The dir command is one of the most useful commands while navigating the command line, and is present in its different forms in several operating systems. In this article, we will look at the Dir command and learn several use cases for it.
What is the dir Command
dir command in Windows OS is a built-in function that allows the user to do the following task:
- View the contents of any directory
- Check file attributes (both hidden and read-only)
- Filter search results based on date or file type.
Basic Syntax
The general syntax of the dir command is:
dir [path] [options]
- Path: specifies the location
- Options: modifies to filter the output
1. List Files & Directories
This command is used to list all files and directories in the current one:
help dir
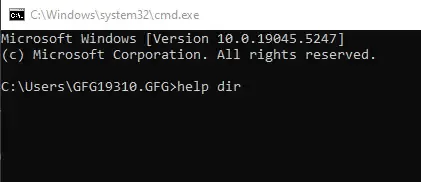
help dir command
Output :
Displays a list of files and subdirectories in a directory.
DIR [drive:][path][filename] [/A[[:]attributes]] [/B] [/C] [/D] [/L] [/N]
[/O[[:]sortorder]] [/P] [/Q] [/R] [/S] [/T[[:]timefield]] [/W] [/X] [/4]
[drive:][path][filename]
Specifies drive, directory, and/or files to list.
/A Displays files with specified attributes.
attributes D Directories R Read-only files
H Hidden files A Files ready for archiving
S System files I Not content indexed files
L Reparse Points O Offline files
- Prefix meaning not
/B Uses bare format (no heading information or summary).
/C Display the thousand separator in file sizes. This is the
.
.
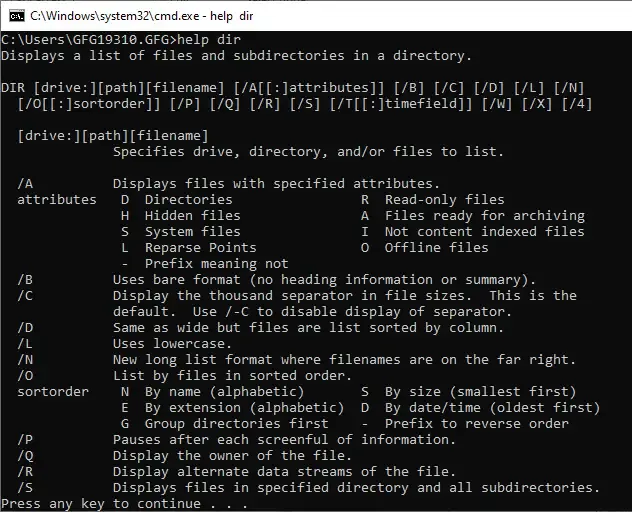
output
Usage explanation:
The command is mainly used for displaying the list of files and subdirectories in a directory. This could be done by executing the Dir command without any arguments.
Dir
dir
Which would produce an output similar to this.
Output
Directory of C:\Users
09/26/2020 11:34 AM <DIR> .
09/26/2020 11:34 AM <DIR> ..
09/02/2020 07:07 PM 1, 000 applese
09/24/2020 08:59 PM <DIR> Public
10/20/2020 06:39 PM <DIR> Soap
1 File(s) 1, 000 bytes
4 Dir(s) 13, 879, 459, 840 bytes free
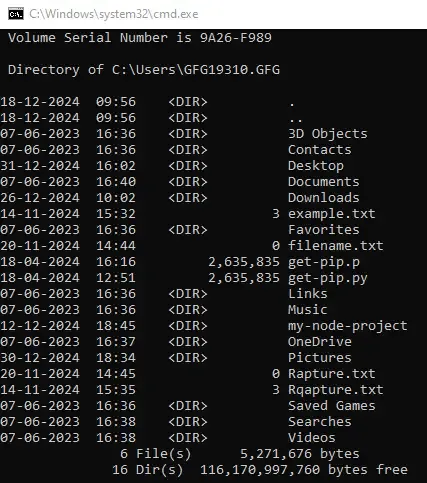
Output
2. List Content of a Specific Directory
The output of the dir command in this enable users to specify a directory to view its contents. The syntax for this command is as follows:
Input
dir C:\Users\gfg19310\Documents
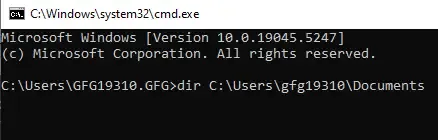
List all content – Input
Output
Directory of C:\Users\gfg19310\Documents
20-03-2023 13:02 <DIR> .
20-03-2023 13:02 <DIR> ..
20-03-2023 13:02 <DIR> Custom Office Templates
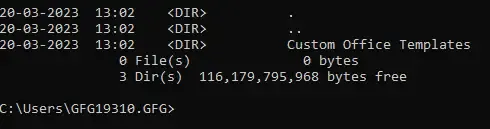
List all content – Output
3. Show Hidden Files
Here, we will use /A option with the H attribute to include hidden files along with it. Here’s the syntax:
Input
dir /A:H
show hidden file – Input
Output
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> AppData
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Application Data [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Cookies [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\INetCookies]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Local Settings [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Local]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> My Documents [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Documents]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> NetHood [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Network Shortcuts]
11-12-2024 05:46 3,670,016 NTUSER.DAT
07-06-2023 16:36 688,128 ntuser.dat.LOG1
07-06-2023 16:36 1,085,440 ntuser.dat.LOG2
02-01-2025 10:40 1,048,576 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.0.regtrans-ms
18-12-2024 09:56 1,048,576 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.1.regtrans-ms
18-12-2024 09:56 1,048,576 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.2.regtrans-ms
18-12-2024 09:56 65,536 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.blf
07-06-2023 16:36 65,536 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e88-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TM.blf
07-06-2023 16:36 524,288 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e88-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TMContainer00000000000000000001.regtrans-ms
07-06-2023 16:36 524,288 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e88-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TMContainer00000000000000000002.regtrans-ms
07-06-2023 16:36 20 ntuser.ini
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> PrintHood [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Printer Shortcuts]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Recent [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Recent]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> SendTo [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\SendTo]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Start Menu [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu]
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Templates [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Templates]
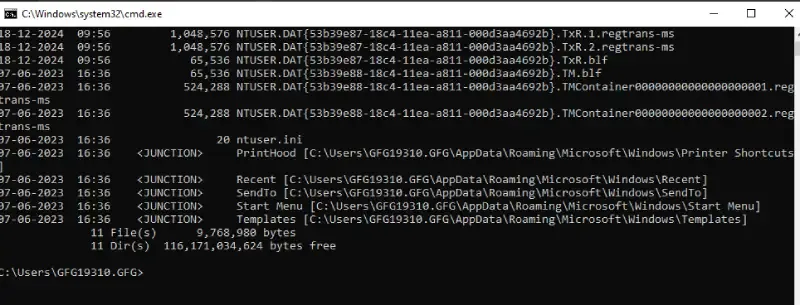
show hidden file – Output
4. List Files with Specific Extensions
To display files with a specific extension (e.g., .txt): Here’s a sample
Input
dir *.txt
Display Text -input
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
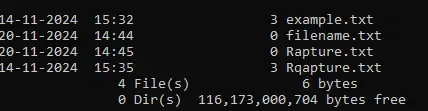
Display Text -Output
5. View Subdirectories
To include all subdirectories and their contents, use the following command:
Input
dir /S
dir /S
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> .
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> ..
0 File(s) 0 bytes
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Searches
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> .
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> ..
08-11-2022 16:52 855 winrt--{S-1-5-21-1623517014-2252875782-278851815-1404}-.searchconnector-ms
07-06-2023 16:37 859 winrt--{S-1-5-21-2245693176-3959787992-2909979321-1244}-.searchconnector-ms
2 File(s) 1,714 bytes
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Videos
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> .
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> ..
26-12-2024 13:37 <DIR> Captures
0 File(s) 0 bytes
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Videos\Captures
26-12-2024 13:37 <DIR> .
26-12-2024 13:37 <DIR> ..
26-12-2024 13:37 185,053 File Explorer 26-12-2024 13_37_47.png
11-10-2023 15:51 23,668 Network Connections .png
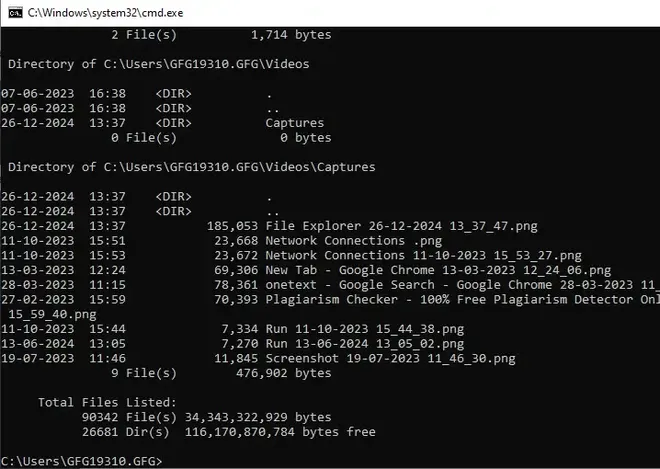
Fetching Directory
6. Sort by Date, Size, or Name
We can fetch data based on date, size or name. Let’s check them out:
By Date:
Input
dir /O:D
dir /O:D
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:37 <DIR> OneDrive
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Searches
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Videos
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
18-04-2024 12:51 2,635,835 get-pip.py
18-04-2024 16:16 2,635,835 get-pip.p
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
30-12-2024 18:34 <DIR> Pictures
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
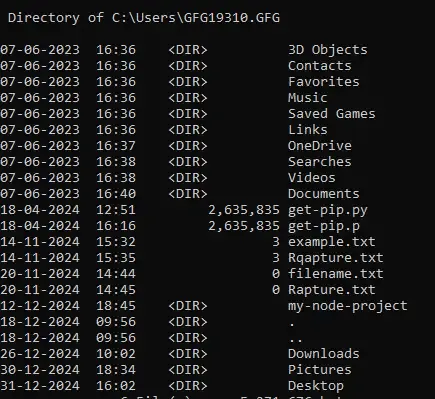
Output
By Size:
Input
dir /O:S
dir /O:S
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Searches
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Videos
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
07-06-2023 16:37 <DIR> OneDrive
30-12-2024 18:34 <DIR> Pictures
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
18-04-2024 12:51 2,635,835 get-pip.py
18-04-2024 16:16 2,635,835 get-pip.p
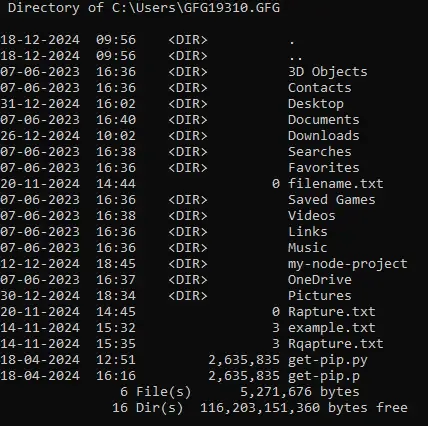
Output
By Name:
Input
dir /O:N
dir /O:N
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
18-04-2024 16:16 2,635,835 get-pip.p
18-04-2024 12:51 2,635,835 get-pip.py
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
07-06-2023 16:37 <DIR> OneDrive
30-12-2024 18:34 <DIR> Pictures
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Searches
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Videos
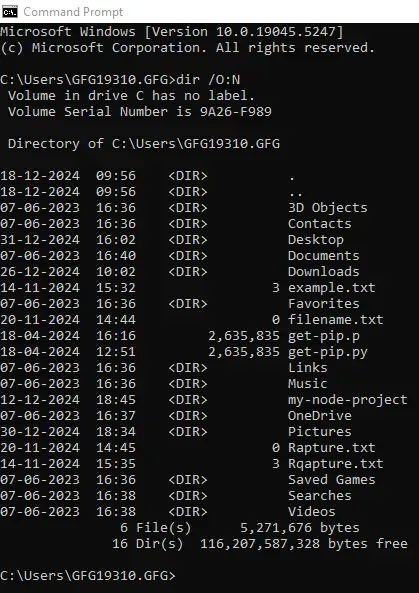
Output
7. View Results Page by Page
This command is used where too many files exists, we can use the /P option to get results one page at a time. Here’s the command:
Input
dir /P
dir /P
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
18-04-2024 16:16 2,635,835 get-pip.p
18-04-2024 12:51 2,635,835 get-pip.py
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
07-06-2023 16:37 <DIR> OneDrive
30-12-2024 18:34 <DIR> Pictures
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Searches
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Videos
Output
8. List File Attributes
We can also include attributes such as read-only files and archives using the following command:
Input
dir /A
dir /A
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> AppData
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Application Data [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming]
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Cookies [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\INetCookies]
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
18-04-2024 16:16 2,635,835 get-pip.p
18-04-2024 12:51 2,635,835 get-pip.py
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> Local Settings [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Local]
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> My Documents [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\Documents]
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
07-06-2023 16:36 <JUNCTION> NetHood [C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Network Shortcuts]
11-12-2024 05:46 3,670,016 NTUSER.DAT
07-06-2023 16:36 696,320 ntuser.dat.LOG1
07-06-2023 16:36 1,003,520 ntuser.dat.LOG2
02-01-2025 10:40 1,048,576 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.0.regtrans-ms
18-12-2024 09:56 1,048,576 NTUSER.DAT{53b39e87-18c4-11ea-a811-000d3aa4692b}.TxR.1.regtrans-ms
18-12-2024 09:56 1,048,57 ..
Output
9. Display File Size
You can also check the file size (in bytes) using the following command:
Input
dir /-C
dir /-C
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> .
18-12-2024 09:56 <DIR> ..
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> 3D Objects
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Contacts
31-12-2024 16:02 <DIR> Desktop
07-06-2023 16:40 <DIR> Documents
26-12-2024 10:02 <DIR> Downloads
14-11-2024 15:32 3 example.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Favorites
20-11-2024 14:44 0 filename.txt
18-04-2024 16:16 2635835 get-pip.p
18-04-2024 12:51 2635835 get-pip.py
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Links
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Music
12-12-2024 18:45 <DIR> my-node-project
07-06-2023 16:37 <DIR> OneDrive
30-12-2024 18:34 <DIR> Pictures
20-11-2024 14:45 0 Rapture.txt
14-11-2024 15:35 3 Rqapture.txt
07-06-2023 16:36 <DIR> Saved Games
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Searches
07-06-2023 16:38 <DIR> Videos
Output
Advanced Syntax
The above-mentioned syntaxes is for general usage. Now, let’s see some of the advanced usage syntax along with their examples.
10. Save Output to a File
We can redirect the output to a text file (dir command) using the syntax below:
Input (file name: rapture.txt)
dir /S > rapture.txt
dir /S > filename
Output
A file name with the provided name will be created containing the directory list.
Output
11. Search for any Specific File
You can search for any file by its name (or even partial name), following this syntax:
Input (file name: rapture – taken as a partial name “rapt”)
dir *rapt*
*filename*
Output
Directory of C:\Users\GFG19310.GFG
03-01-2025 11:03 7,854,908 Rapture.txt
1 File(s) 7,854,908 bytes
0 Dir(s) 116,168,089,600 bytes free
Output
12. Check the Total Number of Files
This syntax will summarise the total count of a file including directory:
Input
dir /W
dir /W
Output
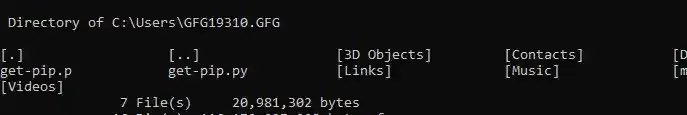
Output
Bonus: Useful cmd Options (Summarization)
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
/P |
Fetch results one page at a time |
/S |
Includes all files in subdirectories. |
/A |
Displays files with specified attributes (e.g., /A:H for hidden files). |
/O |
Sorts output (e.g., /O:D for date, /O:N for name). |
/B |
Displays output in bare format (file names only, without additional details). |
/L |
Displays names in lowercase. |
/T |
Displays time attributes (e.g., /T:C for creation time). |
/Q |
Displays file ownership information. |
The dir command is vastly used among users for managing and exploring directories through different ways and patterns in Windows OS. You can give it all a try and organize your work smoothly.
The dir command is a Command Prompt command used to display a list of the files and subfolders contained in a folder.
For each file or folder listed, the command will, by default, show the date and time the item was last changed, if the item is a folder (labeled with DIR) or file, the size of the file if applicable, and finally the name of the file or folder including the file extension.
Outside of the file and folder list, the dir command also displays the current drive letter of the partition, the volume label, volume serial number, total number of files listed, total size of those files in bytes, the number of subfolders listed, and the total bytes remaining free on the drive.
Dir Command Availability
The dir command is available from within the Command Prompt in all Windows operating systems including Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
Older versions of Windows include the dir command as well but with a few fewer options than we have listed below. The dir command is also a DOS command, available in all versions of MS-DOS.
The dir command can be found in offline Command Prompt versions, like the ones available from Advanced Startup Options and System Recovery Options. The dir command is also included in the Recovery Console in Windows XP.
The availability of certain dir command switches and other dir command syntax may differ from operating system to operating system.
Dir Command Syntax
dir [drive:][path][filename] [/a[[:]attributes]] [/b] [/c] [/d] [/l] [/n] [/o[[:]sortorder]] [/p] [/q] [/r] [/s] [/t[[:]timefield]] [/w] [/x] [/4]
See How to Read Command Syntax if you’re not sure how to interpret the syntax of the dir command as it’s written above or shown in the table below.
| Dir Command Options | |
|---|---|
| Item | Explanation |
| drive:, path, filename | This is the drive, path, and/or filename that you want to see results for. All three are optional since the command can be executed alone. Wildcards are allowed. See the Dir Command Examples section below if this isn’t clear. |
| /a |
When executed alone, this switch shows all types of files and folders, including those with file attributes that typically prevent them from showing up in Command Prompt or in Windows. Use /a with one or more of the following attributes (colon is optional, no spaces needed) to show only those types of files in the command result: a = archive files d = directories h = hidden files i = not content indexed files l = reparse points r = read-only files s = system files v = integrity files x = no scrub files — = Use this as a prefix to any of the above attributes to exclude items with those file attributes from the results. |
| /b | Use this option to show the dir results using «bare» format, which removes the typical header and footer information, as well as all the details on each item, leaving only the directory name or file name and extension. |
| /c | This switch forces the use of the thousands separator when the command is used in a way that shows file sizes. This is the default behavior on most computers, so the practical use is /-c to disable the thousands separator in results. |
| /d | Use /d to limit the items displayed to just folders (contained within brackets) and file names with their extensions. Items are listed top-to-bottom and then across columns. Standard dir command header and footer data remain the same. |
| /l | Use this option to show all folder and file names in lowercase. |
| /n | This switch produces a result with columns in the date > time > directory > file size > file or folder name column structure. Since this is the default behavior, the practical use is /-n which produces columns in the file or folder name > directory > file size > date > time order. |
| /o |
Use this option to specify a sort order for the results. When executed alone, /o lists directories first, followed by files, both in alphabetical order. Use this option with one or more of the following values (colon is optional, no spaces needed) to sort the dir command result in the specified manner: d = sort by date/time (oldest first) e = sort by extension (alphabetical) g = group directory first, followed by files n = sort by name (alphabetical) s = sort by size (smallest first) — = Use this as a prefix with any of the above values to reverse the order (-d to sort by newest first, -s for largest first, etc.). |
| /p | This option displays the results one page at a time, interrupted with a Press any key to continue… prompt. Using /p is very similar to using the dir command with the more command. |
| /q | Use this switch to display the owner of the file or folder in the results. The easiest way to view or change a file’s ownership from within Windows is via the Advanced button in the Security tab when looking at the file’s Properties. |
| /r | The /r option shows any alternate data streams (ADS) that are part of a file. The data stream itself is listed in a new row, under the file, and is always suffixed with $DATA, making them easy to spot. |
| /s | This option shows all the files and folders in the specified directory plus all of the files and folders contained within any subdirectories of that specified directory. |
| /t |
Use this option with one of the values below (colon is optional, no spaces needed) to specify a time field to be used when sorting and/or displaying results: a = last access c = created w = last written |
| /w | Use /w to show results in «wide format» which limits the items displayed to just folders (contained within brackets) and file names with their extensions. Items are listed left-to-right and then down rows. Standard dir command header and footer data remain the same. |
| /x | This switch shows the «short name» equivalent for files whose long names don’t comply with non-8dot3 rules. |
| /4 | The /4 switch forces the use of 4-digit years. At least in newer versions of Windows, the 4-digit year display is the default behavior and /-4 doesn’t result in a 2-digit year display. |
| /? | Use the help switch with the dir command to show details about the above options directly in the Command Prompt window. Executing dir /? is the same as using the help command to execute help dir. |
Dir Command Examples
Below are some of the different ways you can use the dir command:
Run Without Switches
dir
In this example, the dir command is used alone, without any drive:, path, filename specifications, nor any switches, producing a result like this:
C:\>dirVolume in drive C has no label.Volume Serial Number is F4AC-9851Directory of C:\09/02/2015 12:41 PM$SysReset05/30/2016 06:22 PM 93 HaxLogs.txt05/07/2016 02:58 AM PerfLogs05/22/2016 07:55 PM Program Files05/31/2016 11:30 AM Program Files (x86)07/30/2015 04:32 PM Temp05/22/2016 07:55 PM Users05/22/2016 08:00 PM Windows05/22/2016 09:50 PM Windows.old1 File(s) 93 bytes
As you can see, the dir command was executed from the root directory of C (i.e., C:\>). Without specifying where exactly to list the folder and file contents from, the command defaults to displaying this information from where the command was executed.
List Hidden Items
dir c:\users /ah
In the above example, we’re requesting that the dir command show results from the drive: and path of c:\users, not from the location we’re running the command from. We’re also specifying, via the /a switch with the h attribute, that we’d like to only see hidden items, resulting in something like this:
C:\>dir c:\users /ahVolume in drive C has no label.Volume Serial Number is F4AC-9851Directory of c:\users05/07/2016 04:04 AM All Users [C:\ProgramData]05/22/2016 08:01 PMDefault05/07/2016 04:04 AM Default User [C:\Users\Default]05/07/2016 02:50 AM 174 desktop.ini1 File(s) 174 bytes
The small list of directories and the single file you see in the result above doesn’t make up the entirety of the c:\users folder—just the hidden files and folders. To see all files and folders, you would execute dir c:\users /a (removing the h) instead.
Search for File In Any Folder
dir c:\*.csv /s /b > c:\users\tim\desktop\csvfiles.txt
In this slightly more complex, but much more practical, example for the dir command, we’re requesting that our entire hard drive be searched for CSV files and then the bare minimum results are outputted to a text document. Let’s look at this piece by piece:
- c:\*.csv tells the dir command to look at all files (*) that end in the CSV (.csv) extension in the root of the c: drive.
- /s instructs it to go deeper than the root of c: and instead, search for files like this in every folder, as deep as the folders go.
- /b removes anything but the path and file name, essentially creating a readable «list» of these files.
- > is a redirection operator, meaning «send to» somewhere.
- c:\users\tim\desktop\csvfiles.txt is the destination for the > redirector, meaning that results will be written to the csvfiles.txt file instead of in Command Prompt, which will be created at the c:\users\tim\desktop location (i.e., the Desktop you see when you’re logged in).
When you redirect command output to a file, as we did here in this dir command example, Command Prompt doesn’t display anything. However, the exact output you would have seen is instead located inside that text file. Here’s what our csvfiles.txt looked like after the dir command had completed:
c:\ProgramData\Intuit\Quicken\Inet\merchant_alias.csvc:\ProgramData\Intuit\Quicken\Inet\merchant_common.csvc:\Users\All Users\Intuit\Quicken\Inet\merchant_alias.csvc:\Users\All Users\Intuit\Quicken\Inet\merchant_common.csvc:\Users\Tim\AppData\Roaming\condition.2.csvc:\Users\Tim\AppData\Roaming\line.csvc:\Users\Tim\AppData\Roaming\media.csv
While you certainly could have skipped the file redirection, and even the «bare format» switch, the results would have been very difficult to work within the Command Prompt window, making it hard to get to what you were after.
Related Commands
The dir command is often used with the del command. After using dir to find the name and location of the file(s) in any particular folder(s), del can be used to delete files directly from the Command Prompt.
Similar is the rmdir /s command, and older deltree command, used to delete folders and files. The rmdir command (without the /s option) is useful for deleting empty folders that you find with the dir command.
As mentioned above, the dir command is also often used with a redirection operator.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
Программистам часто приходится работать в консоли — например, чтобы запустить тестирование проекта, закоммитить новый код на Github или отредактировать документ в vim. Всё это происходит так часто, что все основные действия с файлами становится быстрее и привычнее выполнять в консоли. Рассказываем и показываем основные команды, которые помогут ускорить работу в терминале под OS Windows.
Для начала нужно установить терминал или запустить командную строку, встроенную в Windows — для этого нажмите Win+R и введите cmd. Терминал часто встречается и прямо в редакторах кода, например, в Visual Studio Code.
Чтобы ввести команду в консоль, нужно напечатать её и нажать клавишу Enter.
Содержимое текущей папки — dir
Выводит список файлов и папок в текущей папке.
C:\content-server>dir
Том в устройстве C имеет метку SYSTEM
Серийный номер тома: 2C89-ED9D
Содержимое папки C:\content-server
06.10.2020 00:41 <DIR> .
06.10.2020 00:37 <DIR> .circleci
16.07.2020 16:04 268 .editorconfig
16.07.2020 16:04 10 .eslintignore
16.07.2020 16:04 482 .eslintrc
06.10.2020 00:37 <DIR> .github
16.07.2020 16:04 77 .gitignore
06.10.2020 00:41 <DIR> assets
06.10.2020 00:41 <DIR> gulp
16.07.2020 16:10 379 gulpfile.js
16.07.2020 16:10 296 320 package-lock.json
16.07.2020 16:10 751 package.json
16.07.2020 16:04 509 README.md
Открыть файл
Чтобы открыть файл в текущей папке, введите его полное имя с расширением. Например, blog.txt или setup.exe.
Перейти в другую папку — cd
Команда cd без аргументов выводит название текущей папки.
Перейти в папку внутри текущего каталога:
C:\content-server>cd assets
C:\content-server\assets>
Перейти на одну папку вверх:
C:\content-server\assets>cd ..
C:\content-server>
Перейти в папку на другом диске:
c:\content-server>cd /d d:/
d:\>
Чтобы просто изменить диск, введите c: или d:.
Создать папку — mkdir или md
Создаём пустую папку code внутри папки html:
d:\html>mkdir coded:\html>dir
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:25 <DIR> code
0 файлов 0 байт
3 папок 253 389 438 976 байт свободно
Создаём несколько пустых вложенных папок — для этого записываем их через косую черту:
d:\html>mkdir css\js
d:\html>dir
Том в устройстве D имеет метку DATA
Серийный номер тома: 0000-0000
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:25 <DIR> code
03.11.2020 19:29 <DIR> css
Создаётся папка css, внутри которой находится папка js. Чтобы проверить это, используем команду tree. Она показывает дерево папок.
Удалить папку — rmdir или rd
Чтобы удалить конкретную папку в текущей, введите команду rmdir:
d:\html\css>rmdir js
При этом удалить можно только пустую папку. Если попытаться удалить папку, в которой что-то есть, увидим ошибку:
d:\html\css>d:\html>rmdir css
Папка не пуста.
Чтобы удалить дерево папок, используйте ключ /s. Тогда командная строка запросит подтверждение перед тем, как удалить всё.
d:\html>rmdir css /s
css, вы уверены [Y(да)/N(нет)]? y
Показать дерево папок — tree
В любом момент мы можем увидеть структуру папок. Для этого используется команда tree.
d:\html>tree
Структура папок тома DATA
Серийный номер тома: 0000-0000
D:.
├───code
└───css
└───js
Если вы хотите посмотреть содержимое всего диска, введите tree в корне нужного диска. Получится красивая анимация, а если файлов много, то ещё и немного медитативная.
Удаление файла — del или erase
Команда для удаления одного или нескольких файлов.
d:\html>del blog.txt
Переименование файла — ren или rename
Последовательно вводим ren, старое и новое имя файла.
d:\html>dir
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:59 0 blag.txt
d:\html>ren blag.txt blog.txt
d:\html>dir
Содержимое папки d:\html
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> .
03.11.2020 19:23 <DIR> ..
03.11.2020 19:59 0 blog.txt
Команды одной строкой
Очистить консоль — cls.
Информация о системе — systeminfo.
d:\html>systeminfo
Имя узла: DESKTOP-6MHURG5
Название ОС: Майкрософт Windows 10 Pro
Версия ОС: 10.0.20246 Н/Д построение 20246
Изготовитель ОС: Microsoft Corporation
Параметры ОС: Изолированная рабочая станция
Сборка ОС: Multiprocessor Free
Информация о сетевых настройках — ipconfig.
d:\html>ipconfig
Настройка протокола IP для Windows
Адаптер Ethernet Ethernet 2:
Состояние среды. . . . . . . . : Среда передачи недоступна.
DNS-суффикс подключения . . . . . :
Список запущенных процессов — tasklist.
c:\>tasklist
Имя образа PID Имя сессии № сеанса Память
========================= ======== ================ =========== ============
System Idle Process 0 Services 0 8 КБ
System 4 Services 0 2 688 КБ
Secure System 72 Services 0 23 332 КБ
…
Справка по командам — help
Команда help без аргументов выводит список всех возможных команд. help вместе с именем команды выведет справку по этой команде.
d:\html>help tree
Графическое представление структуры папок или пути.
TREE [диск:][путь] [/F] [/A]
/F Вывод имён файлов в каждой папке.
/A Использовать символы ASCII вместо символов национальных алфавитов.
В этой статье приведены не все команды и не все их возможности, но вы всегда можете воспользоваться командой help и узнать о том, что ещё может командная строка.
👉🏻 Больше статей о фронтенде и работе в айти в телеграм-канале.
Подписаться
Материалы по теме
- 10 горячих клавиш VS Code, которые ускорят вашу работу
- Полезные команды для работы с Git
- Полезные команды для работы с Node. js
«Доктайп» — журнал о фронтенде. Читайте, слушайте и учитесь с нами.
ТелеграмПодкастБесплатные учебники
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
dir
|
The SpartaDOS X |
|
| Developer(s) | DEC, DR, Intel, Cromemco, MetaComCo, Microsoft, IBM, Datalight, ICD, Inc. |
|---|---|
| Operating system | CP/M, MP/M, ISIS-II, iRMX 86, CDOS, TRIPOS, DOS, MSX-DOS, SISNE plus, 4690 OS, PC-MOS, OS/2, Windows, Singularity, ReactOS, AROS, VMS, RT-11, RSX-11, OS/8, AmigaDOS |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | Command |
| License | CP/M, MP/M: BSD-like MS-DOS: MIT PC-MOS: GPL-3.0-only ReactOS: GPL |
dir, short for directory, is a shell command for listing file system contents; files and directories.[1] Arguably, the command provides the same essential functionality as the ls command, but typically the two commands are described as notably separate concepts, possibly since ls is implemented from a codebase that shares more history than many dir implementations.
The command is often implemented as internal in the operating system shell instead of as a separate application as many other commands are.
Although syntax, semantics and implementations vary, a dir command is available in the command-line interface (CLI) of the operating systems Digital Research CP/M,[2] MP/M,[3] Intel ISIS-II,[4] iRMX 86,[5] Cromemco CDOS,[6] MetaComCo TRIPOS,[7] DOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS,[8] IBM OS/2,[9] Microsoft Windows,[10] Singularity, Datalight ROM-DOS,[11] ReactOS,[12] GNU,[13] AROS[14] and in the DCL command-line interface used on DEC VMS, RT-11 and RSX-11. It is also supplied with OS/8 as a CUSP (Commonly-Used System Program).
The dir command is supported by Tim Paterson’s SCP 86-DOS.[15] On MS-DOS, the command is available in versions 1 and later.[16] It is also available in the open source MS-DOS emulator DOSBox. MS-DOS prompts «Abort, Retry, Fail?» after being commanded to list a directory with no diskette in the drive.
The numerical computing environments MATLAB and GNU Octave include a dir
function with similar functionality.[17][18]
DOS, Windows, ReactOS
[edit]
List all files and directories in the current working directory.
List any text files and batch files (filename extension «.txt» or «.bat»).
Recursively list all files and directories in the specified directory and any subdirectories, in wide format, pausing after each screen of output. The directory name is enclosed in double-quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted is as two separate command-line options because it contains a whitespace character.
C:\Users>dir /s /w /p "C:\Users\johndoe\My Documents"
List any NTFS junction points:
C:\Users>dir /ashVolume in drive C is OS.Volume Serial Number is xxxx-xxxxDirectory of C:\Users12/07/2019 02:30 AM <SYMLINKD> All Users [C:\ProgramData]12/07/2019 02:30 AM <JUNCTION> Default User [C:\Users\Default]12/07/2019 02:12 AM 174 desktop.ini1 File(s) 174 bytes2 Dir(s) 332,659,789,824 bytes free
Traditionally, Unix and Unix-like systems use the ls command for the needs that dir satisfies. But, the GNU operating system, has a dir command that «is equivalent to ls -C -b; that is, by default files are listed in columns, sorted vertically, and special characters are represented by backslash escape sequences».[19] Actually, for compatibility reasons, ls produces device-dependent output. The dir command, on the other hand, produces device-independent output.
- Directory (OpenVMS command)
- List of DOS commands
- tree
- ^ Rügheimer, Hannes; Spanik, Christian (October 22, 1988). AmigaDOS quick reference. Grand Rapids, Mi : Abacus. ISBN 9781557550491 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ «Operating manual» (PDF). cpm.z80.de. Retrieved 2019-10-22.
- ^ Digital Research (1981-09-25). MP/M-86 Operating System — User’s Guide (PDF) (1 ed.). Pacific Grove, CA, USA: Digital Research. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-01-04. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ^ ISIS II Users Guide
- ^ iRMX 86 INTRODUCTION AND OPERATOR’S REFERENCE MANUAL For Release 6
- ^ CDOS USER’S MANUAL
- ^ «Introduction to Tripos» (PDF). Retrieved 2019-10-22.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ «JaTomes Help — OS/2 Commands». www.jatomes.com. Archived from the original on 2019-04-14. Retrieved 2019-07-20.
- ^ «MS-DOS and Windows command line dir command». www.computerhope.com.
- ^ «Datalight ROM-DOS User’s Guide» (PDF). www.datalight.com.
- ^ «GitHub — reactos/reactos: A free Windows-compatible Operating System». October 22, 2019 – via GitHub.
- ^ «GNU Coreutils Manual». Free Software Foundation.
- ^ «AROS Research Operating System». aros.sourceforge.net.
- ^ 86-DOS — Disk Operating System for the 8086 — User’s Manual (PDF). Version 0.3 (Preliminary ed.). Seattle, Washington, USA: Seattle Computer Products, Inc. 1980. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-07-14. Retrieved 2019-07-14. (59 pages)
- ^ Wolverton, Van (2003). Running MS-DOS Version 6.22 (20th Anniversary Edition), 6th Revised edition. Microsoft Press. ISBN 0-7356-1812-7.
- ^ «List folder contents — MATLAB dir». www.mathworks.com.
- ^ «Function Reference: dir». octave.sourceforge.io.
- ^ dir invocation (GNU coreutils) at www.gnu.org
- Wolverton, Van (1990). MS-DOS Commands: Microsoft Quick Reference, 4th Revised edition. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-1556152894.
- Kathy Ivens; Brian Proffit (1993). OS/2 Inside & Out. Osborne McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0078818714.
- Frisch, Æleen (2001). Windows 2000 Commands Pocket Reference. O’Reilly. ISBN 978-0-596-00148-3.
- dir | Microsoft Docs
- Open source DIR implementation that comes with MS-DOS v2.0
- Dir command syntax and examples
The dir command is used to list files and folders in the Windows command prompt (CMD).
dirThe dir command without a path will display a list of files and folders in the current working directory.

You can provide a path to see the listing for a different directory:
dir C:\WindowsBy default, the dir command does not show hidden files and folders. To include hidden files, run the dir command as follows:
dir /aYou can use the /B switch to show the file names only without heading information or summary.
dir /b C:\WindowsThe /s option lists all files in a specified directory and all subdirectories.
dir /sList Files Using Patterns
The dir command supports wildcard character (*) that you can use to describe a pattern to match.
For example, the following command lists all files that begin with the letter A:
dir a*Here is another example that lists all files that have a .doc extension:
dir /b *.docDisplays files with specified attributes
The /A switch is used to list files and folders with specified attributes. For example, the letter H represents the hidden attribute.
dir /a:hThe following table describes each of the values that you can use for Attributes.
| D | Folders. |
| H | Hidden files and Folders. |
| S | System files. |
| L | Reparse Points. |
| R | Read-only files. |
| A | Files ready for archiving. |
| I | Not content indexed files. |
| O | Offline files. |
| — | Prefix meaning not (See examples). |
Examples
List Files and folders in C:\Windows\System32 directory:
dir C:\Windows\System32Obtain a listing of all files in C:\Windows\System32 that ends with the .txt extension:
dir C:\Windows\System32\*.txtSearch for files with .dll extension in C:\Windows\System32 and all subdirectories:
dir /s C:\Windows\System32\*.dllReturns the listing for the parent directory of the current working directory:
dir ..List all files and folders, including hidden files:
dir /aShow hidden files only:
dir /a:hList only folders:
dir /a:dDon’t list folders:
dir /a:-dShow only hidden folders:
dir /a:dhList read only files:
dir /a:rSort the result by name:
dir /o:nThis will sort the result set by size:
dir /o:sSort the result set by size (largest first):
dir /o:-sSort the result by date:
dir /o:dIncludes the name of the owner for each file:
dir /qShow creation time:
dir /t:cShow last access time:
dir /t:aShow the last written time:
dir /t:wRun the dir /? command to see a list of all the available command-line options.
