on August 15, 2010
We normally use Services.msc to start or stop or disable or enable any service. We can do the same from windows command line also using net and sc utilities. Below are commands for controlling the operation of a service.
Command to stop a service:
net stop servicename
To start a service:
net start servicename
You need to have administrator privileges to run net start/stop commands. If you are just a normal user on the computer, you would get an error like below.
C:\>net start webclient System error 5 has occurred. Access is denied. C:\>
To disable a service:
sc config servicename start= disabled
To enable a service:
sc config servicename start= demand
To make a service start automatically with system boot:
sc config servicename start= auto
Note: Space is mandatory after ‘=’ in the above sc commands.
This SC command works on a Windows 7 machine and also on the down-level editions of Windows i.e Windows XP/2003 and Windows Vista. Again, if you do not have administrator previliges you would get the below error.
C:\>sc config webclient start= auto [SC] OpenService FAILED 5: Access is denied.
Note that the service name is not the display name of a service. Each service is given a unique identification name which can be used with net or sc commands. For example, Remote procedure call (RPC) is the display name of the service. But the service name we need to use in the above commands is RpcSs.
So to start Remote procedure call service the command is:
net start RpcSsTo stop Remote procedure call service
net stop RpcSs
These service names are listed below for each service. The first column shows the display name of a service and the second column shows the service name that should be used in net start or net stop or sc config commands.
| Display Name of the service | ServiceName which should be used with ‘net’ and ‘sc config’ commands. |
| Alerter | Alerter |
| Application Layer Gateway Service | ALG |
| Application Management | AppMgmt |
| ASP.NET State Service | aspnet_state |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service | BITS |
| Computer Browser | Browser |
| Bluetooth Support Service | BthServ |
| Bluetooth Service | btwdins |
| SMS Agent Host | CcmExec |
| Indexing Service | CiSvc |
| ClipBook | ClipSrv |
| .NET Runtime Optimization Service v2.0.50727_X86 | clr_optimization_v2.0.50727_32 |
| COM+ System Application | COMSysApp |
| Cryptographic Services | CryptSvc |
| Cisco Systems, Inc. VPN Service | CVPND |
| DCOM Server Process Launcher | DcomLaunch |
| DHCP Client | Dhcp |
| Logical Disk Manager Administrative Service | dmadmin |
| Logical Disk Manager | dmserver |
| DNS Client | Dnscache |
| Lenovo Doze Mode Service | DozeSvc |
| Error Reporting Service | ERSvc |
| Event Log | Eventlog |
| COM+ Event System | EventSystem |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Event Log | EvtEng |
| Fast User Switching Compatibility | FastUserSwitchingCompatibility |
| Windows Presentation Foundation Font Cache 3.0.0.0 | FontCache3.0.0.0 |
| Group Policy Monitor | GPMON_SRV |
| Help and Support | helpsvc |
| HID Input Service | HidServ |
| HTTP SSL | HTTPFilter |
| ThinkPad PM Service | IBMPMSVC |
| Windows CardSpace | idsvc |
| IMAPI CD-Burning COM Service | ImapiService |
| iPassConnectEngine | iPassConnectEngine |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateApp | iPassPeriodicUpdateApp |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateService | iPassPeriodicUpdateService |
| IviRegMgr | IviRegMgr |
| Server | lanmanserver |
| Workstation | lanmanworkstation |
| Lenovo Camera Mute | LENOVO.CAMMUTE |
| Lenovo Microphone Mute | Lenovo.micmute |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts |
| Intel(R) Management and Security Application Local Management Service | LMS |
| McAfee Framework Service | McAfeeFramework |
| McAfee McShield | McShield |
| McAfee Task Manager | McTaskManager |
| Machine Debug Manager | MDM |
| Messenger | Messenger |
| NetMeeting Remote Desktop Sharing | mnmsrvc |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator | MSDTC |
| Windows Installer | MSIServer |
| Net Driver HPZ12 | Net Driver HPZ12 |
| Network DDE | NetDDE |
| Network DDE DSDM | NetDDEdsdm |
| Net Logon | Netlogon |
| Network Connections | Netman |
| Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service | NetTcpPortSharing |
| Network Location Awareness (NLA) | Nla |
| NT LM Security Support Provider | NtLmSsp |
| Removable Storage | NtmsSvc |
| Microsoft Office Diagnostics Service | odserv |
| Office Source Engine | ose |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay |
| Pml Driver HPZ12 | Pml Driver HPZ12 |
| IPSEC Services | PolicyAgent |
| Power Manager DBC Service | Power Manager DBC Service |
| Protected Storage | ProtectedStorage |
| Remote Access Auto Connection Manager | RasAuto |
| Remote Access Connection Manager | RasMan |
| Remote Desktop Help Session Manager | RDSessMgr |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Registry Service | RegSrvc |
| Routing and Remote Access | RemoteAccess |
| Remote Registry | RemoteRegistry |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator | RpcLocator |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs |
| QoS RSVP | RSVP |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi Service | S24EventMonitor |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs |
| Smart Card | SCardSvr |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule |
| Secondary Logon | seclogon |
| System Event Notification | SENS |
| Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess |
| Shell Hardware Detection | ShellHWDetection |
| Print Spooler | Spooler |
| System Restore Service | srservice |
| SSDP Discovery Service | SSDPSRV |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | stisvc |
| System Update | SUService |
| MS Software Shadow Copy Provider | SwPrv |
| Performance Logs and Alerts | SysmonLog |
| Telephony | TapiSrv |
| Terminal Services | TermService |
| Themes | Themes |
| ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service | ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service |
| Telnet | TlntSvr |
| On Screen Display | TPHKSVC |
| Distributed Link Tracking Client | TrkWks |
| TVT Scheduler | TVT Scheduler |
| Windows User Mode Driver Framework | UMWdf |
| Intel(R) Management & Security Application User Notification Service | UNS |
| Universal Plug and Play Device Host | upnphost |
| Uninterruptible Power Supply | UPS |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS |
| Windows Time | W32Time |
| WebClient | WebClient |
| Windows Management Instrumentation | winmgmt |
| Portable Media Serial Number Service | WmdmPmSN |
| Windows Management Instrumentation Driver Extensions | Wmi |
| WMI Performance Adapter | WmiApSrv |
| Security Center | wscsvc |
| Automatic Updates | wuauserv |
| SMS Remote Control Agent | Wuser32 |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSVC |
| Network Provisioning Service | xmlprov |
GUI is very popular due to its simplicity and ease of access. But when it comes to managing or automating Windows services, CLI is simply superior and more efficient if you are used to using it.
To stop a Windows service through Command-Line, you can use the Stop-Service cmdlet in PowerShell or the Net stop command in CMD.
We’ve provided step-by-step guidelines on how to do so below.
How to Stop a Windows Service From Command Line
In addition to the commands mentioned above, you can also use the Set-Service cmdlet in Powershell or theSc stop command in CMD to stop a Windows Service.
Using PowerShell
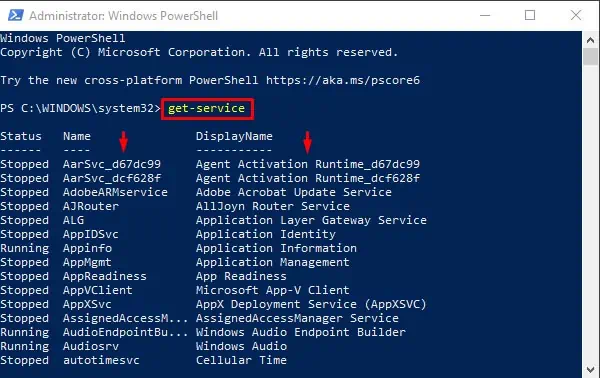
Before going to the actual process, here’s what the commands do.
Get-Servicedisplays a list of all services on the computer.Stop-Serviceis used to stop one or more running services.Set-Servicecan change the properties of a service, including the Status and StartupType.
- Press Windows + X and then press A to open Windows PowerShell (Admin).
- Type and enter
Get-Serviceto get a list of all services. - Type either of the following commands:
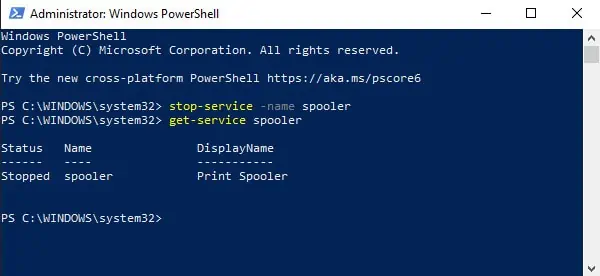
Stop-Service -Name “service-name-here”Set-Service -Name “service-name-here” -Status stopped
Replace “service-name-here” with the Name or DisplayName from Step 2 and press Enter.
For e.g.Stop-Service -Name AJRouter
- Type
get-service “service-name-here“to check if the service is stopped.
Note: If you’re unable to stop the service because of a dependency error, add -Force at the end as such:
Stop-Service -Name “service-name-here” -ForceSet-Service -Name “service-name-here” -Status stopped -Force
Using Command Prompt
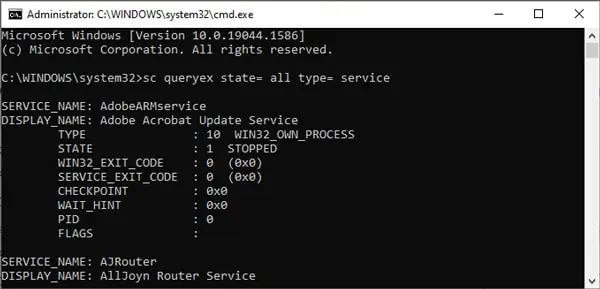
Sc queryex obtains and displays detailed information about all active services by default. With the use of certain parameters, it can also show info on drivers, their state, and more.
Both Net stop and sc stop can stop a service. But Net only works locally while sc can be used over a network.
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type cmd and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to launch Elevated Command Prompt.
- Type
sc queryex state= all type= serviceand press Enter to get a list of all the services. - Note the SERVICE_NAME and DISPLAY_NAME of the service you want to stop. You can replace “service-name-here” with either of these values in Step 5.
For Step 6, replace it with SERVICE_NAME specifically, as DISPLAY_NAME won’t work with thesc stopcommand. - Type and enter
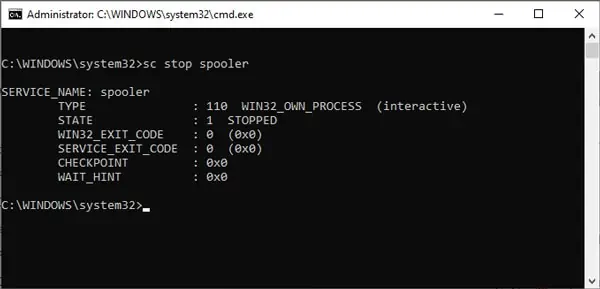
net stop “service-name-here”. - Alternatively, type
sc stop “service-name-here”and press Enter.
For e.g.sc stop spooler
Start/Restart Windows Service from Command Line
In Powershell, you can use the start-service or restart-service cmdlets as appropriate. As CMD doesn’t have a command to restart a service directly, we’ll combine the net stop and net start commands instead.
Powershell
Start-Servicestarts one or more stopped services.Restart-Servicestops, then starts one or more services.
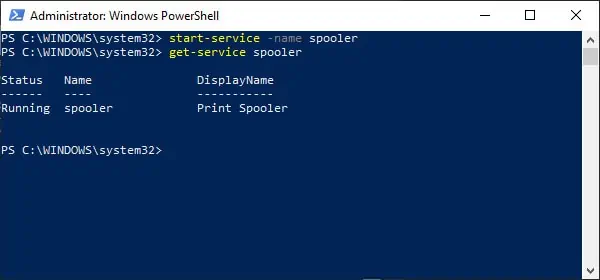
- Press Windows + X and press A to launch Windows PowerShell (Admin).
- Type
Get-Serviceand press Enter to get a list of all services. - Note the Name and DisplayName of the service you want to start. Replace “service-name-here” with either of these values in the next step. Also, note the status.
- If the status is stopped, type the following command and press Enter:
Start-Service -Name “service-name-here” - If the status is running, type the following command and press Enter:
Restart-Service -Name “service-name-here” - Check the status of the service with the following command:
get-service “service-name-here”
Command Prompt
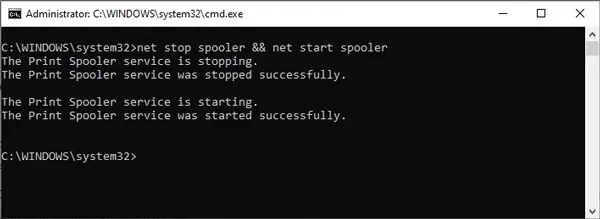
In CMD, you’ll have to stop the service first and restart it afterward. Otherwise, you’ll get a The requested Service has already been started error.
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type cmd and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to launch Elevated Command Prompt.
- Type
sc queryex state= all type= serviceand press Enter to get a list of all the services. - Note the SERVICE_NAME and DISPLAY_NAME of the service you want to stop. You can replace “service-name-here” with either of these values in Step 5.
For Step 6, replace it with SERVICE_NAME specifically as DISPLAY_NAME won’t work with thesc startcommand. - Type
net stop “service-name-here” && net start “service-name-here”and press Enter. - Check the status of the service with the following command:
sc queryex “service-name-here”
Change Windows Service Startup Type from Command Line
You can use the Set-Service cmdlet to change the startup type in Powershell. In Command Prompt, you can instead use the sc config command.
Powershell
The acceptable values for the StartupType parameter are as follows:
- Automatic – The service starts automatically at system startup.
- AutomaticDelayedStart – The service starts automatically, slightly after other automatic services start.
- Manual – The service needs to be started manually by a user or program.
- Disabled – The service cannot be started.
- Press Windows + X to open the quick link menu.
- Press A and accept the prompt to launch Windows PowerShell (Admin).
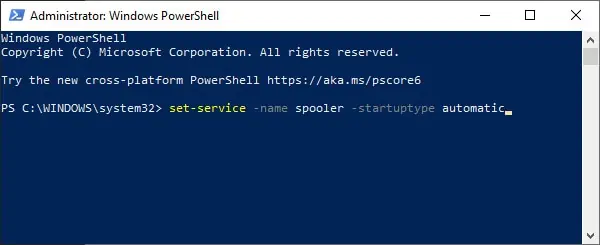
- Type
Get-Serviceand press Enter to get a list of all services. - Note the Name and DisplayName of the service you want to start. Replace “service-name-here” with either of these values in the next step.
- Type the following command, replace Automatic with the appropriate startup type, and press Enter:
Set-Service -Name “service-name-here” -StartupType Automatic
Command Prompt
The acceptable values for the start parameter are as follows:
- auto – The service starts automatically at system startup.
- delayed-auto – The service starts automatically at boot, but with a slight delay.
- demand – The service needs to be started manually by a user or program.
- boot – The boot loader loads the device driver.
- system – The device driver starts during kernel initialization.
- disabled – The service is disabled and won’t start.
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type cmd and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to launch Elevated Command Prompt.
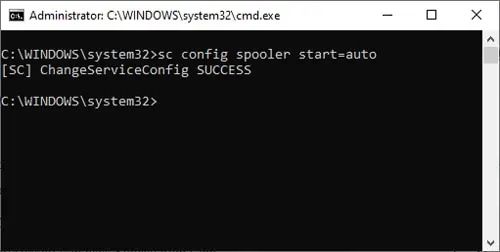
- Type
sc queryex state= all type= serviceand press Enter to get a list of all the services. - Note the SERVICE_NAME and DISPLAY_NAME of the service you want to stop. Replace “service-name-here” with either of these values in the next step.
- Type the following command, replace auto with the appropriate start option, and press Enter:
sc config “service-name-here” start=auto
How to Fix Can’t Stop Windows Service Because Of Access Denied System Error?
If you launch CMD/PowerShell without admin privileges and try to stop a Windows Service, you will encounter this error. To fix this, launch them in elevated mode, and you’ll be able to stop the service.
В этой статье мы познакомимся с простым способом, позволяющим удалить любую службу в Windows 7 средствами самой операционной системы без использования сторонних программ.
Прежде чем начать, необходимо уяснить несколько моментов:
- При удалении службы она навсегда исчезнет из системы, и восстановить ее непросто, а в ряде случаем просто невозможно
- Удаление определенных служб может вызвать неработоспособность тех или иных программ. Поэтому не стоит удалять службу, если вы на 100% не уверены за что она отвечает.
- Не удаляйте системные службы Windows 7, т.к. это может привести к неработоспособности всей системы
Также попытаемся понять, в каких случаях возникает необходимость в удалении службы Windows.
- Зачастую программы при удалении из системы оставляют свои службы нетронутыми, и каждый раз при загрузке компьютера система пытается запустить такую службу, однако из-за отсутствия исполняемых или библиотечных файлов сделать этого не может, генерируя ошибку.
- Некоторые вирусы и трояны для маскировки своих деструктивных действий могут создать в системе новую службу. И даже если, ваш антивирус удалит тело вируса, служба может остаться, и ее придется удалять вручную.
- Возможно также ситуация, когда производительность системы снижается вследствие наличия большого количества процессов, работающих в виде служб, и вы решили удалить (а не просто остановить) ряд ненужных более служб в Windows 7.
Чтобы удалить службу в Windows 7, нужно знать ее имя. Для чего откройте окно управления службами Start -> Settings -> Control Panel-> Systems and Maintenance->Administrative Tools->Services.
В появившемся окне служб найдите ту службу, которую вы планируете удалить (в моем примере это “Adobe Lm Service”)
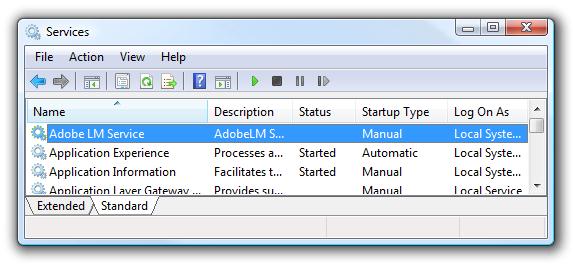
Дважды щелкните по выбранной службе и в появившемся окне свойств в поле «Service name» будет отображено ее имя (у меня имя службы — Adobe LM Service, т.е. оно совпадает с именем в списке служб, но обычно это не так), скопируйте его в буфер обмена.
Затем остановите службу, нажав кнопку «Stop»
Удаляем службу в Windows из командной строки
Откройте окно командной строки (cmd.exe) с правами администратора («Run as administrator»). Чтобы удалить службу в Windows 7 можно воспользоваться системной командой sc. Команда sc.exe – это утилита командной строки, которая используется в Windows 7/Vista/XP для создания, редактирования и удаления служб. Согласно документации TechNet, sc.exe:
sc.exe (Service Controller) осуществляет взаимодействие с установленными службами, получая и задавая их параметры. Утилиту SC.exe можно использовать для тестирования и отладки программ, работающих как службы. Свойства служб хранятся в реестре, параметры команды SC.exe позволяют модифицировать значения этих свойств, а также управлять запуском и остановкой служб. Возможности SC.exe во многом сходны с mmc консолью Services, расположенной в «Панели Управления».
Синтаксис команды удаления службы выглядит так:
sc delete ServiceName
Если имя службы содержит пробелы (как в нашем случае), его нужно взять в кавычки:
sc delete “Adobe LM Service”

В случае успешного выполнения команды sc delete в командной строке должно появиться сообщение [SC] DeleteService SUCCESS
Теперь, если в консоли управления службами нажать F5, вы увидите, что служа удалена и в списке не значится.
Удаляем службу с помощью редактора реестра
Альтернативный метод удаления служб в Windows 7 подразумевает использование редактора реестра.
Откройте редактор реестра (regedit.exe), и перейдите в ветку HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services. В ней содержится список всех служб, установленных в системе.
Найдите имя ветки реестра, соответствующее имени удаляемой службы.
Удостоверьтесь, что в значениях DisplayName and ImagePath содержатся, соответственно имя и путь к исполняемому файлу службы, которую вы планируете удалить.
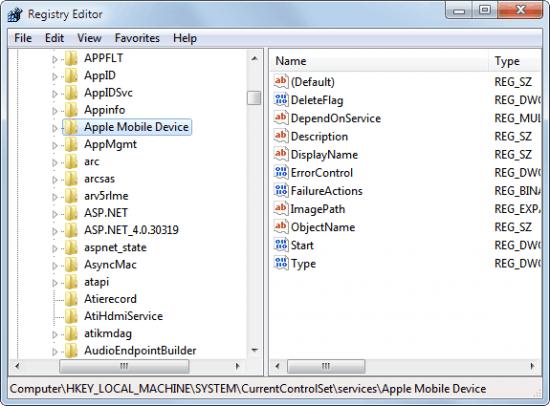
Щелкните правой конкой мыши по имени найденной ветки реестра с именем службы и выберите «Delete». После чего служба будет удалена из системы.
In this post, we will be discussing the topic of how to Enable or Disable Services and how to Start, Stop, Refresh and Restart Services in Windows 11 or Windows 10 using PowerShell, Command Prompt, Task Manager and Net Command.
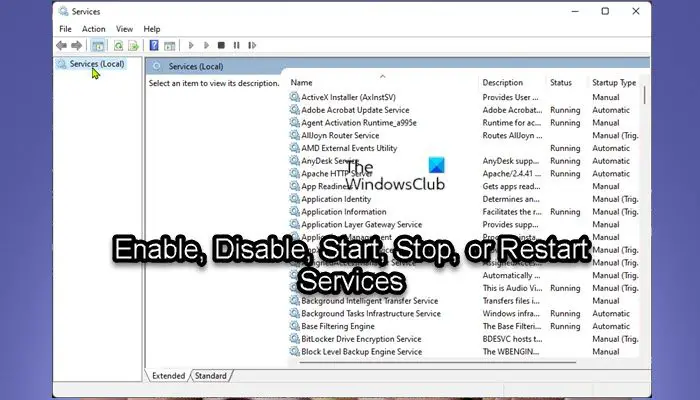
Windows Services are applications that typically start when the computer is booted and run quietly in the background until it is shut down. Essentially, a service is any Windows application that is implemented with the services API and handles low-level tasks that require little or no user interaction.
The Windows OS when installed and running on your device, actually does a great job of automatically managing services, but sometimes you may need to manually enable or disable a service on demand. Keep in mind that if you disable a service, any dependent services are also affected; and enabling a service does not automatically restart its dependent services.
All Windows Services can be accessed after opening the Windows Services Manager and you can Start, Stop, Disable Windows Services using it.
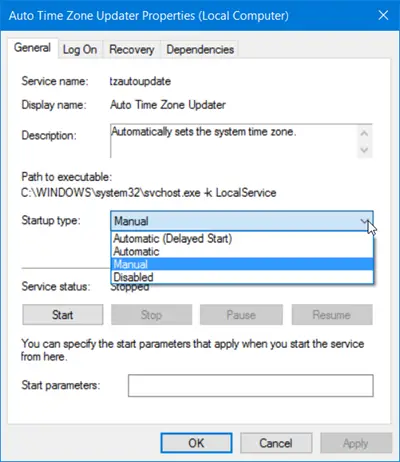
But you can also use PowerShell and Command Prompt to manage Services.
You must be signed in as an administrator to enable and disable services. It is not recommended to disable services unless you know what functions will be affected, and how the system performance will be impacted generally. If you disable a service and you’re unable to access your computer, you can boot into Safe Mode to enable the service.
Before making changes to the services, we recommend you create a system restore point as a necessary precautionary measure in case the procedure causes system malfunction, you can be able to perform System Restore using the restore point to undo the changes.
Use Task Manager to Stop, Restart or Start Windows Services
You can also Stop, Restart or Start Services using the Task Manager.
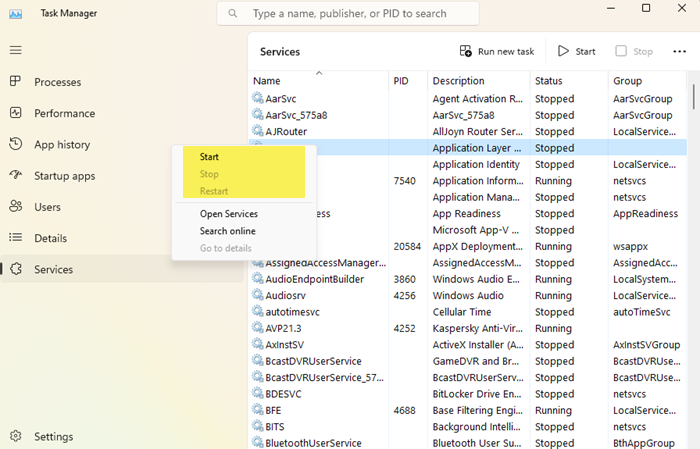
Open the Services tab, right-click on the Service and you will see the available options.
Enable or Disable Windows Services using PowerShell
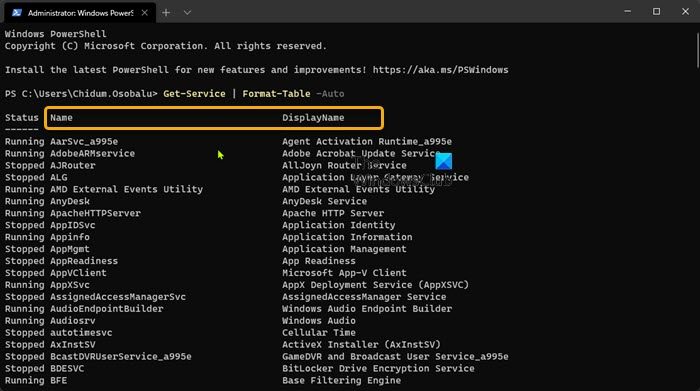
To enable or disable Services using PowerShell in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Press Windows key + X to open Power User Menu.
- Tap A on the keyboard to launch PowerShell (Windows Terminal) in admin/elevated mode.
- In the PowerShell console, type or copy and paste in the command below and hit Enter to check the current state of all Services:
Get-Service | Format-Table -Auto
To Enable a Service, type the command below you want into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
Note: Substitute the ServiceName placeholder in each of the commands with the actual service name you want to enable or disable.
(Automatic (Delayed Start))
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType AutomaticDelayedStart
OR
(Automatic)
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType Automatic
OR
(Manual)
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType Manual
To Enable and Start a Service, type the command below you want into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
(Automatic (Delayed Start))
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType AutomaticDelayedStart -Status Running
OR
(Automatic)
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType Automatic -Status Running
OR
(Manual)
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType Manual -Status Running
To Stop and Disable a Service, type the command below into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType Disabled -Status Stopped
- Exit PowerShell when done.
Enable or Disable Windows Services using Command Prompt
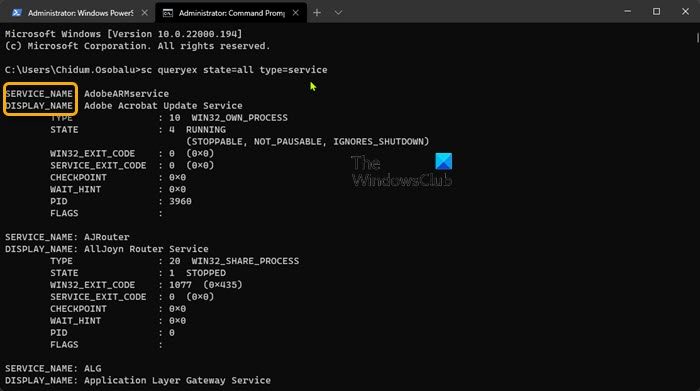
To enable or disable Services using Command Prompt in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Press Windows key + X to open Power User Menu.
- Tap A on the keyboard to open Windows Terminal in admin/elevated mode.
- Select Command Prompt.
- In the CMD prompt console, type or copy and paste in the command below and hit Enter to check the current state of all Services:
sc queryex state=all type=service
To Enable a Service, type the command below you want into the CMD prompt console and hit Enter:
Note: Substitute the ServiceName placeholder in each of the commands with the actual service name you want to enable or disable.
(Automatic (Delayed Start))
sc config "ServiceName" start=delayed-auto
OR
(Automatic)
sc config "ServiceName" start=auto
OR
(Manual)
sc config "ServiceName" start=demand
To Enable and Start a Service, type the command below you want into the CMD prompt console and hit Enter:
(Automatic (Delayed Start))
sc config "ServiceName" start=delayed-auto && sc start "ServiceName"
OR
(Automatic)
sc config "ServiceName" start=auto && sc start "ServiceName"
OR
(Manual)
sc config "ServiceName" start=demand && sc start "ServiceName"
To Stop and Disable a Service, type the command below into the CMD prompt console and hit Enter:
sc stop "ServiceName" && sc config "ServiceName" start=disabled
- Exit Command Prompt when done.
That’s it!
You must be signed in as an administrator to start, stop, or restart service. Also, you will not be able to start a disabled service until you enable the service.
Start, Stop, or Restart Windows Services using PowerShell
To Start, Stop, or Restart Services in PowerShell in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Open PowerShell (Windows Terminal) in admin/elevated mode.
To Start a Service, type the command below you want into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
Note: Substitute the ServiceName and DisplayName placeholder in each of the commands with the actual service name and display name respectively for the Service you want to Start, Stop, or Restart.
Start-Service -Name "ServiceName"
OR
Start-Service -DisplayName "DisplayName"
To Stop a Service, type the command below you want into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
Stop-Service -Name "ServiceName"
OR
Stop-Service -DisplayName "DisplayName"
To Restart a Service, type the command below you want into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
Restart-Service -Force -Name "ServiceName"
OR
Restart-Service -Force -DisplayName "DisplayName"
- Exit PowerShell when done.
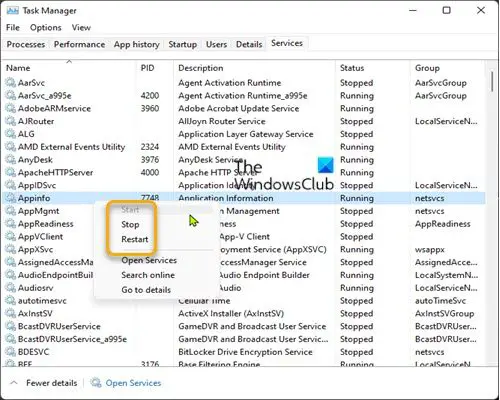
To Start, Stop, or Restart Services in Task Manager in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Open Task Manager.
- Click/tap on the Services tab.
- Now, right-click or press and hold on a Service.
- Click/tap on Start, Stop, or Restart.
Note: Start will only be available if the service status is currently stopped. Stop and Restart will only be available if the service status is currently running.
- Exit Task Manager when done.
Start, Stop, or Restart Windows Services using Net Command
To Start, Stop, or Restart Services using Net Command in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Open Windows Terminal in admin/elevated mode.
- Select Command Prompt or PowerShell.
To Start a Service, type the command below you want into the console and hit Enter:
Note: Substitute the ServiceName and DisplayName placeholder in each of the commands with the actual service name and display name respectively for the Service you want to Start, Stop, or Restart.
net start ServiceName
OR
net start "DisplayName"
To Stop a Service, type the command below you want into the console and hit Enter:
net stop ServiceName
OR
net stop "DisplayName"
- Exit Windows Terminal when done.
Start, Stop, or Restart Services using Command Prompt
To Start, Stop, or Restart Services using Command Prompt in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Open Windows Terminal in admin/elevated mode.
- Select Command Prompt.
To Start a Service, type the command below into the CMD prompt console and hit Enter:
Note: Substitute the ServiceName placeholder in each of the commands with the actual service name for the Service you want to Start, Stop, or Restart.
sc start ServiceName
To Stop a Service, type the command below into the CMD prompt console and hit Enter:
sc start ServiceName
- Exit Command Prompt when done.
How to Refresh a Windows Service?
When you refresh any Windows Service, the contents are re-read into the memory and the changes are reflected the next time the service is accessed. Here’s how you can Refresh a Service:
- Open Services Manager
- Locate the Service you want to refresh
- Right-click on it and select Refresh.
That’s it! Hope you find this post informative and helpful enough.
Read: Services Start, Stop or Startup type grayed out in Windows
What Microsoft startup services can I disable?
There are a couple of Windows 11/10 Services that are safe to disable, including:
- AVCTP service – Disable it if you do not use Bluetooth Audio Device or Wireless Headphones.
- BitLocker Drive Encryption Service – disable it if you do not use BitLocker storage encryption.
- Bluetooth Support Service – Disable it if you do not use any Bluetooth device
- Computer Browser – This will then disable Network discovery of systems on the local network
- Connected User Experiences and Telemetry – Disables Feedback, Telemetry and Data Collection
- Diagnostic Policy Service
- Etc.
Read: Services Start, Stop or Startup type grayed out in Windows
What happens if I disable all Microsoft services?
For example, the wireless services control your Wi-Fi card and if you disable that service, you may be unable to wirelessly connect your Windows 11/10 to a network. Intel has quite a few services which never really hog system resources. Lastly, any graphics card services should remain enabled.
HOT TIP: Windows 11 Repair and Recovery Tool is available FREE for now; go get it while you can as you never know when you may need it!