Версия nginx под Windows использует “родной” Win32 API (не эмуляцию Cygwin).
В настоящий момент в качестве методов обработки соединений используются
select() и poll() (1.15.9),
поэтому не стоит ожидать высокой производительности и масштабируемости.
В силу этого и ряда других известных проблем версия nginx под Windows
рассматривается пока как бета-версия.
На данный момент в ней доступна практически вся функциональность, что и
в версии nginx под UNIX, за исключением
XSLT-фильтра, фильтра изображений, модуля GeoIP и встроенного языка Perl.
Чтобы установить nginx/Windows, скачайте
дистрибутив последней основной версии (1.27.5),
поскольку основная ветвь nginx содержит все известные исправления.
Затем распакуйте дистрибутив, перейдите в каталог
nginx-1.27.5
и запустите nginx.
Вот пример для корневого каталога на диске C:
cd c:\ unzip nginx-1.27.5.zip cd nginx-1.27.5 start nginx
Чтобы увидеть процессы nginx, запустите утилиту командной строки
tasklist:
C:\nginx-1.27.5>tasklist /fi "imagename eq nginx.exe" Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage =============== ======== ============== ========== ============ nginx.exe 652 Console 0 2 780 K nginx.exe 1332 Console 0 3 112 K
Один из процессов главный, другой — рабочий.
Если nginx не запускается, нужно искать причину в
в файле лога ошибок logs\error.log.
Если же лог-файл не создался, то причину этого следует искать
в Windows Event Log.
Если вместо ожидаемой страницы выводится страница с ошибкой, нужно также
искать причины ошибки в файле logs\error.log.
nginx/Windows использует каталог, в котором он был запущен, в качестве
префикса для относительных путей в конфигурации.
В вышеприведённом примере префиксом является
C:\nginx-1.27.5\.
Пути в конфигурационном файле должны задаваться в UNIX-стиле с использованием
прямых слэшей:
access_log logs/site.log; root C:/web/html;
nginx/Windows работает как стандартное консольное приложение (не сервис)
и управляется при помощи следующих команд:
nginx -s stop быстрое завершение nginx -s quit плавное завершение nginx -s reload изменение конфигурации,
запуск новых рабочих процессов с новой конфигурацией,
плавное завершение старых рабочих процессовnginx -s reopen переоткрытие лог-файлов
Известные проблемы
-
Хоть и возможен запуск нескольких рабочих процессов, только один из них
реально работает. - UDP (и, как следствие, QUIC) не поддерживается.
Возможные усовершенствования в будущем
- Запуск в виде сервиса.
-
Использование портов завершения ввода-вывода (I/O completion ports)
в качестве метода обработки соединений. - Использование нескольких рабочих нитей внутри одного рабочего процесса.
Nginx is an open-source, high-performance HTTP server and reverse proxy server. It also functions as a mail proxy server and a generic TCP/UDP proxy server. Renowned for its stability, rich feature set, simple configuration, and low resource consumption, Nginx is often used as a web server or reverse proxy.
This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to install Nginx on a Windows-based operating system. It is worth noting that while Nginx does provide a Windows version, it is mostly recommended for development and testing purposes. For production environments, Linux distributions are typically preferred.
Prerequisites
Before you start with the installation process, make sure you have administrative rights on your Windows system, as they are required for software installation. Additionally, ensure your system meets the minimum hardware requirements for Nginx.
Step 1: Downloading Nginx
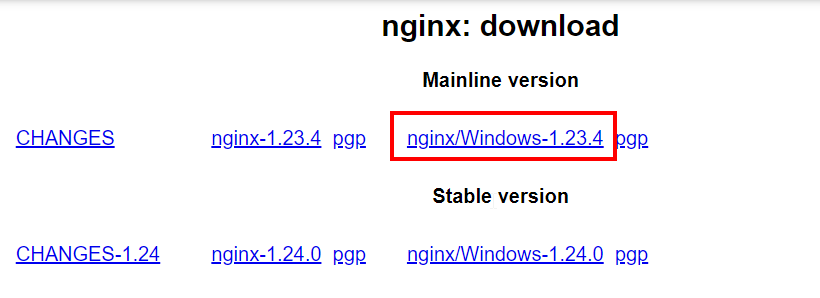
- Go to the Nginx download page.
- Under the “Mainline version”, click on the zip file link for the latest Windows version. The file will start downloading.
Downloading Nginx for Windows
Step 2: Extracting Nginx
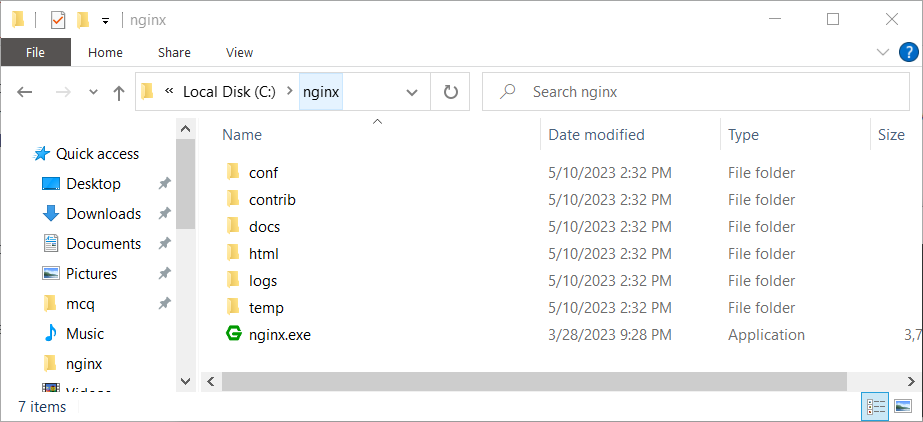
- Once downloaded, locate the zip file, typically in your Downloads folder.
- Extract the zip file to your desired location. For this guide, we will use C:\nginx.
Extracted Nginx code in C:\nginx directory
Step 3: Running Nginx
- Open the Command Prompt with administrative privileges. You can do this by searching for ‘cmd’ in the Start menu, right-clicking on Command Prompt, and selecting “Run as administrator”.
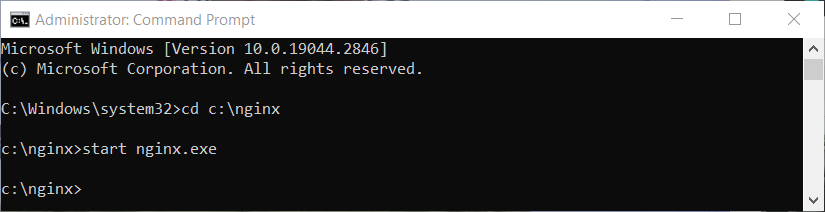
- Navigate to the directory where you extracted Nginx. You can do this by typing cd C:\nginx and hitting Enter.
- Start Nginx by typing start nginx and hitting Enter.
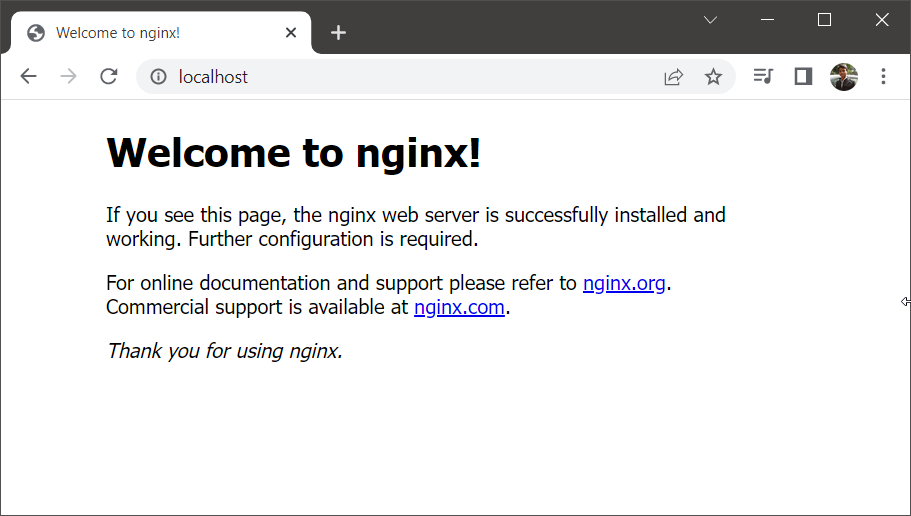
cd C:\nginxstart nginx.exeStarting Nginx service on Windows - Nginx should now be running on your Windows machine. You can check this by opening a web browser and navigating to http://localhost. If Nginx has started successfully, you will see a welcome page.
Verify Nginx on Windows
Step 4: Managing Nginx
Here are some basic commands you can use to manage Nginx:
- To stop Nginx, use the command `nginx -s stop`.
- To quit Nginx gracefully, use `nginx -s quit`.
- To reload the Nginx configuration file, use `nginx -s reload`.
- To reopen the Nginx log files, use `nginx -s reopen`.
Remember to run these commands from the directory where Nginx is installed.
Step 5: Configuring Nginx
The primary configuration file for Nginx is nginx.conf, located in the conf subdirectory of the directory where Nginx was extracted. The configuration file is well-commented and provides a good starting point for configuring your server.
For Nginx to serve your website, you need to edit this file with your specific parameters. You may need to set up server blocks (similar to Apache’s virtual hosts) to specify the document root and other parameters for your website.
After making changes to the configuration file, remember to reload Nginx so that the changes take effect.
Conclusion
This guide provided a basic introduction to installing Nginx on a Windows system. While this should get you started, Nginx’s true power comes from its extensive configurability, allowing you to optimize it for your specific needs. Be sure to check out the official Nginx documentation for more detailed information on how to harness this power.
Having a dependable and fast web server is crucial for delivering content efficiently and promptly. It’s no wonder then why Nginx is one of the most popular web servers currently around. Nginx is an open-source web server and reverse proxy server known for its high performance, stability, and ability to handle a large number of simultaneous connections.
It’s also become an essential tool for web developers and system administrators, as it provides an efficient and scalable solution for serving web content and managing network traffic.
Since Nginx has gained popularity for its performance and flexibility, today we’re guiding you through the process of installing Nginx on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
But first, let’s provide some helpful definitions and background info on this server.
What Is Nginx?

Nginx is an open-source web server and reverse proxy server that was developed by Igor Sysoev in 2004. Nginx became very popular because it is fast, versatile, and can be used as a web server and reverse proxy. This popularity has developed since it was first released.
One of the key design goals of Nginx is to provide high performance and handle a large number of simultaneous connections with minimal resource usage. Nginx achieves this by using an event-driven architecture, which allows it to efficiently manage connections without the need for a large number of dedicated worker processes.
It also serves as an excellent choice for serving static content, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, as well as images and other media files. Nginx can be used as a load balancer as well, distributing incoming network traffic across multiple backend servers to ensure that no single server becomes overwhelmed.
Lastly, Nginx supports a wide range of protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, WebSocket, and more. This flexibility allows Nginx to be used in a variety of applications, from serving traditional web content to managing real-time communication between clients and servers.
Who Uses Nginx?
Nginx is a popular choice among a wide range of professionals, including:
- Web developers: Nginx’s high performance and ability to handle large numbers of connections make it an ideal choice for web developers looking to serve static content or build dynamic web applications.
- System administrators: Its flexibility and extensive configuration options make it a powerful tool for system administrators tasked with managing web servers and network traffic.
- DevOps engineers: DevOps professionals use Nginx as part of their toolkit for deploying, scaling, and managing web applications and infrastructure.
In addition to individual professionals, many well-known companies rely on Nginx for their web server and reverse proxy needs, including:
- Netflix: The popular streaming service uses Nginx as part of its content delivery infrastructure, ensuring smooth and reliable streaming for millions of users.
- Cloudflare: The global content delivery network and web security provider uses Nginx to power its infrastructure, providing fast and secure web experiences for its customers.
- Airbnb: The popular home-sharing platform leverages Nginx to serve its web applications, allowing for efficient handling of high-traffic periods and improved performance for users.
- Zappos: The online fashion retailer uses Nginx to power its websites and keep them running fast and reliably.
These are just a few examples of the many companies that trust Nginx to meet their web server and reverse proxy needs, showcasing the versatility and performance of this powerful tool.
Advantages of Using Nginx
There are several key advantages to using Nginx, which contribute to its widespread adoption:
High Performance With Low Resource Consumption
Nginx’s event-driven architecture makes it so it can handle a large number of simultaneous connections with minimal resource usage. This makes it an excellent choice for serving web content on small and large-scale applications.
Scalable and Extensible
It’s also designed to be easily scalable, allowing it to grow alongside your application as your needs change. Nginx supports a wide range of modules, which can be used to extend its functionality and adapt it to specific use cases.
Flexible Configuration Options
Nginx offers extensive configuration options as well, allowing you to fine-tune its behavior and performance to suit your needs. This flexibility makes Nginx a powerful tool for managing web servers and network traffic.
Supports Reverse Proxy and Load Balancing
As we already mentioned, in addition to serving as a web server, Nginx can also function as a reverse proxy and load balancer. It distributes incoming network traffic across multiple backend servers to prevent the overload of any single server.
Strong Community Support and Documentation
Finally, Nginx has a large and active community, which contributes to its ongoing development and provides support to users.

The official Nginx documentation is extensive and well-organized, making it easy to find the information you need to get started and troubleshoot any issues that arise.
Nginx Prerequisites
Before you install and start using Nginx, it’s helpful to have the following knowledge and skills:
- Basic knowledge of networking and web servers: Familiarity with networking concepts and web server technology will help you understand how Nginx works and how to configure it for your specific use case.
- Familiarity with command line/terminal: Many of the tasks related to installing and managing Nginx will require you to use the command line or terminal, so it’s important to feel comfortable navigating and executing commands in these environments.
System Requirements
Likewise, to install and run Nginx, your system should meet the following requirements:
- Supported operating systems: Nginx is available for a variety of operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. Be sure to use a supported version of your chosen operating system.
- Minimum hardware requirements: While Nginx is known for its low resource consumption, it’s important to ensure your system meets the minimum hardware requirements for running Nginx. At a minimum, you’ll need 512 MB of RAM and 50 MB of free disk space
These requirements may vary depending on your specific use case, so it’s important to consider your application’s needs when determining the appropriate hardware configuration.
Versions
Nginx is available in two primary release channels:
- Nginx stable release: The stable release channel provides a well-tested, production-ready version of Nginx. This version is recommended for most users, as it prioritizes stability and compatibility.
- Nginx mainline release: The mainline release channel includes the latest features and improvements to Nginx but may not have undergone the same level of testing as the stable release. This version is more suitable for users who require cutting-edge features or who want to participate in testing and providing feedback on new developments.
When choosing which version of Nginx to install, consider your specific needs and weigh the benefits of stability versus access to the latest features.
How To Install Nginx
Though the overall installation process is fairly similar across all platforms, we’ve broken up these instructions below to simplify things.
How To Install Nginx on Windows
This section will guide you through the process of installing Nginx on a Windows computer. Simply follow each step to successfully install and run Nginx.
Step 1: Download the Nginx Installer for Windows

- Visit the Nginx download page.
- Choose either the stable release or the mainline release, depending on your preference for stability or access to the latest features.
- Under the selected release, click on the link for the Windows version to download the Nginx installer.
Step 2: Extract the Nginx Archive
- Locate the downloaded Nginx archive (usually in your Downloads folder), which should be a .zip file.
- Right-click on the archive and select Extract All.
- Choose a location for the extracted files (e.g., C:\nginx), and click Extract.
Step 3: Run Nginx
To open a command prompt with administrator privileges, please follow these steps:
- Click on the Start button.
- Type “cmd” without quotation marks.
- Right-click on the Command Prompt result.
- Select Run as administrator.
Then navigate to the directory where you extracted the Nginx files by entering:
cd C:\nginx(replace C:\nginx with the actual path where you extracted the files).
Finally, start Nginx by running the following command:
start nginxStep 4: Verify the Nginx Installation

- Open your web browser and navigate to http://localhost.
- You should see the Nginx welcome page, which confirms that the installation was successful.
Step 5: Configure Nginx as a Windows Service (optional)
By default, Nginx does not run as a Windows service, which means it will not automatically start when your computer boots. If you’d like Nginx to run as a Windows service, you can use a third-party tool like NSSM – the Non-Sucking Service Manager.
- Download the NSSM utility and extract it to a folder on your computer.
- Open a command prompt with administrator privileges, as described in Step 3.
- Navigate to the folder where you extracted NSSM by entering cd C:\path\to\nssm (replace C:\path\to\nssm with the actual path).
- Run the following command to install Nginx as a service:
nssm install nginx C:\nginx\nginx.exe(replace C:\nginx\nginx.exe with the actual path to the nginx.exe file).
- Start the Nginx service by running
nssm start nginx.
With Nginx installed on your Windows machine, you’re now ready to start configuring it to serve your web applications and manage network traffic.
How To Install Nginx on macOS
This section will explain how to install Nginx on macOS. We’ll be using Homebrew, a popular package manager for macOS, to simplify the installation process.

If you don’t have Homebrew installed on your system, follow the Homebrew installation instructions before proceeding.
Step 1: Update Homebrew
Before installing Nginx, it’s a good idea to ensure your Homebrew installation is up to date.
Open a terminal window and run the following command:
brew updateThis command will update Homebrew and its package information to the latest versions.
Step 2: Install Nginx
To install Nginx using Homebrew, run the following command in your terminal:
brew install nginxHomebrew will download and install the latest stable version of Nginx, along with any required dependencies.
Step 3: Start Nginx
Once the installation is complete, you can start the Nginx server using the following command:
brew services start nginxThis command will start Nginx and configure it to run as a background service, automatically starting when your system boots.
Step 4: Verify the Nginx Installation
To verify that Nginx is running, open your web browser and navigate to http://localhost:8080. You should see the Nginx welcome page, indicating that the installation was successful.

Note: By default, Nginx on macOS listens on port 8080, unlike the standard port 80 used by most web servers. You can change this by editing the Nginx configuration file located at /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf.
And that’s it! You’re now ready to start using Nginx.
How To Install Nginx on Linux
We’ll now walk you through the process of installing Nginx on a Linux machine. The specific steps may vary depending on your Linux distribution, but we’ll cover the most common distributions: Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and Fedora.
Ubuntu and Debian
- Update package lists
- Install Nginx
- Start Nginx
CentOS and Fedora
- Add the EPEL repository
- Install Nginx
- Start Nginx
- Verify the Nginx installation
Ubuntu and Debian
Step 1: Update Package Lists
Before installing Nginx, update the package lists for upgrades and new package installations. Open a terminal and run the following command:
sudo apt updateStep 2: Install Nginx
To install Nginx on Ubuntu or Debian, run the following command:
sudo apt install nginxThis command will install the latest stable version of Nginx from the default package repository.
Step 3: Start Nginx
After the installation is complete, start the Nginx service and enable it to start automatically at boot using the following commands:
sudo systemctl start nginx sudo systemctl enable nginxCentOS and Fedora
Step 1: Add the EPEL Repository (CentOS only)
For CentOS users, you’ll need to enable the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository, which provides additional packages not included in the default CentOS repositories. To enable EPEL, run the following command:
sudo yum install epel-releaseStep 2: Install Nginx
To install Nginx on CentOS or Fedora, run the following command:
sudo yum install nginxThis command will install the latest stable version of Nginx from the package repository.
Step 3: Start Nginx
After the installation is complete, start the Nginx service and enable it to start automatically at boot using the following commands:
sudo systemctl start nginx sudo systemctl enable nginxStep 4: Verify the Nginx Installation (all distributions)
To verify that Nginx is running, open your web browser and navigate to http://localhost (or the IP address of your Linux machine if accessing remotely). You should see the Nginx welcome page, indicating that the installation was successful.

And with that, you’ve completed the Nginx installation process on Linux.
Summary
Today, we’ve covered the process of installing Nginx on Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems. By following the steps outlined for your specific platform, you should now have a working Nginx installation ready to handle your web server and reverse proxy tasks.
We encourage you to start using Nginx for your web applications, as it offers excellent performance, scalability, and flexibility. As you continue to work with Nginx, you’ll find a wealth of resources available online to help you learn more and troubleshoot any issues you may encounter. The official Nginx documentation is a great place to start, as well as various community forums and blogs.
Finally, if you’re looking for a reliable hosting solution for your Nginx-powered applications, we recommend Kinsta Application Hosting. Kinsta provides a high-performance, managed hosting environment optimized for Nginx, ensuring your applications run smoothly and securely.
With your new Nginx installation in place, you’re on your way to building and managing powerful web applications and services.
#13
понедельник, 3 июля 2023 г.
9 минут(ы)
756 слов
Установка Nginx на Windows
-
Перейдите на официальный сайт Nginx https://nginx.org/ и перейдите на страницу загрузки https://nginx.org/en/download.html. Загрузите последнюю стабильную версию Nginx для Windows в формате zip.
-
Распакуйте загруженный архив Nginx в каталог на вашем компьютере, например, C:\nginx.
-
Откройте файл nginx.conf, который находится в папке conf в распакованном каталоге Nginx. Внесите необходимые изменения в конфигурацию, например, настройте прослушиваемый порт и корневую директорию вашего веб-сервера.
Откройте командную строку (Command Prompt) от имени администратора и перейдите в каталог, где расположен Nginx (например, C:\nginx). Запустите Nginx, введя следующую команду:
- Откройте веб-браузер и введите http://localhost/ в адресной строке. Если Nginx работает должным образом, вы должны увидеть страницу приветствия Nginx.
Для остановки Nginx можно использовать команду nginx.exe -s stop или закрыть командную строку, в которой был запущен сервер.
Брандмауэр Windows
Если при первом запуске Nginx на Windows появляется запрос на разрешение доступа по сети, это может быть вызвано настройками брандмауэра Windows. Брандмауэр может обнаружить новое приложение и запросить разрешение на доступ к сети.

Для разрешения доступа Nginx к сети, следуйте этим шагам:
-
При появлении запроса на разрешение доступа по сети, нажмите на кнопку «Разрешить доступ» или «Разрешить доступ для общественных сетей» (в зависимости от предлагаемых вариантов).
-
Если запрос на разрешение доступа появляется только для частной сети, но не для общественной, вы можете разрешить доступ только для частной сети. В этом случае, выберите опцию «Разрешить доступ» или «Разрешить доступ для частных сетей».
-
Если запрос на разрешение доступа не появляется автоматически, вы можете открыть настройки брандмауэра Windows вручную. Для этого, откройте Панель управления, найдите «Брандмауэр Windows» и откройте его. Затем выберите «Разрешение приложений через брандмауэр Windows» или «Разрешить приложение через брандмауэр Windows». В списке найдите Nginx и убедитесь, что для него установлено разрешение для доступа по сети.
После разрешения доступа Nginx к сети, брандмауэр Windows больше не будет запрашивать разрешение при каждом запуске сервера.
Если проблема продолжает возникать или запрос на разрешение доступа не появляется, убедитесь, что у вас есть достаточные права администратора для изменения настроек брандмауэра и выполнения операций сети на вашей Windows-машине.
Настройка Nginx под Windows в качестве службы
Вы можете создать службу Windows для Nginx вручную, используя встроенную команду sc. Вот как вы можете сделать это:
-
Скачайте и установите Nginx (если вы еще этого не сделали).
-
Откройте командную строку с правами администратора.
-
Выполните следующую команду, заменив путь до nginx.exe на ваш:
sc create nginx binPath= "C:\path\to\nginx.exe"
Обратите внимание на пробел после binPath=, он обязателен.
Теперь у вас есть служба Windows для Nginx. Вы можете запустить ее, используя следующую команду:
После того как служба создана, вы можете запустить ее также с помощью команды sc start [service name], а остановить — с помощью команды sc stop [service name].
sc start nginx
sc stop nginx
Однако, нужно помнить, что Nginx, запущенный таким образом, не будет иметь всех функций, таких как автоматический перезапуск после сбоев и другие.
Следует также отметить, что команда sc create создает службу с настройками по умолчанию. В частности, служба будет работать под учетной записью LocalSystem и не будет автоматически запускаться при старте системы. Вы можете изменить эти и другие настройки с помощью дополнительных опций команды sc create или через Менеджер служб Windows.
Также стоит отметить, что по умолчанию служба будет работать под учетной записью LocalSystem, что может не соответствовать вашим требованиям к безопасности. Вы можете изменить учетную запись, под которой работает служба, в свойствах службы в Менеджере служб Windows.
Если вы хотите получить больше контроля над службой, рекомендуется использовать инструментом для создания служб Windows. Ниже приведены некоторые альтернативы:
-
WinSW: WinSW — это инструмент, написанный на C#, который также позволяет запускать приложения как службы Windows. Он обеспечивает поддержку XML для конфигурации служб и поддерживает различные функции управления службами, такие как перезапуск, зависимости служб и т.д.
-
SRVANY: Это утилита из набора инструментов Windows Resource Kit от Microsoft, которая позволяет любому Windows приложению работать как служба. Однако утилита довольно старая и не поддерживается на новых версиях Windows.
-
FireDaemon: Это коммерческий продукт, который позволяет создавать и управлять службами Windows для любого приложения. FireDaemon предлагает множество функций, включая планирование, мониторинг, автоматический перезапуск после сбоев и многое другое.
-
AlwaysUp: Еще одна коммерческая утилита, которая может превращать любое приложение в службу Windows. Она обеспечивает набор функций, включая автоматический перезапуск приложения после сбоев, поддержку электронной почты и даже «приглушение» приложений, которые нежелательно запускать в фоновом режиме.
Итак, в зависимости от ваших требований и бюджета, вы можете выбрать любой из этих инструментов для запуска Nginx как службы Windows.
Nginx® is a web-server service, which has gained almost as much market share as Apache® in recent years due
to its excellent performance and flexible feature set. This guide describes how to install Nginx and discusses
the next steps to set up Nginx to serve your site or application.
You need a server running a version of the Windows® Server® operating system.
Nginx comes pre-compiled direct from their website, which makes installation as simple as downloading and extracting a file.
-
Download the latest mainline release from https://nginx.org/en/download.html.
-
Extract the file to the location where you want to install Nginx, such as C:\nginx.
Note: We recommend creating a new directory for Nginx.
Open a CMD prompt and start Nginx with the following command:
C:\nginx\nginx.exe
Note: Replace **C:\nginx** with the directory location where you installed Nginix.
You should be able to navigate to https://localhost/ in the server’s web browser and see the Nginx default web page.
If you see «Welcome to Nginx,» everything is working as intended.
The Nginx project considers the Windows release to be in beta. Functionally, this release is similar to Unix releases, but
some features are missing. For further information, see nginx for Windows.
If you want to serve more than one site, we recommend that you set up Nginx server blocks to accommodate this need.
Updated about 2 months ago