Уровень сложностиПростой
Время на прочтение2 мин
Количество просмотров38K
Для пользователя Linux командная строка Windows кажется чем-то непривычным и неудобным. С появлением WSL казалось, что проблема использования Bash решена, но запуск виртуальной машины требует времени, да и пути в WSL отличаются от Windows. Плюс скорость файловых операций на виртуальной машине хуже.
Ещё есть возможность использовать Bash через MSYS2, но мне хотелось найти что-то более компактное и легковесное, а также простое в настройке и установке.
Так как я часто использовал Linux на роутерах, то познакомился с BusyBox, набор UNIX-утилит командной строки, используемой в качестве основного интерфейса во встраиваемых операционных системах. Оказалось, есть версия BusyBox для Windows. В 2020 году появился Windows Terminal, а в нем есть возможность создавать вкладку с запуском конкретной программы.

Сложив эти два факта, пришла очевидная мысль, использовать BusyBox, содержащий в себе Bash, в Windows Terminal как отдельную консоль.

Для этого необходимо скачать BusyBox 64, и я, например положил файл в C:/Program Files/Busybox. А дальше создать новый профиль Windows Terminal и поменять его имя на Bash и указать команду для запуска как C:/Program Files/Busybox/busybox64.exe bash

У этого подхода был один минус, при запуске терминала не из конкретной папки, а из ярлыка на рабочем столе или из панели задач.
То адрес рабочей папки был C:/Windows/System32, и если случайно ввести команду удаления или создания файла, то мы портим важную системную папку. Обойти возможно используя аналог .bashrc или /etc/profile или .profile.

Но просто создать файл .profile мало, BusyBox для Windows их не считывает, для этого необходимо добавить путь к этому файлу в ENV в “Переменные среды”.

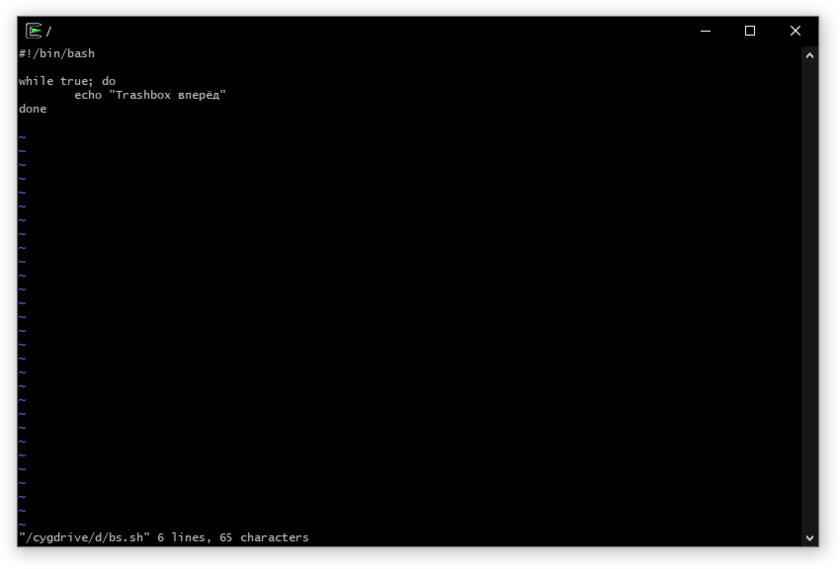
Теперь мы можем написать скрипт, который будет настраивать рабочую директорию при запуске консоли.
#!/bin/bash
domain=$(echo $PWD | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]')
if [ $domain = "c:/windows/system32" ]; then
cd $HOME
fi
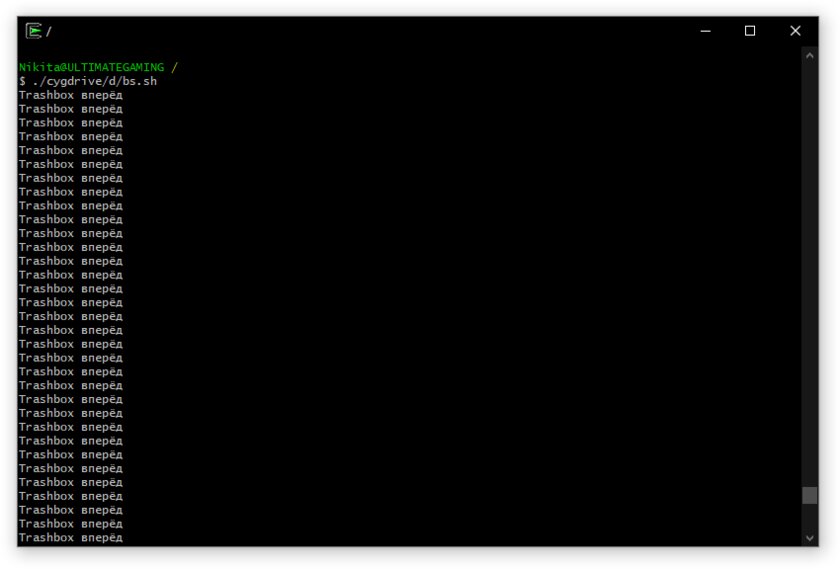
Теперь если мы запустили терминал из ярлыка или панели задач, то рабочей директорией по умолчанию становится домашняя папка пользователя, а если мы запускаем из конкретной папки то, она и становится рабочей директорией.
Мы получили Bash в Windows Terminal с удобной начальной директорией.
Last Updated :
12 Apr, 2025
Did you know you can use Linux right inside your Windows 10 computer—without needing a separate Linux setup? Thanks to a feature called Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), you can now open a Bash shell, run Linux commands, and manage your projects easily.
This guide will help you set up and use the Bash shell on Windows 10, making it simple to explore Linux tools and commands while still using your Windows system. It’s the best of both worlds.
Steps to Install & use Bash Shell Natively on Windows 10
Microsoft, therefore, in their Anniversary Update, added several features to the Windows 10 OS, with bash being one of them. To install and use it on Windows 10, one needs to perform the following steps :
- Start -> Settings -> Update&Security. Under the ‘Use Developer Features’, select ‘Developer mode’.
- Selecting the developer mode will pop the following alert. Click yes, and let the computer restart.
- Go to Control Panel -> Programs and Features -> Turn Windows Features On and Off. In the window that appears, check the ‘Windows Subsystem for Linux’ option, and click OK.
- This will trigger an alert asking for the system to be restarted to complete the installation of the required components. After the restart is complete, go to the command prompt, and type ‘bash’. Follow the instructions that appear to install bash from Windows store. After it is installed, it will be required to create a UNIX username. After completing the installation, exit the prompt.
- To access the shell, simply type ‘bash’ in the Windows command prompt, and everything is good to go.
Note that bash runs natively on Windows 10, which is different from using emulators like ‘cygwin’ for Windows which enabled GNU tools to run on unsupported Windows environment. Also, Linux subsystem for Windows 10 is only available on the 64-bit version of the OS.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you can easily set up and use the Bash shell natively on Windows 10 through the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). This integration allows you to run Linux commands, scripts, and tools directly on your Windows machine, making it a versatile and convenient solution for developers and power users alike. Whether you’re looking to leverage Linux utilities or streamline your development workflow, using Bash on Windows 10 opens up a world of possibilities without leaving the Windows environment.
To run a Bash script on Windows, you can use the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) or Git Bash to execute your script directly from the command line.
Here’s a code snippet to run a Bash script:
bash your_script.sh
Understanding Bash Scripts
What is a Bash Script?
A Bash script is a file that contains a series of commands that the Bash interpreter can execute. These scripts enable you to automate tasks that you would normally perform in the command line interface, making repetitive tasks easier and more efficient. Common use cases for Bash scripts include automating backups, running scheduled tasks, and managing system resources.
The Benefits of Using Bash Scripts
Using Bash scripts has several advantages:
- Efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks through scripts, you save time and reduce the possibility of human error.
- Flexibility: Bash scripts can be used in conjunction with various tools and commands available in a Unix-like environment, extending their capabilities.
- Cross-Platform Nature: Bash scripts can often be run on different operating systems, allowing for more versatile development and deployment options.

Bash Script Options: A Quick Guide to Mastering Choices
Prerequisites for Running Bash Scripts on Windows
Setting Up the Environment
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) enables you to run a Linux distribution alongside your Windows operating system. This allows you to execute Bash scripts natively within a Linux environment. To enable WSL on Windows 10 or 11, follow these steps:
- Open PowerShell as Administrator.
- Run the command:
wsl --install
- Restart your computer.
After installation, you can choose a Linux distribution like Ubuntu from the Microsoft Store.
Installing a Bash Shell
Using Ubuntu / Debian on WSL
Once WSL is enabled, install a Linux distribution from the Microsoft Store. Simply search for «Ubuntu» or «Debian» and click the «Install» button. Upon successful installation, launch the application to complete the setup.
Alternatives
If you prefer not to use WSL, you can opt for Git Bash or Cygwin. Both environments provide a Bash-like experience on Windows.

Run Bash Script: Your Quick-Start Guide to Success
Executing Bash Scripts on Windows
Creating a Bash Script
Writing a Bash script begins with a text editor. Here’s how to create a simple Bash script called `hello.sh` that prints «Hello, World!».
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello, World!"
The first line, known as the shebang (`#!/bin/bash`), indicates which interpreter should be used to run the script.
Running Bash Scripts in WSL
Navigating the Terminal
To run Bash scripts within WSL, you must first open your chosen Linux distribution terminal and navigate to the directory where your script is saved. You can use basic terminal commands such as `cd` (change directory) and `ls` (list files).
Execution Commands
There are two main methods to execute your Bash script in WSL:
- Basic Execution: You can run the script directly by typing:
bash hello.sh
- Making it Executable: To run the script without having to prefix it with `bash`, you can make it executable:
chmod +x hello.sh
After this, you can execute it using:
./hello.sh
Running Bash Scripts in Git Bash
Setting Up Git Bash
To use Git Bash, you first need to install Git for Windows. You can find the installer on the [official Git website](https://git-scm.com/download/win). During installation, you can choose the relevant options to set up your Bash environment.
Executing Scripts in Git Bash
Just like in WSL, create the `hello.sh` script in Git Bash. To run the script, you simply navigate to its directory and execute the following command:
bash hello.sh
Running Bash Scripts in Cygwin
Cygwin Setup
Cygwin provides a large collection of GNU and Open Source tools which provide functionality similar to a Linux distribution on Windows. To install Cygwin, navigate to the [Cygwin website](https://www.cygwin.com/) and download the installer. Follow the setup instructions, selecting the packages you wish to install.
Executing Scripts in Cygwin
After creating your Bash script in the Cygwin terminal, the execution process is similar. Use the `bash` command or mark the script as executable before running it.

Run Bash Script on Mac: A Simple Guide
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Handling Script Errors
When running Bash scripts, you may encounter common error messages, such as «command not found» or «permission denied.» These can be addressed through basic troubleshooting steps—ensure that the command is correctly spelled, the script file exists, and you have the necessary permissions.
Performance Issues
If your Bash script runs slowly, investigate any potential bottlenecks, such as infinite loops or redundant function calls. Optimizing your scripts can lead to better performance and faster execution times.

Mastering Bash for Windows: A Quick Guide for Beginners
Best Practices for Writing and Running Bash Scripts on Windows
Script Organization
For clarity, ensure that your scripts are well-organized. Use comments to document sections of code and explain the purpose of specific commands. This practice not only benefits you but also helps anyone else who may need to use or modify your scripts in the future.
Testing Scripts
Before deploying any scripts, it’s essential to test them thoroughly. Run your scripts in a safe environment and use tools like ShellCheck to check for syntax errors and coding best practices.

Bash Script Closure: Quick Guide to Mastering It
Conclusion
Being able to run Bash scripts on Windows significantly enhances your productivity and allows you to harness the power of automation. By following the steps outlined above, you can easily set up your environment, write and execute Bash scripts effectively. The combination of WSL, Git Bash, and Cygwin provides robust options for integrating Bash into your workflow.

Bash Script Beginning: Your Quick Start Guide to Scripting
Further Reading and Resources
For those looking to deepen their knowledge, check out recommended books, websites, and forums for Bash scripting. Explore tutorials and resources on WSL, Git Bash, and Cygwin to continue your journey into the world of Bash scripting.
Под GNU/Linux-дистрибутивы создано огромное количество полезных и удобных инструментов и приложений для обычных пользователей и разработчиков. Далеко не всё из этого доступно на Windows, но, к счастью, для ОС от Microsoft есть решения, исправляющие эту проблему.
WSL — официальная подсистема Linux внутри Windows
В Windows 10 существует крайне полезная вещь под названием Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). Она позволяет использовать GNU/Linux-среду прямо в Windows и запускать не только команды, но и, например, Bash-скрипты. Для использования WSL необходимо следовать инструкции ниже.
Шаг 1. Проверьте, подходит ли текущая версия Windows требованиям. Для этого нажмите сочетание клавиш Win+R, затем введите winver. Найдите строку «Сборка ОС» — она должна быть свежее версии 14316.
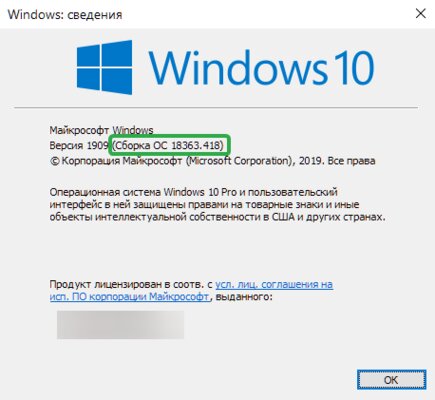
Шаг 2. Запустите стандартную утилиту PowerShell от имени администратора и введите в ней команду для включения WSL:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
Шаг 3. Если версия Windows, определённая в первом пункте, свежее 18362, вы можете установить WSL 2, который в разы быстрее первой версии и обладает доработанным ядром. Введите команду ниже, если нужно установить WSL 2:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
После этого скачайте и установите пакет обновления с официального сайта.
Шаг 4. Перезагрузите компьютер. Если была произведена установка WSL 2, введите в PowerShell от имени администратора следующую команду:
wsl —set-default-version 2
Шаг 5. После перезагрузки откройте фирменный магазин приложений Microsoft Store и найдите подходящий GNU/Linux-дистрибутив. Самым популярным является Ubuntu — вы можете установить любую версию из представленных в Microsoft Store.
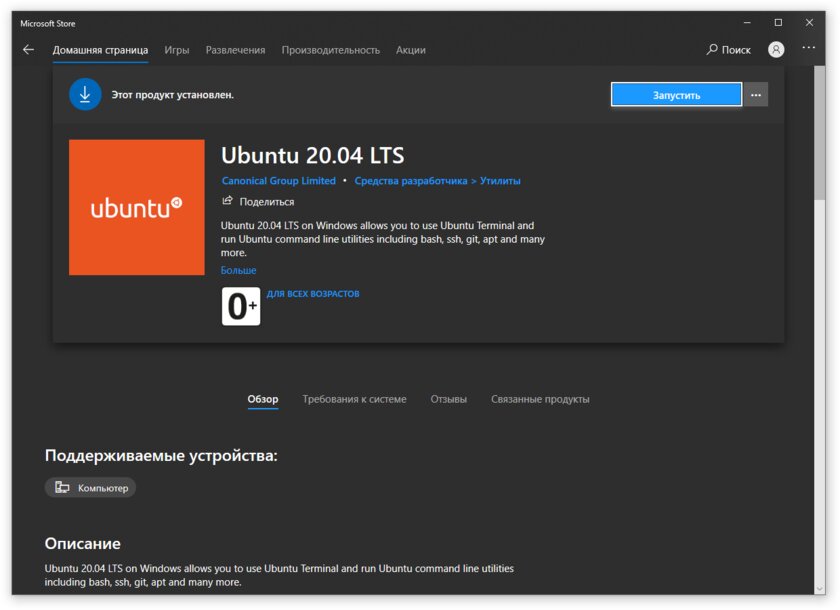
Шаг 6. Как только установка завершится, найдите дистрибутив в меню «Пуск» и запустите его.
Шаг 7. Пройдите этап первоначальной настройки, введя имя нового пользователя и придумав пароль.
Шаг 8. Теперь различные GNU/Linux-команды можно выполнять, запустив дистрибутив, либо введя в командной строке wsl <команда>. Например, для просмотра всех файлов в текущей директории достаточно в командной строке выполнить wsl ls -a.
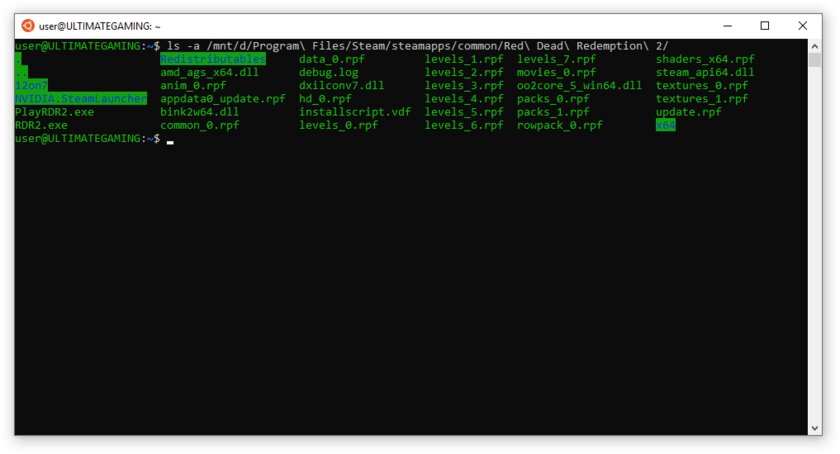
Обращу внимание на то, что путь к дискам в WSL отличается от такового в Windows. Вместо привычного C:/ используйте /mnt/c/. Также не забывайте про экранирование пробелов с помощью символа \ — это также пригодится при вводе путей к файлам.
Помимо выполнения базовых команд, с помощью WSL можно даже запускать приложения с графическим интерфейсом. Правда, рассчитывать на большое количество поддерживаемых подобных программ не стоит.
Шаг 1. Загрузите X-сервер и установите его.
Шаг 2. Запустите его с помощью ярлыка на рабочем столе. В открывшемся окне выберите вариант Multiple windows, затем Start no client. Завершите настройку кнопкой Finish.
Шаг 3. Откройте дистрибутив через меню Пуск и выполните команду export DISPLAY=:0
Шаг 4. Запустив приложение с графическим интерфейсом в WSL, вы увидите новое окно прямо в Windows.
CoreUtils — лёгкий инструмент для запуска базовых команд
Плюс данной утилиты — возможность запуска не только на Windows 10, но и на более старых версиях ОС. Кроме того, она легка и не занимает много места. Не обошлось без недостатков — программа скудна на функционал и не обновлялась очень давно. Она не только не умеет запускать скрипты и приложения с GUI, но и поддерживает лишь самые базовые GNU/Linux-команды. Установка CoreUtils весьма проста.
Шаг 1. Скачайте утилиту с официального сайта.
Шаг 2. Следуйте инструкциям установщика.
Шаг 3. Откройте «Панель управления», в разделе «Система и безопасность» выберите пункт «Система». На панели слева откройте «Дополнительные параметры системы». Нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды» и в открывшемся окне найдите область с заголовком «Системные переменные». В случае, когда там есть переменная Path, выберите её, нажмите «Изменить» и далее создайте новую строку. Содержимым этой строки должен быть путь к папке, который был указан при установке. Если вы ничего не меняли, то введите следующее:
C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\bin
Переменной Path нет? Тогда для начала создайте её кнопкой «Создать», затем в поле имени введите Path, а в поле значения — строку выше.
Шаг 4. Запустите командную строку и выполняйте команды прямо там.
Cygwin — запуск команд и Bash-скриптов
Ещё одна утилита, схожая с CoreUtils, но обладающая более широким функционалом — в том числе и возможностью запуска скриптов. Из минусов — немалый вес и более сложная установка. Разумеется, не идёт ни в какое сравнение с максимально удобным WSL, но для базовых команд вполне подойдёт.
Шаг 1. Загрузите Cygwin и запустите установку.
Шаг 2. Выберите Install from Internet, укажите директории для установки и загрузки пакетов, а также любой подходящий сайт из списка для скачивания файлов.
Шаг 3. В процессе установки можете выбрать необходимые пакеты, либо сразу нажать «Далее», оставив базовый набор.
Шаг 4. Откройте «Панель управления», в разделе «Система и безопасность» выберите пункт «Система». На панели слева откройте «Дополнительные параметры системы». Нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды» и в открывшемся окне найдите область с заголовком «Системные переменные». В случае, когда там есть переменная Path, выберите её, нажмите «Изменить» и далее создайте новую строку. Содержимым этой строки должен быть путь к папке, который был указан при установке. Если вы ничего не меняли, то введите следующее:
C:\cygwin64\bin
Переменной Path нет? Тогда для начала создайте её кнопкой «Создать», затем в поле имени введите Path, а в поле значения — строку выше.
Шаг 5. Команды можно выполнять как через командную строку, так и через специальный терминал.
Шаг 6. Для удаления Cygwin достаточно удалить папку, в которую программа была установлена, а также (по желанию) значение из переменной Path по методу, обратному тому, что был описан в 4 шаге (не удаляйте саму переменную).
Here’s how to set up and use the Linux shell on Windows – using the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
This tutorial is intended for up-to-date versions of Windows 10 from 2020 onwards. I’m not going to cover how to use WSL on older versions of Windows 10 or other methods for Windows 8/7/XP/3.1 because you shouldn’t be using outdated software. If you must use Windows, use a version that still receives security patches!
WSL is a great tool and allows you to pretty much run Linux software on windows as if you had never left Linux. Not everyone has the luxury of being able to install a Linux system due to relying on proprietary software released only for Windows.
Anyway, here’s how to get a Linux shell happening on Windows 10, courtesy of the Windows Subsystem for Linux.
Install Windows Subsystem for Linux
First, you will need to install support for the Windows Subsystem for Linux in Windows 10.
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 2 bash windows 7](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-7-1024x735.png)
This is done from the Settings app – so open it up and then click on Apps.
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 3 bash windows 8](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-8-1024x735.png)
Then click on Programs and Features in the sidebar to the right.
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 4 bash windows 9](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-9-1024x735.png)
Next, click Turn Windows features on or off in the sidebar to the left.
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 5 bash windows 11](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-11-1024x735.png)
Scroll down the list and check Windows Subsystem for Linux, then press OK
Confirm your selection, then allow your computer to restart to complete the installation.
Install Ubuntu From The Windows Store
First, make sure that your copy of Windows 10 is completely up-to-date. Older releases of Windows 10 from before 2020 do not support the Windows Subsystem for Linux.
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 6 bash windows 2](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-2-1024x735.png)
Next, open the Microsoft Store from the Start Menu, or search for ‘store.’
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 7 bash windows 3](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-3-1024x735.png)
Search for ‘Ubuntu’ from Canonical.
To install it, click ‘Get’ and wait for it to download.
This “App” contains a full copy of Ubuntu for the Windows Subsystem for Linux – including the Bash shell, and a full Ubuntu command line environment.
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 8 bash windows 4](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-4-1024x735.png)
Launch the downloaded Ubuntu App by clicking ‘Launch.’
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 9 bash windows 5](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-5-1024x735.png)
A shortcut to Ubuntu will also be added to your start menu.
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 10 bash windows 12 1](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-12-1-1024x764.jpg)
When you launch Ubuntu, you’ll be dropped right into a Linux Bash environment in Windows – cool!
Install the Windows Terminal (Optional)
The terminal which Ubuntu opens is a bit lacking, however. There’s a better Terminal App now available – The Windows Terminal!
Windows Terminal supports things like tabs and custom configurations. You can have a Powershell tab open next to a Bash Terminal; it’s really nice.
It’s in the Windows Store, so search for it and install it.
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 11 bash windows 14 1](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-14-1-1024x764.jpg)
![How to Install & Use Bash (Linux Shell) on Windows 10 [Tutorial] 12 bash windows 15 1](https://cd.linuxscrew.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/bash_windows-15-1-1024x764.jpg)
Conclusion
Windows is still the industry standard for many fields – including graphic design and CAD. Some software development tools are also only supported on Windows.
If you rely on software that can only be run on Windows, running and testing Linux software without having to rely on a cumbersome virtual machine saves both time and resources.





