Sometimes Windows system displays error messages regarding corrupted or missing Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx files. Situations like that can occur, for example, during a software installation process. Each software program requires certain resources, libraries, and source data to work properly. Corrupted or nonexistent Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file can therefore effect in failed execution of the started process.
Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file Windows 7 Event Log. The file was developed by Microsoft for use with Office software. Here you will find detailed information about the file and instructions how to proceed in the event of Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx related errors on your device. You can also download Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file compatible with Windows 10, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows 7, Windows 8 devices which will (most probably) allow you to solve the problem.
Compatible with: Windows 10, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows 7, Windows 8
User popularity
Fix Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx errors
- 1 Information about Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file
- 2 Errors related to Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file
- 3 How to fix Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx related errors?
- 3.1 Scanning for malicious software
- 3.2 System and driver update
- 3.3 System File Checker tool
- 3.4 System recovery
- 4 Download Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx
- 4.1 List of Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file versions
File info
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Filename | Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx |
| File extension | EVTX |
| Type | System |
| Description | Windows 7 Event Log |
| Software | |
|---|---|
| Program | Office 2010 |
| Software | Office |
| Author | Microsoft |
| Software version | 2010 |
| Details | |
|---|---|
| File size | 69632 |
| Oldest file | 2017-04-24 |
| Latest file | 2017-05-10 |

There are various types of errors related to Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file. Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file may be located in wrong file directory on your device, may not be present in the system, or may be infected with malicious software and therefore not work correctly. Below is a list of most common error messages related to Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file. If you encounter one listed below (or similar), please consider the following suggestions.
- Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx is corrupted
- Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx cannot be located
- Runtime Error — Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx
- Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file error
- Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file cannot be loaded. Module was not found
- cannot register Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file:
- Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file could not be loaded
- Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file doesn’t exist
Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx
Application could not be started because Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file is missing. Reinstall the application to solve the problem.
OK
Problems related to Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx can be addressed in various ways. Some methods are meant only for advanced users. If you don’t have confidence in your skills, we suggest consulting a specialist. Fixing Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file errors should be approached with utmost caution for any mistakes can result in unstable or unproperly working system. If you have the necassary skills, please proceed.
Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file errors can be caused by various factors, so its is beneficial to try to fix them using various methods.
Step 1: Scan your computer for any malicious software
Windows files are commonly attacked by malicious software that prevents them from working properly. First step in addressing problems with Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file or any other Windows system files should be scanning the system for malicious software using an antivirus tool.
If by any chance you don’t have any antivirus software installed on your system yet, you should do it immediately. Unprotected system is not only a source of file errors, but, more importantly, makes your system vulnerable to many dangers. If you don’t know which antivirus tool to choose, consult this Wikipedia article – comparison of antivirus software.
Step 2: Update your system and drivers.
Installing relevant Microsoft Windows patches and updates may solve your problems related to Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file. Use dedicated Windows tool to perform the update.
- Go to the Windows «Start» menu
- Type «Windows Update» in the search field
- Choose the appropriate software program (name may vary depending on your system version)
- Check if your system is up to date. If any unapplied updates are listed, install them immediately.
- After the update has been done,restart your computer in order to complete the process.
Beside updating the system, it is recommended that you install latest device drivers, as drivers can influence proper working of Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx or other system files. In order to do so, go to your computer or device producer’s website where you will find information regarding latest driver updates.
Step 4: Restoring Windows system
Another approach is to restore system to previous state, before the Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file error occured. In order to restore your system, follow the instructions below
- Go to the Windows «Start» menu
- Type «System Restore» in the search field
- Start the system restore tool – it’s name may differ depending on version of the system
- The application will guide you through the process – read the messages carefully
- After the process has finished, restart your computer.
If all the above-mentioned methods failed and the Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file problem has not been resolved, proceed to the next step. Remember that the following steps are intended only for advanced users.
Download and replace Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file
The last solution is to manually download and replace Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file in appropriate folder on the disk. Select file version compatible with your operating system and click the «Download» button. Next, go to your web browser’s «Downloaded» folder and copy the downloaded Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file.
Go to the folder where the file should be located and paste the downloaded file. Below is the list of Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file example directory paths.
- Windows 10: C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs\
- Windows 10: C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs\
- Windows 8.1: C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs\
- Windows 8: 1: C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs\
- Windows 7: —
- Windows 7: —
- Windows 8: —
If the steps did not solve your Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx file problem, you should consult a professional. A probability exists that the error(s) might be device-related and therefore should be resolved at the hardware level. A fresh operating system installation might be necessary – a faulty system installation process can result in data loss.
File versions list
Filename
Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx
System
Windows 10
File size
69632 bytes
Date
2017-04-24
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 58b907376bee1b3a39682b6f25275479 | |
| SHA1 | bdb454319956e0dbcb12d4d2f46788837cc51ef8 | |
| SHA256 | 8be6f7167782990c429c86cd83f14701dd619ddee1926de1495c20587308c3e4 | |
| CRC32 | 37d1a186 | |
| Example file location | C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs\ |
Filename
Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx
System
Windows 10
File size
69632 bytes
Date
2017-05-10
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 578f9a37a81fb6dbbadfea7f742ca832 | |
| SHA1 | ea5210b01dce693121c87cf26605e2ded7479990 | |
| SHA256 | 77a04d949ada811beafc64642f7351887efe5b2e6b071ce9d455d19b1d5a6644 | |
| CRC32 | d280f9d4 | |
| Example file location | C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs\ |
Filename
Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx
System
Windows 8.1
File size
69632 bytes
Date
2017-04-24
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 1f9333b8af8c1f2fcea9d602de3cb14d | |
| SHA1 | 510a080295c9cf26cba564566492bb6055527c46 | |
| SHA256 | 59d80d254d4fa3238781bc8ddd83c1438e7c034d298f2d4860b751bab5fde6af | |
| CRC32 | bcc2c1b3 | |
| Example file location | C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs\ |
Filename
Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx
System
Windows 8
File size
69632 bytes
Date
2017-04-24
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | e5f2df3d9efbd9473fe1ca4d9525c4d9 | |
| SHA1 | b4eeb6da6d0ebeac629091d1faa4b08d9b4fbd6f | |
| SHA256 | 8259cb6564b5c44c4b8dd2080e3517636164a5b09a6328ea769e1943cce6ccbb | |
| CRC32 | 20cb7578 | |
| Example file location | 1: C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs\ |
Filename
Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx
System
Windows 7
File size
69632 bytes
Date
-0001-11-30
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 4ce520b215b8ab189ac858d32da8a5e0 | |
| SHA1 | 0f0c1bb9673a94d452d1cb6c100464b762ce9107 | |
| SHA256 | 02064ef05b9c71444e4e31243a5b8da0229830e68e4d0457ac67ff1fd38dc843 | |
| CRC32 | 478b0116 | |
| Example file location | — |
Filename
Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx
System
Windows 7
File size
69632 bytes
Date
2017-05-10
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | ea79a7bc1d2f18cb5d83b528ad5f2bd6 | |
| SHA1 | 2a030ccd506a50bab4684c5e6a62be94721f2788 | |
| SHA256 | 94d0d1f16b7dc405535161fc7a164fa7aade7a7489d0bfb83af4d9dfd22cc263 | |
| CRC32 | 597b4e95 | |
| Example file location | — |
Filename
Microsoft-Windows-Known Folders API Service.evtx
System
Windows 8
File size
69632 bytes
Date
2017-05-10
| File details | ||
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 578f9a37a81fb6dbbadfea7f742ca832 | |
| SHA1 | ea5210b01dce693121c87cf26605e2ded7479990 | |
| SHA256 | 77a04d949ada811beafc64642f7351887efe5b2e6b071ce9d455d19b1d5a6644 | |
| CRC32 | d280f9d4 | |
| Example file location | — |
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Appearance settings
Enable the policy “Prevent users from moving their Windows known folder to Onedrive” and select “Leave them” under options. Enable the policy “Prevent users from redirecting their Windows known folder to their PC” Enable the policy “Silent redirect Windows known folder to OneDrive”
- What is known folder move?
- How do I rearrange folders in OneDrive?
- How do I move documents to OneDrive?
- Can you drag and drop folders into OneDrive?
- What are Windows known folders?
- Can’t move the folder because there is folder?
- Can I rename the OneDrive folder?
- How do I move my Downloads folder to OneDrive?
- Can you move shared files in OneDrive?
- How do I automatically sync files to OneDrive?
- Can you copy and paste in OneDrive?
- How do I stop documents being saved to OneDrive?
What is known folder move?
Known Folder Move (KFM) is a set of Group Policy Objects (GPO) settings that attempt to migrate user data into the OneDrive Sync Client with a minimum of user and/or administrator intervention.
How do I rearrange folders in OneDrive?
To move a file or folder on OneDrive.com:
- Browse to the file or folder that you want to move.
- Select the item you want to move. …
- In the top navigation, select Move to.
- In the Move to pane, browse to the destination folder, and then select Move.
How do I move documents to OneDrive?
Select the files you want to upload, and drag them to OneDrive in the File Explorer Navigation pane. Select File > Save a Copy > OneDrive — Personal.
…
With Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome:
- Select Upload > Files or Upload > Folder.
- Select the files or folder you want to upload.
- Select Open or Select Folder.
Can you drag and drop folders into OneDrive?
Select New > Folder to create a folder. From the folder you want to upload, select the files. Drag and drop the files into the new folder you created in OneDrive.
What are Windows known folders?
Known folders are the standard «Desktop,» «Documents,» «Downloads» and «Photos» folders that Microsoft supplies by default within File Explorer on Windows systems. Microsoft also describes known folders as «global pointers in Windows representing a location on the user’s drive.»
Can’t move the folder because there is folder?
When you find that the folder can’t be moved and receive the error “Can’t move the folder because there is a folder in the same location that can’t be redirected”, you can try re-linking OneDrive to your PC or modifying User Shell Folders Registry Key.
Can I rename the OneDrive folder?
Open the OneDrive app (example shows the app on Windows Phone 10). Now tap on the folder that you want to rename and select Rename.
How do I move my Downloads folder to OneDrive?
How to use Onedrive to backup Documents, Downloads, and Desktop folders.
- right-click on Documents.
- select Properties.
- select Location.
- choose Move.
- choose OneDrive\Documents.
- say Yes to move files.
Can you move shared files in OneDrive?
While you can move shared files, you can’t move shared folders on OneDrive.com. If you sync OneDrive to your computer, any shared folder you move is copied to the destination location and then removed from your OneDrive.
How do I automatically sync files to OneDrive?
To do this, open the OneDrive System Tray icon and select Settings. At the Settings screen, click the tab for Account and click the button to Choose folders. Check the box to Sync all files and folders in OneDrive, especially if you unchecked any folders previously.
Can you copy and paste in OneDrive?
In File Explorer, select the document that you want to copy to OneDrive, right‑click, and then select Copy. … In File Explorer, select OneDrive – Red River College in the left‑hand pane, right‑click in the blank space in the middle window, and then select Paste.
How do I stop documents being saved to OneDrive?
Go to PC Settings, using the PC Settings tile in the Start menu, or swipe in from the right edge of the screen, select Settings, and then select Change PC settings. Under PC settings, select OneDrive. On the File Storage tab, turn off the switch at Save documents to OneDrive by default.
This week is a follow up to this post of a few months ago about getting started with Personal Data Encryption (PDE). That post was really focused on the early introduction of PDE and the functionality that it brings to the table, while this post will basically add-on to that functionality and knowledge. PDE is still a pretty unknown feature that is now actually growing in useful functionalities and could become a very welcome addition to the available data protection capabilities on Windows. With the latest version of Windows 11, version 24H2, PDE now also contains the ability to protect personal data in known Windows folders. Those known Windows folders are Documents, Desktop, and Pictures. That provides organizations with more protection capabilities for personal data, as PDE can be used alongside BitLocker. Main addition is that where the decryption key of BitLocker is released during the boot of the device, the decryption key of PDE is released during the sign-in of the user by using Windows Hello for Business. This post is focused on creating more awareness and showing the new really straight forward configuration options.
Note: Keep in mind that PDE for known Windows folders is available for Windows 11, version 24H2, and later.
When looking at the configuration of PDE for known Windows folders, it all starts with the PDE CSP. That CSP is added to Windows 11, since version 22H2. That CSP contains the EnablePersonalDataEncryption node that can be used to enable PDE. Besides that, starting with Windows 11, version 24H2, that CSP now contains related nodes to enable PDE on specific known Windows folders. That means separate nodes for the Documents, Desktop, and Pictures folders. Those nodes are ProtectFolders/ProtectDocuments, ProtectFolders/ProtectDesktop and ProtectFolders/ProtectPictures. With the latest service release (2409) of Microsoft Intune, there is a new disk encryption template available for PDE. That template is named Personal Data Encryption and can be used to easily configure the different PDE settings, by relying on the PDE CSP. The following eight steps walk through the configuration of enabling PDE for known Windows folders, using that new template.
- Open the Microsoft Intune admin center portal and navigate to Endpoint security > Disk encryption
- On the Endpoint security | Disk encryption blade, click Create > New Policy
- On the Create a profile blade, select Windows > Personal Data Encryption and click Create
- On the Basics page, provide at least a unique name to distinguish it from similar profiles and click Next
- On the Configuration settings page, as shown below in Figure 1, configure the following and click Next
- Switch the slider with Enable Personal Data Encryption (User) to Enable Personal Data Encryption (1)
- Protect Pictures (User): Select Enable PDE on folder (A)
- Protect Documents (User): Select Enable PDE on folder (B)
- Protect Desktop (User): Select Enable PDE on folder (C)

- On the Scope tags page, configure the required scope tags and click Next
- On the Assignments page, configure the assignment for the required user or devices and click Next
- On the Review + create page, verify the configuration and click Create
Note: Besides these minimal required settings, also seriously consider configuring the additional hardening settings that are all available within the Settings Catalog to prevent exposure of the encryption keys.
Experiencing Personal Data Encryption for known Windows folders
When the configurations of PDE for known Windows folders are in place, it’s time to look at the user experience. The addition of known Windows folders, makes the configuration of PDE a lot easier to test and verify. Those folders and the files within those folders will be displayed in File Explorer with a yellow lock icon, as shown below in Figure 2 (number 1 and 2). When looking at the Advanced Attributes of those files it will mention the encryption of content, as shown below in Figure 2 (number 3). And when looking at the Details it will clearly show the use of PDE, as shown below in Figure 2 (number 4).

Besides that, something that might even be more obvious, is the message that the user will receive when not using Windows Hello to sign-in. That message was shown in the previous post about getting started with PDE. That message is shown when the user is trying to use something different then Windows Hello, like username-password. In that case, the user will receive the message to use Windows Hello to access files that are encrypted by their organization.
More information
For more information about Personal Data Encryption and the configuration, refer to the following docs.
- PDE CSP – Windows Client Management | Microsoft Learn
- Personal Data Encryption (PDE) – Windows Security | Microsoft Learn
- PDE settings and configuration – Windows Security | Microsoft Learn
- Frequently asked questions for Personal Data Encryption (PDE) – Windows Security | Microsoft Learn
- Encrypt Windows devices with Intune – Microsoft Intune | Microsoft Learn
Discover more from All about Microsoft Intune
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Known folders are essentially those folders
that the system already knows about — they’re the folders that the
system is designed to provide. The KnownFolders class
contains a host of these folder listings as individual properties. For
example, if you want to access a list of entries in the Administrative
Tools folder of the Control Panel, you use the KnownFolders.AdminTools
property. In fact, you might be surprised at just how many folders it
contains. Here’s a list of the folders you can access (including a
special All property that accesses all the known folders):
| AddNewPrograms | AdminTools | All |
| AppUpdates | CDBurning | ChangeRemovePrograms |
| CommonAdminTools | CommonOEMLinks | CommonPrograms |
| CommonStartMenu | CommonStartup | CommonTemplates |
| Computer | Conflict | Connections |
| Contacts | ControlPanel | Cookies |
| Desktop | DeviceMetadataStore | Documents |
| DocumentsLibrary | Downloads | Favorites |
| Fonts | Games | GameTasks |
| History | ImplicitAppShortcuts | Internet |
| InternetCache | Libraries | Links |
| LocalAppData | LocalAppDataLow | LocalizedResourcesDir |
| Music | MusicLibrary | NetHood |
| Network | OriginalImages | OtherUsers |
| PhotoAlbums | Pictures | PicturesLibrary |
| Playlists | Printers | PrintHood |
| Profile | ProgramData | ProgramFiles |
| ProgramFilesCommon | ProgramFilesCommonX64 | ProgramFilesCommonX86 |
| ProgramFilesX64 | ProgramFilesX86 | Programs |
| Public | PublicDesktop | PublicDocuments |
| PublicDownloads | PublicGameTasks | PublicMusic |
| PublicPictures | PublicRingtones | PublicVideos |
| QuickLaunch | Recent | RecordedTV |
| RecordedTVLibrary | RecycleBin | ResourceDir |
| Ringtones | RoamingAppData | SampleMusic |
| SamplePictures | SamplePlaylists | SampleVideos |
| SavedGames | SavedSearches | SearchCsc |
| SearchHome | SearchMapi | SendTo |
| SidebarDefaultParts | SidebarParts | StartMenu |
| Startup | SyncManager | SyncResults |
| SyncSetup | System | SystemX86 |
| Templates | TreeProperties | UserPinned |
| UserProfiles | UserProgramFiles | UserProgramFilesCommon |
| UsersFiles | UsersLibraries | Videos |
| VideosLibrary | Windows |
The purpose of the KnownFolders class is to
provide you with quick access to every common folder on a system. You
obtain a substantial amount of information about the entries as well.
For example, you can determine whether an entry is simply a link or a
real file. It’s also possible to obtain a list of properties for the
entry. Although the Known Folders example described in the sections
that follow works exclusively with the KnownFolders.Documents property, it does show you what you can achieve using any of the KnownFolder properties.
1. Configuring the Known Folders Example
This example begins with a Windows Forms application. You’ll need to add a List button (btnList) to obtain a list of the known folders and their content, and a list box (lstOutput) to output the results of the query. In addition, you’ll need to add a reference to Microsoft.WindowsAPICodePack.Shell.DLL and provide the following using statement:
using Microsoft.WindowsAPICodePack.Shell;
2. Writing the Known Folders Example Code
The Known Folders example provides you with a view of the kinds of information you can obtain from the KnownFolders.Documents property — it doesn’t describe every kind of information you can obtain. All the KnownFolders properties will provide similar sorts of information. Listing 1 shows the code you need for this example.
Example 1. Displaying known folder information
private void btnList_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Clear the previous information.
lstOutput.Items.Clear();// Display generic information about the Documents
// known folder.
lstOutput.Items.Add("Documents Known Folder:");
lstOutput.Items.Add("\tCanonical Name: " +
KnownFolders.Documents.CanonicalName);
lstOutput.Items.Add("\tCategory: " +
KnownFolders.Documents.Category);
lstOutput.Items.Add("\tDefinition Options: " +
KnownFolders.Documents.DefinitionOptions);
lstOutput.Items.Add("\tFile Attributes: " +
KnownFolders.Documents.FileAttributes);
lstOutput.Items.Add("\tFolder ID: " +
KnownFolders.Documents.FolderId);
lstOutput.Items.Add("\tLocalized Name: " +
KnownFolders.Documents.LocalizedName);
lstOutput.Items.Add("\tLocalized Name Resource ID: " +
KnownFolders.Documents.LocalizedNameResourceId);
lstOutput.Items.Add("\tPath: " +
KnownFolders.Documents.Path);
lstOutput.Items.Add("\tRelative Path: " +
KnownFolders.Documents.RelativePath);// Add a space prior to enumeration.
lstOutput.Items.Add("");// Enumerate the content of the Documents known folder.
foreach (var Document in KnownFolders.Documents)
{
// Output generic object information.
lstOutput.Items.Add("Document Type: " + Document.GetType());
lstOutput.Items.Add("Document Name: " + Document.Name);
lstOutput.Items.Add("Display Name: " +
Document.GetDisplayName(DisplayNameType.Url));
lstOutput.Items.Add("Is this a FileSystem object? " +
Document.IsFileSystemObject);
lstOutput.Items.Add("Is this a link? " + Document.IsLink);// If this is a ShellFileSystemFolder, output some
// additional information.
if (Document.GetType() == typeof(ShellFileSystemFolder))
{
// Convert to a specific type.
ShellFileSystemFolder ThisFolder =
(ShellFileSystemFolder)Document;// Display the ShellfileSystemFolder information.
lstOutput.Items.Add("Parsing Name: " +
ThisFolder.ParsingName);
lstOutput.Items.Add("Path: " + ThisFolder.Path);// Enumerate the documents in the folder.
lstOutput.Items.Add("Contents:");
foreach (var FolderDoc in ThisFolder)
{
lstOutput.Items.Add("\tName: " + FolderDoc.Name);
}
}// Add a space between items.
lstOutput.Items.Add("");
}
}
Each KnownFolders property provides some
basic information about the folder as a whole, so the application
begins by displaying this information. Some information, such as KnownFolders.Documents.Path, appears as a simple string, while other information appears as part of an enumeration, such as KnownFolders.Documents.DefinitionOptions.
These top-level properties are always enumerable because they contain
other elements such as files and folders. So after the code displays
the basic information about the folder, it begins displaying
information about the folder content using a foreach loop.
Notice that the code defines Document as type var. That’s because Document
can be of several different types, depending on the content of the
selected folder. In this case, the two most common content types are ShellFile (for files) and ShellFileSystemFolder (for folders). You could also see a ShellLink object in this case. The point is that you can’t assume anything about the content of Document.
The IDE is smart enough to provide you with a list of basic properties common to all the objects that Document
contains. The code displays a number of these items on-screen. Most of
the properties are simple strings. However, at least one property,
named Properties, is extremely complex, as shown in Figure 1. In this case, there are 43 properties used to define the ShellFile, AccessODBC.DSN, and Figure 1 shows just two of them. You can use Properties to discover significant details about the object in question.
Figure 1. Some properties, such as the one named Properties, are extremely complex.
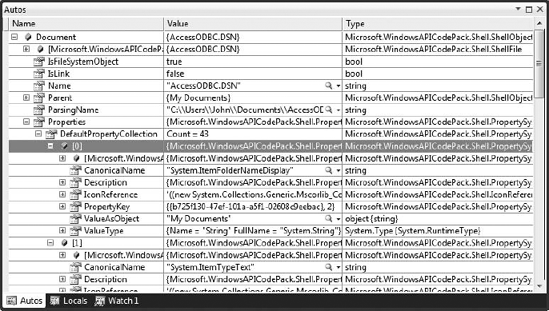
Most of the entries provided as output in this example are properties. However, there’s one method you need to know about, GetDisplayName().
This method comes in handy because it lets you present the display name
for an object using a special format. In this case, the example
presents the display name using the DisplayNameType.Url format.
You need to become familiar with the objects that a particular KnownFolders property can contain. For example, the KnownFolders.Documents property can contain objects of type ShellFileSystemFolder,
which has some special properties. In order to process this special
information, the code first compares the type of the current Document object to typeof(ShellFileSystemFolder). If the object types are the same, the code displays properties that are special for a ShellFileSystemFolder object, such as Path.
Figure 2. Known folder listings tell you a lot about the structure of data on a system.
A ShellFileSystemFolder object is
a container that can hold other objects. The example only processes one
level of objects. Normally, you’d build a recursive routine to parse
the entire folder tree. In this case, the output simply contains the
name of each object within the ShellFileSystemFolder object. Figure 2 shows typical output from this example.
