Обновлено:
Опубликовано:
Тематические термины: MTU, Windows, Linux, FreeBSD
В данной инструкции описаны способы просмотра значения MTU для различный операционных систем. Также в конце статьи будут указания по его смене.
Windows
Linux
FreeBSD
Провайдера
Смена MTU
Дополнительные материалы
Windows
Нажмите комбинащию клавишь Win + R
В появившемся окне введите cmd и нажмите OK

В открывшемся черном окне введите команду:
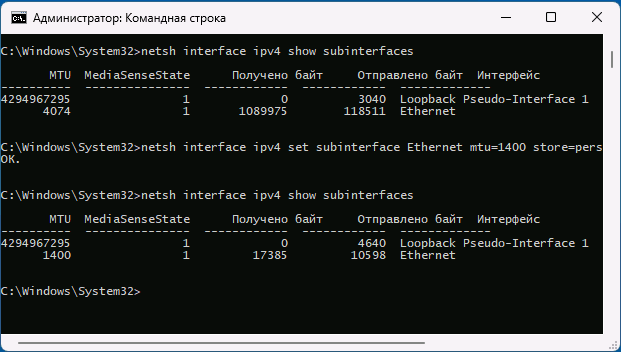
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
В первой колонке ответа мы увидим значение MTU:

* в данном примере, значение MTU равно 1500 для сетевого адаптера Ethernet.
В Powershell можно использовать команду:
Get-NetIPInterface | where {($_.ConnectionState -eq «Connected» )}
Linux
ip address
В более современных системах используется утилита для работы с сетевыми интерфейсами — ip address. Вводим команду:
ip a
В полученном результате находим нужный сетевой интерфейс и строчку на подобие:
eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
* то, что мы ищем — mtu 1500.
ifconfig
В более ранних системах или с установленным ifconfig вводим:
ifconfig eth0
* где eth0 — сетевой адаптер, для которого хотим узнать MTU.
В полученном результате находим что-то на вроде:
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
* где mtu 1500 — наше значение.
FreeBSD
В данной системе работаем с уже описанным выше ifconfig:
ifconfig em0
Получаем:
em0: flags=8843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,SIMPLEX,MULTICAST> metric 0 mtu 1500
Провайдера
Чтобы определить оптимальное значение MTU для нашего сетевого адаптера, подключенного к сети Интернет, необходимо узнать значение, используемое на оборудовании поставщика.
Для этого выполняем ping с запретом фрагментации сетевых пакетов (-f) и выставлением определенного размера пакета (-l):
ping dmosk.ru -f -l 1472
* 1472 будет соответствовать MTU — 1500, так как к пакету мы должны еще прибавить 28 (заголовок).
Наша задача — подобрать значение пакета, при котором будет идти пинг:
Ответ от 90.156.242.197: число байт=1472 время=13мс TTL=56
Ответ от 90.156.242.197: число байт=1472 время=12мс TTL=56
Если мы видим:
Требуется фрагментация пакета, но установлен запрещающий флаг.
Требуется фрагментация пакета, но установлен запрещающий флаг.
Значит значение -l нужно уменьшить, пока сигнал не начнет проходить.
Находим значение, которое стоит на границе с ошибкой и прибавляем к нему заголовок пакета — 28. Так мы получаем наше оптимальное MTU.
На данный момент большинство Интернет провайдеров предоставляет услуги связи с фрагментом в 1500. Старые подключения от Ростелеком или подключения на основе PPPoE могут работать на меньших значениях.
Как изменить MTU
Для смены значения MTU в Windows и Linux нужно использовать командную строку. Для Windows также можно отредактировать реестр.
Подробнее о этом читайте в инструкции Смена MTU.
Читайте также
Другие материалы по теме:
1. Как узнать MAC-адрес сетевой карты.
2. Как поменять MAC-адрес на компьютере с Windows.
3. Настройка сети в Linux с помощью netplan.
4. Настройка сети в CentOS и Rocky Linux.
5. Управление сетевыми маршрутами в CentOS 7.
Настройка MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) знакома большинству пользователей, которые когда-либо настраивали Wi-Fi роутеры, но доступна и в Windows для Ethernet и других подключений. MTU — это максимальный размера блока данных одного пакета в байтах (без учета размера заголовка), стандартный размер — 1500 байт.
При необходимости размер MTU в Windows 11, 10 и других версий можно изменить. В этой инструкции — о том, как это сделать, а также узнать текущий размер MTU.
Способы изменения размера MTU в Windows 11 и Windows 10
Прежде чем приступить, вы можете определить текущий размер MTU для сетевых интерфейсов, для этого достаточно запустить командную строку или Терминал от имени администратора, после чего использовать следующую команду:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces

Размеры MTU будут указаны в первом столбце в результатах выполнения команды. Если вам требуется изменить размер пакета, вы можете использовать один из следующих способов.
Включение Jumbo frame
Первая возможность — включить Jumbo Frame (Jumbo-кадр), позволяющий передавать данные в размере, превышающем стандартные 1500 байт. Для этого используйте следующие шаги:
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R, введите ncpa.cpl и нажмите Enter.
- В списке подключений нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по подключению, для которого нужно включить Jumbo frame и выберите пункт «Свойства».
- Нажмите кнопку «Настроить» для настройки сетевого адаптера.
- На вкладке «Дополнительно» найдите пункт «Jumbo packet» и измените его значение, затем примените настройки.
При включении Jumbo frame соединение может быть кратковременно разорвано, но обычно затем работает исправно. Учитывайте, что настройка Jumbo packet может быть доступна не для всех сетевых карт, также её наличие может зависеть от используемых драйверов.
Изменение MTU в командной строке
Вторая возможность — использование командной строки для изменения размера MTU:
- Запустите командную строку от имени администратора и введите следующую команду, чтобы посмотреть список имен интерфейсов:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
- В следующей команде измените ИМЯ_ИНТЕРФЕЙСА и значение MTU для изменения MTU для соответствующего подключения:
netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface ИМЯ_ИНТЕРФЕЙСА mtu=РАЗМЕР store=persistent
После успешного выполнения команды, размер MTU будет изменен.
Определить оптимальный размер пакета (значение MTU) для текущего Интернет-подключения можно в командной строке с помощью команды, ping адреса_сайта -f -l РАЗМЕР, например:
ping google.com -f -l 1500

Задачей будет поиск такого значения MTU, которое не приводит к сообщениям о необходимости фрагментации пакета.
Все способы:
- Определение текущего размера MTU
- Определение оптимального MTU
- Способ 1: Настройка «Jumbo Frame»
- Способ 2: Консоль
- Способ 3: Сторонние приложения
- Способ 4: «Редактор реестра»
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Определение текущего размера MTU
Перед настройкой параметра Maximum Transmission Unit может понадобиться определение его текущего значения. Обычно оно составляет 1500 байт, но нельзя исключать, что оно будет отличаться.
- Запустите от имени администратора «PowerShell» из контекстного меню кнопки «Пуск».
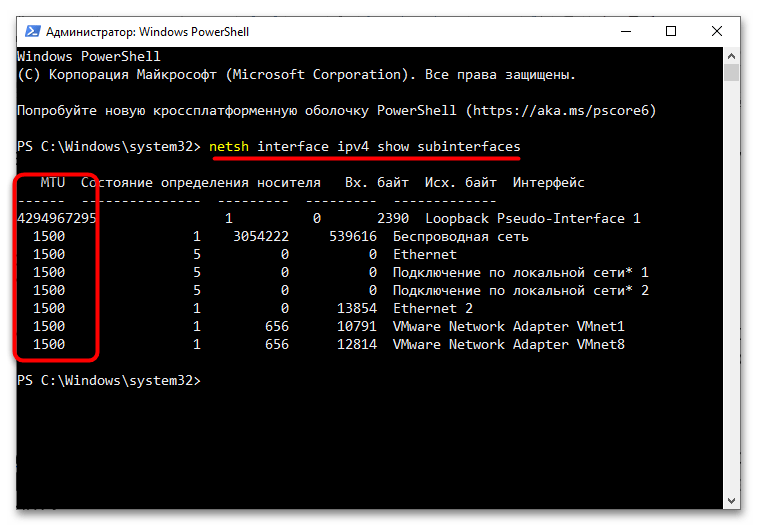
- Выполните команду
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces. Размеры MTU будут указаны в первом одноименном столбце отдельно для каждого подключения – как физического, так и виртуального.
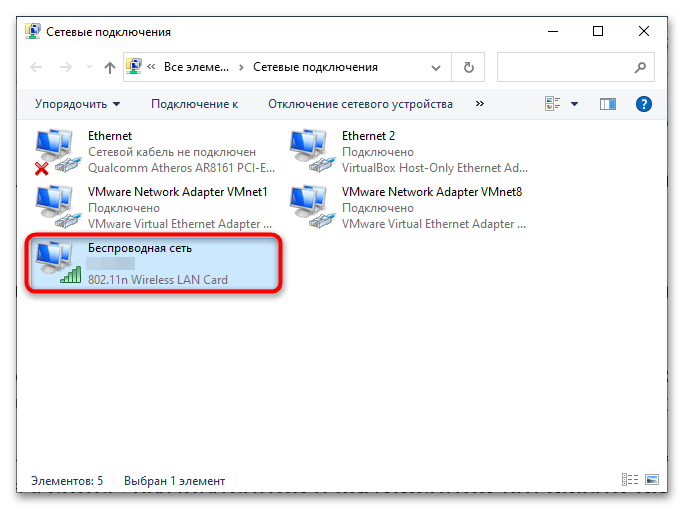
Если на компьютере используется проводное подключение, скорее всего, оно будет называться «Ethernet», если беспроводное – «Wireless», «Wi-Fi» или «Беспроводная сеть».
Определение оптимального MTU
Оптимальным значением MTU является то, при котором пакеты интернет-трафика не фрагментируются. Заданное в Windows 10 значение MTU в 1500 байт не всегда соответствует оптимальному, поэтому определение наиболее подходящего значения MTU не будет излишним.
- Откройте от имени администратора консоль «PowerShell» и выполните команду
ping google.com -f -l 1500. - В случае возвращения командой сообщение «Требуется фрагментация пакета, но установлен ограничивающий флаг» уменьшите значение 1500 на 10-50 единиц и повторите команду.
- Уменьшайте передаваемое в команде пинга значение постепенно, пока сообщение не исчезнет.
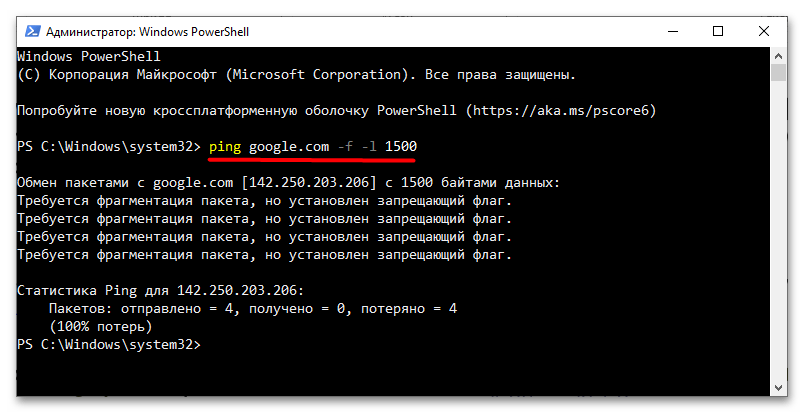
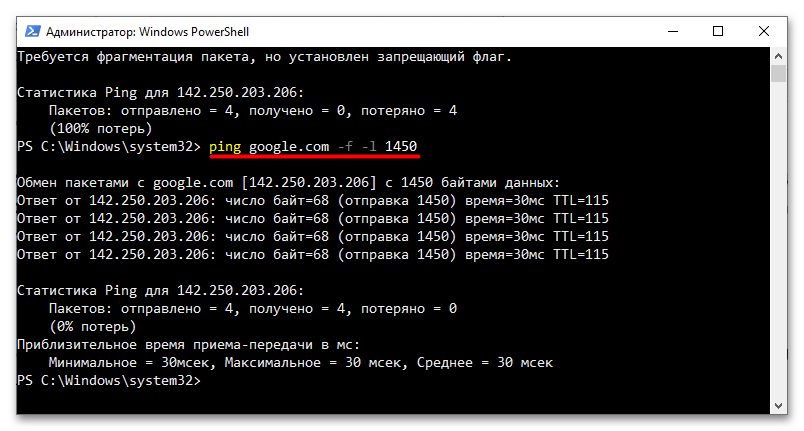
Точно так же можно определить верхнюю границу оптимального значения MTU. Поскольку при выполнении указанной команды не учитывается размер заголовков IP и запросов протокола ICMP, к тестируемому значению желательно добавить 28 байт – так полученный результат будет более точным.
Способ 1: Настройка «Jumbo Frame»
Этот способ предполагает использование графического интерфейса Windows, однако указанная настройка поддерживается не всеми сетевыми адаптерами.
- Откройте «Сетевые подключения», выполнив в вызванном нажатием клавиш Win + R диалоговом окошке быстрого запуска приложений команду
ncpa.cpl. - Кликните правой кнопкой мыши по используемому сетевому адаптеру и выберите из контекстного меню опцию «Свойства».
- В окне «Свойств» адаптера нажмите кнопку «Настроить».
- Переключитесь на вкладку «Дополнительно» и найдите в поле «Свойство» пункт «Jumbo Packet». Выберите из выпадающего списка «Значение» подходящее значение и сохраните настройки.
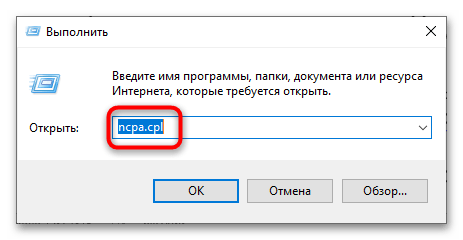


В момент изменения настроек соединение может разорваться на несколько секунд.
Способ 2: Консоль
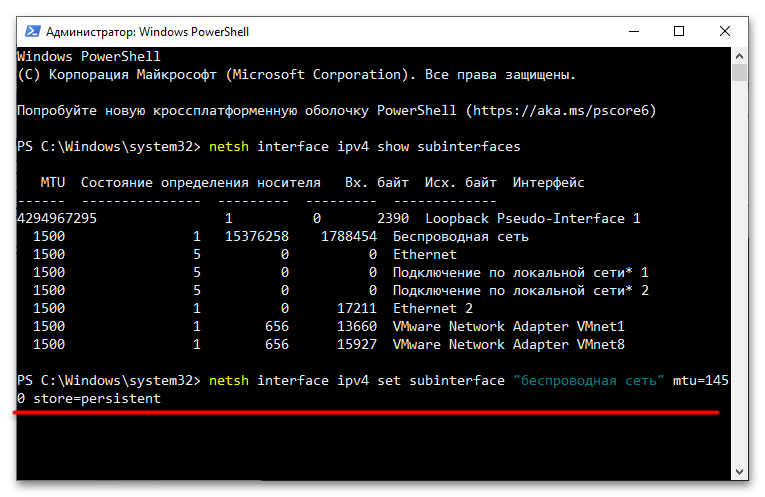
Более гибким способом изменения MTU в Windows 10 является использование консоли.
- Определите название сетевого интерфейса, для которого хотите изменить значение MTU. Посмотреть его можно в окне «Сетевые подключения».
Также можно вывести список подключений командой
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces, выполненной в запущенной от имени администратора «PowerShell» или «Командной строке». - Выполните команду
netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface NAME mtu=SIZE store=persistent, заменив NAME названием нужного сетевого интерфейса, а SIZE – новым размером MTU в байтах.
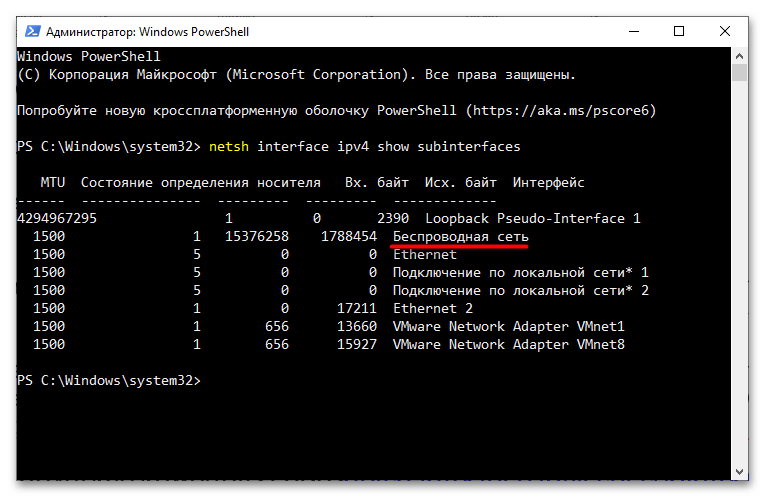
Убедитесь, что интернет-соединение работает нормально.
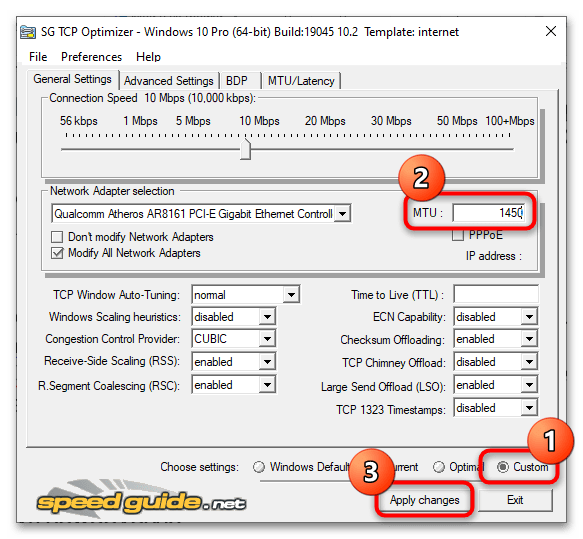
Способ 3: Сторонние приложения
Изменять значение параметра Maximum Transmission Unit могут некоторые сторонние программы для настройки и оптимизации сетевых подключений, например TCP Optimizer.
Скачать TCP Optimizer с официального сайта
- Скачайте приложение с сайта разработчика и запустите от имени администратора. Программа портативная, установки не требует.
- Включив режим «Custom», измените значение в поле «MTU» и нажмите кнопку «Apply changes».
Изменения должны вступить в силу немедленно.
Способ 4: «Редактор реестра»
Вполне рабочий, но не самый удобный способ настройки MTU, поскольку он предполагает ручную правку ключа системного реестра.
- Откройте «Редактор реестра», выполнив в диалоговом окошке быстрого запуска «Выполнить» (Win + R) команду
regedit. - Разверните ключ
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class\{4D36E972-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002bE10318}. Ключ содержит несколько вложенных подразделов с названиями «0000», «0001», «0002» и так далее – внимательно просмотрите их содержимое и выберите тот, где в качестве значения параметра «DriverDesc» будет указано название сетевого адаптера, для которого изменяется MTU. Название можно посмотреть в окошке «Свойств» подключения («Подключение через:»), смотрите шаг 2 в Способе 1. В этом же подразделе будет располагаться параметр «NetCfgInstanceId» – запомните или запишите его значение. - Затем разверните ключ
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfacesи найдите в нем подраздел, имеющий то же название, что и значение параметра «NetCfgInstanceId». Перейдите в него, отыщите тут параметр MTU и установите для него нужное значение в десятичной системе счисления.

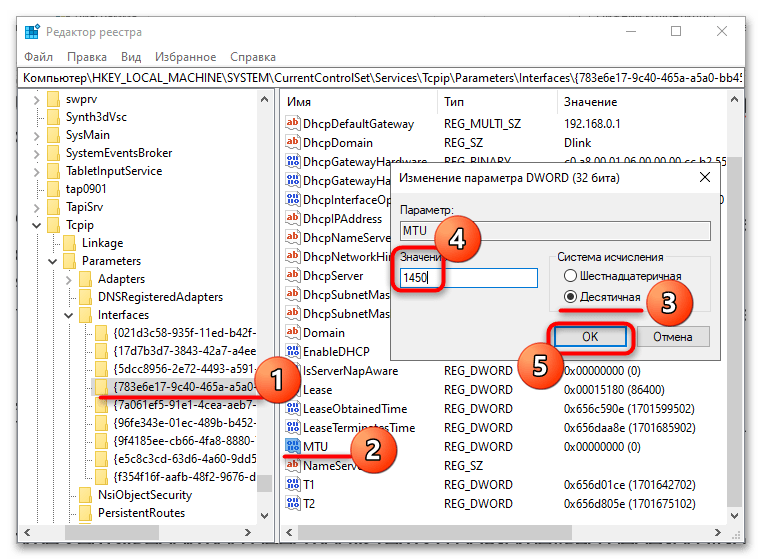
Если параметр MTU отсутствует, его нужно будет создать вручную. Для этого кликните правой кнопкой мыши по подразделу или его пустой области и выберите из контекстного меню «Создать» → «Параметр DWORD».
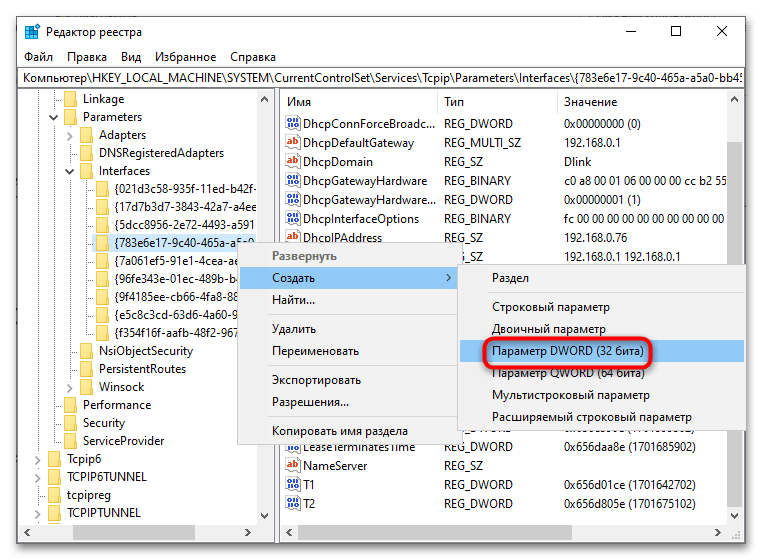
Сохраните настройки, закройте «Редактор реестра» и обязательно перезагрузите компьютер.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
MTU of the Network Interface
The MTU(maximum transmission unit) refers to the largest size of the data payload that can be carried in a single frame by a network protocol at a given layer. For Ethernet Network Interface, the MTU value refers to the maximum size of the data payload, excluding the Ethernet frame’s overhead (e.g., MAC addresses, EtherType, FCS).
Ethernet Frame Structure
The frame consists of 7 key components, divided into three main sections:
- Header:
- Preamble + SFD (8 bytes, physical layer).
- Destination MAC (6 bytes).
- Source MAC (6 bytes).
- EtherType (2 bytes).
- Payload (Data): 46–1500 bytes.
- Frame Check Sequence (FCS): 4 bytes.

For standard Ethernet II frames:
- The maximum data payload size is 1500 bytes.
- This 1500-byte limit is what is commonly referred to as the Ethernet MTU, defining the largest chunk of data that can be transmitted in a single Ethernet frame without requiring fragmentation at the data link layer (Layer 2)
It’s a key parameter in network communication protocols like TCP/IP, determining how much data can be sent in one “chunk” before it needs to be broken down into smaller pieces. MTU applies to various network layers, but it’s most commonly associated with the network interface (e.g., Ethernet, Wi-Fi) you’re using.
In Windows 10 and 11, the MTU value of the network adapter(interface), decides the maximum size of IP data packets(in byte) that can be sent by the computer.
Configuring an proper value of MTU of the network interface will increase the network efficiency. It speeds up the downloading and uploading of data by the apps.
User can view or modify it via the Command Prompt, PowerShell, or sometimes through specific driver settings for your network adapter.
Relationship Between Ethernet MTU(Data link layer) and Network Layer IP Packet
The Network Layer (Layer 3), typically implemented by the Internet Protocol (IP), generates IP packets that need to be transported over a physical network. The Ethernet II frame serves as the vehicle for carrying these IP packets across the data link layer. Here’s how the Ethernet II MTU ties to the IP packet:
1. Encapsulation of IP Packet in Ethernet Payload
- The data payload of the Ethernet II frame encapsulates the entire IP packet, which includes:
- IP Header: Typically 20 bytes for IPv4 (without options) or 40 bytes for IPv6.
- IP Payload: The actual data, such as a TCP segment, UDP datagram, or other protocol data.
- The Ethernet II MTU (1500 bytes) represents the maximum size of the IP packet (IP header + IP payload) that can fit into a single Ethernet frame without requiring fragmentation.

For example:
- For an IPv4 packet:
- Maximum IP packet size = Ethernet MTU = 1500 bytes.
- If the IP header is 20 bytes, the maximum IP payload (data) is 1500 – 20 = 1480 bytes.
- For an IPv6 packet:
- If the IP header is 40 bytes, the maximum IP payload is 1500 – 40 = 1460 bytes.
IP packet size = IP header size + IP payload size
IP payload = TCP Segment = TCP header + TCP payload
Path MTU (PMTU)
Path Maximum Transmission Unit, is the smallest MTU value supported by any link along the entire path between a source and destination in a network. Unlike the MTU of a single network interface (e.g., 1500 bytes for Ethernet), Path MTU considers the full route that packets take across multiple devices—such as routers, switches, and gateways—each of which may have its own MTU limit. The goal is to determine the largest packet size that can travel from sender to receiver without being fragmented.
How Path MTU Works
When a packet travels through a network, it passes through various segments (e.g., your local network, ISP, backbone networks). Each segment has its own MTU, and if a packet exceeds the MTU of any link, it either gets fragmented (split into smaller pieces) or dropped, depending on the protocol settings. Path MTU represents the “weakest link” in this chain—the lowest MTU along the route.
Modern networks use Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD) to dynamically figure this out:
- The sender starts with its local MTU (e.g., 1500 bytes) and sends packets with the “Don’t Fragment” (DF) flag set in the IP header.
- If a router along the path encounters a packet too large for its next link’s MTU, it drops the packet and sends back an ICMP “Fragmentation Needed” message with its MTU value.
- The sender adjusts its packet size downward and retries, repeating until packets pass through without issues.
- The result is the effective Path MTU.
Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD): Windows adjusts MSS dynamically during a connection if PMTUD detects a lower Path MTU along the route, overriding the interface MTU if needed.
Why Path MTU Matters
- Avoiding Fragmentation:
- Fragmentation slows down communication because the receiving end must reassemble packets, and lost fragments require retransmission. PMTU ensures packets are sized to avoid this.
- Improved network efficiency: By avoiding fragmentation, PMTUD reduces the overhead associated with reassembling fragmented packets.
- Reliability:
- Some networks or firewalls block fragmented packets or ICMP messages, breaking connectivity. PMTU helps ensure packets fit within limits upfront.
- Reduced latency: Fragmentation can introduce delays in packet delivery, which PMTUD helps to mitigate.
- Better throughput: Efficient packet transmission leads to higher network throughput.
Example
- Your computer (MTU 1500) sends a packet to a server.
- The packet passes through:
- Your router (MTU 1500)
- ISP gateway (MTU 1492, due to PPPoE)
- Backbone router (MTU 1500)
- Server’s network (MTU 1400, due to a VPN tunnel)
- The Path MTU is 1400 bytes—the smallest MTU in the chain. Packets larger than this would be dropped or fragmented.
Path MTU in Practice
- IPv4: PMTUD is optional but widely used. If ICMP messages are blocked (common in some networks), PMTUD fails, and connectivity issues may arise.
- IPv6: Fragmentation isn’t allowed at intermediate routers; PMTUD is mandatory, and packets exceeding the path MTU are dropped with an ICMPv6 “Packet Too Big” response.
Considerations:
- ICMP blocking: If firewalls or other network devices block ICMP “Fragmentation Needed” messages, PMTUD will not function correctly.
- Dynamic paths: PMTUD is continually performed because network paths can change dynamically.
It is useful to manually find find out the path MTU of the network and use its value to configure the MTU value of the network interface in Microsoft Window.
MSS (Maximum Segment Size)
The TCP Maximum Segment Size (MSS) defines the largest amount of TCP data (payload) that can be transmitted in a single segment. MSS operates at Layer 4 (Transport layer).
The MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) of a network interface in Microsoft Windows directly influences the MSS (Maximum Segment Size) because MSS is derived from the MTU, adjusted for the overhead introduced by the TCP/IP protocol headers.
How MTU Determines MSS
The MSS is essentially the MTU minus the size of the IP and TCP headers.
Therefore: MSS = MTU – (IP header size + TCP header size)
For a standard IPv4 Ethernet interface in Windows with an MTU of 1500 bytes:
- IPv4 Header: Typically 20 bytes (IPv4 without options).
- TCP Header: Typically 20 bytes (without options like timestamps or SACK).
- Total Overhead: 20 (IP) + 20 (TCP) = 40 bytes.
- MSS = 1500 – 40 = 1460 bytes.
- This means a TCP segment can carry up to 1460 bytes of actual data, with the remaining 40 bytes used by IP and TCP headers.
- TCP Segment = TCP Header (20) + TCP Payload (1460) = 1480 bytes
- IP Packet Size = IP Header (20) + TCP Header (20) + TCP Payload (1460) = 1500 bytes (fits within MTU)
- TCP ensures that its segments fit within the MTU, preventing IP fragmentation.
- For IPv6:
- IP Header = 40 bytes (fixed).
- TCP Header = 20 bytes (minimum).
- MSS = 1500 – 40 – 20 = 1440 bytes.

How Windows Handles MSS
- TCP Stack: Windows’ TCP implementation automatically calculates MSS during the TCP handshake. The MSS value is announced in the SYN packet, based on the interface MTU minus headers.
- Adjustment: If PMTUD detects a smaller Path MTU, Windows lowers the effective MSS for that connection without changing the interface MTU.
The Maximum Segment Size (MSS) negotiation is a critical part of establishing a TCP connection, ensuring efficient data transfer by preventing packet fragmentation. Here’s how it works:
The Role of MSS
- MSS defines the largest amount of data (payload) that a device can receive in a single TCP segment.
- It’s crucial for avoiding IP fragmentation, which can negatively impact network performance.
MSS and the TCP Three-Way Handshake:
- MSS negotiation occurs during the initial TCP three-way handshake, the process that establishes a TCP connection.
- SYN (Synchronize) Packet:
- The client initiates the connection by sending a SYN packet to the server.
- Within the TCP header of this SYN packet, the client includes an MSS option, indicating the maximum segment size it can receive.
- SYN-ACK (Synchronize-Acknowledge) Packet:
- The server responds with a SYN-ACK packet, acknowledging the client’s SYN.
- The server’s SYN-ACK also includes its own MSS option, specifying its maximum receivable segment size.
- ACK (Acknowledge) Packet:
- The client sends an ACK packet to confirm the server’s SYN-ACK, completing the handshake.
- By this point, both the client and server have each other’s MSS values.
- SYN (Synchronize) Packet:
Determining the Effective MSS:
- After the handshake, both devices know each other’s MSS.
- The effective MSS for the connection is the smaller of the two advertised MSS values.
- This ensures that neither device sends TCP segments that are too large for the other to handle.
Why This Matters
- Avoiding Fragmentation:
- By agreeing on an MSS, devices prevent IP fragmentation, which can lead to increased latency and packet loss.
- Optimizing Performance:
- Proper MSS negotiation helps optimize network throughput by ensuring that data is transmitted in efficient segment sizes.
This way by setting the value of MTU of the network interface, the effective MSS value for both sending and receiving data packets is controlled.
MSS = MTU – (IP header size + TCP header size)
Network shell (netsh)
Network shell (netsh) is a command-line utility that allows you to configure and display the status of various network communications components.
There are multiple commands to set the MTU value of the network interface.
MTU value range for IPv4 and IPv6 Interface
A network adapter can be assigned both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. Both act as a separate network and requires separate MTU values:
- For IPv4 network interface
- For IPv6 network interface
Valid Range of MTU value in Windows OS for Network interface (without jumbo frames):
- IPv4 MTU value range: 576 to 1500
- IPv6 MTU value range: 1280 to 1500
1. Configure the MTU value of the IPv4 network interface using Interface name
- Run Command Prompt(cmd) or PowerShell in Administrator mode.
2. First you need to know the name of the IPv4 network interface.
To show the list of IPv4 network interfaces run the following command:
- netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
3. Note down the name of the IPv4 network interface that connects to the internet.
4. The netsh command for configuring the MTU value of the IPv4 network interface
Syntax : netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface interface=[network interface name] mtu=[MTU value in bytes] store=persistent
In this case :
- Network Interface name: IntelWiFi
- MTU value in bytes: 14000
Netsh command to set MTU value to 1400 for the IPv4 network interface named IntelWiFi is:
- netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface interface=”IntelAX” mtu=1400 store=persistent

5. Verifying Changes. To confirm the configuration, use the command: netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
2. Configure the MTU value of the IPv6 network interface using Interface name
- Run Command Prompt(cmd) or PowerShell in Administrator mode.

1. You need to find out the name of the IPv6 network interface(if it is available). To show the list of IPv6 network interfaces run the following command:
- netsh interface ipv6 show subinterfaces
2. Note down the Name of the IPv6 network interface that connects to the internet.
3. The Netsh command for configuring the MTU value of the IPv6 network interface
Syntax : netsh interface ipv6 set subinterface interface=[network interface name] mtu=[MTU value in bytes] store=persistent
In this case :
- Network Interface name: IntelWiFi
- Optimal MTU value in bytes: 1300
Netsh command to set MTU value to 1300 for the IPv6 network interface named IntelWiFi is:
- netsh interface ipv6 set subinterface interface=”IntelAX” mtu=1300 store=persistent

4. Verifying Changes.
- To confirm the active configuration, use the command: netsh interface ipv6 show subinterfaces
- To confirm the persistent configuration, use the command: netsh interface ipv6 show subinterfaces store=persistent

3. Configure the MTU value of the IPv4 network interface using interface Index number
Run Command Prompt(cmd) or PowerShell in Administrator mode.
1. First you need to know the Index number of the IPv4 network interface. To show the list of IPv4 network interfaces run the following command:
- netsh interface ipv4 show interfaces

2. Note down the Index number (Idx) of the IPv4 network interface that connects to the internet.
3. The Netsh command for configuring the MTU value of the IPv4 network interface
Syntax : netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface [interface=]<network interface Index number> [mtu=]<MTU value in bytes> store=persistent
In this case :
- Network Interface Index number: 16
- MTU value in bytes: 1300
Netsh command to set MTU value to 1300 for the IPv4 network interface index number 16 is:
⦁ netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface interface=”16″ mtu=1300 store=persistent

4. Verifying Changes. To confirm the configuration, use the command: netsh interface ipv4 show interfaces
4. Configure the MTU value of the IPv6 Network Interface using interface Index number
Run the PowerShell command line tool in Administrator mode.
- First you need to know the Index number of the IPv6 network interface. To show the list of IPv6 network interfaces run the following command:
- netsh interface ipv6 show interfaces

2. Note down the Index number (Idx) of the IPv6 network interface that connects to the internet.
3. The Netsh command for configuring the MTU value of the IPv6 network interface
Syntax : netsh interface ipv6 set subinterface [interface=]<network interface Index number> [mtu=]<MTU value in bytes> store=persistent
In this case :
- Network Interface Index number: 16
- MTU value in bytes: 1400
Netsh command to set MTU value to 1300 for the IPv6 network interface index number 16 is:
⦁ netsh interface ipv6 set subinterface interface=”IntelAX” mtu=1300 store=persistent

4. Verifying Changes
- To confirm the persistent configuration, use the command: netsh interface ipv6 show interfaces store=persistent
- To confirm the active configuration, use the command: netsh interface ipv6 show interfaces store=active
IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA)
IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) is a critical component of the IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). Routers use RA messages to announce their presence on a network and provide essential configuration information to IPv6 hosts.
If router is advertising IPv6 MTU, then that value may override the default or manually configured MTU value of the IPv6 Network interface .
Reference
- What Is Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU)? (Huawei)
- MTU and MSS: What You Need to Know
- Network shell (netsh)
As part of network troubleshooting, you may need to check or change the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) on your Windows machine network interface card. The MTU is the size of a network packet that can be communicated in a single network transmission. Learn more about testing here.
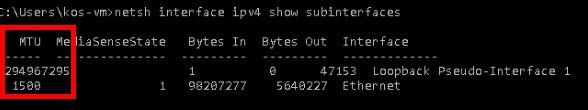
First, let’s check MTU settings in Windows.
1. Open a Command Prompt CMD (Right Click CMD -> Run Ad Administrator)
2. Type the following:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
3. Our MTU size is 1500 which is the default MTU size on most systems.
Change Windows MTU Size
1. Open a Command Prompt CMD (Right Click CMD -> Run Ad Administrator)
2. Type the following commands in order
netsh
interface
ipv4
3. Your command window will now be at the prompt to change MTU using the next command below.
4. Finally, type the following command to change your Windows MTU. In the example, we will be changing the MTU to 1200.
Note: the “Local Area Connection 3” will be name of the interface you see when you ran netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces command. This will likely be a different name.
set subinterface “Local Area Connection 3” mtu=1200 store=persistent

* Please use the comment form below. Comments are moderated.*