Каждый запущенный процесс в Windows имеет свой числовой идентификатор — PID или ИД процесса, который может использоваться для обращения к конкретному процессу, например, для получения информации о нём или принудительного закрытия.
В этой инструкции несколько способов узнать PID процесса в Windows 11 или Windows 10, большинство из которых подойдут и для предыдущих версий системы.
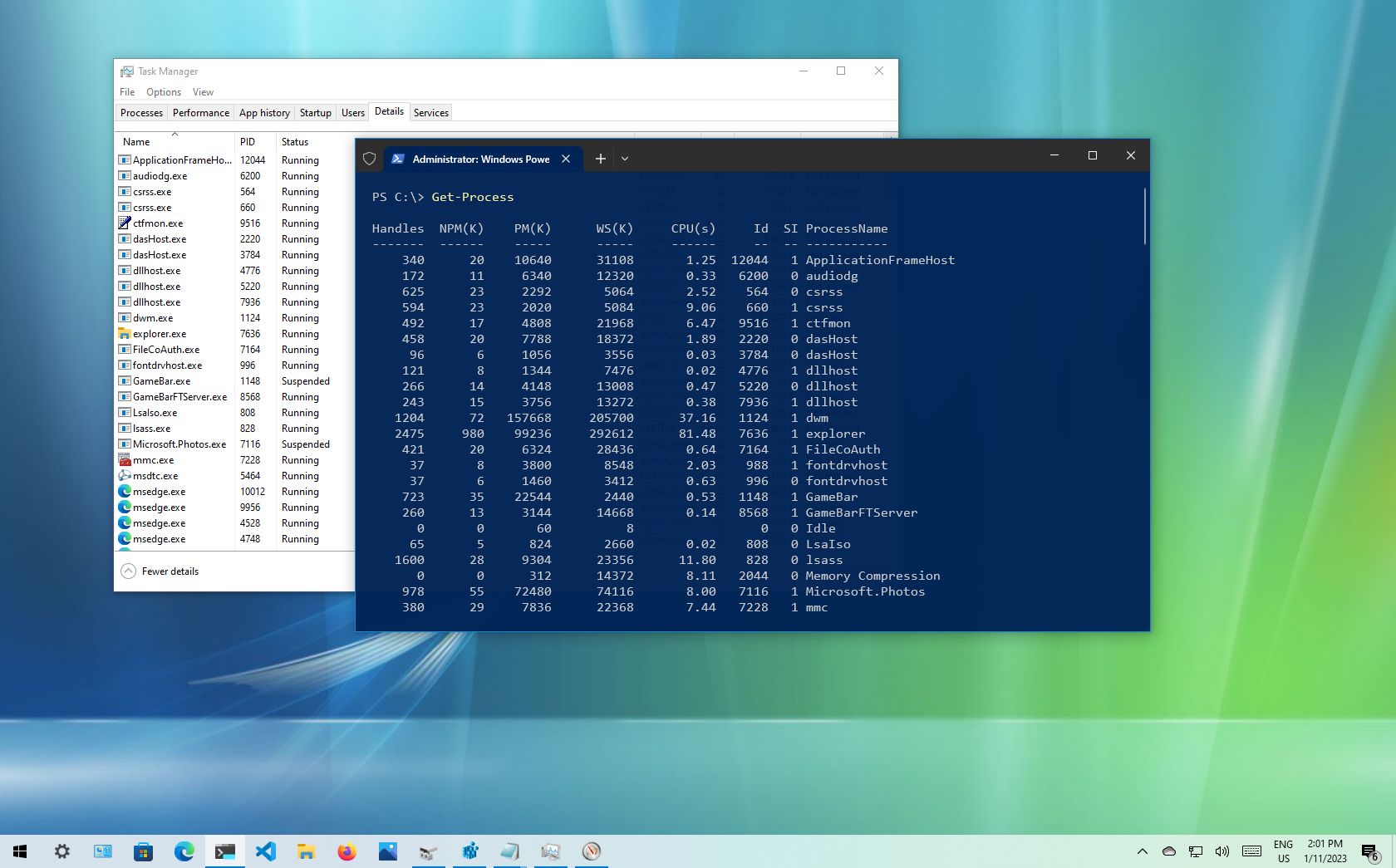
ИД процесса в диспетчере задач
Быстрый и простой способ посмотреть PID процесса в графическом интерфейсе — использовать диспетчер задач Windows, для этого:
- Откройте диспетчер задач: вы можете использовать контекстное меню кнопки «Пуск», нажать клавиши Ctrl+Shift+Esc или использовать меню Ctrl+Alt+Delete для этого.
- В диспетчере задач переключитесь на вкладку «Сведения» (в Windows 11, переключение выполняется в меню) или «Подробности» (в Windows 10).
- Обратите внимание на столбец «ИД процесса» — это и есть нужный PID. Если столбец не отображается, нажмите по заголовку таблицы с процессами правой кнопкой мыши и используйте пункт «Выбрать столбцы», чтобы включить показ нужного столбца.
Для большинства пользователей этого метода будет достаточно для получения нужной информации.
Однако, если узнать PID запущенного процесса требуется при выполнении какого-либо пользовательского скрипта, могут пригодиться описанные в последней части инструкции методы его получения без использования графического интерфейса — в командной строке или PowerShell.
PID процесса в Мониторе ресурсов
Ещё один метод, очень похожий на предыдущий — использование встроенного инструмента «Монитор ресурсов»:
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре, либо нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск» и выберите пункт «Выполнить».
- Введите resmon в диалоговое окно «Выполнить» и нажмите Enter.
- Откроется окно «Монитор ресурсов» в нем, на вкладке «Обзор» вы увидите список процессов, распределенных по группам (использование ЦП, Диска, Сети и Памяти) с указанием их ИД в соответствующем столбце.
Process Explorer
Process Explorer — «продвинутый» диспетчер задач из Microsoft Sysinternals, скачать его можно как в комплекте с другими утилитами, так и отдельно с официального сайта.

После запуска утилиты, информацию о PID процесса вы сможете найти в одноименном столбце.
Командная строка
Получить PID процесса можно с помощью команд командной строки. Шаги будут следующими:
- Запустите командную строку, лучше — от имени администратора (как это сделать).
- Чтобы получить список всех процессов, включая информацию об их PID, введите команду
tasklist
и нажмите Enter.
- Для отображения только процессов с заданными именами файлов (в имени допустимы wildcard-символы, например, *) можно использовать следующую команду:
tasklist /FI "IMAGENAME eq имя_файла.exe"
- Вы можете вывести результат выполнения команды в текстовый файл, пример:
tasklist > C:\pid.txt
С помощью tasklist можно отфильтровать процессы и по другим свойствам, например, получить список только зависших программ, подробнее на тему получения списка не отвечающих программ — в этой статье.
Windows PowerShell или Терминал Windows
И ещё одна возможность для получения PID процессов — использование терминала Windows или PowerShell:
- Запустите Windows PowerShell или Терминал Windows, для этого можно использовать меню по правому клику на кнопке «Пуск».
- Базовый вариант команды:
Get-Process
выдаст список всех процессов, PID будет отображен в столбце Id
- Если в выводе требуется оставить информацию только об имени процесса и его ИД, используйте следующий синтаксис:
Get-Process | Format-Table -Property ProcessName,Id
- Команда для получения информации о PID процессов с указанным именем:
Get-Process | Where {$_.ProcessName -Like "Имя процесса"} | Format-Table -Property ProcessName,Id
На этом всё: надеюсь, подходящий для себя способ получить нужную информацию вы нашли. Знаете другие методы получения PID процессов в Windows? — буду рад вашему комментарию ниже.
(Image credit: Future)
On Windows 10, every process from an app or a service has an identification number known as a Process ID (PID). The PID has various uses, but mainly, it exists to identify each process across the system and programs running multiple instances (such as when editing two text files with Notepad).
Although users do not have to worry about the system processes, the ability to determine their specific system number can come in handy in many scenarios. For instance, when you need to debug an app. A program is stuck, and you must terminate the process manually. Or you need to check the system resources that a particular process is using.
Regardless of the reason, Windows 10 includes at least four ways to check the PID for any process running in the system using Task Manager, Resource Monitor, Command Prompt, and PowerShell.
This guide will walk you through the steps to identify the process identification number for an app or service on Windows 10.
How to determine Process ID from Task Manager
To check the Process ID for an app on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Task Manager and click the top result to open the app.
- Quick tip: You can also open the app by right-clicking the Taskbar and selecting the Task Manager option, right-clicking the Start button and selecting the Task Manager option, or using the «Ctrl + Shift + Esc» keyboard shortcut.
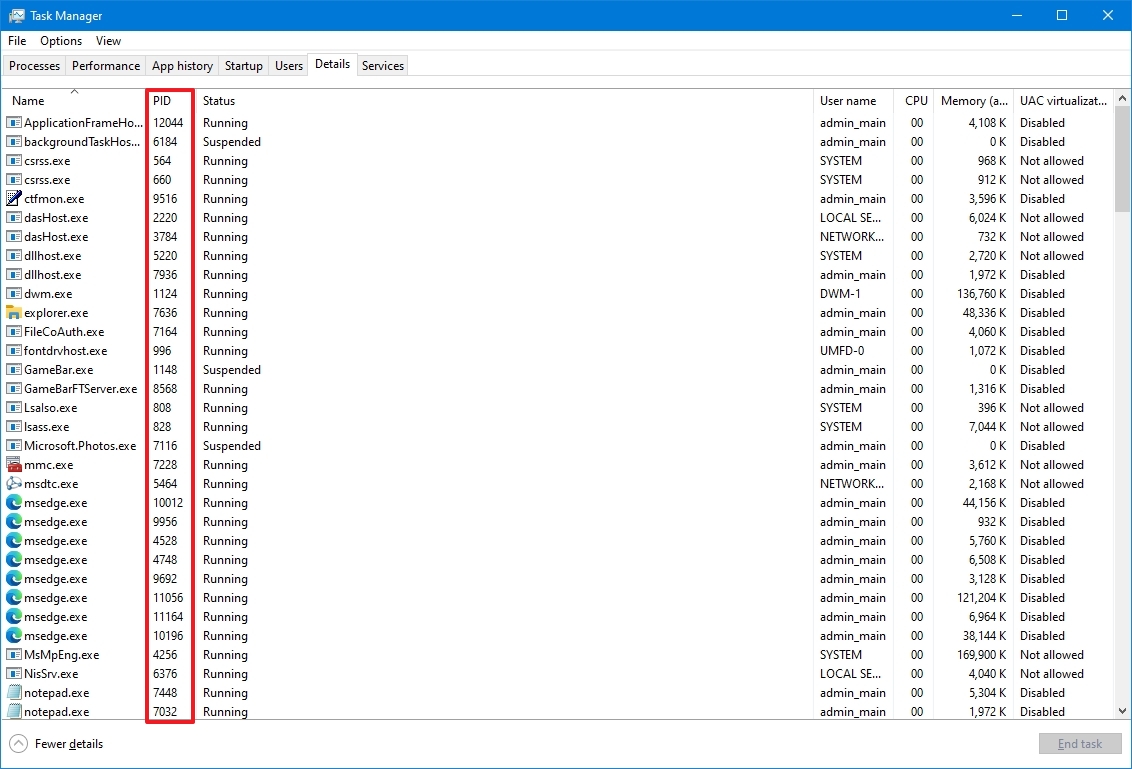
- Click the Details tab.
- Confirm the app’s Process ID in the PID column.
- Click the Services tab.
- Confirm the app’s Process ID in the PID column.
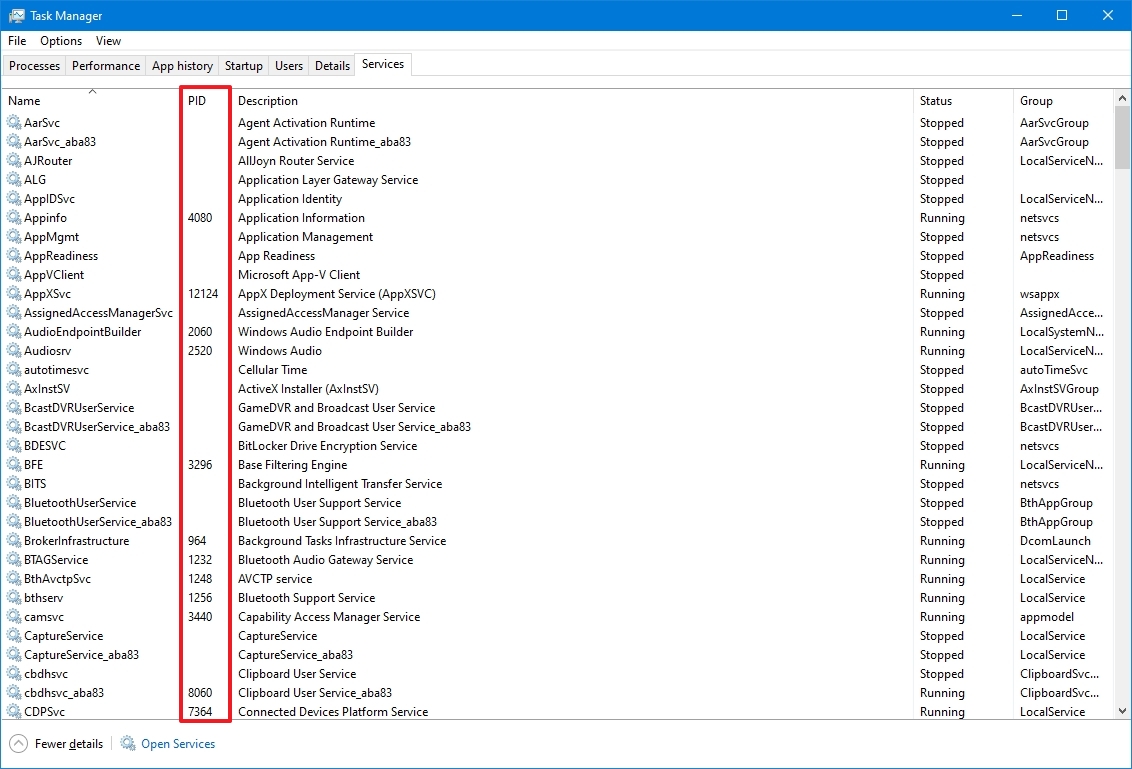
Once you complete the steps, you will know the process identification number for services and applications running and suspended on Windows 10.
How to determine Process ID from Resource Monitor
To find the Process ID for an app with the Resource Monitor console on Windows 10, use these steps:
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Open Start.
- Search for Resource Monitor and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the Overview tab.
- Confirm the Process ID of apps and services in the PID column.
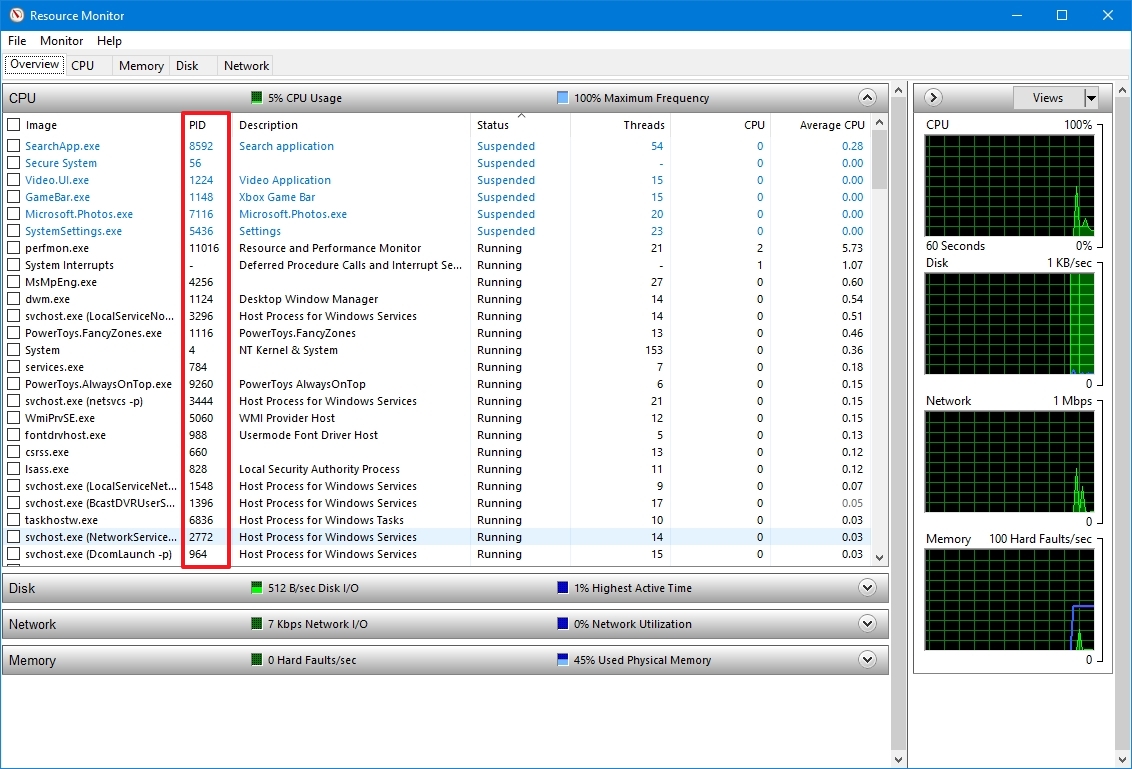
After you complete the steps, you will have an overview of the ID for the running and suspended processes.
How to determine Process ID from Command Prompt
To find out the ID of a process with commands on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt and click the top result to open the terminal.
- Type the following command to view the Process ID list and press Enter: tasklist
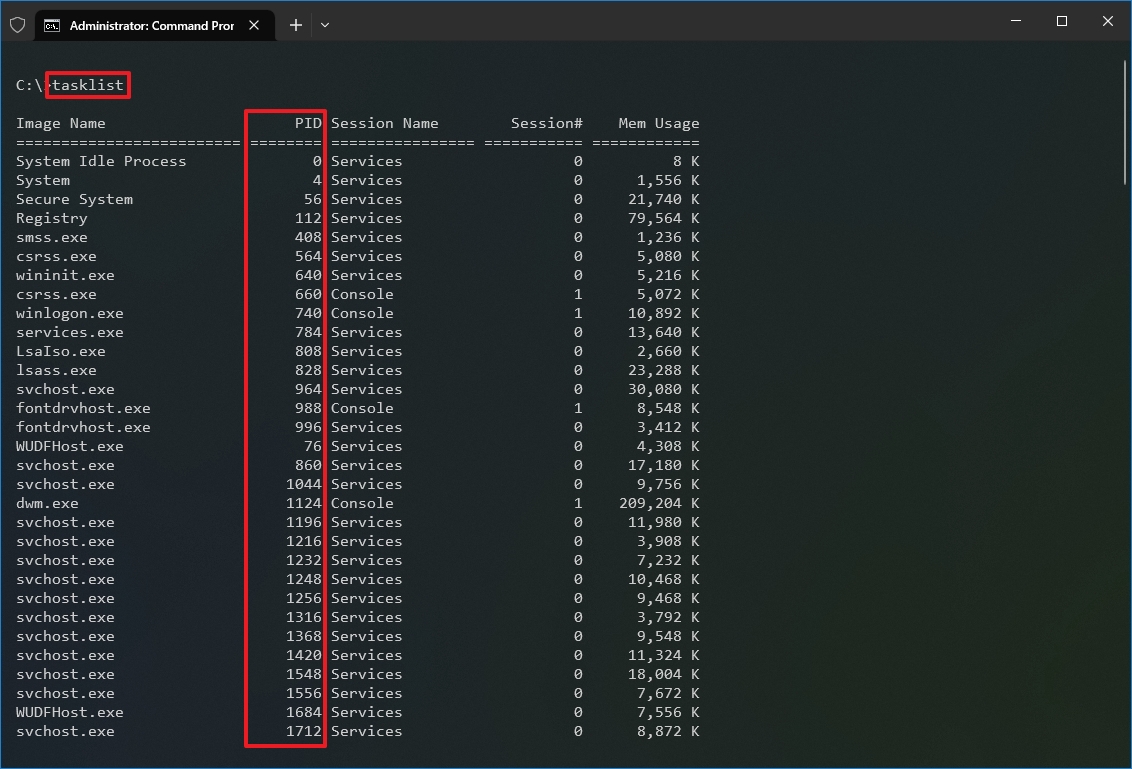
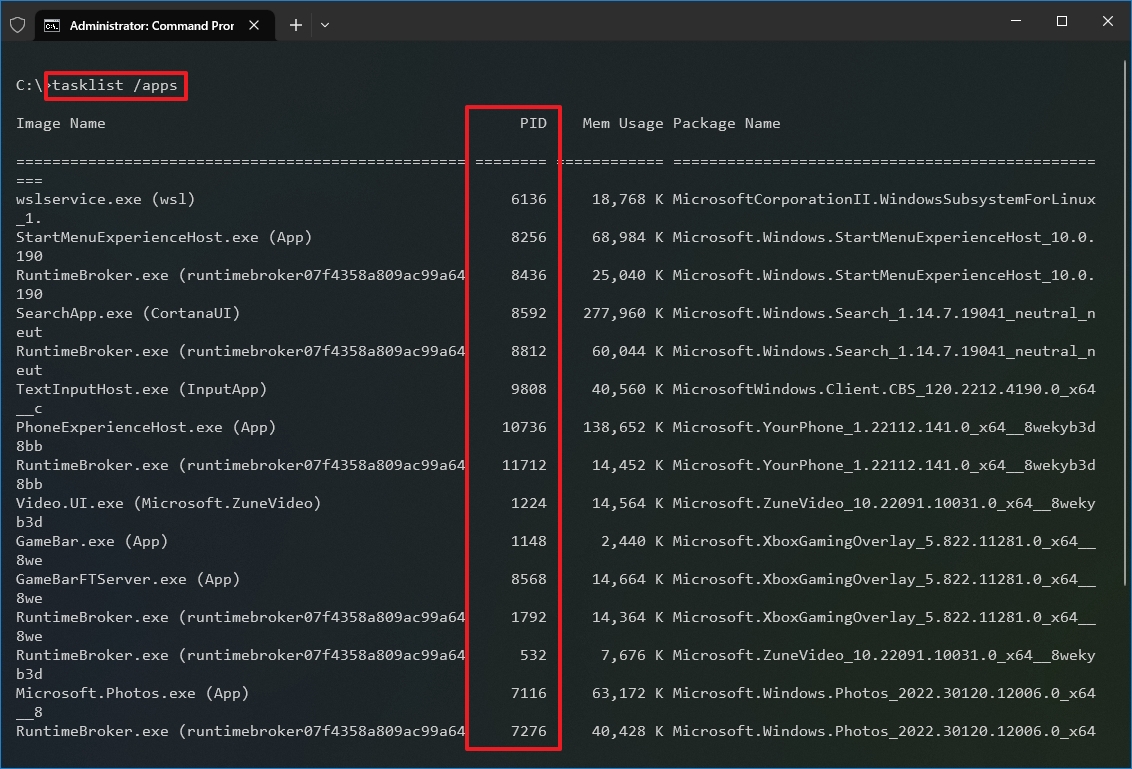
- Type the following command to view a list of Process IDs for Microsoft Store apps and press Enter: tasklist /apps
- Type the following command to get the ID from the process name and press Enter: tasklist /svc /FI «ImageName eq PROCESS-NAME*»
In the command, make sure to replace PROCESS-NAME with the «.exe» name of the process. The * is a wildcard to match part of the name without having to type the exact name of the process. This example shows the processes for Notepad: tasklist /svc /FI «ImageName eq notepad*»
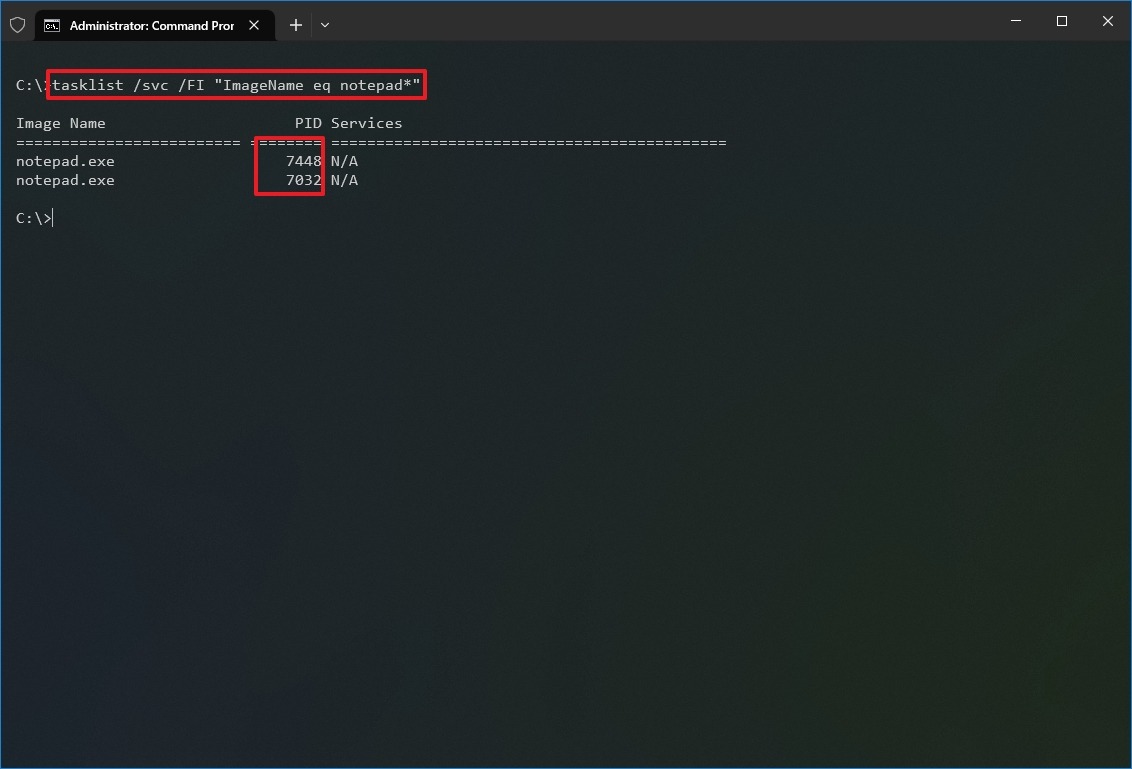
Once you complete the steps, the output will display the IDs for the processes running on the device.
How to determine Process ID from PowerShell
To determine the Process ID of an app or service with PowerShell, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for PowerShell and click the top result to open the terminal.
- Type the following command to view the Process ID list and press Enter: Get-Process
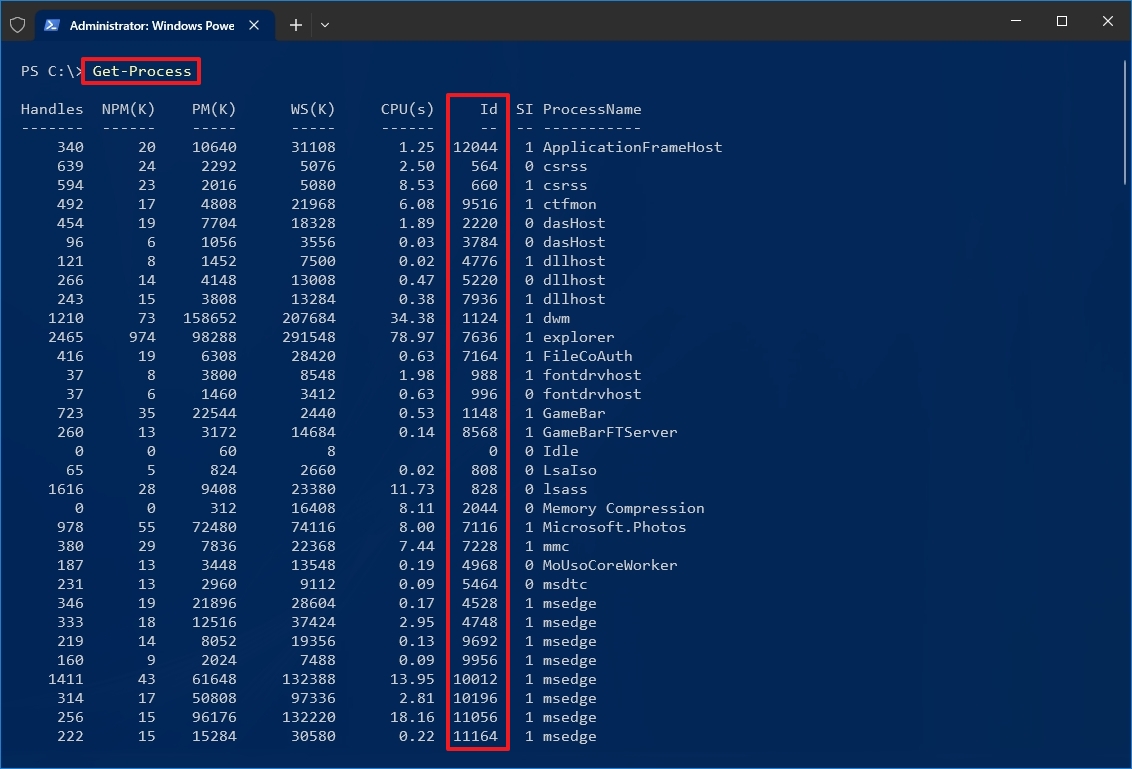
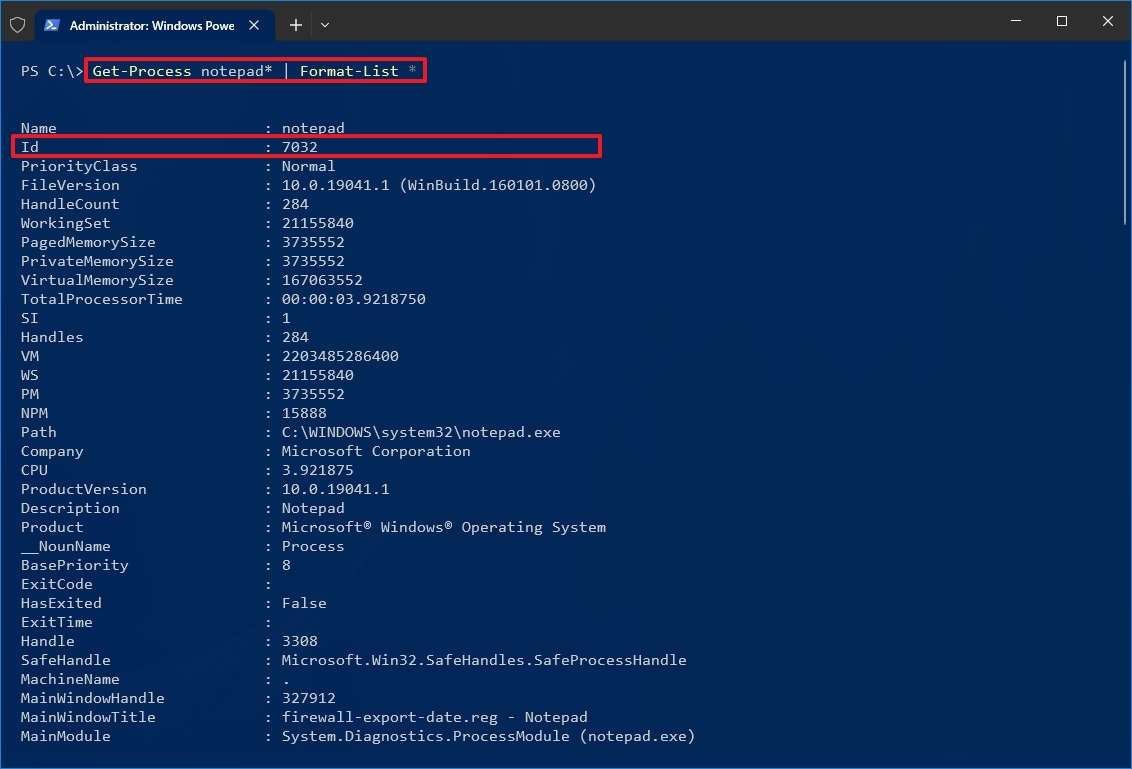
- Type the following command to view information (including ID) about a process and press Enter: Get-Process PROCESS-NAME* | Format-List *
In the command, make sure to replace PROCESS-NAME with the «.exe» name of the process. The * is a wildcard to match part of the name without having to type the exact name of the process. This example shows the Notepad Process ID and all the available information about the process: Get-Process notepad* | Format-List *
- Type the following command to determine the ID and owner of the process and press Enter: Get-Process PROCESS-NAME* -IncludeUserName
In the command, make sure to replace PROCESS-NAME with the «.exe» name of the process. The * is a wildcard to match part of the name without having to type the exact name of the process. This example shows the processes for Notepad: Get-Process notepad* -IncludeUserName
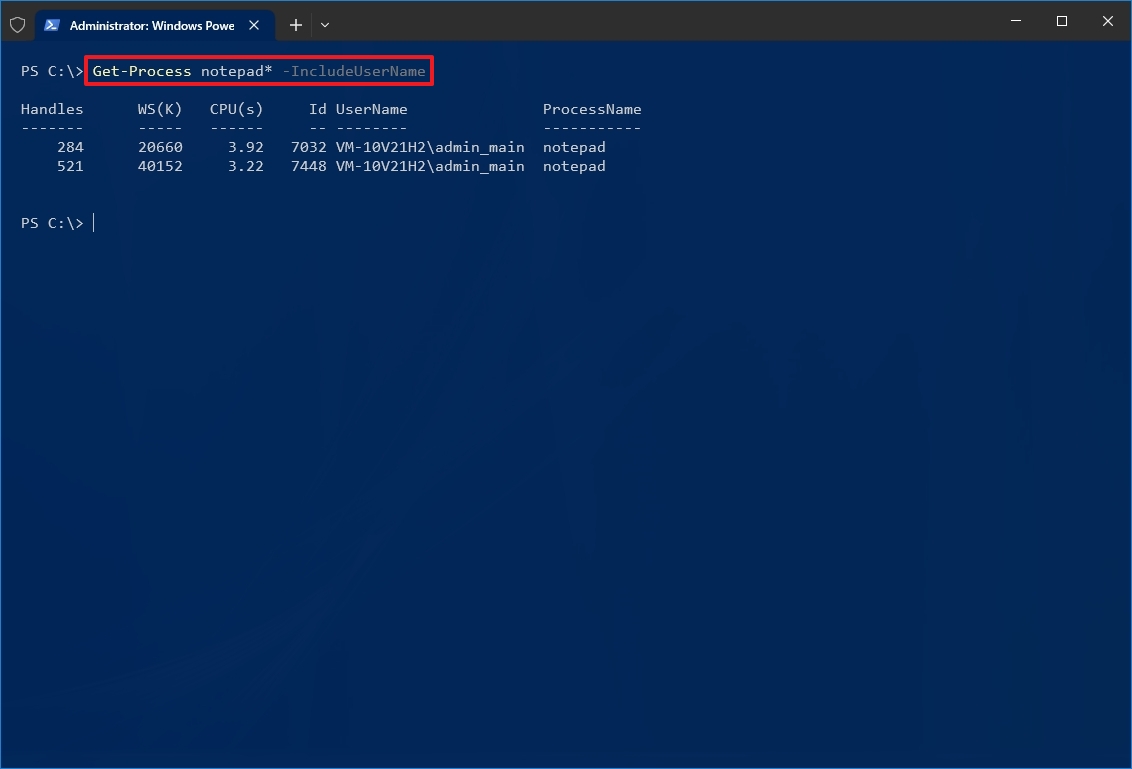
After you complete the steps, the PowerShell output will list the Process ID along with other information about the app or service.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know
Cutting-edge operating system
A refreshed design in Windows 11 enables you to do what you want effortlessly and safely, with biometric logins for encrypted authentication and advanced antivirus defenses.
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
Sign in to your MUO account
In Windows 10, every app, service, or process has an assigned number known as the Process ID. The Process ID (or PID) is mostly used to identify each running or suspended process within a system.
Knowing an app’s PID helps you identify programs running multiple instances, such as when editing two different files using the same app. Also, the PID helps you when you need to terminate a process manually or if you want to check system resources consumed by a certain process.
1. Use the Command Prompt
While you might use Command Prompt to troubleshoot Windows 10 issues, you can also use it to find an app Process ID. Here is how you can do it:
- In the Start menu search bar, search for command prompt and select Run as administrator.
- Type tasklist. Press Enter.
- Command Prompt will now display the PID for the running processes.
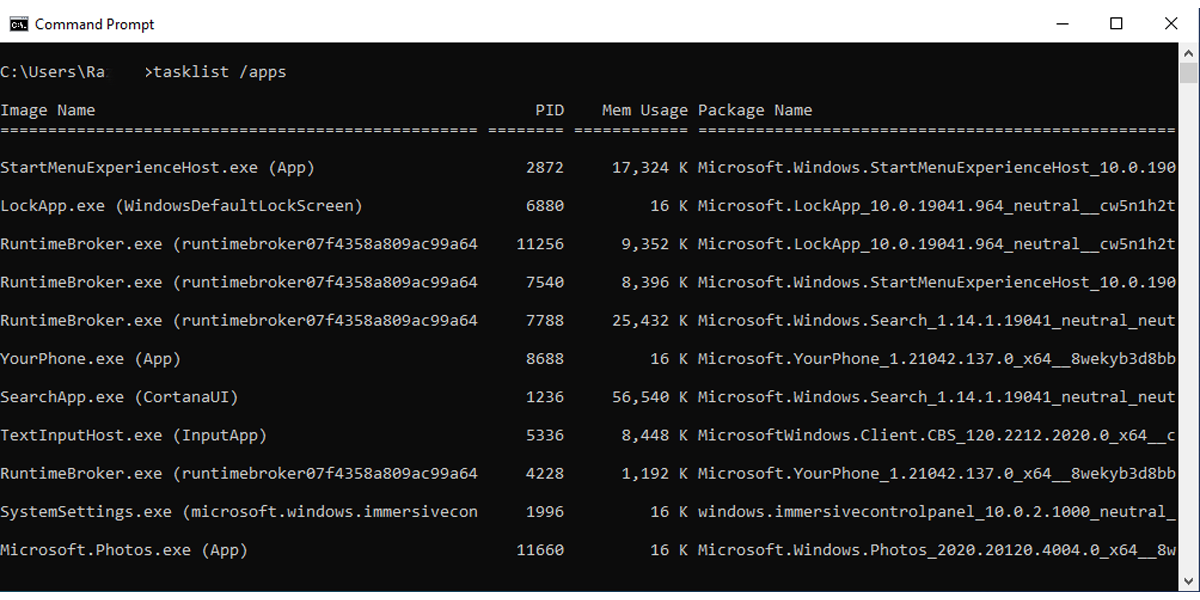
If you want to find out the Process ID for Microsoft Store apps, type tasklist /apps.
2. Use the Task Manager
Follow these steps to check the Process ID using Task Manager:
- Input task manager in the Start menu search bar, right-click the Best match, and select Run as Administrator. Or use the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keyboard shortcut.
- Select the Details tab.
- Check the number next to the app in the PID column.
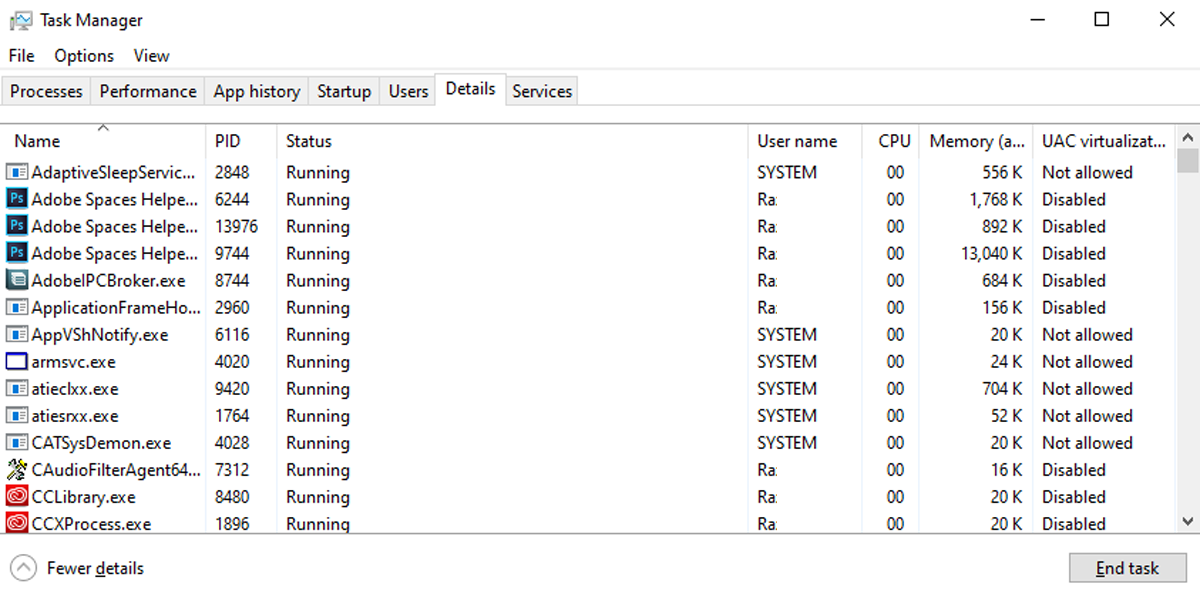
You can also find the PID is displayed within the Services tab.
3. Use PowerShell
Here is how you can check an app’s Process ID using PowerShell:
- In the Start menu search bar, search for powershell and select the Best match.
- Type Get-Process.
- Press Enter.
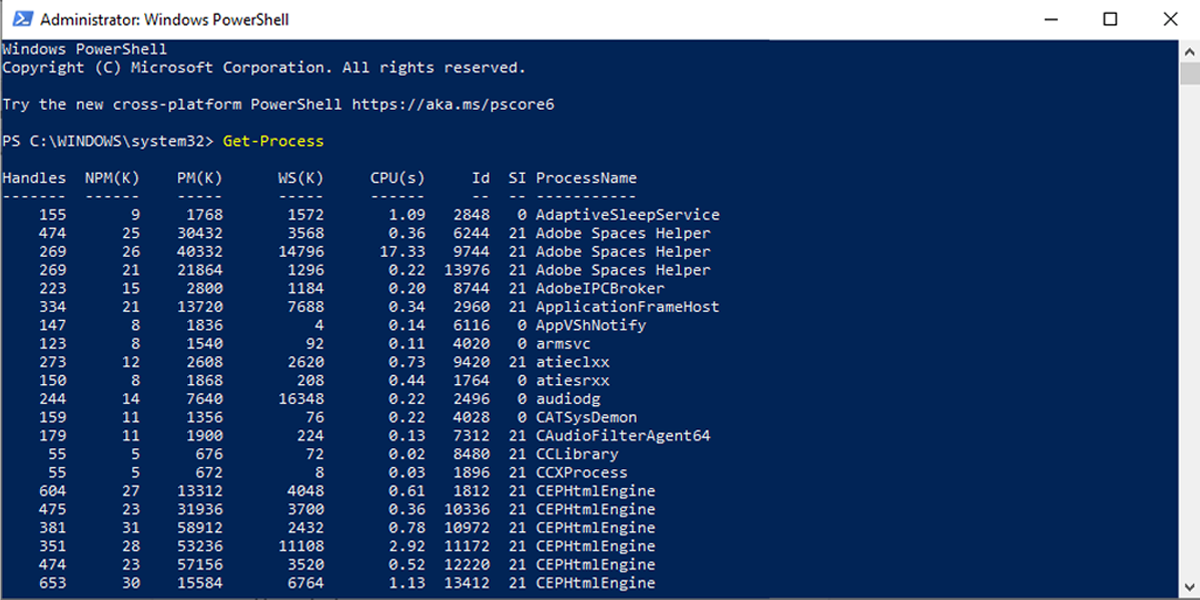
PowerShell will display a list of the app Process IDs together with more information about the apps.
4. Use the Resource Monitor
Resource Monitor is a Windows 10 feature that allows you to check information about hardware and software on your device. Also, you can use it to check an app Process ID easily. Here is how you can do it:
- Input resource monitor in the Start menu search bar. Right-click the Best match and select Run as Administrator.
- Select the CPU tab.
- Check the number next to the app in the PID column.

The Resource Monitor also displays if an app is running or is suspended through the Status column.
If you need to check an app’s Process ID, Windows 10 has at least four ways you can do that. You can use Command Prompt, Task Manager, PowerShell, or Resource Monitor—thankfully, they’re all easy to use.
The process identifier (a.k.a. process ID or PID) is a number used to uniquely identify an active process.
In this short note i will show how to display information about the Windows process (incl. the process name and path to an executable file) by PID from the command-line prompt (CMD) or a Windows PowerShell.
Cool Tip: List processes in Windows from the CMD! Read more →
Execute the tasklist command to get the process name from PID:
C:\> tasklist /FI "pid eq <pid>"
– or –
C:\> tasklist /FI "pid eq <pid>" /V /FO List
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
/FI |
Displays a set of tasks that match a given criteria specified by the filter |
/V |
Displays verbose task information |
/FO |
Specifies the output format |
More information about the process by its PID (including the full path to an executable file) can be retrieved using the wmic command:
C:\> wmic process where "ProcessID=<pid>" get /format:list
Cool Tip: Kill a hanging process in Windows from the CMD! Read more →
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
The tasklist is the Windows command we use to list running processes on a Windows system. Often operates together with taskkill to terminate a running process or processes.
Open a command prompt (CMD or PowerShell), type tasklist, and press Enter:
tasklistThe following screenshot shows the default output of the tasklist command. It shows the Image Name (the name of the program that launched the process), process ID (PID), and the Memory Usage of each task.
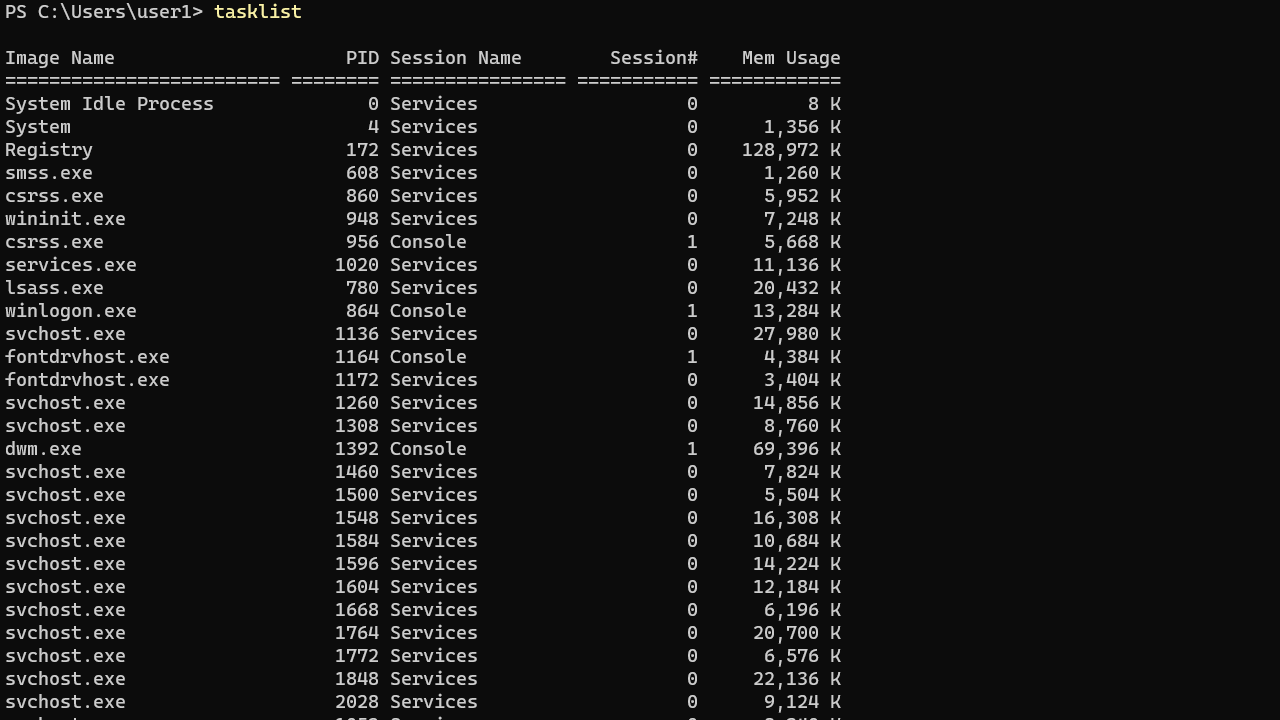
The list can be long, so you may want to pipe the output to the more command (press Enter key to scroll through).
tasklist | moreIf you want to end a process, use the taskkill command to terminate a running process using its process ID (PID) or image name.
taskkill /pid process-ID
taskkill /im image-nameFor example, the following command terminates all instances of the notepad process by its image name.
taskkill /im notepad.exeThe Windows tasklist command supports three output formats: Table (the default), List, and CSV. To change the output format, use the /fo option, as shown in the following example:
tasklist /fo listThe following command saves the current task list into a text file in CSV format:
tasklist /fo csv > tasklist.txtRunning Tasklist Command on a Remote Computer
We can use the tasklist command to list running tasks on a remote computer. Use the /s and /u options to specify the IP Address and username of the remote computer, respectively.
tasklist /s 192.168.1.100 /u user1However, the Firewall must be configured on the remote Windows system to allow the tasklist command. Click the link below for instructions on how to do it.
How to allow tasklist command from Windows Firewall
Command Options
The tasklist command has multiple options, which you can see by typing tasklist /?.
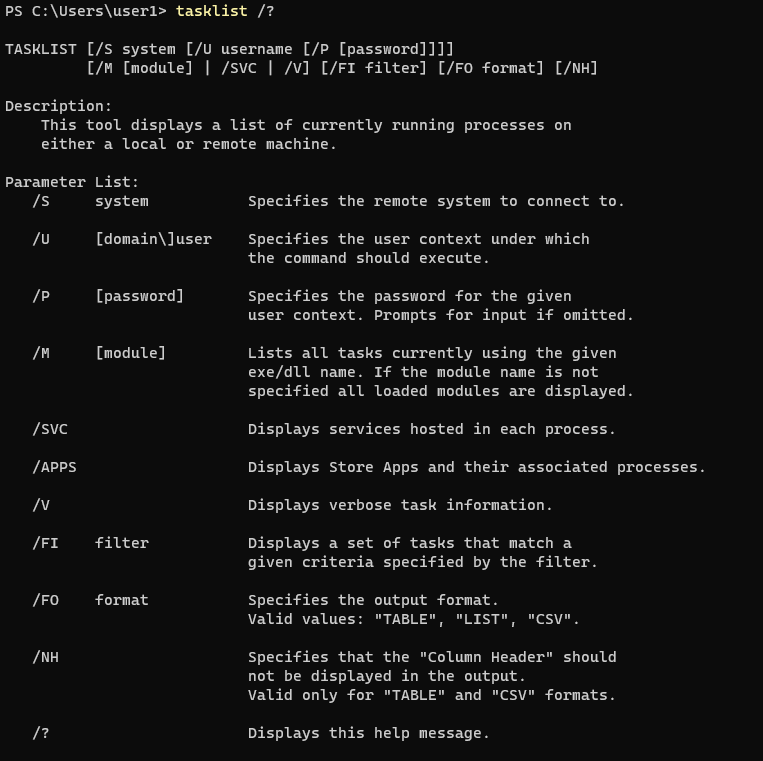
Examples
Use the /V option to display additional information, such as the program’s username and total CPU time:
tasklist /vShow the list of dll files used by each process:
tasklist /mDisplay the services provided by each process:
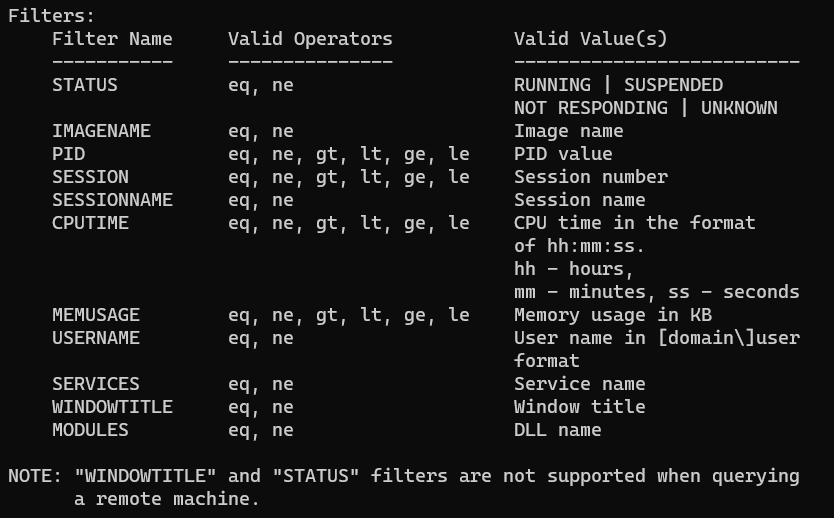
tasklist /svcUsing Filters to List Tasks That Match a Given Criteria
Using the /fi option, you can filter the command output to display the tasks that match the given criteria. The following section presents some examples.
List running processes:
tasklist /fi "status eq running"List tasks that not responding:
tasklist /fi "status eq not responding"List the process that has PID of 0:
tasklist /fi "pid eq 0"List all processes owned by the user user1:
tasklist /fi "username eq user1"Display the services are related the svchost process(es):
tasklist /svc /fi "imagename eq svchost.exe"Show the processes using more than 10MB of memory:
tasklist /fi "memusage gt 10240"You can get a list of all filters by running the tasklist /? command.







