Introduction
Firewalls are a critical component of securing modern networks with internet access. Without firewalls in place, malicious actors could easily access and infect devices on a network. Properly configured firewalls substantially reduce undesirable communications.
This article explains how to create firewall rules using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console and Windows PowerShell on Windows Server 2016 / 2019 / 2022.
What is a Firewall?
A firewall controls the flow of data packets in and out of a network. It acts like a barrier, similar to how a physical firewall prevents the spread of fire between compartments. The firewall allows or blocks connections according to configured firewall rules.
Computers behind a firewall cannot receive data until it passes the filters. This greatly enhances security and reduces unauthorized access risks. Benefits of firewalls:
- Protect devices by blocking undesired traffic
- Notify administrators of connection attempts
- Log activity for monitoring
- Prevent spread of infections
- Reduce hacking risks
How Windows Server 2016 / 2019 / 2022 Firewalls Work
The Windows firewall acts as a barrier between local network devices and external networks. When a connection is attempted to a server, the firewall intercepts the traffic and evaluates it against the defined rules.
Only network packets that match the configured rules are allowed through. For example, a rule could allow TCP traffic on port 80 while blocking other ports. Carefully configured rules optimize security while allowing desired connections.
Windows provides inbound rules to control incoming traffic and outbound rules to filter outgoing traffic. Rules can be tailored for each network profile.
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security provides the management interface for configuring Windows firewall settings. It comes built-in to Windows Server without needing additional licensing or hardware.
There are three default firewall profiles:
- Domain – For corporate networks with detected domain controllers
- Private – For home or office networks behind a gateway device
- Public – For untrusted public networks with internet access
Profiles allow custom rules per network type. You can enable, disable, or configure profiles independently.
Accessing the Firewall Console
To open the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console:
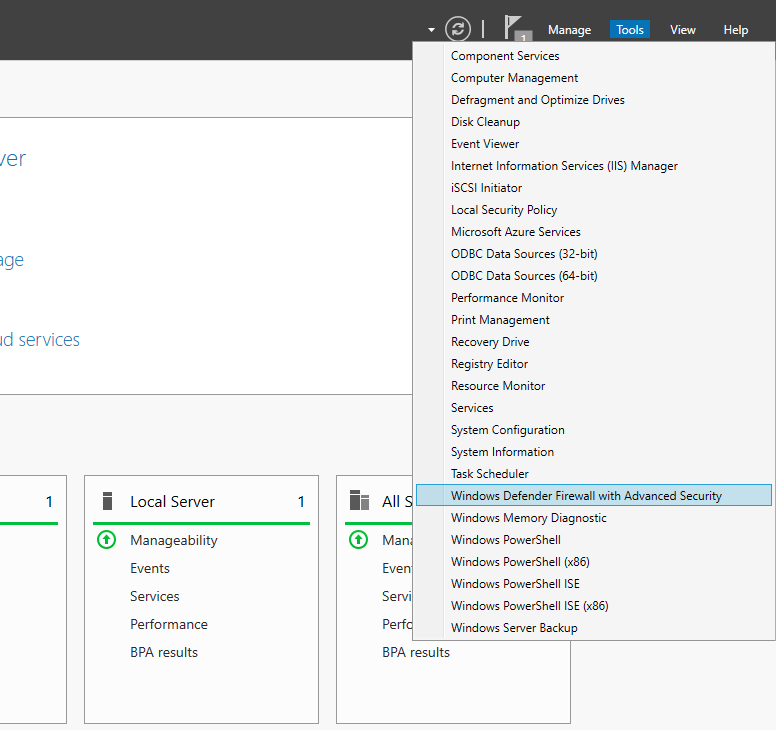
- Open Server Manager > Tools > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
- Search for “firewall” in the Start menu and launch the Windows Firewall shortcut
- Run wf.msc in the Run command (Win + R)
The left menu allows configuring inbound rules, outbound rules, connection security, and monitoring.
Configuring Firewall Rules
Firewall rules control whether to allow or block specific network connections. Rules can filter by:
- Program path
- Port and protocol
- Predefined service
- Source/destination IP
- Network interface
- And more…
Follow these steps to create an inbound firewall rule:
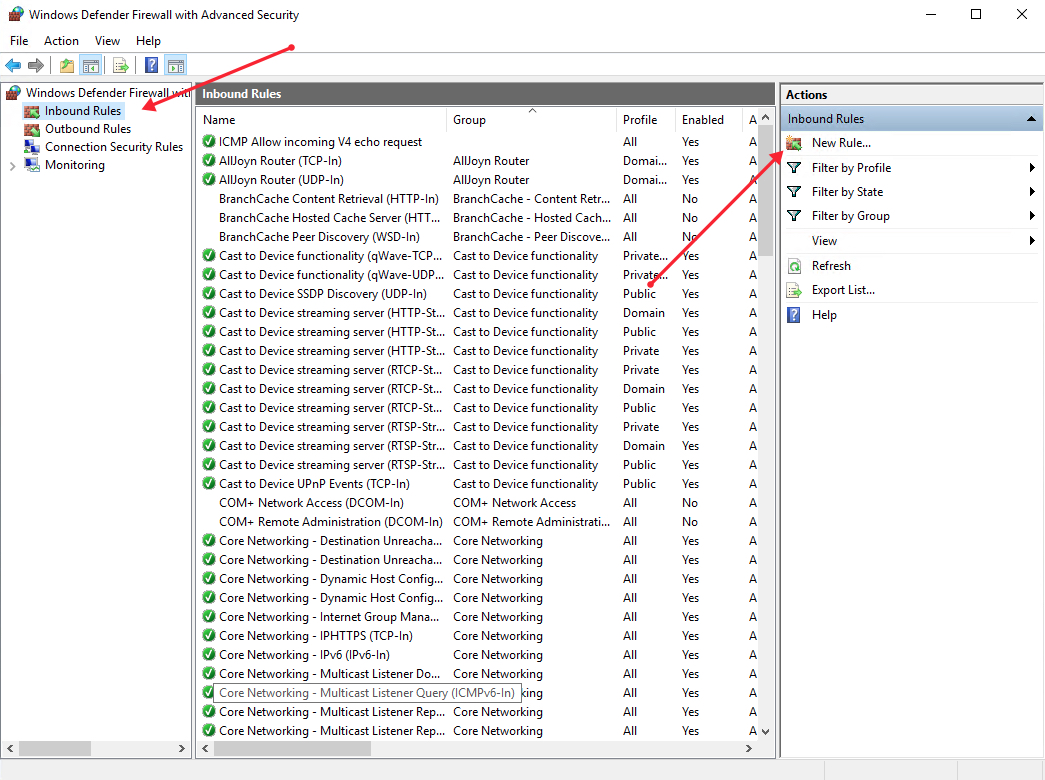
1. Open the Firewall console and select Inbound Rules
2. Click New Rule to launch the rule wizard
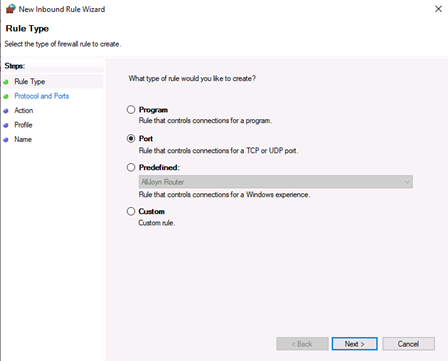
3. Select the rule type – Program, Port, Predefined, or Custom
4. Choose All Programs or a Program path
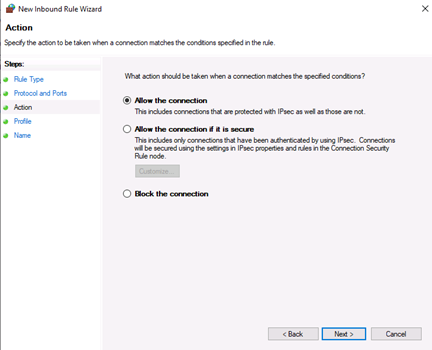
5. Choose Action (allow or block) or allow if connection is secured
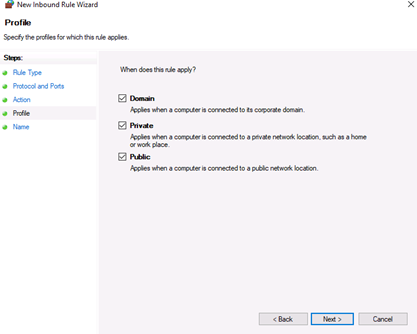
6. Choose profiles
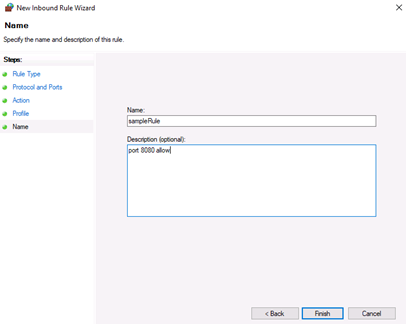
7. Name the rule and click Finish
Repeat the wizard for outbound rules. Once created, rules can be edited or disabled from the console.
Rules can also be created from PowerShell. For example:
PS C:\Users\Administrator> New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Allow SSH" -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 22Monitor active connections under the Monitoring tab.
Conclusion
The Windows Firewall provides a flexible and granular rule-based firewall solution for Windows Server 2016, 2019 and 2022. The advanced interface allows creating detailed rules to filter incoming and outgoing traffic as needed. Monitor activity to verify your rules are working correctly. Careful configuration enhances security while allowing desired connections.
Windows Server 2019 contains a firewall program called Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security. The firewall filters incoming and outgoing traffic on your Windows Server 2019 instance to safeguard it from common network attacks. By default, the firewall is configured to allow access to all pre-installed system programs.
However, several programs may use multiple different ports for operation, and these will be automatically blocked because they don’t match with the rules in your firewall configuration. In this case, you need to open the specific port on Windows Server.
Prerequisites
- Deploy a Windows Server 2019 Instance on Vultr
- A Remote Desktop Connection App
Establish a connection to your server by logging in through any remote desktop app or click the console on your Vultr dashboard to access your server. After you connect you can start configuring your Windows server 2019 firewall rules.
Turn Windows Firewall ON
By default, Windows Defender Firewall is turned on, but in any case, you should confirm the current status and turn on firewall. To do this, click the tools node under server manager and select Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security from the drop down list.
From the open group policy management window, check the current status of Windows Firewall profiles if it is set to ON; otherwise, click the Windows Defender Firewall properties option and turn the service on per profile.
Firewall Rules
Windows Firewall rules allow you to either permit or block specific incoming and outgoing network packets on your server. You can choose multiple parameters for each inbound or outbound rule. A rule can consist of a TCP or UDP port, program name, service, or a protocol to filter for every server profile.
Windows server profiles are grouped into, Domain, Private and Public. Domain represents your server’s connection to a corporate domain network, Private applies to your home or workplace network connection, and Public represents non-secure public network locations.
Open an Inbound Port (Incoming connections)
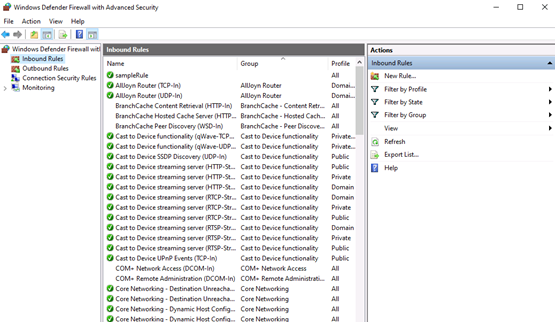
Launch windows defender firewall from the tools sub-menu under server manager. Then, select Inbound Rules on the left panel of the Firewall console.
A list of current rules will be displayed. Now, on the left Inbound Rules sub-menu under actions, click New Rule.
Select Port as the rule type in the rule wizard and click Next.
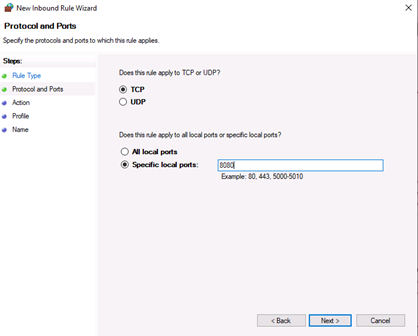
Now, choose whether the new rule applies to a TCP or UDP port on your server. Then, select specific ports and enter your target port number, you can enter a ports range, or multiple ports separated by - and , respectively, then click Next.
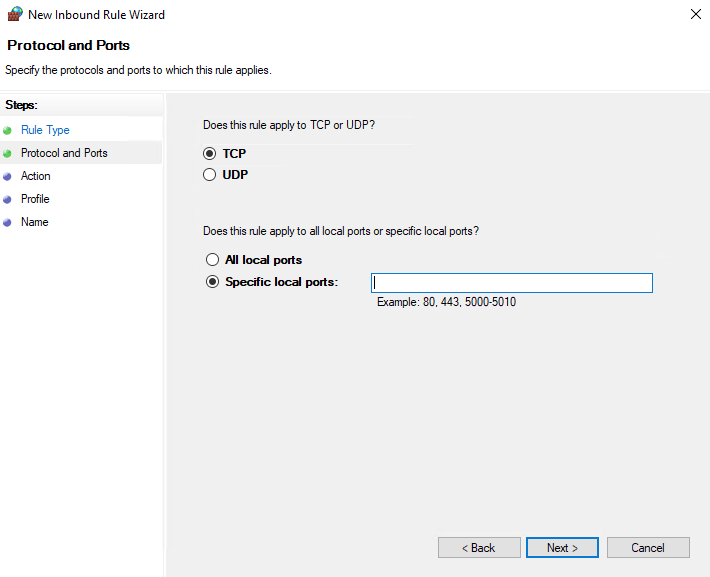
Define your TCP or UDP port rule.
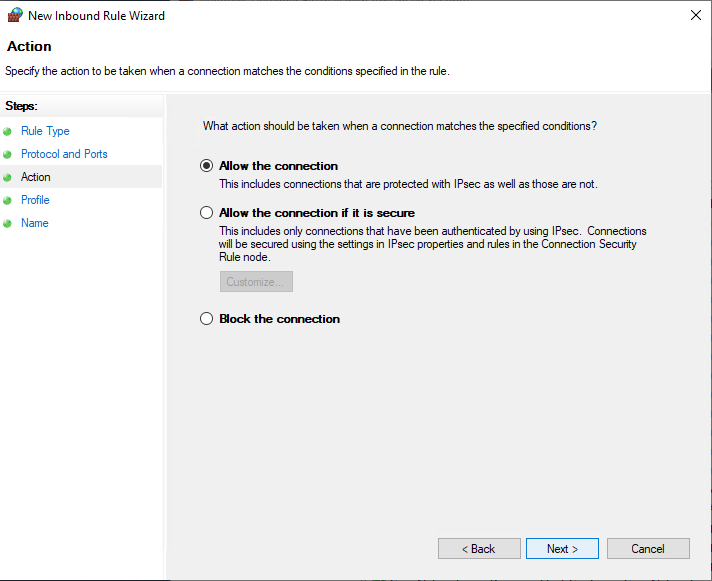
Allow the connectionwill allow incoming connections to the specified server portAllow the connection if it is securewill authenticate with IP security and either deny or allow the connection. For example,httpsconnections will be allowed andhttpblocked.Block the connectionwill block all incoming connections to your server through the specified port
In this case, choose Allow the connection to open the port.
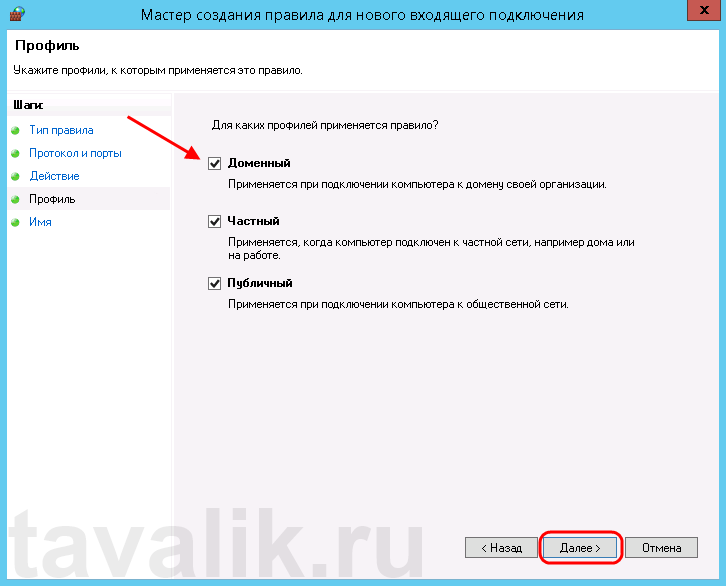
Click Next to assign the new rule to one or more profiles. You can select between Domain, Private, and Public, or choose all to apply the firewall rule on multiple profiles.
Next, give your new firewall rule a custom name and description for easy identification. Then, Click finish to enable the new rule. Your new Inbound (Incoming) port rule will be enabled, and all connections to the server that match the port will be accepted.
Open an Outbound Port (Outgoing connection)
From the Windows Defender Firewall console, click Outbound Rules on the left pane, and a list of available outgoing connection rules will be displayed.
Now, click New Rule on the right pane under the outbound rules node.
In the new outbound rule wizard, select Port as the rule type and click Next.
Now, let’s choose whether the new rule applies to a TCP or UDP port. Then, select specific remote ports and enter the target server port number; you can enter a range of ports, a single port, or multiple different ports you intend to open.
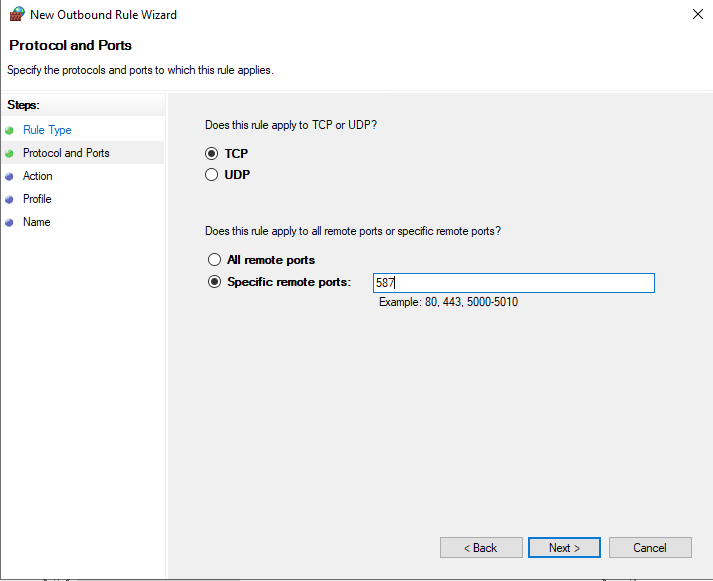
Next, on the Action page, select Allow the connection, then click next to select the server profile on which the rule should be enabled.
Give the new outbound rule a name and description that uniquely describes it. Then, click Finish to enable the outbound rule for the target port to be open on all selected server profiles.
Open a Port through Windows PowerShell
From the Windows start menu, open PowerShell. Then, edit the following command and replace it with your settings.
New-NetFirewallRule -Enabled:True -LocalPort 21 -Protocol TCP -Direction Inbound -Profile Domain -Action Allow -DisplayName example opening a port rule" New-NetFirewallRuleCreates a new Firewall rule.EnabledThis enables the new rule, by default, it will be set to True.LocalPortYour target port number.ProtocolSpecifies the protocol associated with your port number.DirectionSets your target direction to either Inbound (Incoming) or Outbound (Outgoing).ProfileAssigns the new rule to a server profile; you can choose domain, private, or public.Actiondefines the state for the new firewall rule, enter allow.DisplayNamesets a custom name for the new firewall rule
Your Output should be similar to the one below.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> New-NetFirewallRule -Enabled:True -LocalPort 21 -Protocol TCP -Direction Inbound -Profile Domain -Action Allow -DisplayName "example opening a port rule"
Name : {427a1b12-ece6-4d54-847d-de482b227c6c}
DisplayName : example opening a port rule
Description :
DisplayGroup :
Group :
Enabled : True
Profile : Domain
Platform : {}
Direction : Inbound
Action : Allow
EdgeTraversalPolicy : Block
LooseSourceMapping : False
LocalOnlyMapping : False
Owner :
PrimaryStatus : OK
Status : The rule was parsed successfully from the store. (65536)
EnforcementStatus : NotApplicable
PolicyStoreSource : PersistentStore
PolicyStoreSourceType : LocalCongratulations, you just opened a network port on your Windows Server 2019. The server will accept incoming and outgoing connections through the selected ports, but the firewall will block connections from a profile that doesn’t match the port rule.
Firewall is an integral part of any system and can be used to protect a server against unauthenticated access from the outside world. It helps to prevent hackers from logging into servers on the network. Firewall can also be used to set up specific rules in-order to restrict access to specific ports of the system based on IP address.
The basic functionality of a firewall is to control the incoming and outgoing traffic and choose whether to block a particular connection or let it through based on the defined set of security rules.
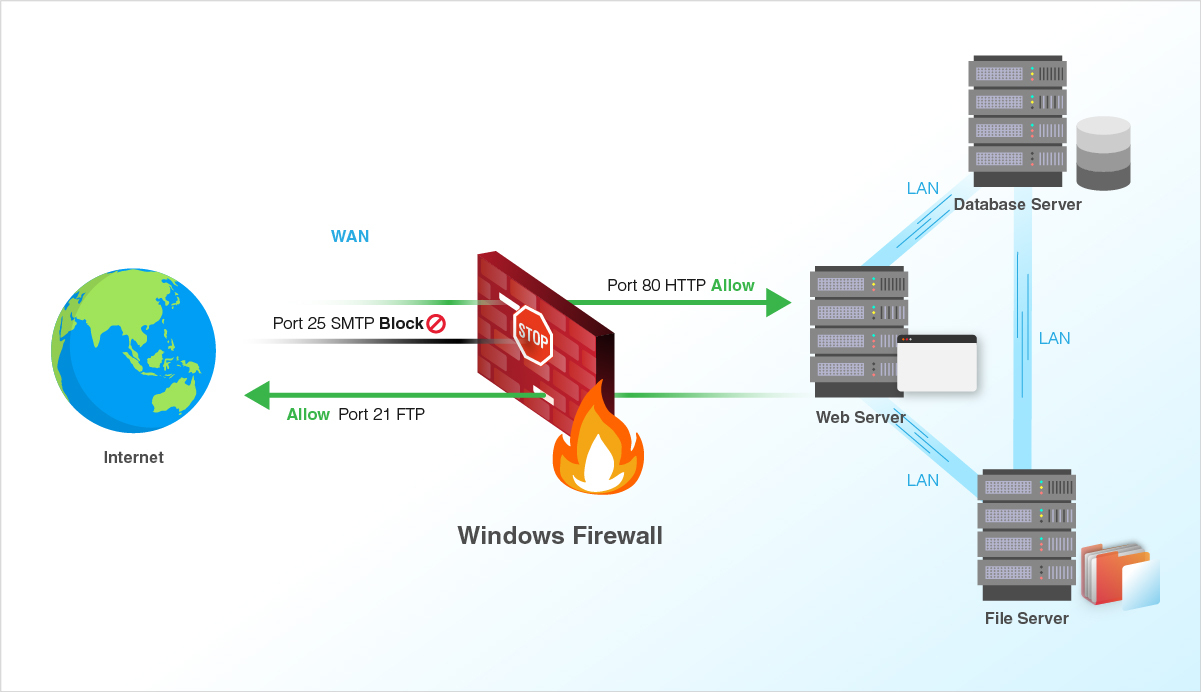
We can use the below steps for managing Windows 2022 firewall settings.
-
Log in to the Windows server and open Firewall using the command
firewall.cplin the run dialog box (*Windows key+R will open Run dialog box). -
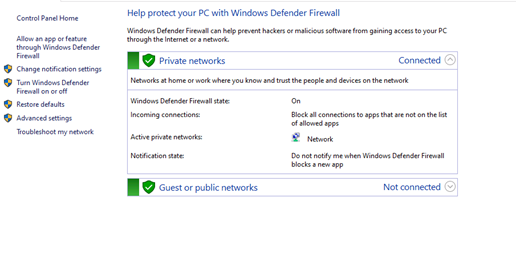
Under firewall settings, there are two sections called
Private networksandGuest or public networkswith green shields to the left of them, which says that the firewall is active. If they are on red shields, then the firewall is disabled. -
Click on either of these sections, it will prompt a
drop-down menuwith details about the current public or private networks. -
Now select the
Advanced settingsoption from the left-hand side of the page.
-
Inbound Rules : Which incoming connections are automatically allowed.
-
Outbound Rules : Which outgoing connections are automatically allowed.
-
Connection Security Rules : Baselines for which connections your computer will allow and which ones it will block.
-
Monitoring : This is an overview of your firewall’s basic monitoring guidelines.
Steps to open/limit a port in Windows 2022
-
Navigate to the
Firewall advanced settingspage. Now select theInbound Rulesoption from the left list options. -
Now right click on the
Inbound Rulesand selectNew Ruleoption. -
Upon selection of the new rule, the box appears and select the
Port. -
Click
Nextand choose the appropriate rule whether it is TCP or UDP and enter your requiredcustom port. -
Now, the action to be performed in the given firewall rule is defined. Choose whether
Allow the connectionorBlock the connection. -
To configure the firewall rule i.e specify the profile in which the rule is to be applied, whether it is public, or private, or a particular Domain.
-
Finally the rule is to be named and saved so as to identify with ease. Click
Finish.
Steps to open/limit a Network in Windows 2022
-
Come to
Advanced Settingsof the Windows firewall and select theInbound Rulesfrom the left pane. -
Now, right-click the rule you wish to configure and then, choose the
Properties.Here you would require to select the rule wisely as below:
-
Allow Particular Network : Create a Firewall rule to Allow a port and use that rule’s properties to edit scope.
-
Block Particular Network : Create a Firewall rule to Block a port and use that rule’s properties to edit scope.
-
Click the
Scope Taband you may be able to add an IP address or a range of IP addresses by clickingAddbutton.You may please select any of the following 2 options and then click
OK.
-
This IP Address or Subnet: Type an IP address (such as 192.168.0.12) or a subnet using Classless Inter Domain Routing (CIDR) notation (such as 192.168.0.0/24) that should be allowed for the firewall rule.
-
This IP Address Range: Using the From and To boxes, type the first and last IP address that should be allowed to use the firewall rule and then click OK.
Related Feature on LayerPanel
- Firewall Overview
Related Tutorials
-
Basic Firewall Information and Rule Setting
-
Setting up Windows Firewall with Advanced Security on Windows Servers 2019
-
Setting up Windows Firewall for your Windows Cloud Servers 2016
-
Installing Telnet Client on Linux and Windows Cloud Servers
-
How to check if TCP / UDP port is open on Linux & Windows Cloud Servers
-
How to Enable & Disable Ping (ICMP Echo Requests) in Windows Server 2022 Firewall
-
How to Enable & Disable Ping (ICMP Echo Requests) in Windows Server 2019 Firewall
-
How to Enable & Disable Ping (ICMP Echo Requests) from IPTables on Linux Cloud Servers
-
Firewall Configuration using Iptables on Ubuntu 14.04
-
How to set up & configure firewall using FirewallD for CentOS 8
-
How to set up & configure Ubuntu Firewall (UFW) for Ubuntu 18
-
How to test Firewall Configuration with Nmap on Linux Cloud Servers
Содержание
- Firewall: настройка межсетевого экрана сервера
- Что это такое?
- Сетевая архитектура
- Создание правила
- Приоритет правил
- Вcтроенный межсетевой экран (firewall) Windows Server 2012 Теретический материал
- Добавление правила в Брандмауэр Windows Server 2012 R2
- Смотрите также:
- Защищаем удаленный сервер на Windows как можем
- За тобой как за огненной стеной
- Защита внутренняя: остановить и не пущать
Firewall: настройка межсетевого экрана сервера
Инструкция по настройке правил Firewall для виртуальных серверов в панели управления Serverspace.
Что это такое?
С помощью межсетевого экрана прямо из панели управления можно управлять доступом к серверу, сетевыми пакетами данных. Данная опция отдельно не тарифицируется и входит в стоимость сервера.
На данный момент существует ограничение в 50 правил, если вам будет недостаточно этого лимита, то увеличить его можно по запросу в техническую поддержку.
Сетевая архитектура
Для избежания конфликта правил межсетевого экрана и его правильной настройки необходимо понимать порядок действия существующих брандмауэров. Во-первых, вы можете настроить брандмауэр для частной сети. Во-вторых, для сервера через панель управления. В-третьих, вы можете настроить внутренний брандмауэр, например, для Linux через iptables, для Windows — встроенный.
Для входящих пакетов первым будет применяться брандмауэр на уровне сети (при наличии). Если пакет прошел, дальше будет применяться фаерволл на уровне сервера, в последнюю очередь будет использоваться внутренний программный механизм. Для исходящих пакетов будет применена обратная последовательность действий.
Мы не рекомендуем одновременно использовать межсетевой экран на уровне сервера и внутренний программный:
Создание правила
Конфигурация брандмауэра доступна для всех VPS и находится в настройках сервера в разделе Firewall.
Важно:
— порядок правил имеет значение, чем меньше порядковый номер правила (чем выше он в списке), тем выше его приоритет. Изменять последовательность правил можно с помощью Drag and Drop, перетащив правило левой кнопкой мыши на нужную позицию;
— по умолчанию — все пакеты данных, как входящие, так и исходящие разрешены.
Для создания правила нажмите кнопку Добавить:
Перед вами откроется окно добавления правила. Необходимо заполнить следующие поля:
Для создания правила нажмите Сохранить.
В нашем примере правило блокирует все входящие на сервер пакеты:
Чтобы созданное правило вступило в силу необходимо сохранить изменения с помощью кнопки Сохранить. Вы можете создать несколько правил и затем сохранить все разом:
После этого страница будет выглядеть следующим образом:
Приоритет правил
Чем меньше порядковый номер правила (чем выше оно в списке), тем выше его приоритет. Например, после того как было создано запрещающее правило для всего входящего трафика, создадим правило разрешающее получать входящие пакеты по 80 порту протокола Tcp. После сохранения изменений при такой конфигурации данный порт все также будет недоступен, в связи с тем, что запрещающее правило имеет более высокий приоритет:
Для изменения приоритета правил перетащите с помощью левой кнопки мыши разрешающее правило на первое место и сохраните изменения:
После сохранение порядковые номера правил изменятся, а также изменится их приоритет:
Теперь конфигурация брандмауэра позволяет получать пакеты по протоколу Tcp по 80 порту, остальные пакеты проходить не будут.
Источник
Вcтроенный межсетевой экран (firewall) Windows Server 2012 Теретический материал
Вcтроенный межсетевой экран (firewall) Windows Server 2012
Firewall (сетевой экран, брандмауэр) — это система компонентов, предназначенная для защиты информационной системы от внешних и внутренних атак. Он также может служить средством управления доступом к информационным ресурсам вашей компании для внешних и внутренних пользователей.
В круг его задач входит не только обеспечение безопасности, но и другие:
Кэширование, это свойство характерно для сетей, содержащих Web-серверы с большим объемом информации, доступной из Internet; Трансляция сетевых адресов (NAT), возможность применения во внутренней сети любого IP адреса; Фильтрация контента, то есть ограничение информации, получаемой из Internet; Переадресация, путем изменения запросов, распределение нагрузки между несколькими серверами.
Сочетание этих возможностей дает определенные преимущества в защите рабочих станций и серверов.
Основные механизмы для пропускания и блокирования трафика:
Фильтр пакетов, принимающий решения на основе анализа заголовков пакетов; Proxy-серверы, контроль на уровне приложений; Шифрование трафика.
Обычно используют сочетание этих механизмов для грамотного планирования системы безопасности сети.
Персональный межсетевой экран появился в операционных системах семейства Windows, начиная с Windows XP / Windows Server 2003. В Windows Server 2012 возможности этого компонента существенно расширены, что позволяет более гибко производить настройки.
Текущие настройки можно посмотреть, запустив из Диспетчера серверов брандмауэр.
Брандмауэр позволяет настраивать правила для входящих и исходящих подключений. А также – правила безопасности подключений.
Правила настраиваются отдельно для входящих и отдельно – для исходящих подключений.
Щелкаем (справа) «Создать правило».
Данный файервол является шлюзом как сетевого, так и прикладного уровней.
Поэтому мы можем создать правило как для программы, так и для порта.
Задание №1. Создайте правило, разрешающее исходящие соединения с сервером по порту 80 (TCP).
Далее необходимо выбрать протокол, по которому будет произведено соединение
После этого мы можем настроить действие с пакетами: можем разрешить подключение по указанному порту, можем – разрешить безопасное подключение (pptp, l2tp+ipsec), либо заблокировать подключение.
Далее создаём профиль, для которого применяется подключение.
И задаём имя правила.
Создайте правило, разрешающее подключение по протоколам PPTP, SSL, HTTP, FTP, Telnet для данного сервера.
Сделайте ваш сервер веб-сервером и FTP-сервером и попросите друга (с другой виртуалки!), чтобы он попытался подключиться к вашему серверу. Если это удалось сделать, то задание выполнено частично правильно.
Проверять, удаётся ли подключиться по протоколу PPTP и SSL, мы будем позже.
Задание №3. Изучите возможности средства «Наблюдение» за фаерволом. Опишите их назначение в отчёте.
Задание №4. Создайте правило, разрешающее отсылку ICMP-пакетов echo reguest. Проверьте его работу для какого-нибудь узла из локальной или внешней сети, используя его ip-адрес (например, командой ping 192.168.0.10 можно проверить доступность компьютера с указанным адресом). Если ответ пришел, можно переходить ко второй части задания. Если ответа нет, попробуйте найти такой узел, который пришлет ответ.
Задание №5. Создайте правило, запрещающее отсылку icmp-пакетов на данный узел. Проверьте его работу.
Задание №6. Изучите возможности мастера создания правил безопасности для нового подключения. Опишите их назначение в отчёте.
Задание №7. Создайте правило безопасности для туннеля.
Обеспечьте проверку подлинности отправителя (компьютера клиента) сервером на основе сертификата компьютера.
Обеспечьте проверку подлинности соединения между любыми конечными точками туннеля.
Создайте VPN туннель между вашим компьютером и компьютером друга.
Задача №8. Обеспечить обмен электронной почтой между внутренним и внешним SMTP серверами.
Настройте правила в соответствие с таблицей:
Задача №9 (доработка задачи №8). Защитите свою сеть от троянских программ (обращаем внимание и на порт источника).
Защищаемая организация имеет сеть 123.45.0.0/16
Запретить из Интернет доступ в сеть 123.45.0.0/16
Но разрешить доступ в подсеть 123.45.6.0/24 данной сети из сети 135.79.0.0/16
При этом специально запретить в защищаемую сеть доступ из подсети 135.79.6.0/24, за исключением доступа к подсети 123.45.6.0/24
Защищаемая организация имеет сеть 123.4.0.0/16
Входящие соединения TELNET разрешаются только с хостом 123.4.5.6
Входящие соединения SMTP разрешаются только с хостами 123.4.5.7 и 123.4.5.8
Входящий обмен по NNTP разрешается только от сервера новостей 129.6.48.254 и только с хостом 123.4.5.9
ВТОРАЯ ЧАСТЬ ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЙ РАБОТЫ
«Изучение настройки файервола в командной строке».
Все задания этой части (№12-№18) необходимо выполнить в командной строке. Не через графический интерфейс!
Программа netsh. exe позволяет администратору настраивать компьютеры с ОС Windows и наблюдать за ними из командной строки или с помощью пакетного файла.
При использовании средства netsh вводимые команды направляются соответствующим помощникам, которые и производят их выполнение.
Многие из описанных параметров конфигурации можно настроить и с помощью программы netsh.
Расмотрим несколько примеров как создавать правила из командной строки, также эти команды можно использовать при написании своих пакетных сценариев cmd, bat, powershell.
Задача №12. Включите файервол.
Включение и выключение файервола:
Включить брандмауэр: netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state on
Выключить брандмауэр: netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off
Включение отдельных профилей:
netsh advfirewall set domainprofile state on
netsh advfirewall set privateprofile state on
netsh advfirewall set publicprofile state on
Отключите частный профиль. Включите профиль в домене и публичный профиль.
Запретите все входящие соединения и разрешите все исходяшие:
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles firewallpolicy blockinbound, allowoutbound
Для всех профилей Блокировать Разрешать
входящий трафик исходящий
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=»HTTP» protocol=TCP localport=80 action=allow dir=IN
Добавляет правило, разрешающее (action=allow) соединения по протоколу TCP (protocol=TCP) для 80 порта (localport=80) для входящего трафика (dir=IN, dir – от direction – направление. OUT – исходящий трафик, IN – входящий трафик).
Разрешите входящие соединения для 80 порта по протоколам TCP и UDP с консоли.
Запретите исходящие соединения на 80 порт.
Откройте диапазон портов для исходящего UDP трафика
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=» =»Port range» protocol=UDP localport=5000-5100 action=allow dir=OUT
Задача №15. Ограничения по IP адресам
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=»HTTP» protocol=TCP localport=80 action=allow dir=IN remoteip=192.168.0.1
Разрешите входящий трафик от веб-сервера с dns-именем yandex. ru (вы должны определить ip-адрес по dns-имени!)
Разрешите входящий трафик от серверов с адресами 192.168.1.4, 192.168.1.5, 192.168.1.6 и запретите от 192.168.1.10, 192.168.1.11
Возможно ограничение и по подсетям.
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=»HTTP» protocol=TCP localport=80 action=block dir=IN remoteip=10.0.0.0/16
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=»HTTP» protocol=TCP localport=80 action=allow dir=IN remoteip=10.0.0.1-10.0.0.10
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=»HTTP» protocol=TCP localport=80 action=block dir=IN remoteip=localsubnet
Доработайте правило из задачи №15 с использованием адресов подсетей для блокировки и разрешения трафика.
Создайте правило, разрешающее входящий трафик программе C:\Windows\explorer. exe
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=»My Application» dir=in action=allow program=»C:\Windows\Explorer. exe» enable=yes
Дополнительно (не к №17):
При необходимости – возможно и комбинирование параметров. Например:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=»My Application» dir=in action=allow program=»C:\MyApp\MyApp. exe» enable=yes remoteip=157.60.0.1,172.16.0.0/16,LocalSubnet profile=domain
Настройте файервол в соответствие со следующими требованиями:
Запретить доступ в подсеть 172.16.0.0/16 Разрешить доступ в подсеть 192.168.2.0/24 Разрешить входящий и исходящий трафик первым 10 адресам подсети 192.168.3.0/24, всем остальным – запретить. Разрешить входящий и исходящий трафик к серверам (их адреса указаны в таблице).
Контроллер домена и DNS-сервер.
Сервер, к которому необходимо обеспечить доступ по SSH и Telnet.
Причём необходимо запретить доступ к SSH серверу, если пользователь в домене организации. Если находится в своей сети – доступ разрешить.
Разрешить полный доступ в сеть приложениям C:\torrent\torrent. exe, C:\windows\explorer. exe C:\Program Files\radmin\radmin. exe
Определите назначение программы Брандмауэр. Перечислите функции, выполняемые программой Брандмауэр. Каким образом исключить программу или сервис из списка с запрещенным доступом? Какие порты могут быть у клиентских приложений и какие – у серверных? Перечислите порты наиболее популярных серверных приложений.
Источник
Добавление правила в Брандмауэр Windows Server 2012 R2
В данной статье я расскажу как добавить разрешающее правило в Брандмауэр Windows Server 2012 R2 (в Windows Server 2008 R2 действия аналогичны). Правило будем добавлять на примере работы сервера 1С:Предприятие 8.х (необходимо открыть порт 1541 для менеджера кластера, порты 1560-1591 для рабочих процессов и порт 1540 для агента сервера).
Некоторые программы и службы при работе через сетевые протоколы используют определенные порты для обмена данными. По умолчанию включенный брандмауэр Windows блокирует подобную сетевую активность. В частности, если попытаться подключиться с клиентской машины к серверу 1С:Предприятие 8.х можно натолкнуться на ошибку:
«Ошибка при выполнении операции с информационной базой (…). Ошибка сетевого доступа к серверу (…). Попытка установить соединение была безуспешной, т. к. от другого компьютера за требуемое время не получен нужный отклик, или было разорвано уже установленное соединение из-за неверного отклика уже подключенного компьютера (…) »
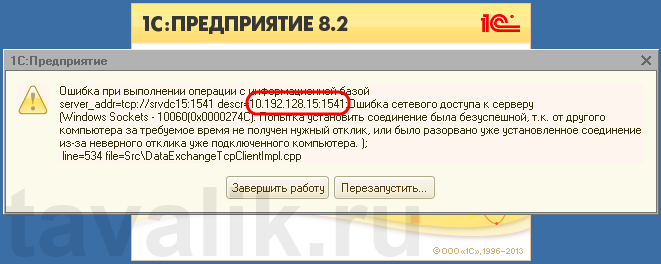
Данная ошибка означает, что по указанному адресу не найден сервер «1С:Предприятия», ну или на сервере закрыт порт (в данном случае порт 1541).
Для открытия порта, заходим на компьютер, где установлен сервер «1С:Предприятия» (в моем примере это компьютер с адресом 10.192.128.15 и установленной на нем операционной системой Windows Server 2012 R2).

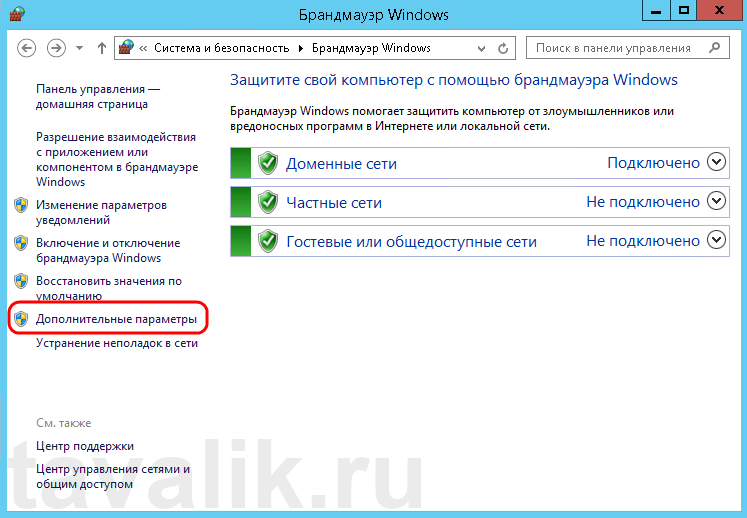
Далее нажимаем на «Дополнительные параметры» (Advanced Settings) в меню слева.
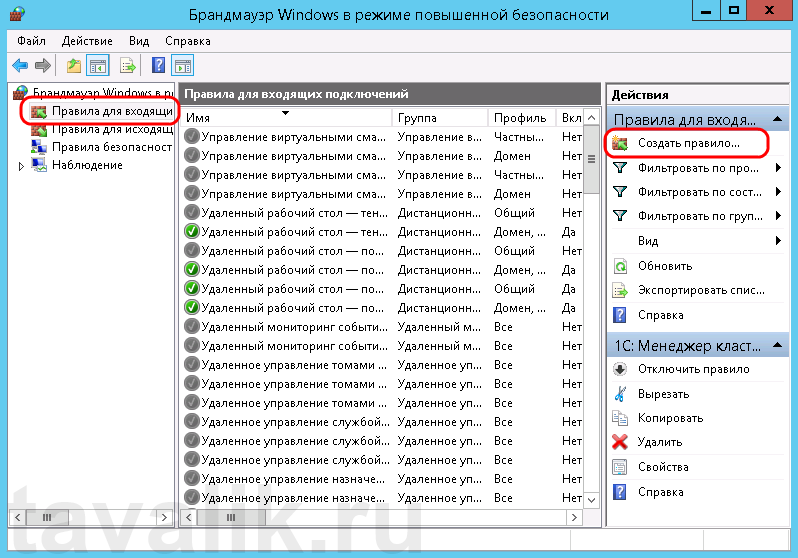
В открывшемся окне, в дереве слева откроем вкладку «Правила для входящих подключений» (Inbound Rules), а затем в меню «Действия» (Actions) выберем пункт «Создать правило…» (New Rule…).
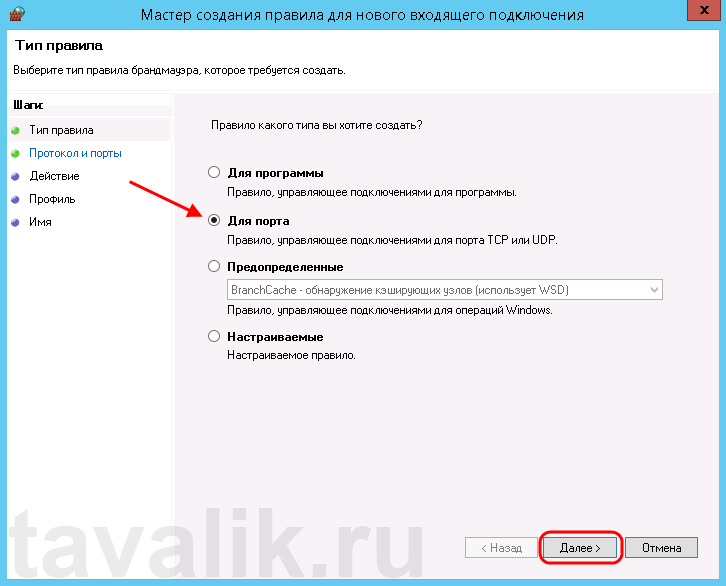
Запустится «Мастер создания правила для нового входящего подключения» (New Inbound Rule Wizard). На первой странице выберем тип правила (Rule Type) «Для порта» (Port) и нажмем «Далее» (Next).
Затем необходимо указать протокол (в нашем примере это TCP) и, непосредственно, номер порта (Specific local ports), который открываем. После чего жмем «Далее» (Next).
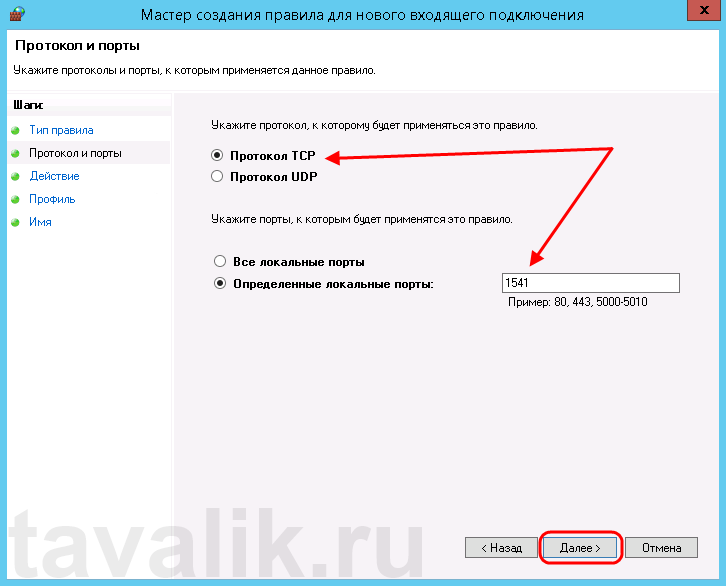
Теперь укажем действие связанное с добавляемым правилом. Выберем «Разрешить подключение» (Allow the connection) и нажмем «Далее» (Next).
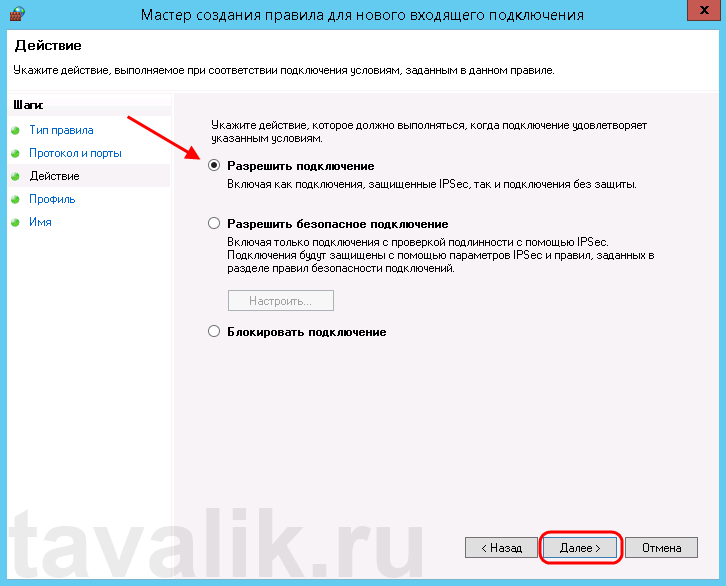
На следующей странице нужно указать, для каких профилей брандмауэра будет действовать правило. Отмечаем нужные профили галочками и жмем «Далее» (Next).
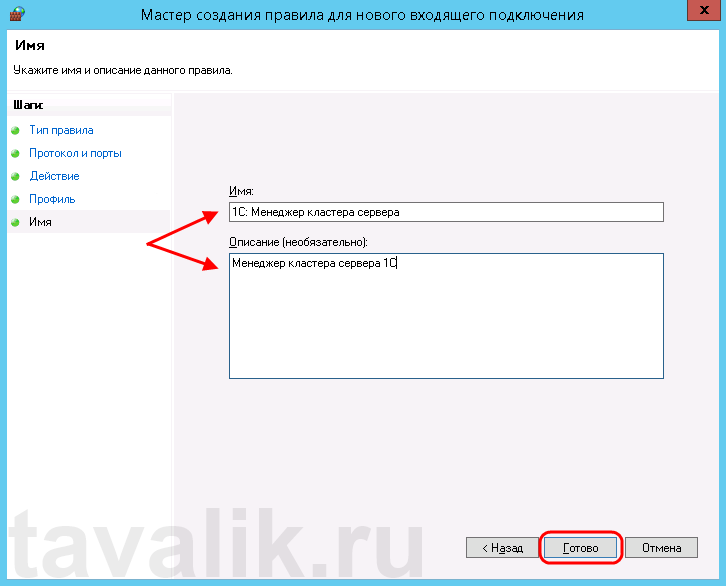
Ну и наконец, вводим имя и описание для нового правила и нажимаем «Готово» (Finish) для завершения работы мастера.
Пробуем снова подключиться к серверу «1С:Предприятия» и видим что ошибка сохранилось, но в сообщении уже другой, 1560-ый порт.
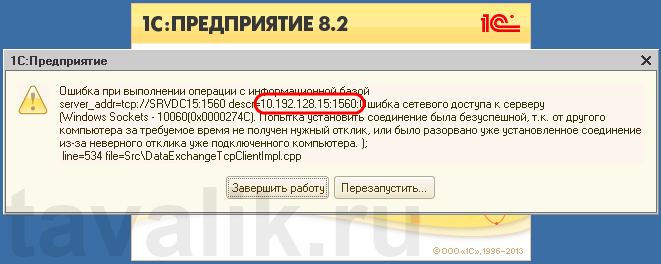
Вышеописанным способом добавим еще одно разрешающее правило, с названием «1С: Рабочие процессы» для всего диапазона портов с 1560 по 1591 (для рабочих процессов 1С), указав их через дефис на шаге «Протокол и порты» (Protocol and Ports).

Теперь, в оснастке «Брандмауэр Windows в режиме повышенной безопасности» (Windows Firewall with Advanced Security) в таблице «Правила для входящих подключений» (Inbound Rules) мы должны увидеть 2 только что созданных правила.
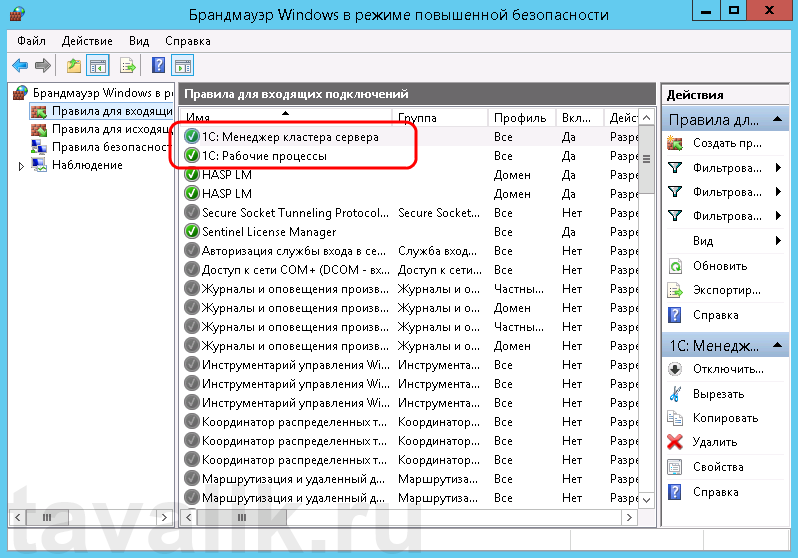
Ну а клиент «1С:Предприятия» должен без ошибок подключиться к серверу. Если же потребуется подключаться к этом серверу через консоль администрирования серверов «1С:Предприятия», то необходимо также открыть порт 1540.
Аналогичным образом добавляются правила для для исходящих подключений (Outbound Rules), запрещающие правила, правила для определенных программ и протоколов. Также любое правило можно изменить, открыв его свойства из данной оснастки.
Смотрите также:
Ниже будет рассказано о том, как добавить новое правило в Брандмауэр Windows Server 2008 R2. А конкретнее, будем добавлять разрешающее правило для порта 1433, который использует Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 или, как…
Ниже приведена небольшая инструкция об изменении политики паролей в Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2. По умолчанию политика паролей определена таким образом, что все пароли учетных записей пользователей должны удовлетворять следующим…
Источник
Защищаем удаленный сервер на Windows как можем

Тема безопасности сервера Windows не раз поднималась, в том числе и в этом блоге. Тем не менее мне хотелось бы еще раз освежить в памяти старые методы защиты и рассказать о малоизвестных новых. Разумеется, будем использовать по максимуму встроенные средства.
Итак, предположим, что у нас есть небольшая компания, которая арендует терминальный сервер в удаленном дата-центре.
При проектировании любой защиты следует начинать с модели угроз — от кого или чего, собственно, будем защищаться. В нашей типовой конфигурации я буду строить оборону от внешних злобных хакеров, от некомпетентных (а может, и немного злонамеренных) пользователей. Начнем с внешнего периметра обороны — фаервола.
За тобой как за огненной стеной
Во времена Windows 2003 встроенный фаервол представлял собой жалкое зрелище, и в случае невозможности применения сторонних средств приходилось использовать IPSec. Пример такой настройки разобран, например, в материале Secure Windows Servers using IPSec Firewall.
Сейчас, с появлением WFP (Windows Filtering Platform) дела стали получше. В принципе, с этим фаерволом так или иначе сталкивался, наверное, каждый системный администратор Windows, поэтому настройка удаленного доступа к серверу только с определенных IP не должна вызывать затруднений. Я обращу внимание на некоторые «фишки», которые используются редко.
По умолчанию фаервол блокирует все входящие соединения, кроме явно разрешенных, но исходящие разрешает все, кроме явно запрещенных. Политику эту можно изменить, открыв управление фаерволом через wf.msc и выбрав «Свойства».
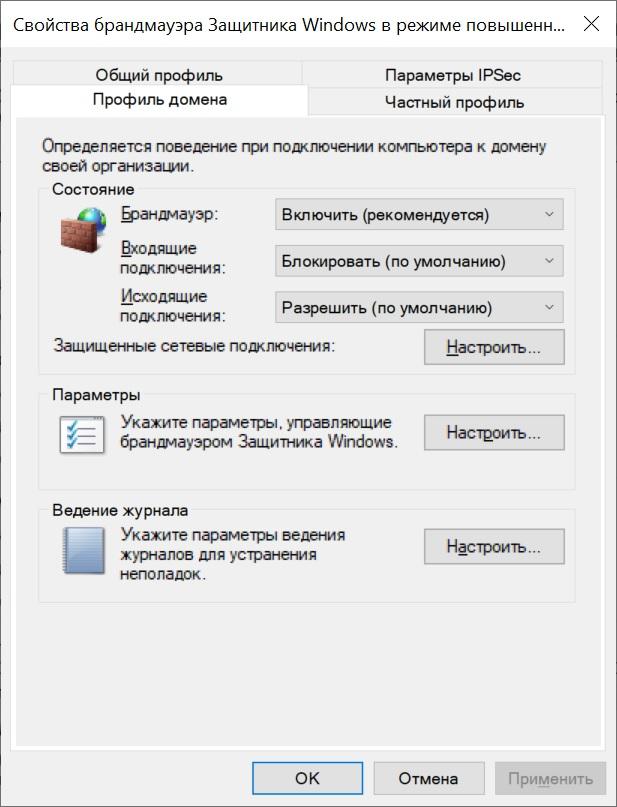
Теперь, если мы захотим запретить пользователям терминального сервера выходить с этого сервера в интернет — у нас это получится.
Стоит отметить, что при настройке правил доступа к серверу (входящие подключения) явно создавать правила для исходящего трафика не нужно. В терминах iptables — established и related всегда разрешены.
Для ценителей командной строки настройку фаервола можно производить в контексте netsh advfirewall. Почитать про команды можно в материале «Брандмауэр Windows 7 в режиме повышенной безопасности», я же добавлю, что блокировка входящих и исходящих подключений включается командой:
Еще одной особенностью фаервола windows является то, что любая программа или настройка меняет его правила без уведомлений. Например, отключили вы все правила на нашем дедике, рядом появился второй, вы сделали между ними локальную сеть, настроили общий доступ и… внезапно у вас включается smb для всех и вся со всеми вытекающими последствиями.
Выхода, по сути, два с половиной (напомню, мы пока говорим только про встроенные средства): регулярно проверять, не изменились ли правила, и использовать старый добрый IPSec или — как по мне, самый разумный вариант — настраивать фаервол групповой политикой. Настройка производится в Конфигурация компьютера — Конфигурация Windows — Параметры Безопасности — Монитор брандмауэра Защитника Windows в режиме повышенной безопасности.
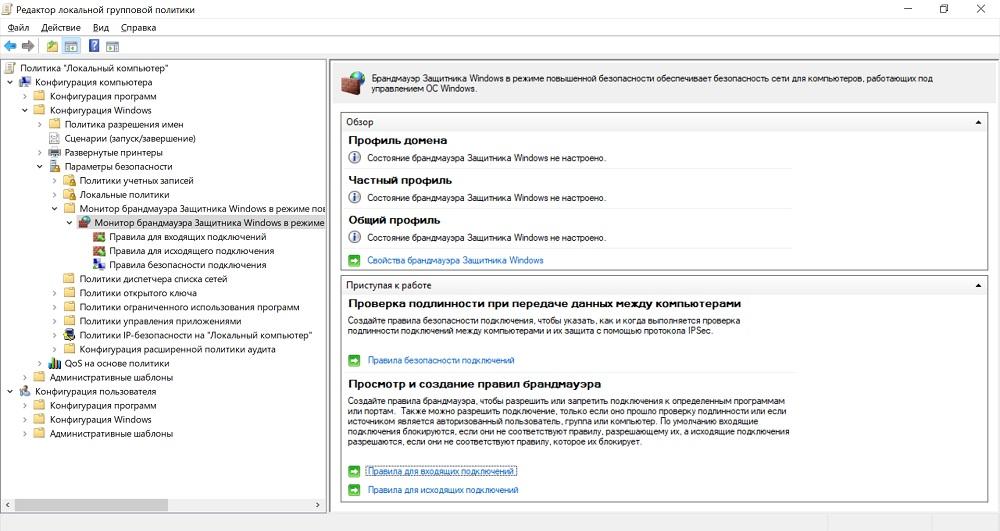
Настройка фаервола групповой политикой.
Также при помощи фаервола windows можно реализовать простой fail2ban. Достаточно включить аудит неудачных попыток входа и при нескольких неудачах подряд блокировать IP источника. Можно использовать самописные скрипты, а можно уже готовые средства, о которых я писал в статье «Как дать шифровальщикам потопить компанию».
Если же встроенного фаервола не хватает и хочется использовать что-то более серьезное, то можно установить стороннее ПО. Жаль, что большинство известных решений для Windows Server — платные. Другим вариантом будет поставить перед сервером роутер. Понятно, что такая установка подойдет, если мы используем colocation, а не аренду сервера где-то далеко-далеко за рубежом. Если же зарубежный дата-центр — это наш выбор, то можно использовать виртуализацию — например, встроенный Hyper-V — и установить в виртуалку привычный GNU\Linux или FreeBSD.
Возникает вопрос: как сделать так, чтоб виртуалка имела прямой выход в интернет, а сервер — нет? Да еще чтобы MAC-адрес сервера не светился хостеру и не требовал тем самым покупки еще одного IP-адреса.
Осторожно! Дальнейшие действия лучше проводить через IP-KVM!
Для этого виртуальную машину нужно снабдить двумя сетевыми адаптерами. Один — для непосредственного подключения к интернету, для него мы сделаем виртуальный коммутатор типа «внешний» и снимем галочку, разрешающую операционной системе взаимодействие с этим коммутатором. Этой самой галочкой мы лишим сервер прямого доступа в интернет (настройку виртуальной машины-фаервола лучше произвести заранее), и его MAC не будет светиться хостеру.
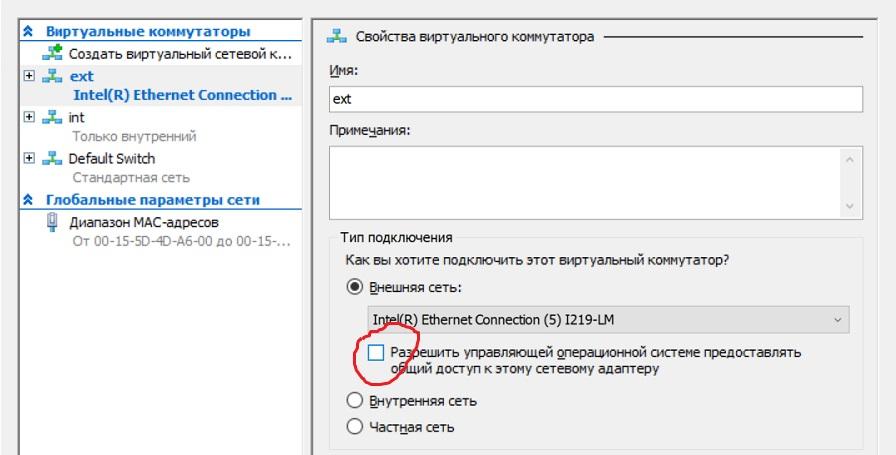
Настройка внешнего виртуального коммутатора.
Другой виртуальный коммутатор следует сделать типа «внутренний» для взаимодействия виртуальной машины и сервера. На нем уже нужно настроить локальную адресацию. Так получится создать виртуальный роутер, стоящий перед сервером и защищающий его.
Заодно на этой виртуальной машине можно настроить любимый VPN до офиса или удаленных сотрудников, не заморачиваясь с ролью «Маршрутизация и удаленный доступ» или со встроенным IPSec, как я рассказывал в статье «Как я базы 1С в Германии прятал». Главное, не забыть проверить автозапуск этой виртуальной машины при старте системы.
Подключаться к такому серверу можно при помощи обычного RDP или использовать HTML5 клиенты с двухфакторной аутентификацией. Стоит на случай брутфорса озаботиться и решениями fail2ban, и блокировкой учетной записи на некоторое время при нескольких неудачных попытках авторизации подряд.
Снаружи сервер мы более-менее защитили, перейдем к защите внутренней.
Защита внутренняя: остановить и не пущать
Конечно, для защиты сервера изнутри очень хочется поставить какой-нибудь антивирус — мало ли что пользователи сервера накопируют или накачают из интернета. Но на практике антивирус на сервере может принести больше вреда, чем пользы. Поэтому я обычно использую механизмы блокировки запуска ПО не из белого списка — в частности, механизм SRP (software restriction policies), о котором я тоже упоминал в статье «Как дать шифровальщикам потопить компанию».
Остановлюсь чуть подробнее на одном подводном камне, о котором часто забываем при включении SRP со стандартными настройками, когда блокируется все, кроме папок Windows и Program Files. Действительно, это отфильтровывает почти всех зловредов. Но не очень работает со злонамеренностью сотрудников, ведь в системных папках есть подпапки с правом на создание объектов пользователями. Например, можно посмотреть на папку C:\Windows\Temp.

Разрешения на папку, которая попадет в белый список.
И такая папка не одна. Можно, конечно, проводить аудит системных папок самостоятельно, а можно довериться людям, которые это уже сделали. Например, специалист Stefan Kanthak в своем блоге (по ссылке есть тестовый вирус EICAR, антивирус может сработать) в довольно агрессивной манере проходится по антивирусам и методам защиты Windows и заодно предлагает уже собранный пакет настроек SRP, который будет блокировать и такие подозрительные папки. По запросу автор предоставляет и программу для конвертирования этих настроек реестра в файлы локальных политик.
Если вы предпочитаете использовать механизм AppLocker c более гибкими настройками, то вам может помочь решение AaronLocker.
Редакция не рекомендует использовать и устанавливать скрипты и прочие программы из интернета без предварительного их изучения.
Если AppLocker появился уже довольно давно, а возраст SRP перевалил за 15 лет, то относительно свежей альтернативой является WDAC (Windows Defender Application Control). Действительно, со времен Security Essentials встроенный «антивирус» обзавелся многими интересными возможностями. Например, WDAC — модуль, который отвечает за политики доступа к приложениям и библиотекам. Ранее он являлся частью Device Guard (защита компьютера, в том числе с применением технологий виртуализации), и немного про его настройку рассказывалось в материале «Принцип работы S Mode в Windows 10 и настройка Device Guard своими руками». Подробнее со всеми тонкостями можно ознакомиться в официальной документации, мне же остается добавить несколько минусов, отличающих его от классических решений вроде SRP и AppLocker:
Зато возможна настройка в срезе приложения: например, если вы хотите дать доступ к cmd.exe вашему скрипту, а не стороннему вирусу — это можно реализовать. Да еще и политику можно применить до загрузки системы, при помощи UEFI.

Блокировка хрома через WDAC.
В целом из-за тягостной настройки сложилось впечатление, что WDAC больше позиционируется не сам по себе для управления компьютерами, а как средство, позволяющее интегрироваться с централизованными MDM-системами вроде Microsoft Intune. Но при этом разработка старых добрых SRP прекращена в Windows 10 1803.
Если говорить про Защитник Windows, нельзя не упомянуть про Credential Guard и Remote Credential Guard.
Первое средство использует опять же виртуализацию, запуская компонент LSA (Local Security Authority) в изолированном от операционной системы процессе, что сильно усложняет процесс кражи хешей паролей и билетов Kerberos. Подробнее про технологию можно почитать в официальной документации. Для работы процессор должен поддерживать виртуализацию, а также в системе должна быть включена безопасная загрузка (Secure Boot) и модуль TPM для привязки учетных данных к оборудованию. Включить Credential Guard можно через групповую политику Конфигурация компьютера — Административные шаблоны — Система — Device Guard — Включить средство обеспечения безопасности на основе виртуализации.
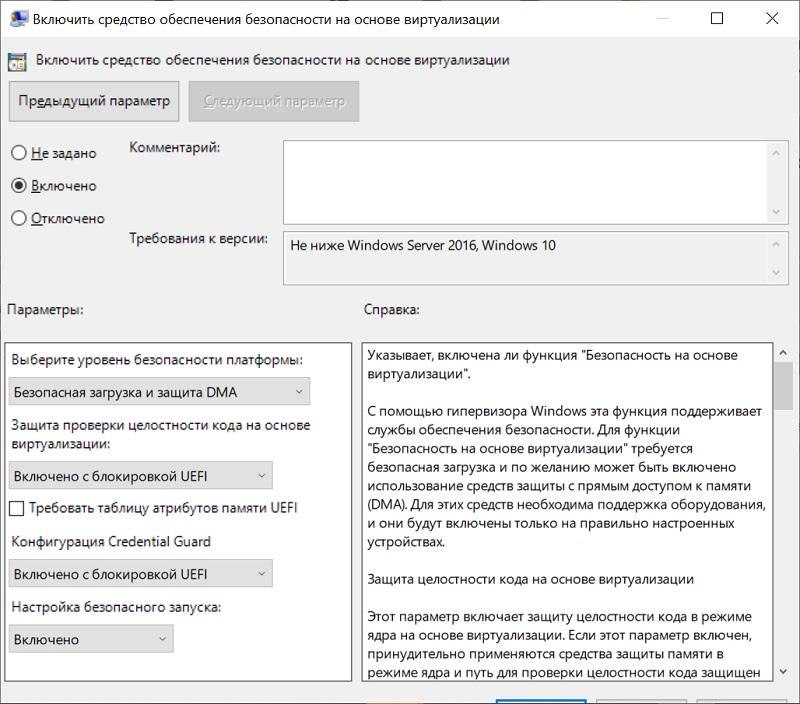
Включение Credential Guard.
Второе средство служит для защиты передаваемых учетных данных (особенно админских!) для удаленного подключения, например, по тому же RDP. Ранее для этих целей предлагался механизм Restricted Admin Mode, но он ограничивал подключение только одним сервером. Подключившись к серверу, нельзя было просто так использовать ресурсы сети, права администратора применялись только к одному серверу а-ля системный аккаунт Local System.
Remote Credential Guard позволяет передавать учетные данные с локальной машины удаленному серверу без явного ввода пароля, что, помимо расширенной безопасности, даст и удобство подключения к серверам (SSO). Почитать подробнее можно в документации, ну а я добавлю, что для работы механизма достаточно включить его поддержку на сервере — например, через реестр командой:
А потом подключаться к серверу командой:
Теперь учетные данные в безопасности, а сервер достаточно защищен. Правда, в материале я осознанно не касался вопросов защиты от злонамеренного хостера, но тут все сводится в общем-то к одному — к шифрованию дисков.
Только зарегистрированные пользователи могут участвовать в опросе. Войдите, пожалуйста.
Источник
Home » KB » SysAdmin » How to Configure Windows Server 2012 Firewall
Firewalls have become an essential part of every network that has access to the Internet. Without firewalls, anyone would be able to access your network and servers and infect them with malicious software. Properly configured, a firewall can substantially decrease undesirable network communications in a local network.
The article will explain how to create a firewall rule using firewall MMC and Windows PowerShell. We are using Windows Server 2012, but the procedure applies to other versions of Windows, with slight variations.

What is a Firewall?
A firewall is a piece of hardware or software that controls the flow of data packets, and it is critical on modern computer systems. It protects private networks and devices from malicious actions coming from public networks in the same way a physical firewall prevents fire from spreading from one area to another. A firewall acts as a defense mechanism which controls network traffic according to the implemented firewall rules.
Computers behind a firewall cannot receive data until the data passes all filters. This enhances security by a large margin and reduces the risk of unauthorized access to private networks. A proper firewall configuration provides your system with a crucial layer of security and lowers the risk of successful hacking attacks. Firewalls can perform many tasks:
- Protect the data on your computer by creating a barrier that blocks any undesired incoming or outgoing traffic.
- Notify you if there are any connection requests from other computers.
- Log activity for later inspection and warn you if any application tries to connect to another computer.
How Windows Server Firewalls Work
As the name suggests, a firewall acts like a barrier between your local devices and the external network. When you send a connection request to your computer or server over the internet, a hacker can interrupt that connection and try to gain access to your private network. With a firewall in place, only the network traffic that matches firewall rules can get through.
The sets of firewall rules you define in the firewall settings review every packet for flagged information. To make the most out of your firewall, you should precisely define both inbound and outbound rules in order to avoid any unwanted connections.
For example, you can set an inbound rule defining that the data communicated through a specific port, such as TCP port 80, can pass the firewall. That means if the firewall sees a packet coming towards any other port, it will drop it and the data will not reach its intended destination.
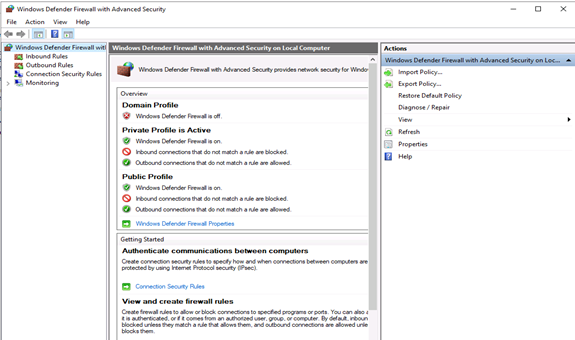
Windows Firewall Server 2012 with Advanced Security
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security is the management console which stores all Windows Firewall configurations. Windows Firewall is a host-based firewall solution embedded with virtually all current Windows operating systems.
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security provides safer inbound and outbound network communications by enforcing rules that control traffic flow for its local machine. There are three available firewall profiles:
- Domain. It is used when a computer connects to the corporate network. It is a network where the device can detect its domain controller.
- Private. We use this profile for computers that connect to a private network, such as home or office. In private networks, the users are always behind a device and not directly exposed to the Internet.
- Public. This profile is used when a computer connects to a public network, such as libraries, airports and other public hotspots. The firewall configurations should be the most restrictive for this profile since these networks are the least secure.
The benefits of using Windows Server Firewall with Advanced Security are numerous:
- It is ready out-of-the-box. It comes preinstalled with personal Microsoft Windows operating systems as well as Server editions. It is also active by default, protecting your operating system from the very first startup.
- It does not need a special license or additional hardware. Once you obtain your copy of a Windows operating system, there are no additional costs.
- It is highly flexible. It offers many advanced functionalities and different levels of controls for the firewall services.
What is the Difference between Windows Firewall and Windows Firewall with Advanced Security?
The difference between the two is the level of functionality available to the end-user, that is, the interface itself. Both of them are the same firewall service. The Windows Firewall is easier to use and more consumer-friendly. It is located in the Control Panel and allows you to perform basic firewall configurations.
The Windows Firewall with Advanced Security offers granular control over the inbound and outbound rules, as well as the default firewall profiles. You can modify all advanced firewall configurations using the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) or Windows PowerShell.
How to Launch Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Console?
You can access the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console in a few different ways. Whichever method you choose, it will open Windows Firewall MMC where you can make further firewall configurations for all profiles.
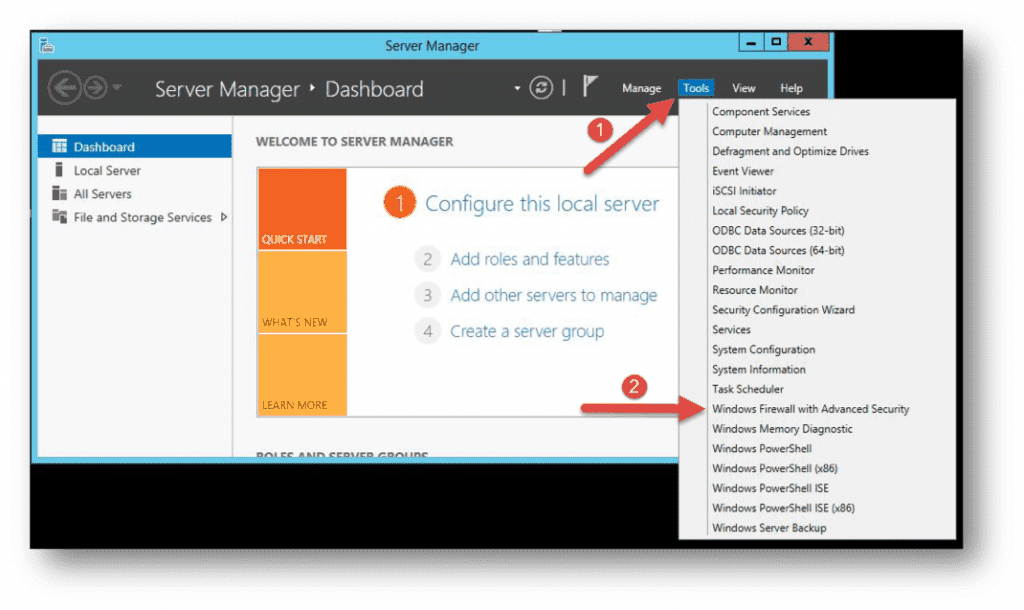

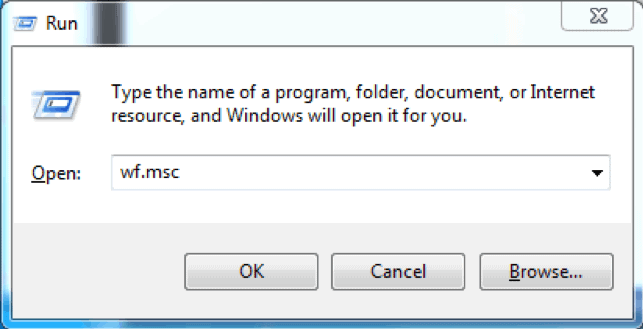
- Use the Server Manager to access the firewall MMC. Once the window opens, go to Tools on the top right side, and locate the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security option toward the bottom of the list.
- Open the Start menu (use the Windows key on your keyboard) and type “firewall”. You should see the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security icon appear as one of the search results.
- Use the Run box to launch Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. Press Win + R keys, type in msc and hit Enter to load the console. You can also use Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell to run this command.
Configure Windows Firewall
Now that you have the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console open, in the middle you can see the summary of the three firewall profiles. Their default configuration is to permit the outgoing traffic and to limit incoming traffic.
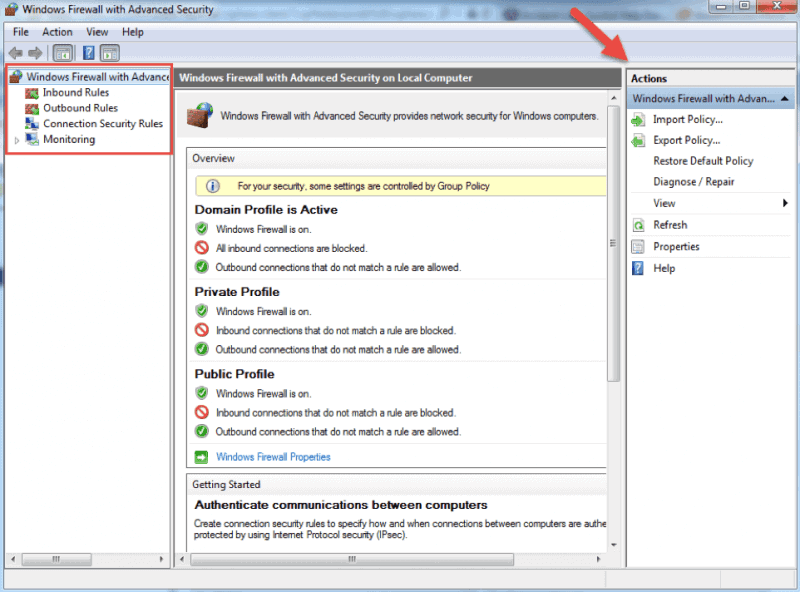
When you select an option from the menu on the left side of the window, you will see its details in the middle section. On the right side, the menu will show the available actions for the option you previously selected.
The Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console allows you to configure inbound and outbound rules, as well as the Internet Protocol security (IPSec) connections. The Monitoring tab allows you to view the active firewall rules and connection security rules for that server.
Firewall Rules
Windows firewall rules allow you to state whether to permit or block specific incoming or outgoing network connections. You can choose between multiple parameters and settings for each individual inbound or outbound rule. This includes selecting a program, a TCP or UDP port, protocol, service, or profile that a rule will apply to.
The procedure is the same when creating inbound rules and outbound rules with Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. I will list the steps for creating an inbound rule and you can follow them in the same order when you want to create an outbound rule.
How to Create Inbound Rules
Launch the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC using the method you prefer. You may want to pin the shortcut to the start menu if you use the console on a regular basis.
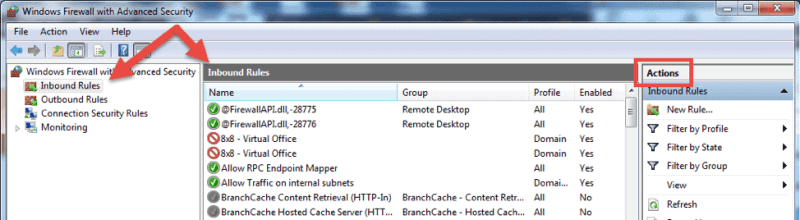
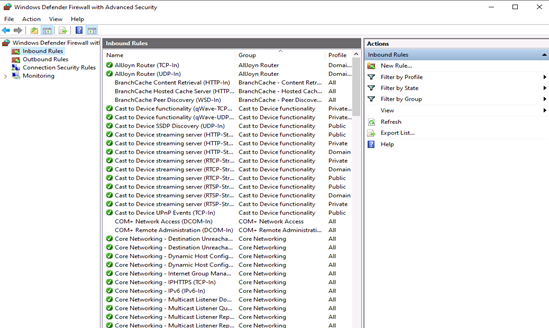
- On the home screen, select the Inbound Rules The console will show all inbound rules in the middle section and available actions in the right pane. You can filter the list by using the available choices.
- Click on New Rule… to start the New Inbound Rule Wizard.The wizard will let you choose the type of rule you want to create. You can choose one out of four types.
- This rule allows or blocks connections for a user-defined program. It allows you to select a path to an executable (*.exe) file. It does not require to insert any program-specific settings.
- A rule based on port settings allows you to permit or block a connection depending on the TCP or UDP port number it uses. You can state multiple ports to apply to this firewall rule.
- This rule contains a list of the most common Windows programs and services. You can select one to allow or block connections for it.
- Custom. This is the most flexible rule in the Wizard. It allows you to create a tailor-made rule with configurations that previous options do not provide. I will proceed with listing the steps for this rule since it covers the most settings.
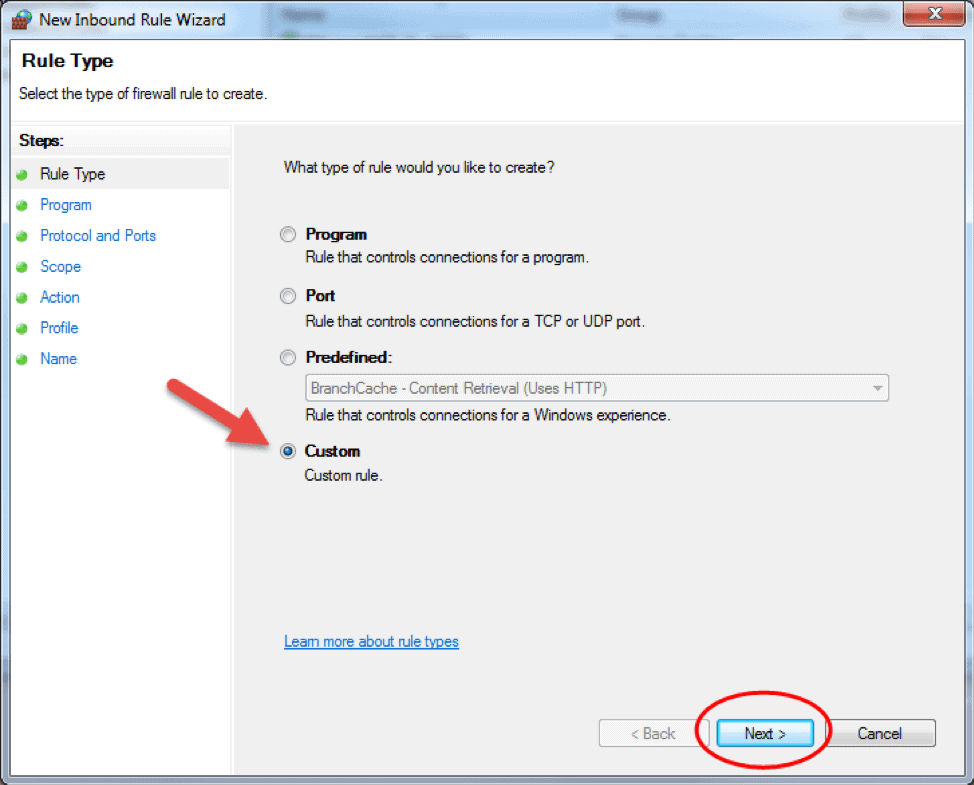
- Click on Custom and click Next to proceed.
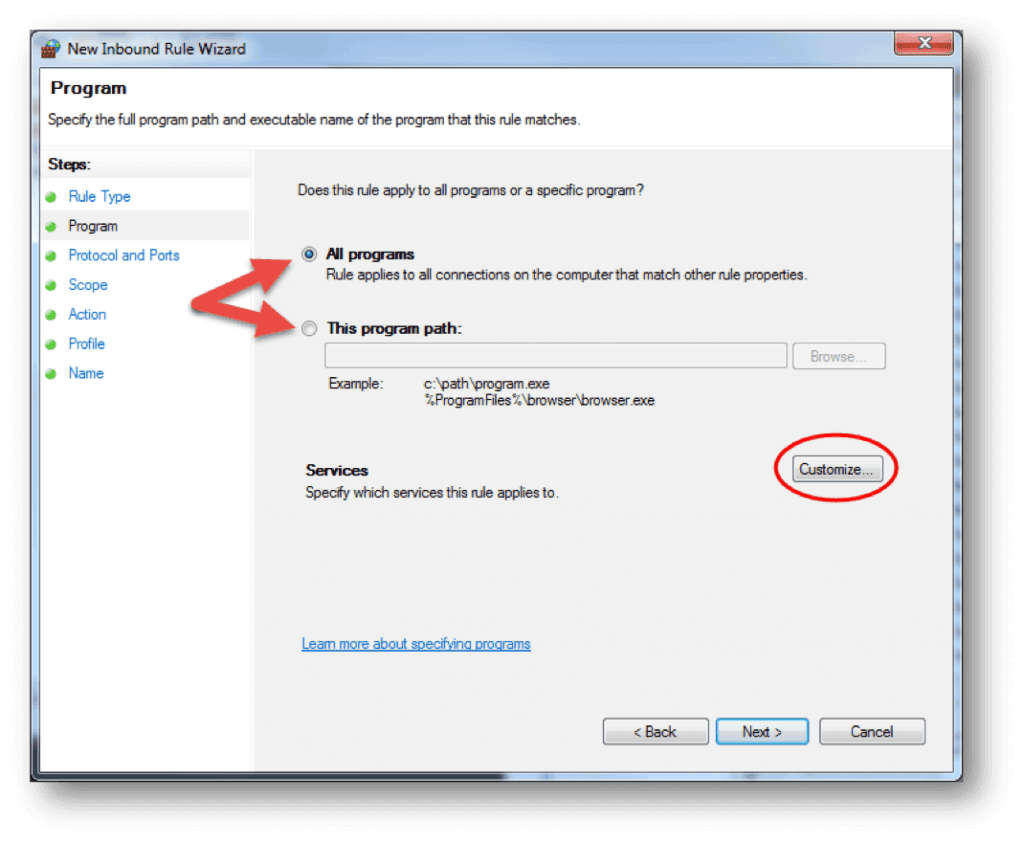
- Choose if the rule will apply to connections for All programs or a specific program on the local machine and click Next. You can click Customize… to select additional settings for the processes of the program you selected.
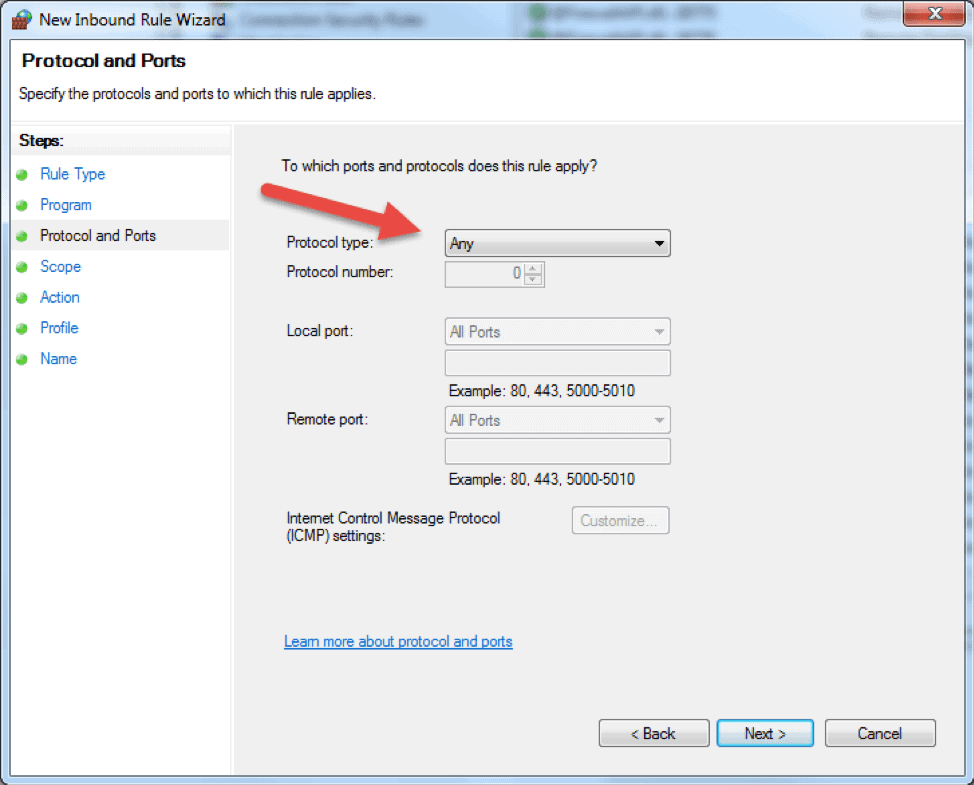
- The following step will allow you to specify the protocol and port for the traffic that this firewall rule will filter. Click Next after you select a protocol type and configure the settings.
- Protocol type. Click on the bar and select the protocol from the dropdown list. You can always select Custom to manually configure the port number. If you select TCP or UDP, you will need to specify local and remote port.
- Protocol number. This field populates automatically after you select a protocol type, and you cannot change it. In order to insert your own port, select Custom in the ‘Protocol type’ dropdown menu.
- Local port. This represents the port on the local machine where you are creating this rule. This section becomes editable if you select TCP or UDP in the ‘Protocol type’ dropdown. Select one of the options from the dropdown box. Note that RPC Endpoint Mapper and RPC Dynamic Ports are available only for TCP inbound rules, and IPHTTPS is available for TCP only. Edge Traversal is available for UDP inbound rules.
- Remote port. This is the port on a remote machine that is trying to establish a connection with the local machine. This section becomes editable if you select TCP or UDP in the ‘Protocol type’ dropdown. Select one of the options from the dropdown box. Note that RPC Endpoint Mapper and RPC Dynamic Ports are available only for TCP inbound rules, and IPHTTPS is available for TCP only. Edge Traversal is available for UDP inbound rules.
- Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) settings. You can customize the ICMP settings if you select ICMPv4 or ICMPv6 in the ‘Protocol type’ dropdown list.
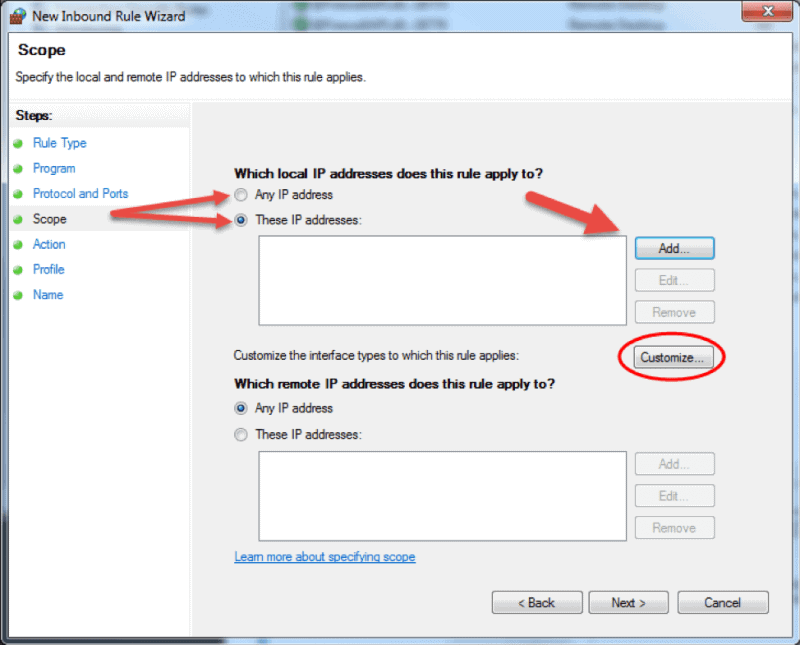
- The Scope step of the wizard allows you to input local and remote IP addresses whose network traffic applies to the current rule.
- Local. If you select ‘Any IP address’ in the local IP addresses section, then the rule applies to the traffic going through the network device that uses a local IP address. This is always the case with the machine where you are creating the rule. Select ‘These IP addresses’ to state that the rule applies to the packets with an address specified in the list. Click Add to insert the IP address to match. You can later edit or remove any of the IP addresses in the list. You can also apply this rule to a specific interface. Click Customize… and select to apply the rule to connections on all interfaces or chose one of the available interfaces listed in the box.
- Remote. If you select ‘Any IP address’ in the remote IP addresses section, then the rule applies to the traffic coming from any IP address included in the list. Select ‘These IP addresses’ to insert the remote IP addresses to which the rule applies. Click Add to specify the IP address to match. You can later edit or remove any of the IP addresses in the list.
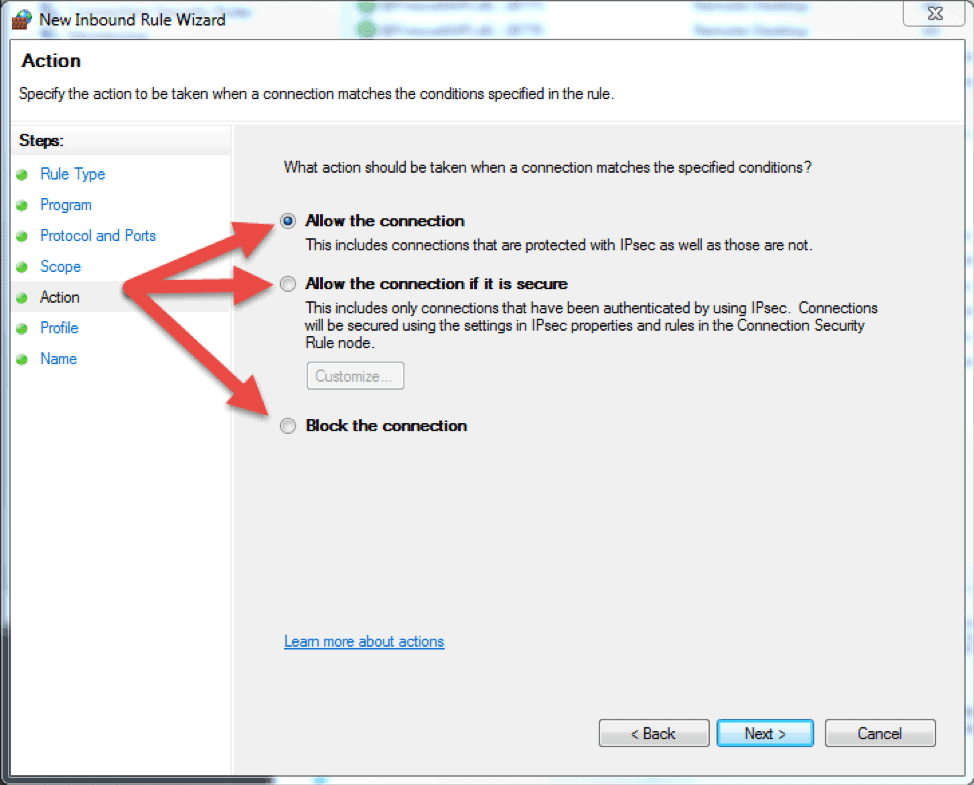
- The next step lets you chose the action the firewall takes when a connection matches the inbound rule configuration. You can select one of the three available options and then click Next to continue.
- Allow the connection. If the connection matches the inbound or the outbound rule configuration, the packets can go through the firewall.
- Allow the connection if it is secure. Select this option to allow only IPSec connections. If you chose this option, two more steps will appear in the wizard: Users and Computers. The additional steps let you chose users and computers you want to block or grant them access. Click on ‘Customize…’ to configure the authentication and integrity requirements.
- Block the connection. This option blocks all network traffic that matches the firewall rule configuration. If a similar rule with ‘allow’ action is in place, then the block action has the priority unless otherwise is stated in the other rule.
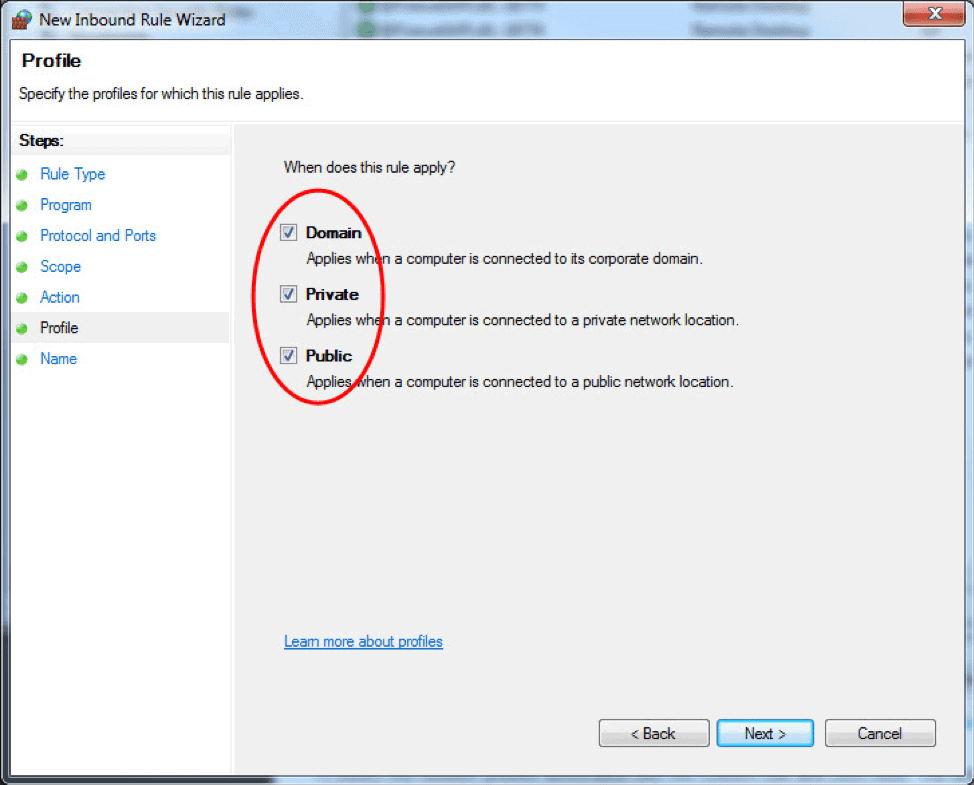
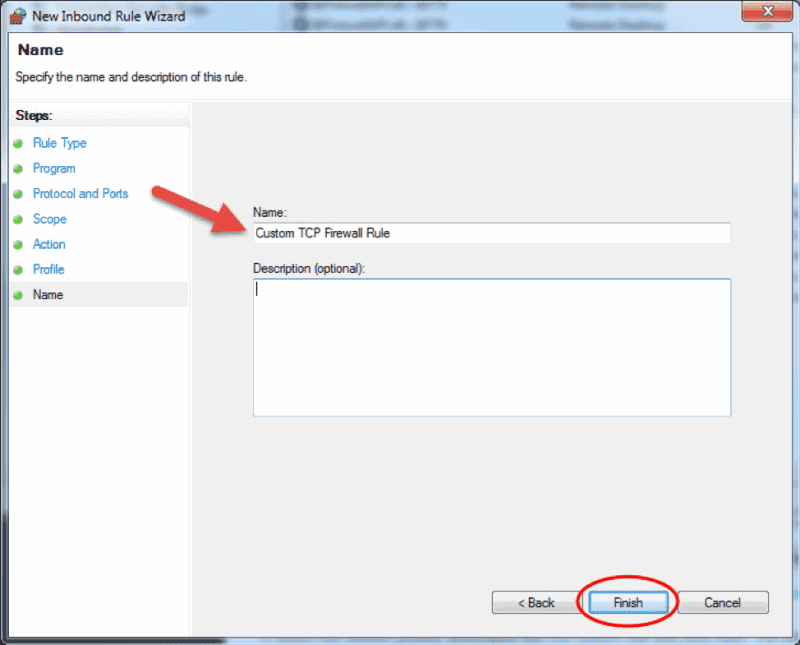
- The Profile step lets you choose the firewall profile the rule will apply to. You can leave everything selected or uncheck a profile that you do not want to include. Click Next to proceed to the final step.
- In the final step, enter the desired name and optional description for this firewall rule, and click Finish.
When you close the wizard, the rule will take effect immediately. You can find the rule in the firewall console when you click on the Inbound rules option. Enabled rules have green checkmark icon while disabled are with grey icons.
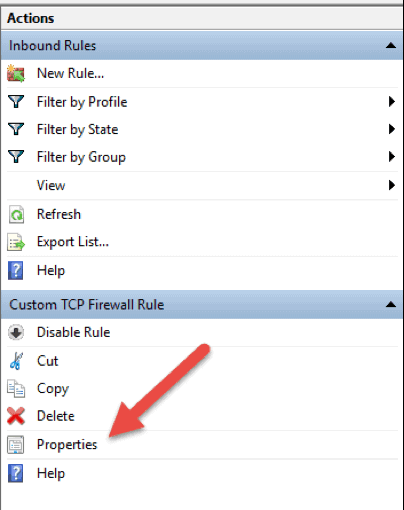
How to Edit a Firewall Rule
To edit any existing rule and make additional configuration, open the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console and select Inbound Rules or Outbound Rules option. Locate and click a rule to see the actions specific to it in the right pane. Select Properties and another window will load where you can edit the rule settings.
You can also disable, cut, copy, or delete the rule you selected. Make sure you highlight the correct rule to avoid changing firewall configurations for wrong rules.
Tip: you can double click a rule to directly open the Properties window.
How to Create a Firewall Rule with Windows PowerShell
1. Launch the PowerShell command line. You can do so by searching for “powershell” in the start menu, or press Win + R keys on your keyboard and type in “powershell” in the Run box.
2. Insert the following command and hit enter:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "TCP custom inbound rule" -Enabled:True -Profile Private -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 1234New-NetFirewallRule. This command creates a rule. It is followed by a string of parameters and their values.-DisplayName. Specifies the display name of the rule.-Enabled. Enables the rule if set to true. If you omit this parameter, it defaults to true.-Profile. Assigns the rule to the specified profile: Domain, Private, orPublic.-Direction. States if the rule applies to inbound or outbound connections. If you leave it out, it defaults to Inbound.-Action.Specify if the firewall rule will block or allow the connection. If you do not state the action, it defaults to Allow.-Protocol. Specify the protocol for the rule. In this case, we used TCP. Omitting the protocol defaults the setting to Any.-LocalPort. Insert the port where the traffic can go through on the local server. Omitting the port number defaults the setting to Any.
This is only one example of how to add a firewall rule using the Windows PowerShell command line. You can find more examples in the Microsoft PowerShell Documentation.
Conclusion
This article explains the basic functions and different types of firewall and details the steps for managing the Windows Server Firewall within the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security interface. The Windows Firewall Management Console is a powerful tool that allows for creating detailed configurations. If you carefully followed the instructions in the article, you are now able to manage the firewall on your Windows Server.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo