How to Completely Delete MySQL From Windows? All Versions
Approved By
Anuraag Singh
Published On
May 8th, 2025
Reading Time
4 Minutes Reading
Summary: Whenever we are managing MySQL on our Windows system, it’s essential for optimal performance. As, it can especially affect your system when the upgrade and reinstallation process is required. So, this guide will explain to you how to uninstall MySQL from Windows 10 or 11 completely using various manual solutions and expert approaches. Also, if you are looking to remove other applications, you can read this manual guide on how to uninstall Google Chrome.
Reasons to Remove MySQL From Windows System
There are several findings as to why we need to uninstall MySQL from Windows system. Let’s cover these points.
- You can install a newer version without any software issues.
- It can fix your corrupted file installation problem and delete any incomplete or pending one.
- By uninstalling, it made it easier to switch to a different database system without any trouble.
- Removing the software or resources which are not used from a long way can boost the overall performance of your systems.
How to Uninstall MySQL From Windows 11 or 10 Using Manual Methods
Let me tell you if you want to remove MySQL from Windows. Then, it is way simple to do it. Just follow these steps carefully with images provided for clarity purposes.
Step 1. Firstly, open Windows Settings via the gear icon in the Start menu or by pressing Win + I.

Step 2. In the settings Window, you need to go to Apps and use the search bar to find “MySQL“.


Step 3. Then, locate MySQL-related programs (e.g., MySQL Server, Workbench, Connector, Shell) and uninstall them.

Step 4. After the process of uninstallation is done, delete the MySQL folder in C:\Program Files.


Step 5. If the folder is hidden, go to the View tab, tick Hidden items checkbox.

Step 6. At last, open the command prompt to verify the uninstallation process if an error appears, and the process is completed.

Note: Type MySQL – -version command in cmd to check that your MySQL file is completely deleted from your system or not.
How to Completely Delete MySQL From Windows? One Click Fully Wipe
If you want to uninstall MySQL from Windows, following the manual solution often comes with some drawbacks and human errors and chances of having residual files after the process which can have the risk of security and takes extra space. To avoid this, you can use SysTools Certified Wiping Software for complete removal and thorough deletion of configuration files, databases, and logs.
Simple Steps to Uninstall MySQL From Windows – Automated Tool
Follow this quick steps mentioned below to completely delete MySQL files from your system. To free up your space and have a smooth operation throughout your work.
Step 1. Open SysTools Data Wipe from the Start menu by right-clicking.

Step 2. Next, click “Select File” or “Select Folder” as per your comfort.

Step 3. Select the folder to wipe. Generally found at C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server <version>\Data\ and click Next to scan.

Step 4. Choose a wiping method.

Step 5. Click Wipe to begin the process.

Step 6. Now, view the wiped file/folder details on the screen.

Step 7. Lastly, you can analyze the data that is wiped by the following report.

Final Verdict
In this write up, we have understood the reasons and how to uninstall MySQL from Windows 10/11 using a manual & professional method. Following these steps will completely remove MySQL and its leftover files. If you plan to reinstall MySQL, it will ensure no conflicting files remain for a smooth setup. This will help prevent errors and improve system performance.
By Mohit Jha
With 5+ years of experience, Mohit is a Microsoft Certified expert known for his cloud migration, cyber security, and digital forensics expertise. He specializes in Microsoft 365, Exchange Server, and Azure AD migration, ensuring seamless transitions for organizations worldwide. His multifaceted role as a meticulous tech writer, diligent researcher, and astute editor underscores his commitment to delivering cutting-edge digital forensics and cloud migration strategies.
View all of Mohit Jha’s posts.
Home » KB » Databases » MySQL » How to Uninstall MySQL in Linux, Windows, and macOS
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) available on Linux, Solaris, macOS, Windows, and FreeBSD. Sometimes, uninstalling the software and a fresh installation is the best solution for resolving bugs, or for fixing compatibility purposes.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to uninstall MySQL on Linux, Windows, and macOS.

Prerequisites
- MySQL installed on Linux, Windows, or macOS system.
- A user account with administrator privileges.
How to Uninstall MySQL {on Linux, Windows, and macOS}?
Depending on the operating system, the process of uninstalling MySQL is different. The sections below show how to uninstall MySQL on Linux, Windows, and macOS, and delete all the associated data.
Uninstall MySQL on Linux
Uninstall MySQL from Linux using the distribution’s default package manager, and the rm command to delete the leftover data. In this tutorial, we will work on Ubuntu, but the instructions for other distros are provided as well.
Follow the steps below:
1. Open a terminal window (Ctrl + Alt + T) and stop the MySQL service and all the related processes. Run the following commands:
sudo service mysql stop
sudo killall -KILL mysql mysqld_safe mysqld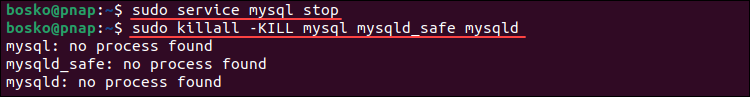
3. Depending on the Linux distribution and package manager you are using, run one of the following commands to uninstall MySQL:
- CentOS, Rocky Linux, and RedHat:
sudo yum remove mysql-client mysql-server -y- Ubuntu and Debian:
sudo apt remove mysql-client mysql-server -y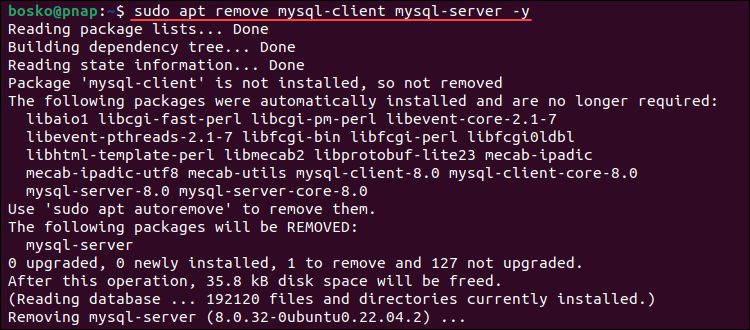
Run autoremove and autoclean to remove unnecessary packages and clean up the package cache:
sudo apt autoremove -y
sudo apt autoclean -y- Fedora:
sudo dnf remove mysql-client mysql-server -y4. After uninstalling MySQL, the next step is to remove residual data. If you still need the data, make a backup before removing it, or rename the directory.
Rename the /var/lib/mysql directory to keep the data if you ever need it again in the future:
sudo mv /var/lib/mysql /var/lib/mysql_directory_backupAlternatively, remove MySQL-related directories by running:
sudo rm -rf /etc/apparmor.d/abstractions/mysql /etc/apparmor.d/cache/usr.sbin.mysqld /etc/mysql /var/lib/mysql /var/log/mysql* /var/log/upstart/mysql.log* /var/run/mysqld5. Remove the mysql user and delete the mysql group, if it exists. Run:
sudo deluser --remove-home mysql
sudo delgroup mysql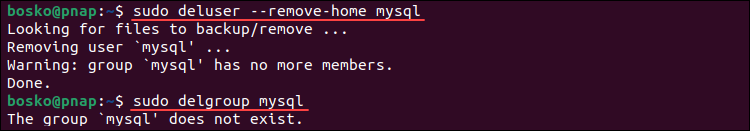
After completing the steps above, you have successfully uninstalled MySQL from your Linux system.
Uninstall MySQL on Windows
Follow the steps below to uninstall MySQL from a Windows operating system:
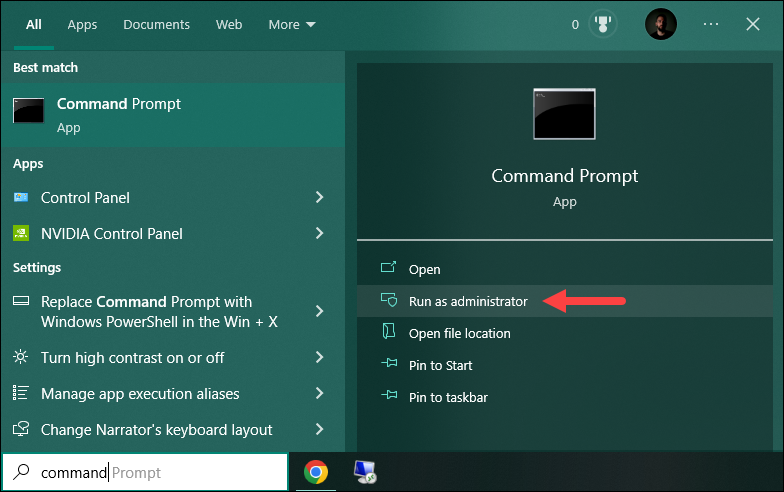
1. Press the Windows key and search for command prompt. Run the app as administrator.
2. Stop the running MySQL server before uninstalling it. The easiest way to stop it is by using the mysqladmin command which was installed automatically during the MySQL installation. In the command prompt, navigate to the bin folder of the MySQL installation directory. For example, the default path is:
cd C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin
After navigating into that path, stop the running server by executing:
mysqladmin -u root -p shutdownThe command asks you for the password and shuts down the running server after confirming it.
3. Next, open the Control Panel. Press the Windows key and search for control panel. Press Enter to open the app.
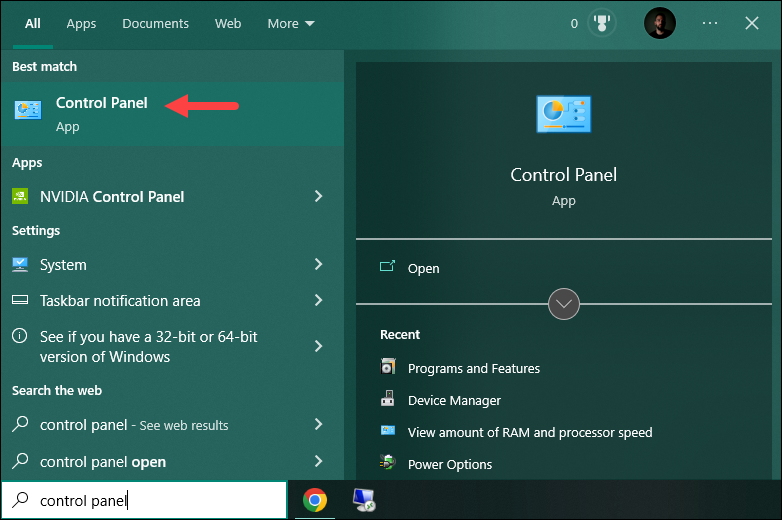
4. Open Programs and Features. In the list of installed programs, locate MySQL and all related programs. Click each one individually and select the Uninstall option.
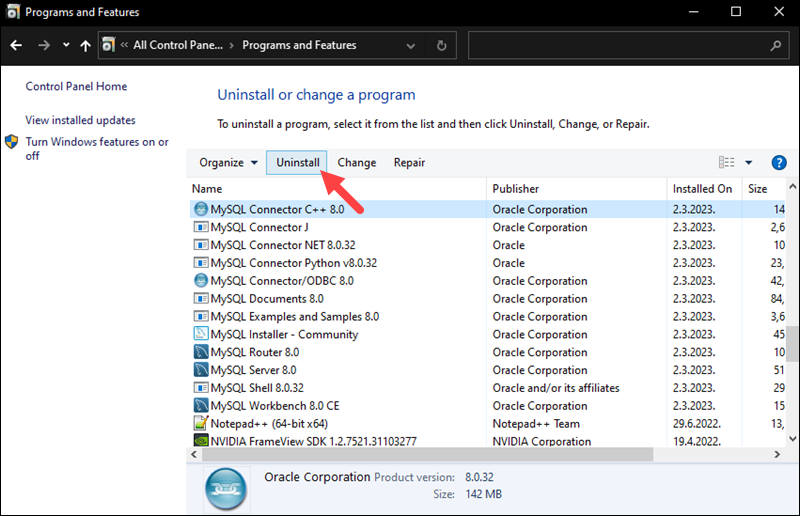
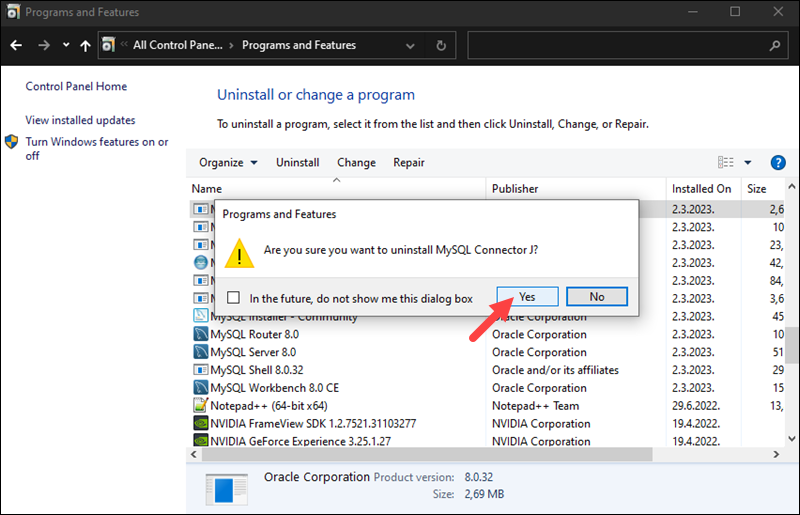
Click Yes for each prompt and wait for the wizard to finish.
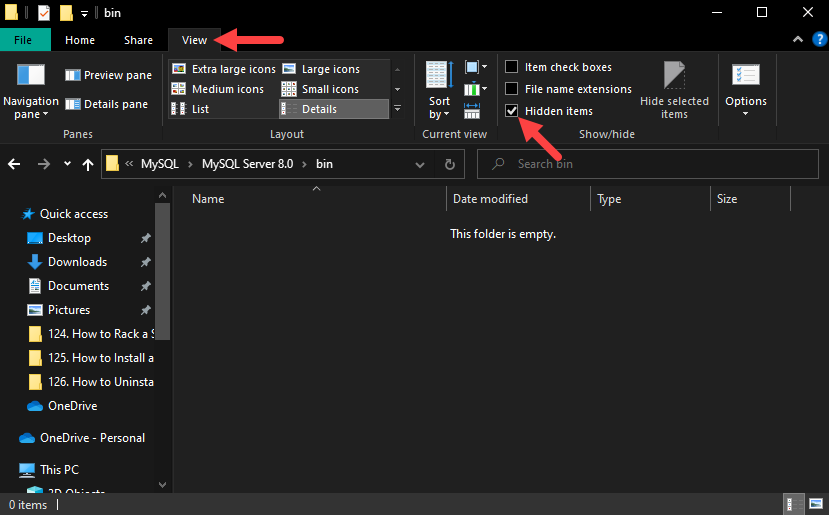
5. After uninstalling all MySQL components, delete the remaining data directories. Since one of the directories is hidden, make sure to enable the Hidden items option in folder settings.
To do so, open any folder using File Explorer, click the View tab, and check the Hidden items option:
Important: If there is critical data that you may still need, make sure to backup MySQL databases before deleting them.
The directories that you need to remove are:
- C:\Program Files\MySQL
- C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL
- C:\ProgramData\MySQL
- C:\Users\[YourUsername]\AppData\Roaming\MySQL
6. After you uninstall all the components and delete the remaining directories, restart the computer for the changes to take effect.
Uninstall MySQL on macOS
Follow the steps below to uninstall MySQL on a macOS system:
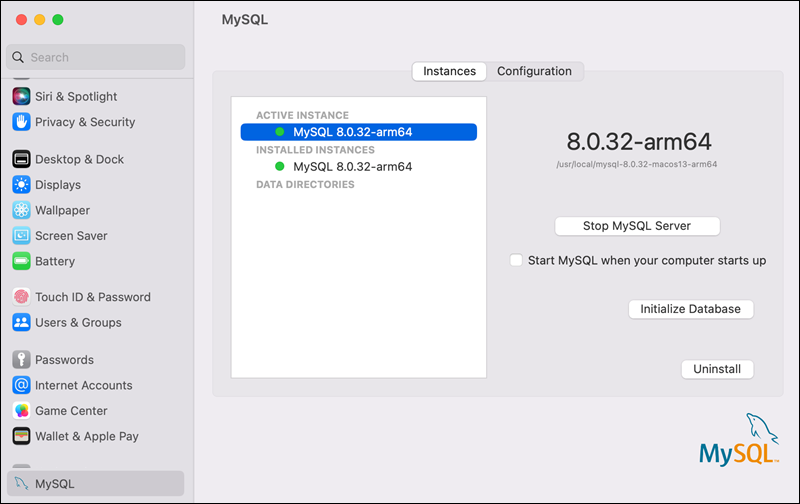
1. Go to System Settings and click MySQL. Click the Uninstall button to remove MySQL from the system.
2. Click the Launchpad icon in the Dock and type Terminal in the search field. Click Terminal to open a new terminal window.
3. Deleting MySQL removes all its databases. If you have critical data stored in MySQL, make sure to back up your files first.
Use mysqldump to back up your databases to a text file. Run the following command:
./mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases > mysqlbackup.sqlThe output is redirected to the mysqlbackup.sql file.
4. Check for running MySQL processes by running the following command:
ps -ax | grep mysql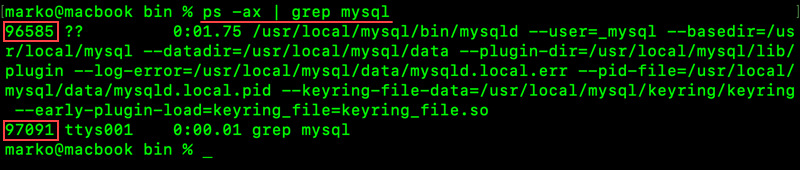
Terminate the running processes using the following syntax:
kill [process_id]For example, to kill the ttys001 process from the image above, run:
kill 970915. Remove the default MySQL directory and all the leftover directories and files. Run these commands:
sudo rm /usr/local/mysql
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/mysql
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/var/mysql
sudo rm -rf /Library/StartupItems/MySQLCOM
sudo rm -rf /Library/PreferencePanes/MySQL*
sudo rm -rf /Library/Receipts/mysql*
sudo rm -rf /private/var/db/receipts/*mysql*Removing all the directories is important especially if you want to install an older MySQL version on Mac.
6. Use a text editor to open the /etc/hostconfig file and remove the following line:
MYSQLCOM=-YES-Note: Some versions of macOS don’t have the /etc/hostconfig file, so skip this step if the file doesn’t exist on your system.
After following the steps above, you have successfully uninstalled MySQL from your macOS system and cleaned up unnecessary files.
Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to uninstall MySQL from Linux, Windows, and macOS operating systems.
For more MySQL tutorials, see how to install and get started with MySQL Workbench on Ubuntu, or how to secure your MySQL installation.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
Posted on Oct 27, 2021
Reading time: 1 minute

If you installed MySQL server using the official MySQL Community Server installer, then you can uninstall it from Windows Control Panel.
Head to the Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features and search for mysql as shown below:
You will see several programs related to MySQL as in the picture above.
To remove MySQL database server, you only need to uninstall the one named MySQL Server x.x which is responsible for starting MySQL server on your computer.
The rest of the programs (connectors, router, etc.) are utility programs to help MySQL runs without any error. You can uninstall them later as well.
Once you double-click on the program name, the uninstallation wizard should appear to guide you on uninstalling the program.
MySQL Server should be removed from your computer once the process is finished.
Optionally, you can also remove any data associated with MySQL, usually located on C:\ProgramData\MySQL.
And that’s how you uninstall MySQL Server installed using the official installer.
If you install MySQL as a part of development tools like XAMPP or WAMP, then you need to uninstall the XAMPP (or WAMP) itself to remove MySQL from your computer.
Thanks for reading! 🙏
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Uninstalling MySQL on Windows
- Uninstalling MySQL on macOS
- Uninstalling MySQL on Linux
- Advanced Uninstallation Tips
- Conclusion
Introduction
MySQL, owned by Oracle, is one of the most widely used open-source relational database management systems (RDBMS). While it’s beneficial to have MySQL installed to manage databases for various applications, there may come a time when you need to uninstall MySQL from your system. This process may involve a bit more than simply dragging a folder to the trash or using a basic uninstall command. In this guide, we will take a step-by-step approach to completely remove MySQL and all its associated files from your system.
This tutorial will focus on uninstalling MySQL from different operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux. We will provide detailed instructions as well as code examples and expected outputs to ensure a smooth uninstallation process.
Uninstalling MySQL on Windows
To uninstall MySQL from a Windows OS, you need to follow these steps:
- Open the Control Panel.
- Navigate to ‘Programs’ -> ‘Programs and Features’.
- Select MySQL Server from the list and click the ‘Uninstall’ button.
After the uninstallation process is complete, you should remove any remaining service instances. Open up the Command Prompt as an administrator and type the following:
sc delete mysqlIf the service is not named ‘mysql’ on your system, replace ‘mysql’ with the correct service name in the above command.
Delete the remaining files and folders manually. You might find MySQL installed in the ‘Program Files’ or ‘ProgramData’ folder. Ensure that you have shown hidden files and folders, and then delete the MySQL folders:
rmdir /S "C:\Program Files\MySQL"
rmdir /S "C:\ProgramData\MySQL"
rmdir /S "C:\Users\[YourUsername]\AppData\Roaming\MySQL"
Replace ‘[YourUsername]’ with your actual username on your Windows system.
Next, you’ll have to clean any MySQL entries from the Windows Registry. Be cautious when editing the registry and ensure to backup before making any changes. Run the Registry Editor (regedit) and delete the following keys:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Eventlog\Application\MySQL
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MySQL AB
Uninstalling MySQL on macOS
Uninstalling MySQL on a Mac system is not much different from the process on Windows, but it requires some terminal commands. Here are the steps:
- Open Terminal.
- Stop the MySQL service using the following command:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server stop
Remove the MySQL folder:
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/mysql*
sudo rm -rf /Library/StartupItems/MySQLCOM
You should also unload the launch agents that automatic start MySQL:
launchctl unload -w ~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.mysql.mysql.plist
rm ~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.mysql.mysql.plist
Finally, you need to remove the MySQL preferences and cached files:
rm -rf ~/Library/PreferencePanes/My*
sudo rm -rf /Library/Receipts/mysql*
sudo rm -rf /Library/Receipts/MySQL*
sudo rm -rf /private/var/db/receipts/*mysql*Uninstalling MySQL on Linux
The process to remove MySQL on Linux systems varies between distributions. Here’s a general guide that applies to systems using the `apt-get` package manager (like Ubuntu).
Stop the MySQL service:
sudo service mysql stopRemove the MySQL packages:
sudo apt-get remove --purge mysql-server mysql-client mysql-common
sudo apt-get autoremove
sudo apt-get autocleanDelete the MySQL configuration and data files:
sudo rm -rf /etc/mysql /var/lib/mysql
sudo rm -rf /var/log/mysql*And again, you can also remove the MySQL users:
sudo deluser mysql
sudo delgroup mysqlNote that these commands may need to be adapted if you’re using a different package manager like `yum` or `dnf` for Red Hat-based systems or `zypper` for openSUSE systems.
Advanced Uninstallation Tips
If you have custom configurations, you may need to manually search and remove those configurations from your system. Use the following command to search for any remaining MySQL related files:
sudo find / -iname '*mysql*'Carefully check the resulting list and delete the files that are meant to be removed. Make sure not to remove system files essential for other applications.
Conclusion
After following the steps in this tutorial, MySQL should be completely removed from your system. While most uninstalled data and service instances will be cleansed through established processes, checking for residual configuration files is good practice. As always, when dealing with system configurations and uninstalling core software components meticulously, ensure every step is understood and properly executed to avoid unintended consequences.
