Last Updated :
16 May, 2024
While working on Windows devices, we used to work on Windows File Explorer for working with files. On File Explorer of Windows, the creation of new files as well as deleting old ones is one of the easiest processes. However, if your File Explorer is not responding, then the process to Delete Folder using CMD can be an alternative.
The Windows Command Prompt is the command line tool that executes different tasks with the help of Windows Commands. Using CMD in Windows, the File Creation for Windows can also be executed. If you are having trouble Deleting Files or Folders on Windows directly by right-clicking, then you can Delete files using CMD.
This article is going to discuss the commands required to Remove Files & Folders using the UsingCommand Prompt of Windows.
Table of Content
- Methods to Delete Files and Folders Using Command Prompt
- Method 1: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using DEL Command
- Method 2: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using RMDIR Command
- Delete a Folder and Subfolders in Command Prompt
Methods to Delete Files and Folders Using Command Prompt
To Erase Windows Files or Folders using CMD, the following guidelines should be used properly. Let us start with the DEL Command Execution.
Method 1: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using DEL Command
Note: DEL Command is used to delete a file. Here, we will take our sample file “hello.txt” located on the desktop, and try to delete it using the del command in CMD. Follow the steps given below to delete the file:
Step 1: Change the Path of the Directory in CMD and set it to the path of the file. Type the following command and press Enter.
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the file hello.txt with the following Windows Command.
del hello.txt

Method 2: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using RMDIR Command
Note: RMDIR Command is used to delete the entire folder or directory. Here, we will take our sample folder named “Tasks” placed on the desktop and try to delete it using RMDIR Command in CMD.
Step 1: Change the Directory’s Path in Command Prompt and set it to the path of the folder.
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the folder Tasks with the following command.
rmdir tasks

From the above discussion, this should become clear that the Deletion of Windows Files using CMD is a matter of a few seconds. You have to just move inside the Windows Directory using the Windows CD Command. And then, as per your choice execute any one of the Windows File Deletion Commands in CMD.
Delete a Folder and Subfolders in Command Prompt
Step 1: Open Command Prompt.
Step 2: Navigate to the directory where the folder you want to delete is located using the cd command.
Command: cd <FolderName>
Step 3: To delete a single folder, use the following command.
Command: rmdir <FolderName>
Step 4: To delete a folder and all its subfolders and files, just include “/s” in between the rmdir and <folderName>, use the following command.
Command: rmdir /s <FolderName>
Step 5: Press Enter to execute the command.
Also Read
- Useful CMD commands for daily use in Windows OS
- CMD Commands to Gather Information of a System
- How to Show all the previously connected WiFi Networks using CMD in Windows?
Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to use Command Prompt in Windows to delete files and folders efficiently when facing issues with File Explorer. We discussed two methods: using the DEL command to delete files and the RMDIR command to delete folders. Additionally, we provided a step-by-step guide on how to delete folders and subfolders using Command Prompt.
on August 5, 2015
Deleting files is one of the frequently done operation from Windows command prompt. This post explains how to use ‘del’ command from CMD for different use cases like deleting a single file, deleting files in bulk using wild cards etc. Before we start to look at the syntax, note that the command works only for files and can’t handle folders.
How to delete a file
Run del command with the name of the file to be deleted, you are done!
del filename
You do not see message after running the command if the file is deleted successfully. Error message is shown only when something goes wrong.
Delete files in bulk
Del command recognizes wildcard(*) and so can be used to delete files in bulk from CMD. Some examples below.
To delete all the files in current folder
del *
To delete all the files with ‘log’ extension
del *.log
Delete all files having the prefix ‘abc’
del abc*
Delete all files having ‘PIC’ somewhere in the file name.
del *PIC*
The above are the basic use cases of del command. Continue to read below for non trivial use cases.
Delete multiple files
‘Del’ command can accept multiple files as argument
del filename1 filename2 filename3 filename4....
Example:
D:\>dir /s /b 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf D:\>del 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf D:\> D:\>dir /s /b D:\>
Delete Read only files
We can’t delete a read-only file using simple‘del’ command. We get access denied error in this scenario.
c:\>attrib readonlyfile.txt A R C:\readonlyfile.txt c:\>del readonlyfile.txt c:\readonlyfile.txt Access is denied. c:\>
A read-only file can be deleted by adding /F flag.
del /F readonlyfile.txt
Alternatively, we can use the below command too
del /A:R readonlyfile.txt

Sometimes it’s just faster to do things with the command line.
In this quick tutorial we’ll go over how to open Command Prompt, some basic commands and flags, and how to delete files and folders in Command Prompt.
If you’re already familiar with basic DOS commands, feel free to skip ahead.
How to open Command Prompt
To open Command Prompt, press the Windows key, and type in «cmd».
Then, click on «Run as Administrator»:
After that, you’ll see a Command Prompt window with administrative privileges:
Screenshot of Command Prompt window
If you can’t open Command Prompt as an administrator, no worries. You can open a normal Command Prompt window by clicking «Open» instead of «Run as Administrator».
The only difference is that you may not be able to delete some protected files, which shouldn’t be a problem in most cases.
How to delete files with the del command
Now that Command Prompt is open, use cd to change directories to where your files are.
I’ve prepared a directory on the desktop called Test Folder. You can use the command tree /f to see a, well, tree, of all the nested files and folders:
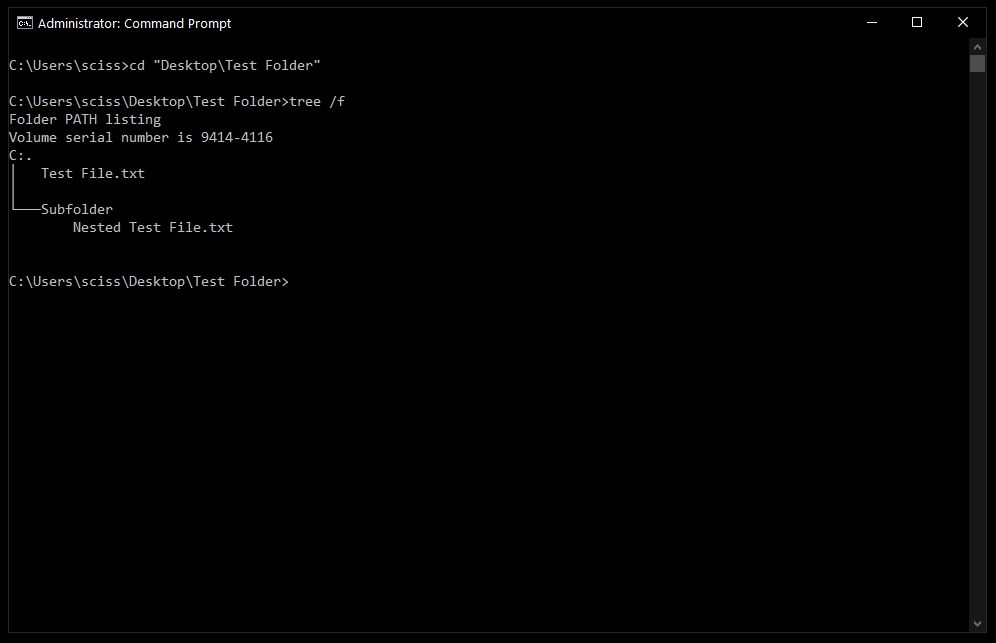
To delete a file, use the following command: del "<filename>".
For example, to delete Test file.txt, just run del "Test File.txt".
There may be a prompt asking if you want to delete the file. If so, type «y» and hit enter.
Note: Any files deleted with the del command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
After that, you can run tree /f to confirm that your file was deleted:

Also, bonus tip – Command Prompt has basic autocompletion. So you could just type in del test, press the tab key, and Command Prompt will change it to del "Test File.txt".
How to force delete files with the del command
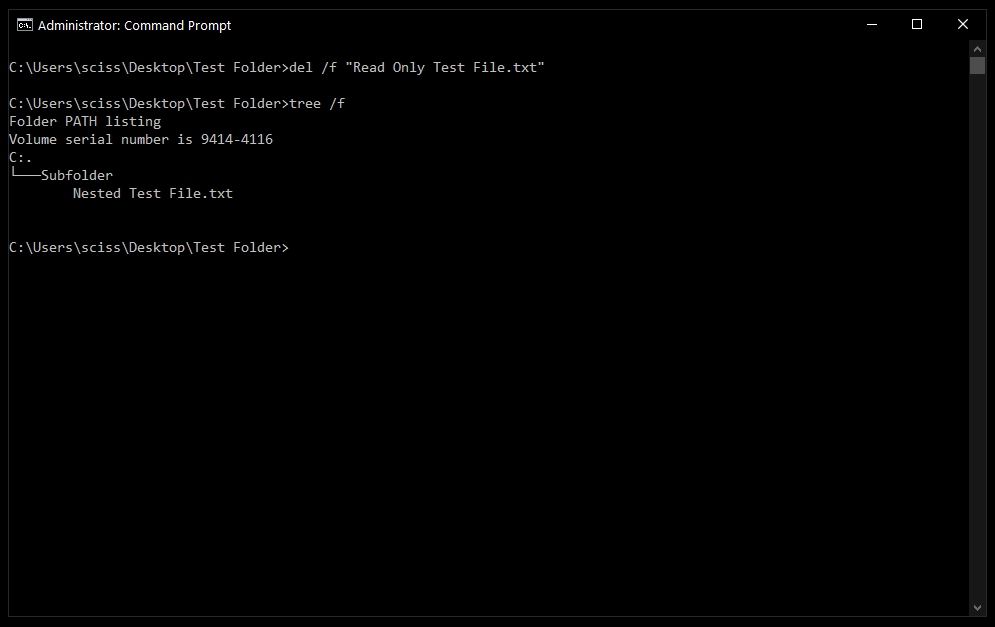
Sometimes files are marked as read only, and you’ll see the following error when you try to use the del command:
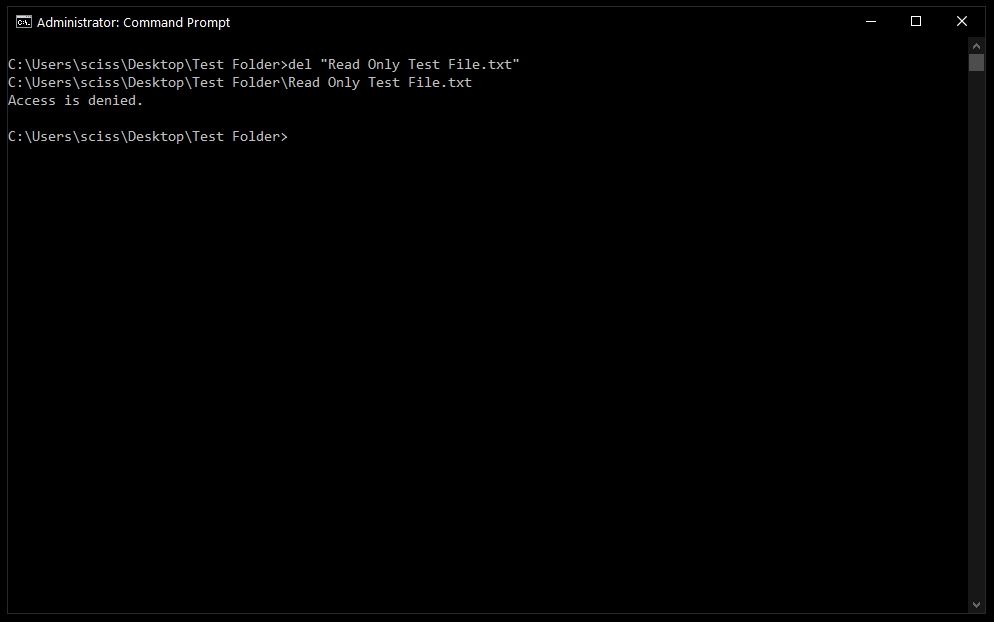
To get around this, use the /f flag to force delete the file. For example, del /f "Read Only Test File.txt":
How to delete folders with the rmdir command
To delete directories/folders, you’ll need to use the rmdir or rd command. Both commands work the same way, but let’s stick with rmdir since it’s a bit more expressive.
Also, I’ll use the terms directory and folder interchangeably for the rest of the tutorial. «Folder» is a newer term that became popular with early desktop GUIs, but folder and directory basically mean the same thing.
To remove a directory, just use the command rmdir <directory name>.
Note: Any directories deleted with the rmdir command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
In this case I want to remove a directory named Subfolder, so I’ll use the command rmdir Subfolder:
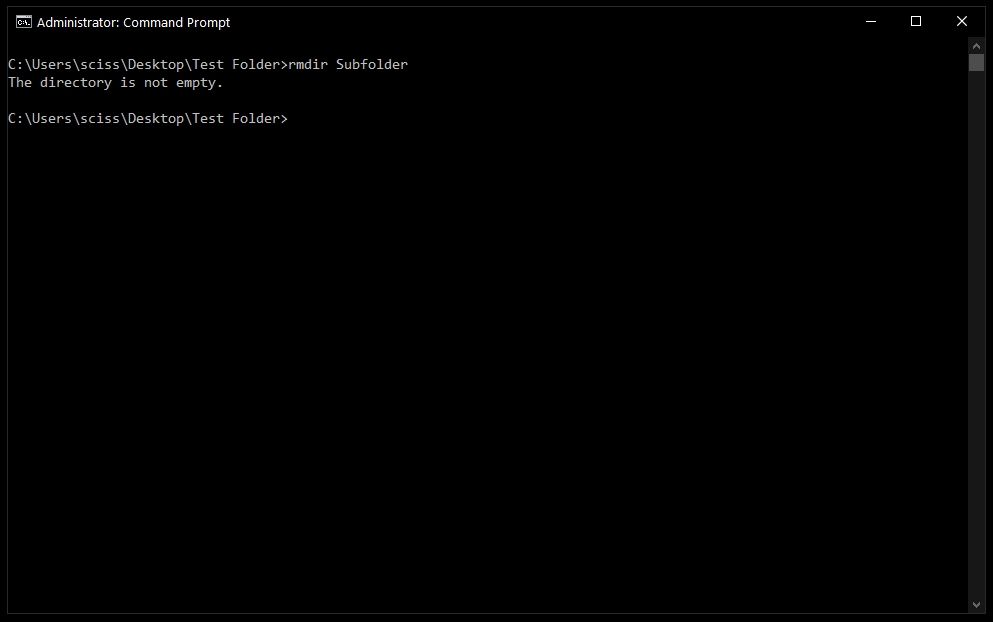
But, if you remember earlier, Subfolder has a file in it named Nested Test File.
You could cd into the Subfolder directory and remove the file, then come back with cd .. and run the rmdir Subfolder command again, but that would get tedious. And just imagine if there were a bunch of other nested files and directories!
Like with the del command, there’s a helpful flag we can use to make things much faster and easier.
How to use the /s flag with rmdir
To remove a directory, including all nested files and subdirectories, just use the /s flag:
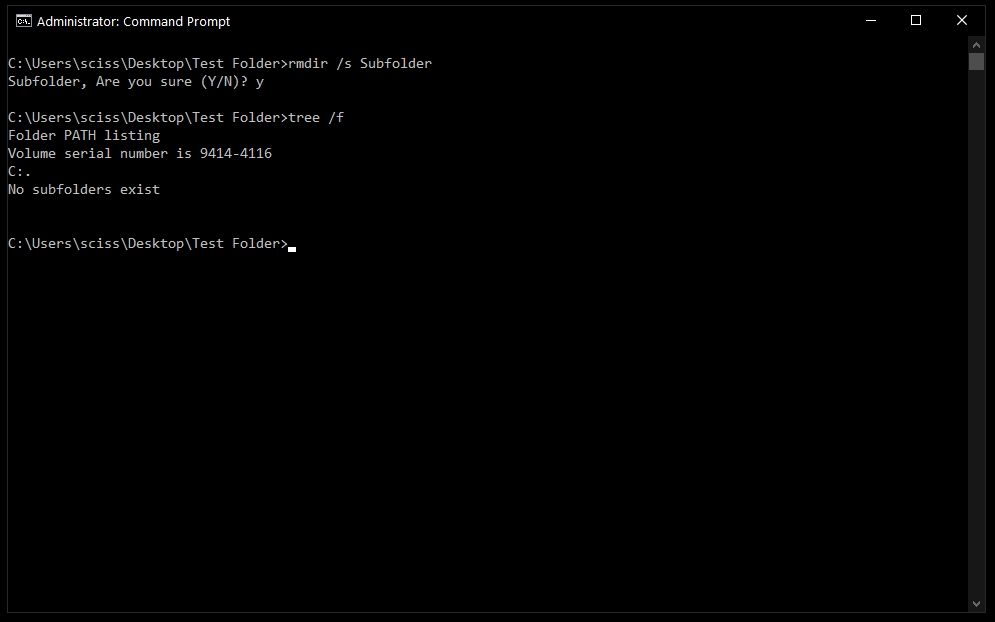
There will probably be a prompt asking if you want to remove that directory. If so, just type «y» and hit enter.
And that’s it! That should be everything you need to know to remove files and folders in the Windows Command Prompt.
All of these commands should work in PowerShell, which is basically Command Prompt version 2.0. Also, PowerShell has a bunch of cool aliases like ls and clear that should feel right at home if you’re familiar with the Mac/Linux command line.
Did these commands help you? Are there any other commands that you find useful? Either way, let me know over on Twitter.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Программистам часто приходится работать в консоли — например, чтобы запустить тестирование проекта, закоммитить новый код на Github или отредактировать документ в vim. Всё это происходит так часто, что все основные действия с файлами становится быстрее и привычнее выполнять в консоли. Рассказываем и показываем основные команды, которые помогут ускорить работу в терминале под OS Windows.
Для начала нужно установить терминал или запустить командную строку, встроенную в Windows — для этого нажмите Win+R и введите cmd. Терминал часто встречается и прямо в редакторах кода, например, в Visual Studio Code.
Чтобы ввести команду в консоль, нужно напечатать её и нажать клавишу Enter.
Содержимое текущей папки — dir
Выводит список файлов и папок в текущей папке.
C:\content-server>dir
Том в устройстве C имеет метку SYSTEM
Серийный номер тома: 2C89-ED9D
Содержимое папки C:\content-server
06.10.2020 00:41 <DIR> .
06.10.2020 00:37 <DIR> .circleci
16.07.2020 16:04 268 .editorconfig
16.07.2020 16:04 10 .eslintignore
16.07.2020 16:04 482 .eslintrc
06.10.2020 00:37 <DIR> .github
16.07.2020 16:04 77 .gitignore
06.10.2020 00:41 <DIR> assets
06.10.2020 00:41 <DIR> gulp
16.07.2020 16:10 379 gulpfile.js
16.07.2020 16:10 296 320 package-lock.json
16.07.2020 16:10 751 package.json
16.07.2020 16:04 509 README.md
Открыть файл
Чтобы открыть файл в текущей папке, введите его полное имя с расширением. Например, blog.txt или setup.exe.
Перейти в другую папку — cd
Команда cd без аргументов выводит название текущей папки.
Перейти в папку внутри текущего каталога:
C:\content-server>cd assets
C:\content-server\assets>
Перейти на одну папку вверх:
C:\content-server\assets>cd ..
C:\content-server>
Перейти в папку на другом диске:
c:\content-server>cd /d d:/
d:\>
Чтобы просто изменить диск, введите c: или d:.
Создать папку — mkdir или md
Создаём пустую папку code внутри папки html:
d:\html>mkdir coded:\html>dir
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:25 <DIR> code
0 файлов 0 байт
3 папок 253 389 438 976 байт свободно
Создаём несколько пустых вложенных папок — для этого записываем их через косую черту:
d:\html>mkdir css\js
d:\html>dir
Том в устройстве D имеет метку DATA
Серийный номер тома: 0000-0000
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:25 <DIR> code
03.11.2020 19:29 <DIR> css
Создаётся папка css, внутри которой находится папка js. Чтобы проверить это, используем команду tree. Она показывает дерево папок.
Удалить папку — rmdir или rd
Чтобы удалить конкретную папку в текущей, введите команду rmdir:
d:\html\css>rmdir js
При этом удалить можно только пустую папку. Если попытаться удалить папку, в которой что-то есть, увидим ошибку:
d:\html\css>d:\html>rmdir css
Папка не пуста.
Чтобы удалить дерево папок, используйте ключ /s. Тогда командная строка запросит подтверждение перед тем, как удалить всё.
d:\html>rmdir css /s
css, вы уверены [Y(да)/N(нет)]? y
Показать дерево папок — tree
В любом момент мы можем увидеть структуру папок. Для этого используется команда tree.
d:\html>tree
Структура папок тома DATA
Серийный номер тома: 0000-0000
D:.
├───code
└───css
└───js
Если вы хотите посмотреть содержимое всего диска, введите tree в корне нужного диска. Получится красивая анимация, а если файлов много, то ещё и немного медитативная.
Удаление файла — del или erase
Команда для удаления одного или нескольких файлов.
d:\html>del blog.txt
Переименование файла — ren или rename
Последовательно вводим ren, старое и новое имя файла.
d:\html>dir
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:59 0 blag.txt
d:\html>ren blag.txt blog.txt
d:\html>dir
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:59 0 blog.txt
Команды одной строкой
Очистить консоль — cls.
Информация о системе — systeminfo.
d:\html>systeminfo
Имя узла: DESKTOP-6MHURG5
Название ОС: Майкрософт Windows 10 Pro
Версия ОС: 10.0.20246 Н/Д построение 20246
Изготовитель ОС: Microsoft Corporation
Параметры ОС: Изолированная рабочая станция
Сборка ОС: Multiprocessor Free
Информация о сетевых настройках — ipconfig.
d:\html>ipconfig
Настройка протокола IP для Windows
Адаптер Ethernet Ethernet 2:
Состояние среды. . . . . . . . : Среда передачи недоступна.
DNS-суффикс подключения . . . . . :
Список запущенных процессов — tasklist.
c:\>tasklist
Имя образа PID Имя сессии № сеанса Память
========================= ======== ================ =========== ============
System Idle Process 0 Services 0 8 КБ
System 4 Services 0 2 688 КБ
Secure System 72 Services 0 23 332 КБ
…
Справка по командам — help
Команда help без аргументов выводит список всех возможных команд. help вместе с именем команды выведет справку по этой команде.
d:\html>help tree
Графическое представление структуры папок или пути.
TREE [диск:][путь] [/F] [/A]
/F Вывод имён файлов в каждой папке.
/A Использовать символы ASCII вместо символов национальных алфавитов.
В этой статье приведены не все команды и не все их возможности, но вы всегда можете воспользоваться командой help и узнать о том, что ещё может командная строка.
👉🏻 Больше статей о фронтенде и работе в айти в телеграм-канале.
Подписаться
Материалы по теме
- 10 горячих клавиш VS Code, которые ускорят вашу работу
- Полезные команды для работы с Git
- Полезные команды для работы с Node. js
«Доктайп» — журнал о фронтенде. Читайте, слушайте и учитесь с нами.
ТелеграмПодкастБесплатные учебники
The del command is a Command Prompt command used to delete files. Various command options are available so that you can remove files that have a certain file extension, delete every file in a folder, get rid of only the files with certain file attributes, and more.
Unlike deleting files normally, data removed with the del command doesn’t end up in Recycle Bin.
This command is the exact same as the erase command.
Del Command Availability
The del command is available from within the Command Prompt in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP operating systems.
It can also be used in Command Prompt in the Advanced Startup Options and System Recovery Options repair/recovery menus.
In Recovery Console in Windows XP and Windows 2000, the delete Recovery Console command can be used instead.
Del Command Syntax
del [/p] [/f] [/s] [/q] [/a[:]] filename [/?]
The availability of certain del command switches and other command syntax might differ from operating system to operating system. Brush up on how to read command syntax if you’re not sure how to interpret the syntax as it’s shows above or described in the table below.
| Del Command Options | |
|---|---|
| Item | Explanation |
| /p | Prompts for confirmation before deleting each file. |
| /f | Force deletes read-only files. |
| /s | Deletes the specified files from all the subdirectories. |
| /q | Quiet mode; suppresses prompts for delete confirmations. |
| /a | Deletes files based on one of the following attributes:
r = Read-only files |
| /? | Use the help switch with the del command to show detailed help about the command’s several options. Executing del /? is the same as using the help command to execute help del. |
Del Command Examples
Here are some examples showing how you can use the command:
Delete File in Specific Folder
del c:\windows\twain_32.dll
In the above example, the del command is used to remove twain_32.dll located in the C:\Windows folder.
Delete File From Current Folder
del io.sys
Here, the command has no path information specified, so the io.sys file is deleted from whatever directory you typed the command from.
For example, if you type del io.sys from the C:\> prompt, the io.sys file will be deleted from C:\.
Delete All EXE Files
del C:\Users\Tim\Downloads\*.exe
This one removes all EXE files from the Tim user’s Downloads folder. The file extension could be replaced with * to delete every file from that folder.
Notice there isn’t a space after Downloads\. Adding a space would break the command and tell Windows to erase the Downloads folder instead of just the EXE files. Because the del command doesn’t remove folders, it would erase every file from it, including not only EXE files but also images, documents, videos, etc.
Delete Every Archived File
del /a:a *.*
Use this del command to delete every archived file in the current working directory. Similar to the io.sys command above, this one would execute on whatever folder Command Prompt is set to.
Delete By Attribute and Extension
del /q /a:r C:\Users\Tim\Documents\*.docx
To combine a few of the del switches, consider this command which will delete every read-only (/a:r) DOCX file from the user’s Documents folder, but will do so in quiet mode (/q) so that you’re not asked to confirm it.
Delete Files From Subfolders
del /s C:\Users\Tim\Documents\Adobe\*.*
This command will delete every file (*.*) from every folder (/s) inside the Adobe folder in the user’s Documents directory. The folders will remain, but every file will get removed.
However, in this example, you’ll be prompted to enter Y for each file to confirm that you do, in fact, want to delete each one. To avoid that, if you’re sure you want to delete every single file, you can add the /q switch before or after the /s switch to run the command in quiet mode.
Just like with the DOCX example above, the wildcard (*.*) in this command can be changed to anything to remove only those files. Use *.MP4 for MP4s, *.MP3 for MP3s, etc.
Del Related Commands
The erase command is identical to the del command, so either can be used with the same result. In other words, you can replace «del» with «erase» in any of the command examples above without interrupting the instructions.
The command forfiles is sometimes used with the del command to remove files that are so-many days old. For example, you might want to delete files that are older than a month in a specific folder, something you can do with forfiles and del but not with just the del command itself.
In Windows XP and newer versions of Windows, rmdir is used to erase a whole folder, while deltree is used for the same purpose in operating systems older than Windows XP.
In MS-DOS, the undelete command is used to restore files that were deleted with the delete command. To undo the del command in newer versions of Windows, try a file recovery program.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
