Step 1: Subscribe to the Chocolatey Newsletter (Optional)
Be the first to know about upcoming features, security releases, and news about Chocolatey.
Step 2: Choose Your Installation Method
Know the Requirements:
- Supported Windows client and server Operating Systems (can run on older Operating Systems)
- PowerShell v2+ (minimum is v3 for install from this website due to TLS 1.2 requirement)
- .NET Framework 4.8 (the installation will attempt to install .NET 4.8 if you do not have it installed)
1. Choose How to Install Chocolatey:
Install Chocolatey for Individual Use:
- First, ensure that you are using an administrative shell — you can also install as a non-admin, check out Non-Administrative Installation.
-
Install with powershell.exe
With PowerShell, you must ensure Get-ExecutionPolicy is not Restricted. We suggest using
Bypassto bypass the policy to get things installed orAllSignedfor quite a bit more security.- Run
Get-ExecutionPolicy. If it returnsRestricted, then runSet-ExecutionPolicy AllSignedorSet-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process.
Now run the following command:
>
- Run
- Paste the copied text into your shell and press Enter.
- Wait a few seconds for the command to complete.
- If you don’t see any errors, you are ready to use Chocolatey! Type
chocoorchoco -?now, or see Getting Started for usage instructions.
This applies to both open source and commercial editions of Chocolatey.
2. Enter Your Internal Repository Url
(this should look similar to https://community.chocolatey.org/api/v2/)
3. Setup Your Environment
- Ensure you are set for organizational deployment
- Download the Chocolatey package
- Put the Chocolatey package on your internal repository
4. Get Your Scripts
1. Save this installation script
Save the following as ChocolateyInstall.ps1:
# Download and install Chocolatey nupkg from an OData (HTTP/HTTPS) url such as Artifactory, Nexus, ProGet (all of these are recommended for organizational use), or Chocolatey.Server (great for smaller organizations and POCs)
# This is where you see the top level API - with xml to Packages - should look nearly the same as https://community.chocolatey.org/api/v2/
# If you are using Nexus, always add the trailing slash or it won't work
# === EDIT HERE ===
$packageRepo = 'INTERNAL REPO URL'
# If the above $packageRepo repository requires authentication, add the username and password here. Otherwise these leave these as empty strings.
$repoUsername = '' # this must be empty is NOT using authentication
$repoPassword = '' # this must be empty if NOT using authentication
# Determine unzipping method
# 7zip is the most compatible, but you need an internally hosted 7za.exe.
# Make sure the version matches for the arguments as well.
# Built-in does not work with Server Core, but if you have PowerShell 5
# it uses Expand-Archive instead of COM
$unzipMethod = 'builtin'
#$unzipMethod = '7zip'
#$7zipUrl = 'https://chocolatey.org/7za.exe' (download this file, host internally, and update this to internal)
# === ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES YOU CAN SET ===
# Prior to running this script, in a PowerShell session, you can set the
# following environment variables and it will affect the output
# - $env:ChocolateyEnvironmentDebug = 'true' # see output
# - $env:chocolateyIgnoreProxy = 'true' # ignore proxy
# - $env:chocolateyProxyLocation = '' # explicit proxy
# - $env:chocolateyProxyUser = '' # explicit proxy user name (optional)
# - $env:chocolateyProxyPassword = '' # explicit proxy password (optional)
# === NO NEED TO EDIT ANYTHING BELOW THIS LINE ===
# Ensure we can run everything
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force;
# If the repository requires authentication, create the Credential object
if ((-not [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($repoUsername)) -and (-not [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($repoPassword))) {
$securePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString $repoPassword -AsPlainText -Force
$repoCreds = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ($repoUsername, $securePassword)
}
$searchUrl = ($packageRepo.Trim('/'), 'Packages()?$filter=(Id%20eq%20%27chocolatey%27)%20and%20IsLatestVersion') -join '/'
# Reroute TEMP to a local location
New-Item $env:ALLUSERSPROFILE\choco-cache -ItemType Directory -Force
$env:TEMP = "$env:ALLUSERSPROFILE\choco-cache"
$localChocolateyPackageFilePath = Join-Path $env:TEMP 'chocolatey.nupkg'
$ChocoInstallPath = "$($env:SystemDrive)\ProgramData\Chocolatey\bin"
$env:ChocolateyInstall = "$($env:SystemDrive)\ProgramData\Chocolatey"
$env:Path += ";$ChocoInstallPath"
$DebugPreference = 'Continue';
# PowerShell v2/3 caches the output stream. Then it throws errors due
# to the FileStream not being what is expected. Fixes "The OS handle's
# position is not what FileStream expected. Do not use a handle
# simultaneously in one FileStream and in Win32 code or another
# FileStream."
function Fix-PowerShellOutputRedirectionBug {
$poshMajorVerion = $PSVersionTable.PSVersion.Major
if ($poshMajorVerion -lt 4) {
try{
# http://www.leeholmes.com/blog/2008/07/30/workaround-the-os-handles-position-is-not-what-filestream-expected/ plus comments
$bindingFlags = [Reflection.BindingFlags] "Instance,NonPublic,GetField"
$objectRef = $host.GetType().GetField("externalHostRef", $bindingFlags).GetValue($host)
$bindingFlags = [Reflection.BindingFlags] "Instance,NonPublic,GetProperty"
$consoleHost = $objectRef.GetType().GetProperty("Value", $bindingFlags).GetValue($objectRef, @())
[void] $consoleHost.GetType().GetProperty("IsStandardOutputRedirected", $bindingFlags).GetValue($consoleHost, @())
$bindingFlags = [Reflection.BindingFlags] "Instance,NonPublic,GetField"
$field = $consoleHost.GetType().GetField("standardOutputWriter", $bindingFlags)
$field.SetValue($consoleHost, [Console]::Out)
[void] $consoleHost.GetType().GetProperty("IsStandardErrorRedirected", $bindingFlags).GetValue($consoleHost, @())
$field2 = $consoleHost.GetType().GetField("standardErrorWriter", $bindingFlags)
$field2.SetValue($consoleHost, [Console]::Error)
} catch {
Write-Output 'Unable to apply redirection fix.'
}
}
}
Fix-PowerShellOutputRedirectionBug
# Attempt to set highest encryption available for SecurityProtocol.
# PowerShell will not set this by default (until maybe .NET 4.6.x). This
# will typically produce a message for PowerShell v2 (just an info
# message though)
try {
# Set TLS 1.2 (3072), then TLS 1.1 (768), then TLS 1.0 (192)
# Use integers because the enumeration values for TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.1 won't
# exist in .NET 4.0, even though they are addressable if .NET 4.5+ is
# installed (.NET 4.5 is an in-place upgrade).
[System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = 3072 -bor 768 -bor 192
} catch {
Write-Output 'Unable to set PowerShell to use TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.1 due to old .NET Framework installed. If you see underlying connection closed or trust errors, you may need to upgrade to .NET Framework 4.5+ and PowerShell v3+.'
}
function Get-Downloader {
param (
[string]$url
)
$downloader = new-object System.Net.WebClient
$defaultCreds = [System.Net.CredentialCache]::DefaultCredentials
if (Test-Path -Path variable:repoCreds) {
Write-Debug "Using provided repository authentication credentials."
$downloader.Credentials = $repoCreds
} elseif ($defaultCreds -ne $null) {
Write-Debug "Using default repository authentication credentials."
$downloader.Credentials = $defaultCreds
}
$ignoreProxy = $env:chocolateyIgnoreProxy
if ($ignoreProxy -ne $null -and $ignoreProxy -eq 'true') {
Write-Debug 'Explicitly bypassing proxy due to user environment variable.'
$downloader.Proxy = [System.Net.GlobalProxySelection]::GetEmptyWebProxy()
} else {
# check if a proxy is required
$explicitProxy = $env:chocolateyProxyLocation
$explicitProxyUser = $env:chocolateyProxyUser
$explicitProxyPassword = $env:chocolateyProxyPassword
if ($explicitProxy -ne $null -and $explicitProxy -ne '') {
# explicit proxy
$proxy = New-Object System.Net.WebProxy($explicitProxy, $true)
if ($explicitProxyPassword -ne $null -and $explicitProxyPassword -ne '') {
$passwd = ConvertTo-SecureString $explicitProxyPassword -AsPlainText -Force
$proxy.Credentials = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ($explicitProxyUser, $passwd)
}
Write-Debug "Using explicit proxy server '$explicitProxy'."
$downloader.Proxy = $proxy
} elseif (!$downloader.Proxy.IsBypassed($url)) {
# system proxy (pass through)
$creds = $defaultCreds
if ($creds -eq $null) {
Write-Debug 'Default credentials were null. Attempting backup method'
$cred = get-credential
$creds = $cred.GetNetworkCredential();
}
$proxyaddress = $downloader.Proxy.GetProxy($url).Authority
Write-Debug "Using system proxy server '$proxyaddress'."
$proxy = New-Object System.Net.WebProxy($proxyaddress)
$proxy.Credentials = $creds
$downloader.Proxy = $proxy
}
}
return $downloader
}
function Download-File {
param (
[string]$url,
[string]$file
)
$downloader = Get-Downloader $url
$downloader.DownloadFile($url, $file)
}
function Download-Package {
param (
[string]$packageODataSearchUrl,
[string]$file
)
$downloader = Get-Downloader $packageODataSearchUrl
Write-Output "Querying latest package from $packageODataSearchUrl"
[xml]$pkg = $downloader.DownloadString($packageODataSearchUrl)
$packageDownloadUrl = $pkg.feed.entry.content.src
Write-Output "Downloading $packageDownloadUrl to $file"
$downloader.DownloadFile($packageDownloadUrl, $file)
}
function Install-ChocolateyFromPackage {
param (
[string]$chocolateyPackageFilePath = ''
)
if ($chocolateyPackageFilePath -eq $null -or $chocolateyPackageFilePath -eq '') {
throw "You must specify a local package to run the local install."
}
if (!(Test-Path($chocolateyPackageFilePath))) {
throw "No file exists at $chocolateyPackageFilePath"
}
$chocTempDir = Join-Path $env:TEMP "chocolatey"
$tempDir = Join-Path $chocTempDir "chocInstall"
if (![System.IO.Directory]::Exists($tempDir)) {[System.IO.Directory]::CreateDirectory($tempDir)}
$file = Join-Path $tempDir "chocolatey.zip"
Copy-Item $chocolateyPackageFilePath $file -Force
# unzip the package
Write-Output "Extracting $file to $tempDir..."
if ($unzipMethod -eq '7zip') {
$7zaExe = Join-Path $tempDir '7za.exe'
if (-Not (Test-Path ($7zaExe))) {
Write-Output 'Downloading 7-Zip commandline tool prior to extraction.'
# download 7zip
Download-File $7zipUrl "$7zaExe"
}
$params = "x -o`"$tempDir`" -bd -y `"$file`""
# use more robust Process as compared to Start-Process -Wait (which doesn't
# wait for the process to finish in PowerShell v3)
$process = New-Object System.Diagnostics.Process
$process.StartInfo = New-Object System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo($7zaExe, $params)
$process.StartInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = $true
$process.StartInfo.UseShellExecute = $false
$process.StartInfo.WindowStyle = [System.Diagnostics.ProcessWindowStyle]::Hidden
$process.Start() | Out-Null
$process.BeginOutputReadLine()
$process.WaitForExit()
$exitCode = $process.ExitCode
$process.Dispose()
$errorMessage = "Unable to unzip package using 7zip. Perhaps try setting `$env:chocolateyUseWindowsCompression = 'true' and call install again. Error:"
switch ($exitCode) {
0 { break }
1 { throw "$errorMessage Some files could not be extracted" }
2 { throw "$errorMessage 7-Zip encountered a fatal error while extracting the files" }
7 { throw "$errorMessage 7-Zip command line error" }
8 { throw "$errorMessage 7-Zip out of memory" }
255 { throw "$errorMessage Extraction cancelled by the user" }
default { throw "$errorMessage 7-Zip signalled an unknown error (code $exitCode)" }
}
} else {
if ($PSVersionTable.PSVersion.Major -lt 5) {
try {
$shellApplication = new-object -com shell.application
$zipPackage = $shellApplication.NameSpace($file)
$destinationFolder = $shellApplication.NameSpace($tempDir)
$destinationFolder.CopyHere($zipPackage.Items(),0x10)
} catch {
throw "Unable to unzip package using built-in compression. Set `$env:chocolateyUseWindowsCompression = 'false' and call install again to use 7zip to unzip. Error: `n $_"
}
} else {
Expand-Archive -Path "$file" -DestinationPath "$tempDir" -Force
}
}
# Call Chocolatey install
Write-Output 'Installing chocolatey on this machine'
$toolsFolder = Join-Path $tempDir "tools"
$chocInstallPS1 = Join-Path $toolsFolder "chocolateyInstall.ps1"
& $chocInstallPS1
Write-Output 'Ensuring chocolatey commands are on the path'
$chocInstallVariableName = 'ChocolateyInstall'
$chocoPath = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable($chocInstallVariableName)
if ($chocoPath -eq $null -or $chocoPath -eq '') {
$chocoPath = 'C:\ProgramData\Chocolatey'
}
$chocoExePath = Join-Path $chocoPath 'bin'
if ($($env:Path).ToLower().Contains($($chocoExePath).ToLower()) -eq $false) {
$env:Path = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path',[System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine);
}
Write-Output 'Ensuring chocolatey.nupkg is in the lib folder'
$chocoPkgDir = Join-Path $chocoPath 'lib\chocolatey'
$nupkg = Join-Path $chocoPkgDir 'chocolatey.nupkg'
if (!(Test-Path $nupkg)) {
Write-Output 'Copying chocolatey.nupkg is in the lib folder'
if (![System.IO.Directory]::Exists($chocoPkgDir)) { [System.IO.Directory]::CreateDirectory($chocoPkgDir); }
Copy-Item "$file" "$nupkg" -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
}
# Idempotence - do not install Chocolatey if it is already installed
if (!(Test-Path $ChocoInstallPath)) {
# download the package to the local path
if (!(Test-Path $localChocolateyPackageFilePath)) {
Download-Package $searchUrl $localChocolateyPackageFilePath
}
# Install Chocolatey
Install-ChocolateyFromPackage $localChocolateyPackageFilePath
}
2. Make script accessible by internal url
Put the script somewhere internally that can be accessed by a url (like a raw/binary repository in Nexus, Artifactory, or ProGet). Do NOT put the script on a NuGet type repository (where your packages will be), create a new Raw/Binary repository.
3. Install/Deploy Chocolatey internally
Now you can do similar to the individual side, but your command will be something like:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('INTERNAL REPO URL/ChocolateyInstall.ps1'))
3. Add the following to your playbook
# Note: `chocolateyDownloadUrl is completely different than normal
# source locations. This is directly to the bare download url for the
# chocolatey.nupkg, similar to what you see when you browse to
# https://community.chocolatey.org/api/v2/package/chocolatey
node['chocolatey']['install_vars']['chocolateyDownloadUrl'] = 'INTERNAL REPO URL/check_this/chocolatey.VERSION.nupkg'
node['chocolatey']['upgrade'] = true
include_recipe 'chocolatey::default'
The install of Chocolatey is separate from the Chef built-in resources. You will need the Chocolatey Cookbook.
3. Add the following to your DSC script:
cChocoInstaller InstallChocolatey
{
InstallDir = "C:\ProgramData\chocolatey"
ChocoInstallScriptUrl = "INTERNAL REPO URL/ChocolateyInstall.ps1"
}
Requires cChoco DSC Resource. See docs at https://github.com/chocolatey/cChoco.
## Note: `chocolatey_download_url is completely different than normal
## source locations. This is directly to the bare download url for the
## chocolatey.nupkg, similar to what you see when you browse to
## https://community.chocolatey.org/api/v2/package/chocolatey
class {'chocolatey':
chocolatey_download_url => 'INTERNAL REPO URL/check_this/chocolatey.VERSION.nupkg',
use_7zip => false,
}
Requires Puppet Chocolatey Provider module. See docs at https://forge.puppet.com/puppetlabs/chocolatey.
5. If applicable — Chocolatey configuration/installation
See infrastructure management matrix for Chocolatey configuration elements and examples.
Chocolatey Licensed Install:
Are you also installing a commercial edition of Chocolatey?
Please see Install the Licensed Edition.
Advanced Chocolatey Install:
Are you installing behind a proxy, need a completely offline install, or wanting to install a licenced edition of Chocolatey? Need even more options? Visit our Documentation or take our new Installation Course to help you get up and running with Chocolatey!
Chocolatey is a package manager for Windows 10 that simplifies software installation and management. It allows users to easily discover, download, and install thousands of software packages using a command-line interface. With Chocolatey, users can automate the installation process, reducing the risk of human error and saving time.
Chocolatey provides a centralized repository of software packages, which are verified and validated to ensure they are free from malware and viruses. This makes it a secure and reliable way to manage software on Windows 10 machines. Additionally, Chocolatey allows users to easily update and uninstall software packages, making it a convenient tool for maintaining software dependencies.
In this article, we will cover the installation process of Chocolatey on Windows 10, including the necessary commands and configuration options.
Installing Chocolatey on Windows 10 using Command Prompt (CMD)
For those who have installed NodeJS on Windows know that Chocolatey comes preinstalled on NodeJS. To separately install Chocolatey Windows using Command Prompt, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open Command Prompt as Administrator
To open Command Prompt as an administrator, right-click on the Start button and select “Command Prompt (Admin)” or type “cmd” in the search bar and right-click on the result to select “Run as administrator”.
Step 2: Execute the Installation Command
Once the Command Prompt is open, execute the following command:
@"%SystemRoot%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "[System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = 3072; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))" && SET "PATH=%PATH%;%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\chocolatey\bin"
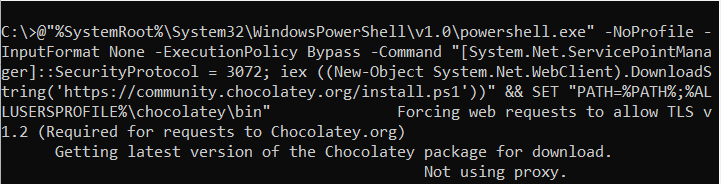
The output indicates that the installation process was completed successfully. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps and messages:
- TLS v1.2 enabled: The script forced web requests to allow TLS v1.2, which is required for requests to Chocolatey.org.
- Chocolatey package downloaded: The script downloaded the latest version of the Chocolatey package (2.3.0) from the Chocolatey API.
- Package extracted and installed: The script extracted the package to a temporary location and installed Chocolatey on the local machine.
- Environment variable set: The script created a ChocolateyInstall environment variable and set it to C:\ProgramData\chocolatey.
- Repository setup: The script set up the Chocolatey package repository and created the necessary folders.
- Shim file created: The script created a shim file for the command line in C:\ProgramData\chocolatey\bin.
- PATH environment variable updated: The script added C:\ProgramData\chocolatey\bin to the PATH environment variable.
- CLI ready: The script announced that the Chocolatey CLI (choco.exe) is now ready to use.
Warnings and Notes
There are two warnings and a note in the output:
- Warning: Close and reopen shell: The script warns that you may need to close and reopen your shell before you can use Choco.
- Warning: Profile file does not exist: The script warns that the profile file does not exist at C:\Users\Taimo\OneDrive\Documents\WindowsPowerShell\Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1, so it did not set up tab completion.
Note: Restart PowerShell and/or consoles: The script notes that you may need to shut down and restart PowerShell and/or consoles before using Choco.
To verify that Chocolatey was installed successfully, you need to open a new prompt as an administrator. After that run the following command:
choco -v

If the installation was successful, you should see the version of Chocolatey installed on your system.
Experience the Best with Ultahost Windows VPS!
With Ultahost, hosting a Windows VPS has never been easier or faster. Enjoy ultra-fast SSD NVMe speeds without any slowdowns, all at an cheap cost.
Installing Chocolatey using PowerShell
To install Chocolatey by using PowerShell, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open PowerShell as Administrator
To open PowerShell as an administrator, right-click on the Start button and select “Windows PowerShell (Admin)” or type “PowerShell” in the search bar and right-click on the result to select “Run as administrator”.
Step 2: Check the Execution Policy
Before Chocolatey Windows installs, you need to ensure that the execution policy is not restricted. Run the following command:
Get-ExecutionPolicy
This command will return the current execution policy. If it returns “Restricted”, you need to change it to “AllSigned” or “Bypass” to install Chocolatey.
Step 3: Set the Execution Policy
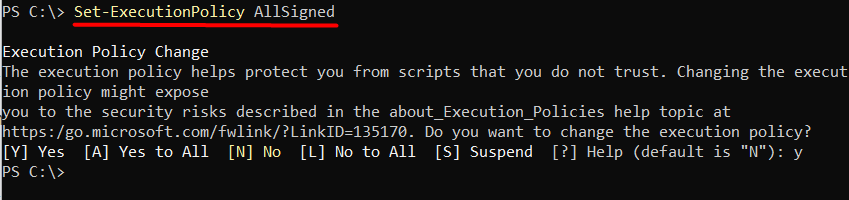
If the execution policy is restricted, run one of the following commands to change it:
Set-ExecutionPolicy AllSigned
or
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass
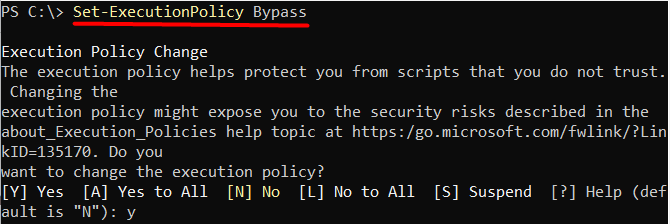
The “AllSigned” policy requires all scripts to be signed by a trusted publisher, while the “Bypass” policy bypasses all restrictions.
Step 4: Install Chocolatey
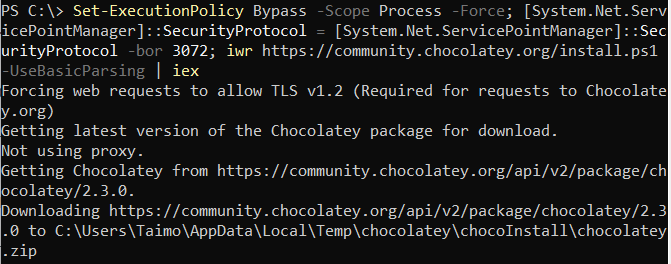
Once the execution policy is set, run the following command to install Chocolatey:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor 3072; iwr https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1 -UseBasicParsing | iex
Real-World Use Cases for Chocolatey
Chocolatey is a powerful package manager that can be used in a variety of scenarios, including:
- DevOps and Continuous Integration: Chocolatey can be used to automate the installation of software dependencies and tools in your DevOps pipeline, ensuring that your development environment is consistent and reproducible.
- IT and System Administration: Chocolatey can be used to manage software installations and updates across your organization, simplifying the process of keeping your systems up-to-date and secure.
- Personal Productivity: Chocolatey can be used to automate the installation of software and tools on your personal computer, saving you time and effort.
Common Chocolatey Commands
Here are some common Chocolatey commands that you may find useful:
- choco install: Installs a package and its dependencies.
- choco upgrade: Upgrades a package to the latest version.
- choco uninstall: Uninstalls a package and its dependencies.
- choco search: Searches for packages in the Chocolatey repository.
Chocolatey Integrations
Chocolatey integrates with a variety of tools and platforms, including:
- PowerShell: Chocolatey can be used directly from PowerShell, allowing you to automate package installations and updates.
- Visual Studio: Chocolatey can be used to manage software dependencies and tools in your Visual Studio projects.
- Docker: Chocolatey can be used to manage software installations and updates in your Docker containers.
Best Practices for Using Chocolatey
Here are some best practices for using Chocolatey:
- Use the latest version of Chocolatey: Make sure you are using the latest version of Chocolatey to take advantage of new features and security updates.
- Use secure sources: Only install packages from trusted sources to ensure that your system remains secure.
- Keep your packages up-to-date: Regularly update your packages to ensure that you have the latest security patches and features.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored two methods for installing Chocolatey on Windows 10, using Command Prompt and PowerShell. Both methods are straightforward and require only a few steps to complete. The Command Prompt method involves executing a single command to download and install Chocolatey, while the PowerShell method requires setting the execution policy and then running a command to install Chocolatey.
Regardless of the method used, the end result is the same: a successful installation of Chocolatey on your Windows 10 system. With Chocolatey installed, you can easily manage packages and dependencies, making it a valuable tool for developers and system administrators alike. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can quickly and easily get started with Chocolatey and begin taking advantage of its powerful package management capabilities.
Installing Chocolatey on Windows 10 can streamline software management but it might face limitations on personal systems. Upgrading to Ultahost Windows 10 VPS offers a more robust and flexible environment that provides dedicated resources ensuring optimal performance for Chocolatey package installations and updates.
FAQ
What is Chocolatey?
Chocolatey is a package manager for Windows that simplifies the installation, updating, and management of software packages. It’s similar to package managers like apt for Ubuntu or Homebrew for macOS.
Why Should I Use Chocolatey?
Chocolatey streamlines the installation of software and management of updates, which can save time and effort. It’s especially useful for automating the setup of development environments or managing multiple software packages on your system.
Do I Need to Restart My Computer After Installation?
Generally, you do not need to restart your computer. However, you may need to restart your Command Prompt or PowerShell window to recognize the new environment variables.
What Permissions Are Required?
You need to run the Command Prompt or PowerShell as an Administrator to install Chocolatey. This is required because the installation script needs to make changes to system directories and environment variables.
Can I Install Chocolatey Using Windows PowerShell?
Yes, Chocolatey can be installed using either Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell. The command provided above works in both environments when run with administrative privileges.
Chocolatey is a Windows counterpart to the Linux apt package manager or yum package manager. The software offers a CLI-based package installation and management in Windows with the community-maintained package repository.
In this tutorial, you will learn to install Chocolatey on Windows 10 and learn basic Chocolatey commands.

Prerequisites
- Windows 7+/Windows 2003+ (including Server Core, but excluding Windows Nano Server).
- .NET Framework 4.x+.
- A user account with administrator privileges.
What Is Chocolatey?
Chocolatey is a command-line package manager and installer for Windows operating systems. With the NuGet packaging infrastructure and the Windows PowerShell technology at its core, Chocolatey simplifies and automates the process of installing software and keeping it up to date.
When installing applications, Chocolatey silently configures and installs any dependencies required by the package. Chocolatey also allows users to wrap package installers, executable files, zips, and scripts into compiled packages.
Install Chocolatey on Windows
There are two ways to install Chocolatey on Windows:
- Using the Command Prompt.
- Using Windows PowerShell.
Both installations require an account with administrative shell access.
You can also install a portable, non-administrative Chocolatey version if you don’t have administrative shell access. However, the number of packages available is much smaller than the standard Chocolatey installation.
Install via Command Line
Follow the steps below to install Chocolatey using the Command Prompt:
1. Press the Windows key and type «cmd«. Select the Run as administrator option.
2. Run the following command:
@"%SystemRoot%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "[System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = 3072; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))" && SET "PATH=%PATH%;%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\chocolatey\bin"Wait for the installation process to finish to start using Chocolatey.
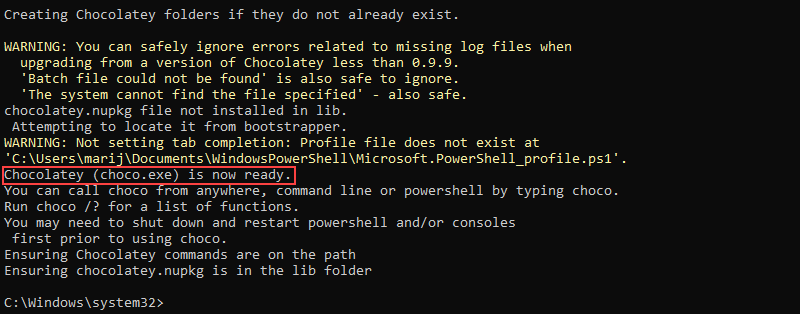
Note: Make sure to close and reopen the shell before using Chocolatey to ensure all the environment variables are loaded correctly.
via PowerShell
Installing Chocolatey via PowerShell involves an additional step compared to installing via the Command Prompt. Follow the steps below to install Chocolatey using Windows PowerShell:
1. Press the Windows key and type «PowerShell». Select the Run as administrator option to open the Windows PowerShell.
2. Before installing Chocolatey, ensure that Get-ExecutionPolicy is not restricted. This PowerShell safety feature controls the conditions for loading configuration files and scripts, thus preventing the execution of malicious programs.
Check the status by running:
Get-ExecutionPolicy
In the example above, the execution policy is restricted. If the execution policy is not restricted, skip Step 3, and proceed with installing Chocolatey.
3. Unrestrict the PowerShell execution policy by running:
Set-ExecutionPolicy AllSigned 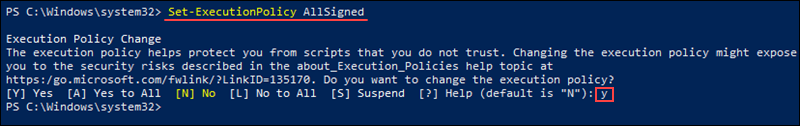
When prompted, type Y to change the execution policy and press Enter to confirm.
4. Install Chocolatey by running:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor 3072; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))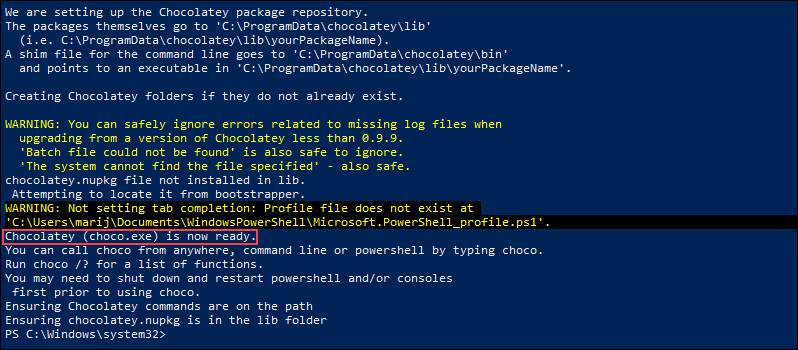
Wait for the installation to complete before you start using Chocolatey.
Chocolatey Features
The core of Chocolatey is the Windows Automation Language which utilizes PowerShell to perform different operations. One of Chocolatey’s most noteworthy features is the ability to keep all the installed software up to date with a single command. Thus, it helps keep all software updated with the latest security features.
Other prominent Chocolatey features are described below.
Packages
Chocolatey packages are nupkg files that contain metadata about the package’s dependencies and versioning with optional automation scripts or embedded software. The packages are compiled NuSpec files compatible with vanilla NuGet packages.
The focus is on managing packages to contain the necessary dependencies and software required for proper functioning. The compiled package file encapsulates everything, saving time by automating the installation and updating process.
Important: If you decide to build packages for Chocolatey, follow the distribution rights governing which software is redistributable in packages.
Chocolatey’s package repository is one of the largest Windows repositories online. Chocolatey also allows users to search the repository and copy the installation command from the website.
Chocolatey Client Software
The Chocolatey client software allows users to connect to software repositories to download packages. The software repository can be the Chocolatey community repository, its main software repository, or an alternative one.
The unified CLI supports every Windows installer type with a single command. It means that every piece of software (MSI, EXE, etc.) can be installed using Chocolatey, eliminating the need for running installers outside the command line.
Chocolatey executes all files using choco.exe. To see the list of arguments and options Chocolatey accepts, run:
choco --help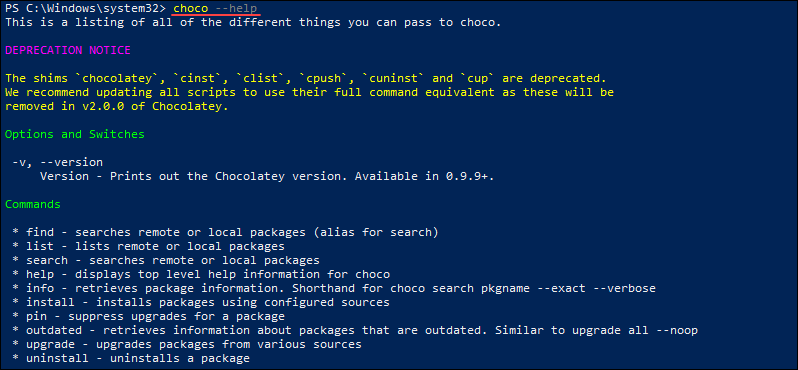
The command outputs the Chocolatey help file and all the accepted arguments and options.
Chocolatey GUI
The GUI app is available in the Chocolatey community repository and allows users to perform most of the tasks available using the CLI. The GUI simplifies the process for users not accustomed to using the CLI.
To install the Chocolatey GUI app, open Windows PowerShell or the Command Prompt as an administrator and run the following command:
choco install chocolateyguiWhen prompted, type A and press Enter to allow Chocolatey to run all the necessary scripts and automatically resolve any dependencies.
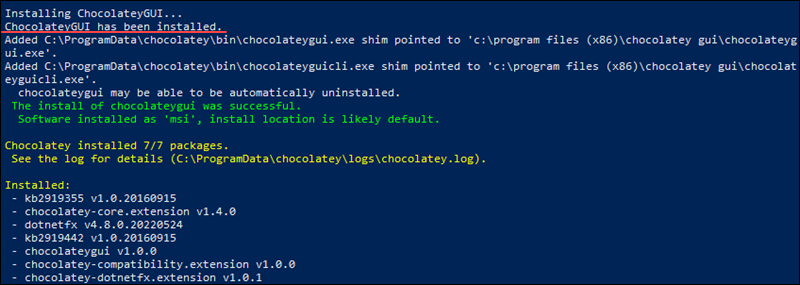
After the installation completes, run the Chocolatey GUI app.
Combined with the Chocolatey agent, the GUI app allows non-admins to install software as well. Below is the app’s homepage.

Repositories
Chocolatey allows users to install packages from remote official or custom repositories. The default repository is community-managed, and it is the largest online registry of packages for Windows. Currently, the repository contains over 9500 unique packages.
Note: Chocolatey doesn’t recommend using the community repository in organizations.
To add a custom repository, specify the source using the following syntax:
choco source add -n=[name] --source='https://[URL]'- Replace
[name]with the name for the new source. - Replace
[URL]with the repository web address.
For example:
choco source add -n=choco2 --source='https://example.com'Alternatively, install the Chocolatey Server, an IIS-backed repository supported directly by Chocolatey. It is available as a package in the community repository.
To install Chocolatey Server, run:
choco install chocolatey.server -yThe -y flag automatically answers Yes to any prompts during the installation.
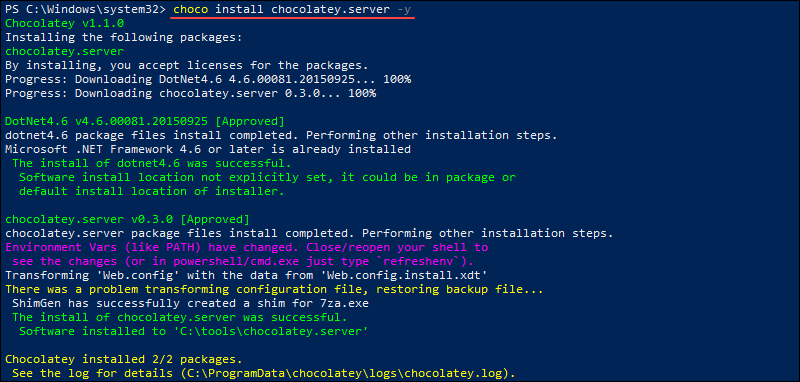
The output provides information about the installed packages and dependencies.
Security
Chocolatey is highly secure and has a strict policy on malicious and pirated software. The following features add up to Chocolatey’s security:
Package Moderation
Each package submitted to the Chocolatey repository goes through multiple moderation reviews, which include an automatic virus scan.
The moderation usually involves a human review to include safety, quality, and correctness checks. On the other hand, automated, machine-based moderation is reserved for trusted packages that come from trusted sources or software vendors.
Each script in the package is also revised to ensure they do only what they are supposed to, preventing malware or virus infections. The packages failing the moderation process are returned to the developers for adjustments.
CDN Download Cache
Chocolatey is open source but offers enhanced functionality, additional PowerShell functions, and exclusive features such as a CDN download cache for its licensed users.
The CDN download cache ensures that the packages on the community repository remain available even if the original website is down. This feature eliminates the possibility of getting a 404 error. A package copy is cached on Chocolatey’s private CDN, making it permanently available to licensed users.
Each cached copy is checked for viruses and checksummed to ensure there is no difference from the original package.
Antivirus Integration
Another Chocolatey security feature available to licensed users is the runtime antivirus protection during package download and installation. Users can choose between scanning packages with VirusTotal or integrating Chocolatey with their installed antivirus software. The default setting is to use VirusTotal.
When the packages download content from the Internet, Chocolatey CLI automatically checks any executables before running. The packages are scanned against more than 50 antivirus scanners.
The CLI automatically fails the install if any results return positive for viruses. In case of a fake positive, users can override the process and install the content anyway.
Since some scanners are more rigorous than others, Chocolatey CLI doesn’t flag a package as positive until at least five scanners identify it as such. The value can be adjusted to a higher or lower number using the following syntax:
choco config set virusCheckMinimumPositives [number]For example, the following command instructs Chocolatey CLI to fail any future installations if there are ten positive virus scans:
choco config set virusCheckMinimumPositives 10Audits
The Chocolatey for Business plan includes the auditing feature to allow users to keep track of who installed a package and the exact installation time and date. The provided information is often critical for audit reports. The installation date and time are in ISO 8601 UTC time.
To view installed packages along with information on the user who installed the package and the installation time, run:
choco list -lo --audit -rBasic Chocolatey Commands
After installing Chocolatey, start with the basic commands, such as searching, installing, or listing installed packages. Run the commands either in Windows PowerShell or in the Command Prompt.
The following table shows an overview of the basic commands, of which the most important ones are further explained in the sections below:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
search |
Search remote or local packages. Alias for find. |
list |
See a list of installed packages. |
install |
Install a package. |
pin |
Prevent further package upgrades. |
upgrade |
Update a package to the latest version. |
uninstall |
Uninstall a package. |
push |
Push a compiled nupkg package to the specified source. |
source |
Show and configure default Chocolatey sources. |
help |
Show the Chocolatey help file. |
export |
Export the list of currently installed packages. |
download |
Download packages from remote resources to local ones. |
convert |
Convert a package from one type to another. |
Install Program
Use the following syntax to install one or multiple packages:
choco install [pkg|packages.config] [pkg2 ...]- Any package name ending with .config is considered a packages.config file.
For example, to install the 7zip package from the default repository, run:
choco install 7zip -y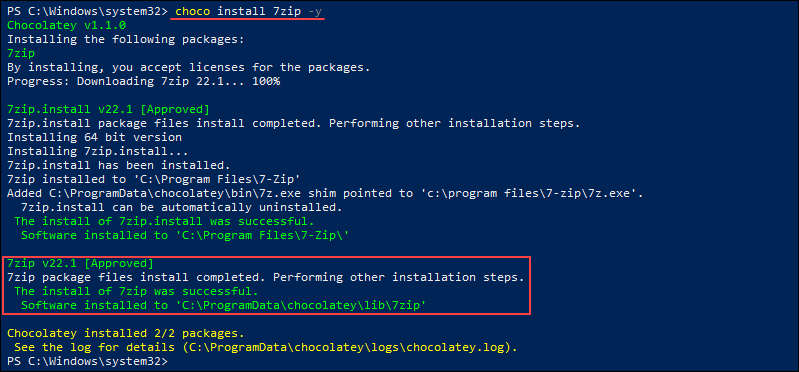
Update Program
The upgrade command upgrades the specified package or list of packages. If the package is not installed, upgrade installs it instead.
The syntax is:
choco upgrade [pkg] [pkg2 ...]For example, to upgrade the Opera browser package, run:
сhoco upgrade opera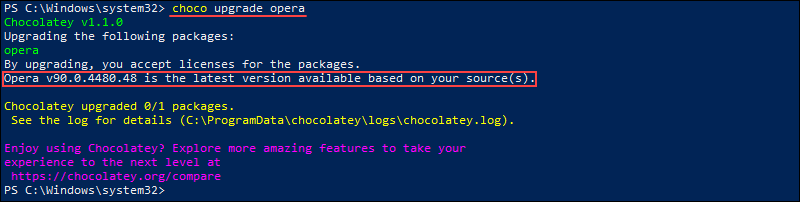
Since there is no new version available, Chocolatey states that the package version is already the latest available.
Update All Programs
Add the all flag to the upgrade command to update all installed packages. Run:
choco upgrade allNote: The cup command was an alias for choco upgrade, but it is now deprecated and will be removed as of version 2.0.0.
In the following example, Chocolatey outputs that all packages installed are the latest available version:
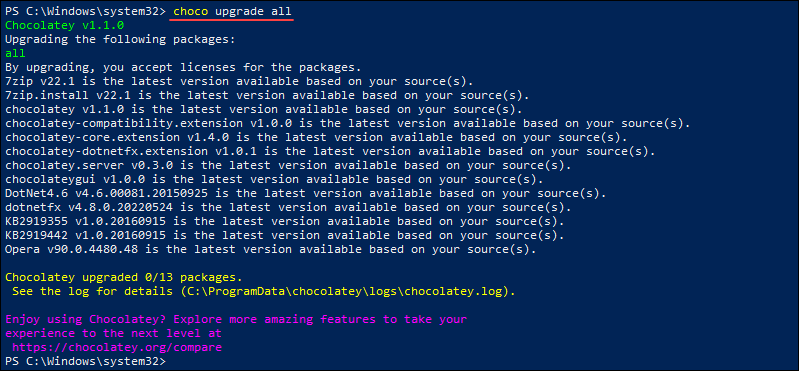
Search For a Program
The search command allows users to search for a package locally or remotely. Although search is currently an alias for the list command, starting from version 2.0.0, list will work only for local and installed packages. search and find will be used for remote sources as well.
The syntax for searching for a package is:
choco search [pkg]For example, to search for 7zip packages, run:
choco search 7zip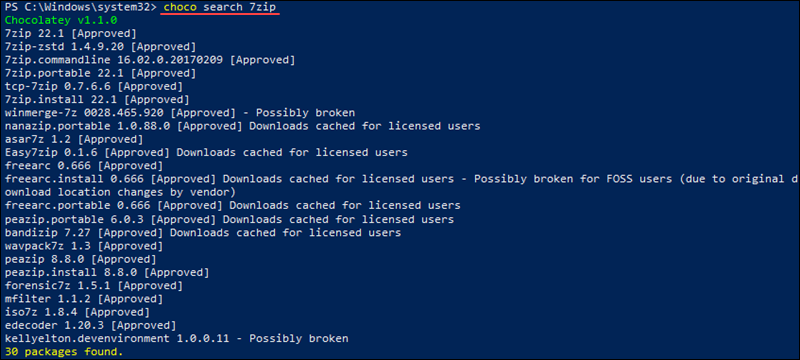
The command outputs all the results from the search along with the program version and a description (if available).
See Installed Programs
The list command allows users to see all the programs installed on their system using Chocolatey. Run the following command:
choco list --local-onlyFor example:
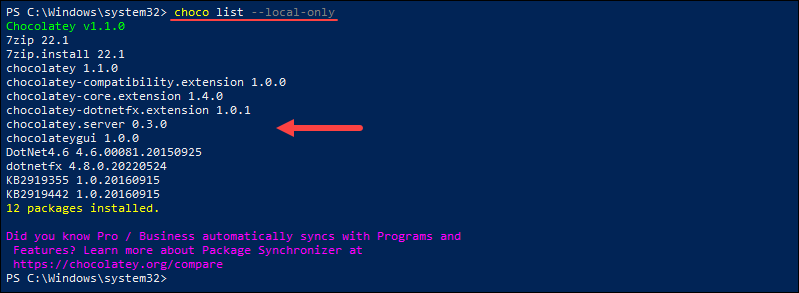
The output shows a list of packages on the system installed using Chocolatey.
Update Chocolatey
It is important to periodically check for new program version because each new version may address important security issues or include bug fixes and patches. Run the following command to update the Chocolatey client to the latest available version:
choco upgrade chocolatey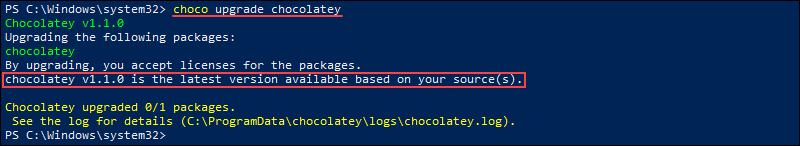
The program checks for a new version and installs it when available. Alternatively, the output is a message saying that your version is the latest available version.
Conclusion
This guide showed how to install and use Chocolatey on Windows 10. If you don’t like Chocolatey, try using Winget, a Windows native package manager aiming at making software management simpler and more efficient.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
This article explain how to install Chocolatey on Windows 10.
Chocolatey is Package Management Tools that is like apt-get or yum on Linux.
The following lists are the table of contents about this article.
- Target audience
- How to install
- Confirm Chocolatey is installed
- Install something to example
- How to check installed packages
- How to uninstall package
- How to update package
- Reference articles
Target audience
- Those who want to use functions like apt-get or yum on Windows.
How to install
Execute the following command on Command Prompt as Administrator.
@"%SystemRoot%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))" && SET "PATH=%PATH%;%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\chocolatey\bin"
Or, execute the following command on PowerShell as Administrator.
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))
Confirm Chocolatey is installed
After execute install, execute the following command on Command Prompt or PowerShell.
If version information appears like the following information, install was a success.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>choco -v
0.10.15
Install something to example
Refer to the above article, let’s install 7zip as a test.
Execute the following command on Command Prompt or PowerShell as Administrator.
When installing it, Command Prompt and Powershell will ask you if you want to continue. Press “Y” to continue a process.
How to check installed packages
Execute the following command on Command Prompt or PowerShell.
How to uninstall package
Execute the following command on Command Prompt or PowerShell.
When uninstalling a package, you have to specify package that uninstalling.
And Command Prompt and Powershell will ask you if you want to continue. Press “Y” to continue a process.
choco install [package name]
For example, if uninstalling 7zip, execute the following command on Command Prompt or PowerShell.
How to update package
If you want to update all packages, execute the following command,
if you want to specify package, execute the following command on Command Prompt or PowerShell.
choco update [package name]
Reference articles
Представьте себе: вам нужно установить новые программы на ПК с Windows 10. Скорее всего, вы будете искать веб-сайт разработчика, пытаясь найти нужную страницу, а затем, как правило, будете переадресованы на страницу загрузки программы для скачивания установщика, после загрузки и установки в добавок к искомой программе вы можете получить абсолютно ненужные дополнительные программы и это в самом лучшем раскладе.
Вы, вероятно, знакомы с этой процедурой, поскольку она практически не менялась за время существования Windows, с тех пор как программное обеспечение стало распространяться в Интернете. У систем Unix есть альтернативный подход, хотя установка программ обрабатывается менеджерами пакетов, которые требуют минимального пользовательского ввода и часто управляются с помощью командной строки. В настоящее значительно вырос интерес к распространению этих преимуществ в Windows 10 с помощью сторонних менеджеров пакетов.
Сегодня мы познакомимся с Chocolatey, альтернативным менеджером пакетов для Windows, который больше ориентирован на пользователя, которому нужны классические программы и приложения.
Chocolatey в первую очередь управляется с помощью командной строки. Не беспокойтесь, если вы новичок в консольных приложениях — введите команды, как показано в документации, и вы не сталкнетесь с какими-либо проблемами. Chocolatey также имеет дополнительный графический интерфейс, который мы рассмотрим позже.
Установка Chocolatey
Чтобы установить Chocolatey, откройте PowerShell от имени администратора из меню «Пуск». Затем скопируйте и вставьте следующую строку сценария и нажмите клавишу Enter:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))
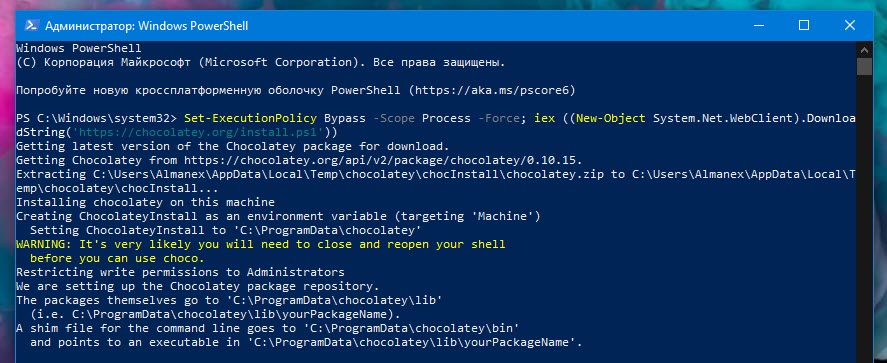
Это позволит настроить PowerShell для работы внешних сценариев перед загрузкой и запуском сценария установки Chocolatey. Для получения более подробной информации об этом процессе, вы должны обратиться к собственной документации Chocolatey. Если вы обеспокоены тем, что делает скрипт, вы должны проверить его вручную перед запуском команды.
Установка программ с помощью Chocolatey
Основной особенностью данного менеджера пакетов, является возможность установки программного обеспечения Windows с помощью одной команды. Вместо того, чтобы посещать веб-сайт и вручную выбирать установщик, вы можете запустить PowerShell и ввести что-то вроде следующего:
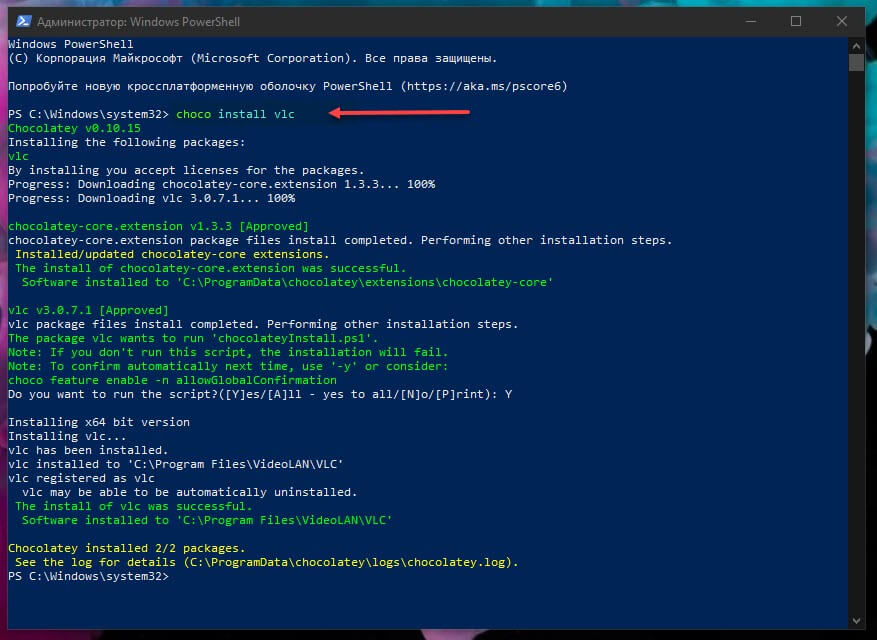
Это позволит загрузить и установить VLC Media Player в вашу систему, не требуя никаких дополнительных действий с вашей стороны. Вы увидите информацию о прогрессе, отображаемую на вашей консоли, когда VLC будет добавлен в вашу систему. Затем вы найдете его в меню «Пуск», как если бы вы запускали установщик самостоятельно.
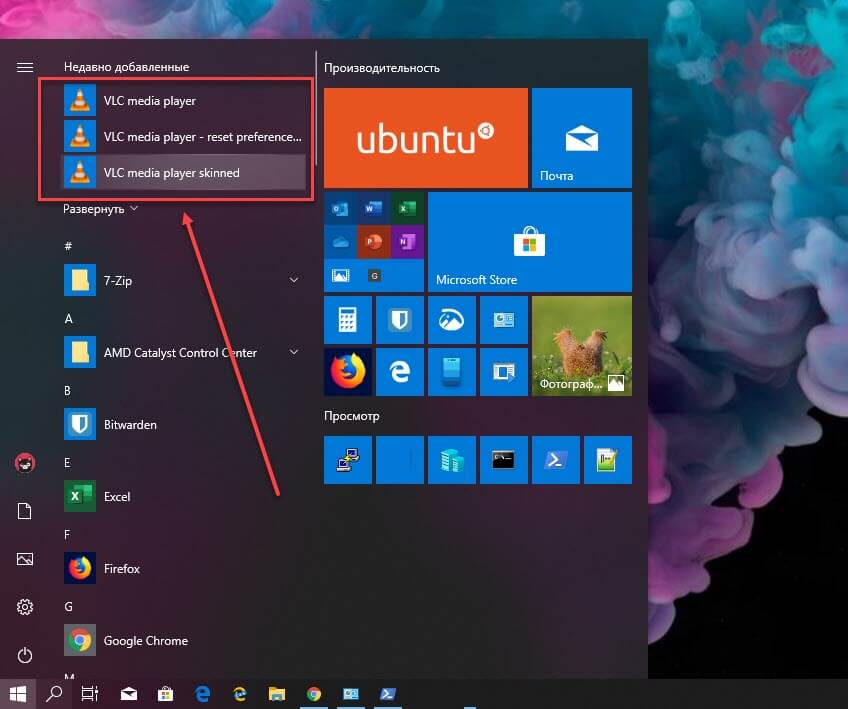
Примечание: Некоторые программы могут попросить вас запустить скрипт во время их установки. При запросе введите «A» для «All» в консоли и нажмите клавишу Enter, чтобы подтвердить это приглашение и завершить установку.
Без лишней скромности — Chocolatey поддерживает тысячи разных программ, точнее 6869 пакетов, поддерживаемых сообществом. Вы можете посмотреть их, в хранилище пакетов Chocolatey. Некоторые из самых популярных вариантов включают Chrome, Adobe Reader, Firefox, WinRAR и Skype. В хранилище пакетов отображается имя, которое нужно добавить к команде «choco install» для установки любой программы.
Обновление установленных программ
Менеджер пакетов упрощает обновление установленных программ. Выполните следующую команду, чтобы обновить все программы в вашей системе, установленные с помощью Chocolatey:
Вы также можете передать имя для обновления одной программы:
Chocolatey проверит, требуются ли обновления, и автоматически установит новую версию. Если вы хотите узнать, доступны ли обновления, не устанавливая их, вместо этого запустите
choco outdated
Еще команды
Есть несколько других команд, которые вы, вероятно, найдете полезными.
При вводе команды «choco list -lo» будет показан список всех установленных вами программ.
Вы также можете использовать поиск:
choco search имя программы
Замените запрос имя программы, чтобы искать в хранилище пакетов и отобразить все доступные программы, так что вам даже не понадобится веб-браузер для поиска нового программного обеспечения.
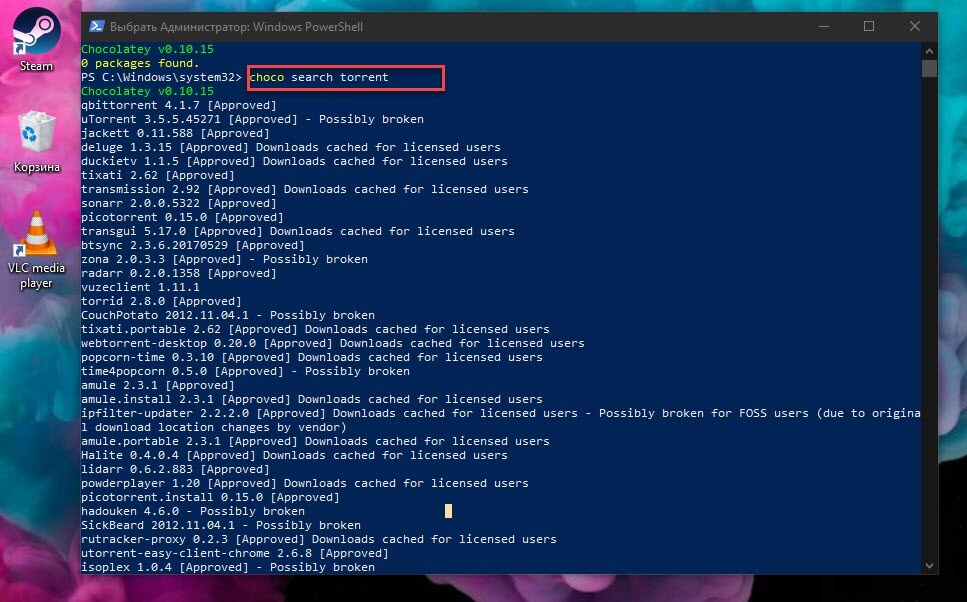
Например, будем искать торрент клиент:
choco search torrent
Получаем вывод, выберем, например transmission. Да, да, популярный торрент клиент, ранее доступный только для Mac OS X и Linux дистрибутивов — Transmission официально выпущен для Windows 10.
Получив таким образом имя, устанавливаем его командой:
choco install transmission
Несколько секунд и программа установлена, запустите ее с помощью ярлыка на рабочем столе или найдите ее в меню «Пуск».
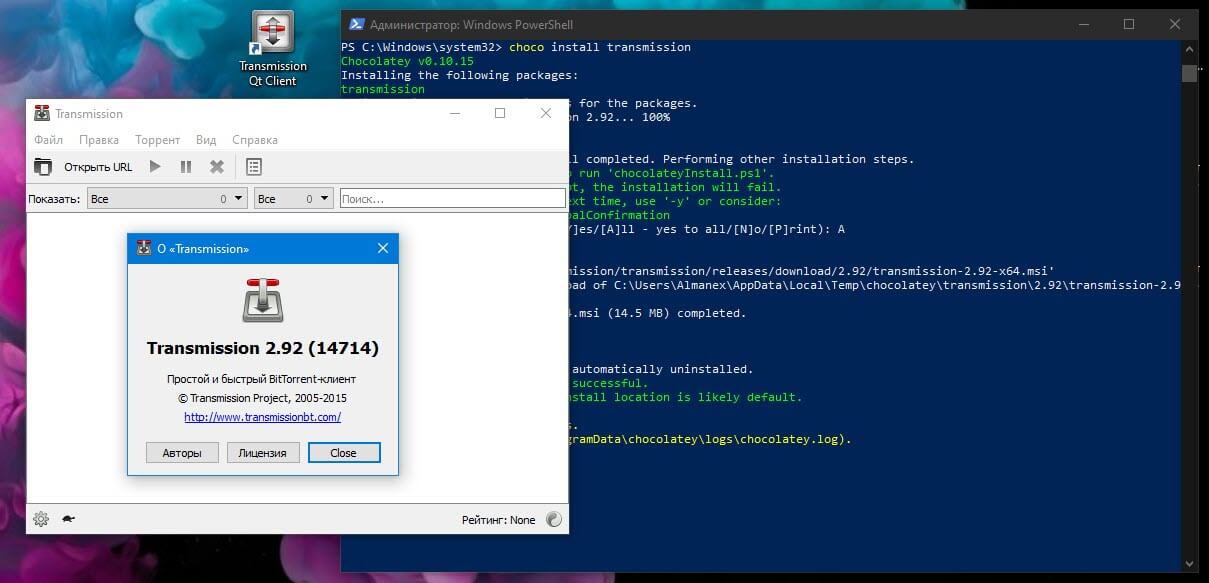
Когда дело доходит до удаления программы, используйте команду «choco uninstall», добавляя имя программы. Менеджер отслеживает удаление приложений другими способами — если вы устанавливаете программу с Chocolatey, но затем удаляете ее из приложения «Параметры Windows» или Панели управления, она также автоматически исчезает из менеджера пакетов.
Мы рассмотрели в этой статье, самые простые возможности. Для опытных пользователей существует множество параметров конфигурации, а также возможность запуска локальных прокси-серверов, кэшей и репозиториев пакетов.
Графический Интерфейс
Наконец, стоит отметить, что Chocolatey имеет дополнительный графический интерфейс, который помогает вам взаимодействовать с вашими пакетами и устанавливать новые. Как и следовало ожидать, установка пользовательского интерфейса осуществляется через саму Chocolatey!
Запустите «choco install chocolateygui», чтобы установить графический интерфейс.
choco install chocolateygui
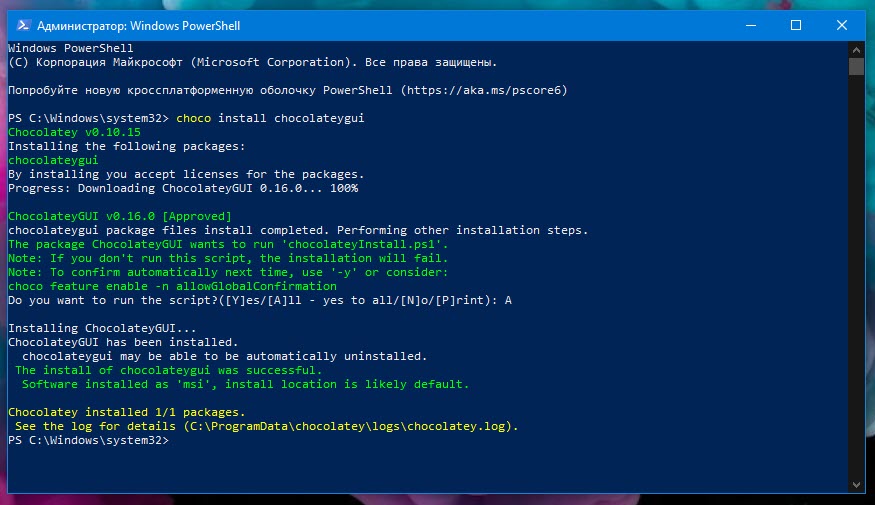
После этого вы сможете запустить графический интерфейс из меню «Пуск» с помощью ярлыка «Chocolatey GUI».
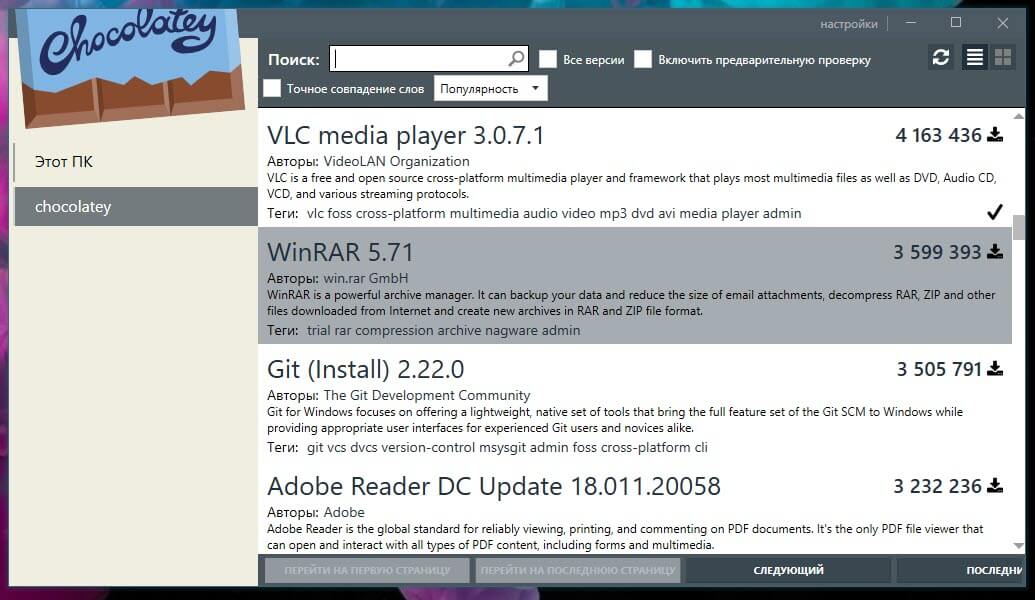
Это дает вам простой графический интерфейс для просмотра установленных пакетов, проверки обновлений и настройки параметров Chocolatey. Вы можете просмотреть каталог программ, нажав «Chocolatey» на левой боковой панели. Здесь вы можете искать новые программы и устанавливать их одним кликом мыши, избегая дальнейшего использования PowerShell.
Поделись этим.
