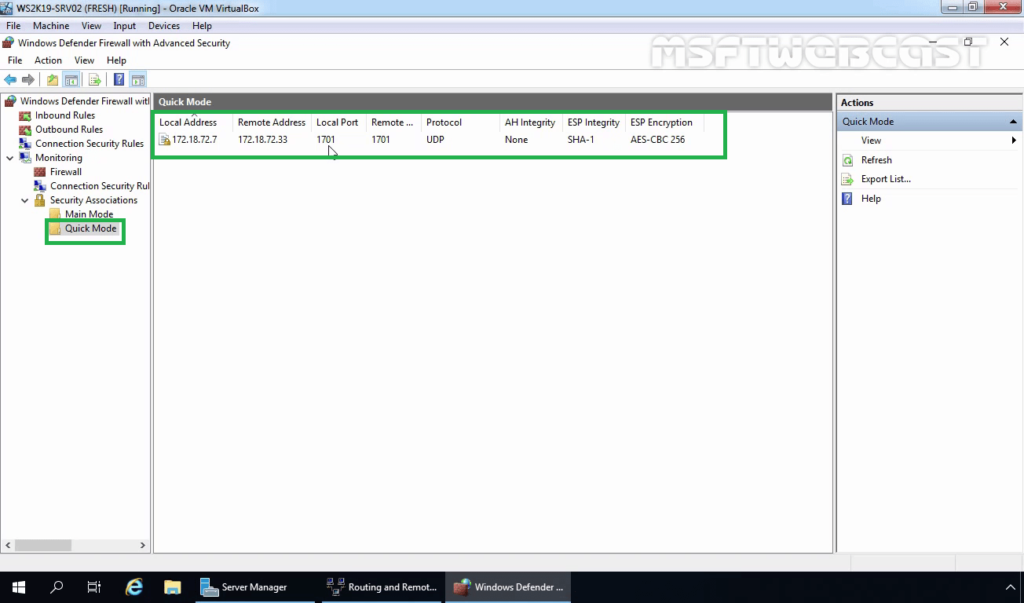
- Local Address: Local IP Address of VPN Server.
- Remote Address: VPN Client IP Address.
- Local Port: UDP 1701
- Remote Port: UDP 1701
- ESP Integrity Mode: SHA-1
- ESP Encryption Mode: AES -CBC 256 Bit
In this post, we have learned the steps to setup L2TP/IPsec VPN with a Pre-shared key on Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10.
Thank you for reading. Have a nice day.
Post Views: 5,572
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is used to securely create a tunnel for data between your local computer to a remote server. On Windows Server 2019, you can configure a VPN to provide network access to connected clients and allow connected devices to communicate securely.
This guide explains how to set up a fresh Windows Server 2019 as an L2TP over IPSec, or a PPTP VPN, using the routing and remote access feature. Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) with IPSec offers robust encryption for connections to the server. On the other hand, the Point to Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is simple to deploy but not as secure.
To set up the VPN server, we shall use the built-in Routing and Remote access feature, which offers a graphic interface to configure remote networking features such as Dial-up, LAN routing, NAT, and VPN.
Requirements
- Deploy a Windows Server 2019 Instance on Vultr
- Remotely connect to the server and log in as an Administrator
Create a New VPN User
For the VPN service to work well, it must authenticate with a valid user account to the server. So, you need to create a new user on the server.
Click Tools under server manager and select Computer Management from the drop-down list to create a new user.
Once the computer management window pops up, expand Local Users and Groups from the left pane and right-click Users to select New User on the sub-menu.
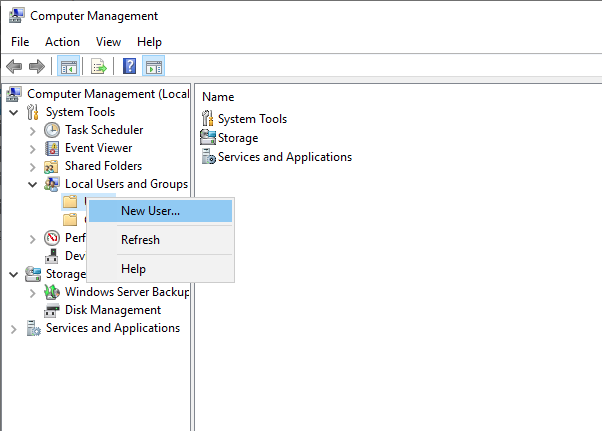
Under the New User dialog box, enter a username, full name, and password for the VPN user, then click create and close the window.
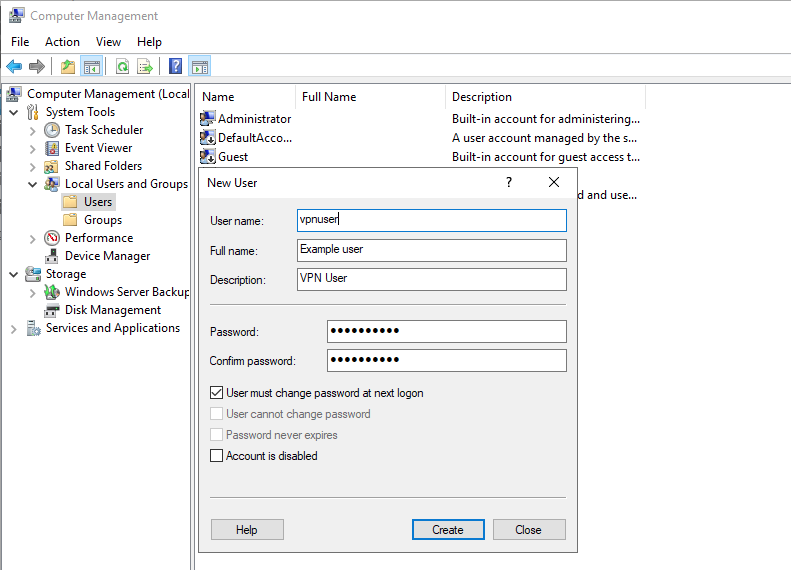
The new user will now be listed on the list of active server users, right-click on the new user and select properties.
Under the user properties window, navigate to the Dial-in tab and click Allow access under Network Access Permission. Click OK for changes to take effect.
Install the Routing and Remote Access Features
Procedure 1: Through Server Manager
From the Windows start menu, open Server Manager, click Manage, then select Add Roles and Features from the drop-down list.
From the open window, click next and select Role-based or feature based installation, then select your server from the pool. Select Remote Access, Remote Access Administration from the list of server roles.
Next, select DirectAccess and VPN (RAS) and Routing from the features list, then click to Install IIS, which is required for remote access to work well.
Procedure 2: Using Windows PowerShell
You can also install Remote Access from Windows Powershell.
From the Windows start menu, open an Administrative Powershell, then install Remote access by pasting the following code to the console.
Install-WindowsFeature RemoteAccess
Install-WindowsFeature DirectAccess-VPN -IncludeManagementTools
Install-WindowsFeature Routing -IncludeManagementTools
Your output should be similar to:
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Install-WindowsFeature RemoteAccess
>> Install-WindowsFeature DirectAccess-VPN -IncludeManagementTools
>> Install-WindowsFeature Routing -IncludeManagementTools
Success Restart Needed Exit Code Feature Result
------- -------------- --------- --------------
True No Success {Remote Access}
True No Success {RAS Connection Manager Administration Kit...
True No Success {Routing}Configure Routing and Remote Access
Open Server Manager and click Tools on the top toolbar. From the drop-down list, select Remote Access Management.
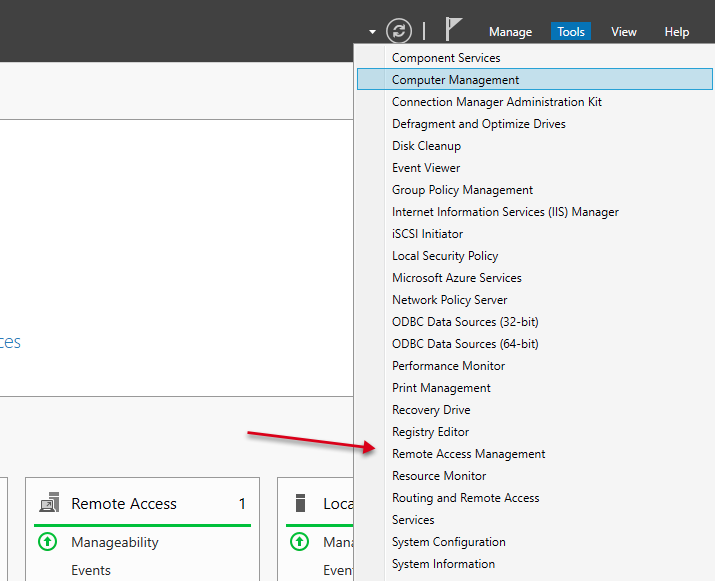
In the open Routing and Remote Access window, right click on your server name just below Server status, then select Configure and Enable Routing and Remote Access from the drop-down menu.
Now, select Custom configuration to configure remote access manually.
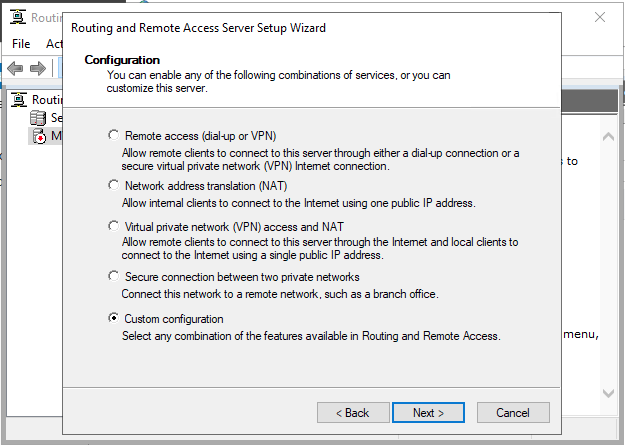
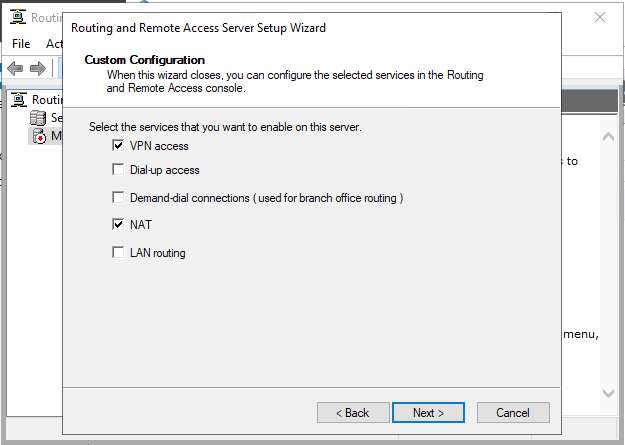
Select VPN Access and NAT as services you want to enable on your server, click next to finish the configuration, and start the service.
Setup a PPTP VPN
Now that Remote Access is running, you can set up your PPTP VPN. To get started, you must assign connected clients** static IP Addresses to avoid possible connection issues. To do this, right-click on your server under the Routing and Remote Access window and select Properties from the drop-down list.
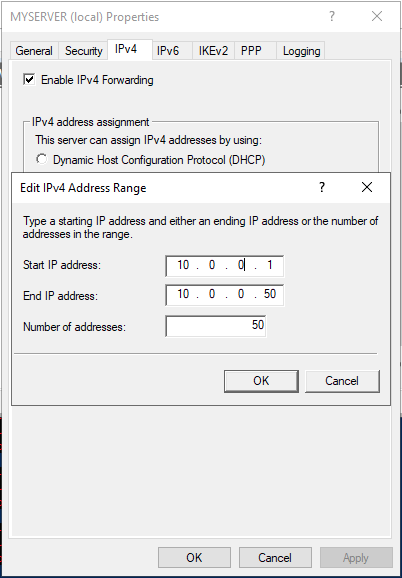
Click IPV4 in the Open Window, then select Static address pool. Now, click Add to craft a new IP Address range from the open pop-up window. In this guide, we use the range 10.0.0.1 to 10.0.0.50, and the server will automatically calculate the number of available addresses.
Click OK to save your static IP Address configuration. You will be prompted to restart Routing and Remote Access for changes to apply; simply click OK.
Configure NAT and enable PPTP
We need to configure Network Address Translation (NAT) for connected clients to use the Internet. On the left pane of the same routing and remote access window, expand the IPv4 options under your server. Right-click on NAT and select New Interface.
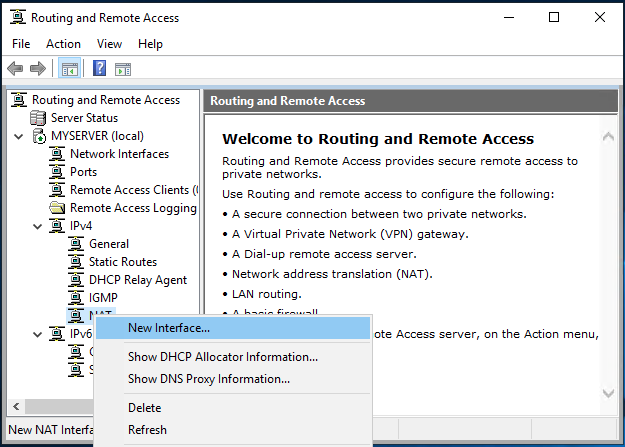
Under the open dialog window, select Public interface and enable NAT on the interface.
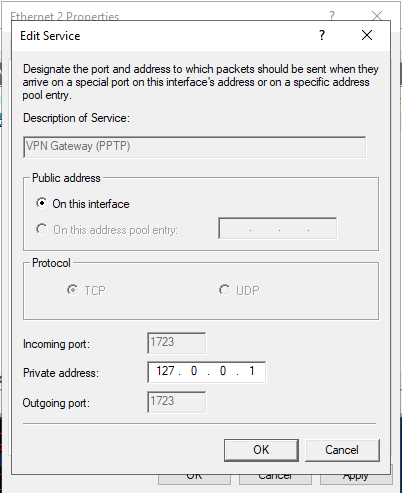
Next, navigate to Services and Ports and click VPN Gateway (PPTP) from the drop-down list.
Click Edit to set a Private address for the VPN service, change the current address 0.0.0.0 to 127.0.0.1, and click OK to save.
Finally, click OK to save all changes, then right-click on your server from the left pane and click Restart under the All Tasks sub-menu.
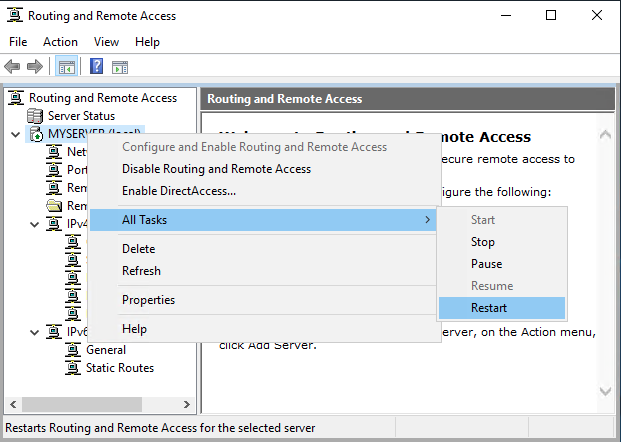
This will restart routing and remote access services making your server ready for incoming VPN connections.
Configure Windows Firewall to accept Incoming PPTP VPN Connections
Click Tools from the Windows server manager and select Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security from the drop-down list.
Under the open Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security window, select Inbound Rules on the left pane, then click New Rule on the right pane.
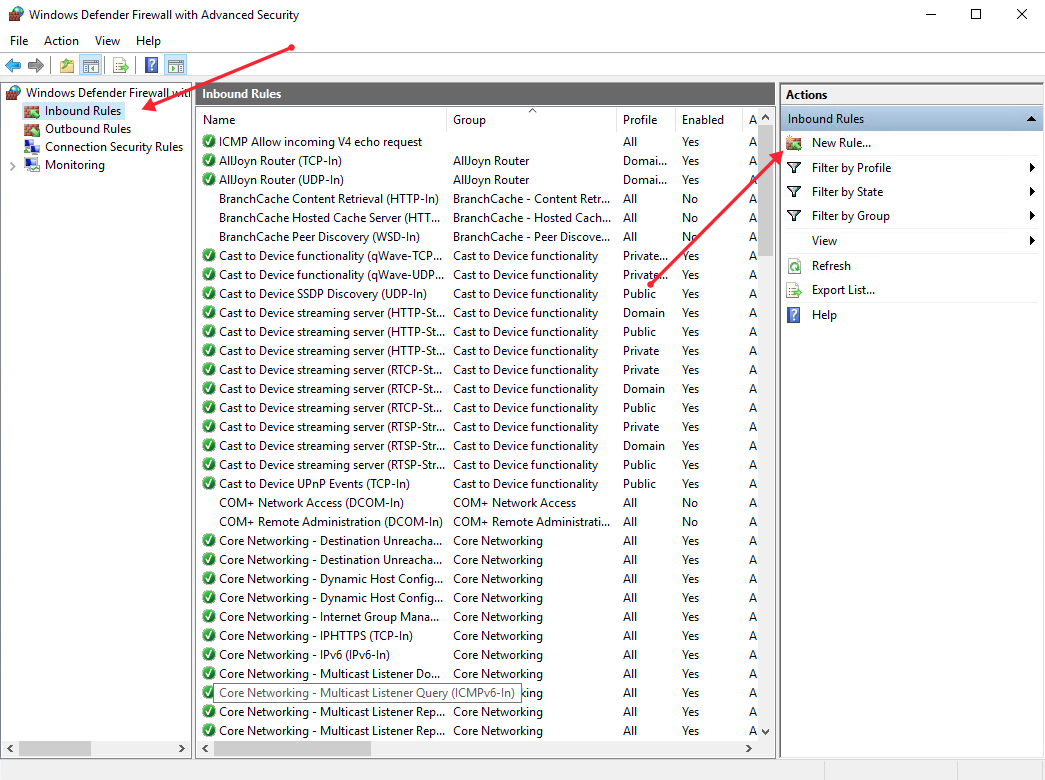
In the open new Inbound rule wizard, click Predefined and select Routing and Remote Access from the list.
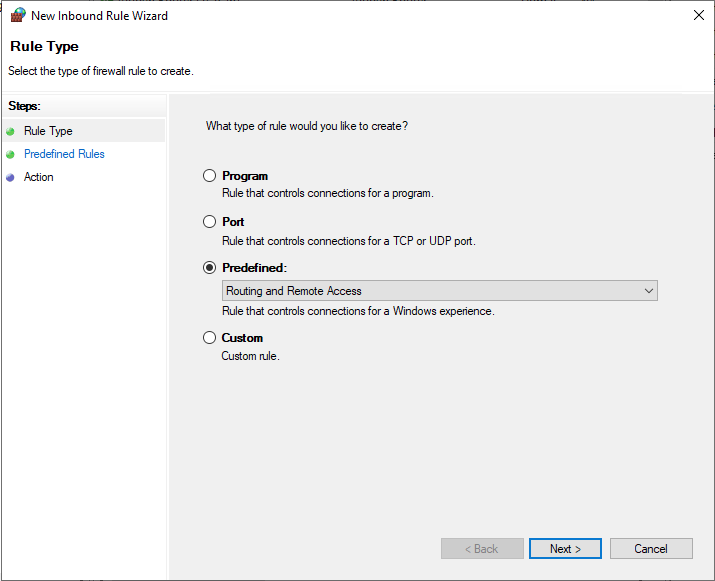
Under predefined rules, choose Routing and Remote Access (PPTP-In), click next to allow the connection, then finish for the new Firewall rule to be applied and test your new PPTP VPN server.
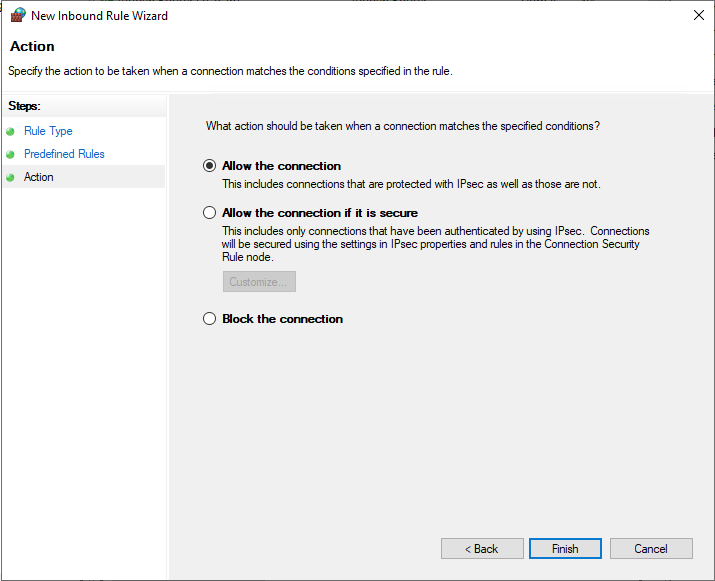
Test your PPTP VPN
Using your personal computer (PC) or Smartphone, go to Networks, Add a new VPN and select PPTP as the VPN type. Then, enter the VPN username and password created earlier to connect.
In this guide, we cover and test the PPTP VPN on a Windows 10 PC. To get started, click the start menu and search for Control Panel, then, click Network and Internet.
Under Network and Internet, open the Network and Sharing Center and click Set up a new connection or network.
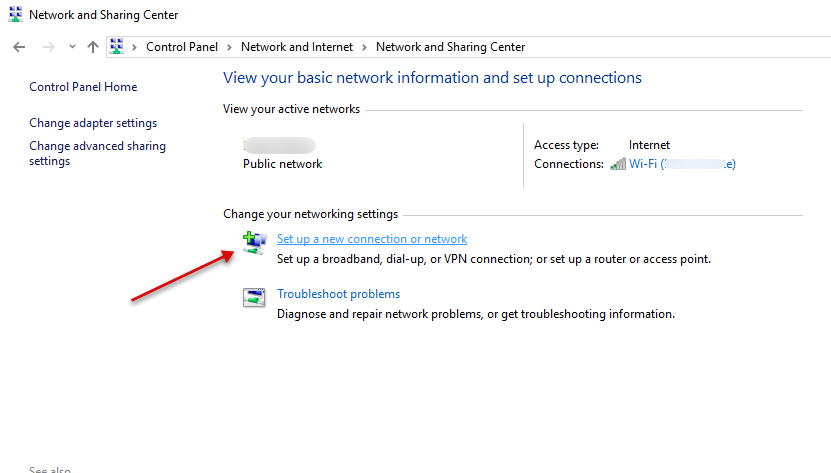
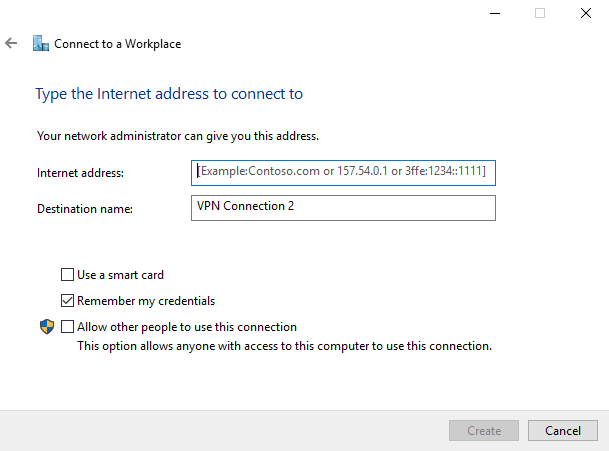
Under the open window, select Connect to a workplace and click Use my Internet connection (VPN).
Then, enter your server’s public IP Address (Check your Vultr server dashboard), assign the connection a name, and click create.
Now, on the left pane, click Change adapter settings, then right click your created VPN interface and select Properties.
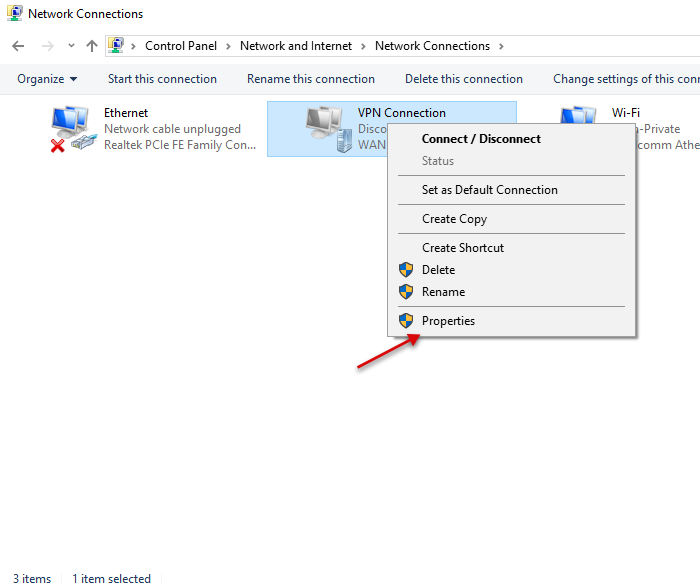
Under the pop-up, click Security, then choose Point to Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) under Type of VPN.
Finally, under Allow these protocols, select CHAP and MS-CHAP v2, then click OK to apply changes.
Your new VPN is configured successfully. Click the network connection icon on the taskbar, select your VPN on the list and click Connect to enter the VPN username and password created earlier to establish a connection to your new PPTP VPN server.
Setup L2TP with IPSEC
Open server manager, click Tools, and open Remote Access Management, then right-click your server on the left pane to select Properties from the drop-down list.
Under server properties, navigate to the Security tab, and click Allow custom IPSec policy for L2TP/IKEv2 connection to enter your new pre-shared key.
In this guide, we use 12345678, choose something stronger, then navigate to IPV4 to set a static address pool and click OK to apply changes.
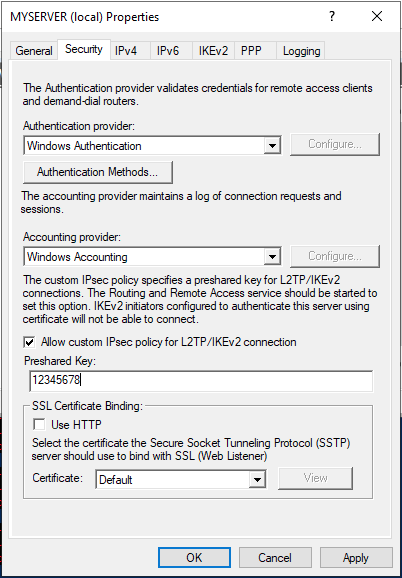
Keep note of the pre-shared key (PSK) since it will be required for every user establishing a connection to the VPN server.
From the left pane, expand the IPV4 sub-menu and right-click on NAT, then select New Interface. If you set PPTP earlier, click NAT and edit the existing interface you already created.
Navigate to the Services and Ports tab and select VPN Gateway [L2TP/IPSec], then click edit to change the private address from 0.0.0.0 to 127.0.0.1. Click OK to save changes and restart remote access from the left pane under All Tasks.
This will restart Routing and Remote Access, then save the applied L2TP configurations.
Allow L2TP Connections through Windows Firewall
Open Windows Defender with Firewall, select inbound rules and add a new rule. Select Predefined and from the list, choose Routing and remote access.
Under Predefined rules, select Routing and Remote Access [L2TP-In] and click next.
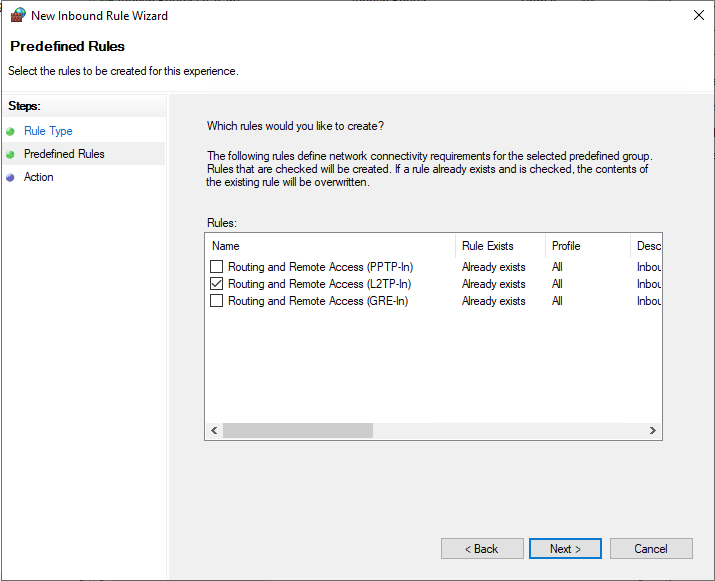
Finally, allow the connection and click Finish to apply the new Firewall rule.
Connect and Test Your L2TP VPN server
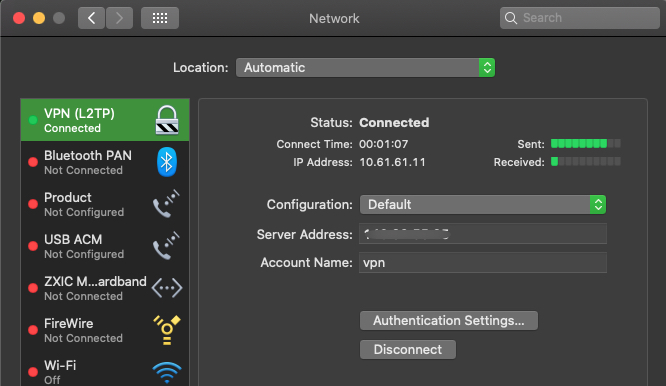
In this guide, we test the new L2TP with IPSec VPN on a mac. To get started, open System Preferencesand click Network.
Under the Network Preferences window, click the + sign and select VPN under the Interface dialog box. Then, choose L2TP with IPSec as the VPN Type and assign your connection a name.
Click create, then enter your public server IP Address (server address) and username (Account name). Next, click Authentication Settings to enter your account password and Pre-shared key (Shared secret) created earlier.
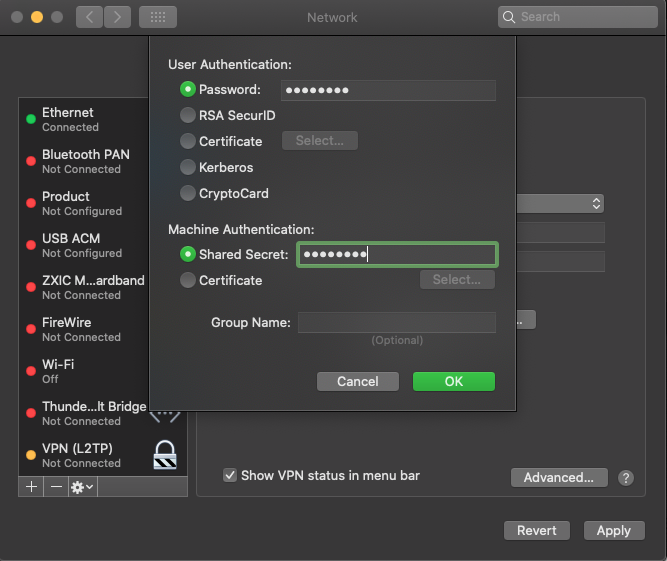
Next, click Advanced and select Send all Traffic over VPN Connection, then click Apply, and finally click Connect to establish a connection with your new L2TP VPN server.
Conclusion
You have set up a VPN on your Windows server 2019 instance; you can choose to create both PPTP and L2TP VPNs with different users connecting through your server without any limitations.
For every connected device, they will be able to access the Internet through your server and interact with other connected computers.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) – это безопасное соединение, защищающее вас, при использовании публичных (открытых, не защищенных) сетей. Данный протокол шифрует интернет-трафик и скрывает ваши личные данные от других пользователей сети. Злоумышленникам будет труднее отследить ваши действия в сети Интернет или украсть у вас важные файлы/данные. Безопасное соединение шифрует данные в режиме реального времени, как говорится “на лету”, маскируя ваш IP-адрес. VPN-соединение действует как фильтр, шифрующий всю отправляемую и получаемую информацию. Даже если она попадёт в руки злоумышленников, они не смогут её расшифровать. Так же, VPN позволяет объединять удаленные компьютеры в одну локальную сеть, позволяя безопасно работать из дома, как будто ты находишься в локальной сети офиса.
Настройка VPN на Windows Server 2019
Для начала работы с VPN в среде Windows Server вам потребуется установить роль Удаленный доступ, это делается стандартными средствами операционной системы Windows Server.

В Службах ролей необходимо выбрать роль DirectAccess и VPN (RAS) .

После установки роли Удаленный доступ ее следует настроить, проще всего это сделать, нажав на значок с желтым треугольником в Диспетчере серверов и выбрать в появившемся списке пункт Запуск мастера начальной настройки.

В появившемся окне выбираем пункт Развернуть только VPN.

Затем в оснастке Маршрутизация и удаленный доступ щелкаем правой кнопкой мыши по строке с сервером и выбираем в выпадающем меню Настроить и включить маршрутизацию и удаленный доступ.

После чего появится хорошо знакомое окно мастера настройки, предлагающее сразу несколько типовых конфигураций, однако у него есть свои особенности, например, если у вашего сервера всего один сетевой интерфейс, то настроить вариант Удаленный доступ (VPN или модем) мастер вам не даст. Поэтому выбираем самый нижний пункт – Особая конфигурация.

В следующем окне достаточно поставить галочку Доступ к виртуальной частной сети (VPN) и завершить работу мастера.

После завершения работы мастера служба Маршрутизации и удаленного доступа будет запущена и можно приступить к настройке сервера удаленного доступа. Если же данная служба у вас уже установлена и настроена в иной конфигурации, то щелкните правой кнопкой по строке сервера и выберите Свойства, в открывшемся окне на закладке Общие установите опции: IPv4-маршрутизатор локальной сети и вызова по требованию и IPv4-сервер удаленного доступа.
Настройка PPTP и/или L2TP сервера удаленного доступа
Откроем оснастку Маршрутизация и удаленный доступ и перейдем к свойствам сервера через одноименный пункт в меню правой кнопки мыши, прежде всего убедимся, что настройки на закладке Общие соответствуют приведенным на скриншоте выше. Затем переключимся на закладку Безопасность и убедимся, что в качестве Поставщика службы проверки подлинности стоит Windows – проверка подлинности, а Поставщик учета – Windows-учет, еще ниже установим флаг Разрешить пользовательские политики IPsec для L2TP- и IKEv2-подключения и в поле Общий ключ укажите парольную фразу для предварительного ключа.

Нажав на кнопку Методы проверки подлинности откроем окно, в котором выберем только Протокол EAP и Шифрованная проверка (Microsoft, версия 2, MS-CHAP v2), остальные протоколы не являются безопасными и должны быть отключены.
На закладке IPv4 укажем опцию Назначение IPv4-адресов – Статический пул адресов и добавим новый пул для выдачи адресов из него удаленным клиентам. Количество адресов должно быть не менее количества клиентов плюс один адрес, так как первый адрес из пула присваивается серверу. Что касается самого диапазона адресов, то его выбор зависит от конфигурации сети, если вы будете использовать маршрутизацию, то он не должен пересекаться с локальной сетью, если же хотите использовать ProxyARP, то наоборот, должны выделить принадлежащий локальной сети диапазон. В нашем случае используется второй вариант.

На этом настройка сервера может считаться законченной, следующим шагом следует разрешить подключения нужным пользователям, для этого в свойствах пользователя перейдем на закладку Входящие звонки и в блоке Права доступа к сети укажем Разрешить доступ. Теперь указанный пользователь может подключаться к нашему серверу используя свои учетные данные.

Также не забудьте проверить настройки брандмауэра, чтобы убедиться, что правила Маршрутизация и удаленный доступ GRE-входящий, PPTP-входящий (для PPTP) и L2TP-входящий (для L2TP) включены.

Proxy ARP
Сетевое взаимодействие в пределах одной IP-сети осуществляется на канальном (L2) уровне, в сетях Ethernet для этого используются MAC-адреса устройств. Для того, чтобы выяснить MAC-адрес узла по его IP применяется протокол ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), использующий широковещательные запросы, на которые отвечает только обладатель указанного IP-адреса. Выдавая удаленным клиентам адреса из диапазона основной сети мы как бы помещаем их в общую IP-сеть, но так как VPN – это соединение точка-точка, ARP-запросы от удаленных клиентов в сеть попадать не будут, единственный узел который их получит – сам VPN-сервер.
Для решения данной проблемы используется технология Proxy ARP, которая, как понятно из названия, представляет прокси-сервер для ARP-запросов, позволяя удаленным клиентам работать так, как будто бы они действительно находились в одной сети, без каких-либо дополнительных настроек. При использовании RRAS никаких дополнительных действий делать не нужно, Proxy ARP работает по умолчанию.
VPN-сервер за NAT
Так как мы используем Windows Server, то с большой долей вероятности он будет находиться внутри сетевого периметра и нам понадобится настроить проброс портов на маршрутизаторе. Для этого нужно четко понимать, как работает VPN-соединение и какие порты и протоколы следует передавать.
Начнем с PPTP, прежде всего клиент устанавливает управляющее TCP-соединение на порт 1723, затем, после успешной аутентификации создается соединение для передачи данных с использованием протокола GRE.
Таким образом для работы PPTP-сервера за NAT нужно:
- пробросить порт 1723 TCP
- разрешить прохождение GRE-трафика
С первым понятно, а вот с GRE могут возникнуть затруднения. Если вы используете маршрутизатор на базе Linux, то обратитесь к следующей нашей статье, если оборудование Mikrotik, настроенное по нашей инструкции, то достаточно пробросить только 1723 TCP, прохождение GRE будет разрешено конфигурацией брандмауэра, в остальных случаях следует обратиться к документации на свою модель маршрутизатора.
С L2TP сложнее, точнее не с ним самим, а с IPsec, который не поддерживает NAT. Для обхода этих ограничений используется протокол NAT-T, который инкапсулирует пакеты IPsec в UDP, позволяя успешно проходить через NAT. Поддержка данного протокола включена по умолчанию практически во всех ОС, кроме Windows. Для включения поддержки NAT-T следует внести изменения в реестр, найдите ветку:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PolicyAgent:
Создать в ней AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule с параметром DWORD и значением 2.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\RasMan\Parameters :
- AllowL2TPWeakCrypto – изменить на 00000001 (ослабляет уровень шифрования, для L2TP/IPSec используются алгоритмы MD5 и DES)
- ProhibitIPSec – изменить на 00000000 (включает шифрование IPsec, которое часто отключается некоторыми VPN клиентами или утилитами)
Это можно быстро сделать при помощи PowerShell:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PolicyAgent" -Name "AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule" -Type DWORD -Value 2 -Force
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Rasman\Parameters" /v AllowL2TPWeakCrypto /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Rasman\Parameters" /v ProhibitIpSec /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /fПосле чего систему следует перезагрузить. Данные изменения нужно внести как на сервере, так и на клиенте.
При установлении L2TP/IPsec соединения между узлами прежде всего создается зашифрованный IPsec-канал, для этого используется протокол обмена ключами IKE (порт 500 UDP) и протокол NAT-T (порт 4500 UDP), затем уже внутри безопасного IPsec-соединения поднимается L2TP-туннель на порт 1701 UDP и происходит аутентификация пользователя.
Обратите внимание, аутентификация пользователя в L2TP, в отличии от PPTP, происходит внутри защищенного IPsec-канала, что делает данный тип соединения более безопасным.
Таким образом для работы L2TP/IPsec сервера за NAT нужно:
- пробросить порт 500 UDP
- пробросить порт 4500 UDP
- внести изменения в реестр для включения NAT-T как на сервере, так и на клиенте (только для Windows)
Вопреки распространенному заблуждению порт 1701 UDP пробрасывать не нужно.
Настройка VPN-подключения в Windows
С одной стороны это простой вопрос, с другой – имеются определенные тонкости, на которые мы как раз и обратим внимание. В Windows 10 для первичной настройки VPN-подключения служит современное приложение, которое предельно простое и не охватывает дополнительных настроек.

Поэтому после того, как вы создадите в нем подключение, следует перейти к его свойствам и на закладке Параметры – Параметры PPP установить в открывшемся окне все флажки. Это позволит использовать все возможности протокола PPP и получить оптимальное качество связи. Обратите внимание, что данные опции должны также поддерживаться со стороны сервера, в противном случае их использование в одностороннем порядке может привести к ошибкам при установлении связи.

Затем на закладке Безопасность установите в Шифрование данных – обязательное, а в пункте Проверка подлинности выберите Протокол расширенной проверки подлинности (EAP).
И наконец на закладке Сеть перейдите в свойства протокола IP версии 4 (TCP/IP 4) и нажмите Дополнительно, в открывшемся окне снимите флаг Использовать основной шлюз в удаленной сети, в противном случае весь исходящий трафик будет направлен в туннель.

После чего можем подключаться и пробовать получить доступ к ресурсам удаленной сети, если вы все сделали правильно, то проблем возникнуть не должно.
Настройка VPN-подключения в Linux
В данной части нашего материала мы будем рассматривать настройку клиентских Linux-систем при помощи графического окружения и Network Manager, настройка серверных систем выходит за рамки текущей статьи. В качестве примера мы будем использовать Ubuntu, но все сказанное будет справедливо для любых основанных на Debian систем, а с некоторыми уточнениями – для любых дистрибутивов.
Поддержка PPTP присутствует практически в любом дистрибутиве по умолчанию. Достаточно перейти в Настройки – Сеть и добавить новое VPN-подключение.

Заполняем основные настройки: адрес сервера, имя и пароль пользователя.

Затем нажимаем кнопку Дополнительно и в открывшемся окне в разделе Аутентификация оставляем только MSCHAPv2, обязательно включаем Использовать шифрование MPPE и выбираем ниже 128 бит (наиболее защищенное), также устанавливаем флаг Включить Stateful Encryption для уменьшения накладных расходов на шифрование. Флаги сжатия оставляем включенными.

Закрываем данное окно с сохранением данных и переходим на закладку IPv4, где в разделе Маршрутизация устанавливаем флаг Использовать это подключение только для ресурсов этой сети, в противном случае в туннель пойдет весь трафик узла.

На этом настройка подключения завершена, можно подключаться.
Для работы с L2TP потребуется установить дополнительные пакеты:
apt install network-manager-l2tp-gnomeПосле чего в доступных типах подключения появится L2TP. Основные настройки ничем не отличаются от PPTP, также адрес сервера, имя и пароль пользователя.

Затем откроем Настройки PPP, в разделе Аутентификация также выберем только MSCHAPv2, а вот опции шифрования оставляем выключенными, так как чистый L2TP шифрования не использует, для защиты канала здесь применяется IPsec. Флаги сжатия также оставляем установленными по умолчанию.

Затем переходим в Настройки IPsec, это наиболее сложная и ответственная часть настроек, так как от них напрямую зависит безопасность соединения. В поле Pre-shared key введите Общий ключ, а ниже потребуется указать используемые шифры. Большинство материалов в сети интернет копируют друг у друга откровенно старые и слабые наборы шифров, что не соответствует реалиям сегодняшнего дня, хотя соединение с такими значениями будет работать. Мы же будем использовать максимально безопасные значения, для этого в поле Phase1 Algorithms укажите aes256-sha1-ecp384, а в поле Phase2 Algorithms – aes256-sha1.
Также имеет смысл установка флага Enforce UDP Encapsulation, который принудительно включает NAT-T, в случае если вы точно знаете, что ваш сервер находится за NAT, без этой опции протокол включается автоматически при обнаружении первого устройства с NAT.

Сохраняем настройки и переходим на вкладку IPv4, где также в разделе Маршрутизация ставим флаг Использовать это подключение только для ресурсов этой сети, чтобы направить в туннель только трафик для сети офиса.

Наши специалисты помогут Вам настроить безопасное VPN-соединение. Работайте с DIGIT TOP – участвуйте в создании кластера информационной безопасности!
Introduction
In this article we will explain how to set up L2TP/IPSec VPN on Windows Server 2019.
A VPN or Virtual Private Network is used to securely tunnel the data from a local computer to a remote server. You can visualize VPN as a private network distributed across the internet or public network. Using VPN, different devices can securely talk to each other as if they are connected over a private network.
There are various VPN tunneling protocols are available. In this tutorial, we will configure a fresh VPS running Windows Server 2019 as an L2TP over IPSec VPN. L2TP or Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol is a tunneling protocol but it does not provide strong encryption. IPSec comes into picture here, which provides very strong encryption to data exchanged between the remote server and client machine.
We will leverage on Remote and Remote Access Services (RRAS) which provides easy to use interface to configure networking features such as VPN, NAT, Dial-Up Access server, Lan Routing, etc.
Prerequisites
- Cloud VPS, Pure performance VPS or Dedicated Server with Windows Server 2019 installed.
- You must be logged in via Remote Desktop Protocol as an administrative user.
Step 1: Update System
Search for Windows Powershell and open it in Administrative mode by right-clicking and selecting Open as Administrator.
Install Windows update module for Powershell by running the command.
Install-Module PSWindowsUpdate
You may be prompted for confirmation, press Y and enter all the time.
Now get the list of latest updates by running.
Get-WindowsUpdate
Finally, install the updates by running the command.
Install-WindowsUpdate
Once updates are installed, restart the computer by running the command.
Restart-Computer
Step 2: Install Remote Access Role
Open Powershell again in administrative mode and run the following command to install the Remote Access feature with Direct Access and VPN (RAS) and Routing along with management tools.
Install-WindowsFeature RemoteAccess Install-WindowsFeature DirectAccess-VPN -IncludeManagementTools Install-WindowsFeature Routing -IncludeManagementTools
Step 3: Configure Routing and Remote Access
Open Server Manager and navigate to Tools >> Remote Access Management.
On the left pane, right-click on your local server and click Configure and Enable Routing and Remote Access.
In Configure and Enable Routing and Remote Access Wizard, select Custom Configuration radio button as we will manually configure the routing and access. Click Next button.
Next, select VPN Server and NAT checkboxes and click next to see a summary of the selection.
Finally, on clicking Finish button, you will see a prompt to start the Routing and Remote Access Services. Click on the Start Service button.
Step 4: Configure VPN Properties
Now that we have our VPN running, let’s go ahead and configure it. Under the Routing and Remote Access window, on the left pane, right-click on your local server and click Properties.
Navigate to the security tab and click on Allow custom IPSec policy for L2TP/IKEv2 connection and put a very long PSK(Pre-shared key). You can use any tool to generate a random key.
Make sure to note down the PSK as we will need to share the PSK with every user who wants to connect to the VPN server.
Now, go to IPv4 tab and under IPv4 address assignment select static address pool. Click Add button and you will get a pop up to put IP address ranges. Put the starting address and ending address of the IP address range you want the users to assign to.
Click the OK button to save the address range and finally click OK to save the changes. You may get a warning saying you need to restart the Routing and Remote Access for changes to apply, you can safely click OK and ignore it for now as we will restart the service after completing next step.
Step 5: Configure NAT
On the same left pane of Routing and Remote Access window, expand your local server and then expand IPv4. You will see the NAT object there. Right-click on NAT and then click on New Interface option.
Select Ethernet and click OK to proceed further. On NAT tab, select Public interface connected to Internet radio button and also select Enable NAT on this interface checkbox.
Now, go to Services and Ports tab and select VPN Server(L2TP/IPSec – running on this server) checkbox. It will open up a new interface for editing the service.
Change the private address from 0.0.0.0 to 127.0.0.1 and click OK to save.
Finally, Click OK to save the NAT interface.
Step 6: Restart Routing and Remote Access
On the left pane of Routing and Remote Access window, right-click on your local server and click on Restart under All Tasks.
This will restart the Routing and Remote Access services and all the changes we have made will be applied.
Step 7: Configure Windows Firewall
On the start menu, search for Windows defender firewall and open it. Click on Advanced settings on windows defender firewall.
Under Advanced setting, click on Inbound Rules on the left pane and then click on New Rule on right side pane.
Windows Server 2019 has predefined rules which we need to enable for VPN to work. In New Inbound Rule Wizard click on Predefined radio button and select the Routing and Remote Access from the drop-down.
Under Predefined Rules select Routing and Remote Access(L2TP-In) checkbox and click Next.
Under Action select, the option Allow the connection and click Finish.
The firewall is now configured to allow inbound traffic on UDP port 1701.
Step 8: Create VPN User
Search for Computer Management in the start menu and under Computer Management window expand Local users and group.
Right-click on Users and click on New User under Local users and group to create a new user.
On New User prompt, provide a username, full name, and strong password. Uncheck User must change the password on next login checkbox. Click Create to create a new user.
Once the user is created, return to Computer Management interface and you will find the user which you have just created in the list of users. Right-click on the user and click Properties option.
On your VPN users properties, navigate to Dial-in tab. Now, select Allow access option for Network Access Permissions setting. Click OK to save the properties.
Our L2TP/IPSec VPN server is now ready and can accept the connections.
Step 9: Connecting VPN Clients.
You will need to share the PSK and Windows username and password to the user who wishes to connect to the remote VPN server. You can also follow the tutorials on Snel website to learn how to connect to the remote server.
- How to connect L2TP/IPsec VPN on Mac OS X
- How to connect L2TP/IPsec VPN on Windows 10
Step 10: Monitoring VPN
Search for Remote Access Management Console in the start menu and open the console. You should see the status of the VPN. If you have followed the tutorial correctly, you will see all green checkmark on all services. You can also view the details of connected clients on this console.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have successfully configured a fresh Windows Server 2019 server as an L2TP/IPSec VPN servers. You can now use the VPN server to securely connect to the other connected devices. You can also use this VPN server as a proxy server to securely access the internet. You have now set up L2TP/IPSec VPN on Windows Server 2019.
Readers help support Windows Report. We may get a commission if you buy through our links.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Using a VPN on a Windows Server has a lot of advantages.
It allows users in a small environment to access remote clients or firewalls to Windows Server.
If you’re here to discover the exact steps for installing a VPN on Windows Server 2019, here’s everything you need to know.
Does Windows Server have a built-in VPN?
Affirmative, you can set up a VPN on Windows Server using the right protocols. Plus, there are certain versions that allow this operation
More exactly, it’s possible to use a VPN connection on a Windows Server 2019 and get increased privacy for your server.
In order to set up a VPN connection on this Windows Server edition, you have to use L2TP or PPTP VPN protocols.
How can I set up a VPN on Windows Server 2019?
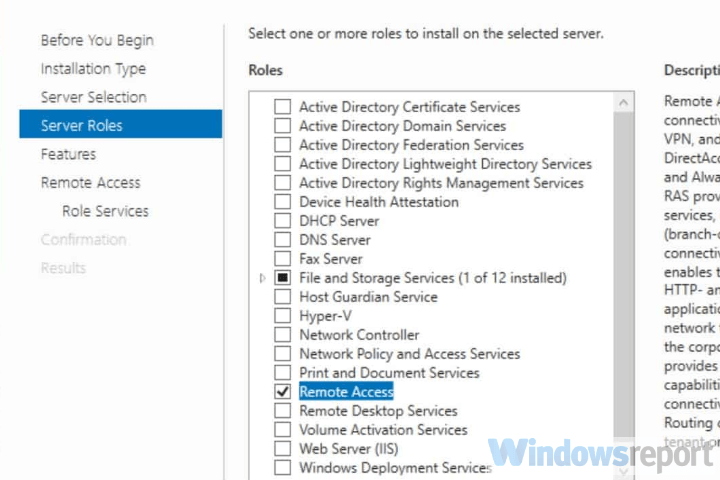
1. Install Remote Access using Server Manager
- Open Server Manager
- Go to Manage > Add Roles and Features Wizard
- Check the Remote Access box and click Next
- At Role Services, check the DirectAccess and VPN (RAS) box and click Next
- Click Install
- Once setup is over, you might have to restart the server
An alternative solution is to install and configure Remote Access using PowerShell.
2. Set up the VPN
- Click on the Open the Getting Started Wizard
- Choose Deploy VPN only
- In the Routing and Remote Access Management Console, right-click on the Server name
- Select Configure and Enable Routing and Remote Access from the context menu
- Choose Custom configuration and click Next
- Select VPN access
- Start the VPN service

You shouldn’t stumble upon any issues at this stage if you use the dedicated wizard.
Setting up a VPN on a Windows Server implies technical knowledge, so you have to learn how to configure it on your PC.
In a few words, you need to initially create a new VPN user and then set up routing and remote access features.
Here you have the required setup names and technologies you can use for securing your Windows Server:
- Windows Server 2019 VPN setup L2TP
- Windows Server 2019 VPN Ikev2 setup
- Windows Server 2019 SSTP VPN setup
- Windows Server 2019 PPTP VPN setup
- setup IPSec VPN Windows Server 2019
In conclusion, you can install a VPN on your Windows Server 2019 in three easy steps: setting up Remote Manager using Server Manager or PowerShell, installing the VPN, and managing VPN access permissions.
In case you need a fresh OS install, simply download Windows Server 2019 right away! Plus, join our VPN Troubleshooting Hub for additional guides.
If you experienced any technical difficulties, please let us know by dropping a comment in the section below.
Aleksandar Ognjanovic
Aleksandar’s main passion is technology. With a solid writing background, he is determined to bring the bleeding edge to the common user. With a keen eye, he always spots the next big thing surrounding Microsoft and the Windows OS.
Focused on Windows errors and how to solve them, he also writes about the OS’s latest features as well as its interface.
In his free time, he likes to read, listen to music, and enjoy the nature. Hiking is one of his newly found passions.
