Обновлено:
Опубликовано:
Тематические термины: MTU, Windows, Linux, FreeBSD
В данной инструкции описаны способы просмотра значения MTU для различный операционных систем. Также в конце статьи будут указания по его смене.
Windows
Linux
FreeBSD
Провайдера
Смена MTU
Дополнительные материалы
Windows
Нажмите комбинащию клавишь Win + R
В появившемся окне введите cmd и нажмите OK

В открывшемся черном окне введите команду:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
В первой колонке ответа мы увидим значение MTU:

* в данном примере, значение MTU равно 1500 для сетевого адаптера Ethernet.
В Powershell можно использовать команду:
Get-NetIPInterface | where {($_.ConnectionState -eq «Connected» )}
Linux
ip address
В более современных системах используется утилита для работы с сетевыми интерфейсами — ip address. Вводим команду:
ip a
В полученном результате находим нужный сетевой интерфейс и строчку на подобие:
eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
* то, что мы ищем — mtu 1500.
ifconfig
В более ранних системах или с установленным ifconfig вводим:
ifconfig eth0
* где eth0 — сетевой адаптер, для которого хотим узнать MTU.
В полученном результате находим что-то на вроде:
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
* где mtu 1500 — наше значение.
FreeBSD
В данной системе работаем с уже описанным выше ifconfig:
ifconfig em0
Получаем:
em0: flags=8843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,SIMPLEX,MULTICAST> metric 0 mtu 1500
Провайдера
Чтобы определить оптимальное значение MTU для нашего сетевого адаптера, подключенного к сети Интернет, необходимо узнать значение, используемое на оборудовании поставщика.
Для этого выполняем ping с запретом фрагментации сетевых пакетов (-f) и выставлением определенного размера пакета (-l):
ping dmosk.ru -f -l 1472
* 1472 будет соответствовать MTU — 1500, так как к пакету мы должны еще прибавить 28 (заголовок).
Наша задача — подобрать значение пакета, при котором будет идти пинг:
Ответ от 90.156.242.197: число байт=1472 время=13мс TTL=56
Ответ от 90.156.242.197: число байт=1472 время=12мс TTL=56
Если мы видим:
Требуется фрагментация пакета, но установлен запрещающий флаг.
Требуется фрагментация пакета, но установлен запрещающий флаг.
Значит значение -l нужно уменьшить, пока сигнал не начнет проходить.
Находим значение, которое стоит на границе с ошибкой и прибавляем к нему заголовок пакета — 28. Так мы получаем наше оптимальное MTU.
На данный момент большинство Интернет провайдеров предоставляет услуги связи с фрагментом в 1500. Старые подключения от Ростелеком или подключения на основе PPPoE могут работать на меньших значениях.
Как изменить MTU
Для смены значения MTU в Windows и Linux нужно использовать командную строку. Для Windows также можно отредактировать реестр.
Подробнее о этом читайте в инструкции Смена MTU.
Читайте также
Другие материалы по теме:
1. Как узнать MAC-адрес сетевой карты.
2. Как поменять MAC-адрес на компьютере с Windows.
3. Настройка сети в Linux с помощью netplan.
4. Настройка сети в CentOS и Rocky Linux.
5. Управление сетевыми маршрутами в CentOS 7.
Обратите внимание. В мае 2025 года существенное снизились цены на вечные виртуальные серверы VPS/VDS в России и Нидерландах. Для читателей блога дополнительная скидка 10%. Подробнее.
Параметр MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit; максимальная единица передачи) означает максимальный размер пакета, который может быть передан по сети без фрагментации. В этой статье я расскажу как узнать его оптимальное значение и скорректировать если вы столкнулись с проблемами передачи данных по сети, например, по неизвестной причине не открываются определенные веб-страницы или присутствуют ошибки при передаче файлов.
При использовании неправильного размера MTU возможны проблемы с открытием некоторых сайтов в браузерах, сбои в работе VoIP-телефонии, проблема с приемом или передачей файлов по сети. Для исправления такой ситуации нужно проверить установленное текущее значение MTU, а также выяснить оптимальный его размер. Использование оптимального размера MTU может значительно улучшить производительность сети. Максимальная скорость достигается, когда все пакеты в потоке имеют длину, равную значению MTU.
Во многих сетевых устройствах имеется возможность установить вручную значение MTU для нужного интерфейса, но нужно правильно определить его оптимальный размер.
Важно!!! Если доступ в Интернет и передача данных работают корректно, не стоит экспериментировать с параметром MTU, т.к. при выполнении неверных действий вы можете только ухудшить работу домашней сети.
Типовые значения MTU для различных сетевых топологий
Каждый тип среды имеет свой максимальный размер пакета передачи.
- Ethernet — 1500
- PPPoE — 1492
- L2TP — 1460
В самом массовом сегменте в сетях Ethernet, то есть у большинства у нас дома и на работе, значение MTU равно 1500.
Однако, при подключение к другим сетям, например к интернету, в зависимости от типа подключения значение MTU может быть иным и важно, чтобы оно было оптимальным.
Где необходимо настраивать значение MTU? Если провайдер использует подключение PPPoE, а у вас дома Wi-Fi роутер, то настраивать значение MTU необходимо в маршрутизаторе на интерфейсе к которому подключен провайдер.
Самый простых и точный способ определения оптимального размера MTU в Windows
Чтобы узнать текущее значение MTU воспользуемся утилитой ping. С помощью неё будем отправлять запросы в сеть и изменять размер пакета до тех пор, пока не появится, либо исчезнут сообщение о необходимости фрагментации пакета.
Для запуска команды ping нажмите комбинацию клавиш [win]+[r] и наберите cmd.
Затем нажмите клавишу [OK]
Теперь в интерфейсе командной строки введите команду:
ping ya.ru -l 1500 -f
здесь:
- -l 1500 — длина отправляемого пакета
- -f — запрет на фрагментацию пакетов при передаче
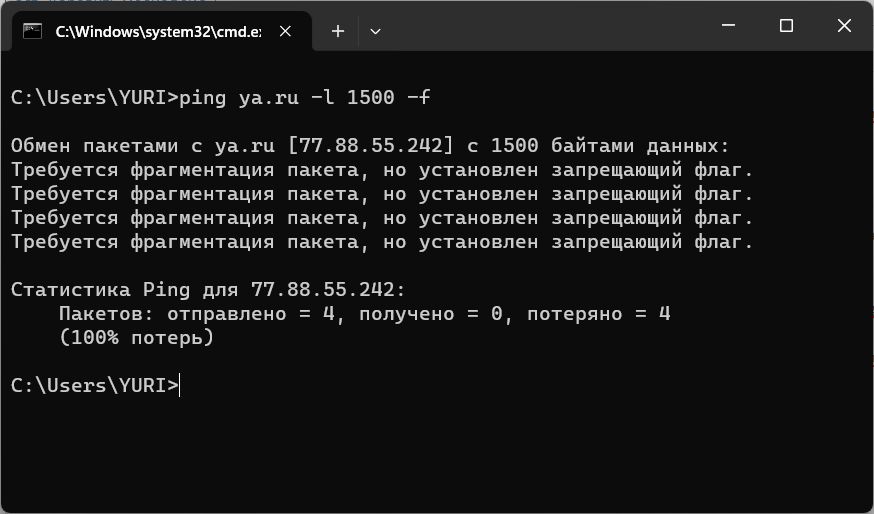
В моем примере видно, что значение MTU при доступе в интернет меньше типового значения для сетей Ethernet 1500 байт.
Будем плавно уменьшать размер отправляемого пакета, пока он не перестанет фрагментироваться.
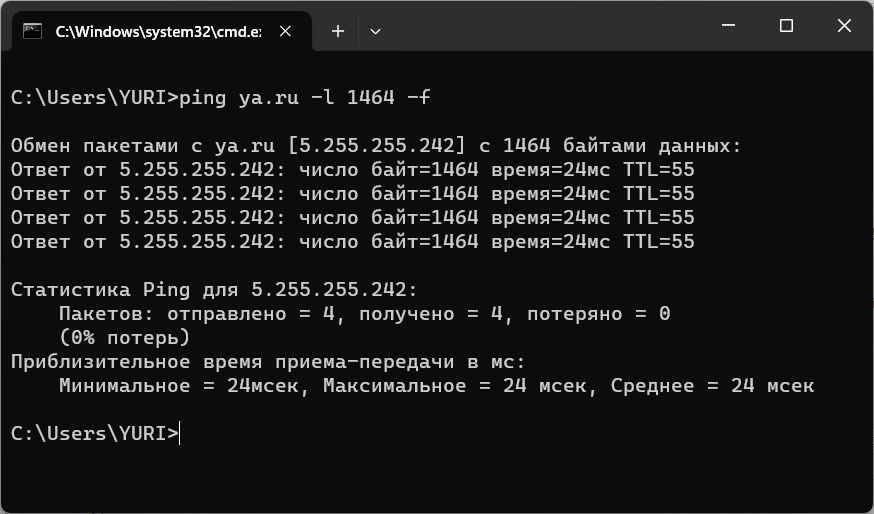
Получаем результат, что пакеты длиной 1464 байта не фрагментируются. Но это еще не значение MTU! К полученному значению необходимо прибавить 28 байт которые зарезервированы под заголовок данных (20 байт для заголовка IP и 8 байт для заголовка запроса протокола ICMP). Для нашего примера MTU=1464+28=1492 байт — это и есть оптимальное значение параметра MTU.
В моем примере значение MTU 1492 байта необходимо прописать на внешнем интерфейсе маршрутизатора подключенного к провайдеру интернет.
Какие бывают проблемы когда неправильно настроен MTU
Возможные варианты неоптимального MTU:
- В большинстве случаев вы ничего не заметите
- Уменьшение скорости передачи данных, медленно открываются сайты
- Некоторые (многие, все) сайты не открываются.
Постскриптум
Как правило, домашние маршрутизаторы в зависимости от типа подключения самостоятельно определяют оптимальное значение MTU и дополнительно ничего настраивать не нужно.
Благодарности
При написании статьи были использованы следующие источники:
- Как определить оптимальный размер MTU
After I released the MTU Optimizer, a small tool for determining the optimal MTU, some days ago, let’s look at how to determine the optimal MTU by hand, how to read the currently set MTU and how to set new MTU value now. Of course we will discuss the whole thing for the three major operating systems: Windows, OSX and Linux.
Before we look at the implementation within the individual operating systems, we first briefly clarify what the MTU is and how its optimal value can be calculated.
Theory – Identify ideal MTU
The MTU (Maximum Transfer Unit) describes the maximum packet size of a protocol. It therefore indicates the maximum size of a data packet, so that it can be transmitted via a protocol. If a data packet is larger, it becomes fragmented – i.e. divided into several packages.
For example, let’s assume that we (=PC) would have a factory for sugar packets and our packet size (=configured MTU) would be 1.5kg. Now the bakery has ordered 5 packages (5 x 1.5 kg) of sugar, but our postman (=network interface) can only transfer packets with a maximum size of 1kg (=protocol limit). What is he doing now? He fragments our sugar packets and divides them into 1kg and 0.5kg packs. So he needs two packages for transmission of one of our initial sugar packages. In addition, the postman has more work, because he has to mark which packages belong together. These multi-packets (=overhead) slow down the sending of packets (=data transfer speed).
No products found.
To solve the problem and speed up the shipping, we would have to dimension our packaging size (=MTU) so that the postman does not have to repackage (=fragment). The ideal MTU is 1kg in our case. In order to determine this value, we would have to ask the postal worker for the size limit, when he starts repackaging. The same story is true for computer systems.
In the IT, we send a data package by ping command and tell ping the size of the package as well as the info that this package should not be fragmented. If the packet size is too large, ping tells us that the package is not ok and that the package had to be fragmented, if it shall be send sucessfully.
ping -f -l 1550 www.google.de Pinging www.google.de [216.58.213.195] with 1550 bytes of data: Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set.
Now we reduce the packet size until the error message of the fragmentation is omitted. This gives us the optimal package size. However, since the MTU also includes protocol information, we still have to add 28 bytes (20 bytes = IPv4 header and 8 bytes = ICMP) to the package size value to get the optimal MTU.
Read current MTU in Windows
To display the current MTU by console, use the following command, which must be entered into the CMD (Win + R key, “CMD”, “Ok” button):
netsh interface ipv4 show interfaces
This command generates a list that looks like this (or something similar):
Idx Met MTU State Name --- ---------- ---------- ------------ --------------------------- 10 25 1528 connected Ethernet 5 55 1528 disconnected WiFi 15 55 1528 disconnected Ethernet 2
The “MTU” column shows the MTU currently set for an interface. In addition, the “Idx” column is interesting since we need the Id from this column to set a new MTU value later.
Determine the optimal MTU in Windows
To determine the optimal MTU in Windows, we use the ping command in the console. By means of the “l” parameter, we set the packet size (this should be larger than the expected MTU for the time being) and use the “f” parameter to indicate that the package should not be fragmented.
ping -f -l 1550 www.google.de
Now we repeat the call and reduce the buffer size (in example 1550) with each call. If the ping could be executed and no longer show “packet needs to be fragmented but DF set” we are almost ready. To get the MTU size we add 28 bytes (header infos).
Set the MTU value in Windows
To set the MTU for a network interface, we need the desired MTU value as well as the ID of the network interface. The Id can be taken from the interface list from the section “Read current MTU in Windows” of this article. We found the MTU in the last paragraph. With the two values we can now set the MTU in the CMD with the following command.
netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface {id} mtu={mtu} store=persistent
The placeholders {id} as well as {mtu}, must be exchanged by the corresponding values. If the command does not work, please restart the CMD by right-clicking “Run as administrator”.
MTU in OSX
Read current MTU in OSX
To read out the current MTU in OSX, either the network setting dialog or a short terminal command can be used. If the MTU shall be read out via the settings dialog, it can be found in “System Settings -> Network -> Additional Options -> Hardware”. On the hardware tab, set the configuration to “manual” and the MTU to “custom”. The MTU can then be read out. (Important: If the MTU shall be set by the system, the hardware dialog must be closed with “Cancel”!)
If the MTU shall be read out via the terminal, this can be done via the following shell command:
networksetup -getMTU {iface}
The value {iface} must be replaced by the name of the interface that is to be read out. A list of all interfaces and their names can be displayed using the ifconfig command.
Determine the optimal MTU in OSX
The determining the best MTU works (as also in Windows and Linux) by use of the ping command. For this purpose the parameters “D” and “s” must be set. The “D” parameter stands for “Do not fragment” and indicates that the package should not be fragmented. The “s” parameter specifies the size of the data packet. This initially hast to be set a little bit too large.
ping -D -s 1550 example.com
Now execute the command until the ping is successful. The “s” parameter must be reduced for each execution. If the ping is successful, add 28 to the “s” parameter value and take this sum as the MTU.
Set MTU value in OSX
To set the MTU in OSX, either the hardware dialog in the network settings (see paragraph “Reading current MTU in OSX”) or a command in the terminal can be used.
networksetup -setMTU {iface} {mtu}
The value {iface} must be replaced by the name of the interface and the value {mtu} by the MTU value. If necessary, the command must be executed via “sudo”.
MTU in Linux
Read current MTU in Linux
To display the current MTUs for network interfaces in Linux, the following command is suitable. (This must be entered in the shell/terminal.):
ifconfig| grep mtu
As a result, you should get a list of interfaces as well as their MTU values. At the beginning of the line is the respective identity, at the end of the line the MTU value.
enp3s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1384 lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536 vmnet1: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 vmnet8: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
If the command does not work, try the following command, which creates a similar list:
ip ad | grep mtu
Those who prefer to click through dialogs instead of writing console commands can find the MTU in most Linux distributions also on the graphical interface. In Kubuntu for example the MTU can also be read out via the connection editor, as shown in the adjacent screenshot. In other distributions, there are similar paths/dialogs.
Determine the optimal MTU in Linux
In order to determine the optimal MTU value in Linux, the ping command is suitable – as is the case with Windows and OSX. However, the individual parameters differ slightly under Linux. The “c” parameter specifies how many pings should be sent. The “M” parameter with the value “do” indicates that the packages should not be fragmented in any case and the parameter “s” parameter specifies the size of the package.
ping -c 2 -M do -s 1550 www.google.de
Again, you start with an obviously too large data packet and gradually reduce the value until the ping is successful. If the packet is still too large, the following (or similar) error message appears: “ping: local error: Message too long”.
If the ideal packet size is found, 28 bytes (20 bytes TCP header, 8 bytes ICMP (Ping) header) must be added to get the MTU value.
Set the MTU value in Linux
To set the MTU in Linux, either GUI dialogs or shell commands can be used. If the MTU is to be set via the graphical interface, the same dialog, which we have used two paragraphs above to read the MTU, can be used.
If the MTU is to be set via the shell, this can be done with Debian/Ubuntu systems via the network interface config file. (Other distros may require other config steps.)
nano /etc/network/interfaces
The individual interface configurations are located within the file. At the end of each interface configuration you can append
mtu {mtu}
to set a fixed MTU value. The value {mtu} of course has to be replaced by the desired MTU value. After the configuration file has been saved and closed, the interfaces should be restarted.
/etc/init.d/networking restart
No products found.
Настройка MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) знакома большинству пользователей, которые когда-либо настраивали Wi-Fi роутеры, но доступна и в Windows для Ethernet и других подключений. MTU — это максимальный размера блока данных одного пакета в байтах (без учета размера заголовка), стандартный размер — 1500 байт.
При необходимости размер MTU в Windows 11, 10 и других версий можно изменить. В этой инструкции — о том, как это сделать, а также узнать текущий размер MTU.
Способы изменения размера MTU в Windows 11 и Windows 10
Прежде чем приступить, вы можете определить текущий размер MTU для сетевых интерфейсов, для этого достаточно запустить командную строку или Терминал от имени администратора, после чего использовать следующую команду:
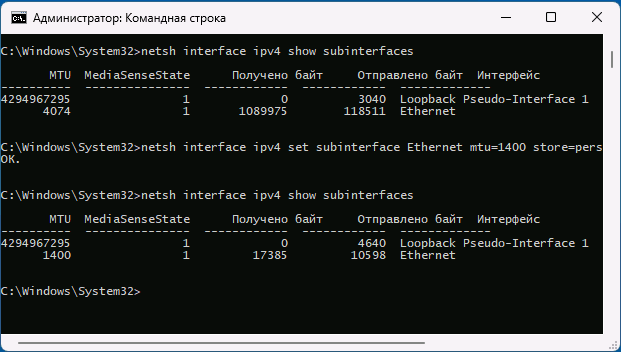
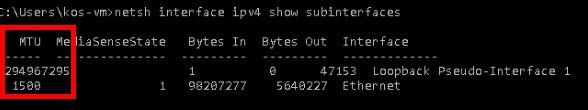
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces

Размеры MTU будут указаны в первом столбце в результатах выполнения команды. Если вам требуется изменить размер пакета, вы можете использовать один из следующих способов.
Включение Jumbo frame
Первая возможность — включить Jumbo Frame (Jumbo-кадр), позволяющий передавать данные в размере, превышающем стандартные 1500 байт. Для этого используйте следующие шаги:
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R, введите ncpa.cpl и нажмите Enter.
- В списке подключений нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по подключению, для которого нужно включить Jumbo frame и выберите пункт «Свойства».
- Нажмите кнопку «Настроить» для настройки сетевого адаптера.
- На вкладке «Дополнительно» найдите пункт «Jumbo packet» и измените его значение, затем примените настройки.
При включении Jumbo frame соединение может быть кратковременно разорвано, но обычно затем работает исправно. Учитывайте, что настройка Jumbo packet может быть доступна не для всех сетевых карт, также её наличие может зависеть от используемых драйверов.
Изменение MTU в командной строке
Вторая возможность — использование командной строки для изменения размера MTU:
- Запустите командную строку от имени администратора и введите следующую команду, чтобы посмотреть список имен интерфейсов:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
- В следующей команде измените ИМЯ_ИНТЕРФЕЙСА и значение MTU для изменения MTU для соответствующего подключения:
netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface ИМЯ_ИНТЕРФЕЙСА mtu=РАЗМЕР store=persistent
После успешного выполнения команды, размер MTU будет изменен.
Определить оптимальный размер пакета (значение MTU) для текущего Интернет-подключения можно в командной строке с помощью команды, ping адреса_сайта -f -l РАЗМЕР, например:
ping google.com -f -l 1500

Задачей будет поиск такого значения MTU, которое не приводит к сообщениям о необходимости фрагментации пакета.
As part of network troubleshooting, you may need to check or change the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) on your Windows machine network interface card. The MTU is the size of a network packet that can be communicated in a single network transmission. Learn more about testing here.
First, let’s check MTU settings in Windows.
1. Open a Command Prompt CMD (Right Click CMD -> Run Ad Administrator)
2. Type the following:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
3. Our MTU size is 1500 which is the default MTU size on most systems.
Change Windows MTU Size
1. Open a Command Prompt CMD (Right Click CMD -> Run Ad Administrator)
2. Type the following commands in order
netsh
interface
ipv4
3. Your command window will now be at the prompt to change MTU using the next command below.
4. Finally, type the following command to change your Windows MTU. In the example, we will be changing the MTU to 1200.
Note: the “Local Area Connection 3” will be name of the interface you see when you ran netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces command. This will likely be a different name.
set subinterface “Local Area Connection 3” mtu=1200 store=persistent

* Please use the comment form below. Comments are moderated.*