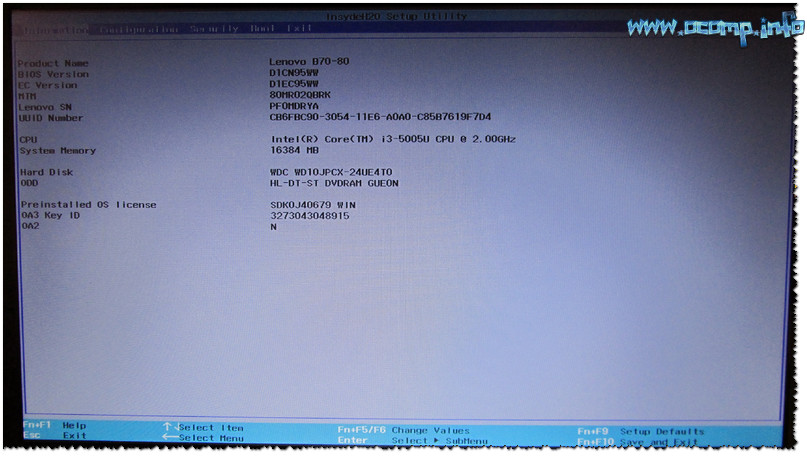
Introduction#
This document will cover various topics on managing BIOS/UEFI for Lenovo Think PCs. As these products are aimed at commercial customers, there are unique scenarios which require special considerations to support large fleets of PCs in an enterprise environment. This document will focus on how to update and manage BIOS/UEFI settings using typical IT practices in such an environment. This document may contain references to Microsoft Deployment Toolkit [MDT] or System Center Configuration Manager [SCCM]; however, in general, the same principles will apply to other systems management solutions.
Updating BIOS#
Overview#
Updating or installing a new version of the BIOS can be done two ways: by manual install or through automation. The BIOS can be updated through different methods: in the OS (Windows), in WinPE (Windows Pre-execution Environment), by an EFI-bootable USB drive, or a DOS-bootable USB drive. In some organizations other aspects are to be considered when updating the BIOS, such as performing an update when a Supervisor Password is present or even a fully automated PXE deployment that can, with some management, update the BIOS in your organization in a tightly controlled environment.
Updating the BIOS has to be done carefully to ensure that it is applied to the system without issue. BIOS updates for Lenovo Think brand devices are best applied from a local resource, such as the C:\ drive or the system drive in the full running Operating System, or from the X:\ drive in WinPE. Applying the update from a network resource is not advised. Were the connection to be lost in the middle of an update, irreparable damage could be done to the BIOS, potentially rendering the device unusable.
OS#
Updating the BIOS in the Operating System can be done a few different ways: manually, by script, by software deployment push, or by a task sequence. Currently, each of the three Think brands have their own BIOS installation process.
ThinkPad Manual Installation#
ThinkPad uses the WINUPTP tool to apply the updates under the OS or WinPE. Under the OS, WINUPTP.exe can be used. Under WinPE and depending on the model the WINPEUPTP.exe or WINUPTP64.exe should be used. These come from the extracted files location of the BIOS update package from the support site. To manually install a ThinkPad BIOS update, navigate to the Lenovo Support page, enter in the model of ThinkPad, and download the BIOS Update for Windows (BIOS Update Utility). After it is downloaded, run the downloaded program to begin the extraction process.

Step 1: Accept the EULA and click Next.

Step 2: Leave the default location selected for extraction and click Next.

Step 3: Click Install. The program will extract to the default location on the hard drive.

Step 4: Once completed, the installer should have a check mark on the page. Leave the check box checked and click Finish. This should immediately prompt to begin the BIOS Update.

Step 5: Select Update ThinkPad BIOS if not already selected and click Next.

Step 6: Follow the instructions on this screen and click Next.

Step 7: Follow the instructions and click Yes to continue.

Step 8: Wait while it prestages the new ROM image file. DO NOT POWER OFF THE SYSTEM at this point.

Step 9: Click OK to reboot the system immediately.

Step 10: After it reboots, the laptop will begin to write the prestaged BIOS image to the chip. At this point, DO NOT POWER OFF the laptop!!!

Step 11: When the BIOS update completes, it will reboot the computer.

Step 12: If an update for the Embedded Controller firmware is included in the update, the system will show the splash screen with text stating “Flashing Embedded Controller.” Allow this process to complete and the system will reboot to the OS.
ThinkPad Automated Installation#
To automate the ThinkPad BIOS update, the WINUPTP tool (including WINUPTP64 and WINPEUPTP) has a –s command line parameter to suppress any prompts or message boxes from displaying during installation of the update. WINUPTP also supports a –r command line parameter to force a reboot after prestaging the new BIOS image file. During the reboot, the computer may boot three times, once to apply the BIOS update to the ROM, once to potentially install an embedded controller update, and a final time to boot back into the operating system.
Assuming that the BIOS update is to be applied during a task sequence, from either MDT or SCCM, in the full operating system, there are a few items that need to be touched on. First, installing the BIOS update from a local hard drive is the safest choice. Since that is a requirement, use a copy command to copy the BIOS installer from the network to the local hard drive. Second, in a step to run an executable, call the WINUPTP tool with the –s command line parameter. The final step is to initiate a system reboot through the task sequence.
It is best practice to not use the –r command line parameter in a task sequence. When running task sequences, it is best practice to allow the task sequence to control the reboot and not allow the installing executable to do so. Allowing the task sequence to control the reboot will allow the task sequence to make all necessary changes to the computer, including setting up to resume the task sequence in the correct location after the reboot sequence has completed.
When updating a ThinkPad BIOS, if a Supervisor password is set and the “Flash BIOS Updating by End-Users” is set to factory default (Enabled), there are no additional steps to be taken to update the BIOS. If the “Flash BIOS Updating by End-Users” is not set to factory default (Enabled), then steps will need to be taken to switch the setting to Enabled using the Think BIOS Configuration Tool or the BIOS Settings VBScripts. After that is set to allow the update to be run, the BIOS can be updated. If needed, utilize the tools mentioned to change the setting back after applying the BIOS update.
WINUPTP Options#
| Option |
Description |
WinPEUPTP Support? |
| /s or -s |
Silent update. No GUI, return to Windows after BIOS/ECFW update. |
Always Support |
| /r or -r |
Reboot after BIOS/ECFW update |
Support |
| /sr or -sr |
Reboot after BIOS/ECFW update. (Silent update) |
Support |
| /bcp or -bcp |
Clear customized logo. |
Support(*) |
| /w or -w |
Command line password. How to use: WINUPTP -w «Supervisor password» |
Support |
| /fbc or -fbc |
Clear MOR flag |
Support(*) |
| /m or -m |
Update model number |
Support |
| /f or -f |
No warning message for update BIOS/ECFW though less than 25% Battery capacity |
Support |
(*) X13s is not supported for this feature.
WINUPT Return Codes#
| Return Code |
Description* |
| 0 |
BIOS update is successful and system reboots.(normal update) |
| 1 |
BIOS update is successful and system does not reboot. (silent update) |
| -1 |
WINUPTP Option is undefined. |
| -3 |
This utility does not support this system or OS. |
| -4 |
This utility works on Administrator authority. |
| -5 |
BIOS image file does not match this system. |
| -6 |
EC image file is damaged. |
| -7 |
EC image file does not match this system. |
| -8 |
The custom start up image file is not support. |
| -9 |
BIOS image file is same as BIOS ROM. |
| -10 |
AC/Battery is detached or battery is not charged. |
ThinkCentre Manual Installation#
ThinkCentre executes Flash.cmd from the extracted files location. To manually install a ThinkCentre BIOS update, navigate to the Lenovo Support page, enter in the model of ThinkCentre, and download the “Flash UEFI BIOS update (Flash from operating system version)”. After it is downloaded, run the downloaded program to begin the extraction process.

Step 1: Accept the EULA and click Next.

Step 2: Leave the default location selected for extraction and click Next. This will extract the files and then automatically kick off the installation.

Step 3: Click Yes to continue with the BIOS update.

Step 4: Press the “N” key and press.

Step 5: Press the “N” key and press . Once is pressed, a command window will pop up with yellow writing. Wait while it loads the ROM file into the BIOS update inbox. DO NOT POWER OFF THE SYSTEM at this point. The system will reboot on its own.

Step 6: Writing the new boot block.

Step 7: Writing the new image.

Step 8: Writing the new nvram block.

Step 9: Writing the new main block. After writing the main block, the computer will reboot on its own. It may restart a second time if it needs to program the embedded controller.

Step 10: Booting up.
ThinkCentre Automated Installation#
To automate the ThinkCentre BIOS update, the FLASH.CMD file can be executed with the /quiet command line parameter. FLASH.CMD executes WFlash2.exe with predetermined command line parameters attached. FLASH.CMD is designed to pass any command line parameters to the WFlash2.exe in the command file.
To update the BIOS in an automated solution use the command line parameter /quiet. The /quiet command line parameter will allow the update of the BIOS through WFlash2.exe without physical presence or other interaction.
Some versions of WFlash2.exe support the /sccm parameter. The /sccm parameter is intended for use in a task sequence and will suppress the reboot until the administrator chooses to do so. Check the readme.txt in the extracted BIOS folder or run WFlash2.exe /? to verify that the version of WFlash2.exe you are using supports this option.
If there is a Supervisor password controlling access to the BIOS and the Require Admin Pass when Flashing BIOS setting is set to NO, there is nothing to do to apply the BIOS update. In the event that there is a Supervisor password controlling access to the BIOS and the Require Admin Pass when Flashing BIOS setting is set to YES, WFlash2.exe has a command line parameter to allow input of the password for execution in an automated solution. The command line parameter is /pass:nnnnnn where nnnnnn is the password.
Example:
Flash.cmd /quiet /pass:Qwerty
ThinkStation Manual Installation#
ThinkStation executes Flash.cmd or Flashx64.cmd from the extracted files location, depending on the operating system architecture. To manually install a ThinkStation BIOS update, navigate to the Lenovo Support page, enter in the model of ThinkStation, and download the «Flash UEFI BIOS update (Flash from operating system version)». After the package is downloaded, execute it to begin the extraction process.

Step 1: Click Next on the Welcome screen.

Step 2: Accept the EULA and click Next.

Step 3: Leave the default location selected for extraction and click Next.

Step 4: Click Install. The program will extract to the default location on the hard drive.

Step 5: Click Finish to complete the extraction. Navigate to the folder where the BIOS update was extracted and execute Flash.cmd (If the account does not have administrator rights, right click on the .cmd file and select “Run as Administrator”).

While the update executes, the keyboard and mouse will be inaccessible. This is to prevent any actions from interfering with the execution. After the command window closes, manually restart the computer. The computer will then reboot to the Lenovo splash screen a few times and will boot back into the operating system.
ThinkStation Automated Installation#
To automate the ThinkStation BIOS update, either AFUWIN.exe or AFUWINx64.exe can be executed with a set of command line parameters. Use the following command to perform the silent update:
X86: AFUWIN.exe /P /B /N /R /SP /RTB /FIT /Q
OR
X64: AFUWINx64.exe /P /B /N /R /SP /RTB /FIT /Q
If there is a Supervisor password controlling access to the BIOS and the Require Admin Pass when Flashing BIOS setting is set to NO, there is nothing to do to apply the BIOS update. In the event that there is a Supervisor password controlling access to the BIOS and the Require Admin Pass when Flashing BIOS setting is set to YES, then steps will need to be taken to switch the setting to NO using the Think BIOS Configuration Tool or the BIOS Settings VBScripts. After that is set to allow the update to be run, the BIOS can be updated. If needed, utilize the tools mentioned to change the setting back after applying the BIOS update.
WinPE#
Besides a full Windows installation, the BIOS can be updated through WinPE as well. Updating the BIOS in WinPE would typically be completed by a task sequence in MDT or SCCM, but the updates can be applied by script as well. WinPE, while lightweight, has a couple of challenges when preparing to deploy a BIOS. WinPE requires optional components to create the underlying framework needed for the BIOS update installers to run. WinPE may also require network drivers be injected to make a connection to a centralized repository of BIOS updates for copying to a local drive.
When planning the build of the WinPE image, it is best to understand which Think branded product(s) will be updated, the method of getting BIOS updates to the local device, and the method of installing the update.
Note
- The following examples will be using the Windows ADK for Windows 10, version 1607.
- The optional components can be found in the installation of the Windows ADK, (C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Assessment and Deployment Kit\Windows Preinstallation Environment).
All of the Think branded products will require the following optional components to be installed in the WinPE boot image.
Scripting:
\WinPEOCs\WinPE-Scripting.cab
\WinPEOCs\<Language>\WinPE-Scripting<Language>.cab
WMI:
\WinPEOCs\WinPE-WMI.cab
\WinPEOCs\<Language>\WinPE-WMI<Language>.cab
ThinkPad will require an additional optional component to be installed in the WinPE boot image. The ThinkPad BIOS Update tool runs some HTML components in the background, requiring the HTA Optional Component be installed.
HTA:
\WinPEOCs\WinPE-HTA.cab
\WinPEOCs\<Language>\WinPE-HTA<Language>.cab
During testing, the order of installation was determined to be of importance. The order was found to be:
- HTA – If deploying ThinkPad systems
- Scripting
- WMI
The default configuration for MDT will install the required optional components. SCCM will need the HTA Optional Component added to the WinPE boot image. The others will already be in the WinPE image.
ThinkPad has one other requirement for installing the BIOS while in WinPE. It requires the battery.inf to be loaded. This enables the installers to verify there is a fully charged battery and ensure that the system meets the requirements of the installer. The battery.inf can be loaded from %systemroot%\INF\ using the command drvload.
The command is as follows:
drvload %systemroot%\INF\Battery.inf
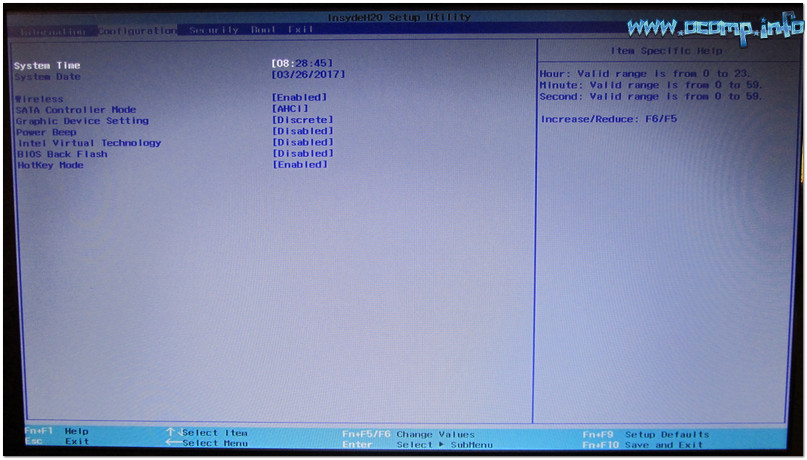
Configuring BIOS#
BIOS Security Settings#
With information security becoming a prime for organizations, Lenovo is actively and diligently working to protect customer data. One of the first layers of security we provide is within our hardware, specifically the BIOS. BIOS Security governs how accessible the operating system can be to users, administrators, and hackers. Lenovo currently stands on the premise that our BIOS should be highly secure, therefore we will err on the side of security over manageability. We strive to be more secure than other manufacturers while retaining a reasonable level of manageability.
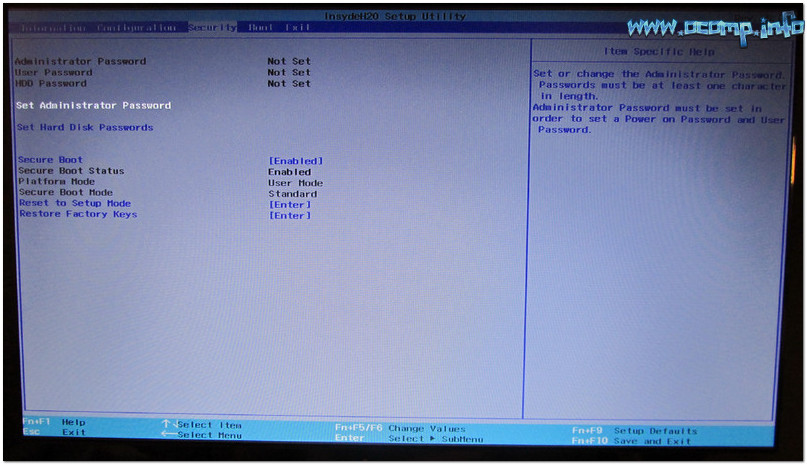
Lenovo utilizes passwords to control access to different aspects of the computer. Passwords are not set from the factory unless requested by a customer and implemented for a specific custom model being ordered. Passwords can be utilized to protect the BIOS interface, power on of the computer, and hard disk.
The BIOS interface is protected by the Supervisor Password (SVP). The Supervisor password must be provided when any settings are changed via scripting. The Supervisor password must be entered when accessing the BIOS by physical means in order to provide access to various security settings.
The powering on of the device is protected by the Power-On Password (POP). This will allow the computer to power on directly to a password prompt but go no further until the correct password is entered. The computer will not prompt for any other type of boot via the F12 boot menu. This will limit the access to the OS and BIOS.
These passwords can be set manually through the BIOS interface itself or can be set/changed by script with the limitation of the Supervisor Password. Lenovo does not support the ability to set the initial password by script to limit the security exposure of locking both administrators and users out of a computer. Once the Supervisor password is set, it can be changed by script. Many customers opt to have Lenovo set the Supervisor password at the factory. Once the customer knows the preset password, they can change it during initial deployment of the computer in their environment.
For more information about BIOS Security around passwords, check https:\pcsupport.lenovo.com and search for the specific model. The User Guide in the documentation area will contain specifics on these passwords.
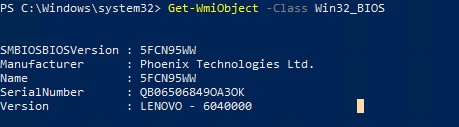
Lenovo leverages WMI through scripting API’s to detect if any of the BIOS passwords are set. The script returns the state of the following passwords: Supervisor (SVP), Power on (POP), User HDD, and User HDD and Master HDD. Using this information, an administrator can determine if a computer has passwords set in their environment.
Using the following PowerShell script, running as administrator, the return code will range from 0 to 7.
(gwmi -Class LenovoBIOSPasswordSettings -Namespace root\wmi).PasswordState
The result will map to one of the values in the table below:
| 0 |
No password set |
| 1 |
Power on password set |
| 2 |
Supervisor password set |
| 3 |
Power on password and Supervisor password set |
| 4 |
User HDD or User HDD and Master password set |
| 5 |
Power on password and (User HDD or User HDD and Master password) set |
| 6 |
Supervisor password and (User HDD or User HDD and Master password) set |
| 7 |
Power on password, Supervisor password, and (User HDD or User HDD and Master password) set |
Note
The information provided by the script will only return the state of the passwords, it will not return the actual passwords.
OS Optimized Defaults#
To make our BIOS compliant with the Microsoft Windows 8 and/or Windows 10 Certification Requirements, Lenovo has implemented a single setting, that when enabled and the default settings loaded, will set a group of settings to ensure the computer meets the requirements set forth by Microsoft and allow Windows 8 and newer operating systems to be installed on the hardware. When the setting is disabled and the default settings are loaded, the OS Optimized Defaults will set the settings in a state where they will not be compliant to the Microsoft Windows 8 and/or Windows 10 Certification Requirements and allow all (Windows 7 and prior) operating systems to be installed on the hardware.
The settings that OS Optimized Defaults controls are as follows:
| ThinkPad |
CSM Support, UEFI/Legacy Boot, UEFI/Legacy Boot Priority, Secure Boot, and Secure Rollback Prevention |
| ThinkCentre |
CSM Support, Boot Mode, Boot Priority, and Secure Boot |
| ThinkStation |
CSM Support, Boot Mode, Boot Priority, and Secure Boot |
Once Secure Boot is Enabled on a system, the setting cannot be changed to Disabled by script using the WMI BIOS Interface. It has to be manually disabled if there is a need. With security being a high profile topic in organizations, we took the step of only allowing our scripting to make the computer more secure, not less secure. Any action to make the computer less secure would have to be performed with physical presence.
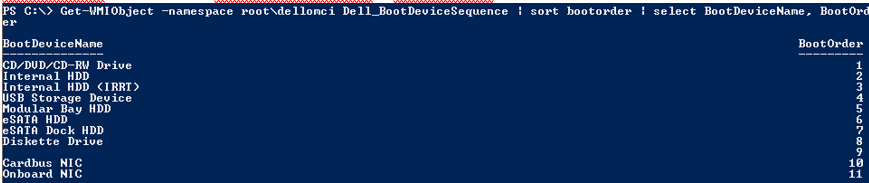
WMI BIOS Interface#
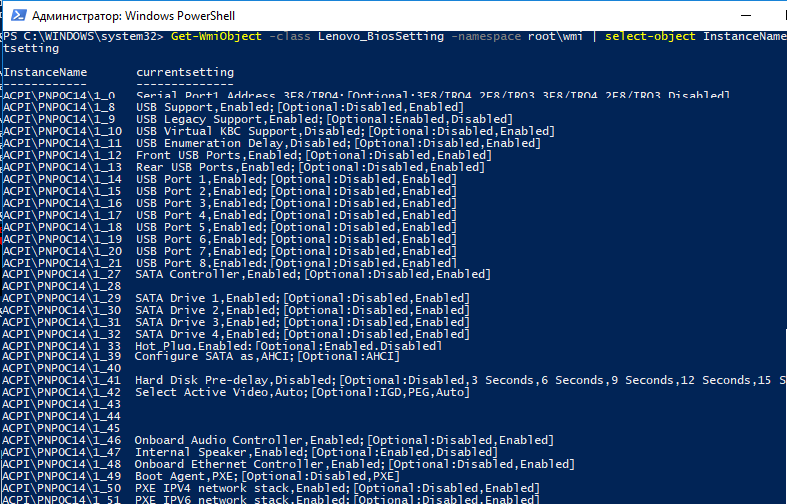
Through WMI methods, Lenovo has provided the ability to read and configure some BIOS Settings via scripting. The settings available to be changed by scripts are limited to non-security settings. Lenovo provides VBScripts as well as an HTA Tool called Think BIOS Config tool to facilitate easier manipulation of BIOS settings from both a scripted context as well as a graphical context. These capabilities are implemented on most Think branded devices.
To find more information on a particular BIOS setting for a system such as name, explanation or default value, navigate to https://pcsupport.lenovo.com . Type in the Model or MTM of the system and select the correct one from the drop down list. Click on Documentation and then look for the User Guide in the list of documents. In the User Guide, there will be a full listing of settings, descriptions, available values, and default values to reference.
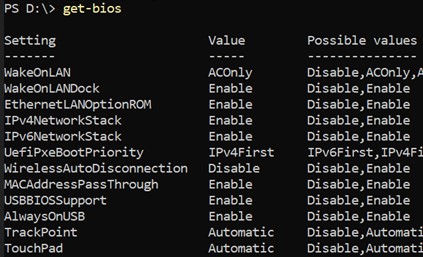
The Think BIOS Config tool is an HTA that can be run with an interface or directly from a command line to perform BIOS configurations. When double clicking the .hta file, it will run and provide a dynamic interface that shows all settings in the BIOS that are configurable by script for that computer.
Note
Think BIOS Config tool will ask for UAC elevation, since accessing the BIOS through WMI requires elevated privileges.
Each setting will show the current value associated with the setting. In drop down lists it will provide all possible values for that setting. When a value is changed for a setting, the setting name will turn red as a visual indicator that the setting is now different. To commit changes to be applied on the next reboot, use the Save Changed Settings button.
The interface also has the ability to create an .INI file with a full list of settings to use for other systems of the same model. The interface has the ability to import a previously created .INI file to configure a full set of settings or a subset of settings to be applied to a computer.
The Think BIOS Config tool has the ability to be run from a command line for System Administrators to change settings through a SCCM software push or SCCM or MDT task sequence for deploying an operating system.
Full documentation for the execution of the Think BIOS Config tool can be found in the User Guide which is included in the .zip file available in this blog post .
In addition to the Think BIOS Config tool, Lenovo has VBScripts to assist with changing and viewing BIOS Settings. The 5 scripts are ListAll.vbs, LoadDefaults.vbs, SetConfig.vbs, SetConfigPassword.vbs, and SetSupervisorPassword.vbs.
The ListAll.vbs script iterates through all settings, displaying the setting name, the current setting, and a list of all possible settings. The ListAll.vbs script is best used in an Administrator command prompt with cscript.
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.15063]
(c) 2017 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>cscript.exe ListAll.vbs
The LoadDefaults.vbs script will load the factory defaults for the computer. To find the defaults, reference the User Guide documentation for the specific model.
The SetConfig.vbs and SetConfigPassword.vbs are used to set individual settings. The only difference between the two scripts is that SetConfigPassword.vbs requires an extra parameter for the input of the Supervisor password to change the setting, when a Supervisor password is set on the BIOS.
The final script is the SetSupervisorPassword.vbs script. This script facilitates the change of the Supervisor password when one is currently set on the BIOS. This script does not allow for the initial setting of the BIOS Supervisor Password.
The provided VBScripts can also be incorporated into a software deployment through SCCM or through a SCCM or MDT task sequence for OSD.
For PowerShell examples, see Appendix B. Sample PowerShell commands in the BIOS Setup using Windows Management Instrumentation Deployment Guide .
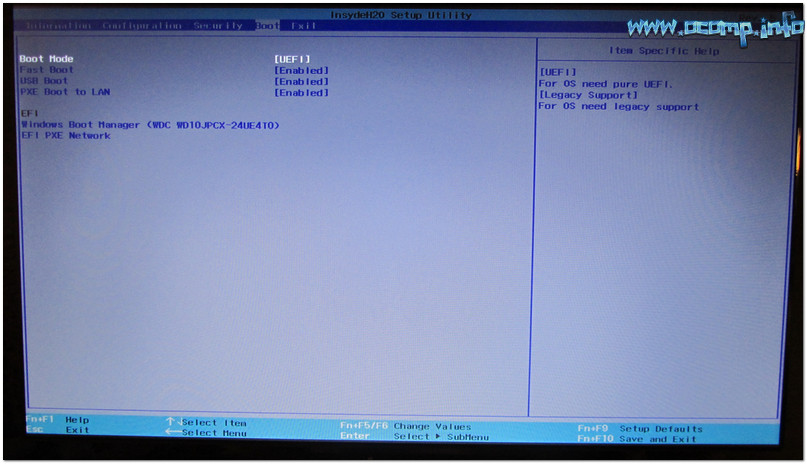
OS Specific Considerations#
Specific BIOS considerations need to be taken when deploying an operating system, such as BIOS Mode, secure boot status, and other features that can enhance the experience provided by the operating system. Below, we have laid out suggested settings in the BIOS for getting the best performance, upgradability, and features for a specific operating system or group of operating systems.
| Windows 10 x64 / Windows 8.1 x64 |
UEFI |
On the Restart tab in BIOS, set OS Optimized Defaults – Enabled and then load default settings. These settings will allow the hardware to run in UEFI mode These settings will allow for a GPT partition, Device Guard/Credential Guard (with supervisor password), and Secure Boot enabled, all of which will allow an organization to leverage the full potential of Windows 10 operating system. |
| Windows 7 x64 |
UEFI |
On the Restart tab in BIOS, set OS Optimized Defaults – Disabled and load the defaults. On the Startup Tab, set the UEFI/Legacy (Boot Mode) to UEFI Only. On the Config Tab, in the Network group, set both UEFI IPv4 Network Stack and UEFI IPv6 Network Stack to Enabled. Deploy Windows 7 x64 to the hardware with a GPT partition. This will enable an easier transition to Windows 10 in the future. |
| Windows 7 x86/ Windows 7 x64 |
Legacy |
On the Restart Tab in BIOS, set OS Optimized Defaults – Disabled and load the defaults. Doing this will allow the computer to create an MBR partition and run all hardware in Legacy Mode for the older operating system. |
Common Terms and Acronyms#
BIOS – Basic Input/Output System
SCCM – Configuration Manager or System Center Configuration Manager
MDT – Microsoft Deployment Toolkit
OSD – Operating System Deployment
TPM – Trusted Platform Module
UEFI – Unified Extensible Firmware Interface
WMI – Windows Management Interface