In today’s interconnected world, the need for efficient and seamless communication is more important than ever. One crucial aspect of this is ensuring that text and characters are correctly encoded, allowing for compatibility across different platforms and languages. In Windows 10, setting the UTF-8 encoding is a vital step to enable smooth communication and eliminate any potential issues with character display and compatibility.
The UTF-8 encoding, which stands for Unicode Transformation Format-8, is a widely used character encoding that supports a vast range of characters from various scripts and languages. By setting the UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10, you guarantee that your system can handle and display text in different languages accurately. This ensures that you can read and share content from around the world without any distortion or loss of information. With the increasing diversity of content and the global nature of communication, setting UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10 is an essential step to enable seamless communication across different languages and platforms.
To set Utf-8 encoding in Windows 10, follow these steps:
- Open the Control Panel.
- Select «Clock and Region» and then click on «Region.»
- In the «Formats» tab, click on «Additional settings.»
- Go to the «General» tab, and under «Language for non-Unicode programs,» select «UTF-8.»
- Click «OK» and restart your computer.

Understanding UTF-8 Encoding in Windows 10
Setting UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10 is crucial for ensuring proper handling and display of characters from different languages and scripts. UTF-8 is a variable-width character encoding that supports almost all characters in the Unicode standard, making it the most widely used encoding worldwide. By setting UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10, you can avoid issues such as garbled text, incorrect character rendering, and missing characters when working with files, websites, or applications that use non-ASCII characters.
1. Setting UTF-8 Encoding for System Locale
The first step to setting UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10 is to configure the system locale settings. The system locale determines the default encoding used by applications and services for non-Unicode programs. Here’s how you can set the UTF-8 system locale:
- Open the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows 10 Start menu and selecting the corresponding result.
- In the Control Panel, click on «Clock and Region» or «Clock, Language, and Region» depending on your system configuration.
- Under the «Region» or «Region and Language» section, click on «Change date, time, or number formats.»
- In the Formats tab of the Region settings, click on the «Additional settings» button.
- In the «Customize Format» window, navigate to the «Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support» section and check the box.
- Click OK to apply the settings and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Setting the system locale to UTF-8 ensures that non-Unicode applications and services use this encoding by default, reducing the risk of character-related issues when working with different languages and scripts.
Benefits of Setting UTF-8 Encoding for System Locale
By setting UTF-8 encoding for the system locale, you gain several benefits:
- Compatibility: UTF-8 is widely supported across different platforms, applications, and programming languages, ensuring optimal compatibility and interoperability.
- Character Support: UTF-8 supports nearly all characters and symbols from every major writing system, making it suitable for multilingual applications and content.
- Future-Proofing: UTF-8 is the recommended encoding for future-proofing your systems and applications. It allows seamless incorporation of new characters and scripts as Unicode continues to evolve.
- Global Reach: With UTF-8 encoding, your content can reach a global audience without language or character-based restrictions.
2. Configuring UTF-8 Encoding for Individual Applications
While setting the system locale to UTF-8 is crucial, individual applications can also have their own encoding settings. Configuring UTF-8 encoding for specific applications ensures that they handle non-ASCII characters correctly. Here’s how you can configure UTF-8 encoding for some popular applications:
Microsoft Office Applications
To set UTF-8 encoding for Microsoft Office applications such as Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, follow these steps:
- Open the respective Office application (e.g., Word, Excel).
- Click on «File» at the top left corner and select «Options.»
- In the Options window, navigate to the «Advanced» tab.
- Scroll down to the «International» section.
- Under «Choose the encoding standard to use when saving files,» select «UTF-8.»
- Click OK to save the changes.
Configuring UTF-8 encoding for Microsoft Office applications ensures that you can save and work with documents containing non-ASCII characters without any issues.
Web Browsers
Web browsers are key tools for accessing and viewing websites with different language content. Here’s how you can configure UTF-8 encoding in popular web browsers:
Google Chrome
To set UTF-8 encoding in Google Chrome, follow these steps:
- Open Google Chrome and click on the three-dot menu icon at the top right corner.
- Select «Settings» from the drop-down menu.
- Scroll down and click on «Advanced» to expand the advanced settings.
- Under the «Languages» section, click on «Language and input settings.»
- In the «Languages» settings, click on the «Add» button under the «Customize languages» section.
- Search for «English» in the language list and select «English (United States).»
- Drag «English (United States)» to the top of the list.
- Click «Done» to save the changes.
Configuring UTF-8 encoding in Google Chrome ensures that the browser can handle and display different language content correctly.
3. Troubleshooting UTF-8 Encoding Issues
Despite configuring UTF-8 encoding, you may still encounter issues with character handling in Windows 10. Here are some troubleshooting steps to resolve UTF-8 encoding issues:
Check File Encoding
If you experience character rendering issues with a specific file, check its encoding. Most text editors allow you to view and change the encoding of a file. Ensure that the file’s encoding matches the expected UTF-8 encoding.
Update Applications
If you encounter character handling issues in specific applications, ensure that you have the latest version installed. Application updates often include bug fixes and improvements related to character encoding.
Verify Font Support
In some cases, character rendering issues can occur due to insufficient font support. Ensure that you have appropriate fonts installed for the languages and scripts you are working with. Additionally, check the font settings within applications to ensure they are set to handle UTF-8 encoded characters.
4. Embracing UTF-8 Encoding for Seamless Multilingual Experience
Setting UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10 is a crucial step towards embracing multilingualism and ensuring smooth communication across languages. By configuring the system locale and individual application settings, you can avoid character-related issues and enjoy a seamless experience regardless of the languages and scripts you work with.

Setting utf-8 Encoding in Windows 10
Utf-8 encoding is a character encoding standard used to represent text in various languages, including English. Windows 10, by default, uses a different encoding called ANSI, which may not support all characters from different languages. However, it is possible to set utf-8 encoding in Windows 10 to ensure proper rendering of characters and support for international languages. Here’s how:
Method 1: Changing System Locale
To set utf-8 encoding, you can change the system locale in Windows 10. Follow these steps:
- Open the Control Panel and go to the «Clock and Region» section.
- Select «Region» and click on the «Administrative» tab.
- Click on «Change System Locale» and check the «Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support» option.
- Click «OK» and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Method 2: Changing File Encoding
If you want to set utf-8 encoding for specific files, you can change their encoding individually. Here’s how:
- Right-click on the file and select «Properties.»
- Go to the «General» tab and click on «Advanced» under «Attributes.»
- In the «Advanced Attributes» window, check the «UTF-8» option under «File Origin
Key Takeaways: How to Set Utf-8 Encoding in Windows 10
- Utf-8 encoding is important for displaying and storing international characters in Windows 10.
- Open Notepad or any text editor to create a new UTF-8 encoded file.
- Choose File > Save As and select UTF-8 encoding from the Encoding dropdown menu.
- Change the file extension to .txt if necessary and click Save.
- You can also set Utf-8 encoding as the default for all new files in Notepad.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions related to setting Utf-8 encoding in Windows 10:
1. What is Utf-8 encoding?
Utf-8 encoding is a way of representing characters in a computer system. It allows for the representation of all the characters in the Unicode character set, which includes a vast range of characters used in various languages and symbols. Utf-8 is widely used and recommended for text encoding formats because it can encode any character in a concise and efficient manner.
2. Why should I set Utf-8 encoding in Windows 10?
Setting Utf-8 encoding in Windows 10 is important to ensure that your system can correctly display and handle text in different languages, including characters and symbols that are not present in the default encoding. Utf-8 encoding allows for universal compatibility and ensures that the correct characters are displayed when working with files, websites, or applications that use Utf-8 encoding.
3. How can I set Utf-8 encoding in Windows 10?
To set Utf-8 encoding in Windows 10, you can follow these steps:
- Open the Control Panel by searching for «Control Panel» in the Windows Start menu and selecting it.
- Click on «Clock and Region» and then on «Region».
- In the Region dialog box, click on the «Administrative» tab.
- Under the «Language for non-Unicode programs» section, click on the «Change system locale» button.
- In the «Region Settings» dialog box, select «Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support» and click on «OK».
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.
4. Can I change the Utf-8 encoding for specific applications only?
No, the Utf-8 encoding setting in Windows 10 applies system-wide and affects all applications. Changing the encoding setting will ensure that Utf-8 characters are displayed correctly in all programs that use Utf-8 encoding. It is a global setting that affects the entire operating system.
5. Are there any other encoding options available in Windows 10?
Yes, Windows 10 supports various encoding options, including Utf-8, which is the recommended and widely used encoding format. Other options include ANSI, which is mostly used for backward compatibility with older software, and Unicode, which is a more generic term that refers to various character encoding schemes, including Utf-8. However, Utf-8 is the preferred encoding format for its compatibility and efficiency.
Setting UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10 is essential for ensuring compatibility with various languages and characters. By following a few simple steps, you can easily configure your system to use UTF-8 encoding, allowing you to work with multilingual content without any issues.
To set UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10, you need to navigate to the Region settings in the Control Panel. From there, you can access the Administrative tab and change the system locale to use UTF-8 encoding. This will enable your computer to recognize and display characters from different languages accurately.
Once you have set the UTF-8 encoding, you will be able to seamlessly work with files and applications that contain characters from various languages. This is particularly useful for web development, international communication, and working with documents that require special characters.
By ensuring that your Windows 10 system is set to UTF-8 encoding, you can eliminate any potential character display issues and improve overall compatibility. It’s a simple but crucial step that can make a significant difference in your work with multilingual content.
Кодировка текста – это схема нумерации символов, в которой каждому символу, цифре или знаку присвоено соответствующее число. Кодировку используют для сохранения и обработки текста на компьютере. Каждый раз при сохранении текста в файл он сохраняется с использованием определенной схемы кодирования, и при открытии этого файла необходимо использовать такую же схему, иначе восстановить исходный текст не получится. Самыми популярными кодировками для кириллицы сейчас являются UTF-8, Windows-1251 (CP1251, ANSI).
Для того чтобы программа смогла правильно открыть текстовый файл, иногда приходится вручную менять кодировку, перекодируя текст из одной схемы в другую. Например, не редко возникают проблемы с открытием файлов CSV, XML, SQL, TXT, PHP.
В этой небольшой статье мы расскажем о том, как изменить кодировку текстового файла на UTF-8, Windows-1251 или любую другую.
Блокнот Windows
Если вы используете операционную систему Windows 10 или Windows 11, то вы можете изменить кодировку текста с помощью стандартной программы Блокнот. Для этого нужно открыть текстовый файл с помощью Блокнота и воспользоваться меню «Файл – Сохранить как».
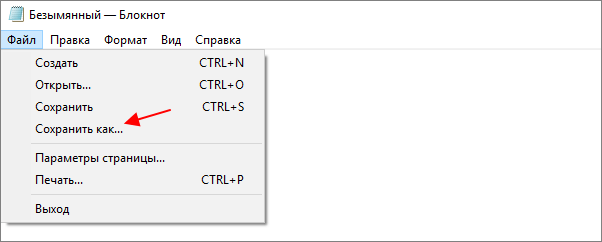
В открывшемся окне нужно указать новое название для файла, выбрать подходящую кодировку и нажать на кнопку «Сохранить».
К сожалению, для подобных задач программа Блокнот часто не подходит. С ее помощью нельзя открывать документы большого размера, и она не поддерживает многие кодировки. Например, с помощью Блокнота нельзя открыть текстовые файлы в DOS 866.
Notepad++
Notepad++ (скачать) является одним из наиболее продвинутых текстовых редакторов. Он обладает подсветкой синтаксиса языков программирования, позволяет выполнять поиск и замену по регулярным выражениям, отслеживать изменения в файлах, записывать и воспроизводить макросы, считать хеш-сумы и многое другое. Одной из основных функций Notepad++ является поддержка большого количества кодировок текста и возможность изменения кодировки текстового файла в UTF-8 или Windows 1251.
Для того чтобы изменить кодировку текста с помощью Notepad++ файл нужно открыть в данной программе. Если программа не смогла правильно определить схему кодирования текста, то это можно сделать вручную. Для этого нужно открыть меню «Кодировки – Кириллица» и выбрать нужный вариант.
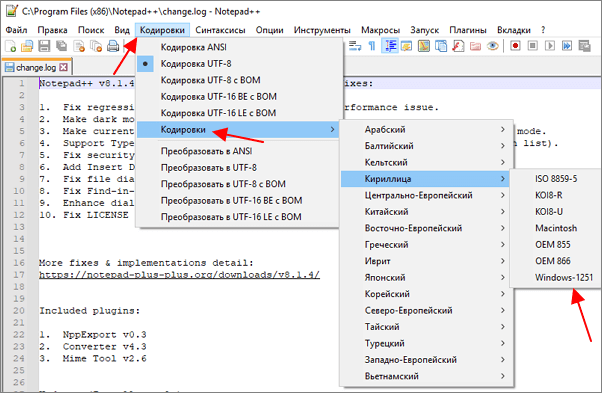
После открытия текста можно изменить его кодировку. Для этого нужно открыть меню «Кодировки» и выбрать один из вариантов преобразования. Notepad++ позволяет изменить текущую кодировку текста на ANSI (Windows-1251), UTF-8, UTF-8 BOM, UTF-8 BE BOM, UTF-8 LE BOM.
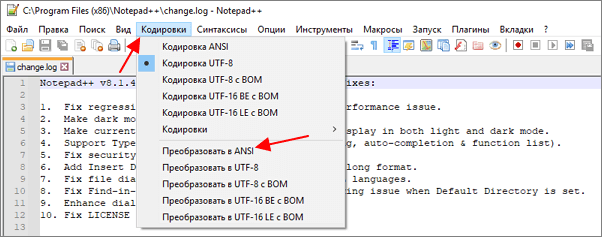
После преобразования файл нужно сохранить с помощью меню «Файл – Сохранить» или комбинации клавиш Ctrl-S.
Akelpad
Akelpad (скачать) – достаточно старая программа для работы с текстовыми файлами, которая все еще актуальна и может быть полезной. Фактически Akelpad является более продвинутой версией стандартной программы Блокнот из Windows. С его помощью можно открывать текстовые файлы большого размера, которые не открываются в Блокноте, выполнять поиск и замену с использованием регулярных выражений и менять кодировку текста.
Для того чтобы изменить кодировку текста с помощью Akelpad файл нужно открыть в данной программе. Если после открытия файла текст не читается, то нужно воспользоваться меню «Файл – Открыть».
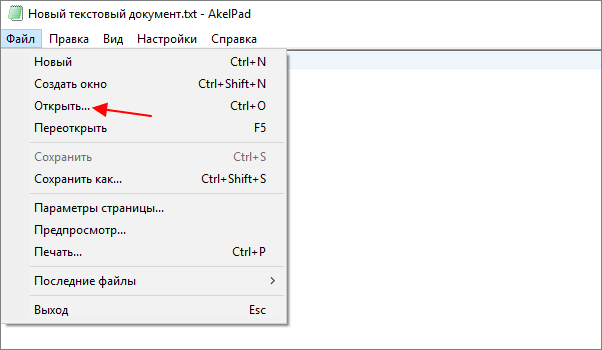
В открывшемся окне нужно выделить текстовый файл, снять отметку «Автовыбор» и выбрать подходящую кодировку из списка. При этом в нижней части окна можно видеть, как будет отображаться текст.
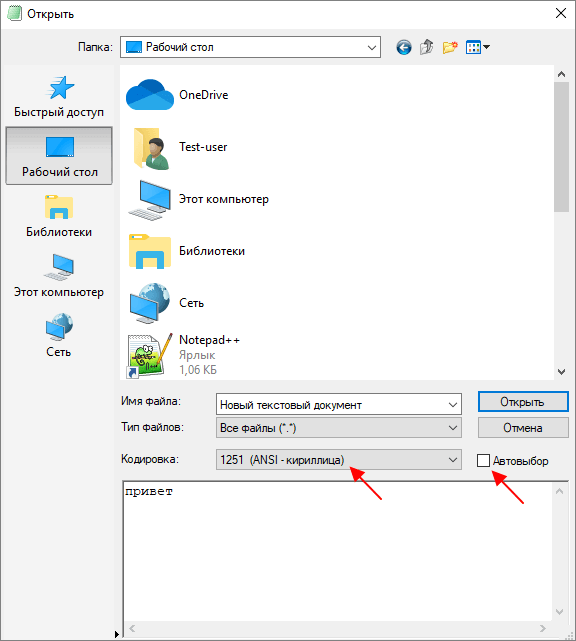
Для того чтобы изменить текущую кодировку текста нужно воспользоваться меню «Файл – Сохранить как» и сохранить документ с указанием новой схемы кодирования.
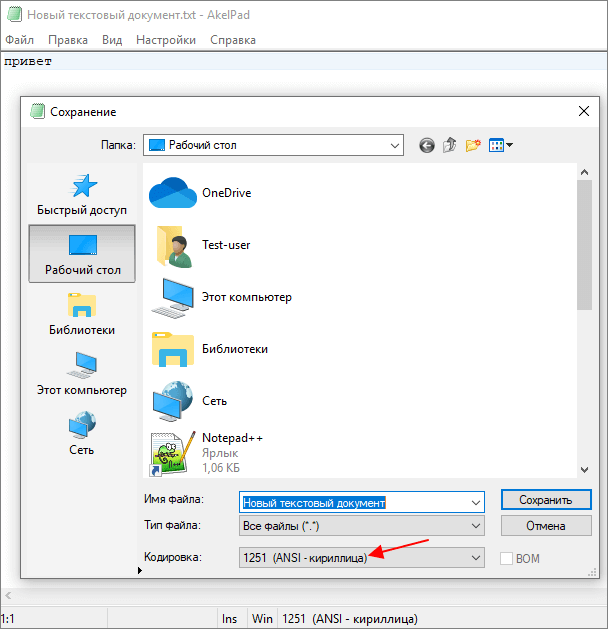
В отличие от Notepad++, текстовый редактор Akelpad позволяет сохранить файл в практически любой кодировке. В частности, доступны Windows 1251, DOS 886, UTF-8 и многие другие.
Посмотрите также:
- Чем открыть PDF файл в Windows 7 или Windows 10
- Как перевернуть страницу в Word
- Как копировать текст с помощью клавиатуры
- Как сделать рамку в Word
- Как сделать буклет в Word
Автор
Александр Степушин
Создатель сайта comp-security.net, автор более 2000 статей о ремонте компьютеров, работе с программами, настройке операционных систем.
Остались вопросы?
Задайте вопрос в комментариях под статьей или на странице
«Задать вопрос»
и вы обязательно получите ответ.
Setting Utf-8 Encoding in Windows 10 allows users to ensure compatibility and proper display of international characters in their applications and documents. With the increasing globalization of communication, it is crucial to have the ability to view and work with text in different languages seamlessly. Utf-8, a widely adopted character encoding standard, offers comprehensive support for a vast range of languages, making it essential for anyone dealing with multilingual content.
To set Utf-8 Encoding in Windows 10, users can follow a straightforward process. First, open the Control Panel by searching for it in the Start menu. Then, navigate to the «Clock and Region» section and select «Region.» In the Region settings, go to the «Administrative» tab, and click on the «Change system locale» button. From there, choose Utf-8 as the default language for non-Unicode programs. By making this adjustment, users can ensure that their Windows 10 system supports Utf-8 encoding, enabling seamless interaction with diverse language content.
To set UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10, follow these steps:
- Open the Control Panel.
- Select «Region» or «Region and Language.»
- Click on the «Administrative» tab.
- Under «Language for non-Unicode programs,» click on «Change system locale.»
- Check the box for «Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support.»
- Click «OK» and restart your computer.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to set UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10 and ensure compatibility with international characters and languages.

Understanding Utf-8 Encoding
Utf-8 encoding is a character encoding standard that is commonly used for representing characters in the Unicode character set. It supports almost all characters from all human languages, making it widely used for international communication and data storage. In Windows 10, setting the Utf-8 encoding is crucial to ensure proper display of characters and compatibility with different applications and systems. This article will guide you through the process of setting Utf-8 encoding in Windows 10, empowering you to handle and work with various character sets seamlessly.
Checking Current Encoding Settings
Before diving into the process of setting Utf-8 encoding, it’s important to check the current encoding settings on your Windows 10 system. This will help you understand the current state and determine if any changes are required. Follow the steps below to check the current encoding settings:
1. Open the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
2. In the Control Panel, click on «Clock and Region» and then select «Region.»
3. In the Region window, go to the «Administrative» tab.
4. Under the «Language for non-Unicode programs» section, you will see the current system locale. Note down this information for reference.
Setting Utf-8 as the System Locale
If your current system locale is not Utf-8, you can change it to Utf-8 to enable proper Utf-8 encoding. Follow the steps below to set Utf-8 as the system locale:
1. Open the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
2. In the Control Panel, click on «Clock and Region» and then select «Region.»
3. In the Region window, go to the «Administrative» tab.
4. Under the «Language for non-Unicode programs» section, click on the «Change system locale» button.
5. In the Region Settings window, select «Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support» checkbox.
6. Click on «OK» to save the changes and restart your computer for the settings to take effect.
Testing Utf-8 Encoding
After setting Utf-8 as the system locale, it’s important to test whether the changes have been applied successfully. Follow the steps below to test Utf-8 encoding:
- Open a text editor or any application that allows you to input text.
- Type and save some text that includes characters from different languages, such as accents, diacritics, or non-Latin characters.
- Open the saved file and check if all the characters are displayed correctly without any gibberish or question marks.
- If all characters are displayed correctly, it means that Utf-8 encoding is working properly.
Modifying Utf-8 Encoding in Specific Applications
In some cases, you may encounter issues with Utf-8 encoding in specific applications, even after setting it as the system locale. This can happen if the application has its own character encoding settings that override the system settings. Here’s how you can modify Utf-8 encoding in specific applications:
1. Open the application in which you are facing Utf-8 encoding issues.
2. Look for the application’s language or encoding settings, usually found in the preferences or settings menu.
3. Select Utf-8 as the preferred encoding option.
4. Save the changes and restart the application if required.
Common Applications with Utf-8 Encoding Settings
Many popular applications have Utf-8 encoding settings that can be modified to ensure proper character display. Here are a few examples:
| Application | Location of Utf-8 Encoding Settings |
| Notepad++ | Settings > Preferences > New Document > Encoding |
| Sublime Text | View > Encoding |
| Visual Studio Code | File > Save with Encoding |
| Microsoft Office | Options > Advanced > General > File Locations > File Encoding |
| Browsers (Chrome, Firefox, etc.) | Settings > Advanced > Fonts and Encoding |
Using Utf-8 Encoding for Web Development
Utf-8 encoding plays a crucial role in web development, ensuring that websites can display and handle multilingual content properly. When working with web development tools and frameworks, it’s important to set Utf-8 encoding to ensure seamless language support. Here are some key points to remember when using Utf-8 encoding for web development:
- Set the « tag in the « section of your HTML files.
- Ensure that your server-side scripts and databases are also set to Utf-8 encoding.
- If using a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, check the encoding settings in the CMS admin panel.
- Validate and sanitize user input to prevent potential encoding-related security vulnerabilities.
Setting Utf-8 Encoding for File Opening
Besides setting Utf-8 as the system locale, you may also need to specify the encoding when opening specific files to ensure they are interpreted correctly. The steps below will guide you through the process of setting Utf-8 encoding when opening files:
1. Open the application used to open the file, such as a text editor.
2. In the application, locate the file opening or file import feature.
3. Look for an option related to encoding or character set. The terminology may vary depending on the application.
4. Choose Utf-8 or the appropriate encoding option from the available list.
5. Open the desired file with the specified Utf-8 encoding to ensure proper interpretation of the characters.
Conclusion
Setting Utf-8 encoding in Windows 10 is crucial for proper handling and display of multilingual content. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can ensure seamless support for characters from various languages and encoding standards. Whether it’s setting Utf-8 as the system locale, modifying encoding settings in specific applications, or using Utf-8 for web development, understanding and implementing Utf-8 encoding will enhance your experience in working with diverse character sets.

Setting Utf-8 Encoding in Windows 10
Utf-8 encoding is widely used to support international characters and symbols in various software applications, including Windows 10. To set Utf-8 encoding in Windows 10, follow these steps:
Using Registry Editor
1. Press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type «regedit» and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
3. Navigate to the following registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\FeatureControl\FEATURE_BROWSER_EMULATION
4. Right-click on the empty space in the right pane and select «New» -> «DWORD (32-bit) Value».
5. Name the new value «iexplore.exe».
6. Double-click on the «iexplore.exe» value and set the «Value data» to 8888 (Hexadecimal).
Using Notepad
1. Open Notepad.
2. Click on «File» -> «Save As».
3. In the «Encoding» dropdown, select «Utf-8».
4. Choose the desired location and filename for your file, and click «Save».
With these simple
Key Takeaways: How to Set Utf-8 Encoding in Windows 10
- Open the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
- Click on «Clock and Region» and then select «Region» from the options.
- In the Region window, click on the «Administrative» tab.
- Under the «Language for non-Unicode programs» section, click on «Change system locale».
- Check the box next to «Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support».
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about setting Utf-8 Encoding in Windows 10:
1. How do I change the encoding to Utf-8 in Windows 10?
To change the encoding to Utf-8 in Windows 10, follow these steps:
1. Open the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows Start Menu.
2. Click on «Clock and Region» and then «Region».
3. In the «Formats» tab, click on «Additional settings».
4. In the «Code page conversion tables» section, select «Utf-8» from the drop-down menu.
5. Click «Apply» and then «OK» to save the changes.
2. Why is Utf-8 encoding important?
Utf-8 encoding is important because it supports a wide range of characters and symbols from different languages. It is a universal encoding standard that allows for seamless communication and compatibility between different systems and devices.
By using Utf-8 encoding, you ensure that your text is correctly displayed and interpreted across platforms, making it essential for international communication, website development, and data storage.
3. Can I change the encoding for specific files or folders?
Yes, you can change the encoding for specific files or folders in Windows 10. Follow these steps:
1. Right-click on the file or folder you want to change the encoding for.
2. Select «Properties» from the context menu.
3. In the «Properties» window, go to the «General» tab.
4. Click on the «Advanced…» button.
5. In the «Advanced Attributes» window, check the box next to «Utf-8» under «File Encoding».
6. Click «OK» to save the changes.
4. How can I check the current encoding of a file in Windows 10?
To check the current encoding of a file in Windows 10, follow these steps:
1. Right-click on the file and select «Properties».
2. In the «Properties» window, go to the «General» tab.
3. Under «Attributes», you will see the «Encoding» information.
5. Can I set Utf-8 as the default encoding in Windows 10?
Yes, you can set Utf-8 as the default encoding in Windows 10. Here’s how:
1. Open the Control Panel and click on «Clock and Region» and then «Region».
2. In the «Formats» tab, click on «Additional settings».
3. In the «Code page conversion tables» section, select «Utf-8» from the drop-down menu.
4. Click «Apply» and then «OK» to save the changes.
To summarize, setting UTF-8 encoding in Windows 10 is an important step to ensure compatibility and proper display of characters in various applications. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily change the default encoding settings and avoid any issues with text encoding in your system.
Remember, UTF-8 is a widely accepted and flexible encoding format that supports a wide range of characters from different languages. It is crucial for international communication, web development, and file sharing. Keeping your system’s default encoding as UTF-8 will ensure seamless interactions with texts from around the world.
По умолчанию cmd.exe использует кодировку cp866. Текущую кодировку можно посмотреть командой chcp. Иногда возникает необходимость использовать в терминале юникод. Для этого необходимо использовать шрифт «Lucida Console» и переключить кодировку командой
>chcp <codepage>
Где параметр <codepage> для UTF-8 равен 65001

На сколько мы знаем в командной строке от MS Windows по умолчанию используется кодировка DOS, она же CP866. Сам CP866 появился достаточно давно и активно использовался во времена DOS, но сейчас лучшим вариантов принято считать Юникод (UTF). Соответственно рассмотрим вариант перманентный (постоянный) вариант активации поддержки UTF в ОС Windows.
Кодировки
В основном используется несколько кодировок, а для временного изменения кодировки в экземпляре командной строки используют команду chcp.
- DOS — CP866;
- Windows (Кириллица) — CP1251;
- Unicode UTF-8 — CP65001.
chcp 1251 - для Кириллица
chcp 866 - для DOS
chcp 65001 - для UTF-8
Включаем кодировку UTF-8 в Windows
В большинстве редакциях Windows появилась техническая возможность включить поддержку использования кодировки Unicode UTF-8. Для изменения необходимо пройти по пути «Время и язык» > «Язык» > «Административные языковые параметры» > «Дополнительно» > «Изменить язык системы» и в окне «Региональные стандарты» установить флаг «Бета-версия: Использовать Юникод (UTF-8) для поддержки языка во всем мире», нажать кнопку “ОК”. Система предложить перезагрузить систему, а после перезагрузки командная строка будет по умолчанию иметь кодировку UTF-8.
Скриншоты для представления порядка действий
Вот собственно таким нехитрым действием мы можем изменить кодировку командной строки в системах семейства Windows от домашних до серверных редакций.
