Last Updated :
23 Sep, 2024
The xcopy command in Windows is a powerful tool for copying files and directories. It extends the functionality of the standard copy command by allowing the copy of entire directories along with their subdirectories and files all at once. This makes xcopy highly useful for tasks such as backing up files, migrating data, or automating file management tasks. In this article, we will cover what the xcopy command is how to use it, and provide some common use cases with examples.
Table of Content
- What is the Xcopy Command?
- How to Use the xcopy Command?
- 1. Copy Files
- 2. Copy Entire Directory
- 3. Copy Directory Including Empty Folders
- 4. Copy and Overwrite Files
- 5. Copy Files Based on Date
- 6. Copy Files in Quiet Mode
- 7. Copy Files with Attributes
- 8. Copy Files and Verify
- 9. Copy Files Without Prompting for Destination Confirmation
- Common xcopy Options
- How to Use the Xcopy Command in Windows — FAQs
What is the Xcopy Command?
The xcopy (extended copy) command is used to copy files and directories including the subdirectories and files within them. Unlike the basic copy command, xcopy can handle large-scale directory copying making it perfect for backups, migrations, and file replication.
Basic Syntax:
xcopy [source] [destination] [options]
- [source]: The path to the file or directory we want to copy.
- [destination]: The path to where we want to copy the files.
- [options]: The Various flags that control how the xcopy command behaves.
How to Use the xcopy Command?
1. Copy Files
To copy a file from one location to another using xcopy the basic syntax is:
xcopy C:\source\file.txt D:\destination\
This command copies file.txt from the C:\source directory to the D:\destination directory.
Example:
2. Copy Entire Directory
To copy an entire directory including all its subdirectories and files we can use the /s switch:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /s
The /s option copies all directories and subdirectories except empty ones.
Example:
3. Copy Directory Including Empty Folders
If we also want to include the empty directories in the copy use the /e switch:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /e
The /e switch copies all subdirectories including the empty ones.
Example:
4. Copy and Overwrite Files
If files in the destination already exist and we want to overwrite them we can use the /y option:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /y
The /y option suppresses the prompt that asks if we want to overwrite the file.
Example:
5. Copy Files Based on Date
We can use the /d option to only copy files that have changed after a specific date or if they are newer than the destination files.
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /d
This ensures that only new or modified files are copied saving time and disk space.
Example:
6. Copy Files in Quiet Mode
To suppress output and avoid unnecessary prompts use the /q option:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /q
This copies files quietly without listing each file.
Example:
7. Copy Files with Attributes
To copy system or hidden files we can use the /h option:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /h
Normally, hidden and system files are not copied. The /h switch forces the xcopy command to the include them.
Example:
8. Copy Files and Verify
To ensure that files are copied correctly we can use the /v option which verifies each file after copying:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /v
Example:
9. Copy Files Without Prompting for Destination Confirmation
Sometimes, xcopy will prompt to confirm whether the destination is a directory or a file. To avoid this we can add the /i option:
xcopy C:\source\ D:\destination\ /i
The /i option assumes the destination is a directory and automatically continues.
Example:
Common xcopy Options
Here are some commonly used xcopy options:
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
/s |
The Copies directories and subdirectories except empty ones. |
|
/e |
The Copies of all subdirectories including the empty ones. |
|
/y |
Overwrites files without prompting for confirmation. |
|
/d |
Copies files that have changed since the last copy. |
|
/v |
The Verifies each file after copying to ensure accuracy. |
|
/h |
The Copies hid and system files. |
|
/q |
The Copies files in quiet mode suppressing output. |
|
/i |
Assumes the destination is a directory if it’s unclear. |
|
/f |
It displays the full source and destination of each file copied. |
Conclusion
The xcopy command is a versatile and powerful tool in Windows allowing you to perform advanced file-copying tasks with ease. Whether we’re backing up directories copying only newer files or handling large sets of files across different drives, xcopy offers a range of options to suit your needs. By mastering this command we can save time streamline your file management tasks and ensure that data is efficiently copied with accuracy and precision.

In this tutorial, we will learn how to copy files and folders in the Windows Command prompt.
We are going to look at two cmd commands: Copy and Xcopy.
Note that the copy command has some limitations compared to the xcopy. For example, to copy directories or hidden files, you have to use the xcopy command.
Copy Command
On Windows, we can use the copy command to copy one or more files from one location to another:
copy C:\data\sales.doc C:\backupThe preceding command will copy sales.doc from C:\data\ to C:\backup.
Use the /y switch to overwrite duplicate files without confirmation:
copy /y C:\data\sales.doc C:\backupWe can also save a file to a different name. For example, the following command saves file1.txt as file2.txt in the same directory:
copy file1.txt file2.txtYou can also use wildcards to copy multiple files:
copy /y C:\data\* C:\backup
copy /y C:\data\*.doc C:\backupThe first command copies all files in the C:\data\ directory to C:\backup. The second command copies all files with a .doc extension to the C:\backup.

We can also combine several files into one:
copy file1+file2 file3
copy error* C:\backup\report.txtIn the first line, file1 and file2 are combined to make one file named file3. In the second line, all files whose names start with «error» are copied to the C:\backup, as a single file called report.txt.
You can get a list of all available options with the copy /? command.
Xcopy Command
The xcopy command offers more features. For example, with xcopy, we can copy directories and subdirectories, as well as hidden files.
Command Options
| /Y | Prompt before overwriting an existing file. |
| /H | Copy hidden files/system files. |
| /S | Copy directories and subdirectories. Empty directories are not included by default (use /e for that). |
| /E | Include empty directories. |
| /I | Create the destination folder if it does not exist. Use this option when you want to copy the parent folder itself. |
| /T | Copy directory tree without files. Empty directories are not included by default. Use /e option to include empty folders. |
| /P | Prompt for confirmation before creating each file. |
| /Q | Quiet mode. |
| /exclude | Specify a text file that contains a list of files to exclude. See the examples. |
| /Z | Resume mode. Use this option when copying files over a network. |
| /D:m-d-y | Copies files changed on or after the specified date. |
Examples of Using the Xcopy Command
Copy sales.doc from the current directory to C:\backup:
xcopy sales.doc C:\backupCopy C:\data\accounts (all files including subdirectories) to C:\backup:
xcopy /s /e /h /i /y C:\data\accounts C:\backup\accounts
In the following example (without /I switch), the contents of the folder are copied but not the folder itself:
xcopy /s /e /h /y C:\data\accounts C:\backup\Copy the directory structure of C:\OneDrive to the backup directory:
xcopy /s /e /t /y C:\OneDrive C:\backup\You can use wildcard characters to match patterns. The following command copies all files with a .jpg extension:
xcopy /s /h /y C:\data\*.jpg C:\backupUsing for loop to copy multiple files:
for %i in (sales.doc, products.doc) do xcopy /y %i C:\backupExcluding files with xcopy
With the /exclude, we can provide a text file that contains items we want to exclude.
xcopy /s /e /h /y /exclude:C:\Users\user1\files-to-exclude.txt C:\data\ C:\backup\The files-to-exclude.txt may look like the following:
.doc
sales*In this example, we exclude items with the .doc extension and files whose name starts with sales.
You can get a list of all available options with the xcopy /? command.
on November 25, 2010
Windows has two command line utilities to copy files/directories from command line. Copy command can be used to copy files from one folder to another folder. It can’t be used to copy a complete folder to another location on the disk. Xcopy allows us to do this. Let’s see how we can copy a directory along with all the files and sub directories to another location.
Xcopy /E /I SourceFolder DestinationFolder
Let’s say we need to copy a directory called C:\dir1\sourcedir to a location named D:\data\destinationdir.
Now you can run the below command to copy the complete sourcedir to D:\data\destination
Xcopy /E /I C:\dir1\sourcedir D:\data\destinationdir
In the above command we can also use relative paths of the folders with respect to the current directory.
Understanding the command
/E – This option makes sure that empty subfolders are copied to the destination.
/I – Avoids prompting if the destination is a folder or file. Not required if you are adding a trailing ‘\’ to the destination folder, like below.
Xcopy /E C:\dir1\sourcedir D:\data\destinationdir\
/S – This option is not required if you are using /E. /E ensures that all subfolders are also copied to the destination.
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
- 29.01.2020
- 112 349
- 17
- 02.11.2020
- 34
- 32
- 2

- Содержание статьи
- Описание
- Синтаксис
- Параметры
- Примечания
- Примеры использования
- Справочная информация
- Комментарии к статье ( 17 шт )
- Добавить комментарий
Описание
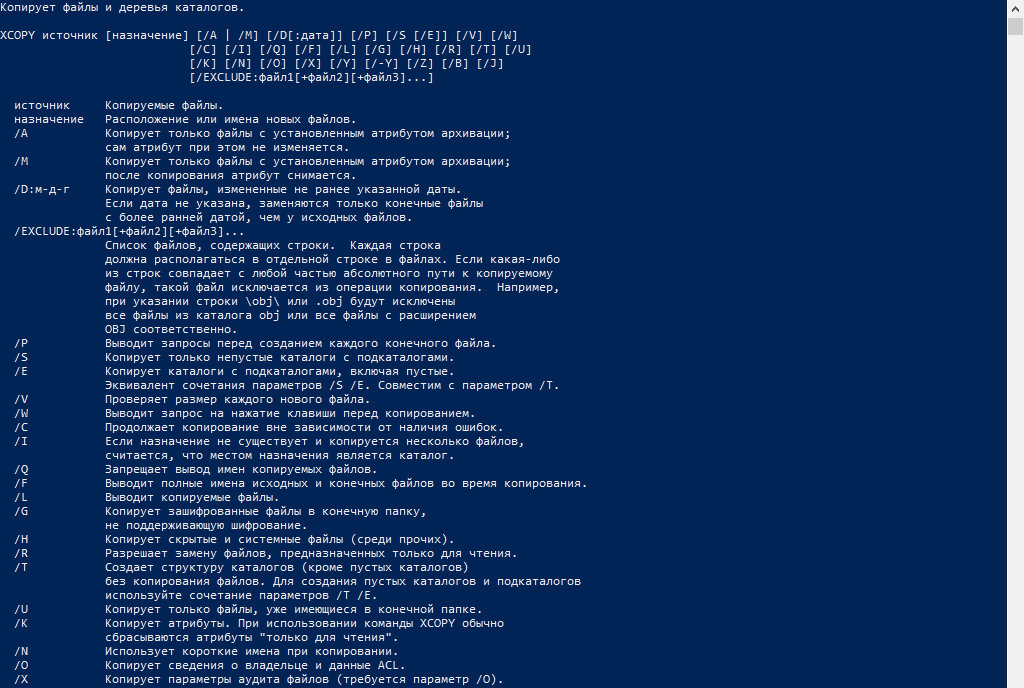
XCOPY — Копирует файлы и каталоги, включая подкаталоги.
Синтаксис
xcopy источник [результат] [/w] [/p] [/c] [/v] [/q] [/f] [/l] [/g] [/d[:мм-дд-гггг]] [/u] [/i] [/s [/e]] [/t] [/k] [/r] [/h] [{/a|/m}] [/n] [/o] [/x] [/exclude:файл1[+[файл2]][+[файл3]] [{/y|/-y}] [/z]
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| источник | Обязательный параметр. Задает местонахождение и имена файлов для копирования. Параметр должен задавать или диск, или путь. |
| результат | Задает место, куда будут скопированы файлы. Параметр может включать имя диска с двоеточием, имя каталога, имя файла или их комбинацию. |
| /w | Выводит следующее сообщение с ожиданием подтверждения начала копирования: Нажмите любую клавишу, чтобы начать копирование файлов |
| /p | Запрашивает подтверждение при создании каждого файла-результата. |
| /c | Игнорирует ошибки. |
| /v | Проверяет каждый скопированный файл на соответствие его оригиналу. |
| /q | Отменяет вывод на экран сообщений команды xcopy. |
| /f | Выводит имена исходных файлов и файлов-результатов в процессе копирования. |
| /l | Отображает список копируемых файлов. |
| /g | Создает незашифрованные файлы-результаты. |
| /d[:мм-дд-гггг] | Копирует только файлы, измененные не ранее заданной даты. Если не включить значение мм-дд-гггг, команда xcopy копирует все файлы-источники, которые новее существующих файлов-результатов. Эта возможность позволяет обновлять только измененные файлы. |
| /u | Копирует (обновляет) только те файлы-источники, которые уже существуют в каталоге результата. |
| /i | Если источником является каталог или источник содержит подстановочные знаки и результат не существует, команда xcopy считает, что результат — это имя каталога, и создает новый каталог. Затем xcopy копирует все указанные файлы в новый каталог. По умолчанию команда xcopy запрашивает подтверждение, является ли параметр результат каталогом или файлом. |
| /s | Копирует каталоги и подкаталоги, если они не пусты. Если параметр /s не задан, команда xcopy будет работать только с одним каталогом. |
| /e | Копирует все подкаталоги, включая пустые. Параметр /e используется с параметрами /s и /t. /t Копирует только структуру подкаталога (т. е. дерево), а не файлы. Для копирования пустых каталогов следует задать ключ /e. |
| /k | Копирует файлы с атрибутом «только для чтения» с сохранением этого атрибута для скопированных файлов, оригиналы которых имеют этот атрибут. По умолчанию команда xcopy удаляет атрибут «только для чтения». |
| /r | Копирует файлы с атрибутом «только для чтения». |
| /h | Копирует системные и скрытые файлы. По умолчанию команда xcopy не копирует системные и скрытые файлы. |
| /a | Копирует только те файлы, которые имеют установленный атрибут «архивный». При использовании параметра /a атрибут «архивный» у исходных файлов не меняется. |
| /m | Копирует только те файлы, которые имеют установленный атрибут «архивный». В отличие от параметра /a, параметр /m очищает атрибут «архивный» у скопированных файлов. |
| /n | Копирует с использованием коротких имен файловой системы NTFS. Параметр /n требуется при копировании из файловой системы NTFS в файловую систему FAT или когда на диске-результате требуется использование соглашения об именах файлов как в файловой системе FAT (8.3). Файлы могут записываться в файловую систему FAT или NTFS. |
| /o | Копирует сведения о принадлежности файлов и избирательной таблице управления доступом (DACL). |
| /x | Копирует сведения о параметрах аудита файла и системной таблице управления доступом (SACL) (подразумевается наличие /p). /exclude:файл1[+[файл2]][+[файл3]] Определяет список файлов, содержащих строки. |
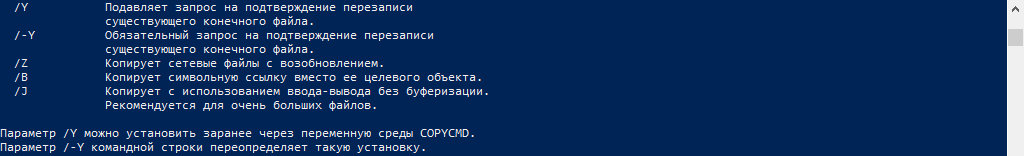
| /y | Устраняет выдачу запроса на подтверждение перезаписи существующего конечного файла. |
| /-y | Выдает запрос на подтверждение перезаписи существующего конечного файла. |
| /z | Копирует по сети в режиме перезапуска. |
| /? | Отображает справку в командной строке. |
Примечания
-
- Использование параметра /exclude
Построчный вывод всех строк в каждом файле. При соответствии выведенной строки части пути копируемого файла, он исключается из процесса копирования. Например, если указана строка «\Obj\», исключается все файлы, расположенные в каталоге «Obj». Например, если указана строка «.obj», исключается все файлы с расширением .obj. - Использование параметра /z
Если во время фазы копирования теряется сетевое подключение (например, если сервер переходит автономный режим, разрывая подключение), копирование возобновляется после восстановления подключения. Использование параметра /z команды вызывает также отображение доли (в процентах) завершенной операции копирования для каждого файла. - Использование параметра /y в переменной среде COPYCMD. Можно применять параметр /y в переменной среде COPYCMD. Эта настройка может быть переопределена использованием параметра /-y в командной строке. По умолчанию если команда copy выполняется не в пакетной программе, при замене требуется подтверждение.
- Копирование зашифрованных файлов
При копировании файлов на том, не поддерживающий шифрованную файловую систему (EFS), возникнет ошибка. Следует предварительно расшифровать файлы или копировать их на том, поддерживающий EFS. - Добавление файлов
Чтобы объединить файлы, укажите один файл-результат, но несколько файлов-источников (с помощью подстановочных знаков или формата файл1+файл2+файл3). - Значение по умолчанию для результата
Если параметр результат не задан, xcopy будет копировать файлы в текущий каталог. - Указание в качестве результата файла или каталога
Если параметр результат не содержит существующий каталок или не заканчивается обратной чертой(\), выводится следующее сообщение:Что означает destination:
имя файла или каталога
(F = файл, D = каталог)?Нажмите F, если файл или файлы должны копироваться в файл. Нажмите D, если файл или файлы должны копироваться в каталог.Чтобы устранить вывод этого сообщения, используйте параметр /i. В результате чего, команда xcopy предполагает, что результат является каталогом, если источник престаляет собой несколько файлов или каталогов. - Использование команды xcopy для установки атрибута «архивный» для файлов результата
Команда xcopy создает файлы с установленным атрибутом «архивный», независимо от состояния этого атрибута у исходных файлов. - Сравнение команд xcopy и diskcopy
Команда xcopy должна быть использована вместо diskcopy при копировании файлов и подкаталогов на диск другого формата. Так как команда diskcopy копирует диски по дорожкам, требуется, чтобы исходный диск и диск-результат имели одинаковый формат. Для команды xcopy это требование не нужно. Обычно следует использовать команду xcopy, если только не требуется получить два диска с одинаковыми образами. - Коды завершения программы xcopy
- Использование параметра /exclude
Для анализа кодов завершения, выведенных командой xcopy, используйте параметр уровень_ошибки в командной строке if пакетных программ.
В следующей таблице перечислены коды завершения с кратким описанием.
| Код завершения | Описание |
|---|---|
| 0 | Файлы скопированы без ошибок |
| 1 | Файлы для копирования не найдены |
| 2 | Нажата комбинация CTRL+C для остановки команды xcopy |
| 4 | Возникла ошибка инициализации. Недостаточно места в памяти или на диске, введено неверное имя диска или неверный синтаксис вызова команды |
| 5 | Диск защищен от записи |
Примеры использования
Чтобы копировать все файлы и подкаталоги (включая пустые подкаталоги) с диска A на диск B, введите:
xcopy a: b: /s /eЧтобы включить в операцию копирования предыдущего примера системные и скрытые файлы следует использовать параметр /h:
xcopy a: b: /s /e /hЧтобы обновить файлы в каталоге \Reports файлами из каталога \Rawdata, измененными после 29 декабря 1993 года, введите:
xcopy \rawdata \reports /d:29-12-1993Чтобы обновить файлы предыдущего примера, уже существующие в каталоге \Reports, независимо от их даты, введите следующую команду:
xcopy \rawdata \reports /uЧтобы получить списк файлов, которые были бы скопированы в предыдущем примере, следует ввести команду:
xcopy \rawdata \reports /d:29-12-1993 /l > xcopy.outСписок файлов, которые были бы скопированы, находится в файле Xcopy.out.
Чтобы скопировать каталог \Customer и все подкаталоги \\Public\Address на сетевой диск H, сохранить у файлов атрибут «только для чтения», введите команду:
xcopy \customer h:\public\address /s /e /k /pЧтобы выдать предыдущую команду, убедиться, что команда xcopy создает каталог \Address и устранить вывод сообщение о создании нового каталога, добавьте параметр /i следующим образом:
xcopy \customer h:\public\address /s /e /k /p /iДля запуска программы xcopy и анализа кодов завершения можно создать пакетный файл и использовать оператор if для обработки кодов завершения в случае возникновения ошибок. Например, следующая пакетная программа использует замещаемые параметры для задания источникаxcopy и результата:
@echo off
rem COPYIT.BAT копирует все файлы во всех подкаталогах
rem исходного диска или каталога (%1) на другой диск
rem или в другой каталог (%2)
?? xcopy %1 %2 /s /e
??if errorlevel 4 goto lowmemory
?if errorlevel 2 goto abort
?if errorlevel 0 goto exit
??:lowmemory ?
echo Недостаточно памяти для копирования файлов,
задан недопустимый ?echo диск или ошибка в синтаксисе командной строки.
?goto exit
??
:abort ?
echo Нажата комбинация CTRL+C для остановки копирования.
?goto exit ?
?
:exitЭта пакетная программа может быть использована для копирования всех файлов каталога C:\Prgmcode и его подкаталогов на диск B следующим образом:
copyit c:\prgmcode b:Командный интерпретатор подставляет C:\Prgmcode вместо параметра %1 и B вместо параметра %2, затем использует команду xcopy с параметрами /e и /s. Если при выполнении xcopy произошла ошибка, пакетная программа считывает код завершения и переходит на метку, указанную в соответствующей инструкции IF ERRORLEVEL. В результате на экран выводится сообщение о характере ошибки и осуществляется выход из пакетной программы.
Справочная информация