В Windows Server 2012R2/2016/2019 вы можете устанавливать и удалять различные роли и компоненты сервера через графический Server Manager. Однако в большинстве случаев эти же самые операции можно выполнить гораздо быстрее из консоли PowerShell. В этой статье мы рассмотрим особенности управления ролями и компонентами в актуальных версиях Windows Server.
Содержание:
- Как вывести все установленные роли и компоненты Windows Server?
- Установка ролей и компонентов Windows Server из PowerShell
- Деплой ролей на множество серверов Windows Server
- Как удалить роль или компонент в Windows Server с помощью PowerShell?
Как вывести все установленные роли и компоненты Windows Server?
Чтобы вывести список всех доступных ролей и компонентов Windows Server используется командлет
Get-WindowsFeature
. Если выполнить его без параметров, появится информация обо всех компонентах.
Как вы видите, отображается название компонента (Display Name), его системное имя (Name) и состояние (Install State: Installed, Available или Removed). Список ролей и компонентов представляет собой дерево со вложенными ролями, которое напоминает то, которые вы видите при установке ролей через графический Server Manager. Для установки и удаления ролей и компонентов через PowerShell, вам нужно знать их системное имя, которое содержится в столбце Name.
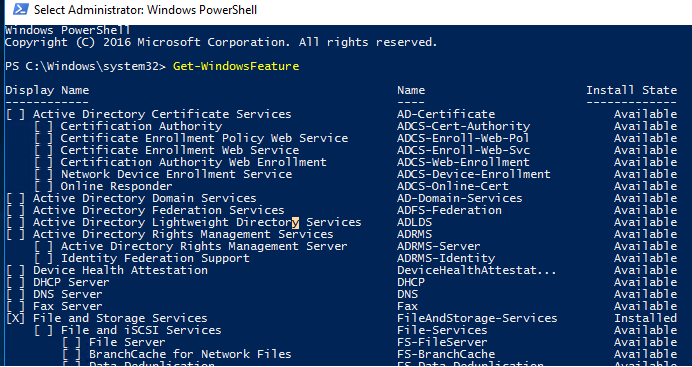
Совет. Если роль или функция находится в состоянии Removed, значит ее установочные файлы удалены из локального репозитария системы (уменьшение размера папки WinSxS) и вы не сможете установить эту роль.
Роли и компоненты удаляются из образа так:
Uninstall-WindowsFeature –Name DHCP –Remove
Чтобы установить удаленную роль, воспользуйтесь командлетом:
Install-WindowsFeature DHCP
(понадобится доступ в Интернет)
Либо вы можете восстановить компоненты их дистрибутива с вашей версией Windows Server. Данная команда установит роль DHCP сервера.
Install-WindowsFeature DHCP -Source E:\sources\sxs
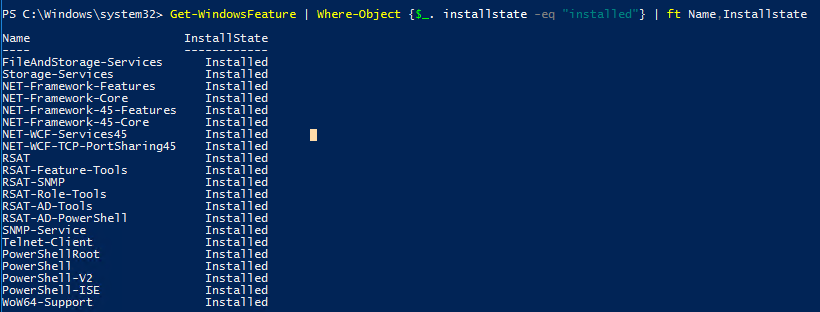
Вы можете вывести список установленных компонентов сервера:
Get-WindowsFeature | Where-Object {$_. installstate -eq "installed"} | ft Name,Installstate
Судя по скриншоту, данный сервер используется как файловый сервер (роли FileAndStorage-Services, Storage-Services). Большинство оставшихся компонентов используются для управления и мониторинга сервера.
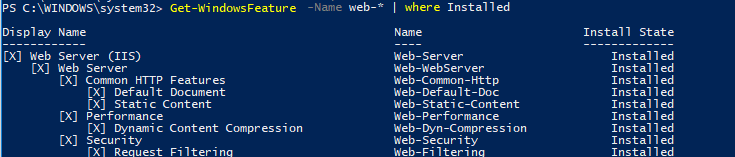
Если вы не знаете точно имя роли, можно использовать знаки подстановки. Например, чтобы проверить какие из web компонентов роли IIS установлены, выполните (немного сократим синтаксис):
Get-WindowsFeature -Name web-* | Where installed
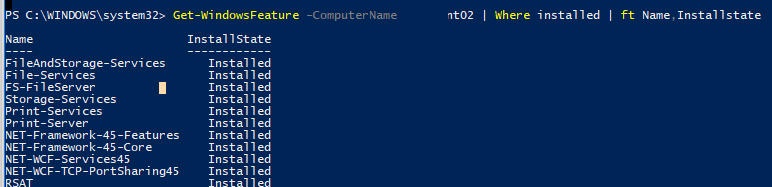
Вы можете получить список установленных компонентов на удаленном Windows Server:
Get-WindowsFeature -ComputerName msk-prnt1 | Where installed | ft Name,Installstate
Судя по установленным ролям Print-Services и Print-Server, этот сервер используется в качестве сервера печати.
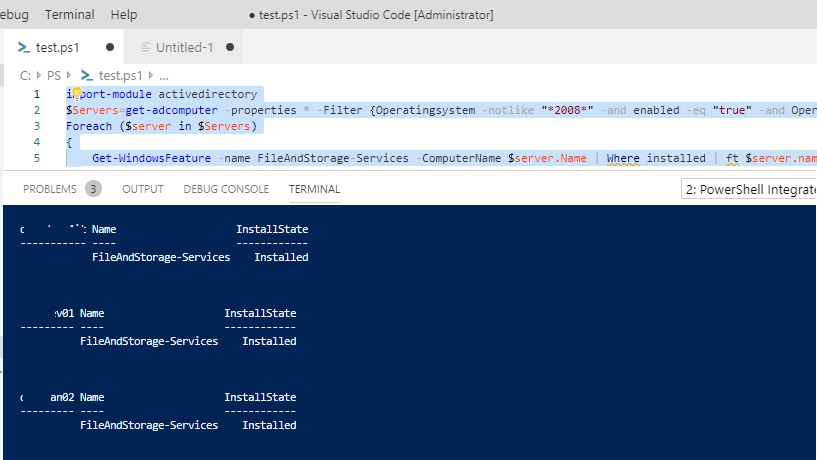
Вы можете использовать командлет Get-WindowsFeature для поиска серверов в домене, на которых установлена определенная роль. Вы можете искать на серверах в определенном OU Active Directory с помощью командлета Get-ADComputer из модуля ActiveDirectory for PowerShell, или по указанному списку серверов (
$servers = ('server1', 'server2')
). Например, нам нужно найти все файловые сервера c ролью FileAndStorage-Services в указанном контейнере AD (я использую редактор PS — Visual Studio Code)
import-module activedirectory
$Servers=get-adcomputer -properties * -Filter {Operatingsystem -notlike "*2008*" -and enabled -eq "true" -and Operatingsystem -like "*Windows Server*"} -SearchBase ‘OU=Servers,OU=MSK,DC=winitpro.ru,DC=ru’ |select name
Foreach ($server in $Servers)
{
Get-WindowsFeature -name FileAndStorage-Services -ComputerName $server.Name | Where installed | ft $server.name, Name, Installstate
}
В результате у нас появился список серверов, на которых установлена данная роль.
Установка ролей и компонентов Windows Server из PowerShell
Для установки ролей и компонентов в Windows Server используется командлет Install-WindowsFeature.
Чтобы установить роль DNS на текущем сервере и инструменты управления (в том числе модуль Powershell – DNSServer), выполните:
Install-WindowsFeature DNS -IncludeManagementTools
По-умолчанию командлет устаналивает все необходимые зависимые роли и компоненты при установке роли. Чтобы вывести список зависимостей до установки воспользуйтесь параметров.
Install-WindowsFeature -name UpdateServices -whatif
Например, для установки роли сервера обновлений WSUS, необходимо установить некоторые компоненты IIS.
What if: Continue with installation?
What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Server Update Services] Windows Server Update
What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Server Update Services] WID Database".
What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Server Update Services] WSUS Services".
What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Windows Authentication".
What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Dynamic Content Compression".
What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Performance".
What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Static Content".
What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Internal Database] Windows Internal Database".
What if: The target server may need to be restarted after the installation completes.
Чтобы установить роль Remote Desktop Session Host, службу лицензирования RDS и утилиты управления RDS на удаленном сервере, воспользуйтесь командой:
Install-WindowsFeature -ComputerName msk-rds21 RDS-RD-Server, RDS-Licensing –IncludeAllSubFeature –IncludeManagementTools –Restart
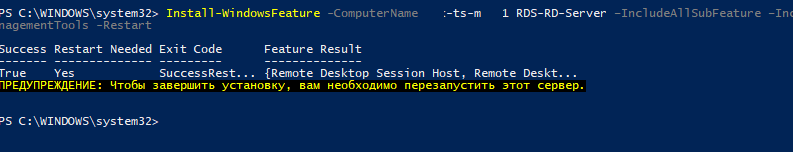
C параметром
–Restart
сервер будет автоматически перезагружен, если установленный компонент это потребует.
Также можно установить компонент такой командой (например роль SMTP сервера):
Get-WindowsFeature -Name SMTP-Server | Install-WindowsFeature
Деплой ролей на множество серверов Windows Server
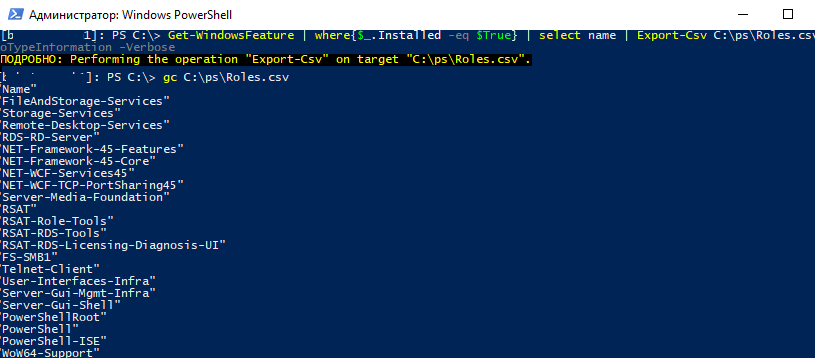
Еще одна интересная возможность при развертывании однотипных серверов. Вы можете установить необходимые компоненты на эталонном Windows Server и экспортируете список установленных ролей в CSV файл:
Get-WindowsFeature | where{$_.Installed -eq $True} | select name | Export-Csv C:\ps\Roles.csv -NoTypeInformation –Verbose
Потом вы можете использовать этот CSV файл для установки такого же набора ролей на других типовых серверах:
Import-Csv C:\PS\Roles.csv | foreach{ Install-WindowsFeature $_.name }
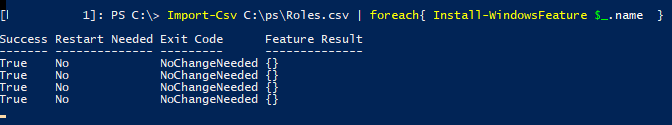
Если роль или компонент уже установлен, команда вернет
NoChangeNeeded
и продолжит установку следующей роли.
Либо для установки одинакового набора ролей сразу на нескольких серверах можно использовать такую команду:
$servers = ('srv1', 'srv2',’srv3’)
foreach ($server in $servers) {Install-WindowsFeature RDS-RD-Server -ComputerName $server}
Как удалить роль или компонент в Windows Server с помощью PowerShell?
Для удаления ролей и компонентов Windows Server используется командлет
Remove-WindowsFeature
.
Например, чтобы удалить роль принт-сервера, выполните команду:
Remove-WindowsFeature Print-Server -Restart
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Appearance settings
This article applies to the following Microsoft® Windows® Server versions: 2012, 2012 R2, 2016, 2019
This article shows how to install and remove Windows Server roles and features by using Server Manager.
Use the following steps to add Windows roles and features:
-
To open Server Manager, click the Server Manager icon in the taskbar or select Server Manager in the Start Menu.
-
Click Manage in the upper right portion of the screen and click Add Roles and Features to open a wizard.
📘
You cannot add roles and features until Server Manager finishes loading. Wait until Server Manager loads before you add roles and features.
-
On the Before you begin page, click Next to begin. You can skip this page in the future by checking Skip this page by default box.
-
On the Select installation type page, choose Role-based or feature-based installation and click Next.
-
On the Server Selection page, choose the server to which you want to add the role or feature. In most cases, this choice is the server you are logged in to. Click Next.
-
Select all desired roles on the Server Roles page. When you add roles, the wizard prompts you to add prerequisite roles and features, if any. After you have selected the desired roles, click Next.
-
Select all desired features on the Features page and click Next.
-
Complete the configuration of the selected roles and features and click Next on each screen.
-
After you complete the initial configuration of the chosen features, the Confirmation page displays and lists a summary of the changes. Verify the changes before proceeding. If you want the server to restart automatically after installation completes, check the box labeled Restart the destination server automatically if required.
-
Click Install to add the chosen roles and features.
-
To open Server Manager, click the Server Manager icon in the taskbar or select Server Manager in the Start Menu.
-
Click on Manager in the upper right portion of the screen and click Remove Roles and Features to open a wizard.
📘
You cannot add roles and features until Server Manager finishes loading. Wait until Server Manager loads before you add roles and features.
-
On the Before you begin page, click Next to begin. You can skip this page in the future by checking Skip this page by default box.
-
On the Select Destination Server page, choose the server from which you want to remove the role or feature. In most cases, this is the server you are logged in to. Click Next.
-
Select roles for removal on the Server Roles page. When you remove roles, the wizard prompts you to remove any roles and features that depend on the role you selected for removal. After you have selected
the desired roles, click Next. -
Select any features for removal on the Features page and click Next.
-
On the Confirmation page, verify the changes before proceeding. If you want the server to restart automatically after installation completes, check the box labeled Restart the destination server automatically if required.
-
Click Remove to remove the chosen roles and features.
Updated 2 months ago
Понижение контроллера домена и удаление роли AD DS
Обновлено:
Опубликовано:
Используемые термины: Active Directory, FSMO.
Мы рассмотрим пример корректного удаление роли Active Directory Domain Services для Windows Server 2012 / 2012 R2 / 2016 / 2019.
Процесс полного удаления разобьем на несколько этапов:
1. Подготовка среды AD
Перенос ролей контроллера домена
Проверка состояния AD
2. Понижение уровня контроллера домена до рядового сервера
Графический интерфейс
Powershell
3. Удаление роли AD DS
Графический интерфейс
Powershell
4. Вывод сервера из домена
Графический интерфейс
Powershell
Вопросы и ответы
Подготовка системы
Если в нашей среде AD не один контроллер домена и мы не хотим удалять сам домен, а только один из его серверов со службой каталогов, стоит выполнить предварительные операции, чтобы минимизировать возможные проблемы.
Перенос ролей контроллера домена
Active Directory насчитывает 5 FSMO ролей, которые отвечают за корректную работу службы каталогов. Смотрим, на каких серверах запущены данные роли с помощью команд в Powershell:
Get-ADForest dmosk.local | ft DomainNamingMaster, SchemaMaster
Get-ADDomain dmosk.local | ft InfrastructureMaster, PDCEmulator, RIDMaster
* где dmosk.local — домен, для которого нужно узнать назначенные роли FSMO.
Если какие-то роли назначены на сервере, который планируется понизить, то необходимо с помощью команды типа:
Move-ADDirectoryServerOperationMasterRole <имя сервера, куда переносим> <название роли>
… передать роль.
Подробнее о передаче и захвате в инструкции Управление FSMO ролями Active Directory с помощью Powershell.
Проверка состояния AD
На любом из контроллеров домена вводим команду:
dcdiag /a /q
Данная команда запустит проверку состояния среды AD и выдаст ошибки, если такие будут. Необходимо обратить внимание на сообщения и, по возможности, решить проблемы.
Понижение контроллера домена
Первым шагом понизим наш сервер до рядового сервера. Это можно сделать с помощью графического интерфейса, Powershell или командной строки.
Графика
Открываем Диспетчер серверов и переходим в Управление — Удалить роли и компоненты:

Если откроется окно с приветствием, то просто нажимаем Далее (при желании, можно поставить галочку Пропускать эту страницу по умолчанию):

В окне «Выбор целевого сервера» выбираем сервер, для которого мы будем понижать уровень AD:

… и нажимаем Далее.
Снимаем галочку Доменные службы Active Directory. откроется окно в котором отобразится список компонентов для удаления — нажимаем Удалить компоненты:

Система вернет ошибку с предупреждением, что сначала нужно понизить AD — кликаем по ссылке Понизить уровень этого контроллера домена:

В следующем окне мы увидим предупреждение о том, что компьютер будет перезагружен и возможность принудительно понизить уровень — просто нажимаем Далее:
Система отобразит роли AD, которые будут удалены. Ставим галочку Продолжить удаление и нажимаем Далее:

Вводим дважды пароль учетной записи локального администратора, который будет использоваться после понижения до рядового сервера:

Кликаем по Понизить уровень:
Процесс займет какое-то время. После мы увидим «Уровень контроллера домена Active Directory успешно понижен»:

Сервер автоматически будет перезагружен.
Powershell
Открываем консоль Powershell от администратора и вводим:
Uninstall-ADDSDomainController
Если в нашей сети это последний контроллер домена, то команда для удаления будет следующей:
Uninstall-ADDSDomainController -LastDomainControllerInDomain -RemoveApplicationPartitions
Система запросит пароль для локальной учетной записи администратора, которая будет использоваться после понижения — задаем новый пароль дважды:
LocalAdministratorPassword: **********
Подтвердить LocalAdministratorPassword: **********
Мы получим предупреждение о перезагрузки сервера. Соглашаемся:
После завершения этой операции сервер будет автоматически перезапущен. Когда вы удалите доменные службы Active
Directory на последнем контроллере домена, этот домен перестанет существовать.
Вы хотите продолжить эту операцию?
[Y] Да — Y [A] Да для всех — A [N] Нет — N [L] Нет для всех — L [S] Приостановить — S [?] Справка
(значением по умолчанию является «Y»): A
Для выполнения команды уйдет некоторое время, после чего сервер уйдет в перезагрузку.
Удаление роли AD DS
После понижения сервера роль, по-прежнему, будет установлена. Для ее удаления мы также можем воспользоваться графической оболочкой или командной строкой.
Графика
В диспетчере серверов кликаем снова по Управление — Удалить роли и компоненты:

Среди серверов выбираем тот, на котором будем удалять роль:

* сервер может быть только один. Тогда выбираем его.
Снимаем галочку Доменные службы Active Directory, в открывшемся окне кликаем по Удалить компоненты:

Галочка для доменных служб будет снята:
… кликаем по Далее несколько раз.
В последнем окне ставим галочку Автоматический перезапуск конечного сервера, если требуется и подтверждаем действие ответом Да:
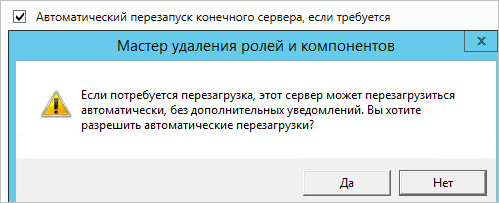
Роль будет удалена, а сервер отправлен в перезагрузку.
Powershell
Запускаем Powershell от администратора и вводим:
Remove-WindowsFeature -Name AD-Domain-Services
Роль контроллера будет удалена. Мы должны увидеть сообщение:
ПРЕДУПРЕЖДЕНИЕ: Чтобы завершить удаление, вам необходимо перезапустить этот сервер.
Перезагружаем сервер:
shutdown -r -t 0
Вывод сервера из домена
В случае, если у нас есть другие контроллеры домена, наш сервер останется в домене. При необходимости его окончательного вывода из эксплуатации, стоит вывести его из среды AD.
Графика
Открываем свойства системы (команда control system или свойства Компьютера) и кликаем по Изменить параметры:
В открывшемся окне нажимаем на Изменить:
И переводим компьютер в рабочую группу:
* в данном примере в группу с названием WORKGROUP.
Система запросит логин и пароль от пользователя Active Directory, у которого есть права на вывод компьютеров из домена — вводим данные.
Если все сделано верно, мы должны увидеть окно:
После перезагружаем сервер или выключаем его.
Powershell
Запускаем Powershell от имени администратора и вводим:
Remove-Computer -UnjoinDomaincredential dmosk\master -PassThru -Verbose
* где dmosk\master — учетная запись в домене с правами вывода компьютеров из AD.
Соглашаемся продолжить, ознакомившись с предупреждением:
Подтверждение
Чтобы войти в систему на этом компьютере после его удаления из домена, вам потребуется пароль учетной записи локального
администратора. Вы хотите продолжить?
[Y] Да — Y [N] Нет — N [S] Приостановить — S [?] Справка (значением по умолчанию является «Y»): Y
Перезагружаем компьютер:
shutdown -r -t 0
… или выключаем:
shutdown -s -t 0
Вопросы и ответы
Дополнительные сведения относительно понижения и удаления AD.
1. Как удалить дочерний домен?
Мы должны быть уверены, что в данном домене не осталось важных ресурсов предприятия. После необходимо по очереди удалить все контроллеры домена по данной инструкции. При удалении последнего сервера AD для дочернего домена, будет удален сам дочерний домен из леса.
2. Как понизить режим работы домена?
Данный режим не понизить — это односторонняя операция. Максимум, что можно сделать, это восстановить службу AD из резервной копии, когда режим был нужного уровня.
3. Что делать, если умер основной контроллер домена?
Рассмотрим несколько вариантов:
- Если есть резервная копия, восстанавливаемся из нее.
- Если в среде несколько контроллеров домена, захватываем FSMO-роли (подробнее в инструкции Управление FSMO ролями Active Directory с помощью Powershell) и вручную удаляем уже несуществующий контроллер. После можно поднять новый контроллер, сделав его резервным.
- Хуже, когда нет ни копий, ни второго контроллера. В таком случае, поднимаем новый контроллер, создаем новый лес, домен и переводим все компьютеры в него.
4. Что делать, если контроллер домена возвращает ошибку при понижении?
Самый лучший способ, разобраться с ошибкой, решив проблему, которая ее вызывает. Если это не удалось сделать, принудительно понижаем сервер командой:
dcpromo /forceremoval
In Windows Server 2012R2/2016/2019, you can use the graphical Server Manager console to install and remove server roles and features. However, in most cases, you can do the same from the PowerShell console much faster. In this article, we’ll consider how to manage roles and features in the modern Windows Server versions with PowerShell.
Contents:
- List all Installed Windows Server Roles & Features via PowerShell
- How to Install Windows Server Roles & Features using PowerShell
- How to Deploy Roles on Multiple Remote Windows Servers?
- How to Uninstall a Role or Feature on Windows Server with PowerShell?
List all Installed Windows Server Roles & Features via PowerShell
User the Get-WindowsFeature cmdlet to display the list of all available Windows Server roles and features. If you run it without parameters, you will see the information about all Windows Server components.
The name of a component (Display Name), its system name (Name) and its state (Install State: Installed, Available or Removed) are displayed. The list of roles and features looks like a tree with nested roles similar to the one you see when you install the roles in the Server Manager GUI. To install and remove any roles or features using PowerShell, you must know their system names listed in the Name column.
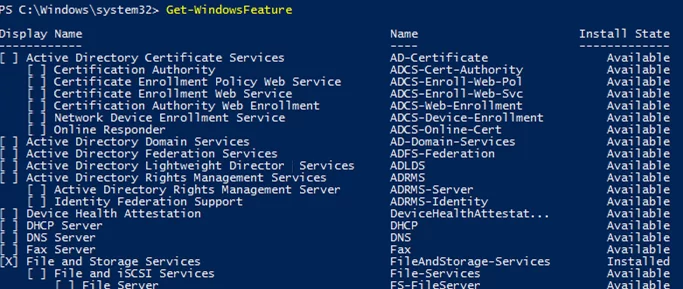
Hint. If a role or a feature is Removed, it means that its installation files are removed from the system component store (to reduce the size of WinSxS folder) and you won’t be able to install the role without direct Internet access or Windows Server installation ISO (see the example with the .Net 3.5 installation).
You can remove roles or components from your image online like this:
Uninstall-WindowsFeature –Name DHCP –Remove
To install a removed DHCP Server role, use this cmdlet:
Install-WindowsFeature DHCP (you will need direct Internet access)
Or you can restore the component binary files from your Windows Server ISO image:
Install-WindowsFeature DHCP -Source E:\sources\sxs
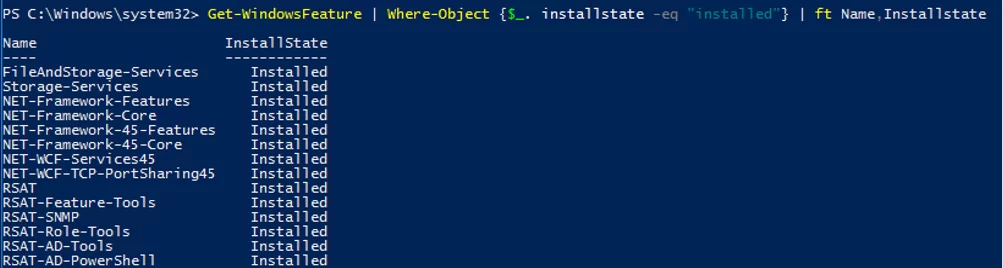
You can list the installed server features:
Get-WindowsFeature | Where-Object {$_. installstate -eq "installed"} | ft Name,Installstate
Based upon the screenshot below, this server is used as a file server (FileAndStorage-Services, Storage-Services roles installed). Most of the other components are used to manage or monitor the server.
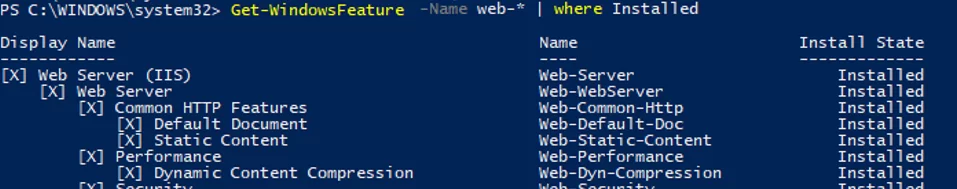
If you do not know the role name exactly, you can use wildcards. For example, to check what web components of the IIS role are installed, run this command (the syntax is a bit shortened):
Get-WindowsFeature -Name web-* | Where installed
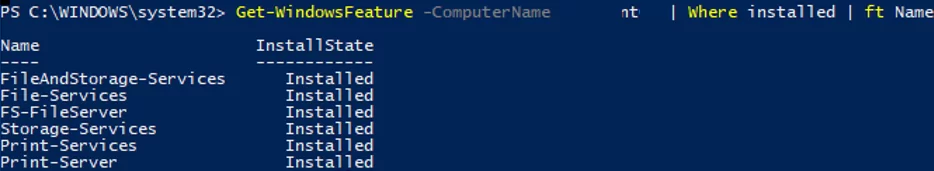
You can get the list of installed components on a remote Windows Server:
Get-WindowsFeature -ComputerName ny-spool1 | Where installed | ft Name,Installstate
Judging by the installed Print-Services and Print-Server roles, this server is used as a print server.
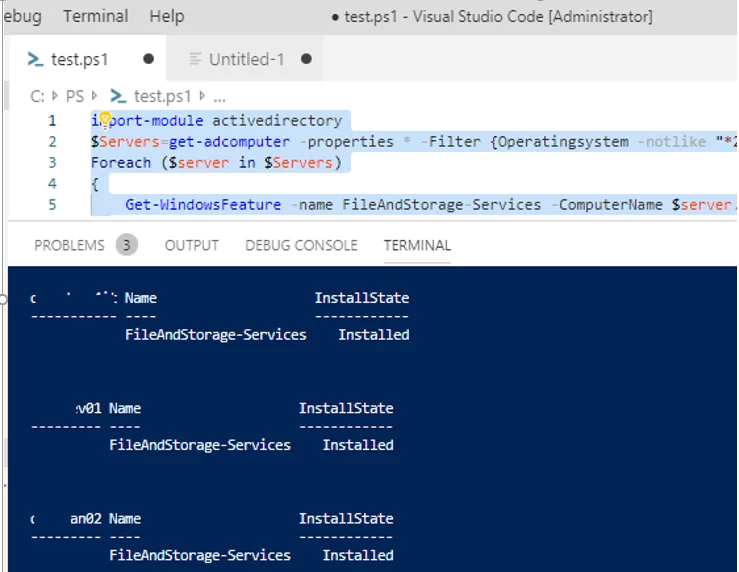
You can use the Get-WindowsFeature cmdlet to find servers in your domain, on which the specific role is installed. You can search your servers in a particular Active Directory OU using the Get-ADComputer cmdlet from the PowerShell ActiveDirectory module or by the provided list of servers ($servers = ('server1', 'server2')).
For example, you want to find all file servers with the FileAndStorage-Services role in the specified AD Organizational Unit. Use the following script:
import-module activedirectory
$Servers=get-adcomputer -properties * -Filter {Operatingsystem -notlike "*2008 R2*" -and enabled -eq "true" -and Operatingsystem -like "*Windows Server*"} -SearchBase ‘OU=Servers,OU=UK,DC=woshub,DC=com’ |select name
Foreach ($server in $Servers)
{
Get-WindowsFeature -name FileAndStorage-Services -ComputerName $server.Name | Where installed | ft $server.name, Name, Installstate
}
In the output, you will get the list of servers, on which the specific role is installed.
How to Install Windows Server Roles & Features using PowerShell
To install roles and features on Windows Server, the Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet is used.
To install the DNS server role and the management tools (including the Powershell DNSServer module) on the current server, run this command:
Install-WindowsFeature DNS -IncludeManagementTools
By default, the cmdlet installs all dependent roles and features. To display the list of dependencies before the installation, use the option WhatIf:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name UpdateServices -WhatIf
For example, to install the WSUS role, you will have to install some IIS components as well.
What if: Continue with installation? What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Server Update Services] Windows Server Update What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Server Update Services] WID Database". What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Server Update Services] WSUS Services". What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Windows Authentication". What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Dynamic Content Compression". What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Performance". What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Static Content". What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Internal Database] Windows Internal Database". What if: The target server may need to be restarted after the installation completes.
To install the Remote Desktop Session Host role, the RDS licensing role, and RDS remote management tools, use the following command:
Install-WindowsFeature -ComputerName lon-rds3 RDS-RD-Server, RDS-Licensing –IncludeAllSubFeature –IncludeManagementTools –Restart
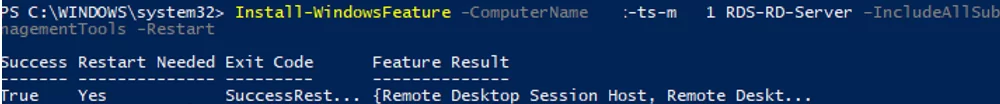
If you add the –Restart parameter, your server will be automatically restarted if required.
You can also install a component with the following command. For example, to install the SMTP server role:
Get-WindowsFeature -Name SMTP-Server | Install-WindowsFeature
How to Deploy Roles on Multiple Remote Windows Servers?
There is another interesting option when you deploy typical servers. You can install the features you want on a reference Windows Server and export the list of the installed roles to a CSV file:
Get-WindowsFeature | where{$_.Installed -eq $True} | select name | Export-Csv C:\PS\InstalledRoles.csv -NoTypeInformation –Verbose
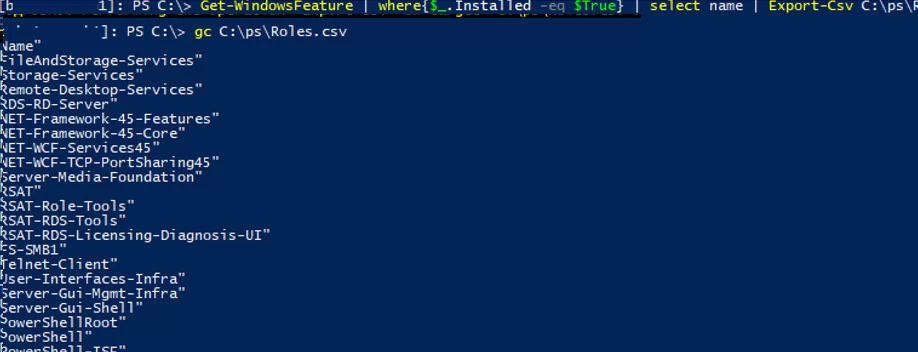
Then you will be able to use this CSV file to install the same set of roles on other typical servers:
Import-Csv C:\PS\Roles.csv | foreach{ Install-WindowsFeature $_.name }
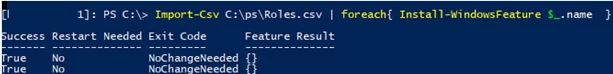
If a role or a feature is already installed, the command will return NoChangeNeeded and continue with the installation of the next role.
Or to install the same role set on multiple remote servers, you can use this command:
$servers = ('ny-rds1', 'ny-rds2',’ny-rds3’,’ny-rds4’)
foreach ($server in $servers) {Install-WindowsFeature RDS-RD-Server -ComputerName $server}
How to Uninstall a Role or Feature on Windows Server with PowerShell?
To remove a Windows Server role or feature, the Remove-WindowsFeature cmdlet is used.
For example, to remove a print server role, run the command:
Remove-WindowsFeature Print-Server -Restart
