With an interface as attractive as Windows 10’s, it is easy to forget that the OS comes with a command line interface as well. You might have forgotten about Command Prompt, but Microsoft hasn’t, and it has brought some handy improvements to Command Prompt with Windows 10 and Windows 11. While it’s not as powerful as its Unix counterpart, there are many Command Prompt tricks that can make it a helpful tool to have. A lot of things that the Command Prompt (also known as CMD) can let you do are not even available in the GUI of the Windows OS, so it’s something you should be using. In this article, we have listed 20+ Command Prompt tricks that you should know in 2024.
If you’re new to Windows, we suggest glancing at our Windows 10 beginner tips article to get a better idea about how the OS works and its features. Now, let’s dive in and check out what you can do with Command Prompt.
1. Encrypt Files Using Command Prompt
One of the most useful things that you can do using the Command Prompt, is encrypting your sensitive data. Encryption is a way to prevent others from taking a peek at your data, and it’s a really important part of ensuring (to some extent, at least), that your files are only yours. With this simple Command Prompt trick, you can easily encrypt files on your Windows PC.
- Launch the Command Prompt, and change your working directory to the folder where your files are. This can be done by using the “cd” command.
- Once you’re done, type “Cipher /E“, and hit Enter. This will encrypt all the files that were inside the folder.
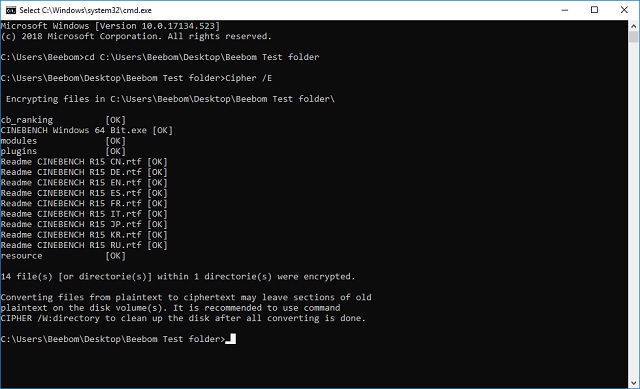
Note: If you try and open these encrypted files, they will open normally for you, however, any other user will not be able to view the files, unless they log in using your account. So make sure that you have a password set.
2. Change the Color of the Command Prompt Window
The Command Prompt window can be unexciting with the default black background and light gray text color. But Windows does allow you to change these colors to suit yourself and make things a bit more intriguing.
- Launch CMD and Right-click on the title bar
- Click on “Properties” and in the separate window that opens, click on “Colors”`
- Here you can choose the colors for the screen text or background as well as for the popup text and background, and also change the transparency of the CMD window
- After you’re done choosing the most fitting colors for your personality, Click OK
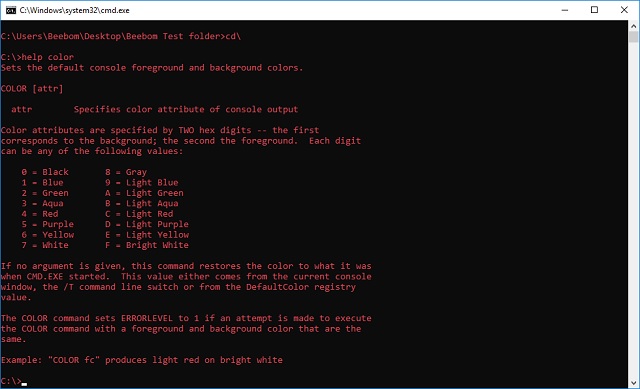
Note: There are a lot of other colors available, and you can check out the entire list by typing “help color“.
3. Change the Prompt Text in Command Prompt
When you first open Command Prompt, the default text of the prompt is very boring. It does reflect the current working directory that the user is in, but it sure could use some customization. If you would like the prompt in your cmd window to say something other than the default, you can use the following trick.
- Launch Command Prompt, and type “prompt” followed by the text that you want. Make sure you add “$G” to the end, to ensure that there is always the “>” sign at the end of the prompt, and you know where your command begins at.
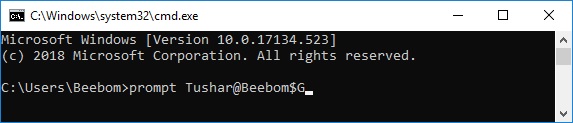
- Hit Enter, and you will see the prompt in the cmd window change to your custom text.
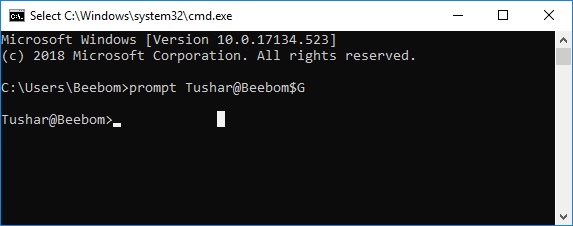
Note: There are some more options like “$G” available, and you check out the entire list by typing “help prompt“. Also, you can reset the prompt back to its original state by typing “prompt” and hitting Enter.
4. Change the Title of the Command Prompt Window
When you launch Command Prompt, you must have seen that the title bar reads “Command Prompt”, or maybe “Administrator Command Prompt”, if you launch it with Administrator privileges. While that is okay, but if you have a lot of cmd windows open, and each of them are working on a different task, then this “Command Prompt” title is not helpful at all. Fortunately, you can change that too.
- Open Command Prompt, and type “title”, followed by the text that you want the Title bar to read.
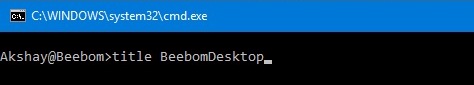
- Hit Enter, and you will see the Title of the cmd window change to the text that you entered.
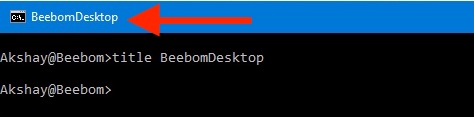
Note: The title changes back to “Command Prompt” once you quit cmd and relaunch it.
5. List Every Driver Installed on Your Windows 10 PC
If you’re trying to troubleshoot an issue or merely looking for a list of all the drivers on Windows 10/11, there’s a command prompt trick you can use. Follow the steps below to see the list of drivers:
- Type in driverquery /FO list /v in CMD, and you will see a list of drivers on your screen.
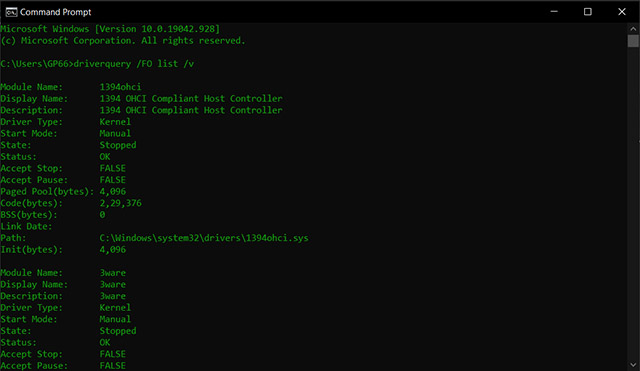
- If you want, you can also copy this output into a text file for easy viewing later. Use this command to save the drivers list to a document:
driverquery > C:\Users\YourUsername\Desktop\driver.txt
6. F1 to F9 Keys are Shortcuts in CMD
All the function keys on your keyboard are also shortcuts for various Command Prompt functions. Here’s what each function key on your keyboard does in CMD:
- F1: Tap or hold this key to retype your last command letter by letter.
- F2: Copies the current command up to a specified character.
- F3: Retypes the entire previous line
- F4: Auto-deletes the current command up to a specified character.
- F5: Similar to F3, but lets you cycle through previous commands.
- F6: Enters the EOF indicator into CMD.
- F7: Opens a list of previously entered commands.
- F8: Similar to F5, but doesn’t stop at the end of your command history in the session. Instead, it goes all the way to the start.
- F9: Enters a previous command by entering a number associated with that line.
7. Hide Folders using Command Prompt
While there is an easy way to hide folders on Windows by using the properties pane of the folder and checking the checkbox that says “Hidden”, the method is not very useful as the folders hidden using this method can easily be viewed if the view options are changed to “Show hidden files and folders”, making it a pretty useless feature. However, just like you can hide folders using Terminal on Mac, using this cmd trick, you can hide your folders in such a way that they will be completely hidden, and Explorer won’t be able to display them at all. Simply follow the steps outlined below:
- Launch Command Prompt, and navigate to the directory where your target folder resides.
- Type “Attrib +h +s +r folder_name“, replacing the “folder_name” with the name of the folder that you want to hide, and press Enter.
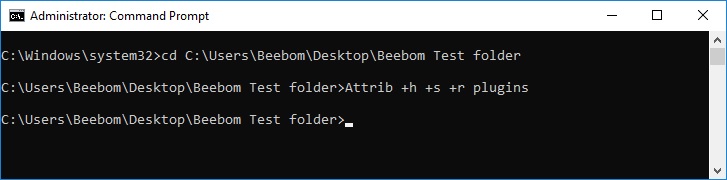
- You can now check that the folder is indeed hidden inside Windows Explorer and can not be seen by anyone.
- To unhide the folder, you can use the command “Attrib -h -s -r folder_name“.
Note: Hidden folders can be viewed using the cmd command “dir /AH”.
8. Copy Command Output to Clipboard
If you have ever tried to copy stuff off the Command Prompt, you must have realized that it is exceedingly difficult, not to mention un-intuitive. However, with this simple trick you can copy the output of any command that you want, directly to your computer’s clipboard, and you can then paste it into any text editor that you want.
- Launch Command Prompt and type the command that you want to copy the output for, followed by “| clip“. For example, I’m using the command “ipconfig | clip“. Hit Enter, and you will see that the cmd window shows no output.
- Open a text editor, such as Notepad, and press Control + V, and you can simply paste the output of the command directly inside Notepad.
9. List all Installed Programs
Another cool trick on the Command Prompt involves listing out all of the Windows 10 apps and programs that are installed on your PC. This is particularly helpful if you need to uninstall a program using the Command Prompt. To list out all the installed programs, simply follow the steps outlined below:
- Launch Command Prompt, and type “wmic product get name“.
- Hit Enter, and you will see a list of all the programs that are installed on your PC.
You can also use wmic to uninstall programs, directly from the cmd window. Simply type “wmic product where “name like ‘%NAMEOFAPP%’” call uninstall /nointeractive” and hit Enter. Obviously, replace “NAMEOFAPP” with the name of the app that you want to uninstall from your PC.
10. Open CMD Window Inside a Directory
Let’s face it, the way Windows handles changing directories using the “cd” command is rather weird. Fortunately, there is a simple way to open Command Prompt windows inside a directory so you don’t have to change directories. This is a really handy trick, especially if the folders you want to access are buried deep inside the filesystem. To open a cmd window inside a directory, just follow the steps below:
- Open the directory in Windows Explorer. In the address bar, type “cmd”, and hit Enter.
- A command window will open inside the directory you had opened in Windows Explorer.
11. Generate Battery Health Report
Windows 10 lets you track vital stats related to the battery’s health by maintaining data related to the battery. This includes stats like factory specifications, full battery capacity, and the current capacity and these are updated with each session. You can generate a report about these stats by using a CMD command, which can be executed as follows:
- Launch Command Prompt as an Administrator or change directory using cd C:\Windows\System32
- Enter command powercfg/energy
- The system will take 60 seconds to analyze and then generate a report in form of an HTML documents
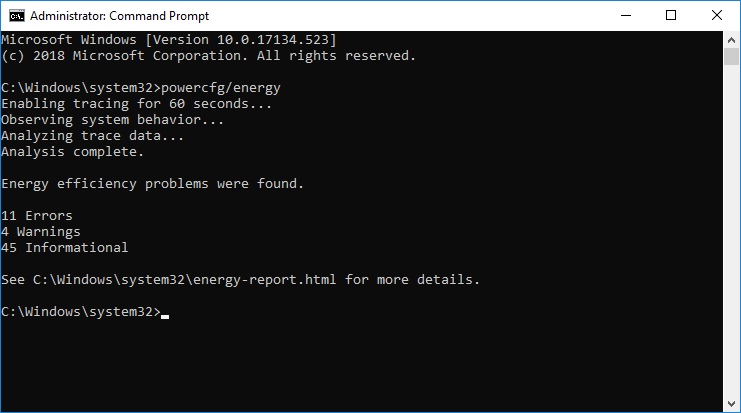
- To access the report, you can head to this location on your Windows 10 computer:
C:\Windows\system32\energy-report.html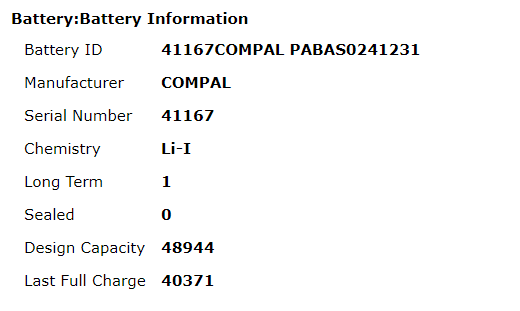
As you can see in our laptop’s case, the battery’s capacity has dropped to 82% to what it was shipped with. If you want a step-by-step direction for generating battery health on Windows, click on the link to read the article.
12. Hide Sensitive RAR Files in Images
CMD facilitates a command which lets you concatenate or fuse two files into a single file. While this command comes in handy in merging the contents of basic file types such as TXT or CSV, you can also use the command to hide a RAR, ZIP, or another archived file inside an image or text file. To achieve this, follow these steps:
- Open CMD in the directory which contains both files using the 10th item in this list or use the cd command to change the directory
- Use command copy /b <RAR_filename>.rar + <image_filename>.<extension> <result_filename>.<extension>.
- In our case, we used copy /b modules.rar+wave.png test2.png
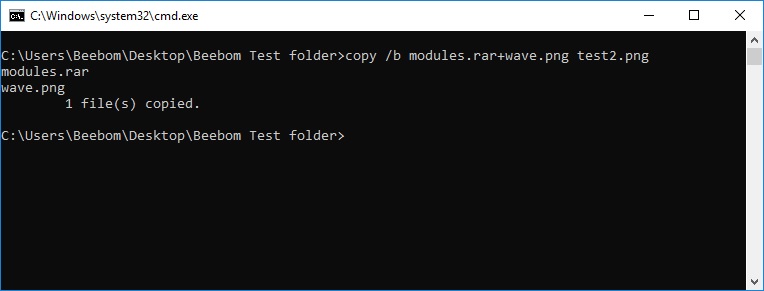
Note: make sure you enter the RAR file first followed by the other file, else you won’t be able to recover the RAR package. The method also works on most common file types including documents and PDFs as long as you add the archive file first.
- This will generate the result file, which in our case is test2.png
This PNG file displays as a normal image file but when you open it with WinRAR or any other extraction tool, it will extract the RAR file which is buried under the image file. This is a good way of saving your sensitive files from curious friends or co-workers or even prevent them from being misused even in case of a data breach.
13. Abort Command Execution
This is one of the best Command Prompt tricks and everyone should know about it. Say, you want to run a specific command but accidentally execute a different command. In that case, to quickly stop the command execution, simply press “Ctrl +C” together and the operation will be aborted instantly.
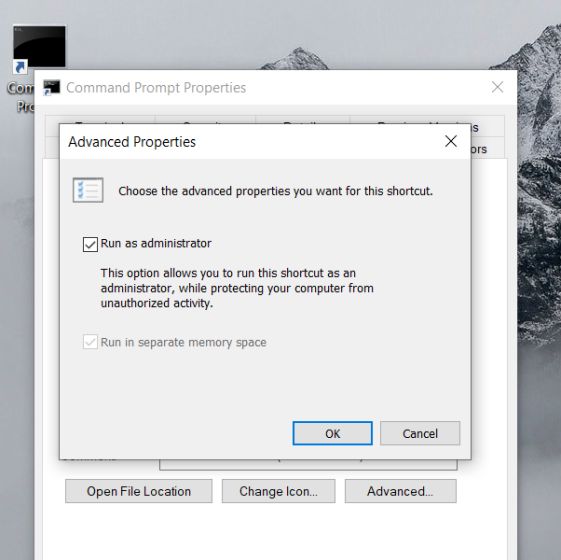
14. Always Run Command Prompt as Administrator
For users who deal with system files and applications know that they always need elevated privileges to tweak and move around things. But on the other hand, Command Prompt always defaults to the normal account which makes it harder for users to gain Administrator access in the middle of an operation. So to save yourself from such situations, you can change the behavior permanently and run Command Prompt with Administrator privilege always.
- Just search for “cmd” in the Start menu and right-click on it. After that, open its file location.
- Now copy the Command Prompt shortcut to your desktop.
- Move to desktop and right-click on the shortcut and open “Properties”.
- Here, click on Advanced and enable “Run as administrator”.
- Now onwards, open CMD from the desktop shortcut and it will always start with the Administrator privilege.
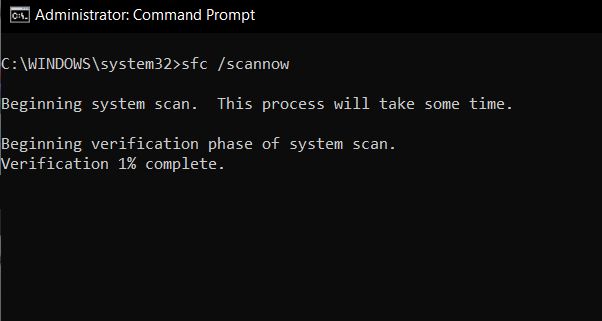
15. SFC /Scannow
SFC (System File Checker) is a relatively new addition to Command Prompt to keep your computer clean and bug-free. It’s a handy command-line tool that will help you fix many system issues. Just run sfc /scannow on Command Prompt and it will start verifying the integrity of all protected system files. Further, it will also repair the damaged files wherever possible. So in the future, if you face any issue, make sure to run this command on your Windows computer.
16. Find Information About Commands
Sometimes we run a command to achieve a certain task, but don’t know much about it. So to learn about specific commands, add /? at the end of any command, and hit enter. Command Prompt will give you a good overview of its usage and syntax. Take an example of SFC from the above point, type sfc /? and hit enter. It will tell you the sub-commands with examples, and what are the other commands related to SFC in a lucid language. This command is similar to the “man” command in Linux.
17. Command Line History
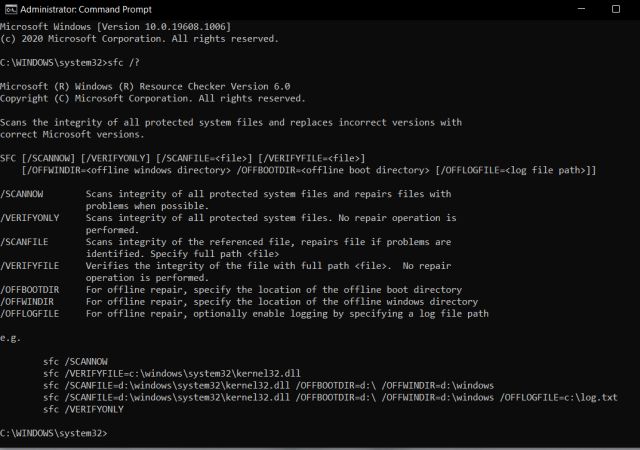
Many users are aware of the ‘UP’ navigation key to move forth and back between commands, but circling back to previous commands that were executed way back is difficult. However, there is the doskey /history command to check all your executed commands in a chronological list. The con is you can’t select the commands and execute them instantly and will have to type it out manually, which is not the best solution.
As a result, if you want to quickly navigate through all your past commands with the ability to execute them immediately, just press the F7 key. You will get a separate window where you can choose a command and execute it then and there. It’s one of the best Command Prompt tricks. Keep in mind, some users need to press the “Fn” key along with F7 to trigger this action.
18. Delete Temp Files to Clear Space
If you’re running low on space and urgently need to clear some trash out, getting rid of temporary files on your PC might be the swiftest action plan. Here’s what you can do to clean out temp files from your PC and regain a considerable amount of space.
- Use the command del /q /f /s %temp%\*
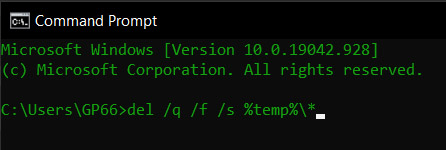
- Use the command del /s /q C:\Windows\temp\* (requires admin privileges)
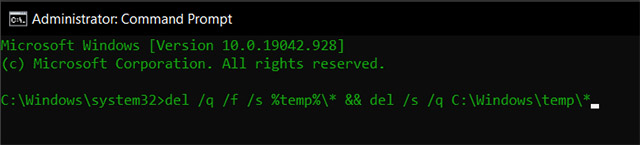
- You can also use both the commands in one go by typing del /q /f /s %temp%\* && del /s /q C:\Windows\temp\*
19. Play an RPG Game in Command Prompt
Do you like playing role-playing games? If so, you should definitely check out Ateraan, which is a text-only role-playing game that works inside the command prompt on your Windows PC.
- Type the command telnet ateraan.com 4002 into CMD and press enter. That will launch the game, and you can create your character and start your journey. GLHF!
20. Move to Windows Terminal
Command Prompt is one of the oldest Windows programs, but recently Microsoft announced a universal command-line tool for Windows that integrrated Powershell, WSL, and Command Prompt at once place; The program’s called the Windows Terminal. One of the advantages of running Command Prompt in Windows Terminla is you get the ability to run multiple tabs to execute multiple commands in the same Window. If you’re wondering how to try out the new Windows Terminal, refer to our guide on the same.
21. View a Directory’s Structure
Using the dir command to get an idea about the structure of a directory could be a hard affair since the command isn’t very presentable. Hence, if you want to look at a directory’s structure in a more neat and precise way, use the tree command. Here’s how the command looks.
tree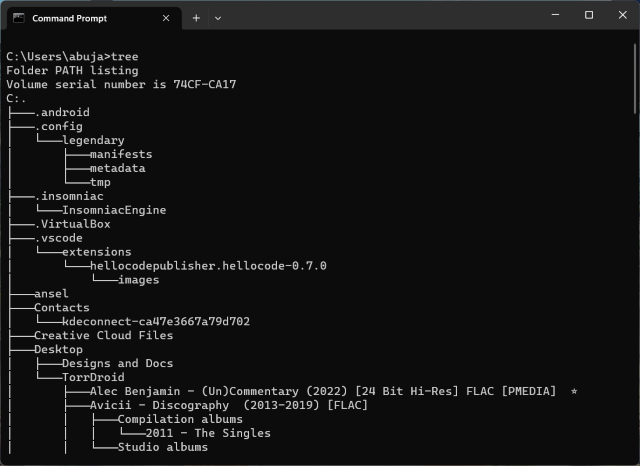
The command will show you the structure of your default directory “C:” If you want to check the structure of other drives, use the drive letter followd by a colon after typing the command.
tree A:Today, I will share the 100+ best CMD tricks you should know. Command Prompt may seem like an old feature of Windows computers. But it is an extremely powerful tool that your PC has. There are so many programs out there that need you to type down some CMD commands to run it. Then why not be a master at it?
Well, just to help you in mastering the CMD, I have shared these command prompt tricks. These tricks will definitely help you to become a CMD ninja at no time. So let’s head into the topic without wasting time.
Must Read: Best IPTV Players for Windows
Contents
- 1 Best CMD Tricks For Windows 11/10/8/7 PC
- 1.1 The Ultimate List of Best Command Prompt Tricks
- 2 Final Words
Best CMD Tricks For Windows 11/10/8/7 PC
1. Getting help
We often feel a need for help with the CMD commands. And performing a Google search for each of those CMD commands can be a pretty hectic task. However, thankfully there is a little CMD trick that will help you to get help for a specific CMD command.
Just add the “ /? ” after the command that you know about and hit enter. Then this command will help you to understand what a specific command does.
2. Check The IP Address Of A Website
This one is one of the best CMD tricks that you can try. There are often when website developers do feel a need to know the IP address of their website.
In such cases, a little CMD command helps a lot. Since checking the IP Address by going to different websites can be challenging. Instead, you can type this command: nslookup website.com
3. Execute Multiple Domains One By One
Want to execute multiple domains one by one? Well, then this command would be pretty handy for you. There are lots of programs that need CMD to get installed on a computer.
So, if you want to run multiple commands at once, relax a bit. Then you can put && between two CMD commands and hit the enter button.
After that, CMD will automatically execute the courses one by one. Plus, you do not have to enter commands again and again. Here is an example of the command: doskey /history&&driverquery
4. Repair the System Files
We all know fact that Windows’s system files often get corrupted. And installing windows, again and again, is a pretty boring task. But thankfully, you can repair system files by running a simple command. This is also one of the best CMD tricks one should know.
Simply type “sfc/scannow” and hit enter, and it will immediately start the scanning and repair process. However, you should open CMD with Administrator rights to execute the code.
5. Function Keys
The function keys are a set of keys on your keyboard that can be used to perform specific tasks in CMD. Here are some of the most useful ones:
- F1: F1 Key prints the characters one by one of your last-used commands.
- F2: This command help in pasting the last used command. However, it only works for some specific commands.
- F3: F3 pastes the last used command and works with every command.
- F4: F4 helps delete commands, but it works only for some specific commands.
- F5: F5 Key pastes the last used code without cycling.
- F6: F6 helps in pasting the ^Z code.
- F7: F7 key displays all the previously used commands.
- F8: F8 key pastes all the cycle-able used commands.
- F9: F9 key lets you paste commands from the list of recently used commands.
6. See PC driver list
Want to know which drivers are installed on your computer? Well, you can use a simple command to learn about it. Simply type down “driverquery” command, and you will get the list of all the installed drivers on your computer.
7. Change the Color of the Command Prompt
Do you know that you can even change the color of your command prompt? Well, for this you have to right-click on the command prompt window. Then go to properties and select a color.
8. Change Font Color
You can also change the font color of your command prompt. For this, you have to use commands like:
- color 1
- color 2
- color 3
- color 4
- color 5
and so on.
9. Command History
Looking for a command that you have previously used but can’t remember now? Well, then try the doskey /history command. This will offer you a list of all the previously used commands.
10. Shut Down the Computer With CMD
You can also shut down, restart, and log off your computer using CMD commands. To do so, here are the commands that you have to use
- For Shutdown: shutdown -s
- For Restarting: shutdown -r
- For Logoff: shutdown -l
11. Create a WiFi Hotspot
You can also take help from CMD to create a wifi hotspot and share the internet with other devices. However, it is a little lengthy process.
- First of all, you have to enter this command “netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=HotspotName key=Password” in the CMD.
- Now enter any name in the ‘HotspotName’ section and enter a password in the ‘Password’ section.
- Now to start the WiFi hotspot, you have to type the “netsh wlan start hostednetwork” command. Also, to switch off the WiFi hotspot, you must use the “netsh wlan stop hostednetwork” command.
The Ultimate List of Best Command Prompt Tricks
Apart from these commands, many of the best CMD tricks are available. You can learn more about them by going through this list.
1. Character Map – charmap
2. Bluetooth Transfer Wizard – fsquirt
3. Calculator – calc
4. Accessibility Wizard – accwiz
5. Administrative Tools – control admintools
6. Automatic Updates – wuaucpl.cpl
7. Add/Remove Programs – appwiz.cpl
8. Add Hardware Wizard – hdwwiz.cpl
9. Certificate Manager – certmgr.msc
10. Check Disk Utility – chkdsk
11. Clipboard Viewer – clipbrd
12. Control Panel – control
13. Component Services – dcomcnfg
14. Computer Management – compmgmt.msc
15. DDE Shares – ddeshare
16. Command Prompt – cmd
17. Date and Time Properties – timedate.cpl
18. Device Manager – devmgmt.msc
19. Direct X Troubleshooter – dxdiag
20. Disk Cleanup Utility – cleanmgr
21. Disk Defragment – dfrg.msc
22. Disk Management – diskmgmt.msc
23. Disk Partition Manager – diskpart
24. Display Properties – control desktop
25. Display Properties – desk.cpl
26. Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility – drwtsn32
27. Driver Verifier Utility – verifier
28. Event Viewer – eventvwr.msc
29. Files and Settings Transfer Tool – migwiz
30. File Signature Verification Tool – sigverif
31. Findfast – findfast.cpl
32. Firefox – firefox
33. Folders Properties – control folders
34. Fonts – control fonts
35. Fonts Folder – fonts
36. Free Cell Card Game – freecell
37. Game Controllers – joy.cpl | Best CMD Commands 2017
38. Group Policy Editor (for xp professional) – gpedit.msc
39. Hearts Card Game – mshearts
40. Help and Support – helpctr
41. HyperTerminal – hypertrm
42. Iexpress Wizard – iexpress
43. Indexing Service – ciadv.msc
44. Internet Connection Wizard – icwconn1
45. Internet Explorer – iexplore
46. Internet Properties – inetcpl.cpl
47. Keyboard Properties – control keyboard
48. Local Security Settings – secpol.msc
49. Local Users and Groups – lusrmgr.msc
50. Logs You Out Of Windows – logoff
51. Malicious Software Removal Tool – mrt
52. Microsoft Chat – winchat
53. Microsoft Movie Maker – moviemk
54. Microsoft Paint – mspaint
55 Microsoft Syncronization Tool – mobsync
56. Minesweeper Game – winmine
57. Mouse Properties – control mouse
58. Mouse Properties – main.cpl
59. Netmeeting – conf
60. Network Connections – control netconnections
61. Network Connections – ncpa.cpl
62. Network Setup Wizard – netsetup.cpl
63. Notepad – notepad
64. Object Packager – packager
65. ODBC Data Source Administrator – odbccp32.cpl
66. On Screen Keyboard – osk
67. Outlook Express – msimn
68. Paint – pbrush
69. Password Properties – password.cpl
70. Performance Monitor – perfmon.msc
71. Performance Monitor – perfmon
72. Phone and Modem Options – telephon.cpl
73. Phone Dialer – dialer
74. Pinball Game – pinball
75. Power Configuration – powercfg.cpl
76. Printers and Faxes – control printers
77. Printers Folder – printers
78. Regional Settings – intl.cpl
79 Registry Editor – regedit
80. Registry Editor – regedit32
81. Remote Access Phonebook – rasphone
82. Remote Desktop – mstsc
83. Removable Storage – ntmsmgr.msc
84. Removable Storage Operator Requests – ntmsoprq.msc
85. Resultant Set of Policy (for xp professional) – rsop.msc
86. Scanners and Cameras – sticpl.cpl
87. Scheduled Tasks – control schedtasks
88. Security Center – wscui.cpl
89. Services – services.msc
90. Shared Folders – fsmgmt.msc
91. Shuts Down Windows – shutdown
92. Sounds and Audio – mmsys.cpl
93. Spider Solitare Card Game – spider
94. SQL Client Configuration – cliconfg
95. System Configuration Editor – sysedit
96. System Configuration Utility – msconfig
97. System Information – msinfo32
98. System Properties – sysdm.cpl
99. Task Manager – taskmgr
100. TCP Tester – tcptest
101. Telnet Client – telnet
102. User Account Management – nusrmgr.cpl
103. Utility Manager – utilman
104. Windows Address Book – wab
105. Windows Address Book Import Utility – wabmig
106. Windows Explorer – explorer.
107. Managing the Boot Configuration Data – bcdedit
108. Editing Boot Settings – bootcfg
109. Encrypting or Decrypting Files/folders – cipher
110. Clearing the screen – cls
111. Managing stored usernames/passwords – cmdkey
112. Changing CMD Color – color
113. Compressing one or more files – compress
114. Converting FAT drives to NTFS – convert
115. Delete files – del
116. Deleting User Profiles – delprof
117. Displaying the list of files and folders – dir
118. Displaying Message On Screen – echo
119. Deleting one or more files – erase
120. Opening the windows Explorer – explorer
121. Formatting a disk – format
122. Knowing file extension – ftype
123. Displaying the Mac Address – getmac
124. Online help – help
125. Displaying the host name – hostname
126. Editing disc label – label
127. Log a user off – logoff
128. Get a log time in a file – logtime
129. Creating .cab files – makecab
130. Creating new folders- md
131. Opening Windows Installer – msiexec
132. Managing the network resources – net
133. Knowing the permissions for a user – perms
134. Testing a network connecting – ping
135. Printing a text file – print
136. Shutdown computer – psshutdown
137. Checking free disk space – freedisk
138. Know the file and volume utilities – fsutil
139. File transfer protocl – ftp
140. Showing the space used in folders – diskuse
141. Deleting a folder and all subfolders – deltree
142. Importing or Exporting Active directory data – csvde
143. Displaying the resultant set of Policy information – gpresult
144. Updating the Group policy settings – gpupdate
145. Replacing the files that are currently in use by the os – inuse
146. Comparing two files – fc
147. Finding a text string in a file – find
148. Finding for a strings in file – findstr
149. Displaying the memory usage – mem
Must Read: Best Firewall for Windows PC
Final Words
So these are some of the best CMD tricks you can try. Undoubtedly, if you use these cmd commands effectively, you will be able to level up your productivity. As well as you will be able to handle your PC easily. Anyway, if you have any questions, please comment below.
Command prompt (CMD) is a tool designed especially for the Windows Operating System which gives you a direct approach to complete tasks, which otherwise, needs a lot of effort and time. It’s so useful that even today we apply it to fix multiple errors and to enable/disable various Windows user settings. The tool works with certain commands.
As we can’t remember each one of them individually, we have come here with a list of 30 Best Commands (cmd.exe) in Windows 10 that you simply can’t ignore working with.
So just buckle up and enjoy the ride.
Compilation of 30 Best Commands (cmd.exe) in Windows 10
1: ipconfig: To find your IP Address within Seconds
If you waste a lot of time figuring out the “IP” (Internet Protocol) then this is one of the best commands meant for you. It permits easily trace out system’s IP address details. Moreover, the tool also displays info about the gateway as well as Router’s pre-specified web interface. After the execution of this command, you view a list of all the networks your system is connected to. The command looks like:
ipconfig /all command
2: shutdown: To create Shutdown shortcuts
This command lets restart or turn off PC within seconds which makes it very effective. The “shutdown” command line is a relief to all the latest versions where it’s very hard to search and execute the shutting down functionality. Using this, you can easily create shortcuts and can effectively place them wherever want, say at the desktop, taskbar or at the Start menu-list. In the advanced versions, you are able to use “cmd.exe” like a switch to turn your PC on/off taking into consideration many advanced options for the startup. For this, just type:
a) shutdown /r /o: To start the PC into various advanced options.
b) shutdown /s /t 0: To perform a regular power off
c) shutdown /r/t 0: To Restart your PC
3: ping: To test if there is no packet loss
You can run this command as: “ping howto-connect.com”. Here, “howto-connect.com” is the name of the server that we want to test. After hitting the Enter key, Windows will start sending packets to the address fed to the input (here, howto-connect.com). IP address will also work for the same in this utility. The server in return would inform that it has received those tiny data packets. This way you check if any of the data packets were not received by the server or if the server is saturated (can no longer hold the data packets).
4: ipconfig /flushdns: To Flush the DNS Resolver Cache
When you change DNS settings, they don’t just take place immediately. Instead, they take time for a complete setup. Meanwhile, if you’ll try to visit a particular site (changed DNS server settings for) time and again, the Windows in return will use the “cache” which retains the record for all the previous responses from that specific address. So this cache ensures that the Windows is fetching Data from the new DNS server by running “ipconfig /flushdns” command even after changing the DNS settings. It looks like:
ipconfig /flushdns
5: sfc /scannow: Scans your System files to fix Errors
Do you know that Windows 10 has an (SFC) System file checking tool as well following its predecessors? Yes, it does. This tool scans all system files and finds out errors in them moreover, replaces if any file is corrupt automatically. To use this “tool” via command prompt, just open up and type:
sfc /scannow
then, press Enter.
6: telnet: Connects you to the Telnet servers
Windows versions also carry a Telnet client approved by the Microsoft itself and this comes uninstalled. So you have to install manually from the Control Panel first. After installing this, use the telnet command to connect to the various telnet servers without needing to practice a 3rd-party software.
It is primarily advised to avoid using the telnet client but certain programs require this in the first place, to set up. This is where you’ll need Telnet. The syntax follows as:
telnet
7: cipher: To Overwrite or to permanently delete a Directory
Cipher has a lot of functions to perform. It is primarily used to manage encryption and write data to a drive and to clear instantly as well. When you run cipher command no deleted data can be restored. So The command allows to directly wipe a drive’s data without seeking for any permissions prior to the execution. This command is:
cipher /w:D:\ (assuming that D is the drive that you want to wipe here).
8: nslookup: To find the IP address of a Domain
Nslookup tells the IP address of the desired server. The same thing takes place when you type a domain name into your browser’s address bar as doing this tracks the IP address of the server first and accordingly, takes to the destination. This is a very passive process. But with “nslookup”, you can directly obtain this IP from your Command prompt within seconds. Furthermore, it can also tell you the server name if you type in the IP address. The syntax is as follows:
nslookup howto-connect.com
here, the server name is “howto-connect.com”.
9: netstat –an: Lists all your Network Connections and Ports
Netstat command allows you see a list of all the network connections along with the name and the details of the port they are operational with. This also informs you about the foreign IPs connected to these ports. The syntax is:
netstat -an
10: fc: To compare two files
You can exercise “fc” to compare certain parameters between 2 given files. It is very useful for those who face a hard time in finding out the differences in the text of two files. But not now, as this command does all within a matter of time. Straightway type ‘fc’ followed by the directory path and the file name to compare them real quick. Type:
fc /l “C:\Program Files (x86) \ABC1.doc” “C:\Program Files (x86) \ABC2.doc”
Here, ABC1 and ABC2 are the files names respectively. C is the drive which contains these files. The above command juxtaposes ASCII (text) in these two documents/files.
Note: Use, ‘/b’ to compare binary output and ‘/c’ for the case of text in the two specified documents.
11: sigverif: To Verify the File Signature
This command works to check if all the system files are digitally signed or not. Windows 10 and all other versions carry the tool popular as File Signature Verification tool. It uses a GUI interface and tells you accordingly that which system files are signed and which remain unsigned. The command performing to launch this signature verification tool is as follows:
sigverif
12: driverquery: Displays all the Installed Drivers
Windows 10 gives you Driver Query as a complementary tool to test your drivers. This tool works to identify the drivers that are being used with an entire list showcasing the installed drivers. If you need some additional information for these drivers, you can modify this command as follows:
driverquery -v (to know details regarding each driver)
driverquery -si (displays the signature information about each driver)
13: repair-bde: To recover the Encrypted data
Now retrieve data from your drive using “repair -bde”command. This is very handy when your drive is protected by the BitLocker. To run this command, you’ll need to have a destination drive, recovery key or the password for BitLocker. The basic format/syntax for this command is:
repair-bde -rk | rp
Here, you’ll need to specify the source and the destination drive along with the key/password followed by the path leading to the key/password. Here are some examples to run this command:
repair-bde c: d: -rk e:\recovery.bek
repair-bde c: d: -rp 111111-111111-111111-111111-111111-111111
14: tasklist: To list all the running tasks on a system
Tasklist, as the name suggests, provides a list of entire tasks active on your PC. This command is also compatible with multiple switches like –m and –svc. The –m switch displays all the DLL modules related to a task while -svc switch lists the services that support each task listed in the prompt. It looks like:
a) tasklist
b) tasklist –m
c) tasklist –svc
15: taskkill: to terminate a task
Taskkill performs the termination of the desired task taking help from its process identification code or the Image name. The syntax of the command includes taskkill followed by –pid or –im, of the task which you want to kill. Here is how this command looks like:
taskkill –pid 4104
taskkill –im iexplore.exe
16: Attrib: To change attributes of a file
Attrib command works to identify attributes of a file within the directory that you are executing the command from. You can use switches like: +a, -a, +h, -h, +I, -I, +r, -r, +s, -s, +v, -v, +x and, -x with this command. When apply with these switches, the command performs different functions as operated.
The syntax is as follows:
attrib [the switch: as listed above] [drive:][path][filename] [/s][/d][/l][/?]
For Example:
attrib +r c:\windows\system\secretfolder
17: bcdboot: To copy boot files
“Bcdboot” can definitely help if you are experiencing problems with the Windows boot-up functionality. This command lets you rebuild BCD inventory (for data) and also repair the existing one. The syntax is like:
bcdboot [/l][/s][/v][/m]
18: XCOPY: To copy files between drives
Now copy your files between drives using the “XCOPY” command. The command-line to copy photos from drive C to the drive F will be:
XCOPY c:\photos f:\photos /s /e
19: CD: To quickly switch between directories
CD command lets quickly access the directory of choice. For example, let’s just say that you are way too far from the C drive and quickly want to reach there. Then the syntax would follow:
cd c:\
This will take you to the C drive.
20: DIR: To see the contents of a directory
Navigating through the Windows Explorer to check data on your directories is very hectic. CMD gives you a power to quickly go through the contents of a directory with just 3 simple alphabets i.e “dir”. The syntax goes like:
dir
21: Assoc: Displays file name extensions
The Assoc command displays all the relevant file extensions and program associations on the system. You are capable of even extending this command to change file parameters like its associations and so on. For e.g. “assoc .txt=” will change the text files to whatever format you enter after the “=” sign in the command line. The syntax to change text files to pdf would be:
assoc .txt=.pdf
22: pathping: Advanced version of Ping
Pathping command is useful if you have a no.of router installed between a system and the device and want to test. This is a Post-established version of the “ping” command. It displays a little information about the routes which the packets take while traveling between multiple nodes. The syntax looks like:
pathping
23: powercfg: To manage your systems power consumption
You can run this command to track PC’s power consumption resources.To manage hibernation type:
powercfg /hibernate on
powercfg /hibernate off
and,
“powercfg /a” (to check power saving states)
Similarly, “powercfg /lastwake” will tell the programs/processes that woke the system from sleep. You, therefore, execute this command to troubleshoot a system if it wakes from sleep too often.
24: recimg.exe
The recimg.exe is the best command helps to design a custom recovery image for Windows 10 operating system. This image contains all the installed apps and Windows system files in their current state. It does not contain documents, user profiles, personal settings, etc. and is a highly sophisticated program. Simply type:
recimg.exe
and it will form a custom recovery image for your Windows version.
25: tracert: To track path of the transmitted packets
The Tracert command traces the path through with the packets are transferred to a known server. It’ll show the information about how each node packet interacts while moving to the destination. So if you are having any issues with the server, simply run this command line:
tracert howto-connect.com
(“howto-connect.com” is the name of the server here)
26: Tree: to obtain a tree structure of a Directory
This is among the best commands and represents the components of a directory/sub-directory into a Tree structure format. Simply open the Command Prompt and type “tree” followed by the drive or any sub-directory you want to see. This will showcase your entire user profile within that directory/path name. The syntax for checking constituents of the C drive (assume) will be:
tree c:/
Note: To zoom in, right-click the top bar of the prompt and go to Properties > Layout tab and change the default height parameter from 300 to something bigger, like 500 or so.
27: netsh interface: To check WiFi Connections
You can also catch the real culprit (in Windows 10) if your system is connected to a wifi network or not using this very effective command line. To know this, type in the following command into the command prompt:
netsh interface show interface | findstr /C: ”Wireless” /C: ”Name”
Executing this command will show the things like Admin State, State, Type moreover the Interface Name.
28: Move: To move files and directories to another location
This is one of the best commands lets change locations of a file. Just type in the simple command in CMD and that’s it. The file will successfully move to the desired location. The syntax for this command goes like:
move <filename> <destination folder>
For example, to move a file named “howto-connect.docx” to the folder “d:\backup\folder”; the command would be:
move howto-connect.docx d:\backup\folder
29: /?: To find the usage of a command
A few commands are very hard to understand, in this case, you will simply type the doubtful one, followed by this argument i.e. “/?”. For example, to see what “shutdown” does through CMD, simply type:
shutdown /?
And, this will show the list of all the switches that could be used with the “shutdown” command to perform numerous functions.
30: net share: To disable administrative shares
Windows shares automatically share some specific folders once it connects to a network. You can easily disable this, or can even eliminate this using a special command line. It is also one of the Best Commands in Windows 10. First of all, to view these shared folders and their locations, type:
net share
Now run the command to disable these shares. Type:
a) net share C$ /delete
b) net share IPC$ /delete
c) net share ADMIN$ /delete
and all other folders who you don’t want to display shares from.
Final Words
Command lines make it very easy to execute really hectic tasks within seconds. These, obviously, are hard to remember but you can easily learn a few of these to impress those tech-geeks and freaks around you. Commands mentioned above are no doubt very effective and functional. So just hold on to these Best Commands (cmd.exe) in Windows 10 and you’ll never ever be going through those very bulky procedures of executing functions within Windows OS.
Feel free to share more commands, which you feel could be important for Windows 10 users. Till then, share this article to lend a helping hand to others.
The Windows Command Prompt tool, and many of its commands, might seem boring or even relatively useless at first glance, but as anyone who has ever used the Command Prompt very often can tell you, there’s much to love!
These tricks will get you excited about many of the mundane-sounding Command Prompt commands like telnet, tree, or robocopy—okay, robocopy sounds pretty cool.
Some of these Command Prompt tricks are special features or fun uses for the Command Prompt itself, while others are just neat or relatively unknown things you can do with certain CMD commands.
Use Ctrl+C to Abort a Command
Just about any command can be stopped in its tracks with the abort command: Ctrl+C.
If you haven’t actually executed a command, you can just backspace and erase what you’ve typed, but if you’ve already executed it, then you can do a Ctrl+C to stop it.
It isn’t a magic wand, and it can’t undo things that aren’t undoable, like a partially complete format command.
However, for things like the dir command that seem to go on forever or questions you’re asked at the prompt that you don’t know the answer to, the abort command is an excellent Command Prompt trick to know.
View a Command’s Results One Page (or Line) at a Time
Ever run a command, like the dir command, that produces so much information on the screen that it’s almost useless?
One way to manage this info dump is to execute the command in a special way so whatever information is generated is shown to you one page, or one line, at a time.
Just type the command, and then follow it with the pipe character and then the more command.
For example, executing the below command will generate the thousands of lines of results that you expect from the dir command, but the more command will pause each page of results with — More — at the bottom of the page, indicating that the command is not done running.
dir /s | more
Just press the spacebar to advance by page, or press Enter to advance one line at a time.
Run Command Prompt as an Administrator Automatically
Many commands require that you open an elevated Command Prompt in Windows—in other words, execute them from a Command Prompt that’s run as an administrator.
You can always right-click any Command Prompt shortcut and choose Run as administrator, but creating a shortcut to do the same thing can be a huge time saver if you’re a frequent Command Prompt power user.
To complete this trick, just create a Command Prompt shortcut on the desktop, enter the shortcut’s properties and then select the Run as administrator box, located in the Advanced button on the Shortcut tab.
If you use Command Prompt via Terminal (you do by default if you’re on Windows 11), setting up admin access is even easier: Open Terminal’s settings to the Defaults page, and enable Run this profile as Administrator.
Become a Command Prompt Power User With Function Keys
The fact that the function keys actually do something in the Command Prompt is maybe one of the best kept secrets about the tool:
- F1: Pastes the last executed command (character by character)
- F2: Pastes the last executed command (up to the entered character)
- F3: Pastes the last executed command
- F4: Deletes current prompt text up to the entered character
- F5: Pastes recently executed commands (does not cycle)
- F6: Pastes ^Z to the prompt
- F7: Displays a selectable list of previously executed commands
- F8: Pastes recently executed commands (cycles)
- F9: Asks for the number of the command from the F7 list to paste
Change the Prompt Text
Did you know the prompt itself is completely customizable thanks to the prompt command? It is, and when we say customizable, we mean really customizable.
Instead of C:\>, you can set the prompt to any text you want, have it include the time, the current drive, the Windows version number (like in this example image), you name it.
One useful example is prompt $m$p$g, which will show the full path of a mapped drive, alongside the drive letter.
You can always execute prompt alone, without options, to return it to its sometimes boring default.
Get Help for Any Command
The help command does not provide help for every Command Prompt command.
However, any command can be suffixed with the /? option, usually called the help switch in Command Prompt, to display detailed information about the command’s syntax and often times even some examples.
The help switch may not be the coolest Command Prompt trick you’ve ever heard of, but it’s hard to disagree that it’s one of the more useful.
Neither the help command nor the help switch offers much in the way of explaining how to interpret the syntax.
How to Read Command Syntax
Save a Command’s Output to a File
An incredibly useful Command Prompt trick is the use of redirection operators, specifically the > and >> operators.
These little characters let you redirect the output of a command to a text file, giving you a saved version of whatever data the command produced in the Command Prompt window.
For example, let’s say you’re about to post a computer problem to an online forum, and you want to provide really accurate information about your computer. An easy way to do that would be to use the systeminfo command with a redirection operator.
For example, you might execute the below command to save the information provided by the systeminfo command to that file. You could then attach the file to your forum post.
systeminfo > c:\mycomputerinfo.txt
Terminal users have it even easier. Just right-click the Command Prompt tab and choose Export Text.
How to Redirect Command Output to a File
View a Drive’s Entire Directory Structure
One of the neatest little commands is the tree command. With tree, you can create a kind of map of the directories on any of your computer’s drives.
Execute tree from any directory to see the folder structure under that directory.
With so much information created with this command, it’s probably a good idea to export the results to a file so you can actually look through it.
Customize the Command Prompt Title Bar Text
Tired of that «Command Prompt» title bar text? No problem, just use the title command to change it to say whatever you like.
For example, let’s say your name is Maria Smith, and you want to express your ownership of the Command Prompt. Execute this and the title bar will change immediately:
title Property of Maria Smith
The change won’t stick, so the next time you open Command Prompt, the title bar will be back to normal.
The title command is usually used to help give a custom appearance in script files and batch files—not that titling it with your name isn’t a good idea!
Copy Text From the Command Prompt
Copying lots of text from the Command Prompt isn’t as easy as copying from other programs, which is part of the reason why saving a command’s output to a file, which you learned about a few tricks back, is so handy.
However, what if you do just want to copy a short section of text to the clipboard? It’s not too hard, but it’s not very intuitive either:
- Right-click anywhere in the Command Prompt window and choose Mark.
- Highlight with your left mouse button whatever you’d like to copy.
- Press Enter or right-click once.
That’s the menu-based method, but surprisingly, you can also use the regular Ctrl+C shortcut, too.
If you chose Mark but then decided you don’t want to copy anything, right-click again to cancel the Mark action, or press the Esc key.
Now you can paste that information anywhere, just like you paste other text.
If QuickEdit Mode is turned on (or you’re in Terminal), right-clicking won’t show a menu. This is actually another tip in this list! See step 20 for the details.
Open the Command Prompt From Any Location
If you’ve ever worked in the Command Prompt for very long, you know that it can be really frustrating executing the cd/chdir command over and over again to get to the right directory.
In Windows, open the folder you’d like to start working from. When you’re there, hold down Shift while you right-click anywhere in the folder.
After the menu pops up, you’ll notice an entry that’s not usually there: Open in Terminal (Windows 11) or Open command window here. Select that, and you’ll start a new instance of the command line, ready and waiting at the right location.
If you’re a Command Prompt power user, you’ll immediately recognize the value in this little trick.
Drag and Drop For Easy Path Name Entry
Most Command Prompt commands require you to specify full paths to files or folders, but typing out a long path can be frustrating, especially when you miss a character and have to start over.
For example, in Windows 11 and 10, this is the path to the Accessories group in the Start Menu:
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Accessories
Who wants to type that all in manually? We don’t.
Just open the folder in Explorer. Once there, drag the folder or file to the Command Prompt window and let go. Like magic, the full path is inserted, saving you a considerable amount of typing depending on the length and complexity of the path name.
This technique doesn’t work in an elevated Command Prompt.
Shut Down or Restart Another Computer
System administrators in a business environment do this all the time for lots of reasons, but you can also shut down or restart another computer on your network, all from your computer’s Command Prompt.
The easiest way to shut down a computer remotely is to execute shutdown /i from the Command Prompt to open the Remote Shutdown Dialog, shown above.
Just enter the name of the remote computer (which you can get by running the hostname command on the other PC), choose what you want to do (restart or shutdown), select some other options, and then select OK.
So whether you’re brushing up on your command skills or just scaring a family member, this Command Prompt trick is a fun one.
You can also shut down or restart another computer strictly from the Command Prompt with the shutdown command, without using the Remote Shutdown Dialog.
Use Robocopy as a Backup Solution
Thanks to the robocopy command, you don’t need to use Window’s backup software or install a free backup software tool.
Just execute the following, obviously replacing the source and destination folders with whatever you’d like to back up and where it should go.
robocopy c:\users\ellen\documents f:\mybackup\documents /copyall /e /r:0 /dcopy:t /mir
The robocopy command with these options functions identically to an incremental backup software tool, keeping both locations in sync.
You don’t have this command if you’re using Windows XP or earlier. However, you do have the xcopy command, which can be used to do something very similar:
xcopy c:\users\ellen\documents f:\mybackup\documents /c /d /e /h /i /k /q /r /s /x /y
No matter which command you choose to use, just create a batch file containing the command and schedule it to run in Task Scheduler, and you’ll have your own custom-made backup solution.
View Your Computer’s Important Network Information
Maybe just for your own information, but certainly when you’re troubleshooting a network or internet problem, you’ll probably at some point need to know details about your computer’s network connection.
Everything you’d want to know about your network connection is available somewhere in the Control Panel in Windows, but it’s much easier to find, and much better organized, in the results from the ipconfig command.
Execute this command in Command Prompt:
ipconfig /all
What displays on-screen next is everything important about your network connection: your IP address, hostname, DHCP server, DNS information, and much, much more.
Microsoft
Map a Local Folder Just Like a Network Drive
The net use command is used to assign shared drives on a network to your own computer as a drive letter, but did you know there’s another command that can be used to do the same thing to any folder on any of your local hard drives?
There is, and it’s called the subst command. Just execute the command followed by the path of the folder you wish to appear as a drive.
For example, let’s say you want your C:\Windows\Fonts folder to appear as the Q: drive. Just execute this command and you’re set:
subst q: c:\windows\fonts
This Command Prompt trick makes accessing a particular location from the Command Prompt much easier and the folder will appear as a drive next to all your real hard drives.
An easy way to delete the «network drive» example here is with the subst /d q: command. Just replace q: with your own drive letter.
Access Previously Used Commands With the Arrow Keys
Marcus Urbenz / Unsplash
Another great Command Prompt trick uses the keyboard arrow keys to cycle through previously executed commands.
The up and down arrow keys cycle through the commands you’ve entered, and the right arrow automatically enters, character by character, the last command you executed.
This might not sound that interesting, but there are several situations where the arrow keys become huge time savers.
Consider this example: You’ve typed out 75 characters of a command and then try to execute it, only to find that you forgot to add an option at the very end. No problem, just press the up arrow and the entire command is automatically entered in the Command Prompt window, ready for you to edit to make it work.
Automatically Complete Commands With Tab Completion
Tab completion is another Command Prompt trick that can save you lots of time, especially if your command has a file or folder name in it that you’re not completely sure of.
To use tab completion, enter the command and then the portion of the path that you do know, if at all. Then press the Tab key over and over to cycle through all the available possibilities.
For example, let’s say you want to change directories to some folder in the Windows directory, but you’re not sure what it’s named. Type cd c:\windows\ and then press Tab until you see the folder you’re looking for.
The results cycle in order, or you can use Shift+Tab to step through the results in reverse.
You know how your smartphone’s texting app automatically guesses what it is you want to type next? Tab completion in Command Prompt is sort of like that—only better.
Find a Website’s IP Address
Want to find the IP address of any website? Use the nslookup command or the ping command, but the former is probably faster.
First, let’s use the nslookup command to find the IP address of lifewire.com.
Just execute nslookup lifewire.com and view the result. Don’t confuse any private IP addresses that also show up in the nslookup results alongside the public IP address of lifewire.com, which is what IP address we’re after.
Now let’s try using the ping command to find it.
Execute ping lifewire.com and then look at the IP address between the brackets in the first line shown. Don’t worry if the ping command «times out» during execution; all we needed here was the IP address.
You can use the same procedure with any website or any hostname on your local network.
What the NSLOOKUP Tool Can Tell You About Internet Domains
Copy and Paste Easier With QuickEdit Mode
A number of these Command Prompt tricks have dealt with making copying and pasting easier. So, how about an even easier way to copy from the Command Prompt (and a secret way to easily paste)?
Just right-click on the Command Prompt title bar and select Properties. On the Options tab, in the Edit Options section, check the QuickEdit Mode box and then select OK.
Enabling QuickEdit Mode is like having Mark enabled all the time, so selecting text to copy is really easy.
As a bonus, this also enables a simple way to paste into the Command Prompt: just right click once and whatever you have in the clipboard is pasted in the Command Prompt window. Normally, pasting involves right-clicking and selecting Paste, so this is still a bit different than you’re used to.
Using Command Prompt through Terminal? Just select text like you would anywhere else, and press Enter or right-click to copy it. No need to turn on QuickEdit Mode.
Watch Star Wars Episode IV
Yes, you read that correctly, you can watch an ASCII version of the full Star Wars Episode IV movie right in the Command Prompt window!
Just open Command Prompt and execute this:
telnet towel.blinkenlights.nl
The movie will start immediately. Check out the tip below if this doesn’t work.
True, this isn’t a terribly productive use of the Command Prompt, nor is it really a trick of the Command Prompt or any command, but it sure is fun! We can’t imagine the work that went into this homage to the sci-fi masterpiece.
Windows Command Prompt is not only useful but also a tool that you should give more respect to by knowing these cool cmd commands. Here is a list of the most used commands in the CMD window or prompt commands that you can type to perform certain tasks in windows.
Command Prompt is one of the most powerful tools in Windows, also known as CMD. CMD is the command-line interpreter on Windows operating systems. Command Prompt interacts with the user through a command-line interface.
Things were not always like this, but with the advent of GUI-based operating systems, people started feeling that computing through command-based tools was boring. This ultimately leads the command prompt into obscurity.
However, the command prompt is not useless. It can be pretty helpful. This article provides some excellent tricks, secrets, and hacks that will make you realize that the Windows Command Prompt is useful and a tool you should give more respect to by knowing these cool cmd commands. Here you will find lots of basic cmd commands, cmd commands for the network, cmd commands tricks, etc.
Also Read: How To Remove Computer Viruses Using CMD
To Open CMD, you need to search for CMD in the Search box, or you can press Windows Key + R, which will eventually open the Run window, where you need to type CMD and hit enter.
1. Accessibility Controls – zaccess.cpl 2. Accessibility Wizard – accwiz 3. Add Hardware Wizard – hdwwiz.cpl 4. Add/Remove Programs – appwiz.cpl 5. Administrative Tools – control admintools 6. Automatic Updates – wuaucpl.cpl 7. Bluetooth Transfer Wizard – fsquirt 8. Calculator – calc 9. Certificate Manager – certmgr.msc 10. Character Map – charmap 11. Check Disk Utility – chkdsk 12. Clipboard Viewer – clipbrd 13. Command Prompt – cmd 14. Component Services – dcomcnfg 15. Computer Management – compmgmt.msc 16. Control Panel – control 17. Date and Time Properties – timedate.cpl 18. DDE Shares – ddeshare 19. Device Manager – devmgmt.msc 20. Direct X Troubleshooter – dxdiag 21. Disk Cleanup Utility – cleanmgr 22. Disk Defragment – dfrg.msc 23. Disk Management – diskmgmt.msc 24. Disk Partition Manager – diskpart 25. Display Properties – control desktop 26. Display Properties – desk.cpl 27. Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility – drwtsn32 28. Driver Verifier Utility – verifier 29. Event Viewer – eventvwr.msc 30. Files and Settings Transfer Tool – migwiz 31. File Signature Verification Tool – sigverif 32. Findfast – findfast.cpl 33. Firefox – firefox 34. Folders Properties – control folders 35. Fonts – control fonts 36. Fonts Folder – fonts 37. Free Cell Card Game – freecell 38. Game Controllers – joy.cpl 39. Group Policy Editor (for xp professional) – gpedit.msc 40. Hearts Card Game – mshearts 41. Help and Support – helpctr 42. HyperTerminal – hypertrm 43. Iexpress Wizard – iexpress 44. Indexing Service – ciadv.msc 45. Internet Connection Wizard – icwconn1 46. Internet Explorer – iexplore 47. Internet Properties – inetcpl.cpl 48. Keyboard Properties – control keyboard 49. Local Security Settings – secpol.msc 50. Local Users and Groups – lusrmgr.msc 51. Logs You Out Of Windows – logoff 52. Malicious Software Removal Tool – mrt 53. Microsoft Chat – winchat 54. Microsoft Movie Maker – moviemk 55. Microsoft Paint – mspaint 56. Microsoft Syncronization Tool – mobsync 57. Minesweeper Game – winmine 58. Mouse Properties – control mouse 59. Mouse Properties – main.cpl 60. Netmeeting – conf 61. Network Connections – control netconnections 62. Network Connections – ncpa.cpl 63. Network Setup Wizard – netsetup.cpl 64. Notepad – notepad 65. Object Packager – packager 66. ODBC Data Source Administrator – odbccp32.cpl 67. On Screen Keyboard – osk 68. Outlook Express – msimn 69. Paint – pbrush 70. Password Properties – password.cpl 71. Performance Monitor – perfmon.msc 72. Performance Monitor – perfmon 73. Phone and Modem Options – telephon.cpl 74. Phone Dialer – dialer 75. Pinball Game – pinball 76. Power Configuration – powercfg.cpl 77. Printers and Faxes – control printers 78. Printers Folder – printers 79. Regional Settings – intl.cpl 80. Registry Editor – regedit 81. Registry Editor – regedit32 82. Remote Access Phonebook – rasphone 83. Remote Desktop – mstsc 84. Removable Storage – ntmsmgr.msc 85. Removable Storage Operator Requests – ntmsoprq.msc 86. Resultant Set of Policy (for xp professional) – rsop.msc 87. Scanners and Cameras – sticpl.cpl 88. Scheduled Tasks – control schedtasks 89. Security Center – wscui.cpl 90. Services – services.msc 91. Shared Folders – fsmgmt.msc 92. Shuts Down Windows – shutdown 93. Sounds and Audio – mmsys.cpl 94. Spider Solitare Card Game – spider 95. SQL Client Configuration – cliconfg 96. System Configuration Editor – sysedit 97. System Configuration Utility – msconfig 98. System Information – msinfo32 99. System Properties – sysdm.cpl 100. Task Manager – taskmgr 101. TCP Tester – tcptest 102. Telnet Client – telnet 103. User Account Management – nusrmgr.cpl 104. Utility Manager – utilman 105. Windows Address Book – wab 106. Windows Address Book Import Utility – wabmig 107. Windows Explorer – explorer. 108. Managing the Boot Configuration Data - bcdedit 109. Editing Boot Settings - bootcfg 110. Encrypting or Decrypting Files/folders - cipher 111. Clearing the screen - cls 112. Managing stored usernames/passwords - cmdkey 113. Changing CMD Color - color 114. Compressing one or more files - compress 115. Converting FAT drives to NTFS - convert 116. Delete files - del 117. Deleting User Profiles - delprof 118. Displaying the list of files and folders - dir 119. Displaying Message On Screen - echo 120. Deleting one or more files - erase 121. Opening the windows Explorer - explorer 122. Formatting a disk - format 123. Knowing file extension - ftype 124. Displaying the Mac Address - getmac 125. Online help - help 126. Displaying the host name - hostname 127. Editing disc label - label 128. Log a user off - logoff 129. Get a log time in a file - logtime 130. Creating .cab files - makecab 131. Creating new folders- md 132. Opening Windows Installer - msiexec 133. Managing the network resources - net 134. Knowing the permissions for a user - perms 135. Testing a network connecting - ping 136. Printing a text file - print 137. Shutdown computer - psshutdown 138. Checking free disk space - freedisk 139. Know the file and volume utilities - fsutil 140. File transfer protocl - ftp 141. Showing the space used in folders - diskuse 142. Deleting a folder and all subfolders - deltree 143. Importing or Exporting Active directory data - csvde 144. Displaying the resultant set of Policy information - gpresult 145. Updating the Group policy settings - gpupdate 146. Replacing the files that are currently in use by the os - inuse 147. Comparing two files - fc 148. Finding a text string in a file - find 149. Finding for a strings in file - findstr 150. Displaying the memory usage - mem 151. Remote desktop protocol - mstsc 152. Managing the domain - netdom 153. Manage the Background intelligent Transfer Service - bitsadmin 154. Enable Or disable Break Capability in CMD - break 155. Change the permissions of files - cacls 156. Call another batch program using one - call 157. Manage the certification authority files and services - certutil 158. Change the folder or go to a specific one - cd 159. Check the NTFS file system - chkntfs 160. Copy one or more files to other location - copy 161. show the mapping inbetween logical and physical processor - coreinfo 162. Import/Export data of an active directory - csvde 163. Display the date or change it - date 164. Display disk usage - diruse 165. View used space in folder - diskuse 166. Show the list of device drivers - driverquery 167. View objects in active directory - dsget 168. Modify objects in an active directory - dsmod 169. Display the print queue status - lpq 170. Display open files - open files 171. Monitor performance in CMD - perfmon 172. Shows remote Access service status - rasdial 173. Managing RAS connections - rasphone 174. Send A Message - msg 175. Create a symbolic Link - mklink 176. Send email from command line - mapisend 178. Manage the performance monitor logs - logman 179. Uncompress the CAB files - expand 180. Loop command - all options files, directory, and list - for 181. Move an active Directory Object - dsmove 182. In order to view items in the Active directory - dsget 183. View the Active directory ACLs - DSACLs 184. Client-side caching for offline files - CSCcmd 185. Monitor and log system activity (Windows event log) - sysmon 186. Edit file and folder permissions - subinacl 187. Save and change the current directory - pushd 188. Display user session - quser 189. Read, export, delete and set keys and values - reg registry 190. Register or unregister a DLL - regsvr32 191. Batch process multiple files - forfiles 192. Search for Items in Active directory - dsquery 193. Cleanup temp file, recycle bin - cleanmgr 194. Compare the contents of two sets of files - comp 195. show the map between logical and physical processor - coreinfo 196. Manage RAS connections - rasdial 197. kill process by process and name id - pskill 198. Disconnect the remote desktop session - tsdiscon 199. Edit the service principal name - setspn 200. Share a folder or printer rmtshare 201. Change the registry permissions - regini 202. Execute a program from different user account - runas
So, these are the best cmd commands. I hope these cmd commands will help you a lot. If you know some other cmd commands, let us know by commenting on the comment box below. Feel free to share this post with your friends!
