Windows 10 поставляется вместе с большим списком «компонентов», которые пользователь может включить или выключить в соответствующем диалоговом окне. Большое количество функций из этого списка создано специально для нужд и потребностей бизнес-пользователей и серверов, но вместе с этим часть компонентов может пригодиться и обычному пользователю.
Все компоненты Windows занимают место на вашем жестком диске, вне зависимости от того, включены они или нет. Иными словами, отключение отдельных компонентов не освободит место на диске компьютера. Кроме того, не стоит включать абсолютно все компоненты Windows, поскольку это негативно скажется на безопасности вашего компьютера, а также ухудшит его производительность. Стоит включать лишь те компоненты, которые вам действительно нужны или те, принцип работы которых вы понимаете. Это же касается и отключения. Бездумное выключение отдельных или всех компонентов системы может привести к нарушению работы приложений или ухудшению защищенности операционной системы.
Компоненты Windows 10
Управлять компонентами Windows можно только из классической панели управления. В Windows 10 Fall Creators Update Microsoft все еще не перенесла раздел с компонентами в новое приложение Параметры Windows. Интерфейс настройки компонентов Windows позволяет настроить виртуализацию Hyper-V, IIS-сервисы, подсистему Linux и так далее. Вы даже можете «отключить» Internet Explorer с помощью окна компонентов Windows 10. Конкретный набор доступных опций будет зависеть от того, какую редакцию Windows вы используете. В Windows 10 Профессиональная будет список побольше, а в Windows 10 Домашняя поменьше.
Где найти программы и компоненты Windows 10
Чтобы добраться до окна настройки компонентов Windows нажмите Win + R и введите optionalfeatures. Сразу же появится небольшое окошко со списком. Как вариант, вы можете ввести команду control, а затем перейти в раздел Программы – Включение или отключение компонентов Windows. Обратите внимание, что изменение компонентов Windows требует от вашей учетной записи наличия прав Администратора.
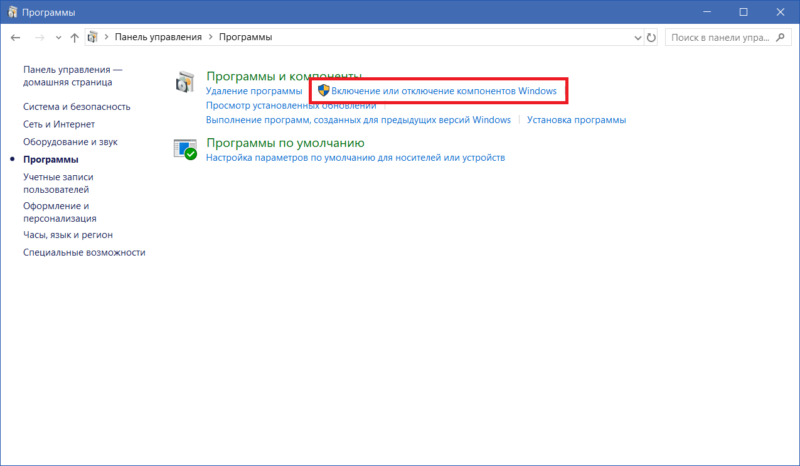
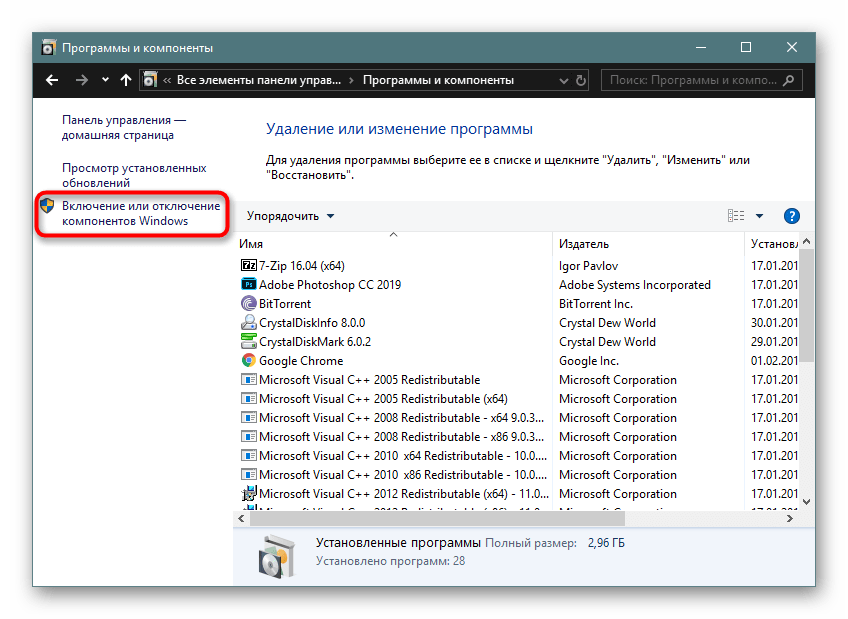
Посмотрите на список компонентов, и вы заметите, что определенные пункты обозначены черными квадратами, а не «птичками». Это означает, что компонент имеет «подкомпоненты» и не все из них активированы. Нажмите на плюсик, и система отобразит список доступных подкомпонентов.
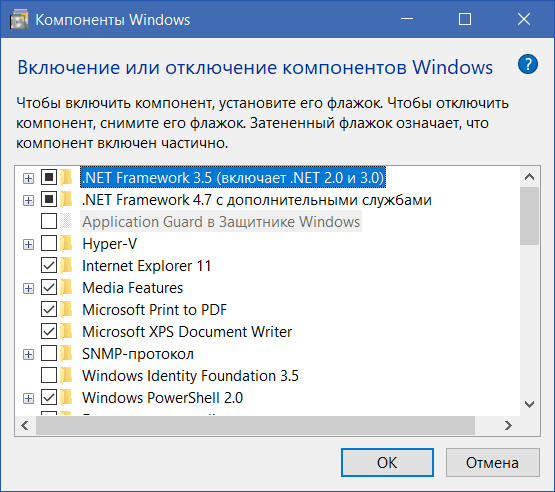
Внесите нужные вам изменения и нажмите Ок. Скорее всего, Windows попросит перезагрузиться, чтобы изменения вступили в силу.
Обратите внимание, что управление компонентами Windows не требует от компьютера активного Интернет-соединения. Их можно включать и выключать в любой момент вне зависимости от того, есть ли Интернет или его нет. Все компоненты уже доступны в системе после установки, а окно настроек лишь включает или отключает их.
Какие компоненты Windows можно отключить
Здесь вы найдете объяснение нескольких компонентов Windows и то, для чего они нужны. Внимательно ознакомьтесь с ним и сами решите, какие из них нужны вашему компьютеру, а какие нет. Имейте ввиду, что отключение тех или иных компонентов может привести к тому, что часть приложений перестанет работать или будет работать с ошибками.
- .NET Framework 3.5 (включает .NET 2.0 и 3.0). Этот компонент должен быть включен, чтобы приложения, написанные с помощью .NET версий 3.0 и старше, работали должным образом. Зачастую Windows сама включает этот компонент, как только определенное приложение делает соответствующий запрос.
- .NET Framework 4.7 с дополнительными службами. Как и .NET 2.0 / 3.0, 4.7 включается автоматически при необходимости. Подробнее об этом вы можете почитать в статье «Что такое .NET Framework».
- Hyper-V. Это технологии виртуализации Microsoft. Они включают в себя сервисы, платформу и графический интерфейс Hyper-V Manager, который необходим для создания, управления и использования виртуальных машин. Этот компонент требует наличия физической поддержки технологий виртуализации процессором вашего компьютера. Он должен быть включен, если вы хотите пользоваться виртуальными машинами на своем компьютере. Если нет, можете его выключить.
- Internet Explorer 11. Старый-добрый «ослик». Если он вам не нужен, можете с чистой совестью отключить его. Подробнее этот процесс описан в статье «Как удалить Internet Explorer в Windows 10».
- Media Features. Этот компонент нужен для работы стандартного проигрывателя Windows Media Player. Отключите Media Features и из вашего компьютера исчезнет Windows Media Player, но при этом функции воспроизведения медиафайлов никак не пострадают.
- Microsoft Print to PDF. Хороший, годный и полезный инструмент, с помощью которого вы можете конвертировать любой документ в PDF-файл. Своего рода «виртуальный принтер», который печатает на цифровых PDF-файлах.
- Microsoft XPS Document Writer. XPS – новый формат документов, представленный с Windows Vista. Как и ОС, особой популярности он не снискал. Microsoft XPS Document Writer предоставляет системе необходимые библиотеки для создания документов формата XPS. Можно смело отключать, если вы никогда не слышали, а значит и не пользовались XPS-файлами.
- SNMP-протокол. Старый протокол для управления роутерами, свитчами и другим сетевым оборудованием. Нужен для тех, у кого рабочее оборудование использует этот протокол, что вполне очевидно. Отключен по умолчанию.
- Windows Identity Foundation 3.5. Очень старые .NET-приложения могут все еще могут требовать наличия этого компонента. .NET 4 включает в себя новую версию этого фреймворка. Как и в случае с .NET 3.5, WIF 3.5 активируется лишь тогда, когда определенное приложение потребует этого.
- Windows PowerShell 2.0. PowerShell – более продвинутая командная и скриптинговая среда, обладающая рядом значительных преимуществ по сравнению с классической командной строкой. PowerShell включена по умолчанию, но вы можете отключить ее, если вам так хочется. Ничего страшного не случится – вы просто не сможете больше пользоваться PowerShell.
- Клиент рабочих папок. С помощью этого компонента пользователи могут синхронизировать папки из корпоративной сети на компьютер.
- Служба активации Windows. Эта служба связана с IIS. Ее надо активировать лишь при запуске определенных серверных приложений. Если у вас таковых нет, то и трогать эту службу не надо. К активации самой операционной системы как продукта эта опция не имеет отношения.
- Клиент TFTP. Используется для передачи файлов на компьютеры и устройства с использованием протокола TFTP. Он старый и небезопасный, в основном используется на реально древних компьютерах.
- Подсистема Windows для Linux. Об этом подробно описано в статье «Как включить Linux в Windows 10».
- Компоненты прежних версий. DirectPlay. Этот компонент когда-то был частью DirectX и использовался в мультиплеере в определенных играх. Windows автоматически установит DirectPlay, если старая игра требует его.
- Поддержка API удаленного разностного сжатия. Быстрый алгоритм для сравнения синхронизированных файлов. Как и большое количество других компонентов, включается лишь по мере необходимости.
- Поддержка общего доступа к файлам SMB 1.0 / CIFS. За счет этой службы компьютер может делиться файлами и принтерами со старыми версиями Windows (от Windows XP / Windows Server 2003 R2 вплоть до Windows 10 NT 4.0). Протокол этот весьма старый и небезопасный, поэтому его можно отключить.
- Службы печати и документов. Клиент интернет-печати, а также факсы и сканирование Windows включены по умолчанию, но вы можете также включить печатные сетевые протоколы LPD и LPR. Надо сказать, что делать этого не стоит, поскольку протоколы уже устарели и требуются в очень редких случаях при подключении определенных сетевых принтеров.
- Соединитель MultiPoint. Этот компонент активирует мониторинг и управление устройством с помощью MultiPoint Manager. Полезен только в корпоративный сетях, где ИТ-специалисты используют соответствующие утилиты управления.
- Средство просмотра XPS. Собственно, приложение для открытия XPS-документов.
- Фильтр Windows TIFF iFilter. Ничего общего с Apple этот компонент не имеет. Он позволяет сервису индексирования Windows производить распознавание текста (OCR). Компонент отключен по умолчанию, поскольку функция сильно нагружает процессор компьютера. TIFF iFIlter нужен для тех, кто часто сканирует бумажные документы и использует TIFF-файлы.
В списке вы найдете еще много других компонентов, которые зачастую отключены. Они включаются автоматически лишь при необходимости, поэтому вручную активировать их мы не рекомендуем. Если они отключены, значит скорее всего они вам не нужны вовсе. Ну а что же касается включенных компонентов, то их описание вы уже нашли в этой статье. Сами решайте, стоит их отключать или нет. В подавляющем большинстве случаев пользователю вовсе не надо открывать окно с компонентами Windows, но все же полезно знать, для чего они нужны и какую функцию выполняют.
Все способы:
- Управление встроенными компонентами в Windows 10
- Что можно отключить
- Решение возможных проблем
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Пользователь Виндовс может управлять работой не только тех программ, которые он установил самостоятельно, но и некоторых системных компонентов. Для этого в ОС есть специальный раздел, позволяющий не только отключать неиспользуемые, но и активировать различные системные приложения. Рассмотрим, как это делается в Windows 10.
Управление встроенными компонентами в Windows 10
Сама процедура входа в раздел с компонентами пока что не отличается от той, что реализовано в предыдущих версиях Виндовс. Несмотря на то, что раздел с удалением программ перенесен в «Параметры» «десятки», ссылка, ведущая на работу с компонентами, по-прежнему запускает «Панель управления».
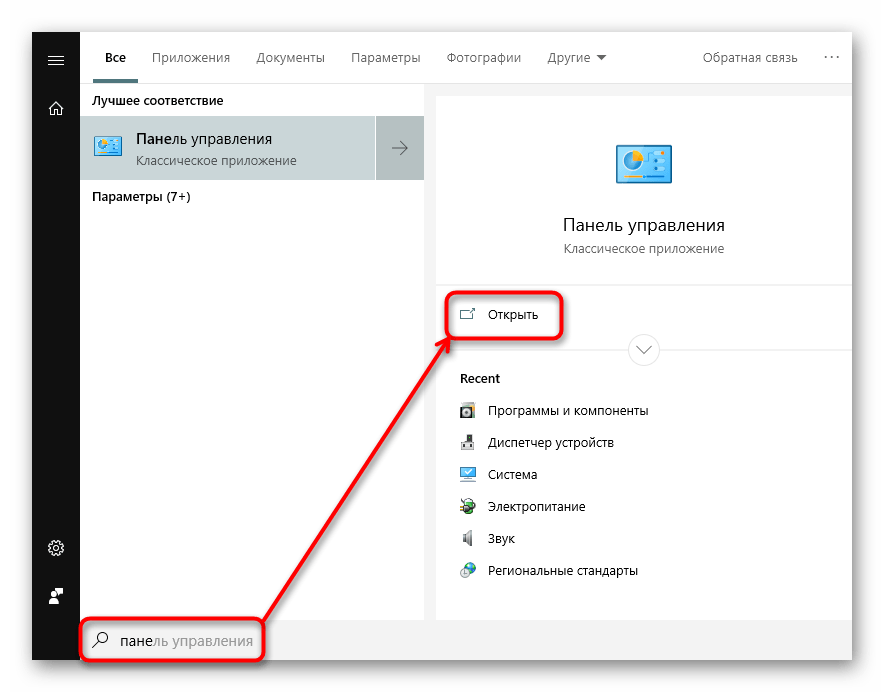
- Итак, чтобы туда попасть, через «Пуск» перейдите в «Панель управления», вписав ее название в поисковое поле.
- Устанавливаем режим просмотра «Мелкие значки» (или крупные) и открываем в «Программы и компоненты».
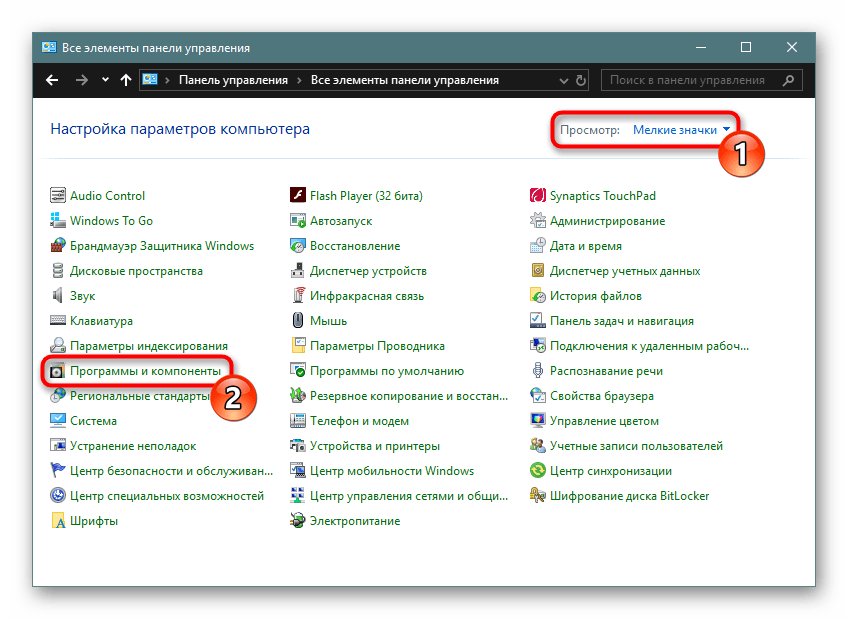
- Через левую панель переходим в раздел «Включение или отключение компонентов Windows».
- Откроется окно, в котором будут отображены все доступные компоненты. Галочкой отмечено то, что включено, квадратиком — то, что частично включено, пустой квадратик, соответственно, означает деактивированный режим.
Что можно отключить
В целях отключения неактуальных работающих компонентов пользователь может воспользоваться приведенным ниже списком, а при необходимости вернуться в этот же раздел и включить нужное. Объяснять, что включить, мы не будем — это каждый пользователь решает для себя сам. А вот с отключением у юзеров могут возникнуть вопросы — не все знают, что же из них можно деактивировать без влияния на стабильную работу ОС. В целом же стоит заметить, что потенциально ненужные элементы уже и так отключены, а работающие лучше не трогать, тем более без понимания того, что вы вообще делаете.
Обратите внимание, что отключение компонентов практически никак не влияет на производительность вашего компьютера и не разгружает жесткий диск. Это имеет смысл делать только если вы уверены в том, что конкретный компонент точно не пригодится или его работа мешает (например, встроенная виртуализация Hyper-V конфликтует со сторонним ПО) — тогда деактивация будет обоснована.
Вы можете и сами решить, что отключать, наведя на каждый компонент курсор мыши — сразу появится описание его предназначения.
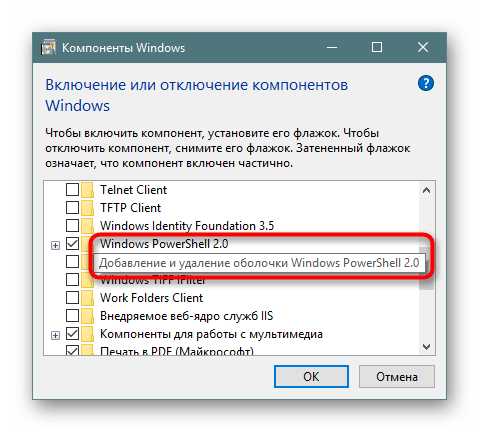
Безопасно можно отключить любые из следующих компонентов:
| Компоненты | Описание |
|---|---|
| Internet Explorer 11 | Если используете другие браузеры. Однако учтите, что разные программы могут быть запрограммированы на открытие ссылок внутри себя только через IE |
| Hyper-V | Компонент для создания виртуальных машин в Windows. Может быть отключено, если пользователь не знает, что такое виртуальные машины в принципе или использует сторонние гипервизоры типа VirtualBox |
| .NET Framework 3.5 (включающий в себя версии 2.5 и 3.0) | В целом отключать его не имеет смысла, но некоторые программы иногда могут задействовать эту версию вместо более новых 4.+ и выше. При возникновении ошибки запуска какой-либо старой программы, работающей только с 3.5 и ниже, потребуется заново включить этот компонент (ситуация редкая, но возможная) |
| Windows Identity Foundation 3.5 | Дополнение к .NET Framework 3.5. Отключить стоит только если то же самое сделали с предыдущим пунктом этого списка |
| SNMP-протокол | Помощник в тонкой настройке очень старых роутеров. Не нужен ни новым маршрутизаторам, ни старым, если те настроены для обычного домашнего использования |
| Внедряемое веб-ядро служб IIS | Приложение для разработчиков, бесполезное для обычного юзера |
| Встроенный модуль запуска оболочки | Запускает приложения в изолированном режиме при условии, что те поддерживают такую возможность. Рядовому юзеру эта функция не нужна |
| Клиент Telnet | Умеет удаленно подключаться к командной строке |
| Клиент TFTP | Умеет передавать файлы по протоколу TFTP. То и другое обычно не используется простыми людьми |
| Клиент рабочих папок | Инструменты для корпоративного использования |
| Прослушиватель RIP | Инструменты для корпоративного использования |
| Простые службы TCPIP | Инструменты для корпоративного использования |
| Службы Active Directory для облегчённого доступа к каталогам | Инструменты для корпоративного использования |
| Службы IIS | Инструменты для корпоративного использования |
| Соединитель MultiPoint | Инструменты для корпоративного использования |
| Компоненты прежних версий | Изредка используется очень старыми приложениями и включается ими самостоятельно при необходимости |
| Пакет администрирования диспетчера RAS-подключений | Предназначен для работы с подключениями через возможности Виндовс. Может быть включен автоматически при надобности |
| Служба активации Windows | Инструмент для разработчиков, не связанный с лицензией операционной системы |
| Фильтр Windows TIFF IFilter | Ускоряет запуск TIFF-файлов (растровых изображений) и может быть отключен, если вы не работаете с этим форматом |
Некоторые из перечисленных компонентов, скорее всего, будут уже отключены. Это значит, что и активация их вам, вероятнее всего, не потребуется. Кроме того, в разных любительских сборках часть перечисленных (и неупомянутых тоже) компонентов может и вовсе отсутствовать — это значит автор дистрибутива уже удалил их самостоятельно при модификации стандартного образа Виндовс.
Решение возможных проблем
Не всегда работа с компонентами происходит гладко: некоторые юзеры вообще не могут открыть это окно или изменить их статус.
Вместо окна компонентов белый экран
Существует проблема, связанная с запуском окна компонентов для дальнейшей их настройки. Вместо окна со списком отображается лишь пустое белое окно, которое не прогружается даже после многократных попыток его запуска. Есть несложный способ исправления данной ошибки.
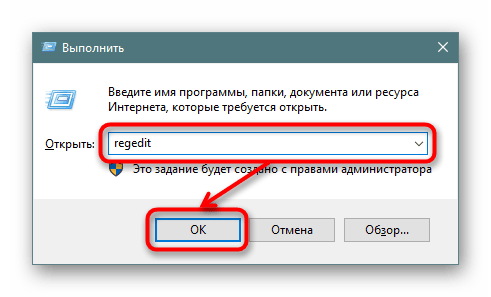
- Открываем «Редактор реестра», нажав клавиши Win + R и вписав в окно
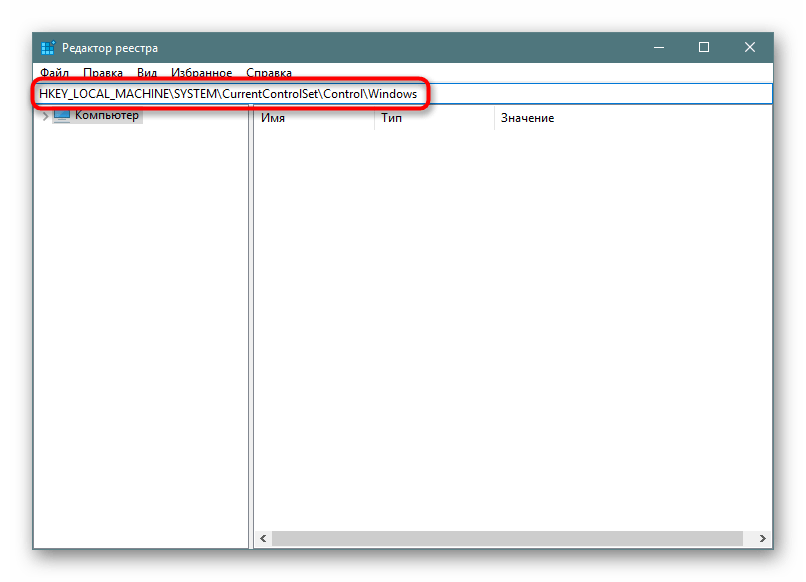
regedit. - В адресную строку вставляем следующее:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Windowsи жмем Enter. - В основной части окна находим параметр «CSDVersion», быстро нажимаем по нему два раза левой кнопкой мыши, чтобы открыть, и задаем значение 0.
Не включается компонент
Когда невозможно перевести состояние какого-либо компонента в активное, поступите одним из следующих вариантов:
- Запишите куда-нибудь список всех работающих на данный момент компонентов, отключите их и перезагрузите ПК. Затем попробуйте включить проблемный, после него все те, что отключили, и снова перезапустите систему. Проверьте, включился ли нужный компонент.
- Загрузитесь в «Безопасном режиме с поддержкой сетевых драйверов» и включите компонент там.
Читайте также: Входим в безопасный режим на Windows 10
Хранилище компонентов было повреждено
Нередкая причина перечисленных выше проблем заключается в повреждении системных файлов, вызывающих сбой в работе раздела с компонентами. Устранить его можно, следуя развернутой инструкции в статье по ссылке ниже.
Подробнее: Использование и восстановление проверки целостности системных файлов в Windows 10
Теперь вы знаете, что именно можно отключать в «Компонентах Windows» и как решить возможные неполадки в их запуске.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
The following is a list of Microsoft Windows components.
Configuration and maintenance
edit
| Component | Description | Command | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Settings | Allows users to change system settings, similar to the Control Panel, but has less options[1] | start ms-settings:
|
Windows 8 |
| Control Panel | |||
| Control Panel | Allows users to view and change basic system settings and controls, such as adding hardware, adding and removing software, controlling user accounts, and changing accessibility options | control.exe
|
Windows 1.0 |
| Device Manager | Allows the user to display and control the hardware attached to the computer, and control what device drivers are used | devmgmt.msc
|
Windows 95 |
| Windows Mobility Center | Centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing | mblctr.exe
|
Windows Vista |
| Security and Maintenance | Centralizes and reports on the status of anti-virus, Automatic Updates, Windows Firewall, and other security-related components of the operating system | Windows XP SP2 | |
| Administrative Tools | |||
| Microsoft Management Console | Provides system administrators and advanced users with a flexible interface through which they may configure and monitor the system | mmc.exe
|
Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack |
| Windows System Assessment Tool | Built-in benchmarking tool that analyzes the different subsystems (graphics, memory, etc.), and uses the results to allow for comparison to other Windows Vista systems, and for software optimizations. It rates the computer’s performance using the Windows Experience Index. | winsat.exe
|
Windows Vista |
| System Restore | Allows for the rolling back of system files, registry keys, installed apps, etc., to a previous state in the event of a system failure | rstrui.exe
|
Windows Me |
| Windows Recovery Environment | Helps diagnose and recover from serious errors which may prevent Windows from booting successfully, or restore the computer to a previous state using System Restore or a backup image | shutdown /r /o
|
Windows Vista |
| Microsoft Drive Optimizer | Rearranges files stored on a hard disk to occupy contiguous storage locations in order to optimize computer performance | dfrgui.exe
|
Windows 95, Windows 2000 |
| Event Viewer | Lets administrators and users view the event logs on a local or remote machine | eventvwr.msc
|
Windows NT 3.1 |
| Resource Monitor (previously Reliability and Performance Monitor) |
Lets administrators view current system reliability and performance trends over time | resmon.exe
|
Windows Vista |
| Logical Disk Manager | Logical volume manager developed by Microsoft in conjunction with Veritas Software | diskmgmt.msc
|
Windows NT 4.0 (Separate Tool), Windows 2000 |
| Registry Editor | Allows users to browse and edit the Windows registry | regedit.exe
|
Windows 3.1 |
| Windows Task Scheduler | Allows users to script tasks for running during scheduled intervals | taskschd.msc
|
Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| Software installation and deployment | |||
| Windows Update | An online service providing updates such as service packs, critical updates and device drivers. A variation called Microsoft Update also provides software updates for other Microsoft products. | control.exe update
|
Windows 98 |
| Windows Installer | An engine for the management of software installation. Includes a GUI framework, automatic generation of the uninstallation sequence and deployment capabilities for corporate networks. | msiexec.exe
|
Office 2000 |
| ClickOnce | Technology for deploying .NET Framework-based software via web pages, with automatic update capabilities. Intended for per-user only applications. | mage.exe and mageUI.exe
|
.NET Framework 2.0 |
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Action Center | View notifications sent from apps and change common settings | Windows 7 |
| Windows Command Prompt | Text-based shell (command line interpreter) that provides a command line interface to the operating system | Windows NT 3.1 |
| PowerShell | Command-line shell and scripting framework. | Windows XP |
| Windows Shell | The most visible and recognizable aspect of Microsoft Windows. The shell provides the container inside of which the entire graphical user interface is presented, including the taskbar, the desktop, Windows Explorer, as well as many of the dialog boxes and interface controls. In Windows Vista, a new compositing glass-like user interface called Windows Aero has been shown. | Windows 95 |
| File Explorer (previously Windows Explorer) |
Provides an interface for accessing the file systems, launching applications, and performing common tasks such as viewing and printing pictures | Windows 95 |
| Windows Search | Starting with Windows Vista, search is a tightly shell-integrated component of Windows. A downloadable Windows Desktop Search software is available for Windows XP and older versions. | Windows Vista, downloadable for older versions |
| Search Folders | Virtual folders that retrieve items based on queries rather than hierarchical folder trees on disk. | Windows Vista |
| Special folders | Folders which are presented to the user through an interface as an abstract concept, instead of an absolute path. This makes it possible for an application to locate where certain kinds of files can be found, regardless of what version or language of operating system is being used. See also Windows Shell namespace. | Windows 95 |
| Start menu | Serves as the central launching point for applications. It provides a customizable, nested list of apps for the user to launch, as well as a list of most recently opened documents, a way to find files and get help, and access to the system settings. By default, the Start Button is visible at all times in the lower left-hand corner of the screen. | Windows 95 |
| Taskbar | The application desktop bar which is used to launch and monitor applications | Windows 95 |
| Task View | Displays all open windows and activities (via timeline) at a glance and switch between virtual desktops, starting in version 2004, users can now rename desktops | Windows 10 |
| File associations | Used to open a file with the appropriate app. Users can assign file associations uniquely to specific actions, known as verbs. | Windows 1.0 |
Applications and utilities
edit
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Easy Transfer | Used to transfer many files at once from one computer to another | Windows Vista |
| Contacts | Keeps a single list of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Windows Vista |
| Camera | Allows the user to take pictures or record video[2] | Windows 8 |
| Calculator | Calculation application | Windows 1.0 |
| Calendar | Calendaring application | Windows Vista |
| Character Map | Utility to view and search characters in a font, copy them to the clipboard and view their Windows Alt keycodes and Unicode names | Windows 3.1 |
| Cortana | Digital personal assistant | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Edge | Web browser | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Feedback Hub | Platform for exchanging communication with Windows Insiders and developers | Windows 10 Version 1607 |
| Groove Music (previously Xbox Music) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing audio. In addition to being a media player, Groove includes the ability to copy music to compact discs, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and let users purchase or rent music from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| Movies & TV (previously Xbox Video) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing video. In addition to being a media player, Movies & TV lets users purchase or rent movies and TV episodes from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| OneDrive (previously SkyDrive) |
Freemium cloud storage folder and sync service | Windows 8 |
| Microsoft OneNote | Integrated note-taking app, based on the Microsoft Office product of the same name | Windows 8 |
| On-Screen Keyboard (osk.exe) | Virtual keyboard | |
| Paint 3D | Simple graphics painting app | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Photos | Simple image viewer | Windows 8 |
| Steps Recorder (called Problem Steps Recorder in Windows 7) |
Utility that allows the user to capture steps they took to reproduce a problem | Windows 7 |
| Windows To Go | Utility to create bootable versions of Windows 8 and above | Windows 8 |
| Notepad | Simple text editor | Windows 1.0 |
| Narrator | Screen reader utility that reads dialog boxes and window controls in a number of the more basic applications for Windows | Windows 2000 |
| Sound Recorder | Simple audio recording app that can record from a microphone or headset, and save the results in WAVE format and Windows Media Audio format in some Windows versions | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions |
| Skype | Messaging and calling service | Windows 8.1, downloadable for previous versions |
| Sticky Notes | Tool for jotting notes on the desktop | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition |
| Private Character Editor | Utility to create private use characters as defined under Unicode and various East Asian encoding schemes | Windows 3.1 East Asian editions |
| Remote Desktop Connection | Client implementation of the Remote Desktop Protocol; allows a user to securely connect to a computer running Terminal Services (Remote Desktop on Windows XP and Server 2003) and interact with a full desktop environment on that machine, including support for remoting of printers, audio, and drives. | Windows XP, downloadable for previous Windows versions |
| Remote Assistance | Allows a user to temporarily take over a remote computer over a network or the internet to offer help with and resolve issues | Windows XP |
| Mobility Center | Allows a user to adjust settings related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Speech Recognition | Allows a user to input voice commands | Windows Vista |
| IExpress | Allows users to create self-extracting, self-installing INF installation-based packages | Internet Explorer 6 |
| Xbox Console Companion (previously Xbox and Xbox Games) |
Account manager for Xbox Live user accounts and a screen recording tool | Windows 8 |
| Xbox Game Bar | Provides a overlay for compatible games allowing for screen capture, chatting over the Xbox network, showing the frame rate of games, and playing music via Spotify[3][4] | Windows 10 May 2019 Update (Version 1903)[5] |
| Magnifier | Screen enlargement app | Windows 98 |
| Fax and Scan | Integrated faxing and image scanning application | Windows Vista, older faxing and scanning applications were present in previous Windows versions |
| Photo Viewer | Simple image viewer that can play a simple slideshow | Windows XP |
| Email aggregator | Windows Vista | |
| Maps | Map viewer that allows users to look for locations, and plan routes | Windows 8 |
| Media Center | Designed to serve as a home-entertainment hub, to be viewed from a distance up to 3 meters (~10 feet) and controlled by specially designed remote controls. Lets users browse and view pictures, videos, and music from local hard drives, optical drives, and network locations, along with viewing, recording and deferred-playing live TV. Features an interactive TV guide with scheduled recording capabilities. Can also be used for visualization of other information (like sports scores) within the interface | Windows XP Media Center Edition |
| Task Manager | Provides information about computer performance and displays details about running applications, processes, network activity, logged-in users, and system services | Windows 3.0 |
| Disk Cleanup | Utility for compacting rarely used files and removing files that are no longer required | Windows 98 |
| Snipping Tool | Screen-capture tool that allows for taking screenshots (called snips) | Experience Pack for Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 |
| Microsoft Store (previously Windows Store) |
Initially known as Windows Store, it started as an app store for Windows 8. In Windows 10, it expanded into a broad digital distribution platform for apps, games, music, digital video and e-books. In 2017, it was renamed Microsoft Store and started offering hardware in United States, Canada and United Kingdom. | Windows 8 |
| MSN apps | Provide information from MSN web services | Windows 8 |
| Alarms & Clock(pre Alarms) | App that allows Windows users to set alarms, stopwatches, timers, and view a world clock | Windows 8 |
| Windows Security (previously Windows Defender Security Center) |
Antivirus | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Solitaire Collection | Set of solitaire card games | Windows 10 Version 1507, downloadable for Windows 8.x |
Windows Server components
edit
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | A set of technologies introduced with Windows 2000 that allows administrators to assign enterprise-wide policies, deploy apps to many computers, and apply critical updates to an entire organization. Active Directory stores information and settings relating to an organization in a central, organized, accessible database. Networks can vary from a small installation with a few objects, to global-scale directories with millions of objects. Related topics: Domain controller, Flexible single master operation |
Windows 2000 and later server versions |
| Group Policy | Provides centralized management of user and computer settings in an Active Directory environment. Group policy can control a target object’s registry, NTFS security, audit and security policy, software installation, logon/logoff scripts, folder redirection, and Internet Explorer settings. Policy settings are stored in Group Policy Objects (GPOs), and may be linked to one or more sites, domains or organizational units. Related topics: Administrative Templates |
Windows 2000 and later |
| Internet Information Services | Web server | Windows NT family |
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| FAT12, FAT16 | The original file systems used with MS-DOS. The standard file systems used with Windows 1.0 through Windows 95. | All versions |
| FAT32 | Extensions to FAT supporting larger disk sizes. The standard file system for Windows 98 and Me. | Windows 95 OSR2 and later versions |
| NTFS | Standard file system of Windows NT; supports security via access-control lists, as well as file system journaling and file-system metadata. Windows 2000 added support for reparse points (making NTFS junction points and Single instance storage possible), Hard links, file compression, and Sparse files. Encryption of data is provided by Encrypting File System. Symbolic links and transactioning of file operations via Transactional NTFS are features new to Windows Vista. Although Windows 9x operating systems cannot read or write NTFS formatted disks, they can access the data over a network if it is shared by a computer running Windows NT. | Windows NT (all versions) |
| ISO 9660 (CDFS) | The predominant file system for CD-ROM and DVD-ROM media. Windows includes support for Joliet extensions and the ISO 9660:1999 standard. ISO 9660:1999 is supported since Windows XP. | MS-DOS and Windows 9x via extensions, such as MSCDEX.EXE (Microsoft CDROM Extension), natively in Windows NT 3.5 |
| Universal Disk Format (UDF) | A file system for storing files on optical media. It is an implementation of the ISO/IEC 13346 standard (also known as ECMA-167). It is considered to be a replacement of ISO 9660. Successive versions of Windows have supported newer versions of UDF. | Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista |
| HPFS | High-Performance File system, used on OS/2 computers. Read and write capability in Windows 95 (where it also listed network computer NTFS-formatted drives as «HPFS», even though it had no direct NTFS capabilities). HPFS write support was dropped in Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 98, and dropped altogether shortly before the release of Windows 2000. | Windows 95 (Read/write), Windows 98, Windows NT (read), 3.1/3.51 (read/write/boot) |
| ReFS | A newer file system, based on NTFS. This system adds built-in integrity checking and removes the need for chkdsk, among other features. The maximum partition size is 1 YB. | Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1 |
| Component | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Windows kernel (Windows NT)
Main article: Architecture of Windows NT |
||
| Ntoskrnl.exe | The Windows kernel image. Provides the kernel and executive layers of the kernel architecture, and is responsible for services such as hardware virtualization, process and memory management, etc. | |
| hal.dll | HAL | Provides and handles the interaction between software and hardware via the Hardware Abstraction Layer. |
| kernel32.dll | This application provides kernel operations to apps in the Win32 mode, like memory management, I/Os, process creation, etc. | |
| Core processes (Windows NT) | ||
| System Idle Process | SIP | A counter which measures how much idle capacity the CPU has at any given time. The process runs in the background and monitors processing bandwidth, occupied memory and the Windows virtual paging file. |
| Session Manager Subsystem | SMSS | Performs several critical boot-time operations, such as the creation of environment variables, starting CSRSS, and performing file-copy operations that were queued up from before the system was booted (pending file rename operations). During system operation, it handles Windows File Protection and the creation of logon sessions via Winlogon. |
| Client/Server Runtime Subsystem | CSRSS | User-mode side of the Win32 subsystem. Provides the capability for applications to use the Windows API. |
| Local Security Authority Subsystem Service | LSASS | Responsible for enforcing the security policy on the system. Verifies users logging on to the computer and creates security tokens. |
| Winlogon | Responsible for handling the secure attention key, loading the user profile on logon, and optionally locking the computer when a screensaver is running. On Windows NT systems prior to Windows Vista, Winlogon is also responsible for loading GINA libraries which are responsible collecting logon credentials from the user. | |
| Svchost.exe | A generic host process name for services that run from dynamic-link libraries (DLLs). Several Svchost processes are typically present on a Windows machine, each running in a different security context, depending on what privileges the contained services require. | |
| Windows on Windows and WoW64 | WoW | An abstraction layer that allows legacy code to operate on more modern versions of Windows; typically this means running 16-bit Windows applications on 32-bit Windows, and 32-bit applications on 64-bit Windows. |
| Virtual DOS machine | NTVDM | Allows MS-DOS apps to run on Intel 80386 or higher computers when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware. Introduced in Windows 2.1; not available in any 64-bit edition of Windows. |
| System startup (Windows NT)
Main article: Booting process of Windows |
||
| NTLDR, IA64ldr, Winload | The bootloader; performs basic system initialization options such as loading the hardware abstraction layer and boot-time device drivers, prior to passing control to the Windows kernel. In versions prior to Vista, NTLDR and IA64ldr also display menus to the user if multiple operating systems are defined in boot.ini, or if F8 is pressed. | |
| Recovery Console | Provides the means for administrators to perform a limited range of tasks using a command line interface, primarily to aid in recovering from situations where Windows does not boot successfully. | |
| ntdetect.com | Used during the boot process to detect basic hardware components that may be required during the boot process | |
| Windows Boot Manager | In Windows Vista and later operating systems, displays boot menus to the user if multiple operating systems are configured in the system’s Boot Configuration Data. | |
| Graphical subsystem | ||
| Desktop Window Manager | DWM | The compositing manager introduced in Windows Vista that handles compositing and manages special effects on screen objects in a graphical user interface |
| Graphics Device Interface | GDI/GDI+ | The kernel graphics component for representing graphical objects and transmitting them to output devices such as monitors and printers |
| Windows USER | The Windows USER component provides core user interface, messaging and visual elements |
This list is not all-inclusive.
| Display name | Service key name | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Directory Service | NTDS | Network Authentication Management | Windows 2000 Server |
| Alerter service | Alerter | Sends administrative alerts over the network to client computers, administrators and users | Windows NT |
| Application Layer Gateway service |
ALG | Provides support for plugins that allow network protocols to pass through Windows Firewall and work behind Internet Connection Sharing | Windows 2000 |
| Application Experience service | Processes application compatibility cache requests for applications as they launch[6] | ||
| Application Management | AppMgmt | Processes requests to enumerate, install, and remove applications that are installed on the computer or deployed through an organization’s network | Windows 2000 |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service |
BITS | Transfers files between machines using idle network bandwidth. Used by Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, and Systems Management Server to deliver software updates to clients, as well as by Windows Messenger. | Windows XP |
| Computer Browser | Browser | Crawls neighboring computers on the network and locates shared resources. One of the computers acts as the Master Browser and supplies this information to other computers designated as browsers.[7] | Windows for Workgroups |
| Delivery Optimization | DoSvc | A peer-to-peer distribution service that downloads Windows updates and Microsoft Store apps from the local network or Internet peers, and redistributes them to others. Can be configured using either the Settings app or Group Policy. The Settings app can turn it on or off, and specify whether the service operates on the local network only, downloads from and uploads to the Internet peers as well. Group Policy allows finer control.[8][9] Delivery Optimization relies on a centralized web service that does not index contents under 10 MB. Computers without Internet access cannot use Delivery Optimization.[10] | Windows 10 Anniversary Update[8] |
| Distributed Link Tracking | TrkWks, TrkSrv | Used to track links to files on NTFS volumes. Windows uses these services to find linked files if they are renamed or moved (locally or to another machine).[11] | Windows 2000 |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator |
MSDTC | Allows transactional components to be configured through COM+ by coordinating transactions that are distributed across multiple computers and/or resource managers, such as databases, message queues, file systems, and other transaction–based resource managers.[12] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| DNS Client | DNSCache | Resolves and caches domain names (e.g. “en.wikipedia.org”) to IP addresses | Windows 2000 |
| Event Log | EventLog | Stores and retrieves events that can be viewed in the event viewer. Part of services.exe.[13] | Windows NT |
| Extensible Authentication Protocol | EAPHost | Provides EAP authentication to connecting clients | Windows 2000 |
| Indexing Service | CISVC | Indexes contents and properties of files on local and remote computers; provides rapid access to files through flexible querying language.[14] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| Interactive Services Detection | UI0Detect | For compatibility; when a service-displayed user interface is detected, it gives the user an option to switch to Session0 to see it | Windows Vista |
| Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess | When enabled, it allows other computers on the local network to access an internet connection that is available to the host computer | Windows 2000;[15] Windows Vista onward[16] |
| Network Location Awareness | NLA | Manages network configurations and information, and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| Network Store Interface Service | NSIS | Collects routing information of active network interfaces, shares this with other services and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| NTLM Security Support Provider | NTLMSSP | Uses the NTLM MS-CHAP protocol to encapsulate and negotiate options in order to provide signed and sealed communication. Deprecated now in favor of Kerberos authentication. | Windows NT |
| Peer Name Resolution Protocol | PNRPSvc | Resolves domain names using Peer Name Resolution Protocol | Windows XP |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay | Enables autodetection and configuration of hardware | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Print spooler [fr] | Spooler | Manages printer devices and moves files into memory for printing | Windows 95, Windows NT |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs | Provides Remote Procedure Call features via remotely accessible Named Pipes | Windows NT family |
| Routing and Remote Access Service | RRAS | API and server software that enables applications to administer the routing and remote-access service capabilities of the operating system, to function as a network router. | Windows 2000 |
| Secondary Logon | SecLogon | Allows users to run apps with a different account than the one they logged in with. Allows non-administrative accounts to perform administrative tasks.[17] | |
| Security Account Manager | SamSs | Manages user account security information | Windows NT family |
| System Event Notification Service | SENS | Monitors system events, such as network, power, logon, logoff, terminal services session connection and disconnection, and delivers these to applications and other system components.[18] | Windows 2000 |
| Superfetch | SysMain | Monitors file usage patterns and boosts system speed by caching frequently accessed files to RAM[19] | Windows Vista |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule | Lets users setup and schedule automated tasks | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts | Enables support for NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) service and NetBIOS name resolution | Windows NT family |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS | Creates multiple versions of files that change. The ability to store persistent snapshots was added in Windows Server 2003.[20] | Windows XP |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv | Manages audio devices for Windows-based apps. Controls all audio functions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Error Reporting | WERSvc | Generates error logs and reports errors. On Windows Vista and later, it notifies of solutions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Firewall | MpsSvc | Blocks unauthorized network connections to and from the computer | Windows Vista |
| Windows Firewall(née Internet Connection Sharing) | SharedAccess | Provides a simple firewall feature which was introduced in Windows XP. It also shares the internet on the local network, if the internet connection sharing feature is turned on.[21] | Windows XP only[22][23] |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | STISvc | Handles scanner and camera inputs | Windows Me |
| Windows Time | W32Time | Synchronizes the system time with external time servers. From Windows Server 2003 forward, full and compliant NTP support is provided.[24] | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Update | WUAUServ | Provides updates for the operating system and its installed components | Windows XP |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSvc (XP), WLANSvc | Configures and manages 802.11 wireless adapters | Windows XP, Server 2003 only |
| Windows Messenger service | Messenger | Allows users to send pop-up messages to other computers over the network | Windows NT family |
| WebClient[25] | Enables Windows-based apps to create and interact with Internet-based files | Windows XP |
- Direct3D
- DirectDraw
- DirectInput
- DirectMusic
- DirectPlay
- DirectShow
- DirectSound
- DirectX Media Objects
- DirectX plugin
- DirectX Video Acceleration
- Administrative share
- Distributed File System
- My Network Places (formerly Network Neighborhood)
- Network Access Protection
- Remote Installation Services
- Server Message Block
- Windows Rights Management Services
Scripting and command-line
edit
- Batch file
- CHKDSK
- Cmd.exe
- ComSpec
- Ipconfig
- Net / Net Send
- Netdom.exe: Windows Domain Manager
- Netsh
- Netstat
- QBasic
- Regsvr32
- Robocopy
- Win32 console
- Windows Script Host
- Windows PowerShell
- XCOPY
- Commit charge
- Kernel Transaction Manager
- Win32 Thread Information Block
- Assembly
- CLI Languages
- Metadata
- .NET Remoting
- ADO.NET
- ASP.NET
- Base Class Library
- Common Intermediate Language
- Common Language Infrastructure
- Common Language Runtime
- Common Type System
- Virtual Execution System
- Windows CardSpace
- Windows Communication Foundation
- Windows Forms
- Windows Presentation Foundation
- Windows Workflow Foundation
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| AppLocker | Policy-based component that enables or disables execution of software based on rules such as location, properties and digital signature | Windows 7 Professional, Enterprise and Ultimate editions Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| BitLocker Drive Encryption | Disk encryption software, designed to protect data by providing encryption for entire volumes | Windows Vista Enterprise and Ultimate editions, Windows Server 2008 |
| Credential Guard | Virtualization-based isolation of stored credentials to prevent theft and pass-the-hash attacks. | Windows 10 Enterprise, Education, IoT Enterprise, or , Windows Server 2016 |
| Data Execution Prevention | Security feature that is intended to prevent an application or service from executing code from a non-executable memory region | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Encrypting File System | File system driver that provides file system-level encryption | Windows 2000 |
| Security Account Manager | Database stored as a registry file | Windows NT 3.1 |
| SYSKEY | Utility that encrypts the hashed password information in a SAM database using a 128-bit encryption key | Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 3 |
| User Account Control | Technology and security infrastructure utility that aims to improve the security of Microsoft Windows by limiting application software to standard user privileges until an administrator authorizes an increase | Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Firewall | Utility designed to block unauthorized access while permitting authorized communications. An earlier edition known as Internet Connection Firewall that was disabled by default was included with the original Windows XP release. | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Windows Defender | Security utility to prevent, remove and quarantine malware (viruses, Trojan horses, etc.) | Downloadable for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Resource Protection | Protects Registry keys and folders in addition to critical system files | Windows Vista |
Deprecated components and apps
edit
| Component | Description | Category | Introduced | Last OS included | Superseded by |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Pinball | Pinball game | Game | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| ActiveMovie | Streaming media technology | API | Windows 95 | Windows Me | DirectShow |
| Cardfile | Personal information manager | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows Me | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail |
| Chess Titans | Chess game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Chess |
| DriveSpace | Disk compression utility | Data compression | MS-DOS | Windows Me | — |
| Windows DVD Maker | DVD authoring software | Video | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| File Manager | File manager app | File manager | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | Windows Explorer |
| FreeCell | FreeCell game | Game | Win32s | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Hearts | Version of the Hearts game using Black Lady scoring | Game | Windows for Workgroups 3.11 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Hearts |
| Windows Insider | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| Windows Help and Support | Online and offline reference manual for troubleshooting. | Utility | Windows Me | Windows 8.1 | Microsoft Tips or Get Started |
| HyperTerminal | Communication utility based on a low end version of HyperACCESS | Communication | Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| Hold ‘Em | Version of the Texas hold ’em game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Hover! | Video game in a combination of bumper cars and capture the flag | Game | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | — |
| InkBall | Game where the user tries to get colored balls into the correct holes | Game | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows Vista | — |
| Internet Explorer | Web browser | Web browser and FTP client. See also: Internet Explorer versions, Features, History, Removal, Browser Helper Objects | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 | Windows 10 | Microsoft Edge |
| Microsoft Mahjong | Version of the Mahjong solitaire game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Mahjong |
| Windows Mail | E-mail client | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Mail (Windows) | |
| Internet Mail and News | E-mail and news client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Minesweeper | Version of the minesweeper game | Game | Microsoft Entertainment Pack, Windows 3.1 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Minesweeper |
| Media Control Interface | An app that can play media files and record sound by passing commands as strings. | API | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | — |
| Windows Media Player | Digital media player app | Media player | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions | Windows 10 | Windows Media Player, Movies & TV, or Groove Music |
| Microsoft Calendar | Calendaring app | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.1 | Windows Calendar, Windows Live Mail, or the Calendar app for Windows |
| Microsoft Diagnostics | Tool that provides detailed technical information about user’s software and hardware | Diagnostics | MS-DOS | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Microsoft System Information |
| Microsoft Fax | Faxing app | Fax | Windows 95 | Windows XP | Windows Fax and Scan |
| Microsoft Private Folder | Tool to protect private data | Personal organizer | Windows XP | Windows XP | |
| Windows Help | Documentation browser that used a proprietary format | Online help | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Microsoft Help |
| Windows Feedback | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| NTBackup | Built-in backup app | Backup | Downloadable for Windows NT 4.0 | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Backup and Restore, Windows Server Backup |
| Outlook Express | E-mail client | Internet Explorer 4 | Windows XP | Windows Mail or Windows Live Mail | |
| Paint | Simple graphics painting app | Application | Windows 1.0 | — | — |
| Program Manager | Shell composed of a task-oriented graphical user interface, consisting of icons (shortcuts for apps) arranged into app groups. | GUI | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Windows Explorer |
| Purble Place | Educational game for children, teaching pattern recognition, shapes, and colors | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| Reader | e-book reader | e-book reader | Windows 8 | Windows 10 Creators Update | Microsoft Edge (PDF), XPS Viewer (XPS), Photos (TIFF)[26] |
| Reversi | Version of Reversi. | Game | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.0 | Internet Reversi only on Windows Me and Windows XP |
| Solitaire | Klondike Solitaire game | Game | Windows 3.0 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Spider Solitaire | Spider Solitaire game | Game | Microsoft Plus! 98 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| System File Checker | Utility that allows users to scan for and restore corruptions in Windows system files | Security | Windows 98 | Windows Server 2003 | Windows Resource Protection |
| Tinker | Puzzle game in which the player controls a robot through various mazes and obstacle courses | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Video for Windows | Multimedia framework | API | Windows 3.1 | Windows 95 | DirectShow |
| Windows Address Book | List of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Contact manager | Internet Explorer 3 | Windows XP | Windows Contacts, People, or Windows Live Mail |
| Windows Desktop Gadgets | Widget engine for Microsoft Gadgets | User interface | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Live tiles |
| Windows File Protection | Sub-system in the operating system, aims to prevent apps from replacing critical Windows system files. | Security | Windows Me as System File Protection | Windows XP | Windows Resource Protection |
| Windows Journal | Notetaking application that allows for the creation of handwritten notes | Accessories | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows 10 Threshold 2 | General improvements in Ink API |
| Windows Messaging | E-mail client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Internet Mail and News, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Windows Messenger | Instant messaging client | Internet messaging | Windows XP | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Windows Live Messenger or Skype |
| Windows Movie Maker | Non-linear video editing software | Video | Windows Me | Windows Vista | Windows Live Movie Maker or Microsoft Photos |
| Microsoft NetMeeting | Video conferencing client | Web conference | Windows 95 OSR2 | Windows XP | Windows Meeting Space |
| Windows Photo Gallery | Image organizer | Photo | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Windows Live Photo Gallery or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Picture and Fax Viewer | Image viewer | Photo | Windows XP | Windows XP | Windows Photo Gallery, Windows Fax and Scan, Windows Live Photo Gallery, Windows Photo Viewer, or Microsoft Photos |
| WordPad | Simple word processor with basic formatting, successor to Microsoft Write. It has facilities to format and print text, but lacks intermediate features such as a spell checker and thesaurus. | Word processor | Windows 95 | Windows 11, version 23H2 | None |
| Microsoft Write | Simple word processor | Word processor | Windows 1.0 | Windows NT 3.51 | WordPad |
- ClearType
- Media Foundation
- Windows Driver Foundation
- Windows Imaging Component
- Windows Management Instrumentation
Miscellaneous (to be categorized)
edit
- ActiveSync
- Compatibility Appraiser collects telemetry information.[27]
- DMRC (Device Metadata Retrieval Client) interfaces to metadata about devices from Windows 7 onwards.[28]
- I/O technologies
- Macro Recorder
- Microsoft Agent
- Prefetcher
- ReadyBoost
- Sync Center
- Text Services Framework
- Universal Audio Architecture
- Windows Color System
- Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI)[29]
- Windows Mobile Device Center
- Windows Rally
- Windows Registry
- Windows Speech Recognition
- XML Paper Specification
- Outline of Microsoft
- List of Unix daemons
- List of games included with Windows
- ^ Shultz, Greg (February 28, 2015). «Control Panel and Settings: Why are both still UI options in Windows 10?». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Get $Windows Camera from the Microsoft Store». apps.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Xbox Support». support.xbox.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ Hoffman, Chris (January 4, 2021). «How to See FPS in Any Windows 10 Game (Without Extra Software)». How-To Geek. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ The Xbox Game Bar Team (May 22, 2019). «Introducing the New Xbox Game Bar». Xbox Wire. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved August 21, 2019.
- ^ «System Services». technet.microsoft.com. Microsoft. 2014. Archived from the original on November 5, 2017. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
The Application Experience service (AELookupSvc) is a part of the Application Compatibility Administrator. It processes application compatibility lookup requests for applications as they are started, provides support for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista–based computers running apps in compatibility mode, reports on compatibility issues, and automatically applies software updates to apps.
- ^ «Description of the Microsoft Computer Browser Service». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved November 3, 2017.
- ^ a b Mackie, Kurt (August 16, 2016). «Microsoft Clarifies Windows 10 ‘Delivery Optimization’«. Redmond Magazine. 1105 Enterprise Computing Group. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (March 29, 2017). «How Delivery Optimization in Windows 10 Creators Update helps avoid data overage fees». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on August 25, 2017. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Dani; Poggemeyer, Liza; Lich, Brian; Kieselbach, Oliver; Childs, Andrew (April 30, 2018). «Configure Delivery Optimization for Windows 10 updates». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 23, 2018. Retrieved July 23, 2018.
- ^ «Distributed Link Tracking on Windows-based domain controllers». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC)». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Event Log». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, notice that the service is listed on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Secondary Logon (Run As): Starting Programs and Tools in Local Administrative Context». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on March 6, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «System Event Notification Service». The Elder Geek. Archived from the original on October 26, 2008. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Myth Busted: Why Disabling SuperFetch on Vista and Windows 7 Is a Bad Idea», retrieved April 2013
- ^ «What Is Volume Shadow Copy Service?: Data Recovery». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived September 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Notice the absence of the service on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Notice that XP is the operating system listed. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «How Windows Time Service Works: Windows Time Service». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on April 22, 2016. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Minasi, Mark; Layfield, Rhonda; Justice, Lisa (2006). Mastering Windows Server 2003: upgrade edition for SP1 and R2 (12 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-470-05645-5. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2010.
There is also a client piece for WebDAV built into XP, 2003, R2, and Vista, called the WebClient Service.
- ^ «Microsoft replaces standalone PDF reader app with Edge». MSPoweruser. November 26, 2017. Archived from the original on August 19, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (April 20, 2015). «KB 2952664 triggers daily telemetry run in Windows 7 — and may be snooping on users: Microsoft bills the ‘compatibility update’ as way to ease the upgrade process to Windows 10 — but it’s collecting data daily». Operating Systems. InfoWorld. InfoWorld, Inc. Archived from the original on June 2, 2017. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
The Microsoft Compatibility Appraiser task runs %windir%\system32\rundll32.exe appraiser.dll,DoScheduledTelemetryRun with the description ‘Collects program telemetry information if opted-in to the Microsoft Customer Experience Improvement Program.’
- ^ Compare: Tulloch, Mitch; Northrup, Tony; Honeycutt, Jerry; Wilson, Ed (2010). Windows 7 Resource Kit. Windows 7 Resource Kit, Microsoft Corporation. Vol. 1. Microsoft Press. p. 708. ISBN 9780735627000. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
The DMRC [(Device Metadata Retrieval Client)] checks the computer’s local metadata cache and metadata store for metadata that applies to the device.
- ^ Solomon, David A.; Russinovich, Mark E.; Ionescu, Alex (June 17, 2009). Windows Internals. Developer Reference (5 ed.). Microsoft Press (published 2009). ISBN 9780735637962. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
The Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI) helps to detect, diagnose, and resolve common problem scenarios with minimal user intervention.
Здесь представлен список компонентов Windows.
Имя сервиса в списке
Ключевое имя
Описание
Появился в
Active Directory Service
NTDS
Network Authentication Management
Windows 2000 Server
Alerter service
Alerter
Sends administrative alerts over the network to client computers, administrators and users
Windows NT
Application Layer
Gateway service
ALG
Provides support for plugins that allow network protocols to pass through Windows Firewall and work behind Internet Connection Sharing
Windows 2000
Application Experience service
Processes application compatibility cache requests for applications as they launch[1]
Application Management
AppMgmt
Processes requests to enumerate, install, and remove applications that are installed on the computer or deployed through an organization’s network
Windows 2000
Background Intelligent
Transfer Service
BITS
Transfers files between machines using idle network bandwidth. Used by Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, and Systems Management Server to deliver software updates to clients, as well as by Windows Messenger.
Windows XP
Computer Browser
Browser
Crawls neighboring computers on the network and locates shared resources. One of the computers acts as the Master Browser and supplies this information to other computers designated as browsers.[2]
Windows for Workgroups
Distributed Link Tracking
TrkWks, TrkSrv
Used to track links to files on NTFS volumes. Windows uses these services to find linked files if they are renamed or moved (locally or to another machine).[3]
Windows 2000
Distributed Transaction
Coordinator
MSDTC
Allows transactional components to be configured through COM+ by coordinating transactions that are distributed across multiple computers and/or resource managers, such as databases, message queues, file systems, and other transaction–based resource managers.[4]
Windows 2000 and later NT-based
DNS Client
DNSCache
Resolves and caches domain names (e.g. “en.wikipedia.org”) to IP addresses
Windows 2000
Event Log
EventLog
Stores and retrieves events that can be viewed in the event viewer. Part of services.exe.[5]
Windows NT
Extensible Authentication Protocol
EAPHost
Provides EAP authentication to connecting clients
Windows 2000
Indexing Service
CISVC
Indexes contents and properties of files on local and remote computers; provides rapid access to files through flexible querying language.[6]
Windows 2000 and later NT-based
Interactive Services Detection
UI0Detect
For compatibility; when a service-displayed user interface is detected, it gives the user an option to switch to Session0 to see it
Windows Vista
Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)
SharedAccess
When enabled, it allows other computers on the local network to access an internet connection that is available to the host computer
Windows 2000;[7] Windows Vista onward[8]
Network Location Awareness
NLA
Manages network configurations and information, and notifies applications of changes
Windows XP
Network Store Interface Service
NSIS
Collects routing information of active network interfaces, shares this with other services and notifies applications of changes
Windows XP
NTLM Security Support Provider
NTLMSSP
Uses the NTLM MS-CHAP protocol to encapsulate and negotiate options in order to provide signed and sealed communication. Deprecated now in favor of Kerberos authentication.
Windows NT
Peer Name Resolution Protocol
PNRPSvc
Resolves domain names using Peer Name Resolution Protocol
Windows XP
Plug and Play
PlugPlay
Enables autodetection and configuration of hardware
Windows 2000
Print Spooler
Spooler
Manages printer devices and moves files into memory for printing
Windows 95, Windows NT
Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
RpcSs
Provides Remote Procedure Call features via remotely accessible Named Pipes
Windows NT family
Routing and Remote Access Service
RRAS
API and server software that enables applications to administer the routing and remote-access service capabilities of the operating system, to function as a network router.
Windows 2000
Secondary Logon
SecLogon
Allows users to run programs with a different account than the one they logged in with. Allows non-administrative accounts to perform administrative tasks.[9]
Security Accounts Manager
SamSs
Manages user account security information
Windows NT family
System Event Notification Service
SENS
Monitors system events, such as network, power, logon, logoff, terminal services session connection and disconnection, and delivers these to applications and other system components.[10]
Windows 2000
Superfetch
SysMain
Monitors file usage patterns and boosts system speed by caching frequently accessed files to RAM[11]
Windows Vista
Task Scheduler
Schedule
Lets users setup and schedule automated tasks
Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95
TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper
LmHosts
Enables support for NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) service and NetBIOS name resolution
Windows NT family
Volume Shadow Copy
VSS
Create multiple versions of files that change. Gained ability to store persistent snapshots in Windows Server 2003.[12]
Windows XP
Windows Audio
AudioSrv
Manages audio devices for Windows-based programs. Controls all audio functions.
Windows XP
Windows Error Reporting
WERSvc
Generates error logs and reports errors. On Windows Vista and later, it notifies of solutions.
Windows XP
Windows Firewall
MpsSvc
Blocks unauthorized network connections to and from the computer
Windows Vista
Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)
SharedAccess
Provides a simple firewall feature which was introduced in Windows XP. It also shares the internet on the local network, if the internet connection sharing feature is turned on.[13]
Windows XP only[14][15]
Windows Image Acquisition (WIA)
STISvc
Handles scanner and camera inputs
Windows ME
Windows Time
W32Time
Synchronizes the system time with external time servers. From Windows Server 2003 forward, full and compliant NTP support is provided.[16]
Windows 2000
Windows Update
WUAUServ
Provides updates for the operating system and its installed components
Windows XP
Wireless Zero Configuration
WZCSvc (XP), WLANSvc
Configures and manages 802.11 wireless adapters
Windows XP, Server 2003 only
Windows Messenger service
Messenger
Allows users to send pop-up messages to other computers over the network
Windows NT family
WebClient[17]
Enables Windows-based programs to create and interact with Internet-based files
Windows XP
Windows 10 унаследовала из прошлых поколений системы ряд компонентов. Некоторые из них все еще полезны, а некоторые попросту расходуют ресурсы компьютера.
Выясняем, что за компоненты Microsoft спрятала в недрах Windows, какие задачи они выполняют и можно ли их отключить.
Что такое компоненты и как ими управлять
Компоненты — это общее название для ряда приложений и программных сервисов, отвечающих за работу некоторых функций Windows. Они как блоки конструктора по отдельности выполняют различные полезные задачи. Одни помогают системе распознавать документы и распечатывать их, другие отвечают за воспроизведение медиафайлов, а все вместе они заставляют Windows работать привычным образом.
Компонентами можно управлять. Если какой-то из них вам не нужен, в настройках системы можно его выключить, тем самым снизив нагрузку на компьютер. Или, наоборот, при необходимости можно включить любой из них (даже устаревший), но перед этим надо убедиться, можно ли это делать.
Почему лучше не спешить с отключением компонентов
Microsoft знает, какие функции нужны основной массе людей, и оставляет их включенными по умолчанию. При этом доступ к их настройкам прячет, чтобы никто случайно не влез и не отключил их вручную, так как это может привести к неприятным последствиям. К примеру, отключение NET Framework выведет из строя львиную долю приложений, разработанных для Windows. А без сервиса «Печать в PDF» вы уже не сможете открывать PDF-файлы и распечатывать их.
Поэтому изменения нужно вносить осторожно. И если очень хочется, то перед тем, как экспериментировать, ознакомьтесь с таблицей в конце статьи. В ней описано предназначение компонентов и возможные последствия их выключения.
Через «Параметры»
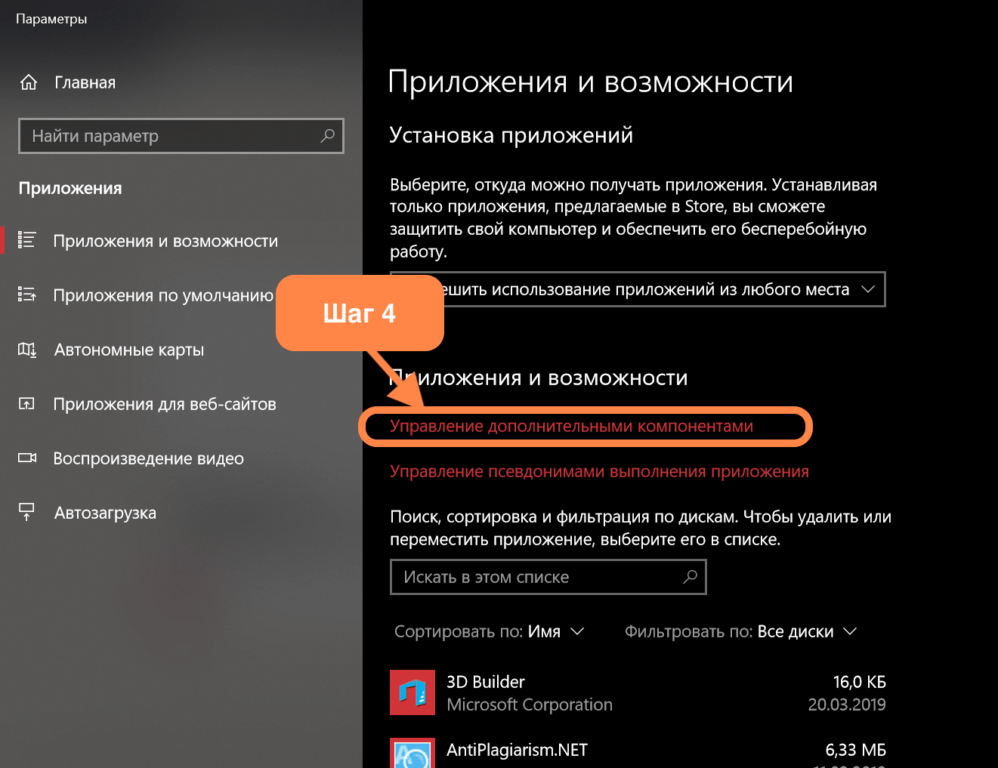
- Открываем поле поиска (справа от кнопки «Пуск» с эмблемой Windows).
- Вводим в него слово «Приложения».
- В результатах поиска появится пункт «Приложения и возможности».
- Найдем строку «Управление дополнительными компонентами» и нажмем на нее.
В открывшемся окне отобразится список системных компонентов, которыми можно отсюда же управлять, например, удалять или восстанавливать.
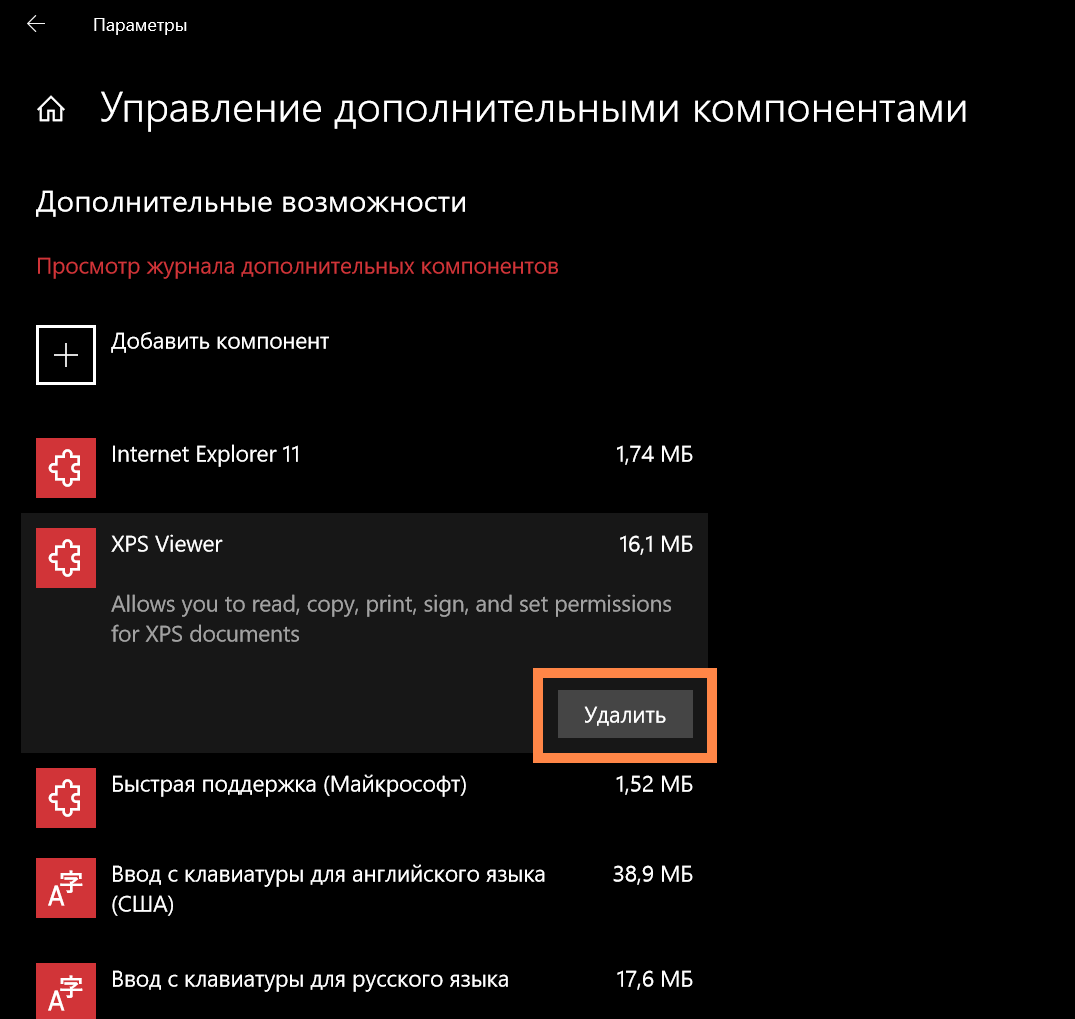
Через «Панель управления»
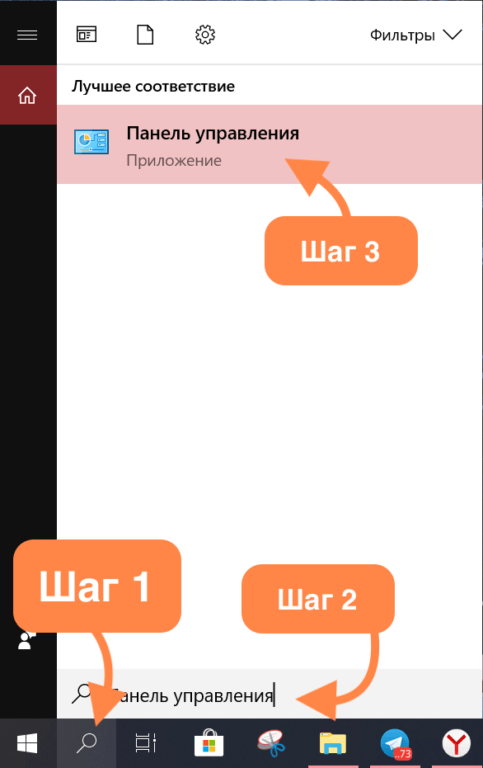
- Открываем поле поиска (справа от кнопки «Пуск» с эмблемой Windows).
- Введим в него словосочетание «Панель управления».
- В результатах поиска появится нужное нам приложение. Открываем его.
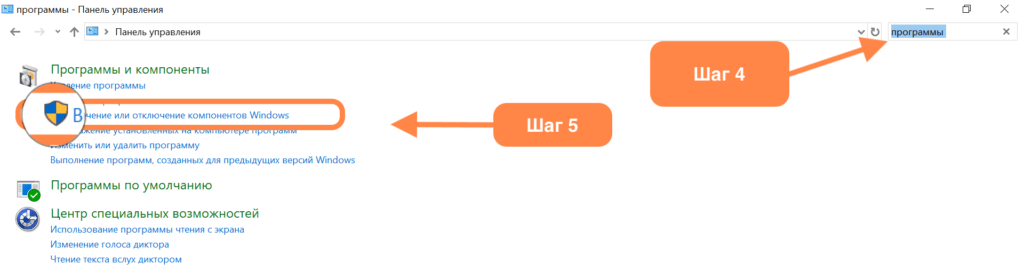
- Открыв «Панель управления», выделяем поле поиска (в верхней части окна) и введим туда слово «Программы».
- Появится меню с заголовком «Программы и компоненты». Выбираем пункт «Включение и отключение компонентов Windows» (его легко найти по значку в виде щита).
- Вводим пароль администратора компьютера (это тот, что вы вводите, когда устанавливаете новые программы и игры).
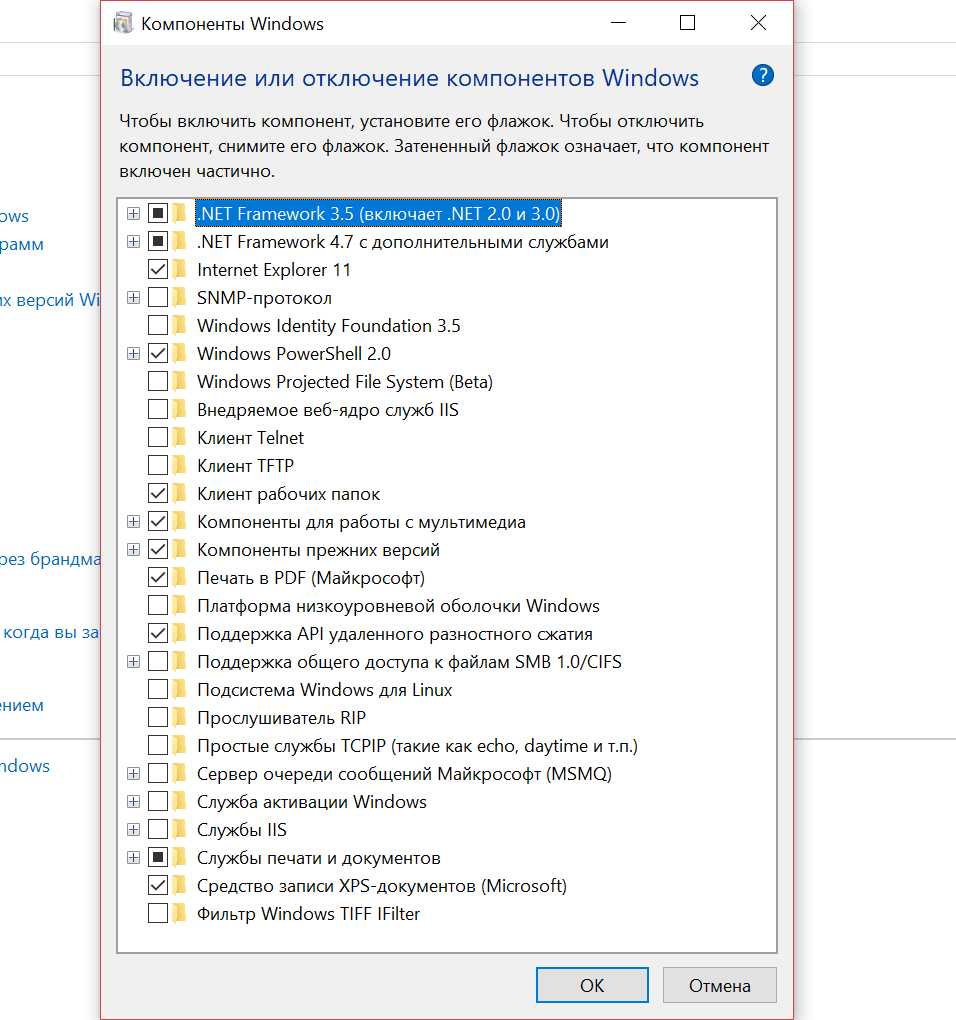
В новом окне откроется список компонентов Windows, которыми можно управлять. Они отображаются в виде файлов и папок с отметками. У каждой отметки свое значение:
- если слева от названия компонента стоит галочка, значит, он включен;
- если слева от названия есть плюс (+), значит, он содержит зависимые службы и сервисы;
- если вместо галочки стоит черный квадрат, значит, некоторые зависимые службы или сервисы включены, а некоторые — нет;
- если нет ни галочки, ни квадратика — компонент не работает.
Список компонентов и их предназначение
Отключение компонентов, помеченных звездочкой, может привести к ошибкам и некорректной работе системы.
|
Название |
Для чего нужен |
|
* NET Framework 3.5 |
Служба, отвечающая за запуск и корректную работу приложений, созданных на базе платформы .NET. Таких приложений для Windows очень много, так что не отключайте этот компонент. Это касается всех служб и сервисов, в названиях которых фигурирует .NET и Identity Foundation. |
|
Hyper-V |
Фирменное программное обеспечение Mirosoft для запуска виртуальных машин. Проще говоря — программа для симуляции полноценного виртуального компьютера в Windows |
|
Internet Explorer 11 |
Встроенный веб-браузер. Майкрософт ежегодно обновляет его, но, кажется, не так уж и много людей пользуется им. |
|
SNMP-протокол |
Отвечает за работу с устройствами, подключенными к сети. |
|
Подсистема Windows для Linux |
Утилита для запуска Linux-приложений в Windows. |
|
Windows PowerShell 2.0 |
Усовершенствованная командная строка для разработчиков. |
|
Внедряемое веб-ядро служб IIS |
Программное обеспечение для веб-разработчиков. Пригодится для отладки кода и разворачивания веб-серверов. |
|
* Компоненты прежних версий |
В них есть часть DirectX, которая используется в старых играх. Если часто играете (особенно в старые игры), оставьте включенным. |
|
Клиент Telnet |
Устаревшая программа для связи с серверами Telnet. |
|
Клиент TFTP |
Небольшая утилита для отправки файлов по протоколу TFTP. |
|
Клиент рабочих папок |
Программа для синхронизации личных файлов с файлами из корпоративного сервера. Грубо говоря, это как работа с персональным облаком (OneDrive или Dropbox), только это облако доступно исключительно сотрудникам конкретной компании и управляется ее же администраторами. |
|
Компоненты для работы с мультимедиа |
Под этими компонентами подразумевается встроенный проигрыватель видео- и аудиофайлов (выключайте, если пользуетесь другим плеером). |
|
Пакет администрирования диспетчера RAS — подключений |
ПО для подключения к удаленным сетям, защищенным с помощью VPN. |
|
Дополнительные языки |
Языковые пакеты. Нужны, если вы хотите поменять язык системы или добавить поддержку других языков. |
|
* Поддержка АРІ удалённого разностного сжатия |
Инструмент для сравнения синхронизируемых файлов. Используется большим количеством программ и системных функций. Его нельзя отключать. |
|
Поддержка общего доступа к файлам SMB 1.0/CIFS |
Программное обеспечение, необходимое для синхронизации данных со старыми версиями Windows. |
|
Прослушиватель RIP |
Инструмент для обновления таблицы маршрутизации в корпоративных Wi-Fi-сетях. |
|
Простые службы TCPIP |
Это устаревший набор функций для командной строки (echo, daytime). |
|
Сервер очереди сообщений Майкрософт |
Служба, которая хранит сообщения в буфере, чтобы в случае обрыва сети отправить их, когда соединение восстановится. |
|
Службы IIS |
Инструмент для веб-разработчиков. Благодаря IIS можно превратить любой Windows-компьютер в полноценный веб-сервер. Для тех, кто не занимается разработкой или использует аналоги (XAMPP, MAMPP), он бесполезен. |
|
Службы XPS |
Набор программ, обеспечивающий поддержку файлов в формате XPS (это непопулярный аналог PDF) на системном уровне. Если не знаете, что такое XPS — отключайте. |
|
* Службы печати и документов |
Это набор служб, отвечающих за работу с принтерами и факсами. Две из них уже устарели – «Монитор LPR-портов» и «Служба печати LPD», их можно отключить. |
|
Фильтр Windows TIFF IFilter |
Инструмент для распознавания текста внутри файлов в формате TIFF. Если не работаете с этим форматом, то лучше выключите, чтобы не тратить ресурсы компьютера зря. |
Загрузка …
Post Views: 5 023