Table of Contents
In this tutorial, we will see 3 ways to start/stop/restart services in Windows. Services are mostly required when you need to have some long running functionality in your Server. As you might be aware Microsoft Windows has number of services running at any point of time. A service is basically a long running executable applications that run in their own Windows sessions. You can run services in multiple user contexts. You don’t have to necessarily use the logged in user account. A service can be started, stopped and restarted. In Windows System, you can use multiple methods to stop/start/restart service that we will see in below section. More on Microsoft official website.

Also Read: VBoxManage — An Introduction to VirtualBox CLI with Examples
Method 1: Using CMD
a) Open CMD
You can go to search box and type CMD to open the command line. Once it shows up, right click on it and then click on Run as administrator.
b) Start/Stop/Restart a Service
If you want to start a service then you need to use net start <service> command. Here we are starting Windows Update services by using net start wuauserv command as shown below.
C:\>net start wuauserv
The Windows Update service is starting.
The Windows Update service was started successfully.
If you want to stop a service then you need to use net stop <service> command. Here we are stopping Windows Update service by using net stop wuauserv command as shown below.
C:\>net stop wuauserv
The Windows Update service is stopping.
The Windows Update service was stopped successfully.
In CMD, there is no such option called restart so what you can do is that you can perform net stop <service_name> and net start <service_name> simultaneously as shown below. This will work as if you have restarted the service.
C:\>net stop wuauserv && net start wuauserv
The Windows Update service is stopping.
The Windows Update service was stopped successfully.
The Windows Update service is starting.
The Windows Update service was started successfully.
Method 2: Using PowerShell
a) Open PowerShell
You can go to search box and type PowerShell. Once it shows up, right click on it and then click on Run as administrator.
b) Start/Stop/Restart a Service
If you want to start a windows service then you need to use Start-Service -Name <service_name> command. You can also check the progress by using -Verbose option.
PS C:\> Start-Service -Name wuauserv -Verbose
VERBOSE: Performing the operation "Start-Service" on target "Windows Update (wuauserv)".
If you want to stop a windows service then you need to use Stop-Service -Name <service_name> command. You can also check the progress by using -Verbose option.
PS C:\> Stop-Service -Name wuauserv -Verbose
VERBOSE: Performing the operation "Stop-Service" on target "Windows Update (wuauserv)".
If you want to restart a windows service then you need to use Restart-Service -Name <service_name> command. You can also check the progress by using -Verbose option.
PS C:\> Restart-Service -Name wuauserv -Verbose
VERBOSE: Performing the operation "Restart-Service" on target "Windows Update (wuauserv)".
Method 3: Using GUI
a) Open Services
You can open Run prompt by pressing Windows+R and then typing services.msc to open Services or you can directly search services.msc in the Search section to open Services. Once it shows up, right click on it and then select Run as administrator.
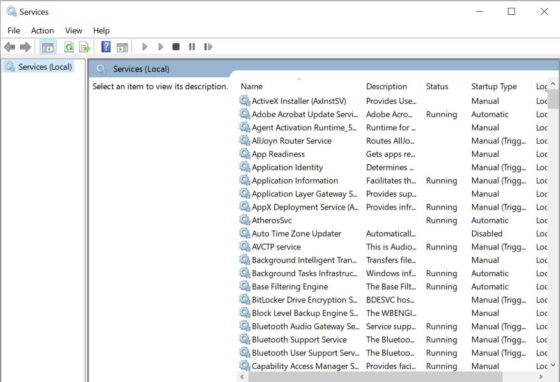
b) Start/Stop/Restart a Service
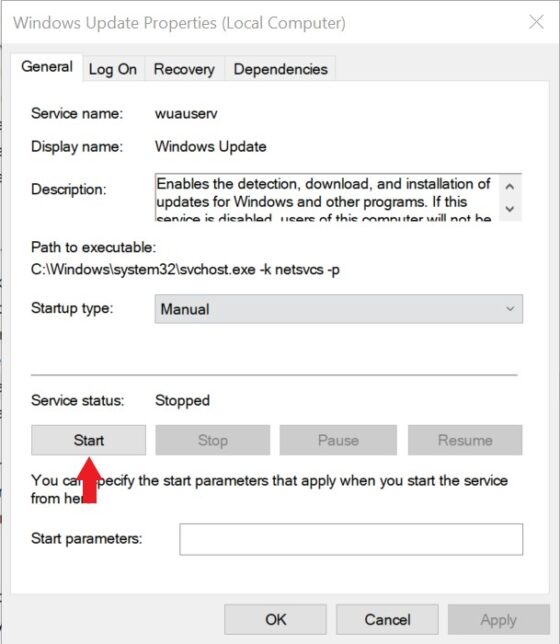
You can double click and open the service as shown below. Then Click on Start to start the service. The other way is to right click on that service and then start from there.
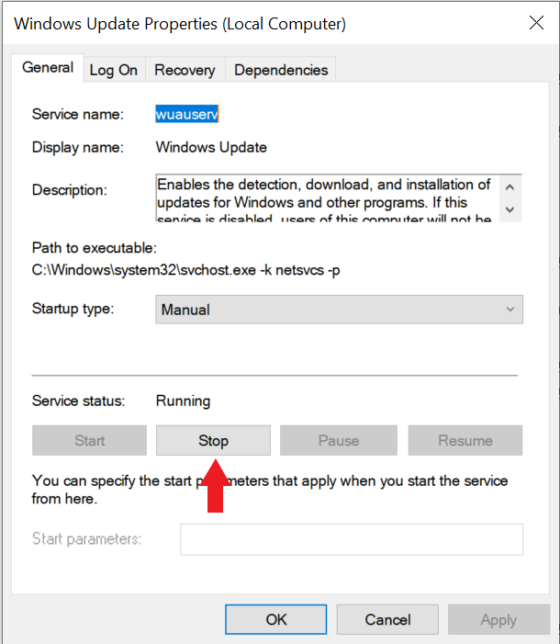
Similarly if you want to stop any service then double click on that service and open it as shown below. Here you can click on Stop to stop the service. Alternatively, you can also right click on that service and then Click on Stop to shutdown the service.
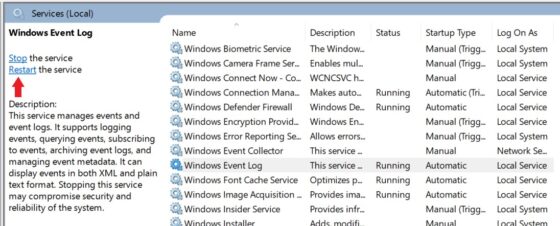
You will also have the option to restart the service. For example here I am restarting the Windows Event Log service by clicking on Restart as shown below. Alternatively, you can also right click on that service and then click on Restart.
Windows Service management through the command line is really a good approach when you want to manage plenty of services and perform day to day actions like stop, start and restart
I think you would agree, If I say GUI is fun for entry-level but when it comes to performing the job smartly and creating automation for efficiency. Command-line is your key
PowerShell has a lot of commands to help us manage the windows server better and create automation and do the boring (or) repetitive tasks swiftly
In this article, we are going to see How to Manage Services from the Windows Command line using PowerShell. We are going to see various examples of How to List , Stop, Start, Restart a Single Service or multiple Services.
To Manage the Services in Windows, We have a pack of Powershell commands and each does a unique job in the Windows Service Management. It helps us perform our day to day needs like Stopping, Starting, Restarting, Listing, Searching, etc
In this article, we are going to see various Windows Powershell commands such as
- Get-Sevice
- Stop-Service
- Start-Service
- Where-Object
- Restart-Service
Not just this, There are few more and look at the index to know what this article is packaged with
I am thrilled and I hope you are too. Let’s march on.
Index
- How to List the Services Windows Command Line
- How to List only Running or Stopped Services in PowerShell
- How to List a Service or Get Service by Name in Windows
- How to Search for the Service[s] by Status, DisplayName, Search String etc.
- How to Stop the Service[s] in Windows Command Line
- How to Start the Service[s] in Windows Command Line
- How to Restart the Service[s] in Windows Command Line
How to List the Services in Windows Command Line
To List, all the Services in your Windows PC or Server, Perform the Following Steps
- Open PowerShell Terminal or PowerShell ISE as Administrator
- Type
Get-Servicein the Terminal
You would be presented with all the available Services on the Windows Machine
The result would container three columns as shown below, Status, Name, and DisplayName
You can search or List a Single or Multiple Services based on any of these columns, which we will see in upcoming sections on this article.
PS C:\Users\sarav>
Get–Service
Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Stopped AarSvc_ba23f Agent Activation Runtime_ba23f Stopped AJRouter AllJoyn Router Service Stopped ALG Application Layer Gateway Service Stopped AppIDSvc Application Identity Running Appinfo Application Information Stopped AppReadiness App Readiness Running AppXSvc AppX Deployment Service (AppXSVC) Running AudioEndpointBu... Windows Audio Endpoint Builder Running Audiosrv Windows Audio Stopped autotimesvc Cellular Time Stopped AxInstSV ActiveX Installer (AxInstSV) Stopped BcastDVRUserSer... GameDVR and Broadcast User Service_... Stopped BDESVC BitLocker Drive Encryption Service
How to List only Running or Stopped Services in PowerShell
In this section we are going to see how to list the windows services based on a Specific State they are in.
To List, Either only Running and Stopped Services, PowerShell Get-Service Command can be used along with one more Filtering command named Where-Object .
It acts like a grep of Linux and it does the job so perfect and precise
So to List Running or Stopped Services in Windows Command line you should do the following
- Open PowerShell Terminal or PowerShell ISE as Administrator
- Use one of the following command based on your requirement
To List Only The Running Services
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running" }
To List only the Stopped Services
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Stopped" }
In fact, You can Use any of the Following State Value in place of Running or Stopped to get the Services in that State.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ContinuePending | The service has been paused and is about to continue. |
| Paused | The service is paused. |
| PausePending | The service is in the process of pausing. |
| Running | The service is running. |
| StartPending | The service is in the process of starting. |
| Stopped | The service is not running. |
| StopPending | The service is in the process of stopping. |
For example, If you would like to Get a Service which is in Paused State then your command should be like this
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Paused" }
How to List a Service or Get Service by Name in Windows
To List or to Get a Service by Name you have to be aware of the Name of the Service or at least a part of the Service name as we can use * wildcard to find the rest.
To List or to Get Service by Name do the following
- Open PowerShell Terminal or PowerShell ISE as Administrator
- Use the following
Get-Servicethe command along with a-Name(or)-DisplayNameparameter
To List a Service named Jenkins I can use any of the following commands and Be informed that Service Name is Case Insensitive
Get-Service -Name jenkins (or) Get-Service -Name jenkins (or) Get-Service -DisplayName jenkins (or) Get-Service -Name JEnKins (or) Get-Service -DisplayName JEnKins (or) Get-Service -Name jen*s
How to Search for the Service[s] by More Filters
Sometimes, Our requirement would not be simpler as we think, It might get complicated when we get a requirement like
We might have to list (or) restart all the tomcat instances running on the server and exclude instance which contains a Specific String in its name
Let’s Suppose, that we have a Windows Server with N number of Tomcat Services (instances) and they are named after their Environment name they belong to like dev, uat etc. like Dev_Tomcat1, Test_Tomcat2, Uat_Tomcat4 and so on.
Now to list only the DEV and UAT instances and not SIT we would have to use some more filters other than just Name or DisplayName
Here are some examples related to this type of scenario.
# All these examples made based on the presence of # Environment Names `SIT` `UAT` `Dev` in the Service Name of # Service Display Name # The Search is By Default CASE INSENSITIVE # Find Tomcat Instances belong to Test Environment Get-Service -DisplayName "*Tomcat*" -Include "*Test*" (or) Get-Service -DisplayName "*Tomcat*" -Include "*tEst*" ---- # Find All Tomcat Instances EXCEPT the ones belong TEST Environment Get-Service -DisplayName "*Tomcat*" -Exclude "*Test*" ---- # You can also add STATUS Filter into this command Get-Service -DisplayName "*Tomcat*" -Exclude "*Test*"|Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"}
We have so far seen, how to list the services in windows machine (PC or Server) using the Powershell command line.
Now we are going to see, How to Stop the Service[s] in Windows PowerShell Command Line
Now let us Split this Part into two as follows
- How to Stop a Single Service by Name
- How to Stop One or More Services matching the Query (or) Search term
Despite you are stopping a Single Service or Multiple Services. You have to first list the Services with Get-Service with necessary Filters like -Name or Status etc.
Once the result is presented, With the help of pipe | symbol you pass all the services to an another Command called Stop-Service
Stop-Service command is responsible to stop the service (or) Services
Simply put, to Stop the Service or Services. You just need to list it first and make sure thats what you want to be stopped and then redirect it to Stop-Service with the help of pipe
Here are some of Windows Stop Service Example commands
# Simply Stop the Service named Jenkins Get-Service -Name Jenkins|Stop-Service --- # Stop all Running Services Get-Service|Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"}|Stop-Service --- # List and Stop All Running *Tomcat* Services Get-Service -DisplayName "*Tomcat*"|Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"}|Stop-Service --- # List and Stop All Running Tomcat Services, # Only Production, No DEV, UAT, SIT ( We Presume Display Name Contains the Environment Name) Get-Service -DisplayName "*Tomcat*" -Exclude "*DEV*" "*SIT*" "*UAT*"|Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"}|Stop-Service
How to Start the Service[s] in Windows Command Line
Now we are going to see, How to Start the Service[s] in Windows PowerShell Command Line
Despite you are Starting a Single Service or Multiple Services. You have to first list the Services with Get-Service with necessary Filters like -Name or Status etc.
Once the result is presented, With the help of pipe | symbol you pass all the services to another Command called Start-Service
Here are some of Windows Start Service from Command Line examples
# Simply Stop the Service named Jenkins Get-Servicec -Name Jenkins|
Start-Service
--- # Stop all Running Services Get-Service|Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"}|
Start-Service
--- # List and Stop All Running *Tomcat* Services Get-Service -DisplayName "*Tomcat*"|Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"}|
Start-Service
--- # List and Stop All Running Tomcat Services, # Only Production, No DEV, UAT, SIT ( We Presume Display Name Contains the Environment Name) Get-Service -DisplayName "*Tomcat*" -Exclude "*DEV*" "*SIT*" "*UAT*"|Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"}|
Start-Service
How to Restart the Service[s] in Windows Command Line
We have just learned how to Stop and Start the services, Now it is a time to learn How to Restart Service from Windows Command Line
To Restart windows Service Command Line do the following
- Open PowerShell Terminal or PowerShell ISE as Administrator
- Use the following
Get-Servicethe command along with a-Name(or)-DisplayNameparameter and List the Services you want to be restarted - In the same Command add a
pipe |symbol at the suffix along with a commandRestart-Service
To Restart Windows Service from Command Line, First we need to list the services that we want to be restarted using Get-Service we can customize and Search for the Services you want using Get-Service parameters like Name and DisplayName , Status etc
Once we have the list ready with Single or Multiple Services that we want to restart.
We can use another command, Given dedicatedly to restart services named Restart-Service
In most cases, we would like to have more control on the Restart process, in such cases, you can try to Stop and Start the services using Stop-Service and Start-Service commands rather directly using Restart-Service
Here are few examples of How to restart the Service in Windows Command Line
# Simply Stop the Service named Jenkins Get-Servicec -Name Jenkins|
Restart-Service
--- # Stop all Running Services Get-Service|Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"}|
Restart-Service
--- # List and Stop All Running *Tomcat* Services Get-Service -DisplayName "*Tomcat*"|Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"}|
Restart-Service
--- # List and Stop All Running Tomcat Services, # Only Production, No DEV, UAT, SIT ( We Presume Display Name Contains the Environment Name) Get-Service -DisplayName "*Tomcat*" -Exclude "*DEV*" "*SIT*" "*UAT*"|Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Running"}|
Restart-Service
So This is how Windows PowerShell commands help us to manage the Windows services from Command line, We learned how to List, stop, start and restart windows services from command line
With this command line, We can stop, start, restart Multiple services at once in bulk that’s what I like the most about it.
If you have any questions for me. Please feel free to comment
Rate this article [ratings] Share it with your friends if you find it worth
Cheers
Rumen Lishkov
Follow us onFacebook orTwitter
For more practical videos and tutorials. Subscribe to our channel
Find me on Linkedin My Profile
For any Consultation or to hire us [email protected]
If you like this article. Show your Support! Buy me a Coffee.
Signup for Exclusive «Subscriber-only» Content
If you manage Windows Services and are comfortable working from the command line, then the Windows NET.EXE command should be in your toolkit. Use it to easily start, stop, pause or restart any service from an elevated command prompt, or in a convenient script/batch file.
Using NET to stop a Windows Service
To stop a service, run:
net stop <Service-Name>
where <Service-Name> is the name of the service. Be sure to enclose it in quotes if it contains a space!
For example, to stop the Print Spooler service (named “Spooler”), run:
net stop Spooler
Here is what it looks like on our Windows Server 2016 computer:
Notice that the NET command will wait for the service to stop before continuing. The only exception is when the service is unresponsive or takes more than 30 seconds to comply.
Starting a Windows Service with NET
To start an idle Windows Service, run:
net start <Service-Name>
If all goes well, your service (and any other service it depends on to operate) will be started after a few seconds:
How to Restart a Windows Service with NET.EXE
To restart a service, say from a batch file, chain the “net stop” and “net start” commands together like this:
net stop <Service-Name>
net start <Service-Name>
NET will also Pause and Resume Windows Services
Not all services support pause and resume, but if you have one that does, NET can come in handy there as well.
To pause a service, type:
net pause <Service-Name>
To resume a paused service, run:
net continue <Service-Name>
You may also like…
on August 15, 2010
We normally use Services.msc to start or stop or disable or enable any service. We can do the same from windows command line also using net and sc utilities. Below are commands for controlling the operation of a service.
Command to stop a service:
net stop servicename
To start a service:
net start servicename
You need to have administrator privileges to run net start/stop commands. If you are just a normal user on the computer, you would get an error like below.
C:\>net start webclient System error 5 has occurred. Access is denied. C:\>
To disable a service:
sc config servicename start= disabled
To enable a service:
sc config servicename start= demand
To make a service start automatically with system boot:
sc config servicename start= auto
Note: Space is mandatory after ‘=’ in the above sc commands.
This SC command works on a Windows 7 machine and also on the down-level editions of Windows i.e Windows XP/2003 and Windows Vista. Again, if you do not have administrator previliges you would get the below error.
C:\>sc config webclient start= auto [SC] OpenService FAILED 5: Access is denied.
Note that the service name is not the display name of a service. Each service is given a unique identification name which can be used with net or sc commands. For example, Remote procedure call (RPC) is the display name of the service. But the service name we need to use in the above commands is RpcSs.
So to start Remote procedure call service the command is:
net start RpcSsTo stop Remote procedure call service
net stop RpcSs
These service names are listed below for each service. The first column shows the display name of a service and the second column shows the service name that should be used in net start or net stop or sc config commands.
| Display Name of the service | ServiceName which should be used with ‘net’ and ‘sc config’ commands. |
| Alerter | Alerter |
| Application Layer Gateway Service | ALG |
| Application Management | AppMgmt |
| ASP.NET State Service | aspnet_state |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service | BITS |
| Computer Browser | Browser |
| Bluetooth Support Service | BthServ |
| Bluetooth Service | btwdins |
| SMS Agent Host | CcmExec |
| Indexing Service | CiSvc |
| ClipBook | ClipSrv |
| .NET Runtime Optimization Service v2.0.50727_X86 | clr_optimization_v2.0.50727_32 |
| COM+ System Application | COMSysApp |
| Cryptographic Services | CryptSvc |
| Cisco Systems, Inc. VPN Service | CVPND |
| DCOM Server Process Launcher | DcomLaunch |
| DHCP Client | Dhcp |
| Logical Disk Manager Administrative Service | dmadmin |
| Logical Disk Manager | dmserver |
| DNS Client | Dnscache |
| Lenovo Doze Mode Service | DozeSvc |
| Error Reporting Service | ERSvc |
| Event Log | Eventlog |
| COM+ Event System | EventSystem |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Event Log | EvtEng |
| Fast User Switching Compatibility | FastUserSwitchingCompatibility |
| Windows Presentation Foundation Font Cache 3.0.0.0 | FontCache3.0.0.0 |
| Group Policy Monitor | GPMON_SRV |
| Help and Support | helpsvc |
| HID Input Service | HidServ |
| HTTP SSL | HTTPFilter |
| ThinkPad PM Service | IBMPMSVC |
| Windows CardSpace | idsvc |
| IMAPI CD-Burning COM Service | ImapiService |
| iPassConnectEngine | iPassConnectEngine |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateApp | iPassPeriodicUpdateApp |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateService | iPassPeriodicUpdateService |
| IviRegMgr | IviRegMgr |
| Server | lanmanserver |
| Workstation | lanmanworkstation |
| Lenovo Camera Mute | LENOVO.CAMMUTE |
| Lenovo Microphone Mute | Lenovo.micmute |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts |
| Intel(R) Management and Security Application Local Management Service | LMS |
| McAfee Framework Service | McAfeeFramework |
| McAfee McShield | McShield |
| McAfee Task Manager | McTaskManager |
| Machine Debug Manager | MDM |
| Messenger | Messenger |
| NetMeeting Remote Desktop Sharing | mnmsrvc |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator | MSDTC |
| Windows Installer | MSIServer |
| Net Driver HPZ12 | Net Driver HPZ12 |
| Network DDE | NetDDE |
| Network DDE DSDM | NetDDEdsdm |
| Net Logon | Netlogon |
| Network Connections | Netman |
| Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service | NetTcpPortSharing |
| Network Location Awareness (NLA) | Nla |
| NT LM Security Support Provider | NtLmSsp |
| Removable Storage | NtmsSvc |
| Microsoft Office Diagnostics Service | odserv |
| Office Source Engine | ose |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay |
| Pml Driver HPZ12 | Pml Driver HPZ12 |
| IPSEC Services | PolicyAgent |
| Power Manager DBC Service | Power Manager DBC Service |
| Protected Storage | ProtectedStorage |
| Remote Access Auto Connection Manager | RasAuto |
| Remote Access Connection Manager | RasMan |
| Remote Desktop Help Session Manager | RDSessMgr |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Registry Service | RegSrvc |
| Routing and Remote Access | RemoteAccess |
| Remote Registry | RemoteRegistry |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator | RpcLocator |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs |
| QoS RSVP | RSVP |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi Service | S24EventMonitor |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs |
| Smart Card | SCardSvr |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule |
| Secondary Logon | seclogon |
| System Event Notification | SENS |
| Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess |
| Shell Hardware Detection | ShellHWDetection |
| Print Spooler | Spooler |
| System Restore Service | srservice |
| SSDP Discovery Service | SSDPSRV |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | stisvc |
| System Update | SUService |
| MS Software Shadow Copy Provider | SwPrv |
| Performance Logs and Alerts | SysmonLog |
| Telephony | TapiSrv |
| Terminal Services | TermService |
| Themes | Themes |
| ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service | ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service |
| Telnet | TlntSvr |
| On Screen Display | TPHKSVC |
| Distributed Link Tracking Client | TrkWks |
| TVT Scheduler | TVT Scheduler |
| Windows User Mode Driver Framework | UMWdf |
| Intel(R) Management & Security Application User Notification Service | UNS |
| Universal Plug and Play Device Host | upnphost |
| Uninterruptible Power Supply | UPS |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS |
| Windows Time | W32Time |
| WebClient | WebClient |
| Windows Management Instrumentation | winmgmt |
| Portable Media Serial Number Service | WmdmPmSN |
| Windows Management Instrumentation Driver Extensions | Wmi |
| WMI Performance Adapter | WmiApSrv |
| Security Center | wscsvc |
| Automatic Updates | wuauserv |
| SMS Remote Control Agent | Wuser32 |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSVC |
| Network Provisioning Service | xmlprov |
Время на прочтение8 мин
Количество просмотров116K
Продолжаем знакомиться с тем, как осуществлять управление службами Windows с использованием PowerShell. В предыдущем посте мы рассмотрели, как получить статус службы на локальном и удаленном компьютере, произвести фильтрацию служб (например, найти только остановленные службы) и определить зависимые службы. В этом посте будут рассмотрены такие достаточно тривиальные вещи, как:
- Остановка службы
- Запуск службы
- Перезапуск службы
- Приостановка и возобновление работы
- Управление удаленными службами
- Настраиваем автозагрузку службы
Мы уделим большее внимание разбору команд в PowerShell для осуществления выше перечисленного на локальном компьютере. В разделе “управление службами удаленных компьютерах” мы рассмотрим, ограничения работы в PowerShell v2 и v3. Подробности под катом.
Предыдущая статья:
Управляем службами Windows с помощью PowerShell. Часть 1. Получаем статус служб
PS C:\> get-service bits
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running bits Background Intelligent Transfer Ser...
Так как команда для получения статуса службы называется Get-Service, догадаться о том, как пишутся другие команды не составит труда. На худой конец мы можем спросить у PowerShell обо всех командах, так или иначе относящихся к работе со службами. Обратите внимание, что мы использовали параметр –noun для получения всех команд, связанных со службами.
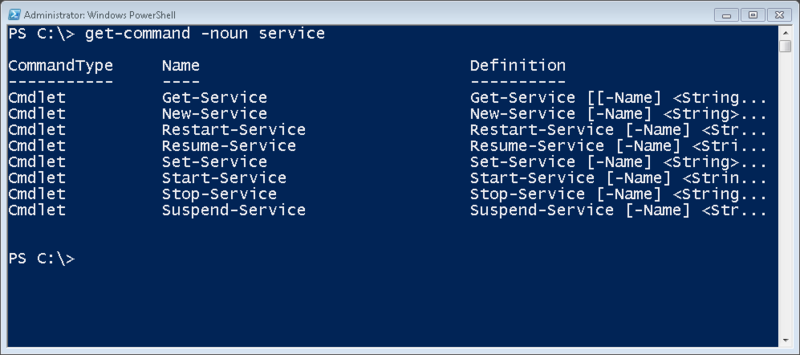
Взглянем на эти команды внимательнее.
STOP-SERVICE
Чтобы остановить службу, мы должны уточнить ее имя.
PS C:\> stop-service wuauserv
Однако в конвейер ничего не будет передано. Некоторые командлеты, такие как Stop-Service, созданы таким образом, что по умолчанию они не записывают объект в конвейер. Мы же заставим это сделать, использовав параметр –Passthru.
PS C:\> stop-service bits -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped bits Background Intelligent Transfer Ser...
Если служба не запущена, то командлет ничего не выведет, равно как и не выдаст никакой ошибки. Поэтому иногда лучше передать объект в Stop-Service (естественно использовав при этом параметр –whatif).
PS C:\> get-service browser | stop-service -WhatIf
What if: Performing operation “Stop-Service” on Target “Computer Browser (browser)”.
Параметр –WhatIf был добавлен для того, чтобы мы посмотрели, что будет, если командлет будет запущен. Когда я удостоверюсь, что это именно та служба, которая меня интересует, я просто удалю -Whatif и остановлю службу.
PS C:\> get-service browser | stop-service
Как я уже упомянул выше, если служба уже остановлена, то командлет ничего не сделает. И использование Stop-Service в этом случае никому не навредит. Однако я все же предпочитают более цивилизованный подход, а именно:
PS C:\> get-service bits | where {$_.status -eq 'running'} | stop-service -pass
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped bits Background Intelligent Transfer Ser...
Если служба запущена, то объект передается в конвейер и отправляется в Stop-Service. Ниже приведен вариант с остановкой нескольких служб.
PS C:\> get-service bits,wsearch,winrm,spooler | where {$_.status -eq 'running'} | stop-service -whatif
What if: Performing operation "Stop-Service" on Target "Print Spooler (spooler)".
What if: Performing operation "Stop-Service" on Target "Windows Remote Management (WS-Management) (winrm)".
What if: Performing operation "Stop-Service" on Target "Windows Search (wsearch)".
Некоторые службы не захотят останавливаться – в силу наличия зависимых служб – что мы и видим на скриншоте ниже.

В таком случае используем параметр –Force. В большинстве случаев это работает, но без “защиты от дурака”. Помните, что команда также остановит зависимые службы.
PS C:\> stop-service lanmanserver -force –PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped Browser Computer Browser
Stopped lanmanserver Server
START-SERVICE
Запуск службы осуществляется аналогичным образом. Он поддерживает параметр –Whatif, и вам придется использовать –Passthru, чтобы увидеть объекты.
PS C:\> start-service wuauserv -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running wuauserv Windows Update
И снова: если служба уже запущена, командлет ничего не сделает. Однако вы можете попытаться запустить службу и получите такую ошибку.
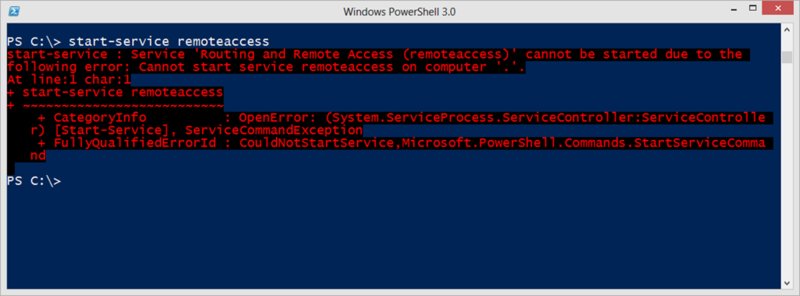
Причиной тому в большинстве случаев является выключенные службы. Как конфигурировать настройки службы, я расскажу в следующей статье.
Если вы хотите запустить службы и все службы, зависимые от нее, используйте следующее выражение:
PS C:\> get-service lanmanserver | Foreach { start-service $_.name -passthru; start-service $_.DependentServices -passthru}
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running lanmanserver Server
Running Browser Computer Browser
Мы должны явно получить зависимые службы, потому что Start-Service не запустит автоматически их.
RESTART-SERVICE
Вы удивитесь, но перезапуск службы работает также как два предыдущих примера. Используйте –Passthru, если хотите убедиться, что служба запущена.
PS C:\> restart-service spooler -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running spooler Print Spooler
Так как мы осуществляем остановку службы, нам может понадобиться параметр –Force.
ПРИОСТАНОВКА И ВОЗОБНОВЛЕНИЕ РАБОТЫ
Работа некоторых служб может быть приостановлена на некоторое время, а затем возобновлена, и мы можем это сделать через PowerShell. Однако если служба не удовлетворяет требованиям, мы получим такие ошибки. (на примере показано, что мы пытались приостановить службу bits)
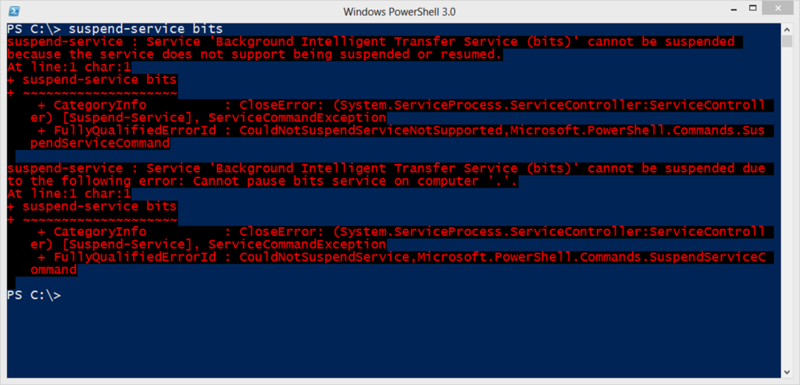
В чем же проблема? Смотрим на объект (используя Get-Service).
PS C:\> get-service bits | select *
Name : bits
RequiredServices : {RpcSs, EventSystem}
CanPauseAndContinue : False
CanShutdown : False
CanStop : True
DisplayName : Background Intelligent Transfer Service
DependentServices : {}
MachineName : .
ServiceName : bits
ServicesDependedOn : {RpcSs, EventSystem}
ServiceHandle : SafeServiceHandle
Status : Running
ServiceType : Win32ShareProcess
Site :
Container :
Если значение свойства CanPauseAndContinue равно True, значит мы можем приостанавливать и возобновлять работу службы. Найдем такие службы:
PS C:\> get-service | where {$_.CanPauseandContinue}
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running LanmanServer Server
Running LanmanWorkstation Workstation
Running MSSQLSERVER SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER)
Running O2FLASH O2FLASH
Running stisvc Windows Image Acquisition (WIA)
Running Winmgmt Windows Management Instrumentation
Как мы видим, не так много служб удовлетворяют этому требованию.
PS C:\> suspend-service o2flash -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Paused O2FLASH o2flash
Готовы возобновить работу службы? Используйте следующее выражение:
PS C:\> resume-service o2flash -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running O2FLASH o2flash
Оба командлета также поддерживают –Whatif.
УДАЛЕННЫЕ СЛУЖБЫ
Как вы могли обратить внимание, все примере выше мы демонстрировали на локальном машине. И это неслучайно. К сожалению даже в PowerShell v3, ни у одного из этих командлетов нет параметра, который позволял бы управлять службой на удаленном компьютере. Get-Service, конечно, поддерживает параметр –Computername, но не более. Службу лицезреть вы сможете, а что-либо с ней сделать не получится. Нет, можно, конечно, если удаленный компьютер работает с PS v2 и включен PowerShell Remoting. Тогда мы можете использовать все выше приведенные команды, используя Invoke-Command для удаленного компьютера или PSSession. С другой стороны, проще управлять одной службой на нескольких серверах.
PS C:\> Invoke-Command {restart-service dns –passthru} –comp chi-dc03,chi-dc02,chi-dc01
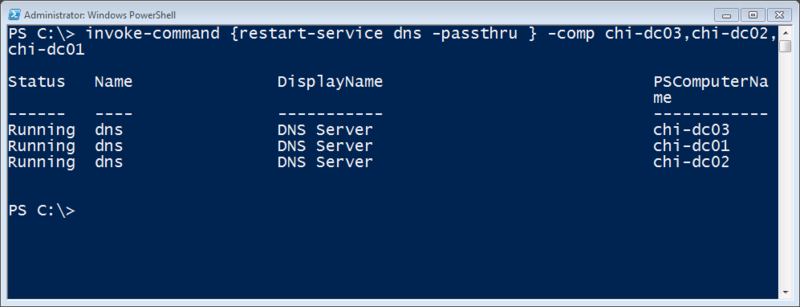
Управление службами на удаленных компьютерах не ограничивается вышеперечисленным, но это уже будет предмет рассмотрения последующих статей.
Все эти командлеты могут быть использованы в конвейерном выражении и зачастую это лучший вариант. Использование Get-Service для получения объектов и последующая передача их в подходящий командлет.
УСТАНАВЛИВАЕМ УДАЛЕННЫЙ СТАТУС
Итак, мы выяснили, что у командлета Stop-Service отсутствует такой полезный параметр как –Computername. Мы можете использовать эти команды в удаленной сессии, обратившись к командлету Invoke-Command, что уже само по себе продуктивно, если вы работаете со службой на нескольких компьютерах. Одно можно запускать, останавливать, перезапускать, ставить на паузу и запускать заново, используя Set-Service.
PS C:\> set-service wuauserv -ComputerName chi-dc03 -Status stopped -WhatIf
What if: Performing operation "Set-Service" on Target "Windows Update (wuauserv)".
Эта команда поддерживает параметр –WhatIf. Вы также должны использовать –Passthru для передачи объектов в конвейер.
PS C:\> set-service bits -ComputerName chi-dc03 -Status running -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running bits Background Intelligent Transfer Ser...
Валидными значениям для параметра –Status являются “запущена” (running), “остановлена” (stopped) и “на паузе” (paused). Помните, что у службы есть зависимые службы, мы не сможете изменять ее, что и продемонстрировано на скриншоте ниже.
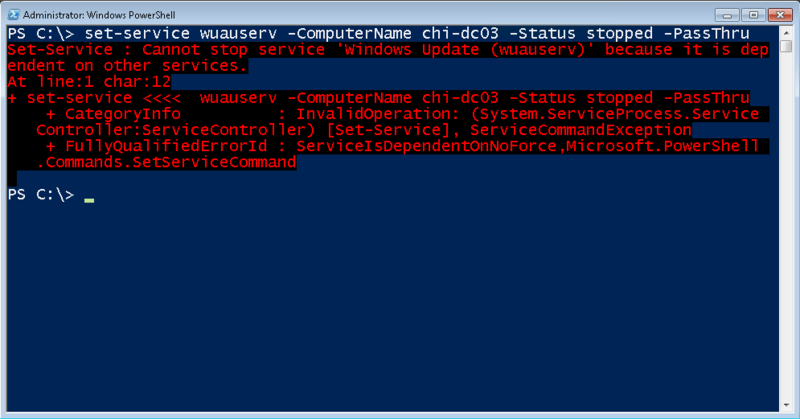
К сожалению, у Set-Service отсутствует параметр –Force, поэтому придется вернуться к использованию PowerShell remoting и Invoke-Command. Если вы хотите перезапустить удаленную службу, используйте следующую команду:
PS C:\> set-service w32time -ComputerName chi-dc03 -Status Stopped -PassThru | set-service -PassThru -Status Running
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running w32time Windows Time
Не забудьте использовать –Passthru, в противном случае вторая команда Set-Service ничего не осуществит.
Что по мне, так я предпочитаю работать сразу с несколькими службами, которые я не могу удаленно остановить, используя Set-Service, хотя их запуск проблем составляет. Я использую Invoke-Command. Но помните, что используя параметр –Computername PowerShell осуществляет подключение, используя RPC и DCOM, что может привести к проблемам с файрволом. Invoke-Command использует PowerShell remoting, который мы может быть еще не настроили или не включили.
УСТАНАВЛИВАЕМ ТИП АВТОЗАПУСКА СЛУЖБЫ
Set-Service полезнен, когда вы хотите включить или отключить службу, используя параметр –StartupType. Если Вы настроили службу, используя значения Automatic, Manual or Disabled. К сожалению, не существует варианта для Automatic (Delayed).
PS C:\> set-service remoteregistry -StartupType Manual -WhatIf
What if: Performing operation "Set-Service" on Target "Remote Registry (remoteregistry)".
PS C:\> set-service remoteregistry -StartupType Manual -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped remoteregistry Remote Registry
Однако, просто взглянув на объект, мы не сможем сказать, к какому типу автозагрузки он относится.
PS C:\> get-service remoteregistry | select *
Name : remoteregistry
RequiredServices : {RPCSS}
CanPauseAndContinue : False
CanShutdown : False
CanStop : False
DisplayName : Remote Registry
DependentServices : {}
MachineName : .
ServiceName : remoteregistry
ServicesDependedOn : {RPCSS}
ServiceHandle : SafeServiceHandle
Status : Stopped
ServiceType : Win32ShareProcess
Site :
Container :
Как это сделать – одна из тем следующей статьи.
Помните, что изменение типа автозагрузки не повлияет на текущий статус службы.
PS C:\> set-service remoteregistry -StartupType Disabled -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running remoteregistry Remote Registry
Так что если вы хотите выключить и остановить (или включить и запустить) службу, передайте объект в подходящий командлет.
PS C:\> set-service remoteregistry -StartupType Disabled -PassThru | Stop-Service -PassThru
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped remoteregistry Remote Registry
Технически, Set-Service позволяет вам изменить отображаемое имя службы и описание, но лично мне никогда не приходилось использовать в своей работе. Я использую Set-Service для включения и выключения служб. Если необходимо управлять службами удаленно, то я использую Invoke-Command.
Все, что я продемонстрировал в последних статьях, было связано с использованием специфических типов объектов службы, которые, как вы могли заметить, имеют некоторые ограничения. В следующей статье мы рассмотрим другие возможности по управлению службами, которые призваны обойти эти ограничения.
Upd:
В посте приведены переводы статей с портала 4sysops.com
Managing Services the PowerShell way – Part 3
Managing Services the PowerShell way – Part 4
