SID (Security IDentifier) – это уникальный идентификатор, который присваивается пользователям, группам, компьютерам или другим объектам безопасности при их создании в Windows или Active Directory. Windows использует SID, а не имя пользователя для контроля доступа к различным ресурсам: сетевым папкам, ключам реестра, объектам файловой системы (NTFS разрешения), принтерам и т.д. В этой статье мы покажем несколько простых способов получить SID пользователя, группы или компьютера, и обратную процедуру – получить объект по известному SID.
Содержание:
- Что такое SID объекта в Windows?
- Как получить SID локального пользователя?
- Узнать SID пользователя или группы в домене Active Directory
- Получить SID компьютера
- Как узнать имя пользователя или группы по известному SID?
- Поиск объектов в Active Directory по SID
Что такое SID объекта в Windows?
Как мы уже сказали, SID (security identifier) позволяет уникально идентифицировать пользовали, группу или компьютер в пределах определенной области (домена или локального компьютера). SID представляет собой строку вида:
S-1-5-21-2927053466-1818515551-2824591131—1103.
В данном примере:
- 2927053466-1818515551-2824591131 – это уникальный идентификатор домена, выдавшего SID (у всего объекта в одном домене эта часть будет одинакова)
- 1103 – относительный идентификатор безопасности объекта (RID). Начинается с 1000 и увеличивается на 1 для каждого нового объекта. Выдается контроллером домена с FSMO ролью RID Master)
SIDы объектов Active Directory хранятся в базе ntds.dit, а SIDы локальных пользователей и групп в локальной базе диспетчера учетных записей Windows (SAM, Security Account Manager в ветке реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SAM\SAM).
В Windows есть так называемые известные идентификаторы безопасности (Well-known SID). Это SID встроенных (BuiltIn) пользователей и групп, которые есть на любых компьютерах Windows. Например:
-
S-1-5-32-544
– встроенная группу Administrators -
S-1-5-32-545
– локальные пользователи -
S-1-5-32-555
– группа Remote Desktop Users, которым разрешен вход по RDP -
S-1-5-domainID-500
– учетная запись встроенного администратора Windows - И т.д.
В Windows можно использовать различные средства для преобразования SID -> Name и Username -> SID: утилиту whoami, wmic, WMI, классы PowerShell или сторонние утилиты.
Как получить SID локального пользователя?
Чтобы получить SID локальной учетной записи, можно воспользоваться утилитой wmic, которая позволяет обратится к пространству имен WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) компьютера.
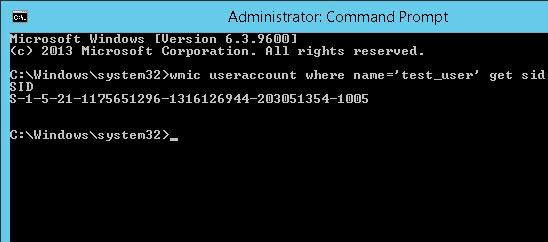
wmic useraccount where name='test_user' get sid
Команда может вернуть ошибку, если репозиторий WMI поврежден. Воспользуйтесь этой инструкцией для восстановления WMI репозитория.
Команда вернула SID указанного пользователя —
S-1-5-21-1175651296-1316126944-203051354-1005
.
Чтобы вывести список SID всех локальных пользователей Windows, выполните:
wmic useraccount get name,sid.
Если нужно узнать SID текущего пользователя (под которым выполняется команда), используйте такую команду:
wmic useraccount where name='%username%' get sid
Можно обратится к WMI напрямую из PowerShell:
(Get-CimInstance -Class win32_userAccount -Filter "name='test_user' and domain='$env:computername'").SID
В новых версиях PowerShell Core 7.x вместо команды Get-WmiObject нужно использовать Get-CimInstance.
Но еще проще получить SID локального пользователя с помощью встроенного PowerShell модуля управления локальными пользователями и группами (Microsoft.PowerShell.LocalAccounts).
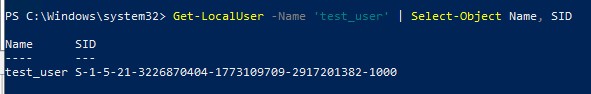
Get-LocalUser -Name 'test_user' | Select-Object Name, SID
По аналогии можно получить SID локальной группы:
Get-LocalGroup -Name tstGroup1 | Select-Object Name, SID
Также вы можете использовать.NET классы System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier и System.Security.Principal.NTAccount для получения SID пользователя с помощью PowerShell:
$objUser = New-Object System.Security.Principal.NTAccount("LOCAL_USER_NAME")
$strSID = $objUser.Translate([System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier])
$strSID.Value
Узнать SID пользователя или группы в домене Active Directory
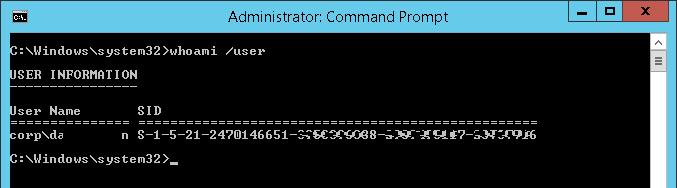
Вы можете узнать SID своей доменной учетной записи командой:
whoami /user
Получить SID пользователя домена Active Directory можно с помощью WMIC. В этом случае в команде нужно указать имя домена:
wmic useraccount where (name='jjsmith' and domain=′corp.winitpro.ru′) get sid
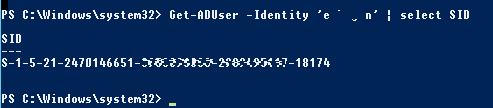
Для получения SID доменного пользователя можно воспользоваться командлетом Get-ADUser, входящего в состав модуля Active Directory Module для Windows PowerShell. Получим SID для доменного пользователя jjsmith:
Get-ADUser -Identity 'jjsmith' | select SID
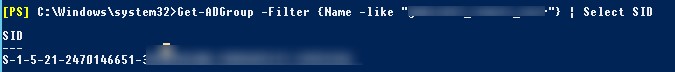
Вы можете получить SID группы AD с помощью командлета Get-ADGroup:
Get-ADGroup -Filter {Name -like "msk-admin*"} | Select SID
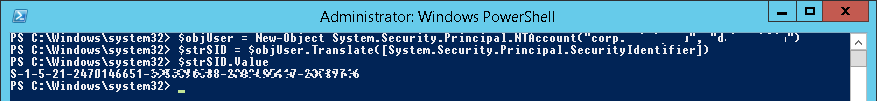
Если на вашем компьютере не установлен модуль AD для PowerShell, вы можете получить SID пользователя с помощью классов .Net:
$objUser = New-Object System.Security.Principal.NTAccount("corp.wintpro.ru","jjsmith")
$strSID = $objUser.Translate([System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier])
$strSID.Value
Эта же команда PowerShell в одну строку:
(new-object security.principal.ntaccount “jjsmith").translate([security.principal.securityidentifier])
Получить SID компьютера
Если компьютер с Windows добавлен в домен Active Directory, у него будет два разных SID. Первый SID – идентификатор локального компьютера (Machine SID), а второе – уникальный идентификатор компьютера в AD.
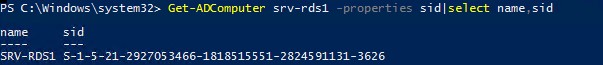
SID компьютера в домене Active Directory можно получить с помощью команды:
Get-ADComputer srv-rds1 -properties sid|select name,sid
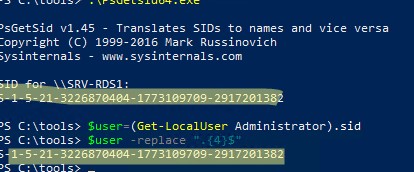
SID локального компьютера (Machine SID) можно получить с помощью бесплатной утилиты PsGetsid (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/psgetsid): Но ее придется скачивать и устанавливать на каждый компьютер вручную.
.\PsGetsid64.exe
Или просто, обрезав последние 4 символа RID и SID любого локального пользователя:
$user=(Get-LocalUser Administrator).sid
$user -replace ".{4}$"
Важно, чтобы у каждого компьютера в домене был уникальный локальный SID. Если вы клонируете компьютеры или виртуальные машины, или создаете их из одного шаблона, то перед тем как добавить их в домен нужно выполнить команду sysprep. Эта утилита сбрасывает локальный Machine SID. Это избавит вас от частых ошибок “Не удалось восстановить доверительные отношения между рабочей станцией и доменом”.
Как узнать имя пользователя или группы по известному SID?
Чтобы узнать имя учетной записи пользователя по SID (обратная процедура), можно воспользоваться одной из следующих команд:
wmic useraccount where sid='S-1-3-12-12452343106-3544442455-30354867-1434' get name
Для поиска имени доменного пользователя по SID используйте командлеты из модуля
RSAT-AD-PowerShell
:
Get-ADUser -Identity S-1-5-21-247647651-3952524288-2944781117-23711116
Чтобы определить имя группы по известному SID, используйте команду:
Get-ADGroup -Identity S-1-5-21-247647651-3952524288-2944781117-23711116
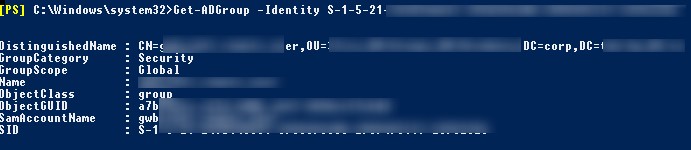
Также можно узнать получить SID группы и пользователя с помощью встроенных классов PowerShell (без использования дополнительных модулей):
$objSID = New-Object System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier ("S-1-5-21-2470456651-3958312488-29145117-23345716")
$objUser = $objSID.Translate( [System.Security.Principal.NTAccount])
$objUser.Value
Поиск объектов в Active Directory по SID
Если вы не знаете к какому типу объекта AD относится SID и какой точно командлет нужно использовать для его поиска (Get-AdUser, Get-ADComputer или Get-ADGroup), вы можете использовать универсальный метод поиска объектов в Active Directory по SID с помощью командлета Get-ADObject
$sid = ‘S-1-5-21-2470146651-3951111111-2989411117-11119501’
Get-ADObject –IncludeDeletedObjects -Filter "objectSid -eq '$sid'" | Select-Object name, objectClass
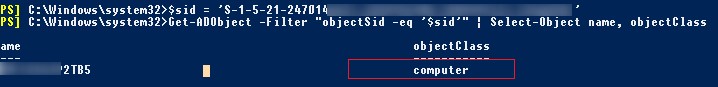
В нашем случае объект AD, который имеет данный SID, является компьютером (objectClass=computer).
183
183 people found this article helpful
Find a user’s SID with WMIC or in the registry
Updated on January 15, 2022
What to Know
- In Command Prompt, type wmic useraccount get name,sid and press Enter.
- You can also determine a user’s SID by looking through the ProfileImagePath values in each S-1-5-21 prefixed SID listed under:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
A common reason why you might want to find the security identifier (SID) for a user’s account in Windows is to determine which key under HKEY_USERS in the Windows Registry to look for user-specific registry data. Matching SIDs to usernames is easy with the wmic command—available from the Command Prompt in most versions of Windows.
How to Find a User’s SID With WMIC
Follow these easy steps to display a table of usernames and their corresponding SIDs. It’ll probably only take a minute, maybe less, to find a user’s SID in Windows via WMIC:
See How to Find a User’s SID in the Registry further down the page for instructions on matching a username to an SID via information in the Windows Registry, an alternative method to using WMIC. The wmic command didn’t exist before Windows XP, so you’ll have to use the registry method in those older versions of Windows.
-
Open Terminal (Windows 11), or open Command Prompt in older Windows versions.
If you’re using a keyboard and mouse in Windows 11/10/8, the fastest way is through the Power User Menu, accessible with the WIN+X shortcut.
If you don’t see Command Prompt there, type cmd into the search bar in the Start menu, and select Command Prompt when you see it.
You don’t have to open an elevated Command Prompt for this to work. Some Windows commands require it, but in the WMIC command example below, you can open a regular, non-administrative Command Prompt.
-
Type the following command into Command Prompt exactly as it’s shown here, including spaces or lack thereof:
wmic useraccount get name,sid…and then press Enter.
If you know the username and would like to grab only that one user’s SID, enter this command but replace USER with the username (keep the quotes):
wmic useraccount where name="USER" get sidIf you get an error that the wmic command isn’t recognized, change the working directory to be C:\Windows\System32\wbem\ and try again. You can do that with the cd (change directory) command.
-
You should see a table displayed in Command Prompt. This is a list of each user account in Windows, listed by username, followed by the account’s corresponding SID.
Now that you’re confident a particular user name corresponds to a particular SID, you can make whatever changes you need to in the registry or do whatever else you needed this information for.
Lifewire / Emily Mendoza
Finding the Username Using the SID
If you happen to have a case where you need to find the user name but all you have is the security identifier, you can «reverse» the command like this (just replace this SID with the one in question):
wmic useraccount where sid="S-1-5-21-992878714-4041223874-2616370337-1001" get name
…to get a result like this:
Namejonfi
How to Find a User’s SID in the Registry
You can also determine a user’s SID by looking through the ProfileImagePath values in each S-1-5-21 prefixed SID listed under this key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
The ProfileImagePath value within each SID-named registry key lists the profile directory, which includes the username.
For example, the value under the S-1-5-21-992878714-4041223874-2616370337-1001 key on the computer you see above is C:\Users\jonfi, so we know that’s the SID for that user.
This method of matching users to SIDs will only show those users who are logged in or have logged in and switched users. To continue to use the registry method for determining other user’s SIDs, you’ll need to log in as each user on the system and repeat these steps. This is a big drawback; assuming you’re able, you’re much better off using the wmic command method above.
FAQ
-
Open the Command Prompt by pressing Windows key+R. Then, enter the following command and press Enter: whoami /user.
-
To create a new user account in Windows, go to Start > Settings > Accounts > Family & others users. Under Other users > Add other user, select Add account. Enter the user’s information and follow the prompts.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
SID stands for Security Identifier. For Windows 10, a security identifier is used to unique represent any security identity of the operating system, such as a user account, thread, process, group, computer account, etc. Any process or account, that contributes to the security aspect of the operating system is assigned a unique ID. This ID is called Security Identifier.
The security identifiers or SIDs are assigned by Windows Domain Controller. The SID is stored in a security database. Whenever a new account, a new group, a new process or a new security context is created, it is assigned an SID that very moment. The number is unique and cannot be used for any other entity. When a user logs in to the system, Windows 10 creates an access token for the user. The access token consists of a lot of information, such as, user rights, user SID, etc. The token provides security related context of the concerned entities. Domain specific SIDs are also there, whose function is to represent the security context of generic users and groups.
Security Identifier (SID) Architecture
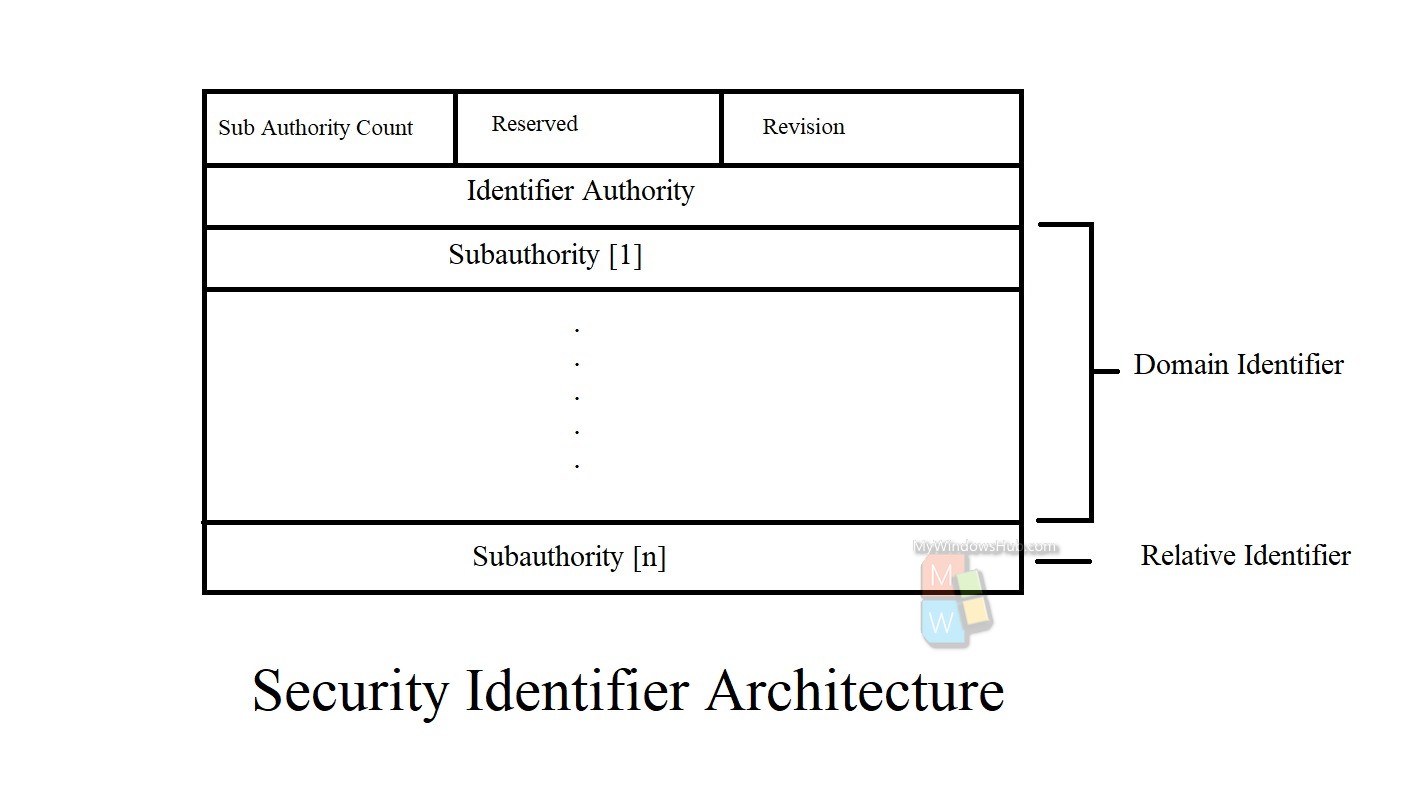
| Revision | This represents the version of the SID structure, that has been used in this particular SID. |
| Identifier authority | Identifies the highest level of authority that can issue SIDs for a particular type of security principal. For example, the identifier authority value in the SID for the Everyone group is 1 (World Authority). The identifier authority value in the SID for a specific Windows Server account or group is 5 (NT Authority). |
| Subauthorities | >Holds the most important information in a SID, which is contained in a series of one or more subauthority values. All values up to, but not including, the last value in the series collectively identify a domain in an enterprise. This part of the series is called the domain identifier. The last value in the series, which is called the relative identifier (RID), identifies a particular account or group relative to a domain. |
1. Using “WhoAmI” command on Command Prompt
Open Command Prompt, copy and paste whoami /user and hit Enter after that.
2. Using “wmic useraccount” command on Command Prompt (For Current User)
Open Command Prompt, copy and paste wmic useraccount where name=’%username%’ get domain,name,sid and hit Enter after that.
3. Using “wmic useraccount” command on Command Prompt (For All Users)
wmic useraccount get domain,name,sid
4. To Find User Name for SID using “wmic useraccount” command
Copy and paste the following command. Hit Enter after that.
wmic useraccount where sid='<sid>’ get domain,name
That’s all!
Загрузить PDF
Загрузить PDF
Из этой статьи вы узнаете, как в Windows выяснить идентификатор безопасности (SID) другого пользователя.
-
В левом нижнем углу откроется меню «Опытный пользователь».
-
Откроется новое окно.
-
Откроется окно командной строки.
-
Это команда для отображения идентификаторов безопасности всех пользователей системы.
- Если вы знаете имя пользователя, введите следующую команду: wmic useraccount where name="USER" get sid (вместо «USER» подставьте имя пользователя).[1]
- Если вы знаете имя пользователя, введите следующую команду: wmic useraccount where name="USER" get sid (вместо «USER» подставьте имя пользователя).[1]
-
Идентификатор безопасности — это длинная цепочка чисел, которая отобразится справа от каждого имени пользователя.
Реклама
Об этой статье
Эту страницу просматривали 5005 раз.
Была ли эта статья полезной?
-
Home
-
Knowledge Base
- What Is SID (Security Identifier) and How to Find It on Windows
By Amy | Follow |
Last Updated
This post will talk about SID (security identifier). It will tell you what Windows user SID is and what does SID means. Besides, it will also introduce you some extra information about SID.
What Is SID
The SID (Security Identifier) or Windows user SID identifies a security principle or security group in Microsoft Windows NT line systems, which is the only meaningful value. What does SID means? From this aspect, you can say that the Windows user SID is similar to a passport that is assigned to each computer in the process of installing operating system.
You can give special privileges to certain user accounts or restrict the activities of certain user accounts under the help of their SIDs. Here comes the need of finding the computer SID on Windows. How to do? MiniTool will provide you with several methods to do that.
Recommended article: What Is MSTSC Command and How to Use It to Run Remote Desktop
How to Find Security Identifier on Windows
As SID in the execution of certain commands associated with the safety of computer is important, it is vital to find the location of computer SID. You can find it via Command Prompt, Registry, as well as PowerShell. How to do? You can check the details in the following content.
Find Security Identifier via Command Prompt
Command Prompt is a Windows built-in utility that can be used to open many windows and fix some errors. It is one of the fastest methods to find the Windows user SID in your Windows 10 PC. Here are detailed steps.
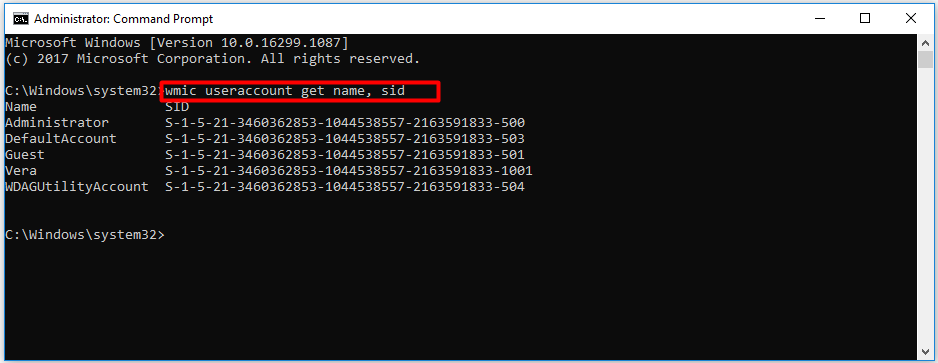
Step 1: Run Command Prompt as administrator in the search box.
Step 2: In the elevated window, type wmic useraccount get name, sid and hit Enter to execute the command. Wait for a while, and then you will get the result.
Tip: If you already know the user name, you can type this command – wmic useraccount where name=‘username’ get sid and press the Enter key to execute the operation.
Top recommendation: Python Is Not Recognized as Internal or External Command [Fixed]
Find Security Identifier via PowerShell
Alternatively, you can also find Windows user SID via PowerShell. Like Command Prompt, this utility is also a Windows built-in program. It has some commons to Command Prompt. You also need to type commands and execute it. Here are steps for that.
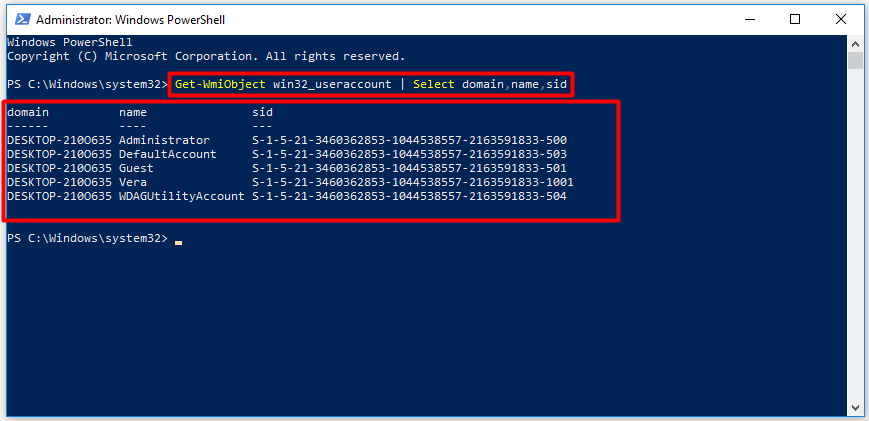
Step 1: Click on the Windows icon at your desktop, and then click the Windows PowerShell (Admin) option from the pop-up menu.
Step 2: In the next window, type the following command and press the Enter key to carry out the operation. Then, you will get the results as shown in the picture below.
Get-WmiObject win32_useraccount | Select domain,name,sid
Top recommendation: How PowerShell Delete File and Folder? Here Are Steps
Find Security Identifier via Registry
You can also find SID on Windows via Registry Editor. The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that is used to store low-level settings for the Microsoft Windows operating system and applications that utilize the Registry. How to find the Windows user SID by using Registry? Here is a full guide for you.
Step 1: Open the Run window by holding the Win and R keys, and then type regedit and click on the OK button to go on. If you are prompted with confirm window, just allow the operation.
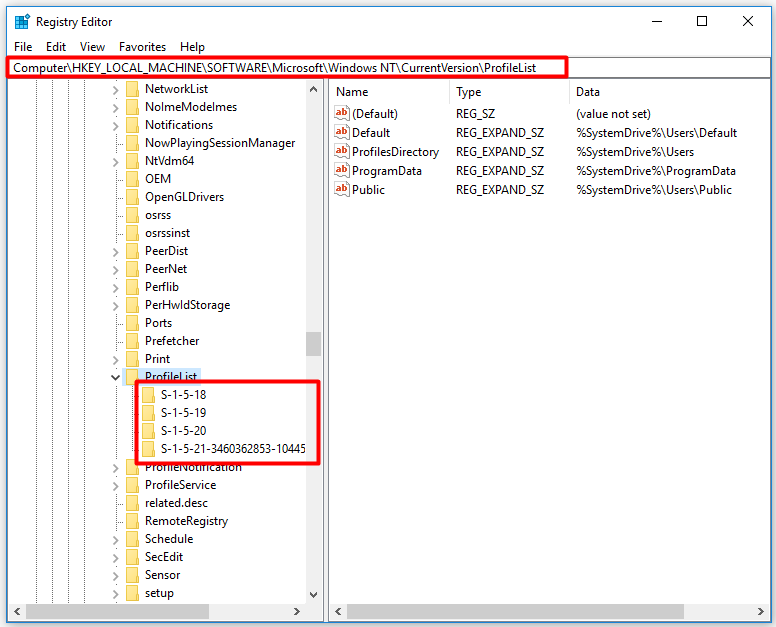
Step 2: After opening Registry Editor, follow the path below to get to the destination. Then, you will see all users and the corresponding SIDs. The results are shown as picture below.
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
The Bottom Line
To sum up, this post mainly introduces what Windows user SID is and how to open it. Therefore, you can have a further understanding of SID. Based on that that, you can find it with the given methods in the post. Here comes the end of this post.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Having writing articles about computer tech for a long time, I am rather experienced especially on the aspect of computer optimization, PC enhancement, as well as tech terms explanation. The habit of looking through tech forums makes me a great computer issues collector. And then, many articles related to these issues are released, which benefit plenty of users. Professional, effective, and innovative are always the pursuit of an editing worker.





