Дата публикации: август 2021 г.
Эта статья предназначена для пользователей, которые не могут выполнить обновление до Windows 11, потому что их компьютер в настоящее время не поддерживает безопасную загрузку. Если вы не владеете подобными техническими сведениями, рекомендуем вам ознакомиться с информацией о поддержке производителя вашего ПК для получения дополнительных инструкций, относящихся к вашему устройству.
Безопасная загрузка — важная функция безопасности, предназначенная для предотвращения загрузки вредоносного программного обеспечения при запуске (загрузке) компьютера. Большинство современных компьютеров поддерживают безопасную загрузку, но в некоторых случаях из-за настроек компьютер может не поддерживать безопасную загрузку. Эти настройки можно изменить во встроенном ПО компьютера. Встроенное ПО, часто называемое BIOS — это программное обеспечение, которое запускается перед загрузкой Windows при первом включении компьютера.
Чтобы получить доступ к этим настройкам, вы можете ознакомиться с документацией производителя вашего компьютера или следовать этим инструкциям: Нажмите Параметры > Обновление и безопасность > Восстановление и нажмите Перезагрузить сейчас в разделе «Особые варианты загрузки». На следующем экране выберите Устранение неполадок > Дополнительные параметры > Параметры встроенного ПО UEFI > Перезапустить, чтобы внести изменения.
Чтобы изменить эти настройки, необходимо переключить режим загрузки компьютера с «Legacy» BIOS (также известного как режим CSM) на UEFI/BIOS (единый интерфейс EFI). В некоторых случаях доступны настройки, которые обеспечивают одновременное включение режимов UEFI и Legacy/CSM. В этом случае необходимо выбрать UEFI в качестве первого или единственного варианта. Если вы не знаете, как внести необходимые изменения для включения режима UEFI/BIOS, мы рекомендуем вам ознакомиться с информацией о поддержке производителя вашего компьютера на его веб-сайте. Вот несколько ссылок на информацию от некоторых производителей компьютеров для начала работы:
-
Dell
-
Lenovo
-
HP
Несмотря на то что требование для обновления устройства с Windows 10 до Windows 11 заключается только в том, чтобы компьютер поддерживал безопасную загрузку с помощью режима UEFI/BIOS, вы также можете включить или включить безопасную загрузку для повышения безопасности.
См. также
Требования к системе Windows 11
Способы установки Windows 11
Справка и обучение по Windows
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
Нужны дополнительные параметры?
Изучите преимущества подписки, просмотрите учебные курсы, узнайте, как защитить свое устройство и т. д.
Если установщик Windows 11, а возможно и какая-то программа или игра (такое тоже возможно) сообщает о том, что его не устраивает состояние безопасной загрузки и её необходимо включить — сделать это сравнительно легко, но возможны нюансы.
В этой инструкции подробно о способах включить безопасную загрузку на вашем компьютере или ноутбуке, при условии, что это возможно. Обратите внимание, если задача — установка Windows 11, существуют возможности запуска установки и без включенной безопасной загрузки (Secure Boot), например — создание загрузочной флешки в Rufus с отключением проверки совместимости при чистой установке, или обновление с обходом требований для установки.
Проверка состояния безопасной загрузки, особенности работы после включения
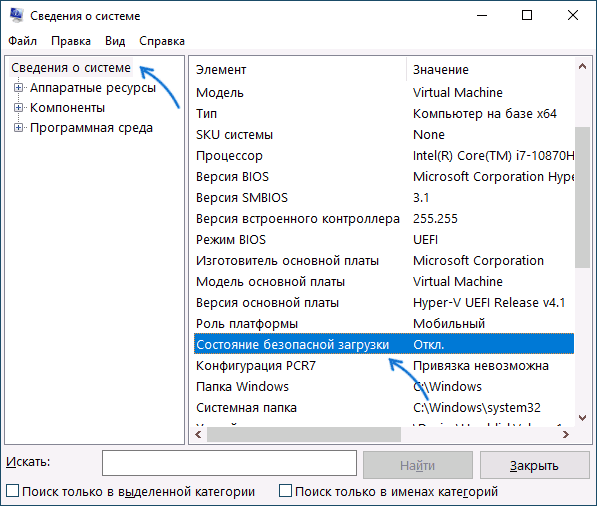
Прежде чем начать, о том, где вы можете проверить текущее состояние безопасной загрузки в Windows 11 или Windows 10:
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск», выберите пункт «Выполнить», введите msinfo32 и нажмите Enter. В разделе «Сведения о системе» вы увидите пункт «Состояние безопасной загрузки» с её текущим статусом.
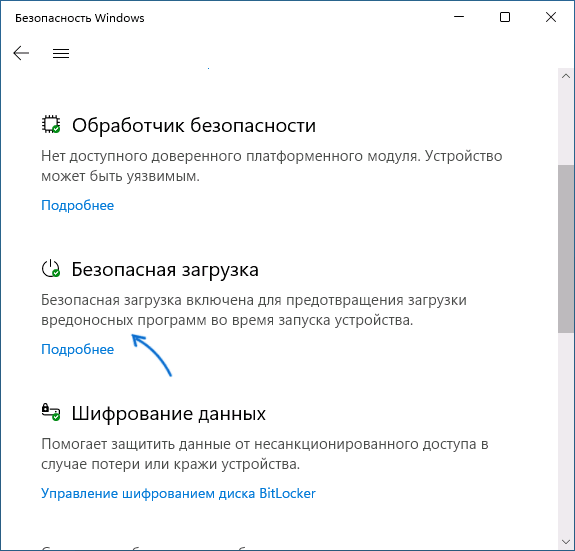
- Можно зайти в окно «Безопасность Windows», например, с помощью значка в области уведомлений и открыть раздел «Безопасность устройства». Если вы наблюдаете там пункт «Безопасная загрузка» с зеленой отметкой, она включена. Иначе — нет.
Ещё один важный момент: загрузка с включенной безопасной загрузкой возможна только для систем, установленных в UEFI-режиме на GPT диск.
Если, к примеру, у вас Windows 10 и установлена в Legacy-режиме на диск MBR, после включения Secure Boot она перестанет загружаться. Возможные варианты действий: конвертировать диск в GPT с помощью mbr2gpt.exe и включить UEFI-загрузку, либо использовать вариант с чистой установкой с флешки и обходом требований Windows 11, как было указано в начале статьи.
Включение безопасной загрузки Secure Boot в БИОС/UEFI
Само включение безопасной загрузки или Secure Boot выполняется не в Windows 11/10, а в БИОС/UEFI вашего компьютера или ноутбука. Для того, чтобы включить её, необходимо:
- Зайти в БИОС при включении/перезагрузке устройства. На ноутбуках для этого обычно используется клавиша F2 (или сочетание Fn+F2), которую необходимо ритмично нажимать сразу после появления заставки производителя (но бывают и другие варианты клавиши), на ПК как правило используется клавиша Delete. Более подробно: Как зайти в БИОС/UEFI на компьютере или ноутбуке.
- Найти раздел БИОС, на котором доступна опция включения (установка в Enabled) функции Secure Boot. Учитывайте, что на очень старых компьютерах такой настройки может и не быть. Как правило, она располагается где-то в разделе Security, Boot, System Configuration, иногда — Advanced Settings. Несколько примеров расположения будут приведены далее.
- Сменить состояние Secure Boot на Enabled (если ранее выполнялась очистка ключей Secure Boot, восстановить их), сохранить настройки БИОС/UEFI (обычно выполняется клавишей F10 или на вкладке Exit) и перезагрузиться обратно в систему.
Примеры расположения опции для включения безопасной загрузки (Secure Boot)
Ниже — несколько примеров, где можно найти опцию включения безопасной загрузки на разных материнских платах и ноутбуках. У вас может отличаться, но логика везде одна и та же.
Ещё раз отмечу: включить безопасную загрузку можно только в случае, если у вас включен режим загрузки UEFI, а режим Legacy/CSM отключен, иначе опция будет недоступна. В некоторых вариантах БИОС переключение в режим загрузки UEFI выполняется путем выбора типа операционной системы (OS Type) между Windows 11/10/8 и «Other OS» (нужно выбрать Windows).
ASUS
На разных версиях материнских плат и ноутбуков включение Secure Boot реализовано слегка по-разному. Обычно пункт «Secure Boot» можно найти на вкладке «Boot» или «Security». При этом для OS Type может потребоваться выставить Windows UEFI Mode (параметр может и отсутствовать).
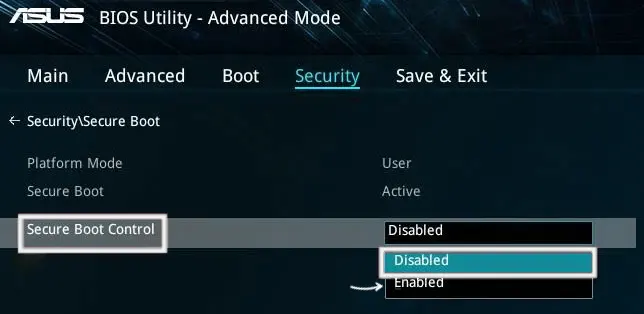
Также, для доступности пункта настройки безопасной загрузки в БИОС может потребоваться перейти в Advanced Mode, обычно — по клавише F7.
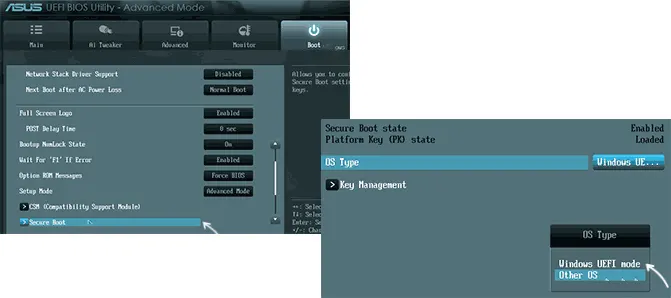
В некоторых случаях может потребоваться восстановление ключей безопасной загрузки, обычно выполняется следующим образом: в Advanced Mode в BIOS на вкладке Boot или в Secure Boot — Key Management выбираем Load Default PK и подтверждаем загрузку ключей по умолчанию.
AsRock
Настройка для включения безопасной загрузки на материнских платах AsRock обычно находится в разделе «Security».

Зайдя в раздел необходимо будет установить значение Secure Boot в Enabled, а если выбор недоступен, включить стандартный Secure Boot Mode и установить ключи по умолчанию (Install default Secure Boot keys).

Acer
Как правило, опция включения Secure Boot на ноутбуках Acer находится либо в разделе Advanced — System Configuration, либо в Boot или Authentication.
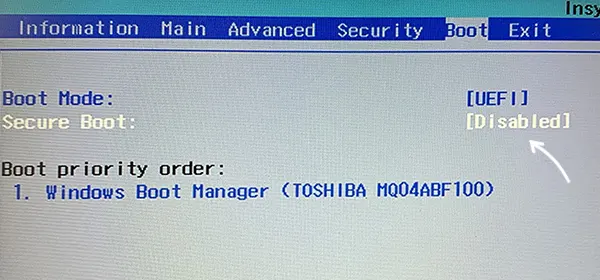
Также помните, о том, что должен быть включен режим загрузки UEFI, а не Legacy/CSM для возможности изменения состояния безопасной загрузки на Enabled.
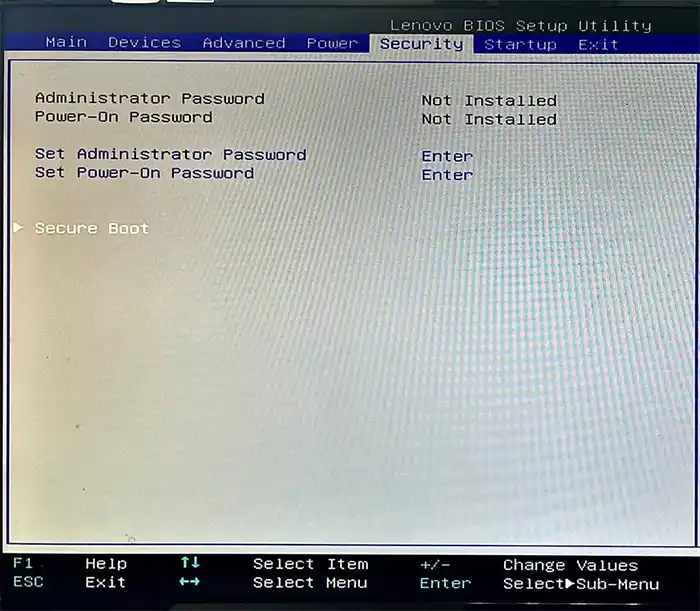
Lenovo
ПК и ноутбуки Lenovo имеют разные варианты интерфейса БИОС, но обычно нужная опция находится на вкладке Security, как на фото ниже:

Ещё один пример с ноутбука Lenovo:
Gigabyte
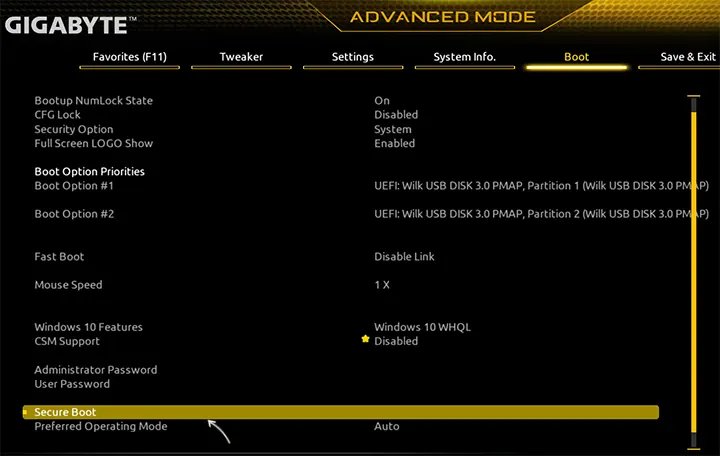
Варианты отключения Secure Boot на материнских платах и ноутбуках Gigabyte могут отличаться, обычно порядок действий следующий:
- На вкладке Boot или BIOS отключить CSM Support, и выбрать тип операционной системы или установить пункт Windows 8/10 Features в, соответственно, Windows 8/10, а не Other OS.
- После этого должен появиться пункт Secure Boot, в который необходимо зайти, чтобы включить безопасную загрузку.
Несколько дополнительных мест расположения опции включения Secure Boot (устанавливаем в Enabled) на старых Dell, Gigabyte, HP:

Также, если в вашем интерфейсе БИОС предусмотрен поиск, можно использовать его:

В случае, если вы не нашли способа включить безопасную загрузку на вашей материнской плате, либо её не удается перевести в Enabled, укажите её марку и модель в комментариях, я постараюсь подсказать, где именно требуется включать этот параметр. Кстати, часто достаточно просто сбросить настройки БИОС (Load Defaults на вкладке Exit), чтобы включить безопасную загрузку, так как на большинстве современных материнских плат она по умолчанию включена.
Having Secure Boot enabled on Windows 11 is a critical step for users wanting to run Microsoft’s latest operating system. Secure Boot is a security mechanism that ensures your computer boots in a protected environment, safeguarding against malicious software. It’s part of the hardware and software requirements introduced with Windows 11, along with the need for a compatible CPU, TPM 2.0, and sufficient RAM and storage.
Although most modern systems have Secure Boot enabled by default, some configurations may show it as inactive due to certain BIOS or firmware settings. While enabling Secure Boot strengthens the overall security posture of a machine, there are cases—such as working with specific Linux instances or older systems—where disabling it might be preferable.
Turning on Secure Boot for Windows 11
Secure Boot works by verifying the digital signatures of drivers, the operating system, and firmware each time your PC starts. Before going through the process of enabling Secure Boot, it’s a good idea to first check whether it’s already active on your system, as the setup can be somewhat involved.
How to check if Secure Boot is already enabled
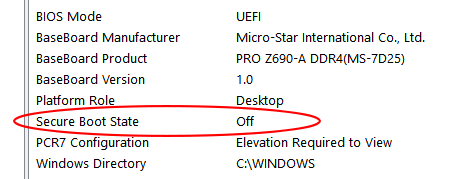
(Image: © Future)
To verify whether Secure Boot is active on your system:
- Click Start
- Type System Information into the search bar and press Enter
- Scroll through the system data list to locate the Secure Boot State
- If the label shows On, then Secure Boot is already enabled. If it shows Off, you’ll need to enable it manually
How to enable Secure Boot in Windows 11
If Secure Boot is not enabled, you can turn it on through the BIOS settings:
- Restart your PC and wait for the BIOS splash screen to appear
- As the splash screen appears, press the key to access the BIOS menu. This is typically Delete, F12, or another key specific to your manufacturer
- Navigate through the BIOS menu to find the Security or Boot section. This may vary depending on your motherboard
- Look for the Secure Boot option. It will typically appear as a toggle or dropdown menu
- Set Secure Boot to Enabled
- Exit the BIOS, save the changes, and restart your PC
Once enabled, your system will now use Secure Boot to help prevent unauthorized software from running during startup.
What is Secure Boot and why is it so important?
Secure Boot acts as a vital system safeguard by verifying the digital signatures of firmware, bootloaders, and drivers before allowing them to run. When your PC boots, Secure Boot verifies that the UEFI firmware is signed and trusted, checking every critical piece of software before it loads.
For instance, if a rootkit—a type of malware that runs deep within the kernel—is present, Secure Boot helps prevent it from being loaded. By ensuring only trusted software is allowed to run, Secure Boot protects against threats like bootkits, which can hijack the bootloader and gain full control over the operating system.
Introduced with Windows 8, Secure Boot is now a fundamental requirement for Windows 11. All certified x86-based Windows devices must have Secure Boot enabled by default, trust Microsoft’s certificates, and allow users to customize Secure Boot to trust non-Microsoft software or disable it entirely if needed.
Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report — the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
Why would you disable Secure Boot?
Although Secure Boot enhances security, there are certain scenarios where disabling it might be necessary. For example, if you’re running specific Linux distributions or legacy versions of Windows, Secure Boot may prevent those operating systems from loading. In such cases, disabling Secure Boot temporarily allows for the installation and use of non-signed software.
However, it’s important to remember that turning off Secure Boot reduces your system’s protection against malware and unauthorized software, so it’s recommended only for specific use cases where compatibility is a concern.
Troubleshooting common secure boot issues
In some cases, you may encounter issues when trying to enable Secure Boot. Here are a few common problems and their solutions:
- Secure Boot is grayed out in BIOS: This can happen if your system is set to Legacy Boot Mode instead of UEFI. To fix this, switch to UEFI Mode in the BIOS settings
- System won’t boot after enabling Secure Boot: Double-check that your operating system and bootloader are UEFI-compliant. If they aren’t, your system may fail to boot, and you’ll need to revert the Secure Boot setting in the BIOS
- Secure Boot is enabled, but Windows still reports it as off: Ensure your BIOS firmware is up to date, as outdated firmware can cause Windows to misreport Secure Boot status
Further reading on Windows 11 and security
To learn more about Windows 11 security features, check out our other guides. We cover everything from how to boot into Windows 11 Safe Mode to managing encryption tools like BitLocker, ensuring your PC meets the latest security standards. For those exploring Linux or other OS setups, see our articles on comparing Windows 11 with Linux, UEFI settings, and switching to Linux from Windows.
В безопасном режиме (Safe Mode) загружаются только программы, установленные на Виндовс по умолчанию. И то не все, потому что работают только те, которые обеспечивают минимальную работоспособность. Набор приложений без заставки (просто черный экран), все значки крупнее обычного и даже будто в пикселях, устройство может даже медленнее работать. В общем, тут все строго и по делу.
Зачем может пригодиться безопасный режим? Это специальная опция для устранения неполадок и выявления причин поломки (или как минимум для сужения круга причин):
- вы обновили драйвера или установили программу и затем устройство перестало загружаться или начало зависать;
- появляется ошибка с синим экраном смерти;
- ПК постоянно перезагружается;
- нужно проверить ПК на вирусы (или загрузить антивирус)
- большинство вирусов не загружаются в этом варианте работы Виндовс;
- при любых сбоях и неисправностях системы.
Когда все спокойно, компьютер не глючит, не выскакивают ошибки, значит, проблема не в ОС и ее программах. Его еще называют диагностическим режимом.
Как включить безопасную загрузку Windows?
На каждой из версий ОС есть несколько способов и вариантов безопасности.
Windows 10, 11
Начнем с самой популярной сейчас 10-ки. Для 11-той алгоритмы похожи. На них наибольшее количество методов.
Из настроек
Меню Пуск (значок Виндовс в левом нижнем углу) – Параметры – раздел Обновление и безопасность («Система» на 11 версии) – Восстановление – Особые варианты загрузки (Расширенные параметры запуска в 11 ОС) – Перезапустить сейчас.
Выбор действия – Поиск и устранение неисправностей – Диагностика – Дополнительные параметры – Параметры загрузки.
Выпадает целый список, среди них нас интересует:
- безопасный режим F4;
- … с загрузкой сетевых драйверов F5, когда необходим интернет или доступ к другим ПК по локальной сети;
- … с поддержкой командной строки F6. Разработчики Microsoft советует использовать ее только айтишникам. Но ниже мы дадим точные алгоритмы, как использовать строку, чтобы не навредить устройству, а наоборот помочь.
В этом списке выбор осуществляется кнопками F (в некоторых случаях только цифрами 4, 5, 6).
С помощью Shift
Зажмите клавишу и в значке питания выберите Перезагрузка.
После перезапуска Виндовс – Выбор действия – Поиск и устранение неисправностей и те же разделы до пунктов F4, 5, 6 (зависит от вариантов режима).
При нарушении нормального рабочего процесса
Когда предыдущий сеанс был резко завершен, без привычного постепенного завершения, то при новом включении сначала на заставке появится надпись Диагностика компьютера. Чтобы специально запустить этот процесс (хотя это и рискованно), принудительно отключите и включите ПК кнопкой питания. Можно даже резко выдернуть розетку. Обычно достаточно трех попыток.
Появится Автоматическое восстановление – Дополнительные параметры – Поиск и устранение неисправностей… и далее тот же путь до списка загрузок – F4.
Через конфигурации системы
Приложение, используемое для запуска системы и поиска и устранения ошибок и поломок.
Win+R – Выполнить – печатаем msconfig. А можно написать название приложения в поисковике меню Пуск.
Откроется Конфигурация системы – Загрузка – Безопасный режим (ставьте галочку) – Минимальная.
В дальнейшем, когда закончите работу, снова откройте в приложение и уберите метку.
С загрузочной флешки
Перед этим в Биос в разделе Boot поставьте на первое место (1st Device) этот USB, чтобы запуск начался с внешнего носителя.
В окне, где предлагается выбрать язык, нажимаем Далее – Восстановление системы – Поиск и устранение неисправностей – Дополнительные параметры – Командная строка. Или попробуйте вместо этого вызвать ее комбинацией Shift+F10.
В черном окне печатаем bcdedit / set {default} safeboot minimal (вместо последнего слова печатаем network, если нужен интернет). Клавиша Enter. Перезагрузите.
Когда нужно вернуться к обычному режиму винды, то снова подключаем флешку, доходим до командной строки, но пишем другую команду bcdedit / deletevalue {default} safeboot. Клавиша Enter. Перезапуск.
Или через окно Конфигурации.
Windows 8
Для восьмерки актуальны те же способы, что и на 10.
Параметры (шестеренка) – Изменение параметров компьютера – Обновление и восстановление – Восстановление… Идем по знакомому алгоритму и выбираем нужный пункт, нажав F4, 5 или 6.
Windows 7
Для семёрки подходит метод с Конфигурацией: вызовите окно Выполнить, нажав Win+X, но перед вкладкой Загрузки сначала выберите Общие – Диагностический запуск.
Причем бывают случаи, когда в этом диагностическом запуске даже не работают устройства, подключенные по USB (мышки и клавиатуры).
А вообще в этой версии, в отличие от 8, 10 и 11, где ускорен процесс загрузки Windows, работает простой способ – перезапуск и удерживание F8.
Безопасная загрузка на Windows 11
Отдельный вопрос для 11 версии. Безопасная загрузка – это специальный вид загрузки, необходимый для установки новой ОС. Не путать с безопасным режимом.
Как включить безопасную загрузку Виндовс 11?
Проверьте есть ли такая конфигурация на вашем устройстве:
Сведения о системе – пункт Режим BIOS – значение UEFI.
Тут же ищем Состояние безопасной загрузки – Вкл.
Чтобы активировать Secure Boot:
Параметры – Обновление и безопасность – Восстановление – Особые варианты загрузки – Перезагрузить сейчас.
Выбор действия – Поиск и устранение неисправностей – Диагностика – Дополнительные параметры – Параметры встроенного ПО UEFI. Перезагрузить.
В UEFI – Secure Boot Control – Enable.
Мы охватили все способы для всех версий. Больше всего методов применяется на последних версиях ОС 10 и 11. Безопасный режим – крайне полезная опция, она есть на любых устройствах (ПК, лэптопы, планшеты и смартфоны).
В 11 Виндовс особый вид безопасной загрузки Secure Boot стал обязательным условием установки. Функция проверяет загружаемую ОС на наличие цифровой подписи, вирусы и осуществляет контроль загрузок. В случае ошибок сразу блокирует установку.
Когда удается войти в Диагностический режим, значит, для вашего ПК еще не все потеряно. Хуже, если не получается зайти:
- попробуйте «откатить» систему до последней сохраненной точки;
- просканируйте систему и дайте ей исправить неполадки: Win+R – Выполнить – печатаем cmd. В черном окне печатаем sfc / scannow и клавиша Enter;
- сторонние утилиты: Safe Mode Fixer и AVZ.
Когда обычный режим тоже не работает, то остается только переустановка ОС.
The process of booting Windows involves launching the operating system on your computer. Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode of an operating system that starts the system with only the minimum set of drivers, services, and applications required to function. By starting in the Windows Safe mode, the system can diagnose and fix various issues preventing the computer from working correctly.
Safe Mode is typically used for troubleshooting purposes and is commonly accessed by pressing a specific key during startup. However, many people are unaware of booting windows 11 in safe Mode. This article will explain six methods, from booting up from the start menu to launching the Command prompt with easy-to-follow steps, so stick with us.
What is Safe Mode in Windows
Windows Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode of Windows that starts the system with only essential drivers and services necessary for the operating system to function. When booting into Windows Safe Mode, non-essential drivers and services are disabled, allowing you to troubleshoot and diagnose issues with your computer. A safe mode is essential for resolving issues with your computer, as it will enable you to isolate and fix problematic drivers and software that may be causing problems.
This article will explore Windows 11 Safe Mode, how to access it, and how it can diagnose and resolve issues on your Windows computer. Whether you are a novice or an experienced user, we aim to provide you with the knowledge and skills to utilize Safe Mode in Windows effectively.

When Should You Start Windows 11 in Safe Mode
Wondering why you bot windows 11 in safe Mode? This section is for you as it will explain various scenarios where starting your Windows 11 PC in Safe Mode may be necessary:
- 🎯Troubleshooting Startup Issues: If your computer is having trouble starting up or is stuck in a boot loop, starting it in Windows 11 Safe Mode can help you identify and fix it.
- 😈Removing Malware and Viruses: Windows 11 Safe Mode can also help remove malware and viruses from your computer.
- ⚡Resolving Driver Conflicts: If you recently installed a new driver or software and are experiencing issues with your computer, starting it in Windows 11 Safe Mode can help you identify and resolve any driver conflicts. In Safe Mode, you can uninstall problematic drivers or software causing issues.
- 🩺Diagnosing Hardware Issues: If your computer is experiencing hardware issues such as overheating, starting it in Windows 11 Safe Mode can help you identify and diagnose the problem. In Windows 11 Safe Mode, your computer uses minimal resources, which can help you determine if the issue is related to hardware or software.

How to Start Windows 11 in Safe Mode
Need help starting windows 11 in safe Mode? Look no further! Please watch this handy tutorial with easy-to-follow steps to help you boot up in safe Mode. Let us look into some significant events:
- 00: 10 — First method using msconfig
- 01: 20 — The second method uses shift and restart
- 03: 00 — Final method using the fail-safe Mode
- 03: 25 — Boot into safe Mode
- 03: 38 — Proceeds to end
- Fix 1. Boot Windows into Safe Mode from the Start Menu
- Fix 2. Cease Normal Booting of Windows 11 to Enter Safe Mode
- Fix 3. Start Safe Mode Using Advanced Startup on Windows 11
- Fix 4. Start Windows 11 in Safe Mode by System Configuration
- Fix 5. Boot Windows 11 in Safe Mode Using a Recovery Drive
- Fix 6. Launch CMD Prompt to Boot into Safe Mode
Fix 1. Boot Windows 11 into Safe Mode from the Start Menu
The Start Menu is a graphical user interface element in the windows operating system that provides quick access to frequently used applications, documents, and settings. This can be useful in troubleshooting and resolving issues with your computer. Here are the steps on how to boot Windows 11 into Safe Mode:
Step 1. Click on the «Start» button in the bottom left corner of your windows.
Step 2. Click on the «Power» icon and hold the «Shift» key on your keyboard.
Step 3. While holding the Shift key, click the «Restart» option.
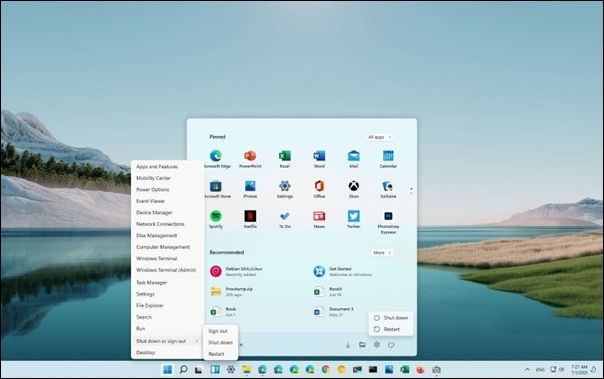
Step 4. Wait till your windows restart. Now, choose Safe Mode from the provided options to boot your computer into Safe Mode.
Fix 2. Cease Normal Booting of Windows 11 to Enter Safe Mode
Cease normal booting of Windows 11 refers to interrupting the normal boot process of your computer and forcing it to start in Windows 11 Safe Mode. Ceasing normal booting can be more complicated than other methods, but it can be helpful when other methods fail. To stop the normal booting of Windows 11 and enter Safe Mode, follow these steps:
Step 1. Press and hold your computer’s «power» button until it shuts down completely.
Step 2. Press the power button again to turn your computer back on.
Step 3. When you see the manufacturer logo on the screen, press the «power» button again until your computer shuts down.
Step 4. Repeat this process two more times. On the third Restart, your computer will automatically enter the Windows Recovery Environment. From here, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart. Finally, press the F5 key to boot your computer into Safe Mode with Networking.
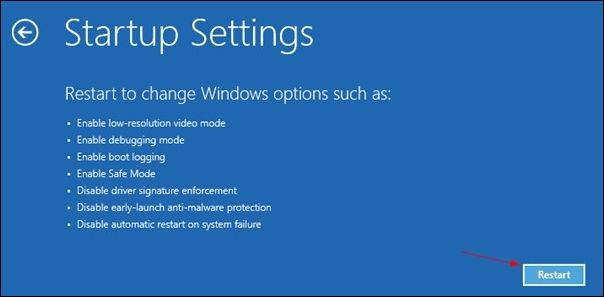
Fix 3. Start Safe Mode Using Advanced Startup on Windows 11
The advanced startup is a Windows 11 feature that allows you to access various troubleshooting options, including Safe Mode, when your computer is having problems. It is a straightforward process that can be very useful in troubleshooting and resolving issues with your computer using the below-mentioned steps:
Step 1. Click on the Start button and select Settings (gear icon).
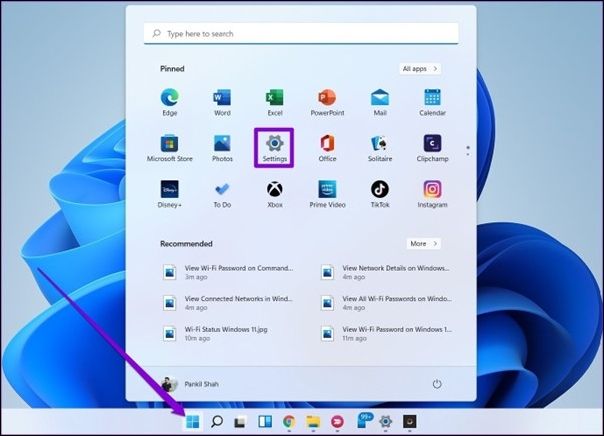
Step 2. In the Settings window, click on the System option.
Step 3. From the System menu, select Recovery from the menu.
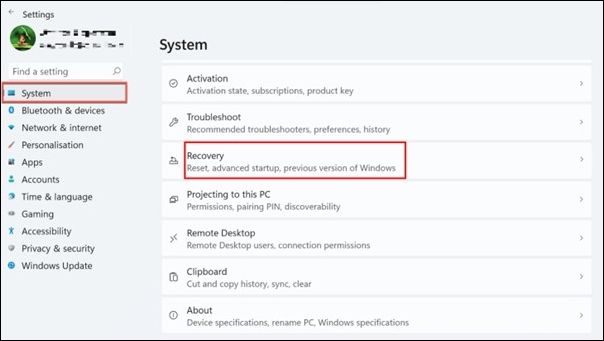
Step 4. The Restart Now button may be found under the Advanced Startup header. Choose Restart under Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Options from now on. Lastly, to start your computer in Safe Mode with Networking, use the F5 key.
Fix 4. Start Windows 11 in Safe Mode by System Configuration
System Configuration, also known as msconfig, is a built-in utility in windows operating systems that allows users to manage system settings and configure various options related to startup and services. It provides an interface to view and modify system startup programs, services, and boot options.
Step 1. Press the Window + R keys on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
Step 2. Type msconfig into the search field and press Enter.
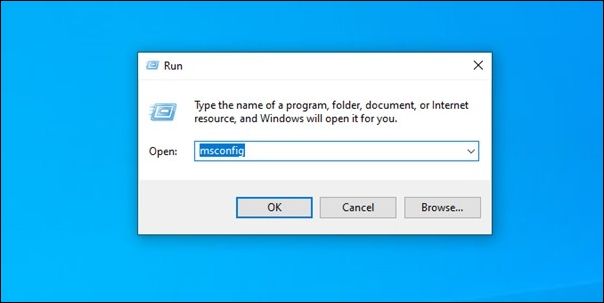
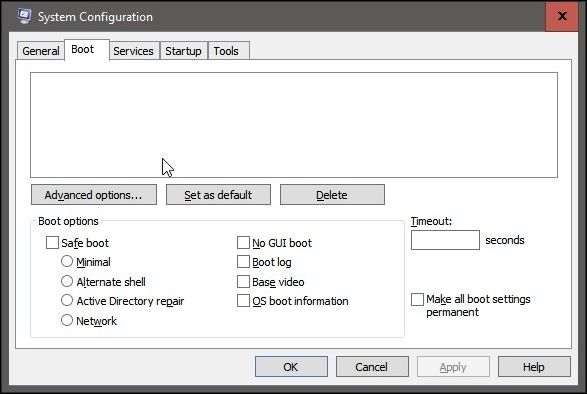
Step 3. In the System Configuration window that appears, click on the Boot tab.
Step 4. Now select the Safe boot option and then click on OK. Your computer will now restart in Safe Mode.
Fix 5. Boot Windows 11 in Safe Mode Using a Recovery Drive
A recovery drive is an efficient tool in windows based-systems that allows users to access the Windows Recovery Environment and troubleshoot several issues related to the system. It is a USB or DVD drive that contains essential system files and drivers. It is a handy tool to help you recover your system in case of a critical error, malware attack, or other issues using the quick and easy steps below:
Step 1. Allow your computer to start up using the bootable USB drive.
Step 2. Pick a keyboard layout option in the «Choose your keyboard layout» window.

Step 3. When «Choose on windows» appear, click on «Troubleshoot.»
Step 4. Lastly, click on «Advanced Options» > «Startup Settings» > «Restart,» and choose the relevant kind.
Fix 6. Launch CMD Prompt to Boot into Safe Mode
CMD prompt, or Command Prompt, is a command-line interface program in windows operating systems that allows users to execute commands and perform various tasks using a command-line interpreter. It provides a text-based interface to interact with the operating system and run system commands, scripts, and batch files. Here are the steps to launch Command Prompt and start windows 11 in Safe Mode:
Step 1. Open the search bar and enter cmd to access Command Prompt.
Step 2. Type shutdown.exe /r /o on the command line and press Enter.

Step 3. Close the pop-up message that appears, allowing windows to reboot into Recovery Mode.
Step 4. After selecting Advanced Options and Startup Settings, choose Troubleshoot. After the computer restarts, you will see the Safe Mode choices if you click Restart in the Startup Settings box.
Several users have proved the efficacy of these fixes to boot Windows 11 Safe Mode. If one of the methods is helpful, share it on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and other social media platforms!
Will I Lost My Data After Booting into Safe Mode
Will starting in Safe Mode delete all data on a computer? The answer is no, Safe Mode is designed to troubleshoot issues and provide a clean boot environment, and it does not delete any data. However, there are certain situations where data loss may occur, such as if you accidentally delete files or mistakenly use the Command prompt to boot the Windows 11 Safe Mode.
To ensure the safety of your data, it is always a good idea to have a backup and recovery plan in place. If data loss does occur, a specialized data recovery tool — EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard can be beneficial.
- It is designed to recover permanently deleted files due to file system malfunctions, system crashes, and accidental file deletion.
- It has a user-friendly GUI that makes it easy for even novice users to recover files quickly.
- Its key features include recovering data from various devices and file types.
- It has a preview function to see recoverable files before Recovery.
- The deep scan mode ensures maximum recovery success.
If your Windows cannot boot in Safe Mode, you can try to create a bootable disk to restore your lost data. Here are the specific steps:
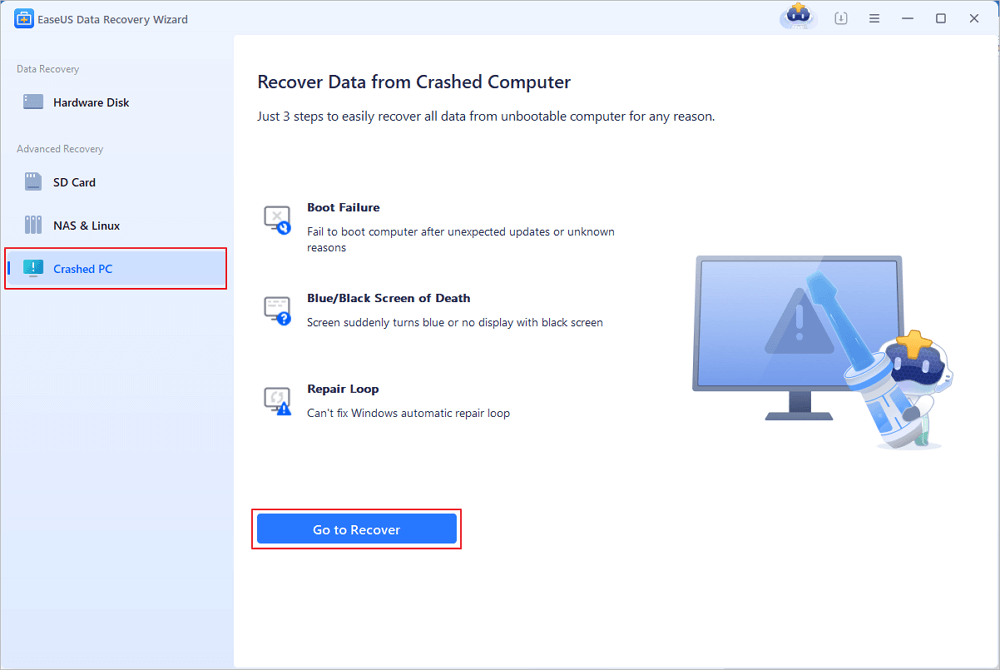
Step 1. Create a bootable disk
Launch EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, choose «Crashed PC» and click «Go to Recover».
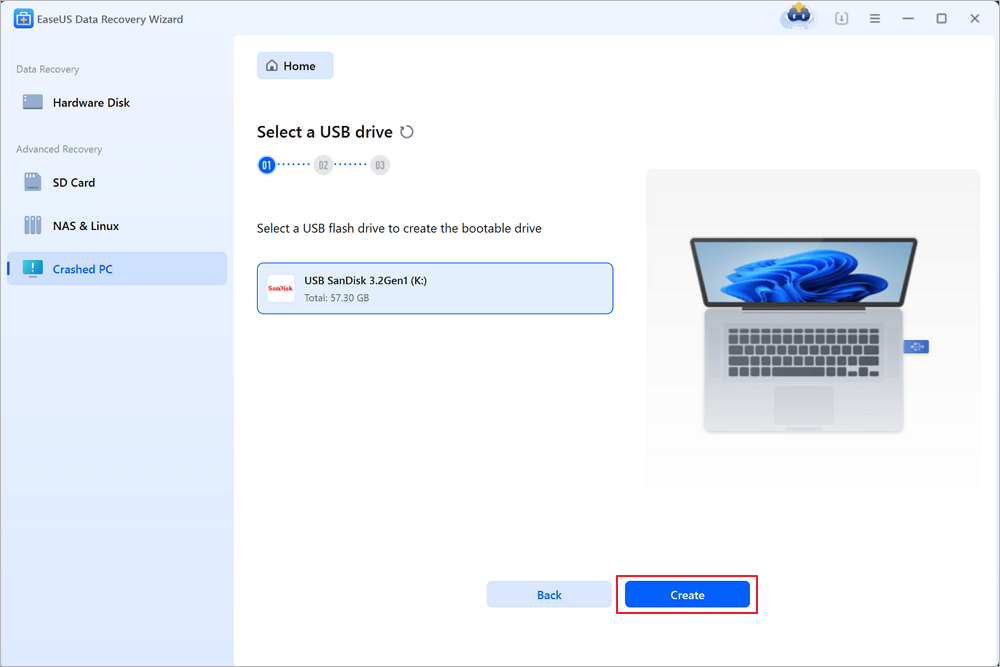
Select an empty USB to create the bootable drive and click «Create».
⚠️Warning: When you create a bootable disk, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard will erase all data saved in the USB drive. Back up important data beforehand.
Step 2. Boot your computer from the bootable USB
Connect the bootable disk to the PC that won’t boot and change your computer boot sequence in BIOS. For most users, it works well when they restart their computer and press F2 simultaneously to enter BIOS.
Set to boot the PC from «Removable Devices» (bootable USB disk) beyond Hard Drive. Press «F10» to save and exit.
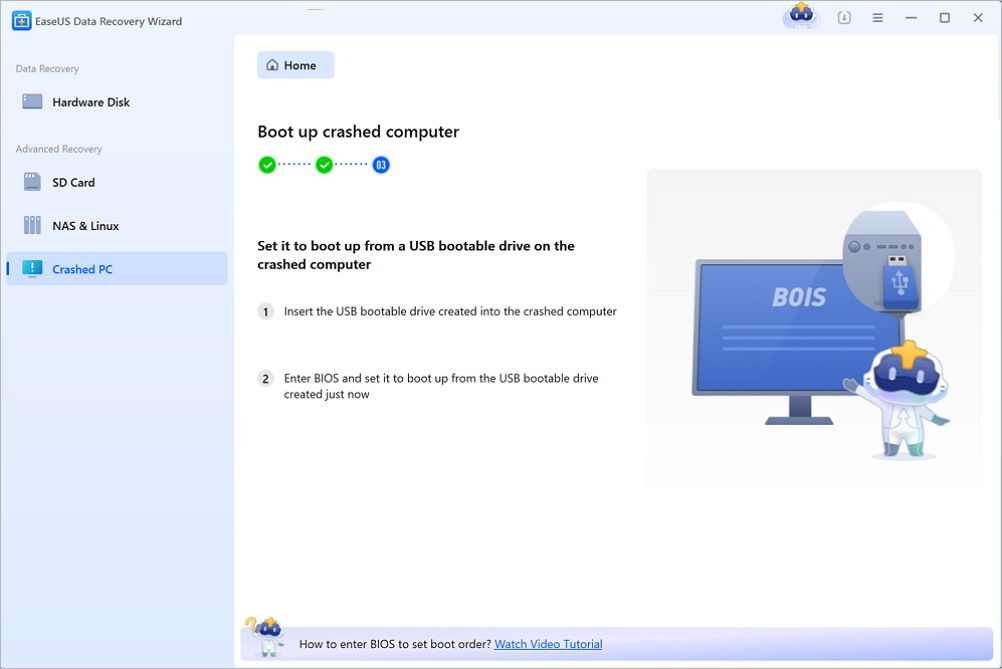
Step 3. Recover data from a crashed system/PC
After booting from EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard bootable disk, select the drive you want to scan to find all your lost files. Preview and recover the files you need to a safe location.
💡Tip: You can restore data on the local disks, external hard drives, and also the cloud storage.
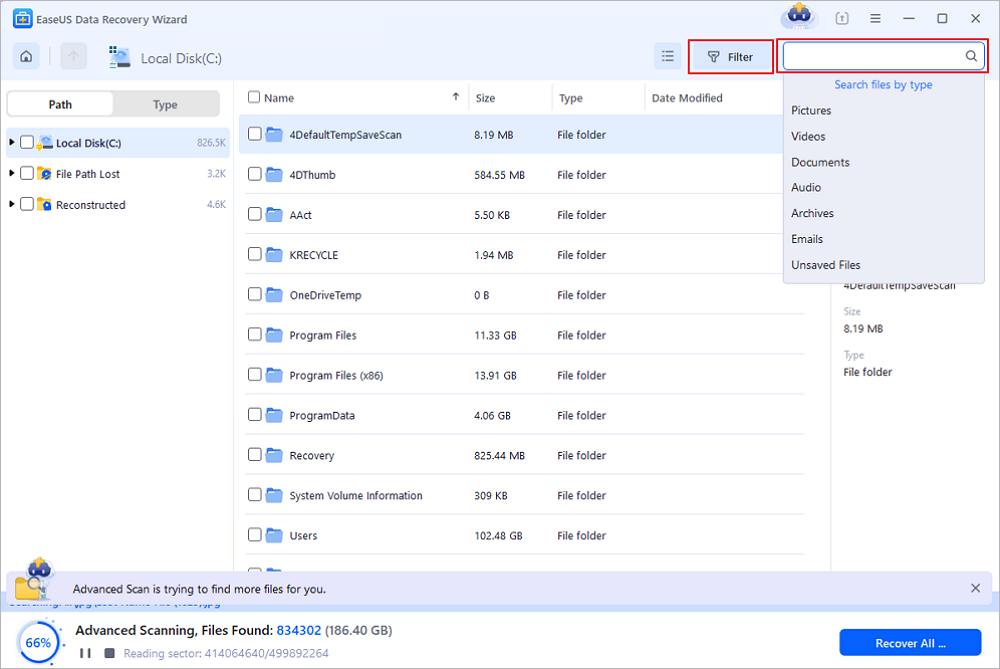
Final Words
In summary, Safe Mode on windows is a powerful tool that allows users to troubleshoot problems on their PC. However, it is essential to note that there is a risk of data loss when using Safe Mode. To ensure data security, users can install specialized data recovery software such as EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, which can recover lost files. Additionally, this post provided step-by-step guides on boot Safe Mode on Windows 11.
Windows 11 Safe Mode FAQs
Are you still having some doubts? Worry no more, as this section will briefly answer some of the commonly asked questions mentioned below:
1. Can I boot Windows 11 in Safe Mode from power off?
Yes, you can boot Windows 11 in Safe Mode from power off. Hold the power button until the computer turns off, then turn it back on. Repeat this process three times, and on the fourth time, Windows 11 will boot into the Advanced Startup options, from where you can access Safe Mode.
2. How to exit Safe Mode?
To exit Safe Mode on Windows 11, click on the Start menu and type «msconfig» in the search bar. Select «System Configuration» and navigate to the «Boot» tab. Deselect the «Safe boot» option and click «OK.» Finally, restart your computer to exit Safe Mode.
3. Can I get to Safe Mode from BIOS?
Yes, you can get to Safe Mode from BIOS on some computers by pressing the F8 key repeatedly during startup. However, depending on the manufacturer and BIOS version, this method may only work on some computers. Another way to access Safe Mode is through Windows’s Advanced Startup Options menu.
4. How do I force my computer to start in Safe Mode?
To force a computer to start in Safe Mode on Windows 11, press and hold the shift key while selecting «Restart» from the Start menu. This will bring up the Windows Recovery Environment, where you can choose «Troubleshoot» > «Advanced options» > «Startup Settings» > «Restart» and then select option 4 or press F4 to start in Safe Mode.