Одна из самых необходимых вещей, которую веб-разработчики захотят установить в Windows 10 для работы веб сервера – это службы IIS (Internet Information Services) . Подробнее про IIS и его сравнение с Apache, другим популярным веб сервером, можно прочесть в нашей статье.

Установка IIS
На самом деле это даже не установка, как таковая, а включение службы, потому что в Windows 10 этот компонент есть сразу, но он просто выключен.
Первым делом нам нужно нажать комбинацию клавиш Win + R, и после того как появится окно “Выполнить”, нам нужно набрать “appwiz.cpl” и нажать OK. Либо мы просто можем пойти в Панель управления и там выбрать пункт Программы – Программы и компоненты – Установка и удаление программ.
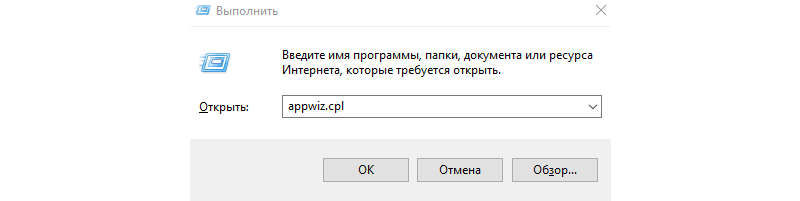
Тут нам нужно выбрать пункт “Включение или отключение компонентов Windows”.
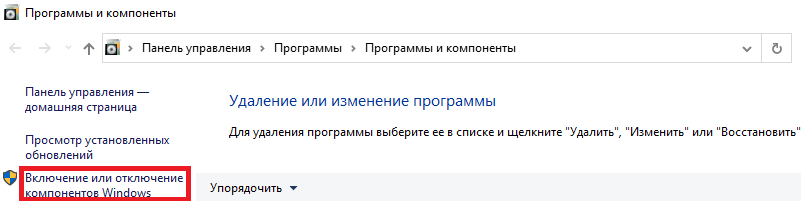
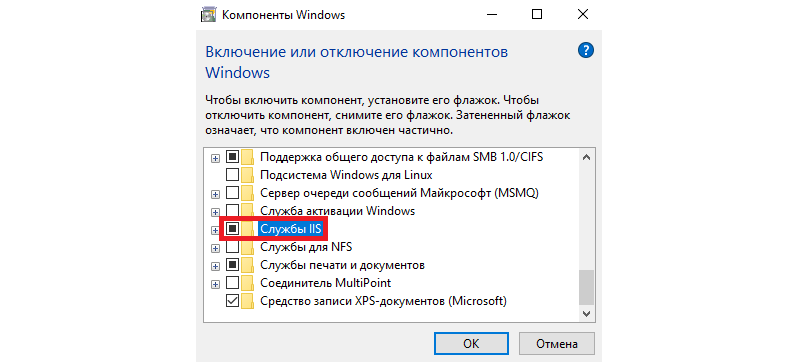
Тут находим пункт “Службы IIS”, ставим на против него галочку и нажимаем ОК, после чего служба будет включена.
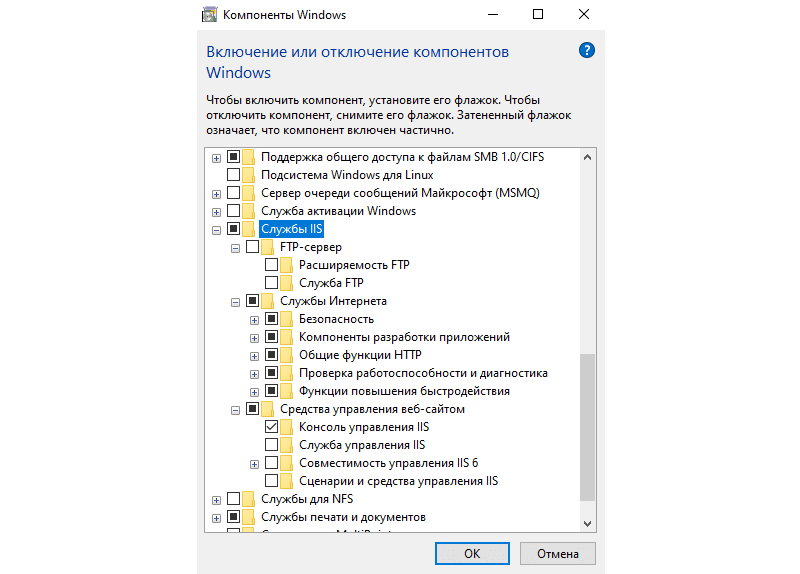
Если вам, как разработчику, нужны дополнительные параметры, то мы можете раскрыть этот пункт, нажав на плюсик, и включить или отключить те функции, которые вам необходимы.
После того как все сделано можно запустить браузер, и вбить в адресной строке localhost, чтобы убедиться, что все работает. Также в меню Пуск и в папке «Средства администрирования» появится пункт «Диспетчер служб IIS». Также туда можно попасть снова нажав Win + R и набрав inetMgr.
In this tutorial, we’ll explain, step by step, how to install IIS on Windows 10 so that you can test code or even publish web content from your desktop.
IIS is Microsoft’s web and FTP server and it is widely used by IT professionals around the world. This is mainly for two reasons. Firstly, it is already included with Microsoft Windows and is very easy to install, and secondly, it’s extremely simple to use.
It can also be installed on any Windows desktop or laptop, which means that you can even test changes or web content without needing to set up a special pilot or test environment.
NOTE: This tutorial will focus just on the installation process for Windows 10. We’re not going to go into any detail about how to use IIS today. If you’re like to learn how to install IIS on Windows Server, check out the tutorial on our blog, “How to Install IIS Web Server”.
Part 1 – Installing IIS on Windows 10
To install Internet Information Services (IIS) on a Windows 10 client device, first, click on the search bar and type «Control Panel» (1) and click on the app that appears in the results (2).

Next, double-click on Programs and Features (3).

A new window will appear. Click on «Turn Windows features on or off» (4).

Another window will now appear showing a list of features. Search the list to find Internet Information Services, expand the options and select the options you wish to install (5). The following options will be selected by default:
- Web Management Tools.
- World Wide Web Services.
«FTP Server» will be unchecked by default, but you can select it if you want to include it.
Once you’ve selected the options you want to install, click on OK (6) to begin the installation. You will then see a window with a progress bar until the process has finished.
There’s no need to restart your system to begin using the service, but we recommend it to clear the installation buffers, etc. and ensure the best performance.

Part 2 – Checking That IIS Has Been Installed Correctly
Now that the installation process has finished, it’s time to check that it has been installed correctly. First, open your web browser and type «127.0.0.1» in the address bar (7), which, if everything has run smoothly, will show the information loaded from the web server.

Another way of checking that IIS is running correctly is to open the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. Simply type «IIS» in the search bar (8) and click on Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager (9).

This will open the IIS Manager, which you can use to carry out all configuration and administration tasks for the web server.

If either of these two checks work correctly, you can safely say that you have installed IIS on your Windows 10 device. Congratulations!
Summary
In this tutorial, we’ve shown how you can quickly install IIS (Internet Information Services) on your Windows 10 device so that you can test out web content and changes from your desktop.
The process is really simple, and you should find everything you need in this tutorial, but if you have any problems, don’t hesitate to contact us.
And if you’re interested in learning about other things you can do on Windows 10, check out our article on How to Install Hyper-V on Windows 10.
Thanks for choosing Jotelulu!
Служба IIS (Internet Information Services) необходима для работы ASP.NET серверной части СпрутМонитор.
1. Перейдите в Панель Управления -> Программы -> Установка программ. Щелкните на пункт меню (слева) Включение и отключение компонентов Windows.
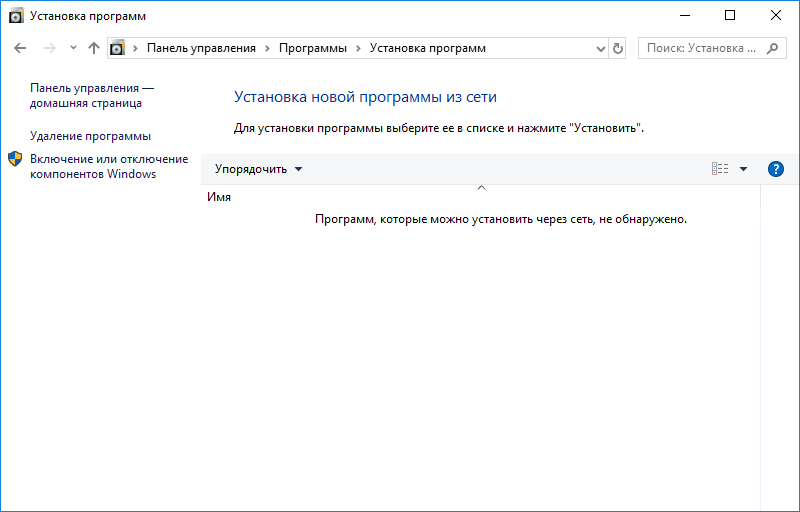
2. Отметьте пункт Службы IIS, и нажмите кнопку ОК:
3. Дождитесь окончания установки всех необходимых компонентов:
4. После завершения установки, рекомендуется перезагрузить компьютер.
5. Запустите браузер и перейдите по адресу http://localhost/. Если открылась тестовая страница IIS, значит установка произведена успешно.
См. также: Установка серверной версии СпрутМонитор.
Installing IIS on Windows 10 is pretty straightforward. First, you access the «Turn Windows features on or off» menu, then find and enable Internet Information Services (IIS). Finally, hit OK and let Windows do its magic. Voilà, you’ve got yourself a running web server!
Let’s walk through the steps to get IIS up and running on your Windows 10 computer. This will allow you to use your machine as a web server, enabling you to host websites, applications, and more locally.
Step 1: Open Control Panel
Go to the Start menu, type «Control Panel,» and click on it.
The Control Panel is where you can manage various system settings and features on your computer.
Step 2: Access Programs and Features
In the Control Panel, select «Programs,» then click on «Programs and Features.»
«Programs and Features» is the place to go when you want to install, uninstall, or manage different software components on your computer.
Step 3: Turn Windows Features On or Off
On the left sidebar, click «Turn Windows features on or off.»
This menu allows you to enable or disable various Windows components, including IIS.
Step 4: Locate Internet Information Services
In the Windows Features window, scroll down and find «Internet Information Services.»
IIS is listed among many other optional features you can enable or disable in Windows.
Step 5: Enable Internet Information Services
Check the box next to «Internet Information Services» and click OK.
By enabling this feature, you’re telling Windows to install IIS and make it available on your computer.
Step 6: Wait for the Installation
Windows will take a few moments to install IIS. Just be patient.
During this time, Windows is adding necessary files and configuring settings to enable IIS on your system.
Step 7: Verify the Installation
Open a web browser and type «http://localhost» in the address bar.
If everything is installed correctly, you should see the IIS welcome page, confirming that IIS is now up and running on your computer.
After completing these steps, IIS will be installed on your Windows 10 machine. You can now use it to host websites, develop web applications, and perform various other tasks related to web servers.
Tips for Installing IIS in Windows 10
- Check System Requirements: Make sure your version of Windows 10 supports IIS. Most versions do, but it’s always good to double-check.
- Enable Additional Features: Within IIS, you can enable additional features like FTP Server or Web Management Tools for more functionality.
- Keep It Updated: Regularly check for updates to keep IIS running smoothly and securely.
- Use a Firewall: Ensure your firewall settings allow traffic through port 80 and 443 for HTTP and HTTPS, respectively.
- Backup Your System: Before making major changes, it’s always wise to have a backup of your system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is IIS?
IIS stands for Internet Information Services. It’s a web server software package designed by Microsoft for Windows systems.
Is IIS free?
Yes, IIS is included as a part of Windows, so there is no additional cost to use it.
Can I run IIS on Windows 10 Home?
No, IIS is not available on Windows 10 Home. You’ll need Windows 10 Pro or Enterprise.
How do I access the IIS Manager?
After installing IIS, type «IIS» in the Start menu and select «Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.»
What can I do with IIS?
IIS allows you to host websites, develop web applications, and manage server settings, among other things.
Summary of Steps
- Open Control Panel.
- Access Programs and Features.
- Turn Windows Features On or Off.
- Locate Internet Information Services.
- Enable Internet Information Services.
- Wait for the Installation.
- Verify the Installation.
Conclusion
There you have it—installing IIS in Windows 10 is like a walk in the park once you know the steps. This guide should make it clear and straightforward for you. With IIS, you can transform your personal computer into a versatile web server, opening up a world of possibilities for web development and hosting.
Still curious about what IIS can do? Dive deeper by exploring Microsoft’s documentation or join online forums to see how others are utilizing this powerful tool. Installing IIS in Windows 10 is a great starting point, but it’s just the beginning. So go ahead, take the plunge, and start creating amazing web applications right from your own machine!
Kermit Matthews is a freelance writer based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania with more than a decade of experience writing technology guides. He has a Bachelor’s and Master’s degree in Computer Science and has spent much of his professional career in IT management.
He specializes in writing content about iPhones, Android devices, Microsoft Office, and many other popular applications and devices.
Read his full bio here.
- Author
- Recent Posts
I started writing code around 20 years ago, and throughout the years, I have gained a lot of expertise from hands-on experience as well as learning from others. This website has also grown with me and is now something that I am proud of.
Installing Internet Information Services (IIS) on Windows 10 might seem daunting at first, but it’s actually a straightforward process that enables you to host websites and applications directly on your PC. Whether you’re planning to use IIS for web development or to host a personal website, you’ll find that enabling and configuring this service can open up a world of possibilities for your online projects.

From my personal experience, I can say that once you’ve enabled IIS through the Control Panel, Command Line, or PowerShell, you’ll be ready to start hosting your own HTTPS-enabled websites. Imagine having your site up and running locally, making it easier to test and develop without extra complications. Enabling IIS gives you full control over your web server settings, making it a powerful tool for both novice and seasoned developers.
Moreover, configuring IIS allows you to set up a localhost environment, which is indispensable for testing new features before going live. Troubleshooting your own web server might sound tricky, but with IIS, you get extensive options to manage and configure settings easily. Starting and testing your first website through IIS is just a few steps away, making it an excellent choice for anyone serious about web development.
JUMP TO TOPIC
- Setting Up Your Windows Environment for IIS
- Understanding Windows Features Related to IIS
- Navigating the Control Panel and Using ‘Turn Windows Features on or Off’
- The Installation Process of IIS
- Using the GUI for IIS Setup
- Command Line Methods: DISM and PowerShell
- Configuring IIS
- Setting Up Websites and Application Pools
- Security Features and Protocols Configuration
- Performance Monitoring and Diagnostics Tools
- Hosting Web Applications on IIS
- Deploying ASP.NET and PHP Applications
- Integrating with Databases and Setting Up WordPress
- Managing the Default Website and Custom Web Pages
Setting Up Your Windows Environment for IIS
To install IIS on Windows 10, you need to configure your system correctly. Follow these steps to ensure that your environment is properly set up and ready for IIS.
Understanding Windows Features Related to IIS
Windows 10 includes several features that are essential for IIS. These “Windows Features” must be enabled to run IIS smoothly.
I start by checking the installed operating system. This varies slightly between Windows 8, Windows 10, and Windows Server 2012. Once verified, I proceed to the “Programs and Features” section.
Essential Windows Features for IIS:
- Internet Information Services
- Web Management Tools
- World Wide Web Services
- Application Development Features
- Common HTTP Features
These components are integral to the functionality of IIS. Without them, running a web server on your Windows operating system will be problematic.
Navigating the Control Panel and Using ‘Turn Windows Features on or Off’
Access “Turn Windows Features on or off” from the Control Panel. This is your hub for enabling and disabling optional features in your operating system.
I start by opening the Control Panel. This can be done by searching “Control Panel” in the Start menu. Once inside, I navigate to “Programs and Features”. Here I find “Turn Windows Features on or off.”
In the window that appears, I must ensure all necessary IIS components are checked.
| Feature | Description |
| Internet Information Services | The primary web server feature for hosting websites. |
| Web Management Tools | Tools for managing your IIS server. |
| World Wide Web Services | Essential for running websites and web applications. |
| Application Development Features | Supports development frameworks like .NET. |
| Common HTTP Features | Fundamental HTTP support for websites. |
After selecting the desired features, I click “OK” to install them. Windows will configure and install these components automatically.
Ensuring these steps are followed precisely means your Windows environment will be ready for IIS installation and configuration.
The Installation Process of IIS
Installing Internet Information Services (IIS) in Windows 10 can be done using different approaches. These include the graphical user interface (GUI) and command line methods such as DISM and PowerShell. Each method has its advantages, making it suitable for different user preferences.
Using the GUI for IIS Setup
To install IIS using the GUI, start by opening Control Panel from the Windows search bar. Once opened, make sure the View by option is set to Category. This setting makes navigation easier.
Next, select Programs followed by Turn Windows features on or off. In the window that appears, scroll down and check the box next to Internet Information Services. Clicking OK will start the installation process.
After installation, open IIS Manager by typing inetmgr in the Windows search bar. Here, you can manage sites, configure applications, and monitor performance.
Command Line Methods: DISM and PowerShell
For more control, you might prefer using command line tools like DISM and PowerShell. With DISM, open an elevated Command Prompt and type:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:IIS-DefaultDocument
This command starts installing IIS and any related features.
Alternatively, using PowerShell can simplify the process. Open a PowerShell window with administrative privileges and use:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName IIS-WebServerRole
PowerShell’s flexibility also allows you to script multiple configurations at once, saving time for repeated setups.
Both methods require administrative rights and complete quickly, adding IIS to your system without the need for interactive dialogs.
Configuring IIS
Configuring IIS ensures optimal performance and security for your web server. It involves setting up websites and application pools, configuring security features, and utilizing performance monitoring tools.
Setting Up Websites and Application Pools
To set up a website in IIS:
- Open IIS Manager by typing
inetmgrin the search bar. - Navigate to the Sites folder, right-click, and select Add Website.
- Enter a name for your site in the Site name field.
- Set the Physical path to your website’s directory.
- Configure the Binding section to use
HTTPand set the IP address toAll Unassigned.
Creating and managing Application Pools is crucial for isolating different web applications. This helps in enhancing security and optimizing resource usage.
- In IIS Manager, go to Application Pools.
- Click Add Application Pool.
- Name the pool and choose the .NET CLR version.
- Ensure Start application pool immediately is checked.
Security Features and Protocols Configuration
Configuring security in IIS involves setting up protocols like SSL for secure communication and adjusting permissions to control access.
- To enable SSL, purchase and install an SSL certificate.
- Open IIS Manager, select your site, and click Bindings.
- Add an HTTPS binding, select the appropriate SSL certificate, and apply.
Additionally, FTP can be secured with FTPS:
- Install the FTP server role in IIS.
- Configure an FTP site and enable FTP over SSL (FTPS).
Permissions are critical in securing your server:
- In IIS Manager under your site, select Edit Permissions.
- Adjust the security settings under the Security tab by adding or restricting user access appropriately.
Performance Monitoring and Diagnostics Tools
Monitoring performance and diagnosing issues are key components in maintaining a healthy IIS environment.
Use the IIS Manager built-in tools for performance monitoring:
- Open IIS Manager and select your website.
- Under Manage Website, click Advanced Settings to review performance settings.
For detailed diagnostics:
- Use Failed Request Tracing in IIS to log detailed failure information.
- Enable Logging to monitor HTTP transactions.
Windows Performance Monitor provides real-time data and includes a variety of counters to track server performance:
- Type
perfmonin the search bar to open Performance Monitor. - Add counters related to IIS, such as Processor Time and Bytes Sent/sec.
These tools ensure that you can proactively manage and troubleshoot your IIS installations efficiently.
Hosting Web Applications on IIS
Hosting web applications on IIS involves deploying applications, integrating database services, and managing websites to ensure seamless access and functionality.
Deploying ASP.NET and PHP Applications
Deploying ASP.NET applications on IIS is straightforward. First, I ensure the IIS installation is complete and the ASP.NET modules are enabled. I use the Solution Explorer in Visual Studio to publish my application.
PHP applications are also easy to deploy. I usually install the PHP module for IIS, configure the relevant .ini files, and copy the PHP application files to the wwwroot directory. Then, I set appropriate handler mappings.
Key steps:
- Install relevant modules (ASP.NET or PHP)
- Publish and configure applications
- Set handler mappings and permissions
Integrating with Databases and Setting Up WordPress
Integrating databases with IIS-hosted applications is crucial for dynamic websites. For ASP.NET, I configure connection strings to my SQL Server database in the web.config file. In PHP, I primarily work with MySQL, editing the config.php file.
Setting up WordPress involves creating a MySQL database, downloading WordPress, and placing files in wwwroot. I run the WordPress installer via browser, follow the setup steps, and ensure the wp-content directory has writable permissions.
Important points:
- Database configuration in application files
- MySQL or SQL Server integration
- WordPress installation and setup
Managing the Default Website and Custom Web Pages
Managing the IIS Default Web Site and custom web pages includes configuring settings, managing bindings, and creating virtual directories. I modify the physical path of the Default Web Site to point to my application’s directory.
I use bindings to assign the site to specific IP addresses or hostnames. Creating virtual directories allows me to host multiple applications under one domain. Using SSL/TLS certificates ensures secure HTTPS access.
Steps include:
- Modify physical path
- Set up bindings and SSL certificates
- Create virtual directories for multiple apps
Handling the Default Web Site and custom web pages ensures a tailored, secure, and efficient hosting environment on IIS.
