From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft Corporation which provides a user with a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a network connection.[1] The user employs RDP client software for this purpose, while the other computer must run RDP server software.
Several clients exist for most versions of Microsoft Windows (including Windows Mobile but the support has ended), Linux (for example Remmina), Unix, macOS, iOS, Android, and other operating systems. RDP servers are built into the server and professional editions of Windows operating systems but not home editions; an RDP server for Unix and OS X also exists (for example xrdp). By default, the server listens on TCP port 3389[2] and UDP port 3389.[3]
Microsoft currently refers to their official RDP client software as Remote Desktop Connection, formerly «Terminal Services Client».
The protocol is an extension of the ITU-T T.128 application sharing protocol. Microsoft makes some specifications public on their website.[4]
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/remote/remote-desktop-services/remotepc/change-listening-port?tabs=regedit
Every server and professional version of Microsoft Windows from Windows XP onward[5] includes an installed Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) («Terminal Services») client (mstsc.exe) whose version is determined by that of the operating system or by the last applied Windows Service Pack. The Terminal Services server is supported as an official feature on Windows NT 4.0 Terminal Server Edition, released in 1998, Windows 2000 Server, all editions of Windows XP except Windows XP Home Edition, Windows Server 2003, Windows Home Server, on Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs, in Windows Vista Ultimate, Enterprise and Business editions, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 and on Windows 7 Professional and above. The home versions of Windows do not support RDP.
Microsoft provides the client required for connecting to newer RDP versions for downlevel operating systems. Since the server improvements are not available downlevel, the features introduced with each newer RDP version only work on downlevel operating systems when connecting to a higher version RDP server from these older operating systems, and not when using the RDP server in the older operating system.[clarification needed]
Based on the ITU-T T.128 application sharing protocol (during draft also known as «T.share») from the T.120 recommendation series, the first version of RDP (named version 4.0) was introduced by Microsoft with «Terminal Services», as a part of their product Windows NT 4.0 Server, Terminal Server Edition.[1] The Terminal Services Edition of NT 4.0 relied on Citrix’s MultiWin technology, previously provided as a part of Citrix WinFrame atop Windows NT 3.51, in order to support multiple users and login sessions simultaneously. Microsoft required Citrix to license their MultiWin technology to Microsoft in order to be allowed to continue offering their own terminal-services product, then named Citrix MetaFrame, atop Windows NT 4.0. The Citrix-provided DLLs included in Windows NT 4.0 Terminal Services Edition still carry a Citrix copyright rather than a Microsoft copyright. Later versions of Windows integrated the necessary support directly. The T.128 application sharing technology was acquired by Microsoft from UK software developer Data Connection Limited.[6]
This version was introduced with Windows 2000 Server, added support for a number of features, including printing to local printers, and aimed to improve network bandwidth usage. The RDP clients available through the Windows 2000 Terminal Server Disk Creation Tool is tested and working on even 16 bit Windows 3.1 using 3rd party TCP/IP libraries such as Trumpet WinSock.
This version was introduced with Windows XP Professional and included support for 24-bit color and sound. It is supported on Windows 2000, Windows 9x, and Windows NT 4.0.[7] With this version, the name of the client was changed from Terminal Services Client to Remote Desktop Connection; the heritage remains to this day, however, as the underlying executable is still named mstsc.exe.
This version was introduced with Windows Server 2003, included support for console mode connections, a session directory, and local resource mapping. It also introduces Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.0 for server authentication, and to encrypt terminal server communications.[8] This version is built into Windows XP Professional x64 Edition and Windows Server 2003 x64 & x86 Editions, and also available for Windows XP as a download.
This version was introduced with Windows Vista and incorporated support for Windows Presentation Foundation applications, Network Level Authentication, multi-monitor spanning and large desktop support, and TLS 1.0 connections.[9] The RDP 6.0 client is available on Windows XP SP2, Windows Server 2003 SP1/SP2 (x86 and x64 editions) and Windows XP Professional x64 Edition through KB925876. Microsoft Remote Desktop Connection Client for Macintosh OS X is also available with support for Intel and PowerPC Mac OS versions 10.4.9 and greater.
This version was released in February 2008 and is first included with Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 and later backported to Windows XP with Service Pack 3. The RDP 6.1 client is available on Windows XP SP2, Windows Server 2003 SP1/SP2 (x86 and x64 editions) and Windows XP Professional x64 Edition through KB952155.[10] In addition to changes related to how a remote administrator connects to the «console»,[11] this version has new functionality introduced in Windows Server 2008, such as connecting remotely to individual programs and a new client-side printer redirection system that makes the client’s print capabilities available to applications running on the server, without having to install print drivers on the server[12][13] also on the other hand, remote administrator can freely install, add/remove any software or setting at the client’s end. However, to start a remote administration session, one must be a member of the Administrators group on the server to which one is trying to get connected.[14]
This version was released to manufacturing in July 2009 and is included with Windows Server 2008 R2, as well as with Windows 7.[15] With this release, also changed from Terminal Services to Remote Desktop Services. This version has new functions such as Windows Media Player redirection, bidirectional audio, multi-monitor support, Aero glass support, enhanced bitmap acceleration, Easy Print redirection,[16] Language Bar docking. The RDP 7.0 client is available on Windows XP SP3 and Windows Vista SP1/SP2 through KB969084,[17] and is not officially supported on Windows Server 2003 x86 and Windows Server 2003 / Windows XP Professional x64 editions. It is also not officially supported on Windows Server 2008.
Most RDP 7.0 features like Aero glass remote use, bidirectional audio, Windows Media Player redirection, multiple monitor support and Remote Desktop Easy Print are only available in Windows 7 Enterprise or Ultimate editions.[18][19]
Release 7.1 of RDP was included with Windows 7 Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 in 2010. It introduced RemoteFX, which provides virtualized GPU support and host-side encoding.
This version was released in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. This version has new functions such as Adaptive Graphics (progressive rendering and related techniques), automatic selection of TCP or UDP as transport protocol, multi touch support, DirectX 11 support for vGPU, USB redirection supported independently of vGPU support, etc.[20][21] A «connection quality» button is displayed in the RDP client connection bar for RDP 8.0 connections; clicking on it provides further information about connection, including whether UDP is in use or not.[22]
The RDP 8.0 client and server components are available on Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 through KB2592687. The RDP 8.0 client is also available for Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1, but the server components are not. The RDC 8.0 client includes support for session encryption using the TLS 1.2 standard.[23] The add-on requires the DTLS protocol to be installed as prerequisite.[22] After installing the updates, for the RDP 8.0 protocol to be enabled between Windows 7 machines, an extra configuration step is needed using the Group Policy editor.[24]
A new feature in RDP 8.0 is limited support for RDP session nesting; it only works for Windows 8 and Server 2012 though, Windows 7 and Server 2008 R2 (even with the RDP 8.0 update) do not support this feature.[25]
The «shadow» feature from RDP 7, which allowed an administrator to monitor (snoop) on a RDP connection has been removed in RDP 8. The Aero Glass remoting feature (applicable to Windows 7 machines connecting to each other) has also been removed in RDP 8.[21][22]
This version was released with Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2. The RDP 8.1 client, like the RDP 8.0 client, is available on Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 through KB2923545 but unlike the RDP 8.0 update for Windows 7, it does not add a RDP 8.1 server component to Windows 7. Furthermore, if RDP 8.0 server function is desired on Windows 7, the KB 2592687 (RDP 8.0 client and server components) update must be installed before installing the RDP 8.1 update.[26][27]
Support for session shadowing was added back in RDP version 8.1. This version also fixes some visual glitches with Microsoft Office 2013 when running as a RemoteApp.[26]
Version 8.1 of the RDP also enables a «restricted admin» mode. Logging into this mode only requires knowledge of the hashed password, rather than of its plaintext, therefore making a pass the hash attack possible.[28] Microsoft has released an 82-page document explaining how to mitigate this type of attack.[29]
Version 10.0 of the RDP was introduced with Windows 10 and includes the following new features: AutoSize zoom (useful for HiDPI clients).
In addition graphics compression improvements were included utilizing H.264/AVC.[30]
- 32-bit color support. 8-, 15-, 16-, and 24-bit color are also supported.
- Encryption: option of legacy 56-bit or 128-bit RC4 and modern MITM-resistant TLS since version 5.2[8]
- Audio Redirection allows users to process audio on a remote desktop and have the sound redirected to their local computer.
- File System Redirection allows users to use their local files on a remote desktop within the terminal session.
- Printer Redirection allows users to use their local printer within the terminal session as they would with a locally- or network-shared printer.
- Port Redirection allows applications running within the terminal session to access local serial and parallel ports directly.
- The remote computer and the local computer can share the clipboard.
- Compression goes beyond a framebuffer and takes advantage of font knowledge and tracking of window states (inherited from T.128); later extensions add more content-aware features (e.g MS-RDPCR2).
Microsoft introduced the following features with the release of RDP 6.0 in 2006:
- Seamless Windows: remote applications can run on a client machine that is served by a Remote Desktop connection. It is available since RDP 6.[31]
- Remote Programs: application publishing with client-side file-type associations.
- Terminal Services Gateway: enables the ability to use a front-end IIS server to accept connections (over port 443) for back-end Terminal Services servers via an https connection, similar to how RPC over https allows Outlook clients to connect to a back-end Exchange 2003 server. Requires Windows Server 2008.
- Network Level Authentication
- Support for remoting the Aero Glass Theme (or Composed Desktop), including ClearType font-smoothing technology.
- Support for remoting Windows Presentation Foundation applications: compatible clients that have .NET Framework 3.0 support can display full Windows Presentation Foundation effects on a local machine.
- Rewrite of device redirection to be more general-purpose, allowing a greater variety of devices to be accessed.
- Fully configurable and scriptable via Windows Management Instrumentation.
- Improved bandwidth tuning for RDP clients.[citation needed]
- Support for Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.0 on both server and client ends (can be negotiated if both parties agree, but not mandatory in a default configuration of any version of Windows).
- Multiple monitor support for allowing one session to use multiple monitors on the client (disables desktop composition)
Release 7.1 of RDP in 2010 introduced the following feature:
- RemoteFX: RemoteFX provides virtualized GPU support and host-side encoding; it ships as part of Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1.
The latest version of RDP supports Transport Layer Security (TLS) version 1.1, 1.2 and 1.3 to protect RDP traffic.[32]
Version 5.2 of the RDP in its default configuration is vulnerable to a man-in-the-middle attack. Administrators can enable transport layer encryption to mitigate this risk.[33][34]
RDP sessions are also susceptible to in-memory credential harvesting, which can be used to launch pass the hash attacks.[35]
In March 2012, Microsoft released an update for a critical security vulnerability in the RDP. The vulnerability allowed a Windows computer to be compromised by unauthenticated clients and computer worms.[36]
RDP client version 6.1 can be used to reveal the names and pictures of all users on the RDP Server (no matter which Windows version) in order to pick one, if no username is specified for the RDP connection.[citation needed]
In March 2018 Microsoft released a patch for CVE-2018-0886, a remote code execution vulnerability in CredSSP, which is a Security Support Provider involved in the Microsoft Remote Desktop and Windows Remote Management, discovered by Preempt.[37][38]
In May 2019 Microsoft issued a security patch for CVE-2019-0708 («BlueKeep»), a vulnerability which allows for the possibility of remote code execution and which Microsoft warned was «wormable», with the potential to cause widespread disruption. Unusually, patches were also made available for several versions of Windows that had reached their end-of-life, such as Windows XP. No immediate malicious exploitation followed, but experts were unanimous that this was likely, and could cause widespread harm based on the number of systems that appeared to have remained exposed and unpatched.[39][40][41]
In July 2019, Microsoft issued a security patch for CVE-2019-0887, a RDP vulnerability that affects Hyper-V.[42]
In April 2025, a security researcher discovered that it is possible to log into accounts through RDP using passwords that have already been revoked. According to Microsoft, this was by design, and not a bug or vulnerability.[43]
Since the release of Remote Desktop Connection, there have been several additional Remote Desktop Protocol clients created by both Microsoft and other parties including Microsoft Remote Desktop, rdesktop, and FreeRDP.
In addition to the Microsoft-created Remote Desktop Services, open-source RDP servers on Unix include FreeRDP (see above), ogon project and xrdp. The Windows Remote Desktop Connection client can be used to connect to such a server. There is also Azure Virtual Desktop which makes use of RDP and is a part of the Microsoft Azure platform.
There is also a VirtualBox Remote Display Protocol (VRDP) used in the VirtualBox virtual machine implementation by Oracle.[44] This protocol is compatible with all RDP clients, such as that provided with Windows but, unlike the original RDP, can be configured to accept unencrypted and password unprotected connections, which may be useful in secure and trusted networks, such as home or office LANs. By default, Microsoft’s RDP server refuses connections to user accounts with empty passwords (but this can be changed with the Group Policy Editor[45]). External and guest authorization options are provided by VRDP as well. It does not matter which operating system is installed as a guest because VRDP is implemented on the virtual machine (host) level, not in the guest system. The proprietary VirtualBox Extension Pack is required.
Microsoft requires third-party implementations to license the relevant RDP patents.[46] As of February 2014, the extent to which open-source clients meet this requirement remains unknown.
Security researchers reported in 2016-17 that cybercriminals were selling compromised RDP servers on underground forums as well as specialized illicit RDP shops.[47][48] These compromised RDPs may be used as a «staging ground» for conducting other types of fraud or to access sensitive personal or corporate data.[49] Researchers further report instances of cybercriminals using RDPs to directly drop malware on computers.[50]
- Comparison of remote desktop software
- Desktop virtualization
- Secure Shell
- SPICE and RFB protocol
- Virtual private server
- ^ a b Deland-Han. «Understanding Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) – Windows Server». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on October 17, 2020. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
- ^ «How to change the listening port for Remote Desktop». Microsoft. January 31, 2007. Archived from the original on November 4, 2007. Retrieved November 2, 2007. Microsoft KB article 306759, revision 2.2.
- ^ «Service Name and Transport Protocol Port Number Registry». Internet Assigned Numbers Authority. January 9, 2015. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ «rdesktop: A Remote Desktop Protocol Client». www.rdesktop.org. Archived from the original on December 1, 2008. Retrieved November 29, 2008.
- ^ Microsoft. «Connecting to another computer Remote Desktop Connection». Archived from the original on January 16, 2013. Retrieved December 22, 2012.
- ^ Implementing Collaboration Technologies in Industry, Bjørn Erik Munkvold, 2003; Chapter 7
- ^ «Windows XP Remote Desktop Connection software [XPSP2 5.1.2600.2180]». Microsoft.com. August 27, 2012. Archived from the original on September 8, 2010. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ a b «Configuring authentication and encryption». January 21, 2005. Archived from the original on March 18, 2009. Retrieved March 30, 2009. Microsoft Technet article
- ^ «Remote Desktop Connection (Terminal Services Client 6.0)». June 8, 2007. Archived from the original on July 17, 2007. Retrieved June 20, 2007. Microsoft KB article 925876, revision 7.0.
- ^ «Description of the Remote Desktop Connection 6.1 client update for Terminal Services in Windows XP Service Pack 2». microsoft. Archived from the original on August 29, 2008. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ «Changes to Remote Administration in Windows Server 2008». Terminal Services Team Blog. Microsoft. December 17, 2007. Archived from the original on March 5, 2009. Retrieved February 10, 2008.
- ^ «Terminal Services Printing». TechNet – Windows Server 2008 Technical Library. Agozik-Microsoft. January 10, 2008. Archived from the original on January 21, 2014. Retrieved February 10, 2008.
- ^ «Introducing Terminal Services Easy Print: Part 1 – Remote Desktop Services (Terminal Services) Team Blog – Site Home – MSDN Blogs». Blogs.msdn.com. Archived from the original on February 13, 2014. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ «Securing Remote Desktop (RDP) for System Administrators | Information Security Office». security.berkeley.edu. Archived from the original on October 12, 2020. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
- ^ «Remote Desktop Connection 7 for Windows 7, Windows XP & Windows Vista». Terminal Services Team Blog. Microsoft. August 21, 2009. Archived from the original on August 27, 2009. Retrieved August 21, 2009.
- ^ «Using Remote Desktop Easy Print in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2». Blogs.msdn.com. Archived from the original on May 8, 2010. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ «Announcing the availability of Remote Desktop Connection 7.0 for Windows XP SP3, Windows Vista SP1, and Windows Vista SP2». Blogs.msdn.com. Archived from the original on March 8, 2010. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ «Aero Glass Remoting in Windows Server 2008 R2». Blogs.msdn.com. Archived from the original on June 27, 2009. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ «Remote Desktop Connection 7 for Windows 7, Windows XP & Windows Vista». Blogs.msdn.com. Archived from the original on August 27, 2009. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 Remote Desktop Services (RDS) – Windows Server Blog – Site Home – TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. May 8, 2012. Archived from the original on October 5, 2013. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ a b «How Microsoft RDP 8.0 addresses WAN, graphics shortcomings». Searchvirtualdesktop.techtarget.com. Archived from the original on February 9, 2014. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ a b c «Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) 8.0 update for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2». Support.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on October 25, 2012. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ «Incorrect TLS is displayed — Windows Server». June 5, 2024.
- ^ «Get the best RDP 8.0 experience when connecting to Windows 7: What you need to know – Remote Desktop Services (Terminal Services) Team Blog – Site Home – MSDN Blogs». Blogs.msdn.com. Archived from the original on February 12, 2014. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ «Running a Remote Desktop Connection session within another Remote Desktop Connection session is supported with Remote Desktop Protocol 8.0 for specific scenarios». Support.microsoft.com. November 2, 2012. Archived from the original on January 17, 2014. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ a b «Update for RemoteApp and Desktop Connections feature is available for Windows». Support.microsoft.com. February 11, 2014. Archived from the original on February 9, 2014. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ «Remote Desktop Protocol 8.1 Update for Windows 7 SP1 released to web – Remote Desktop Services (Terminal Services) Team Blog – Site Home – MSDN Blogs». Blogs.msdn.com. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ «New «Restricted Admin» feature of RDP 8.1 allows pass-the-hash». Labs.portcullis.co.uk. October 20, 2013. Archived from the original on February 10, 2014. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ «Mitigating Pass-the-Hash (PtH) Attacks and Other Credential Theft Techniques». Microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 21, 2014. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ «Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) 10 AVC/H.264 improvements in Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview». Microsoft.com. Archived from the original on August 17, 2016. Retrieved January 12, 2016.
- ^ «[MS-RDPERP]: Remote Desktop Protocol: Remote Programs Virtual Channel Extension». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 14, 2012. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ «[MS-RDPBCGR]: Enhanced RDP Security». April 23, 2024.
- ^ «National Vulnerability Database (NVD) National Vulnerability Database (CVE-2005-1794)». Web.nvd.nist.gov. July 19, 2011. Archived from the original on September 14, 2011. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ «Configuring Terminal Servers for Server Authentication to Prevent «Man in the Middle» Attacks». Microsoft. July 12, 2008. Archived from the original on November 6, 2011. Retrieved November 9, 2011.
- ^ «Mimikatz and Windows RDP: An Attack Case Study». SentinelOne. June 6, 2019. Archived from the original on October 16, 2020. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS12-020 – Critical». Microsoft. March 13, 2012. Archived from the original on February 13, 2014. Retrieved March 16, 2012.
- ^ «CVE-2018-0886 – CredSSP Remote Code Execution Vulnerability». microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 23, 2018. Retrieved March 23, 2018.
- ^ Karni, Eyal. «From Public Key to Exploitation: How We Exploited the Authentication in MS-RDP». Archived from the original on March 23, 2018. Retrieved March 23, 2018.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin. «Even the NSA is urging Windows users to patch BlueKeep (CVE-2019-0708)». ZDNet. Archived from the original on September 6, 2019. Retrieved June 20, 2019.
- ^ Goodin, Dan (May 31, 2019). «Microsoft practically begs Windows users to fix wormable BlueKeep flaw». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on July 22, 2019. Retrieved May 31, 2019.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 14, 2019). «Microsoft warns of major WannaCry-like Windows security exploit, releases XP patches». The Verge. Archived from the original on September 2, 2019. Retrieved June 20, 2019.
- ^ Ilascu, Ionut (7 August 2019). «Microsoft Ignored RDP Vulnerability Until it Affected Hyper-V». Bleeping Computer. Archived from the original on 8 August 2019. Retrieved 8 August 2019.
- ^ Goodin, Dan (April 30, 2025). «Windows RDP lets you log in using revoked passwords. Microsoft is OK with that». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 13, 2025.
- ^ «VirtualBox Manual: 7.1. Remote Display (VRDP Support)». VirtualBox. Archived from the original on November 21, 2019. Retrieved February 27, 2020.
- ^ Bens, Jelle (January 31, 2010). «Jelle Bens: Windows 7 RDP with blank password». Jellebens.blogspot.ru. Archived from the original on May 8, 2013. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
- ^ «Remote Desktop Protocol Licensing Available for RDP 8». Blogs.msdn.com. December 11, 2014. Archived from the original on February 8, 2018. Retrieved February 8, 2018.
- ^ GReAT (June 15, 2016). «xDedic – the shady world of hacked servers for sale». SecureList. Archived from the original on December 15, 2018. Retrieved December 15, 2018.
- ^ Kremez, Vitali; Rowley, Liv (October 24, 2017). ««Ultimate Anonymity Services» Shop Offers Cybercriminals International RDP Servers». Archived from the original on December 15, 2018. Retrieved December 15, 2018.
- ^ Bisson, David (July 19, 2018). «Dark Web ‘RDP Shops’ Offer Access to Vulnerable Systems for as Little as $3». Security Intelligence. Archived from the original on December 15, 2018. Retrieved December 15, 2018.
- ^ Ragan, Steve (July 19, 2018). «Samsam infected thousands of LabCorp systems via brute force RDP». CSO Online. Archived from the original on December 15, 2018. Retrieved December 15, 2018.
- Remote Desktop Protocol – from Microsoft’s Developer Network
- Understanding the Remote Desktop Protocol – from support.microsoft.com
- MS-RDPBCGR: Remote Desktop Protocol: Basic Connectivity and Graphics Remoting Specification – from Microsoft’s Developer Network
В Windows для подключения к рабочему столу удаленного компьютера по протоколу RDP (Remote Desktop) по-умолчанию используется порт TCP 3389. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как изменить номер стандартного порта для службы RDP на другой (применимо как к дестопным версиям Windows, так и к Windows Server).
Содержание:
- Изменить номер RDP порта в Windows
- PowerShell скрипт для смены номера RDP порта в Windows
После того, как вы включили RDP доступ в Windows, служба TermService (Remote Desktop Services) начинает слушать на порту 3389.
В современных версиях Windows для подключений удаленного рабочего стола также используется протокол UDP с тем же номером порта 3389. При использовании VPN, транспортный UDP протокол может вызывать проблемы с зависанием RDP сессий.
Для чего может понадобиться замена стандартного RDP порта 3389 на другой?
- Чаще всего это используется, чтобы спрятать RDP/RDS хост от автоматических сканеров портов, которые ищут в Интернете хосты Windows с открытым дефолтным RDP портом 3389.
- Смена RDP порта позволит уменьшить вероятность эксплуатации RDP уязвимостей, уменьшить количество попыток удалённого подбора паролей по RDP (не забывайте периодически анализировать логи RDP подключений), SYN и других типов атак.
- Обычно смена RDP порт используется на компьютерах с прямым подключением к интернету (VPS/VDS), или в сетях, где пограничный маршрутизатор перенаправляет порт 3389/RDP в локальную сеть на компьютер/сервер с Windows.
Несмотря на смену порта, не рекомендуется выставлять открытый RDP порт в Интернет. Сканеры портов по сигнатуре ответа могут понять, что на новом порту находится RDP Listener. Если вы хотите открыть внешний RDP доступ к компьютеру в локальной сети, лучше использовать такие технологии подключения, как VPN, RD Web Access, шлюз RD Gateway и другие.
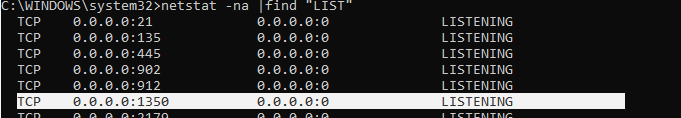
При смене номера RDP порта на нестандартный, нежелательно использовать номера портов в диапазоне от 1 до 1023 (известные порты). Выберите неиспользуемый порт в пользовательском диапазоне (1024 до 49151) или из RPC (49152 — 65535). Проверьте, что выбранный порт не слушается другими процессами (например, порт 1350).
netstat -aon | findstr ":1350" | findstr "LISTENING"
Изменить номер RDP порта в Windows
В нашем примере мы изменим номер порта, на котором ожидает подключения служба TermService на 1350.
Для быстрой замены номера RDP порта на указанный, достаточно выполнить следующие команды с правами администратора:
set p=1350
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp" /v PortNumber /t REG_DWORD /d %p% /f
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Custom-RDP-Port-TCP" protocol=TCP localport=%p% action=allow dir=IN
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Custom-UDP-Port-UDP" protocol=UDP localport=%p% action=allow dir=IN
net stop TermService /y
net start TermService
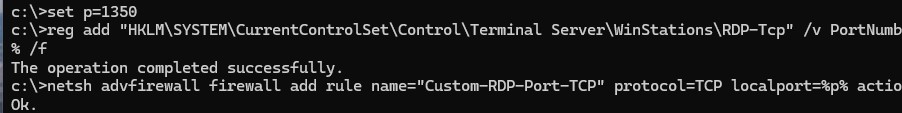
Этот набор команд изменит номер RDP порта, создаст разрешающие правила для нового порта в файерволе и перезапустит службу TermService.
Рассмотрим, что делают эти команды и как изменить дефолтный номер RDP порта вручную.
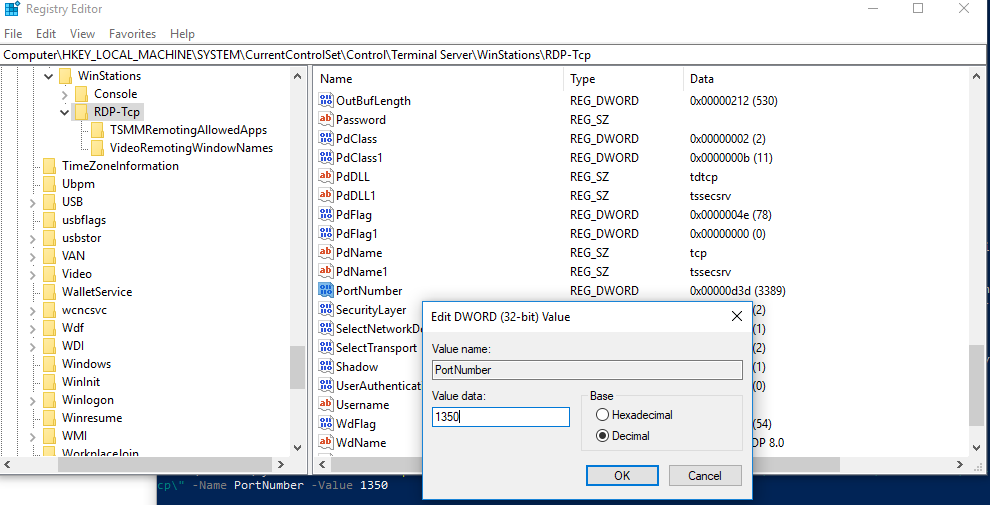
- Откройте редактор реестра (
regedit.exe
) и перейдите в ветку HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp - Найдите DWORD параметр реестра с именем PortNumber. В этом параметре указан порт, на котором ожидает подключения служба Remote Desktop. Значение по умолчанию 3389 (decimal)
- Измените значение этого порта. Я изменил RDP порт на 1350 в десятичном значении (Decimal);
хalert] Можно изменить значение параметра реестра с помощью PowerShell:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\" -Name PortNumber -Value 1350
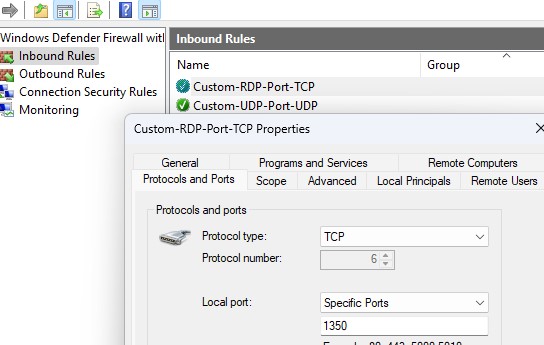
[/alert] - Создайте новые правила в Windows Firewall, разрешающие входящие подключения на новый номер RDP порта (если вы перенастраиваете удаленный сервер через RDP, создайте разрешающее правило в файерволе до перезапуска службы TermService, иначе вы потеряете доступ к хосту). Вы можете создать разрешающее входящее правило для нового TCP/UDP порта RDP вручную из консоли Windows Firewall with Advanced Security (
wf.msc
) или с помощью PowerShell команд:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "NewRDPPort-TCP-In" -Direction Inbound -LocalPort 1350 -Protocol TCP -Action allow
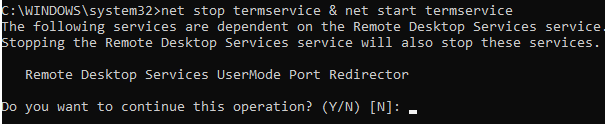
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "NewRDPPort-UDP-In" -Direction Inbound -LocalPort 1350 -Protocol UDP -Action allow - Перезагрузите Windows или перезапустите службу удаленных рабочих столов командой:
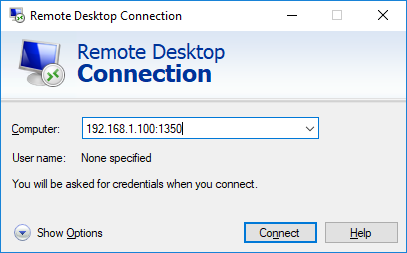
net stop termservice & net start termservice - Теперь для подключения к данному Windows компьютеру по RDP, в клиенте mstsc.exe нужно указывать порт RDP подключения через двоеточие следующим образом:
Your_Computer_Name:1350
или по IP адресу
192.168.1.100:1350
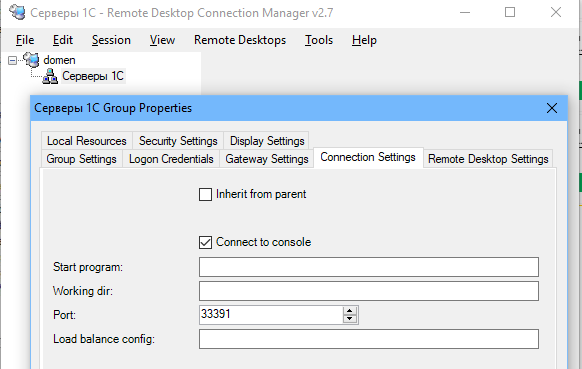
или из командной строки:
mstsc.exe /v 192.168.1.100:1350Если для управления RDP подключений вы используете менеджер RDCMan, новый номер RDP порта подключения указывается на вкладке “Connection Settings”.
- В результате вы должны успешно подключитесь к рабочему столу удаленного компьютера по новому номеру RDP порта (с помощью команды
netstat –na | Find "LIST"
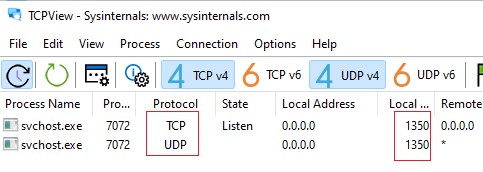
убедитесь, что служба RDP теперь слушает на другом порту).
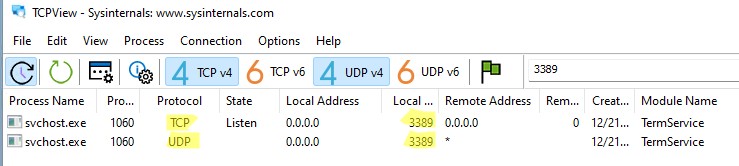
Обратите внимание, что номер UDP порта RDP также изменился на 1350 (проще всего проверить это с помощью утилиты TCPView).
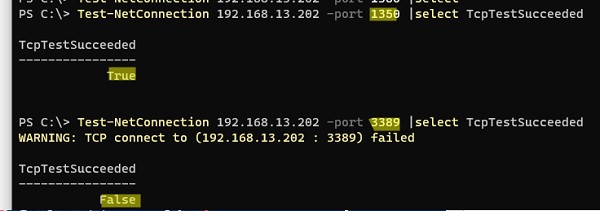
С помощью команды Test-NetConnection, проверьте что старый RDP порт теперь закрыт (
TcpTestSucceeded : False
):
Test-NetConnection 192.168.13.202 -port 3389 |select TcpTestSucceeded
Если вы хотите изменить номер RDP порта сразу на нескольких компьютерах в домене, можно воспользоваться групповыми политиками. Создайте новую GPO, которая распространит параметр реестра PortNumber с новым значением RDP порта на компьютеры домена.
PowerShell скрипт для смены номера RDP порта в Windows
Полный код PowerShell скрипта для смены номера RDP порта, создания правила в брандмауэре и перезапуска службы RDP может выглядеть так:
Write-host "Укажите номер нового RDP порта: " -ForegroundColor Yellow -NoNewline;$RDPPort = Read-Host
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-TCP\" -Name PortNumber -Value $RDPPort
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "NewRDPPort-TCP-In-$RDPPort" -Direction Inbound –LocalPort $RDPPort -Protocol TCP -Action Allow
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "NewRDPPort-UDP-In-$RDPPort" -Direction Inbound –LocalPort $RDPPort -Protocol UDP -Action Allow
Restart-Service termservice -force
Write-host "Номер RDP порта изменен на $RDPPort " -ForegroundColor Magenta
Если на удаленном компьютере включен WinRM, вы можно изменить номер порта RDP удаленно с помощью командлета Invoke-Command:
Invoke-Command -ComputerName PC1name -ScriptBlock {Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-TCP\" -Name PortNumber -Value 1350}

TSplus Бесплатная пробная версия удаленного доступа
Ultimate альтернатива Citrix/RDS для доступа к рабочему столу/приложениям. Безопасное, экономичное, локальное/облачное.
Что такое порт RDP?
Порты RDP — это сетевые порты, которые облегчают коммуникацию между удаленным клиентом и сервером с использованием протокола удаленного рабочего стола. По умолчанию RDP использует TCP-порт 3389. Этот раздел расскажет о основах портов RDP, о том, как они работают, и об их роли в удаленных рабочих подключениях.
Порт по умолчанию и его роль
Порт RDP по умолчанию,
3389
, используется протоколом удаленного рабочего стола для установления соединения между клиентом и сервером. Когда пользователь запускает сеанс RDP, клиентское программное обеспечение отправляет запрос через порт 3389 на сервер, который прослушивает тот же порт для входящего трафика RDP.
Значимость этого порта заключается в его стандартизированном использовании, которое обеспечивает совместимость и простоту настройки. Однако его распространенность также делает его объектом злонамеренной деятельности.
Процесс коммуникации
Процесс коммуникации включает несколько этапов:
-
Запрос клиента: Клиент отправляет начальный запрос на подключение к IP-адресу сервера и порту 3389. Этот запрос включает необходимые учетные данные аутентификации и параметры сеанса.
-
Ответ сервера: Сервер отвечает серией сообщений рукопожатия для установления безопасного канала связи. Это включает обмен ключами шифрования и настройками сеанса.
-
Инициализация сеанса: После завершения рукопожатия сервер инициализирует сеанс, позволяя клиенту взаимодействовать с удаленным рабочим столом. Это взаимодействие обеспечивается через серию пакетов данных, которые передают ввод с клавиатуры, движения мыши и обновления экрана.
Альтернативные порты
Порт 3389 является портом по умолчанию, однако можно настроить RDP для использования альтернативных портов.
Изменение порта по умолчанию
Может повысить безопасность, уменьшив риск автоматизированных атак, нацеливающихся на порт 3389. Это включает изменение настроек реестра на сервере Windows и обеспечение согласованности правил брандмауэра и сетевых конфигураций с новым портом.
Важность портов RDP
Порты RDP необходимы для включения функциональности удаленного рабочего стола. Они обеспечивают беспрепятственное взаимодействие между удаленными клиентами и серверами, облегчая различные задачи удаленного доступа и управления. Этот раздел исследует значение портов RDP в различных контекстах.
Возможность удаленной работы
Порты RDP критичны для удаленной работы, позволяя сотрудникам получать доступ к своим офисным компьютерам из дома или других удаленных мест. Эта возможность обеспечивает непрерывность работы и производительность, независимо от физического местоположения.
Удаленные рабочие столы позволяют получить доступ к корпоративным ресурсам, приложениям и файлам, как если бы пользователь был физически присутствовал в офисе. Это особенно полезно для организаций с распределенными командами или тех, кто внедряет гибкие рабочие политики.
Техническая поддержка
Команды поддержки ИТ полагаются на порты RDP для устранения неполадок и решения проблем на удаленных системах. Путем доступа к удаленному рабочему столу персонал поддержки может проводить диагностику, применять исправления и управлять конфигурациями, не выходя на место.
Эта возможность удаленного доступа сокращает время простоя и повышает эффективность операций поддержки. Она позволяет быстро решать проблемы, минимизируя влияние на конечных пользователей и обеспечивая бесперебойную работу бизнеса.
Управление сервером
Администраторы используют
Порты RDP
Для удаленного управления серверами. Эта функциональность важна для поддержания здоровья сервера, выполнения обновлений и управления приложениями, особенно в крупных центрах обработки данных и облачных средах.
Управление удаленным сервером через RDP позволяет администраторам выполнять задачи, такие как установка программного обеспечения, изменение конфигурации и мониторинг системы из любого места. Это крайне важно для поддержания времени работы и производительности критической инфраструктуры.
Виртуальные рабочие столы
Порты RDP также поддерживают виртуальную инфраструктуру рабочего стола (VDI), предоставляя пользователям доступ к виртуализированной среде рабочего стола. Эта настройка становится все более популярной в организациях, стремящихся централизовать управление рабочими столами и улучшить безопасность.
Среды VDI позволяют пользователям получать доступ к своим рабочим столам с различных устройств, обеспечивая последовательный и безопасный пользовательский опыт. Порты RDP облегчают коммуникацию между клиентскими устройствами и виртуальными рабочими столами, размещенными на централизованных серверах.
Проблемы безопасности с портами RDP
While RDP порты критически важны для
удаленный доступ
, они также могут быть уязвимы к кибератакам, если не обеспечены должной безопасностью. В этом разделе обсуждаются распространенные угрозы безопасности, связанные с портами RDP, и предоставляются подробные объяснения каждой из них.
Атаки методом перебора
Атаки методом перебора паролей включают в себя систематическую попытку хакеров различных комбинаций имени пользователя и пароля для получения доступа к сеансу RDP. Эти атаки могут быть автоматизированы с использованием скриптов, которые непрерывно пытаются войти в систему до успешного входа.
Для смягчения этого риска необходимо внедрить политики блокировки учетных записей, которые временно блокируют доступ после определенного количества неудачных попыток. Кроме того, использование сложных паролей и их изменение может помочь защититься от атак методом перебора.
Перехват RDP
RDP захват происходит, когда несанкционированный пользователь получает контроль над активной сессией RDP. Это может произойти, если злоумышленник получает доступ к учетным данным сеанса или использует уязвимость в протоколе RDP.
Для предотвращения захвата RDP крайне важно использовать надежные механизмы аутентификации и регулярно отслеживать активные сеансы. Также можно снизить риск, гарантируя, что только уполномоченный персонал имеет доступ к учетным данным RDP и используя время ожидания сеанса.
Использование уязвимостей
Необновленные системы с известными уязвимостями в RDP могут быть использованы злоумышленниками. Например, уязвимости, такие как BlueKeep (CVE-2019-0708), широко сообщались и эксплуатировались в дикой природе, подчеркивая необходимость регулярных обновлений и патчей.
Администраторам следует быть в курсе последних рекомендаций по безопасности и незамедлительно применять патчи. Внедрение надежного процесса управления патчами может помочь защитить от эксплуатации.
Атаки Man-in-the-Middle
В атаке типа «человек посередине» злоумышленник перехватывает коммуникацию между клиентом и сервером. Это может привести к захвату или изменению чувствительных данных без ведома обеих сторон.
Использование сильных протоколов шифрования и обеспечение проведения сеансов RDP по безопасным каналам, таким как VPN, может снизить риск атак «человек посередине». Регулярное обновление стандартов шифрования и протоколов также является важным.
Лучшие практики по обеспечению безопасности портов RDP
Для смягчения рисков безопасности необходимо внедрить bewые практики для
защита портов RDP
Этот раздел предоставляет исчерпывающее руководство по улучшению безопасности соединений RDP.
Измените порт RDP по умолчанию
Изменение порта по умолчанию с 3389 на другой номер порта может сделать более сложным задачу поиска и нацеливания на ваши службы RDP для злоумышленников. Для этого необходимо изменить настройки реестра на сервере Windows, чтобы указать новый номер порта.
Для изменения порта RDP:
-
Откройте редактор реестра и перейдите к
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumber
.
-
Измените номер порта на желаемое значение и убедитесь, что он не конфликтует с другими службами.
-
Обновите правила брандмауэра, чтобы разрешить трафик через новый порт.
-
Информируйте пользователей о новой конфигурации порта.
Включить сетевую аутентификацию уровня (NLA)
Уровень сети аутентификации (NLA) требует, чтобы пользователи прошли аутентификацию перед установлением полной сессии RDP. Этот предварительный шаг аутентификации помогает предотвратить несанкционированный доступ и снижает риск атак отказа в обслуживании.
Для включения NLA:
-
Откройте диалоговое окно Свойства системы и перейдите на вкладку Remote.
-
Отметьте флажок для «Разрешить подключения только с компьютеров, работающих с удаленным рабочим столом с сетевой аутентификацией уровня».
-
Примените настройки и убедитесь, что все клиенты поддерживают NLA.
Используйте надежные пароли
Гарантировать, что все учетные записи с доступом по RDP имеют сложные, уникальные пароли. Надежные пароли обычно включают комбинацию прописных и строчных букв, цифр и специальных символов.
Соблюдение политики паролей, требующей регулярных изменений и запрещающей повторное использование старых паролей, может повысить безопасность. Использование менеджеров паролей также может помочь пользователям эффективно управлять сложными паролями.
Реализовать двухфакторную аутентификацию (2FA)
Двухфакторная аутентификация добавляет дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя второй формы верификации, такой как код, отправленный на мобильное устройство, в дополнение к паролю. Это значительно снижает риск несанкционированного доступа даже в случае компрометации пароля.
Для внедрения 2FA:
-
Выберите решение 2FA, совместимое с RDP.
-
Настройте сервер RDP для интеграции с решением 2FA.
-
Гарантировать, что все пользователи зарегистрированы и понимают процесс двухфакторной аутентификации.
Ограничить доступ по RDP
Ограничьте доступ по RDP к определенным IP-адресам или используйте виртуальные частные сети (VPN) для ограничения удаленных подключений. Это можно достичь путем настройки правил брандмауэра для разрешения трафика RDP только с доверенных IP-адресов.
Для ограничения доступа по RDP:
-
Определите список разрешенных IP-адресов.
-
Настройте правила брандмауэра для блокировки всех других IP-адресов.
-
Используйте VPN для обеспечения безопасного подключения для удаленных пользователей.
Регулярно обновляйте и исправляйте системы
Поддержание систем обновленными с последними патчами безопасности критически важно для защиты от известных уязвимостей. Регулярно проверяйте обновления от Microsoft и устанавливайте их незамедлительно.
Для обеспечения регулярных обновлений:
-
Реализуйте систему управления патчами.
-
Запланируйте регулярные окна технического обслуживания для установки обновлений.
-
Проверьте обновления в тестовой среде перед их развертыванием в продакшн.
Отслеживание журналов RDP
Регулярно проверяйте журналы RDP на наличие подозрительной активности или попыток несанкционированного доступа. Инструменты мониторинга могут помочь обнаружить и предупредить администраторов о потенциальных нарушениях безопасности.
Для мониторинга журналов RDP:
-
Включить аудит для подключений по RDP.
-
Используйте централизованные решения для ведения журналов, чтобы собирать и анализировать логи.
-
Настройте оповещения о необычной активности или неудачных попытках входа.
TSplus Решение для удаленного доступа
TSplus Удаленный доступ
Улучшает безопасность и удобство RDP, предлагая продвинутые функции, такие как двухфакторная аутентификация, перенаправление портов и шифрование SSL. Он упрощает удаленный доступ с помощью удобного интерфейса, централизованного управления и надежных мер безопасности, что делает его идеальным решением для безопасных, эффективных и масштабируемых подключений к удаленному рабочему столу.
Заключение
Порты RDP являются важным компонентом удаленных служб рабочего стола, обеспечивая беспрепятственный удаленный доступ и управление. Однако они также представляют существенные риски безопасности, если не обеспечены должным образом. Понимая роль портов RDP и применяя лучшие практики для их защиты, организации могут безопасно использовать возможности удаленного рабочего стола, не подвергая опасности безопасность.

TSplus Бесплатная пробная версия удаленного доступа
Ultimate альтернатива Citrix/RDS для доступа к рабочему столу/приложениям. Безопасное, экономичное, локальное/облачное.

Microsoft developed the proprietary Remote Desktop Protocol to offer customers a graphical interface for connecting to other computers through a network connection. For this, the user uses RDP client software, while the other machine has to be running RDP server software.
RDP port number is 3389 which provides network access for a remote user over an encrypted channel.
Before opening the RDP port, bear in mind the following.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password requirements for user accounts and discourage the use of default or easily guessable passwords.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implement two-factor authentication, which adds an extra layer of security by requiring an additional verification step, such as a code sent to a mobile device, along with the password.
- Network Level Authentication (NLA): Enable NLA, a security feature that requires users to authenticate before establishing a remote desktop connection. It helps prevent unauthorized access attempts.
- Use SSL/TLS Encryption: Configure RDP to use SSL/TLS encryption for secure communication between the client and server. This helps protect data confidentiality during transit.
- Firewall Protection: Configure firewalls to allow RDP traffic only from trusted IP addresses or networks. Restricting access to RDP ports (default: TCP port 3389) helps minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
- Regular Updates and Patches: Keep the RDP client and server systems up to date with the latest security patches and updates. This helps address any known vulnerabilities.
- Account Lockout Policies: Implement account lockout policies to automatically lock out user accounts after a certain number of failed login attempts. This helps prevent brute-force attacks.
- Limit User Access: Grant RDP access only to authorized users who need it for their specific roles. Regularly review and revoke access for users who no longer require remote access.
- Session Timeouts: Configure session timeouts to automatically disconnect idle RDP sessions after a specific period of inactivity. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access if a session is left unattended.
- Monitor and Audit: Implement logging and monitoring mechanisms to track RDP connection attempts and activities. Regularly review logs for any suspicious or unauthorized access attempts.
Configure SSL/TLS encryption for RDP
Configuring SSL/TLS encryption for Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) involves obtaining and installing an SSL certificate on the RDP server. Here’s a general overview of the steps involved:
- Obtain an SSL Certificate: Acquire an SSL certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA). You can choose between a self-signed certificate or a certificate issued by a recognized CA. It is generally recommended to use a certificate from a trusted CA to ensure widespread client compatibility.
- Install the SSL Certificate: Install the SSL certificate on the RDP server. The exact steps may vary depending on the operating system and RDP server software being used. Typically, it involves importing the certificate into the server’s certificate store.
- Configure RDP to Use SSL/TLS: Enable SSL/TLS encryption in the RDP server settings. The process may differ depending on the specific RDP server software being used. Typically, you need to specify the SSL certificate to be used for encryption.
- Configure Firewall and Port Forwarding: Ensure that your firewall allows incoming connections on the SSL/TLS port (default: TCP port 3389) and forwards them to the RDP server.
- Test the SSL/TLS Connection: Verify the SSL/TLS configuration by connecting to the RDP server using an RDP client that supports SSL/TLS encryption. Ensure that the connection is established successfully.
It’s important to note that the specific steps for configuring SSL/TLS encryption for RDP may vary depending on the operating system and RDP server software being used. It is recommended to refer to the documentation or support resources provided by the specific RDP server software or consult with your system administrator for detailed instructions tailored to your environment.
Additionally, be sure to keep the SSL certificate up to date, renewing it as necessary, and regularly update the RDP server software to address any security vulnerabilities and take advantage of the latest security features.
You can check the current port by running the following PowerShell command:
Get-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp' -name "PortNumber"
For example:
PS C:\Users\controller> Get-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp' -name "PortNumber"PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations
PSChildName : RDP-Tcp
PSDrive : HKLM
PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
PortNumber : 3389

What port need to open to allow remote desktop?
TCP port 3389 has to be open in order to use Remote Desktop. Moreover, with RDP 8.0, acceleration is enabled by opening UDP port 3389.
The port that the terminal server (or PC being connected) uses can be changed. It is not possible to modify the UDP port individually since it utilises the same port number as the TCP option.
Since RDP 8.0 (included with Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, and accessible through an update for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2), UDP acceleration has been made available.
We can set custom RDP port numbers using following path.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
How to Change the Remote Desktop Port on Windows?
- Open the Registry Editor (
regedit.exe) and go to the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp; - Find the DWORD parameter with the name PortNumber. This parameter shows the port, on which the Remote Desktop service is listening. The default is 3389 (decimal);
- Change the value of this parameter. I have changed the RDP port to 3390.
- If your machine has a Windows Firewall, you will need to create a new rule that enables inbound connections to your new RDP port.
- In the Windows Defender Firewall panel, you may manually create an allowed incoming rule for your new TCP/UDP RDP port.
- Reboot your computer.
- You must provide the new RDP connection port in your mstsc.exe client to connect to this Windows host using Remote Desktop.
You may also change the RDP port by running the PowerShell command below. The new RDP port will be 3390 in this command.
$portvalue = 3390Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp' -name "PortNumber" -Value $portvalue
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'RDPPORTLatest-TCP-In' -Profile 'Public' -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort $portvalue
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'RDPPORTLatest-UDP-In' -Profile 'Public' -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol UDP -LocalPort $portvalue
So, that’s all in this blog. I will meet you soon with next stuff .Have a nice day !!!
Recommended contents
How to Check the Active Directory Database Integrity
Disabling and Enabling the Outbound Replication
DFS Replication Service Stopped Replication
What is Strict Replication Consistency
The replication operation failed because of a schema mismatch between the servers involved
Troubleshooting ad replication error 8418 the replication operation failed because of a schema mismatch between the servers
How to export replication information in txt file
Repadmin Replsummary
Enabling the outbound replication
Disabling and enabling replication on schema master domain controller
How to enable strict replication consistency
How to prevent lingering objects replication in active directory
AD replication process overview
How to force active directory replication
Change notification in replication process
How to check replication partner for a specific domain controller
dcdiag test replications
Guys please don’t forget to like and share the post.Also join our WindowsTechno Community and where you can post your queries/doubts and our experts will address them .
You can also share the feedback on below windows techno email id.
If you have any questions feel free to contact us on admin@windowstechno.com also follow us on facebook@windowstechno to get updates about new blog posts.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
He is an Active Directory Engineer. He has been working in IT industry for more than 10 years. He is dedicated and enthusiastic information technology expert who always ready to resolve any technical problem. If you guys need any further help on subject matters, feel free to contact us on admin@windowstechno.com Please subscribe our Facebook page as well website for latest article. https://www.facebook.com/windowstechno
The Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a network communication protocol that enables remote communication between two devices. It is Microsoft’s proprietary protocol to provide network access over an encrypted channel for remote users. RDP is commonly used by network administrators to diagnose problems, log in to servers, and carry out other actions.

How RDP works:
The Remote Desktop Protocol requires two components for successful remote connection. These are:
- RDP server
- RDP client
Your Windows PC serves as a typical RDP server, while any computer with an RDP client app installed acts as an RDP client. Microsoft features its own client app for Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, with alternatives available for Linux OS and other platforms.
RDP is responsible for transmitting screen information from the remote server to the RDP client. It also shares input from the client’s peripheral devices like keyboard and mouse with the RDP remote server. However, most of the data flow from the RDP server to the client as the graphical screen information is extensive compared to data from the peripheral devices.
RDP requires additional protocols for successful remote connection. These include the TPKT that enables translation of information units between the two suites of networking protocols called TCP and ISO so its a good thing if your company needs remote desktop services. RDP also needs X.224 and T.125 MCS to set up a remote connection and enable multiple channels.
Port 3389 is the default port to power Remote Desktop Services on Windows operating system. The Remote Desktop feature must be enabled on a PC before it can listen to remote connections on port 3389. Since this port is well known to script kiddies and bots, it is often an easy target for exploitation. Therefore, proper security measures need to be taken to avoid cyberattacks.
Security vulnerabilities:
The Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC) observed a 153 percent increase in cyber-attacks in 2019. Many of these attacks led to significant network downtime and resulted in costly remediation efforts. The MS-ISAC attributes the surge to ransomware infections affecting Managed Service Providers.

Ransomware attacks are malware attacks that block access to systems and their resources until the ransom is paid. Ransomware attackers encrypt critical files on the infected system, block their access, and threaten to delete them if the victims refuse to submit to their demands. These demands, often in the form of ransom amounts, are typically displayed as a ransom note on the victim’s screen.
As a result of security compromises and vulnerabilities, victims lose access to important systems and files and experience significant financial losses due to legal costs and restitution efforts. The effects of these attacks can be particularly catastrophic when emergency services like 911 call centers and critical infrastructure like hospitals fall victim to it.
To prevent your network from such attacks, network administrators and engineers recommend changing the default RDP port as the first line of defense. While this may not fool a smart attacker, it certainly limits the number of attacks.
How to modify the RDP Port?
Changing the default RDP port from 3389 requires editing in the Windows registry. Changing the registry may be risky; therefore, it is a good idea to back up your data before saving any changes.
Here is how you can modify the RDP port by editing the registry value.
- Type regedit in the Command Prompt to enter the Registry Editor.
- Locate the following registry branch/subkey and click it.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp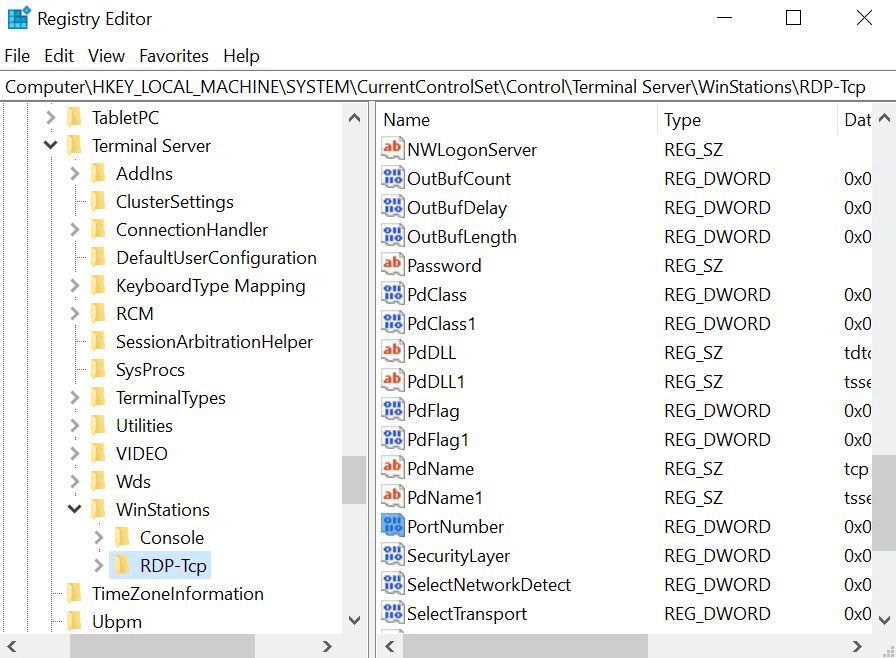
- Navigate to the registry entry PortNumber in the Edit menu.
- Click on Modify and select Decimal in the “Edit DWORD Value” window.
- Type a new port number and select OK when done.
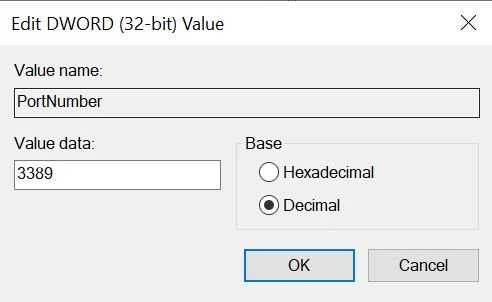
Reboot the system for the new port assignment to take effect. The system should now specify the new port in the client properties.
If you do not use port 3389 as a default RDP port, you can look up the current RDP port number by using the following command:
Get-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP Tcp' -name "PortNumber"Additional recommendations:
To further protect your network and resources, there are more steps that you can take to safeguard your devices and avoid losses and severe downtime.
- Set up strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication.
- Place good account lockout policies. Lack of account lockout policy means that the RDP protocol can be used to access the admin password with brute force attacks. In brute force attacks, the hacker tries all possible passwords to login into the network.
- Allow remote access to RDP clients you trust.
- Follow the Principle of Least Privilege, which limits the level of access required to perform duties.
- Make sure that only authorized users can access the network. Review RDP login attempts from anonymous hosts and look for any anomalous activity on the network.
- Regularly update the RDP server and client software to ensure that the latest versions are installed on your system.
Final thoughts:
With the Windows Remote Desktop feature, you can connect two devices with the right RDP server and client apps installed on them. Once connected, you can view content on the remote display, access files, and interact with the local device using RDP. However, with the exponential rise in the number of cyberattacks, you must take security measures to protect your data from prying eyes.
Author Bio: Audrey Throne has an ongoing affair with the words that capture readers’ attention. Her passion for writing dates back to her pre-blogging days. She loves to share her thoughts related to business, technology, health and fashion.
Find her on Twitter: @audrey_throne