In my articles, you often see instructions to open the command prompt as admin. In Windows 10 also, you will need to use it from time to time, so I would like to share with you the various ways to open an elevated command prompt. Let’s explore them right now.
Before you start reading, I strongly recommend you to see my previous article, «Do you know all these ways to open an elevated command prompt in Windows?». It covers all the possible ways to open an elevated command prompt in previous versions of Windows. Many of the tricks from that article still work in Windows 10.

This way is very handy in Windows 10. Starting with Windows 8, Microsoft has implemented the Power Users menu, which contains many useful items like Control Panel, Network Connections and so on. Windows 10 also comes with such a menu. It contains the Command Prompt (Admin) item which is exactly what we need.
To access this menu in Windows 10, press Win + X shortcut keys together on the keyboard.
Tip: You can customize the Win+X menu with our freeware tool called Win+X Menu Editor. Check it out.
Update: This option has been removed in Windows 10 Creators Update. See the following article to learn about this change in detail: Windows 10 build 14986 replaces Command Prompt with PowerShell everywhere. To restore the command prompt in the Win + X menu, see this tutorial: Add Command Prompt back to Win+X Menu in Windows 10 Creators Update.
In Windows 10, you can use the search box inside the Start menu. Type cmd there and press CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER to launch the command prompt elevated. This also works on the Start screen.
Launch an elevated command prompt instance from a non-elevated one
You can launch an elevated instance of the command prompt from a non-elevated one. You might wonder why you would need to do this. Let me show you with an example scenario.
Whenever you press the SHIFT key and hold it and then right click on a folder in Explorer, you get the usual «Open command window here» menu item.

This is very handy, you just opened a command window at the path you wanted. Now what if you need an elevated command prompt at that path? Command Prompt does not provide any way to open an elevated command window at the same path.
Update: The context menu option has been removed in Windows 10 Creators Update. You can restore it as follows:
Add Command Prompt to Context Menu in Windows 10 Creators Update
To resolve this issue and improve usability, you can use a little application I coded called ELE. It is able to reopen an already opened command prompt as administrator and keeps the current path.
Usage of ELE:
Simply typing ele — opens a new console window as administrator in the current directory.
ele /x — opens a new console window in the current directory and closes the original console window. If ELE is started from a file manager, it just opens a new elevated console at the current path.

Copy-paste ele.exe in any folder which is included in your system %PATH% environment variable, e.g. C:\Windows or C:\Windows\system32. That will make it accessible from any folder and you won’t need to type the full path to ele.exe every time you want to elevate the command prompt.
That’s it!
Support us
Winaero greatly relies on your support. You can help the site keep bringing you interesting and useful content and software by using these options:
If you like this article, please share it using the buttons below. It won’t take a lot from you, but it will help us grow. Thanks for your support!
What to Know
- Open Task Manager and select Run new task (in Windows 11) or File > Run new task (in Windows 10/8).
- Type cmd in the text field and check the Create this task with administrative privileges box.
- Choose OK and follow any User Account Control requirements.
This article explains how to open an elevated Command Prompt in Windows 11, 10, or 8. It also includes instructions for Windows 7 and Vista, along with additional information on why you need an elevated Command Prompt and how to tell whether you have administrator privileges.
How to Open an Elevated Command Prompt in Windows 11, 10, or 8
If you’re using a keyboard with Windows 11, Windows 10, or Windows 8, you can open an elevated Command Prompt quickly from the Power User Menu. Just use the WIN+X keyboard shortcut and then select Terminal (Admin) (in Windows 11) or Command Prompt (Admin) (in Windows 10/8). Choose Yes on any User Account Control messages that might appear.
Depending on your settings and Windows configuration, Command Prompt may be replaced by Windows Powershell. If you’re using Windows 11, the option in the Power User Menu is for Terminal; you can get to Command Prompt after opening that program.
Another method is to use Task Manager:
-
Open Task Manager. The quickest way, assuming you’re using a keyboard, is via CTRL+SHIFT+ESC, but there are several other methods outlined in that link. One easy way is to type task manager into the search bar on the taskbar.
-
Select Run new task at the top (Windows 11), or go to File > Run new task.
Don’t see the File menu? You may first have to select More details at the bottom of the Task Manager window to show a more advanced view of the program, including the File menu.
-
In the Create new task window you see now, type the following in the Open text field:
cmd…but don’t do anything else just yet!
-
Check the box that says Create this task with administrative privileges.
Don’t see this box? That means that your Windows account is a standard account, not an administrator account. Your account must have administrator privileges to be able to open an elevated Command Prompt this way. Follow the Windows 7/Vista method below, or try the tip just below these instructions.
-
Choose OK and then follow any User Account Control requirements that might appear next. An elevated Command Prompt window will now appear, allowing unrestricted access to executing commands.
Feel free to close Task Manager. It does not need to remain open to use Command Prompt.
How to Open an Elevated Command Prompt in Windows 7 or Vista
These are alternative steps you can follow on Windows 7 or Windows Vista:
-
Locate the Command Prompt shortcut, usually in the Accessories folder in the Start Menu.
If you’re having trouble finding it, see How to Open Command Prompt (the non-elevated kind). But first, there’s an intermediate step you need to take.
-
Right-click it and choose Run as administrator.
-
Accept any User Account Control messages or warnings.
An elevated Command Prompt window should appear, allowing access to commands that require administrative level privileges.
When Do You Need an Elevated Command Prompt?
Some commands available in Windows require that you run them from an elevated Command Prompt. Basically, this means running the Command Prompt program (cmd.exe) with administrator-level privileges.
You’ll know if you need to run a particular command from within an elevated Command Prompt because it’ll clearly tell you that in an error message after running the command.
For example, when you try to execute the sfc command from a normal Command Prompt window, you’ll get the «You must be an administrator running a console session in order to use the sfc utility» message.
Try the chkdsk command and you’ll get an «Access Denied as you do not have sufficient privileges or the disk may be locked by another process. You have to invoke this utility running in elevated mode and make sure the disk is unlocked» error.
Other commands give other messages, but regardless of how the message is phrased, or what Command Prompt command we’re talking about, the solution is simple: open an elevated Command Prompt and execute the command again.
More About Elevated Command Prompts
Don’t let all the discussion above convince you that you should, or need to, run Command Prompt as an administrator for most commands. For almost all Command Prompt commands, no matter what version of Windows, it’s perfectly okay to execute them from a standard Command Prompt window.
To be able to open an elevated Command Prompt window, either a) your Windows user account must already have administrator privileges, or b) you must know the password to another account on the computer that has administrator privileges. Most home computer user’s accounts are set up as administrator accounts, so this isn’t usually a concern.
How to Tell if You Have Administrator Privileges
There’s a very easy way to tell if the Command Prompt window you’ve opened is elevated or not: it’s elevated if the window title says Administrator; it’s not elevated if the window title just says Command Prompt.
An elevated Command Prompt window opens to the system32 folder. A non-elevated Command Prompt window instead opens to the user’s folder: C:\Users\[username]. The only exception is if you’ve opened an elevated Command Prompt via Terminal, in which case it might also open to the user’s folder.
If you plan on frequently using an elevated Command Prompt, then you should consider creating a new shortcut to Command Prompt that automatically starts the program with administrator-level access. See How to Create an Elevated Command Prompt Shortcut if you need help.
In Windows XP, users have Administrator privileges by default. When you open a Command Prompt in XP, it will be elevated unless you have another type of profile.
FAQ
-
To open a Command Prompt, select Start icon and search for command prompt. Select the command prompt from the search results. You can also go to Start > Windows System and choose Command Prompt from the folder group.
-
Mac users don’t have Command Prompt. Instead, they use the Terminal program. To open Terminal, go to Finder, open the /Applications/Utilities folder, and select Terminal. Or, enter Terminal into Spotlight Search.
-
To change directories via the Command Prompt, type cd followed by a space and the folder name. For example, type cd Documents to change from your current folder to the Documents folder.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
Using the instructions here you will have the ability to open Command Prompt as administrator in Windows 10 from Start, Search, Run, taskmgr, PowerShell, and more. This application allows running commands that help you fix multiple issues, change settings, and access different files. When you stuck in anything on Windows 10 the first tool you remember is CMD. Administrative authority makes you capable to run a task in elevated mode.
We already discussed How to Launch Elevated Command Prompt on Windows 10 but now some additional ways are available for the same. So here we have come with a collection of all methods to open cmd with admin rights.
How to Open Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows 10
Here are 12 Ways to Open Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows 10 –
1] Quickest and easiest way to run cmd as admin
Step-1: Click on the Start icon.
Step-2: Type cmd.
Step-3: Press ctrl+shift+enter on keyboard.
Step-4: Once User Account Control (UAC) dialog appears, select Yes.
2] Open command prompt as administrator from Run dialog
- Press Win+R and let the Run dialog box appear.
- Write down either cmd or cmd.exe in the empty text field onward to Open.
- Press ctrl, shift, and enter simultaneously.
- Click Yes when a UAC dialog prompts to seek permission.
3] Take the help of Windows search bar
- Press Windows and S keys.
- Type “cmd”
- Click – Run as administrator.
- A UAC will prompt up for authentication; choose Yes.
4] Open Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows 10 Via Win+X menu
In the recent versions of Windows 10, you notice rather Windows PowerShell (Admin) in the Power user menu (Win+X). But for launching easily, you can replace it with Command Prompt (Admin) via a small tweak in Settings. This will help you to open cmd with administrative privilege in only 2 clicks. Here’s how –
- Open Windows Settings (by pressing Win and I).
- Select Personalization.
- Select Taskbar from the left-pane and then shift to the right.
- Toggle on the option – “Replace Command Prompt with Windows PowerShell in the menu when I right-click the Start button or press Windows Key+X”.
- From now onward, whenever you will open the Power user menu, you will view Command Prompt (Admin) in the list.
- Simply press Win+X and choose the same.
5] Open command prompt as administrator by means of Task Manager
Important – Before proceeding forward, make sure that you have signed in as administrator.
- Right-click on the Taskbar and select Task Manager or directly press “Ctrl+Alt+Esc”.
- From the menu bar, click on File option.
- Press and hold the Ctrl key and at the same time click Run new task.
- It will right away open cmd as admin.
6] Again using Task Manager
- Open Task Manager using the method given in the previous way.
- Click on File from the uppermost menu bar and choose Run new task.
- Type either cmd.exe or cmd the provided space and check the box for “Create this task with administrative privileges”.
- Click – OK.
7] Through Start menu
- Press Windows key to bring up the Start menu
- Click on # from the top.
- Select W alphabet from the list.
- Click Windows System from here and to expand its options.
- Right-click on Command Prompt, move the cursor over “More”
- Then choose – “Run as administrator”.
- When you see a User Account Control popup, click the Yes to give consent.
8] Switch PowerShell to Command Prompt
- Press “Win+X” hotkey and select “Windows PowerShell (Admin)” from the Power user menu.
- When the User Account Control shows up in the display, click the Yes button to allow it.
- In the “Administrator: Windows PowerShell”, type cmd after PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> and hit the Enter key.
- This will immediately switch the PowerShell utility to Command prompt.
9] Open Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows 10 From System32 Directory
- Press – Win+E.
- Select This PC in Quick access and then Perform a double click on “(C:)” (we assume that this is your system drive).
- Double click – Windows folder.
- From the next window, locate System32 and double-click on the same to enter it.
- Once this directory appears, find cmd.exe.
- Right click on the same and opt Run as administrator from the list.
- Finally, hit the Yes button once the UAC arrives.
- Alternatively, to get access to the location you may copy-paste “C:\Windows\System32” into the Run dialog box and hit Enter.
10] Via Run command
- Press Win+R.
- Paste
C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exein Run dialog - Hit – ‘ctrl+shift+enter’.
- Choose Yes when User account control prompt appears.
11] Create Desktop shortcut
- Right-click on the desktop.
- and move cursor on New and select Shortcut.
- A wizard entitled Create Shortcut will show up.
- Copy C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe paste into the given area
- Click Next.
- Provide a name for this shortcut.
- Click on Finish.
- You will notice a new shortcut for the “CMD” on the desktop. Right-click on the same and select Properties.
- In the Shortcut tab, move down to the bottom and click the Advanced button.
- Mark – Run as administrator
- Hit the – OK.
- Finally, click on Apply and thereafter OK button to save the changes.
- In future, whenever you need to open command prompt as administrator, just double-click on the shortcut.
12] Assign a shortcut key to open cmd as admin
- Follow the previous method to create a shortcut key of Command Prompt and give it administrative authority.
- Right-click on the desktop shortcut and select – Properties.
- Go to Shortcut key area and click on the box located beside it.
- Now, press your preferred key from the keyboard. When you will type C and the system automatically generated a shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+C.
- Lastly, click on Apply and then OK to make the changes effective.
- To open cmd as admin, you just require hitting the shortcut key you just created.
Methods:
1] Quickest and easiest way to run cmd as admin
2] From Run dialog
3] Take the help of Windows search bar
4] Via Win+X menu
5] By means of Task Manager
6] Again using Task Manager
7] Through Start menu
8] Switch PowerShell to Command Prompt
9] From System32 Directory
10] Via Run command
11] Create Desktop shortcut
12] Assign a shortcut key
That’s all!!
The Command Prompt is a powerful tool in Windows that lets you run commands to manage files, troubleshoot problems, and control system settings. But some commands require administrator access to work properly. Opening the Command Prompt as an administrator—often called “elevated mode” gives you full control to perform advanced tasks on your computer.
In this guide, we will discuss quick and easy ways to open the Command Prompt with administrator rights on your Windows 10 and 11.
Method 1: Using Windows Search (Windows 10 & Windows 11)
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
Step 1: Open the Start Menu and Type «CMD»
Press the Windows Key or Click on the Start Menu and Type Command Prompt or CMD and proceed ahead.
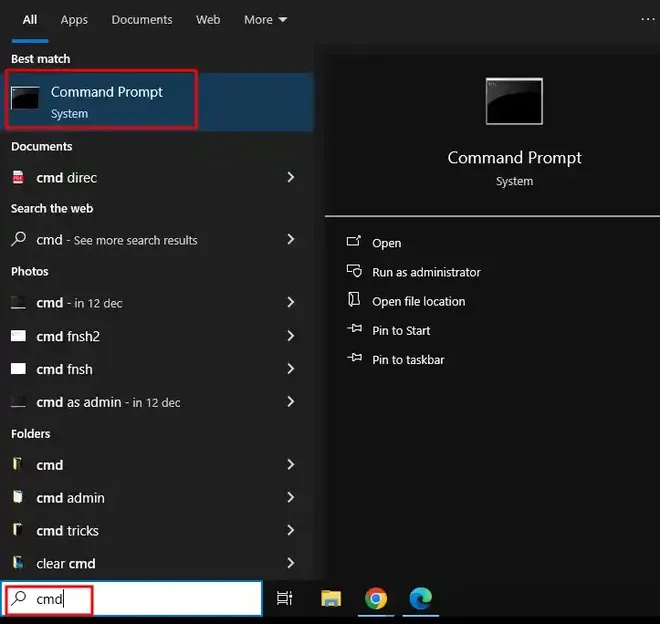
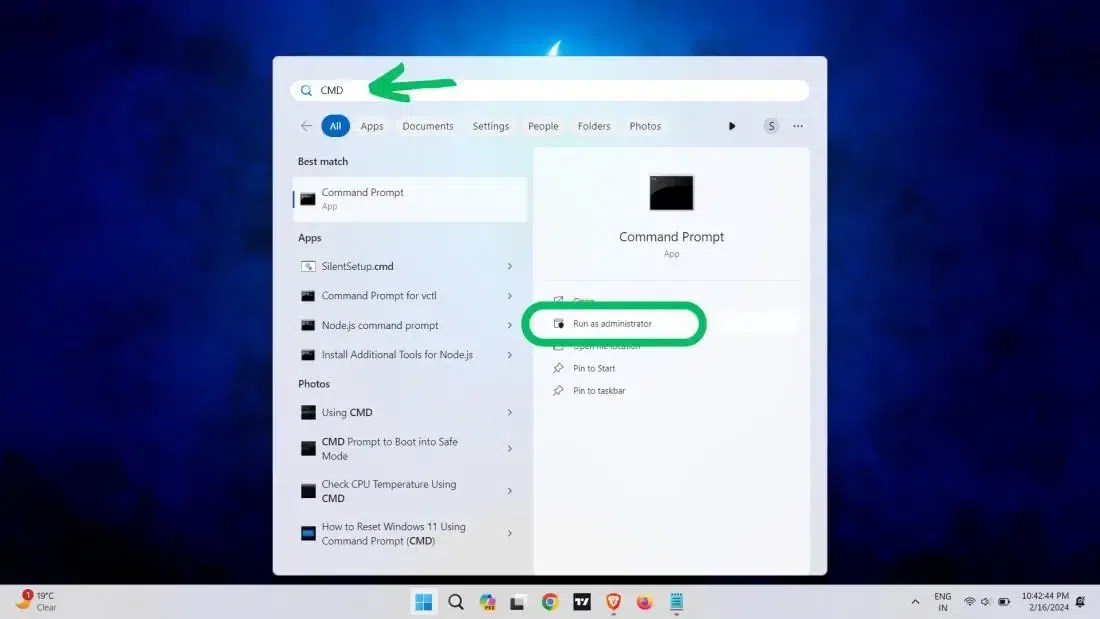
Step 2: Select «Run as Administrator»
Right-click on «Command Prompt» and select «Run as administrator».
Method 2: Run Dialog Box (Win 10 & 11)
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
Step 1: Open Dialog Box or Press Win + R
First, press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog. Now, type «CMD» or Command prompt
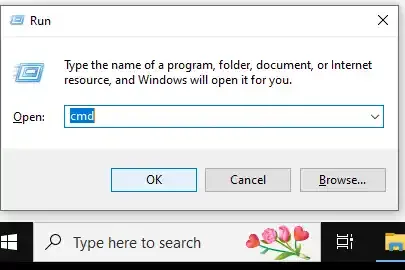
Step 2: Hold down Ctrl + Shift to enter Admin Mode
Press Ctrl + Shift + Enter or click «OK» while holding Ctrl + Shift.

You might be asked to enter admin password. Provide the same & proceed with the Command Prompt administrator rights.
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
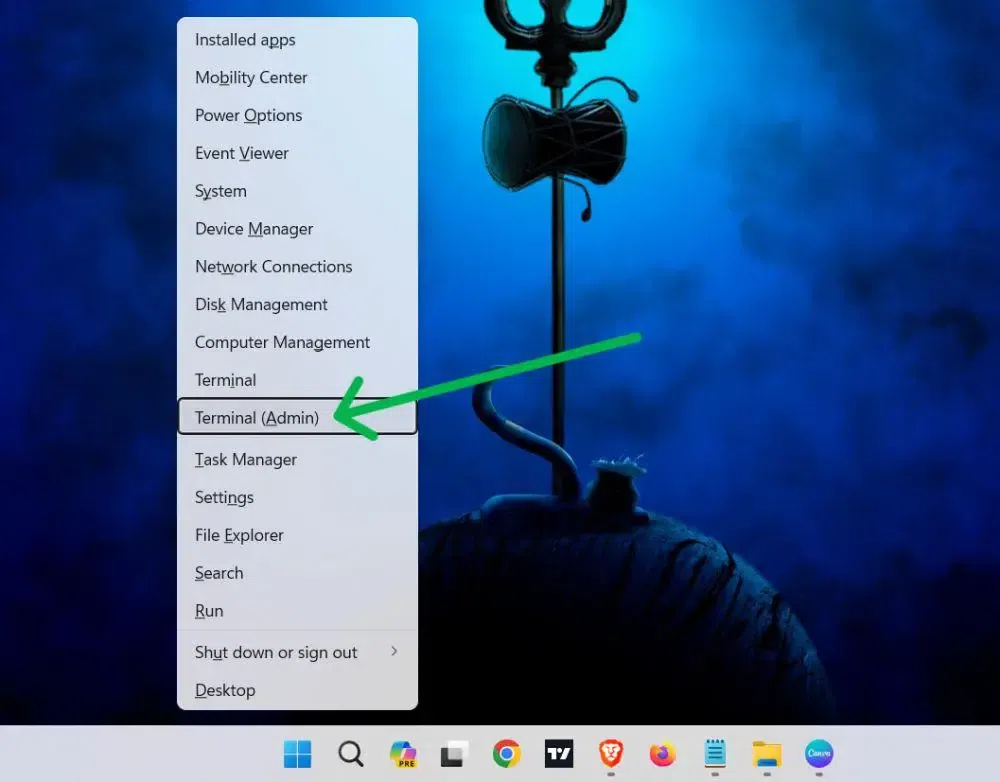
Step 1: Open Power User Menu
Go to Start Button or press Win + X
Step 2: Select Admin
Now, click on «Terminal (Admin)» from the menu.
Step 3: Hover and click to visit Command Prompt
Then, Click on the arrow from the menu and Select «Command Prompt«
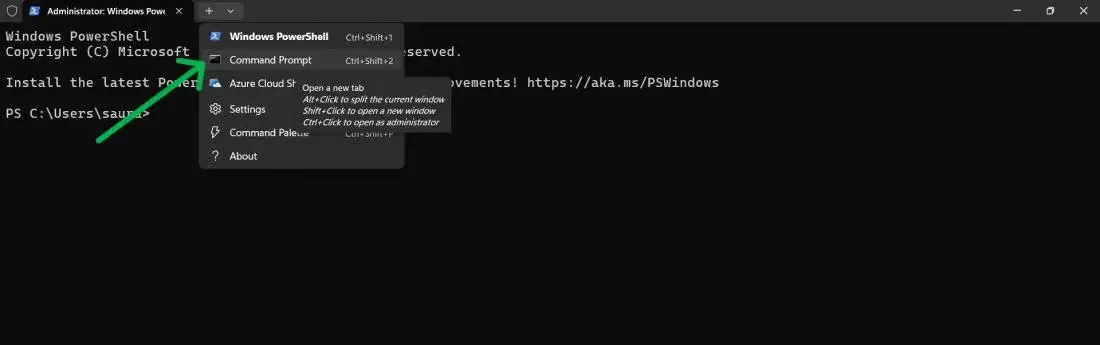
By following this method, anyone can open command prompt using these 3 simple steps.
Note: This method is suitable forWindows 11
Step 1: Type Windows Tools in the search box
Click on the Start menu and type Windows Tools
Step 2: Click to Open as Administrator
Make a right click and select «Run as Administrator»
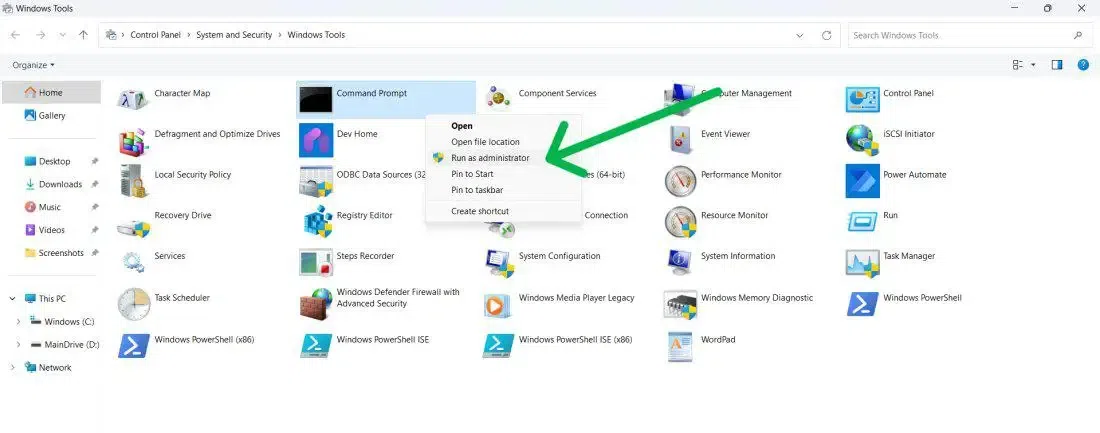
Method 5: Using Task Manager (Win 10 & Win 11)
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
Step 1: Open Task Manager and click to Run New Task
Click the Start Menu and type «Task Manager»
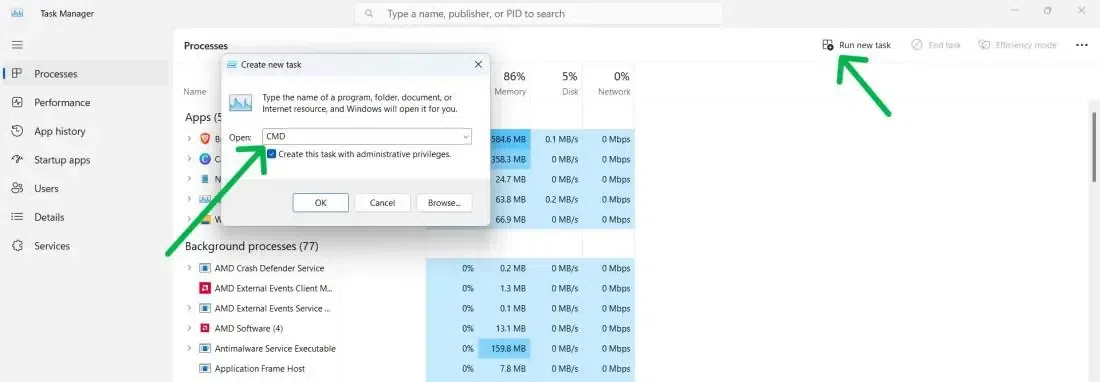
Step 2: Create a New Task to Run CMD with Administrative Rights
Create a new task in the File menu and select Run New Task. Check «Create this task with administrative privileges», and click OK.
Method 6: Use Control Panel (Windows 11)
Note: This method is suitable for Windows 11
Ypu can use Windows Control Panel to open Command Prompt with admin rights, here’s what you need to do:
Step 1: Press Win + R and type Control Panel
Now, on the Control Panel Search bar type «Windows Tools» and click on it.
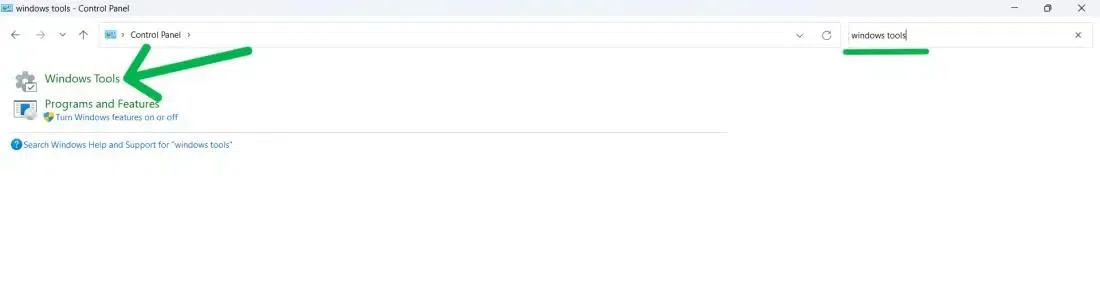
Step 2: Click to Run as Administrator
Right-click on the Command Prompt and Click Run as administrator.
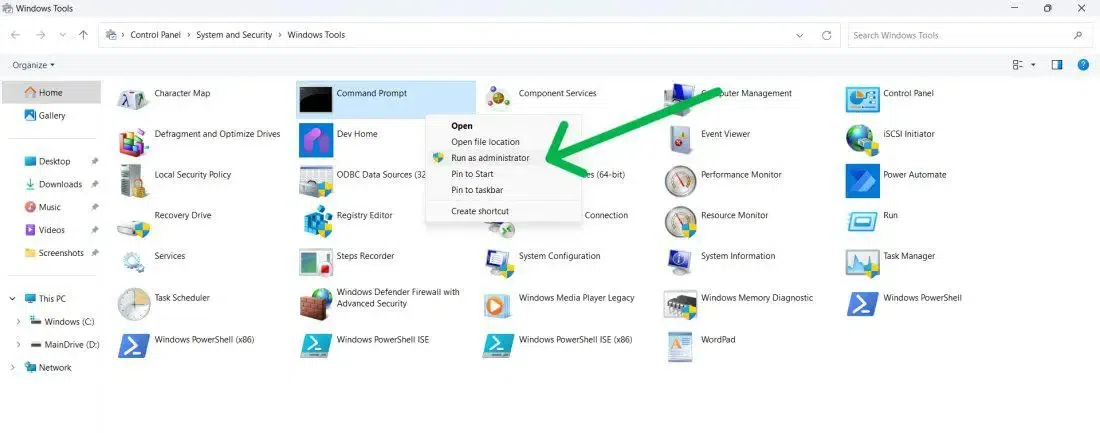
Method 7: Windows File Explorer
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
Step 1: Open File Explorer
Open File Explorer or press Win + E and type CMD
Step 2: Select «Run as Administrator»
Make a right-click and select «Run as admin»
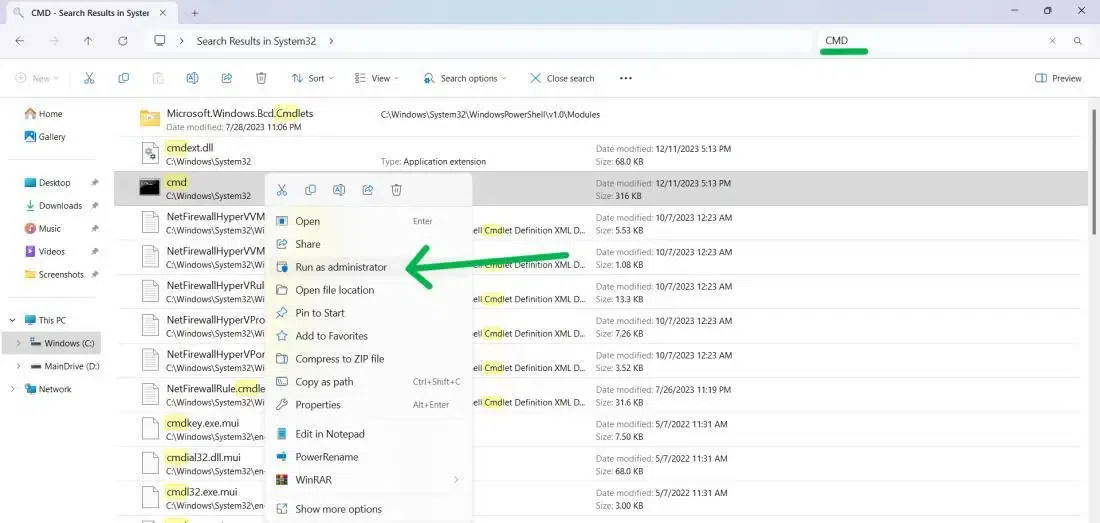
Method 8: Using Desktop Shortcut
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
Step 1: Open File Explorer
Press Win + E and type Command Prompt or CMD
Step 2: Show more options > Create Shortcut
Press Win + D to get the desktop then right-click CMD then from the menu select «Properties» and then navigate to the «Shortcut» tab
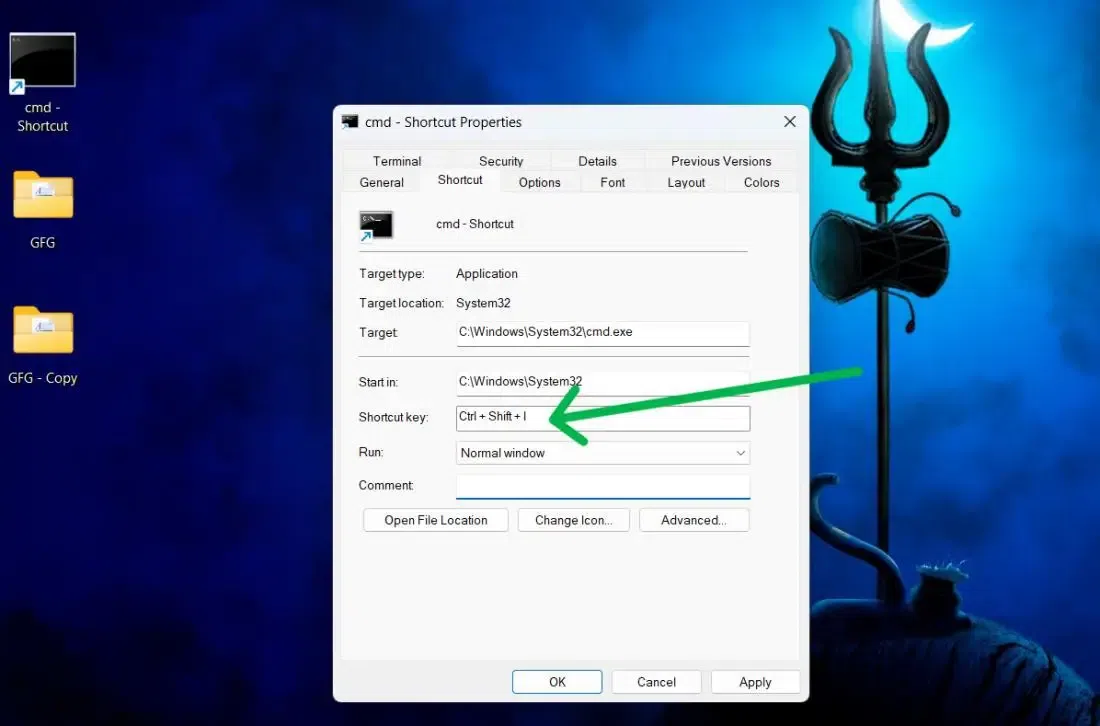
Step 3: Create your custom shortcut
In the Shortcut key field, press a key combination of your choice.
Why Open Command Prompt as Administrator
The Command Prompt or CMD is a powerful tool for performing various system tasks. Running it as an administrator grants you admin access to:
- Modify System Settings
- Run Admin commands like sfc /scannow i.e. system scans
- Manage User Accounts
- Access and edit restricted files
Without administrator access, many essential commands will not work, so knowing how to open it with admin access is critical for users who manage system settings, developers, or anyone performing any troubleshooting related tasks.
Conclusion
Understanding how to open the Command Prompt as Administrator is essential for both casual users and power users. Whether you’re managing system configurations, running scans, or troubleshooting issues, knowing how to run CMD with elevated privileges will enhance your ability to manage your system effectively.
A lot of the fixes and tweaks featured on the web will require you to open a Command Prompt window as an administrator. This can be confusing for non-technical persons because a lot of articles don’t mention the actual steps of opening an elevated Command Prompt.

Most of the time, opening a Command Prompt window as a regular user is more than enough. But there are some situations where you’ll need administrative privileges – you will be required to perform certain actions in an elevated Command Prompt window.
What is an elevated command prompt?
The elevated Command Prompt mode was introduced with Windows Vista and has been an integral part of this OS up until Windows 11. In an attempt o protect the user from those potentially harmful commands, Microsoft restricted the functionality of some commands to the elevated mode only. This means that some commands will only work as long as you run them from an elevated Command Prompt.
Note: You can easily distinguish between a normal Command Prompt window and an elevated one by looking at the starting point. The Elevated Command Prompt starts in the System32 folder while the normal Command Prompt window starts in the User Profile folder.
As with most Windows-related things, you can open an elevated Command Prompt in several different ways. While most of the methods featured in this article can be replicated on the older Windows versions, keep in mind that this article was tailored specifically for Windows 10 and Windows 11.
Here’s a list of different methods that can be used to open an elevated Command Prompt on the latest operating systems released by Microsoft.
Note: Keep in mind that not all methods will work on both Windows 10 or Windows 11. Pay attention to the label under each method to see if it’s compatible with your Windows version.
Open an elevated Command Prompt via the Start menu
Works on Windows 10 & Windows 11.
This is the standard approach that most people use on every Windows version. It’s arguably the longest route but can be considered the most simple method since all the steps are done through the user interface.
Here’s a quick guide to opening an elevated Command Prompt via the Start menu:
- Click the Start menu in the bottom left corner. You can also press the Windows key for the same result.
- With the start menu opened, type “cmd” to automatically use the search function. Wait until the search results are generated, then right-click on Command Prompt and choose Run as Administrator.
Note: You can also use the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keyboard combination if you want o to avoid right-clicking.
This is the classic approach. If you’re looking for a quicker way, move to the other methods below.
Open an Elevated Command Prompt via the Power User Menu
Only works on Windows 10.
If you’re on Windows 10, you can open an Elevated Command Prompt directly from the Power User Menu.
Note: Keep in mind that the Command Prompt (Admin) sub-menu is no longer available on Windows 11.
To access the Power User Menu, right-click on the Start icon or press Windows key + X. Then, simply click on Command Prompt (Admin) to open an Elevated Command Prompt. You will then be asked to confirm the administrative permissions via a User Account Control (UAC) window – hit Yes at the prompt to open the Elevated Command Prompt.
Update: Update Keep in mind that if you have updated your Windows 10 version with the Creators Update, you will see Windows Powershell (Admin) instead of Command Prompt (Admin). This change was implemented by Microsoft in order to tempt more users to migrate to Powershell. On Windows 11, the equivalent is Windows Terminal (Admin).
Note: If you want the old behavior back on Windows 10, you can follow this article (here) to replace the Windows Powershell (Admin) with Command Prompt.
But you can also click on Windows Powershell (Admin) and then type “cmd” inside the Elevated Powershell window to switch to an Elevated Command Prompt window.

Use the Run box to open an Elevated Command Prompt
Works on Windows 10 & Windows 11.
Another way to go around opening an Elevated Command Prompt window is to make use of the run box. Normally, opening Command Prompt from the Run box will not have administrative privileges, but we have a workaround for this.
To open an Elevated Command Prompt window via the Run box, press Windows key + R to bring up the Run menu. Then, type ” cmd ” but instead of pressing Enter directly, press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open it with administrative privileges. You’ll then be prompted by a UAC (User Account Control) window in which you’ll have to hit Yes.

Create an elevated Command Prompt shortcut
Works on Windows 10 & Windows 11.
If you find yourself running Command Prompt command that requires administrative privileges, it makes sense to create a dedicated shortcut for an Elevated Command Prompt. This is arguably the most efficient way of opening an Elevated Command Prompt window, but it requires some time setting it up.
Here’s a quick guide to creating a shortcut for an Elevated Command Prompt:
- Right-click anywhere on a free space (on the desktop or in a folder) and choose New > Shortcut.
Note: Right-clicking on Windows 11 will bring up the newer, slimmer context menu. Click on Show More Options to make the old menu visible.
Show More Options on Windows 11 - In the box directly under “Type the location of the item” type ” CMD ” and hit the Next button.
- At the next button, grant the newly created shortcut a name and hit the Finish button to finish the process.
- Next, right-click on the newly created shortcut and choose Properties. Then, go to the Shortcut tab, and click the Advanced button.
- In the Advanced Properties window, check the box next to Run as administrator and hit OK. Finally, click on Apply to save the changes.
Open a CMD Prompt using the Quick Link Menu
Only works on Windows 11.
- Press Windows key + X key to open up the Quick Link menu on Windows 11.
- From the list of available options, click on Windows Terminal (Admin).
Accessing the Windows Terminal app on Windows 11 Note: This is the newer terminal app available with Windows 11. It allows you to input both CMD and Powershell commands.
That’s it. Your Elevated Command Prompt window is configured and ready to be used. But keep in mind that even if you set it to run with administrative privileges, you’ll still be prompted by the UAC window.
Run CMD Commands from the Terminal App via Search
Only works on Windows 11.
- Press Windows key + S key to open up the Windows Search functionality on Windows 11.
- In the search box that just appeared, type Windows Terminal.
- Next, right-click on Windows Terminal from the list of results and click on Run as Administrator from the context menu.
Run the Windows Terminal app with admin access - Run the CMD commands inside the newly opened Windows Terminal app.
Run CMD commands in Windows Terminal opened via Task Manager
Only works on Windows 11.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open up Task Manager.
- Once you’re inside the Task Manager, click on More details if the simple interface just opened.
Expanding the Task Bar interface Note: If you are already on the regular interface, skip this step altogether.
- next, click on File from the ribbon menu at the top, then click on Run New Task.
Running a new task - Inside the Create new task box that just appeared, type ‘wt’ and then check the box associated with Create this task with administrative privileges before clicking Ok.
Creating a new task - Once you’re inside the Windows Terminal interface, you can input your CMD commands.
Run CMD commands in Windows Terminal opened via Run box
Only works on Windows 11.
- Press Windows key + R to open up a Run dialog box.
- Inside the newly appeared Run box, type ‘wt’ and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open up a Windows Terminal app with admin privileges.
Open up a Windows Terminal app - Inside the elevated Windows Terminal, type the CMD commands as you would usually do.









