#статьи
-
0
Руководство для начинающих и тех, кому не понравился GitHub.
Иллюстрация: Оля Ежак для Skillbox Media
Программист, консультант, специалист по документированию. Легко и доступно рассказывает о сложных вещах в программировании и дизайне.
GitLab — это сервис для хранения кода, управления версиями и совместной разработки программного обеспечения. В статье мы подробно разберём его основные термины, поймём, для чего он используется и потренируемся на своём компьютере.
Вы узнаете:
- что такое GitLab;
- зачем он нужен;
- как он помогает разработчику;
- чем GitLab отличается от GitHub;
- как с ним работать на своём компьютере.
GitLab — это веб-платформа для управления проектами и репозиториями программного кода, работа которой основана на популярной системе контроля версий Git. Чтобы понять, что она умеет и как именно помогает разработчикам, начнём с разбора основных понятий.
Система контроля версий Git используется для хранения промежуточных версий кода. Например, когда разработчик вносит в него изменения или добавляет новые части, то в Git он делает это с помощью коммитов.
Коммит (commit) — это пакет изменений, хранящий информацию с добавленными, отредактированными или удалёнными файлами кода. Благодаря этому основной код проекта всегда можно вернуть в работоспособное состояние, восстановив его прошлые версии.
Репозиторий. Место, где хранится код и дополнительные файлы, необходимые для его работы или вёрстки окон приложения: иконки, картинки и так далее. Репозиторий похож на обычную папку на компьютере, только с дополнительными функциями. Например, у каждого файла, который он хранит, есть история изменений.
Ветки (branch). Это параллельные линии разработки, которые существуют независимо друг от друга. В Git-системах разработчики пишут код в отдельных ветках, избегая таким образом конфликтов между вносимыми изменениями.
Когда бэкендер, фронтендер или другой специалист завершает работу над кодом в своей ветке, он создаёт запрос на слияние (merge request) с главной веткой (master или main), где находится основной код программы, чтобы перенести туда свои изменения.
Слияние — это процесс объединения двух или более веток в одну.
Другие разработчики могут оценить изменения и прокомментировать их. После тестирования и утверждения со стороны сеньора или тимлида запрос на слияние выполняется. В GitLab можно настроить процесс разработки так, чтобы изменения автоматически вносились в основную ветку при выполнении определённых условий, например после успешного прохождения тестов.
GitLab помогает командам совместно разрабатывать программное обеспечение: планировать процессы, тестировать код, собирать проект и публиковать релизы.
В GitLab можно создавать задачи и группировать их в проекты, назначая ответственных и определяя дедлайны. Этим он похож на Jira, «Битрикс24» и другие приложения для менеджеров.
С его помощью тимлид или старший разработчик могут проверить скорость, с которой команда выполняет задачи. Это полезно при планировании спринтов, когда требуется определить времязатраты на разработку той или иной фичи в приложении.
Участники могут совместно работать над проектом в GitLab благодаря системе репозиториев и веток. Разработчики пишут код параллельно друг с другом, не переживая о совместимости новых или изменённых частей программы.
После написания или обновления части кода разработчик подаёт запрос на слияние своей ветви с главным репозиторием проекта. Сеньор-разработчик или тимлид проверяют его и принимают запрос на слияние или же отправляют код на доработку, оставляя комментарии.

GitLab автоматизирует процессы тестирования при внесении любого изменения в код. Например, когда в проект добавляют новую функцию или изменяют старую, GitLab отправляет её в центральный репозиторий, где автоматически запускается тестирование.
Обычно этот процесс устроен следующим образом:
- Система проверяет код на ошибки компиляции.
- После этого запускаются тесты, написанные разработчиками: модульные — для проверки отдельных частей кода, интеграционные, проверяющие работу нового кода со старым, и другие. Цель всех тестов — убедиться, что новые изменения не ломают существующую функциональность приложения.
- Разработчик получает отчёт о пройденных тестах и при необходимости дорабатывает код. Когда все необходимые изменения будут внесены, GitLab интегрирует их в основной репозиторий проекта.
В GitLab есть репозитории контейнеров — автономных исполняемых пакетов, включающих в себя всё необходимое для работы приложения: библиотеки, файлы конфигураций и другое. Благодаря этому они запускаются в любой системе, вне зависимости от её окружения. Контейнеры создаются, развёртываются и управляются на платформе Docker.

В репозитории проекта можно хранить разные версии контейнеров для своего приложения и настроить их автоматическое обновление при изменении кода.
Встроенные средства continuous integration (CI) и continuous deployment (CD) автоматизируют весь процесс от сборки кода до загрузки приложения или его новой версии в среду выполнения: на веб-сервер, мобильное устройство или другую платформу.
Разработчик может определить тип окружения, например, выбрав продакшен-сервер, и автоматически развёртывать приложение в нём после тестирования.
В GitLab встроено несколько вариантов развёртывания «из коробки». Их выбирают в зависимости от задач:
- Сине-зелёное развёртывание (blue-green deployment). Используется две среды: рабочая («синяя») и тестовая («зелёная») — для проверки работы приложения после внесения изменений. Когда новую версию кода проверили, она становится «зелёной».
- Канареечное развёртывание (canary deployment). Сначала новая версия приложения разворачивается для небольшой части пользователей. Так её тестируют в реальных условиях, ограниченной аудитории, а затем становится основной для всех.
- Плавное развёртывание (rolling deployment). Приложение заменяется новой версией без прерывания работы. Если у команды несколько серверов, она обновляет код на одном из них, затем на следующем и так далее.
Эти стратегии снижают риски, возникающие при установке новых версий приложения. Например, связанные с его несовместимостью с конкретными пользовательскими устройствами. В случае сине-зелёного или канареечного развёртывания можно быстро откатиться к стабильной версии приложения.
И это не всё. В GitLab есть готовые шаблоны CI/CD templates. Это наборы инструкций или конфигураций для автоматизированной сборки, тестирования и развёртывания кода. Вместо того чтобы каждый раз создавать конфигурацию с нуля, разработчики могут использовать готовый шаблон и настроить его параметры для своего приложения.
GitLab собирает различные метрики процесса CI/CD и производительности приложения: время сборки, процент успешного прохождения тестов, количество выявленных ошибок и другие. Если их не хватает, то можно интегрировать сторонние инструменты мониторинга, например Prometheus или Grafana.
GitLab не только предоставляет разработчикам хранилище кода со встроенной системой контроля версий Git, но и облегчает работу с помощью дополнительных возможностей.
Гибкие настройки доступа к репозиториям с кодом. В проекте может работать несколько десятков специалистов. GitLab позволяет настроить их права доступа к репозиториям — определить, кто может читать, редактировать или загружать код. Например, пользователи с гостевым доступом к репозиторию могут просматривать его, но не вносить изменения. Это повышает безопасность проекта и облегчает управление разработкой.
Можно настроить доступ к отдельным веткам, а также создать группы пользователей, которые участвуют в нескольких проектах одновременно.
Инструменты управления CI/CD. Continuous integration (CI) и continuous deployment (CD) — подход в разработке программного обеспечения, который автоматизирует процессы сборки, тестирования и развёртывания приложения.
Непрерывная интеграция (continuous integration, CI) — это практика, при которой код регулярно, чаще всего несколько раз в день, сливается в общий репозиторий с автоматизированной сборкой проекта. Благодаря этому можно быстро выявить баги в коде и проблемы совместимости с существующей кодовой базой.
Непрерывное развёртывание (continuous deployment, CD) — продолжение CI. Когда код успешно проходит тестирование после слияния, система автоматически разворачивает изменения в рабочей среде. Это означает, что новая версия приложения сразу становится доступной для заказчиков и пользователей.
База знаний. В GitLab есть инструменты для создания вики-страниц с документацией проекта. Они поддерживают различные форматы: текст, изображения, видео и таблицы.
Благодаря базе знаний о проекте новые сотрудники могут быстро понять, как настроить рабочую среду, какие версии библиотек использовать и так далее.
Проекты и задачи. В GitLab реализована система управления разработкой. В ней можно создавать задачи для членов команды, выбирая ответственных и устанавливая дедлайны, и описывать результаты работы.
Интеграция с другими инструментами. GitLab поддерживает интеграцию с популярными платформами и сервисами, использующимися в разработке: Docker, Kubernetes, Jira, Slack и другими.
В общем, GitLab — это централизованное место не только для хранения кода, но и для управления проектами, ведения базы знаний и автоматизации процессов разработки.
GitLab и GitHub — это два популярных веб-сервиса для хостинга проектов с использованием системы контроля версий Git. Внешне они очень похожи, но между ними есть несколько различий:
- GitHub — это облачный сервис, принадлежащий Microsoft, на котором вы можете хранить свои проекты и управлять ими. В отличие от него, GitLab можно развернуть на своём собственном сервере.
- В GitHub для работы с CI/CD придётся использовать дополнительный инструмент — GitHub Actions. GitLab — это полностью интегрированное решение со встроенными инструментами CI/CD.
- В бесплатной версии GitHub в приватных репозиториях используется два уровня доступа: владелец (owner) и соавтор (collaborator). В GitLab таких ограничений нет. Количество пользователей с разным уровнем доступа не ограничено.
В целом и GitLab, и GitHub предоставляют одинаковый набор возможностей. Разница лишь в том, что в GitHub часть из них доступна через интеграции со сторонними приложениями, а в GitHub они есть по умолчанию.
Работа с GitLab проходит в несколько шагов: создание аккаунта и репозитория, добавление пользователей и веток, загрузка файлов проекта, внесение изменений в код и слияние веток.
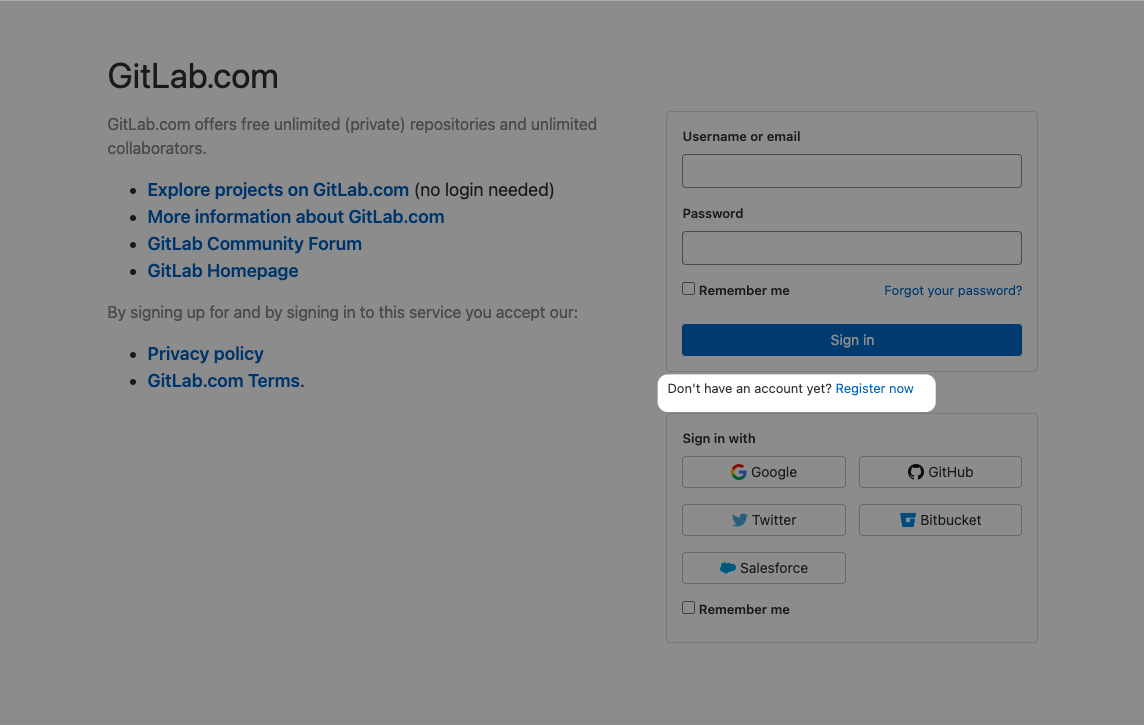
Если у вас ещё нет учётной записи на GitLab, то начните с создания аккаунта на официальном сайте и заполните регистрационную форму:
- Username: уникальное имя вашего аккаунта.
- Email: рабочая или личная электронная почта.
- Password: пароль с надёжной комбинацией.
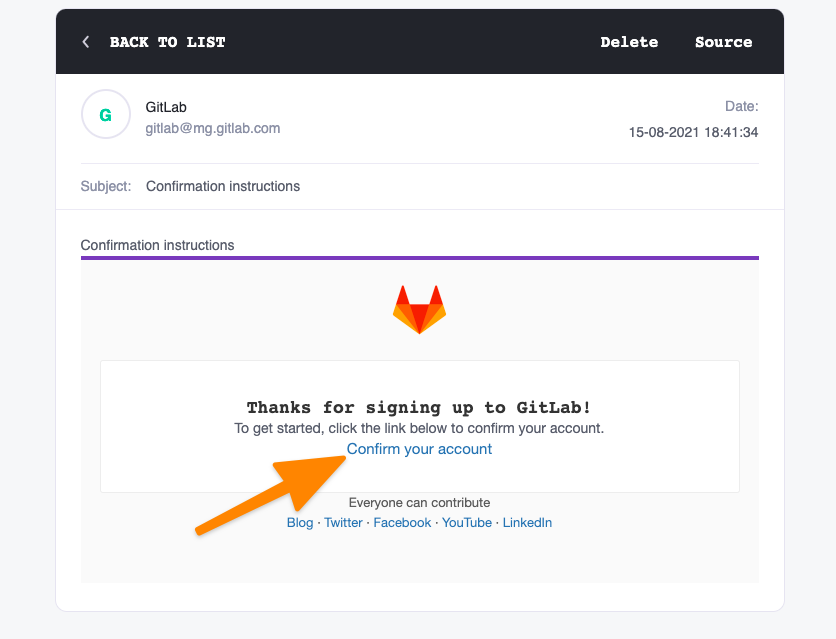
После регистрации подтвердите её по ссылке из письма, отправленного на электронную почту. Теперь ваш аккаунт в GitLab создан и готов к работе.
На главной странице или в боковой панели нажмите на значок + и выберите пункт New project/repository:
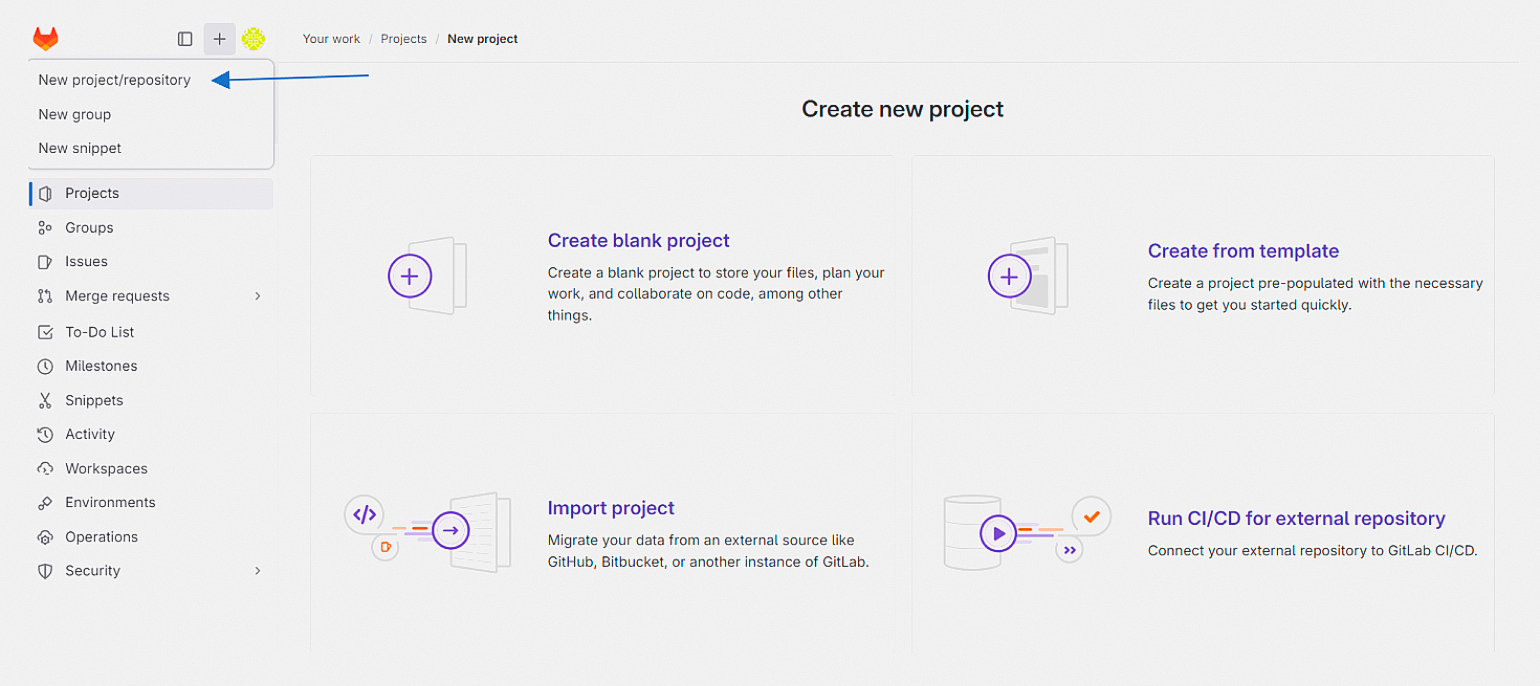
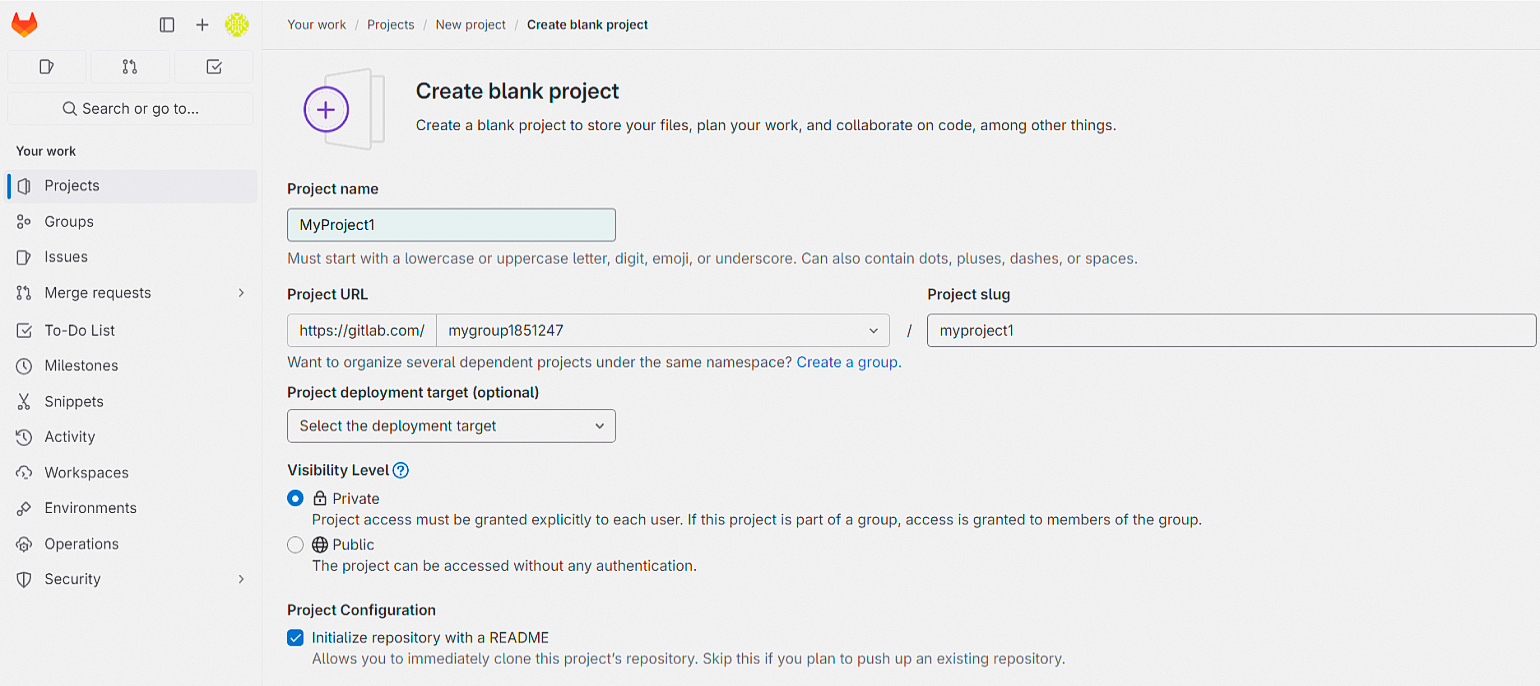
Создать проект в GitLab можно несколькими способами: с нуля, на основе шаблона, импортировать его из другого сервиса или компьютера или с помощью CI/CD. Мы начнём работать с пустого проекта, поэтому выберите Create blank project и заполните информацию:
- Project name: имя проекта.
- Project slug определяется автоматически на основе Project name.
- Visibility Level: Public — для всех, Private — только для вас и выбранных соавторов проекта.
- Initialize repository with a README: автоматически создаст README в вашем репозитории. Это текстовый файл, который содержит информацию о проекте: описание его задач, принципов работы, инструкцию по установке и настройке.
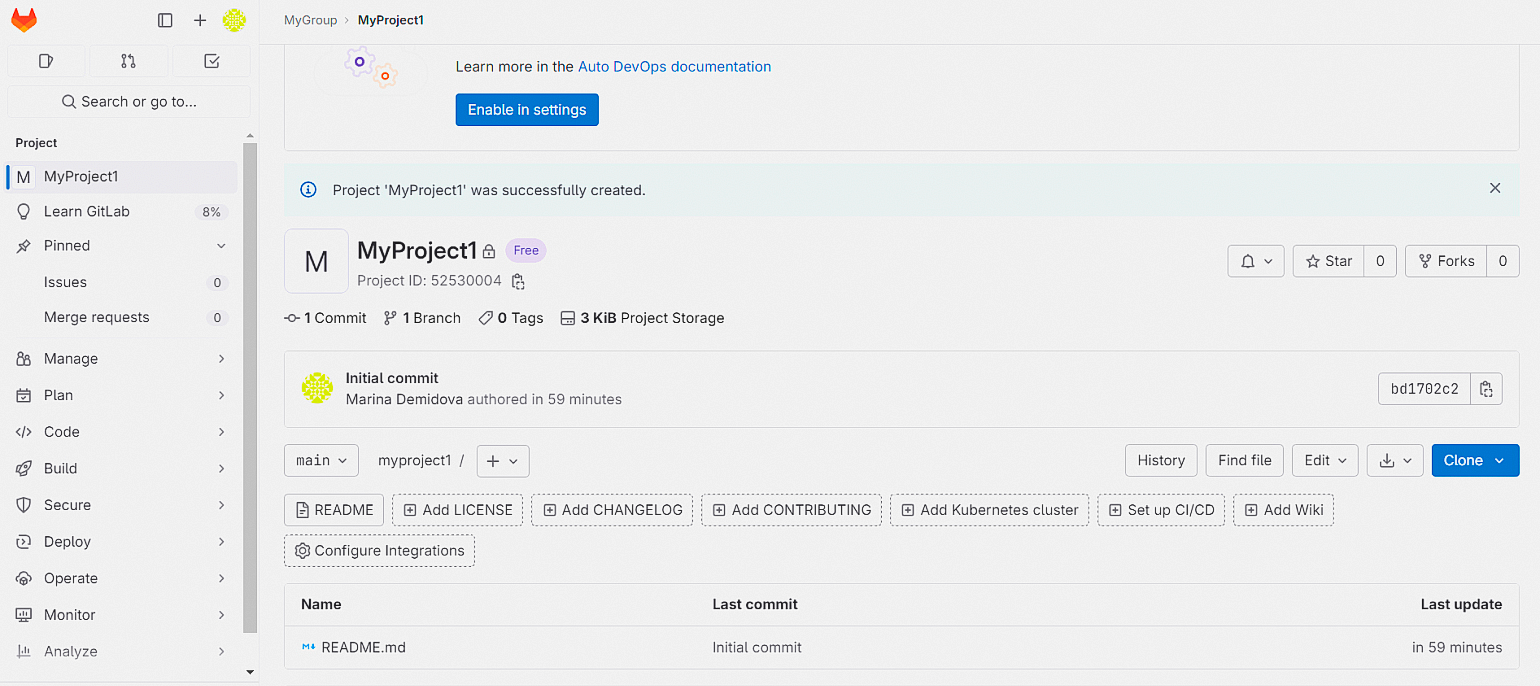
После заполнения данных нажмите кнопку Create Project. Теперь репозиторий готов к работе:
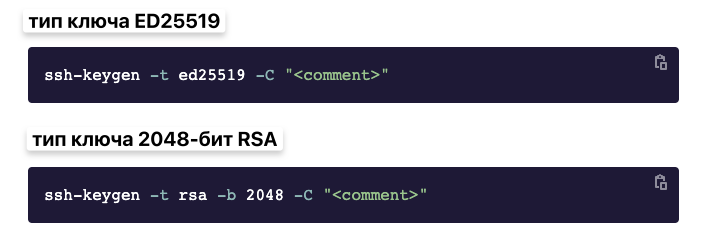
SSH-ключи используются для аутентификации вашего компьютера на удалённом сервере, в данном случае на сервере GitLab. Благодаря этому вы можете подтверждать свою личность без ввода пароля.
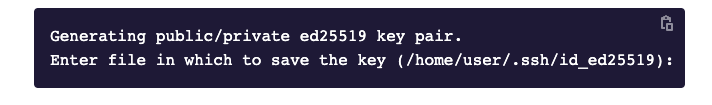
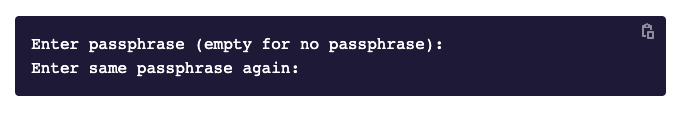
Чтобы создать ключ, откройте терминал или командную строку и введите команду для генерации ключей ssh-keygen. Если вы хотите сгенерировать их в определённой папке, то введите путь до неё.
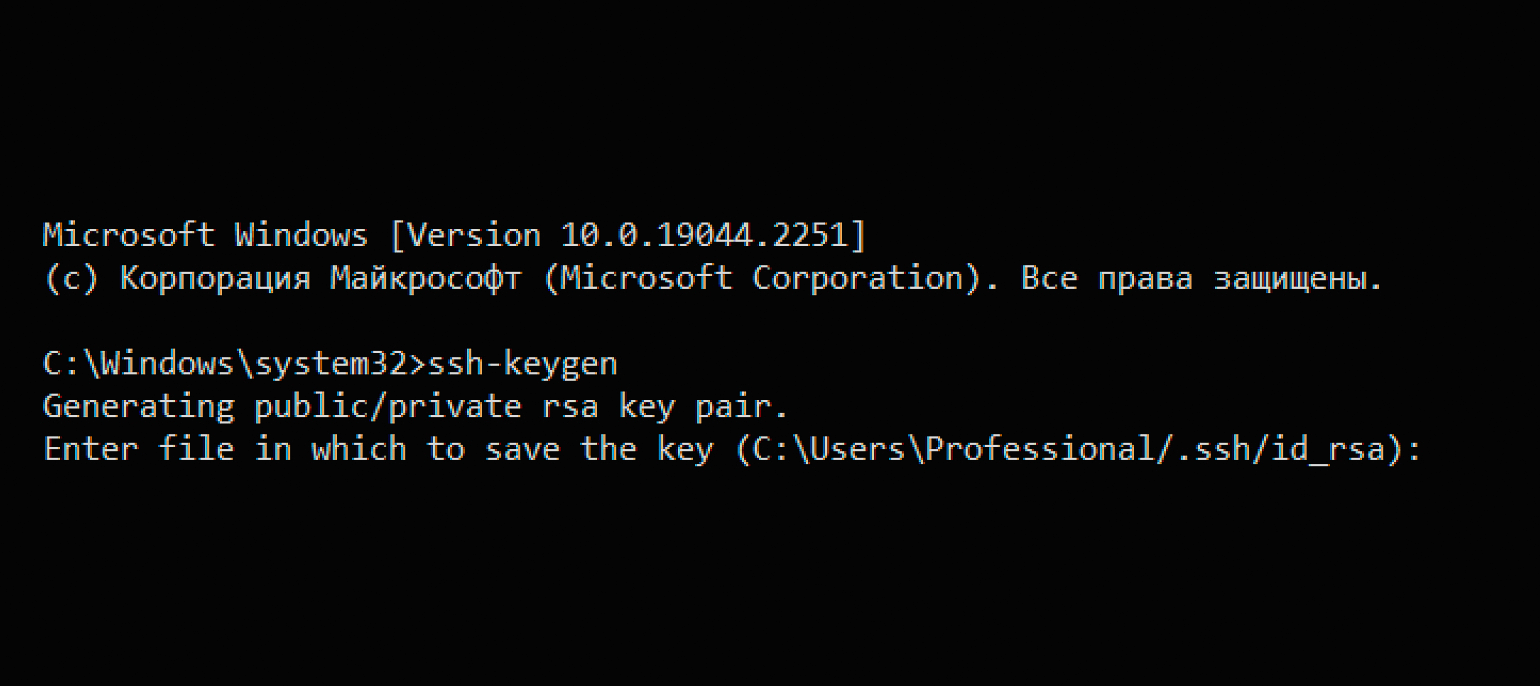
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
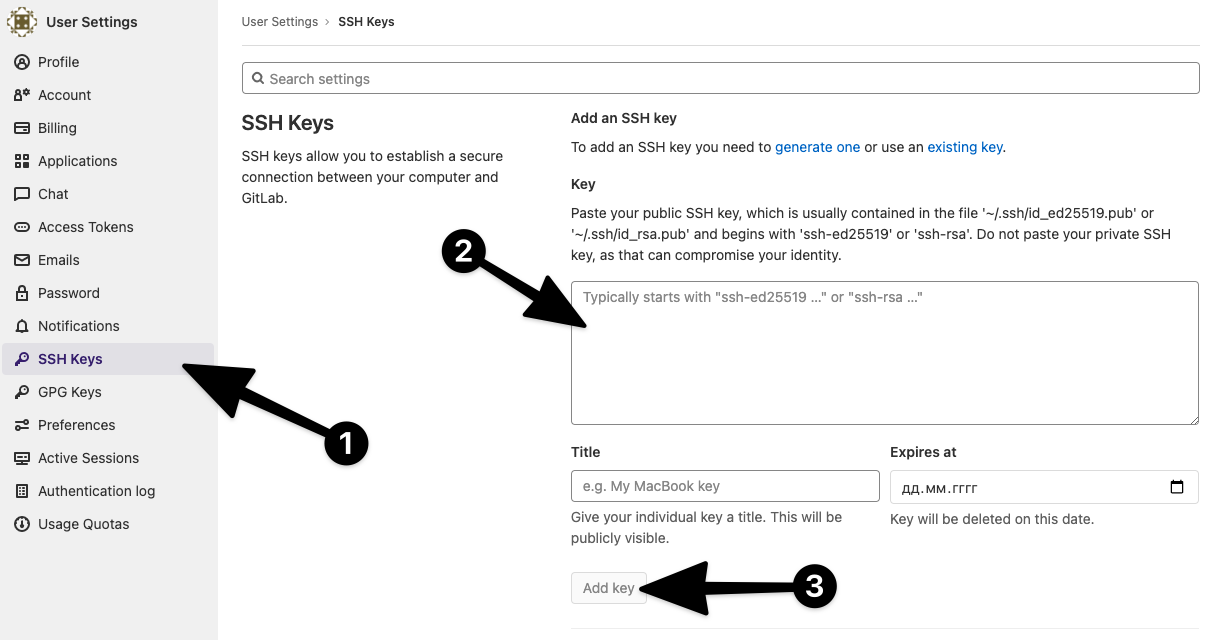
Теперь в указанной папке у вас появится два файла с ключами — приватный и открытый. Для создания ключей в GitLab нужен второй — файл с расширением .pub. Откройте его в текстовом редакторе и скопируйте содержимое в буфер обмена.
Перейдите в свой репозиторий на сайте GitLab, нажмите на кнопку Add SSH key:
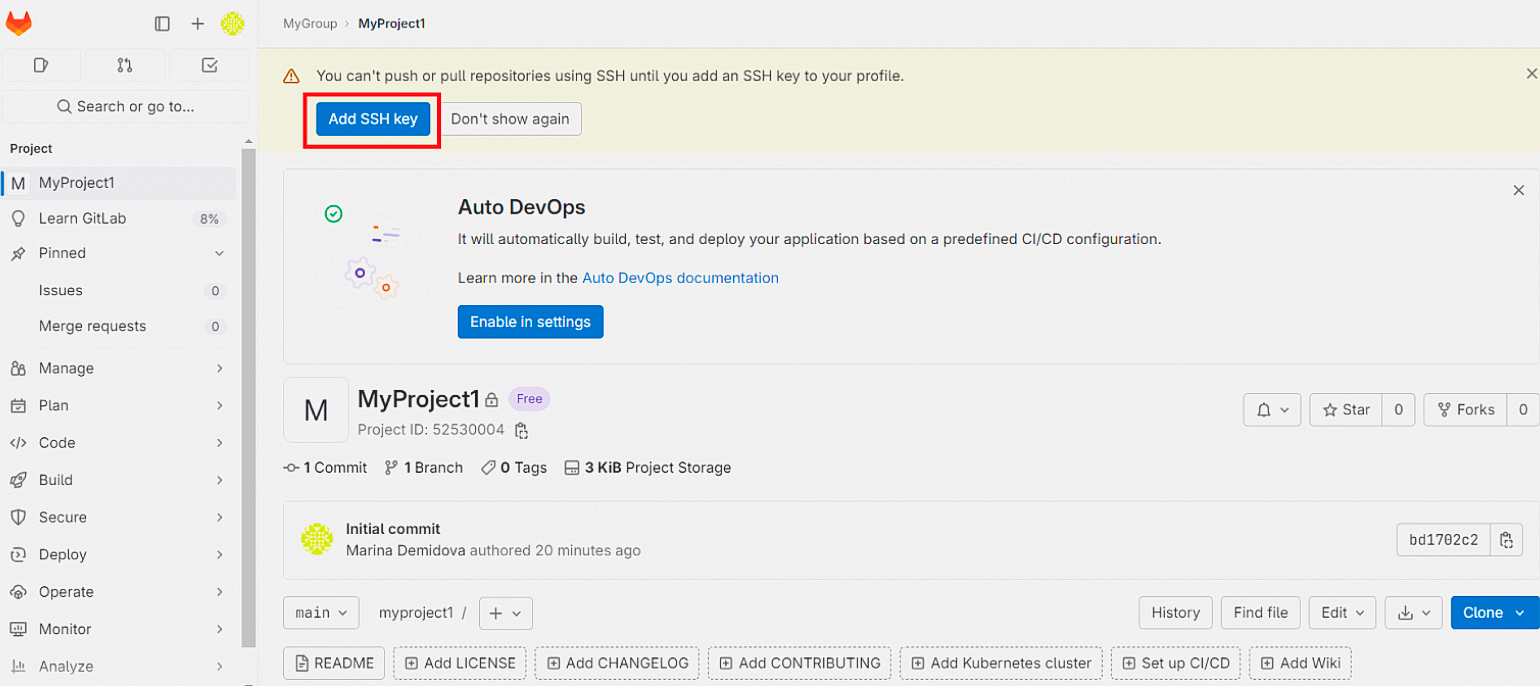
А затем на кнопку Add new key:
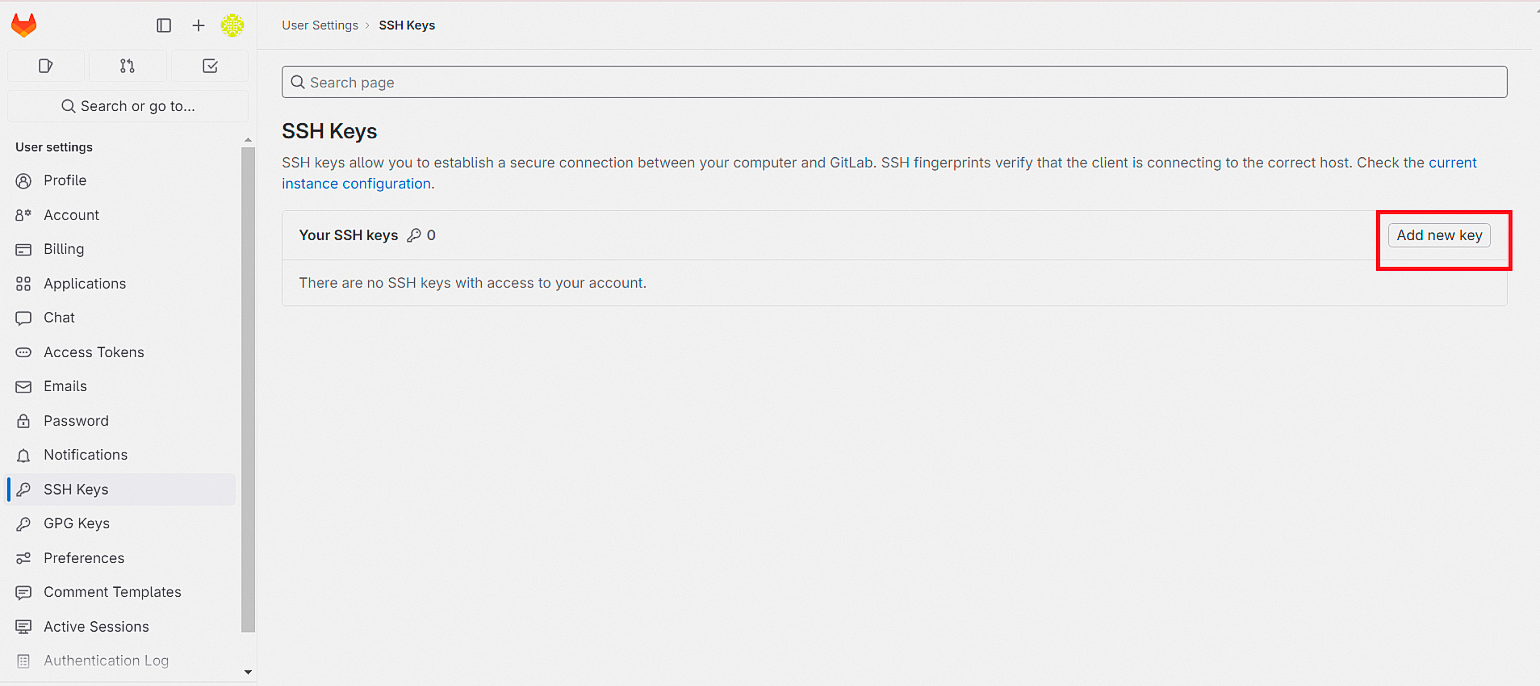
Вставьте скопированный ключ в поле Key и дайте ему осмысленное имя, например, совпадающее с именем репозитория.
Вы можете загрузить существующие файлы проекта в свой репозиторий или создать новые. Для этого нажмите на + и выберите New file или Upload file.
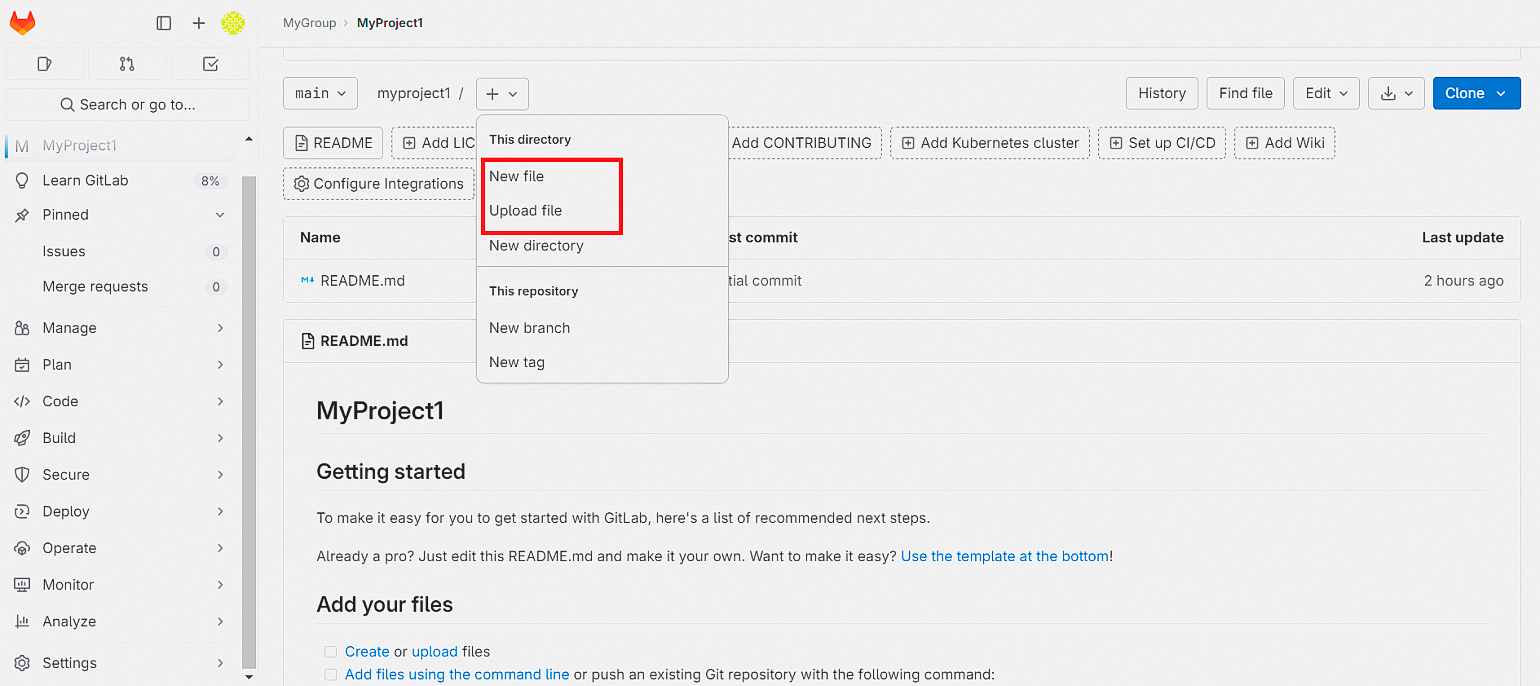
Теперь вы можете редактировать код непосредственно в веб-интерфейсе. Для этого нажмите кнопку Edit:
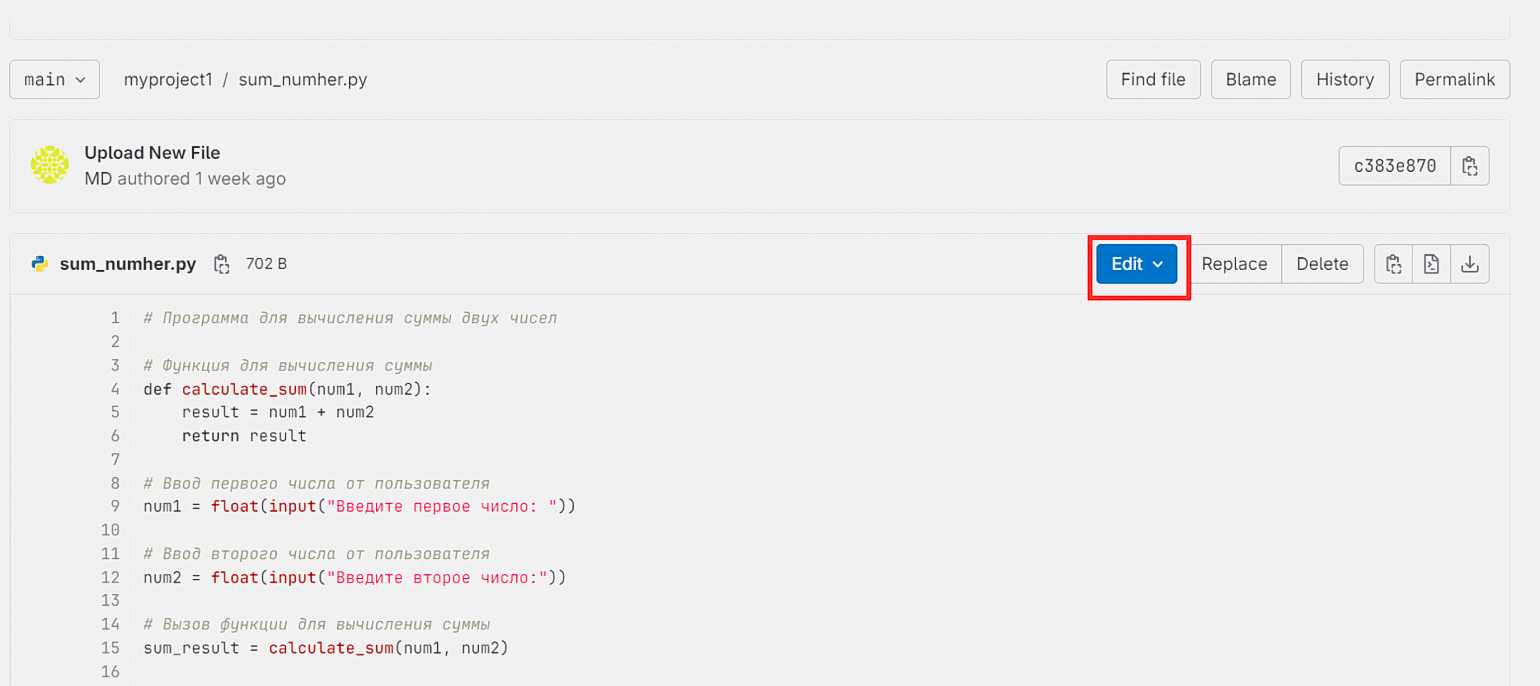
Репозиторий можно клонировать на свой компьютер и работать в удобном редакторе или IDE. Подробнее об этом напишем дальше.
Каждая ветка представляет собой отдельное направление работы. В них разработчики создают новые функции, исправляют ошибки, тестируют изменения и проводят эксперименты, которые не влияют на основной проект и другие ветки. После завершения работы в ветке производится её слияние с основной веткой.
По умолчанию в новом репозитории есть одна ветка — main. Обычно с кодом в main не работают напрямую, а вносят изменения посредством слияния с другими ветками.
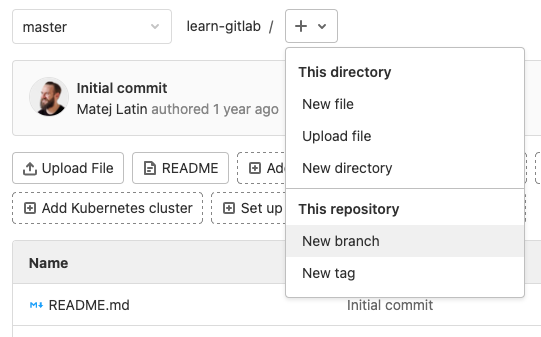
Чтобы создать новую ветку нажмите на + и выберите пункт меню New branch.
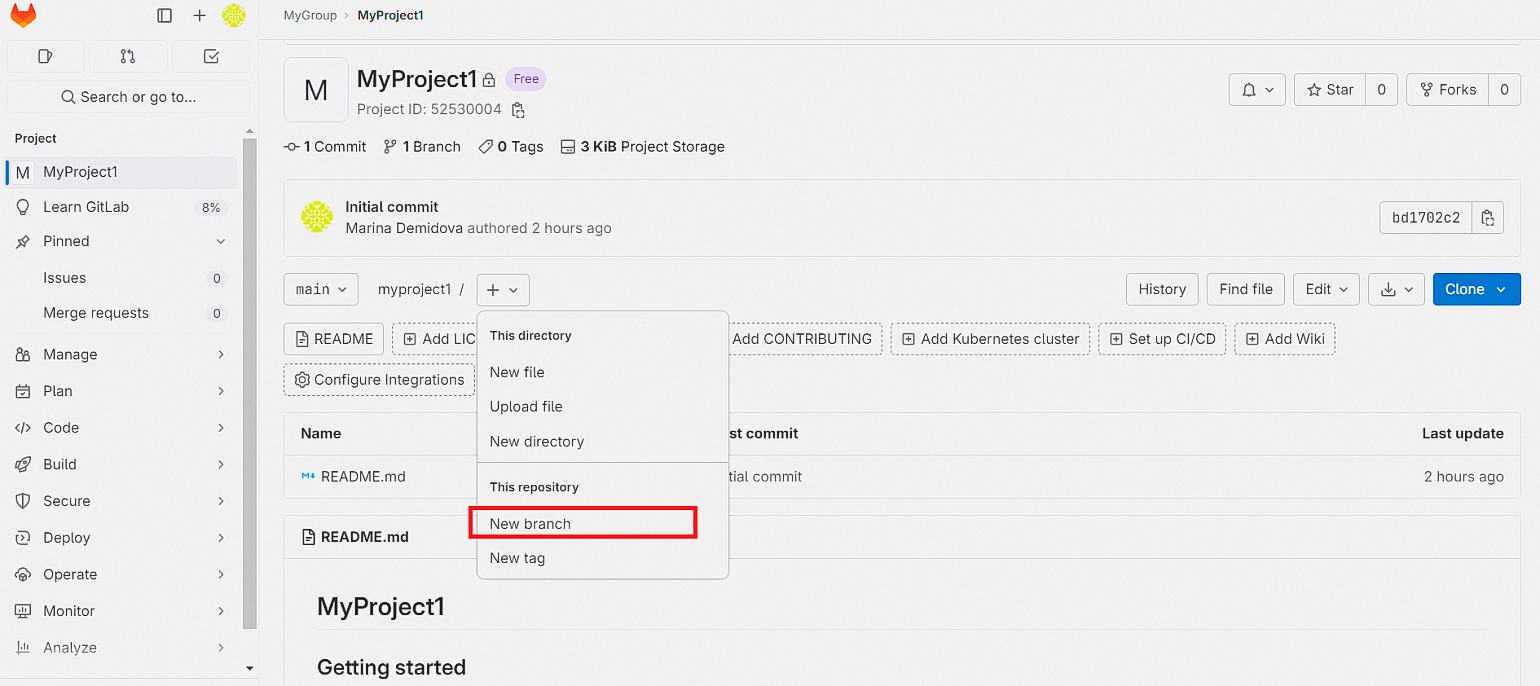
Новая ветка содержит копии всех файлов проекта. Теперь можно вносить изменения в код, добавлять новые фичи в ПО, исправлять ошибки, и это не будет влиять на основной код.
Чтобы перенести новый код в основную ветку, нажмите на кнопку Commit changes внизу страницы.
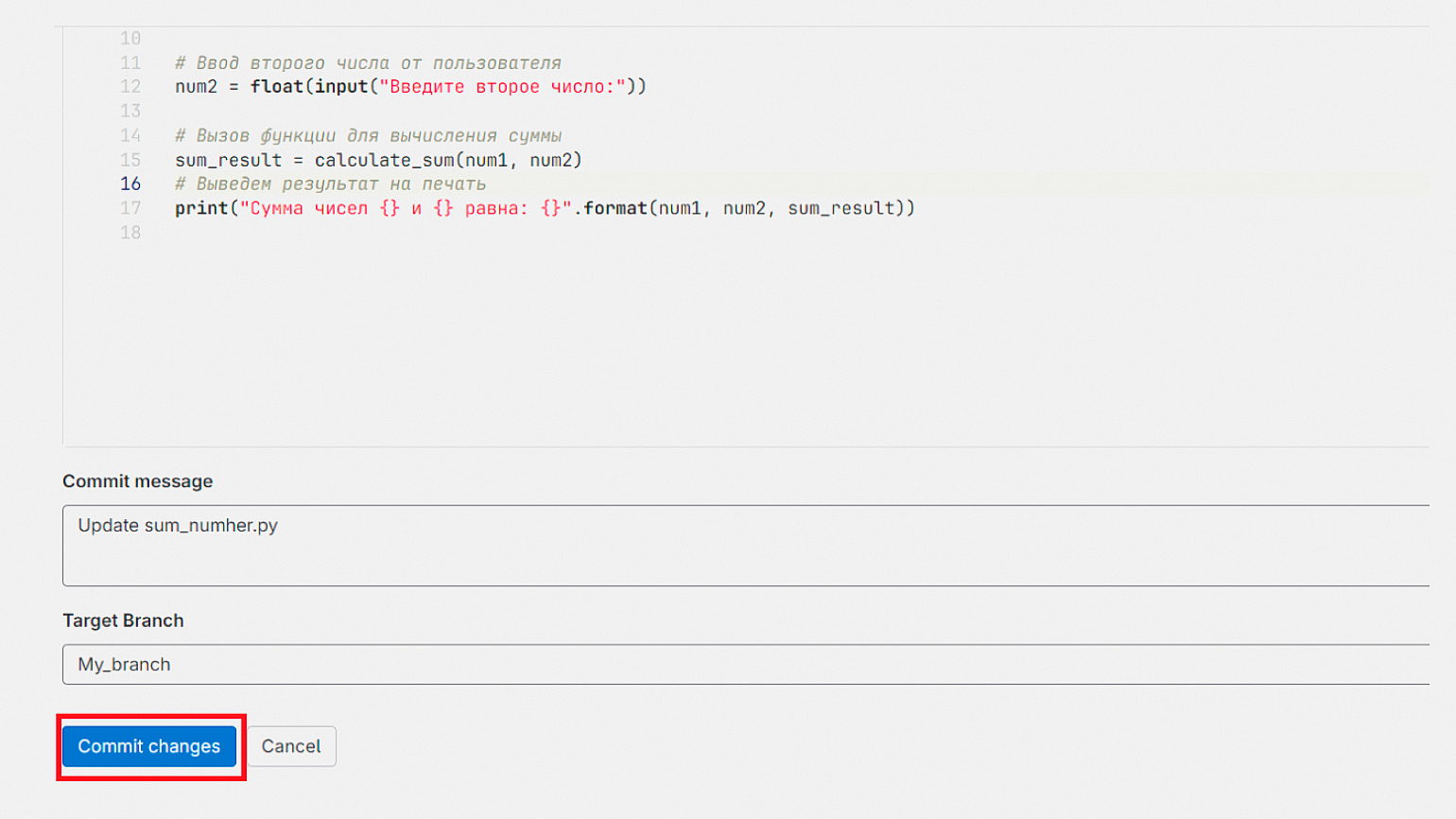
А затем нажмите на кнопку Create merge request, создав запрос на слияние.
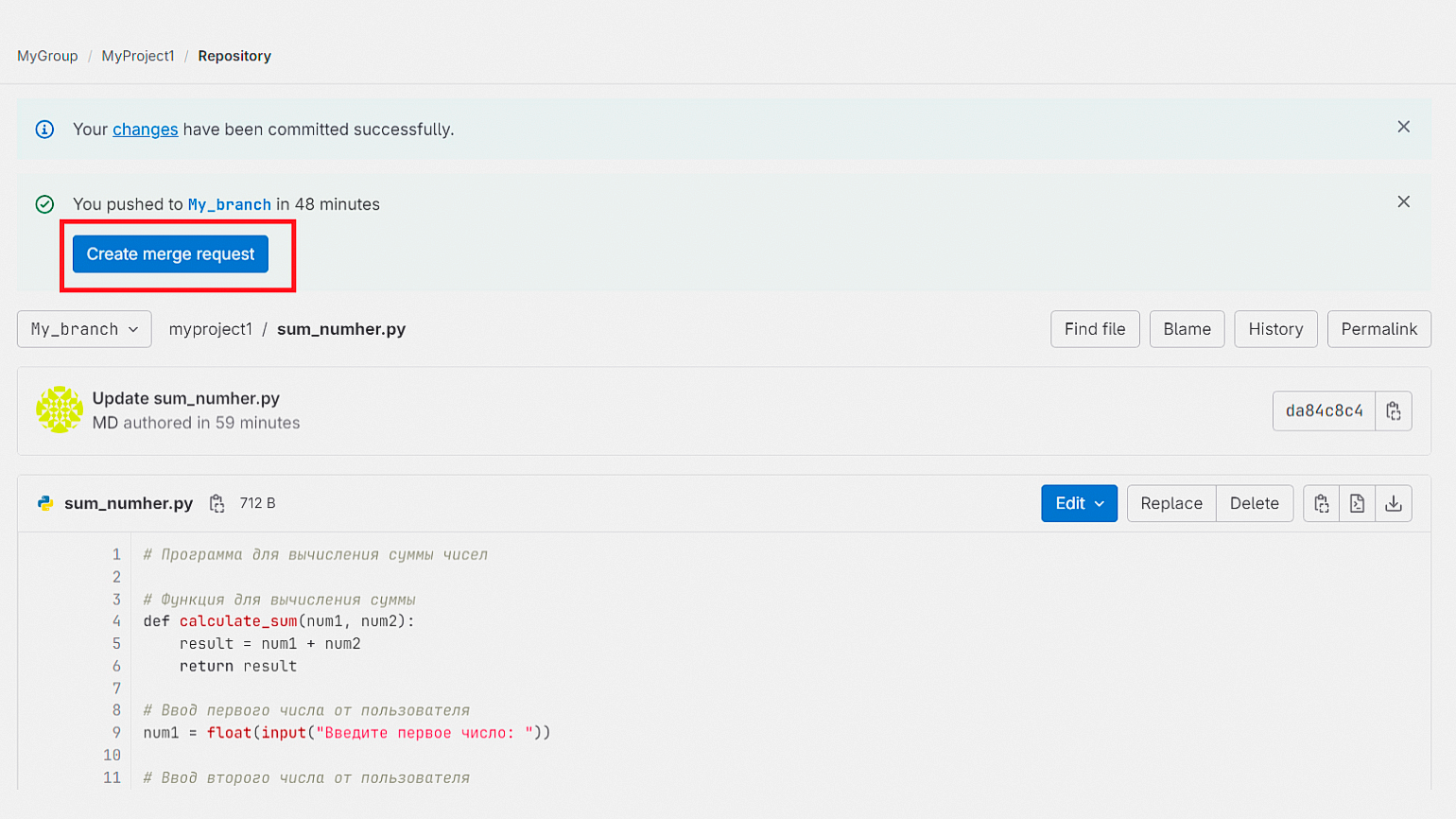
На открывшейся странице введите название слияния, опишите его, указав, что именно вы изменили, и выберите ответственных за проверку. Теперь нажмите на кнопку Create merge request внизу страницы.
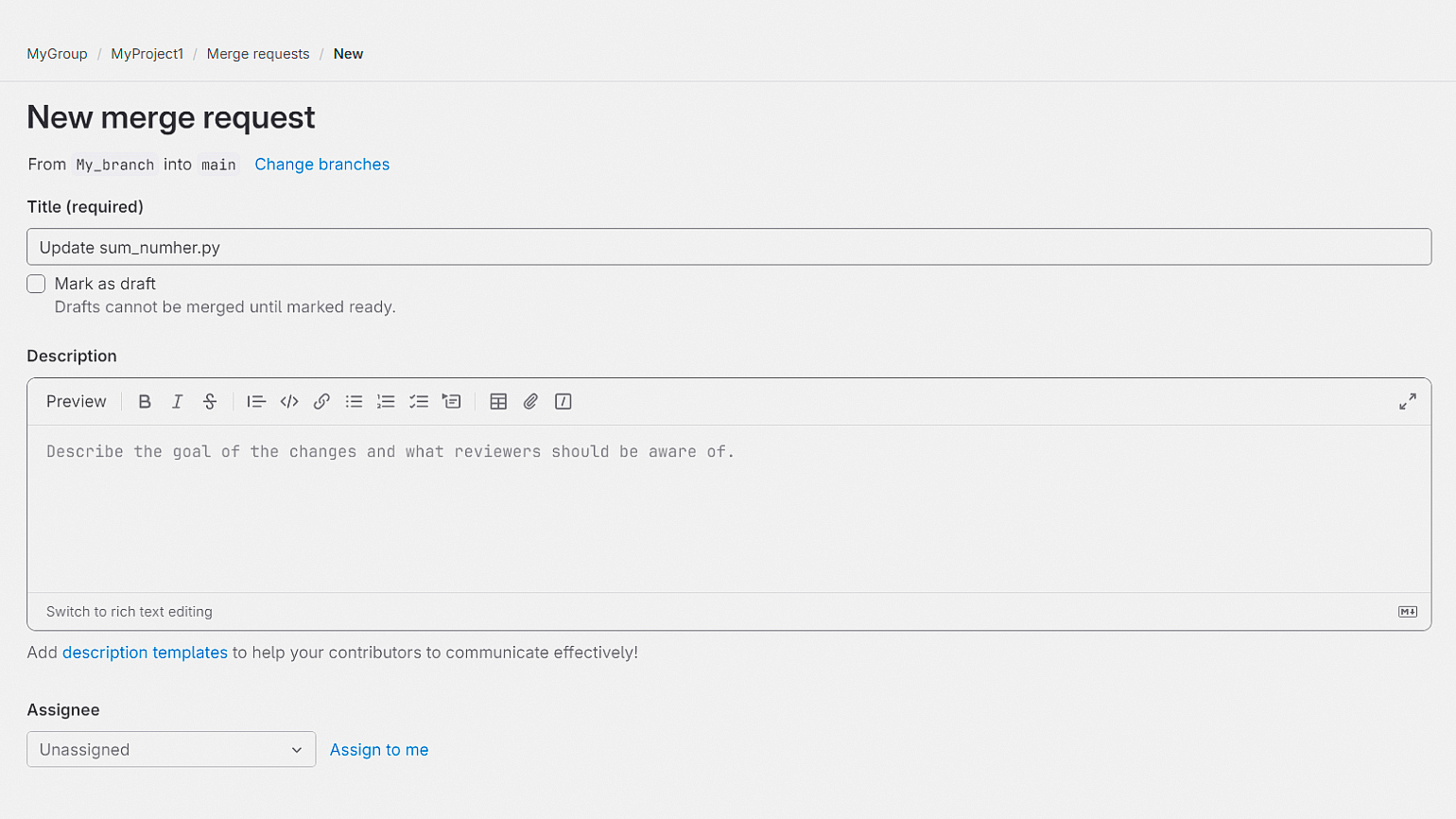
Чтобы принять изменения на следующей странице, нажмите кнопки Approve и Merge:
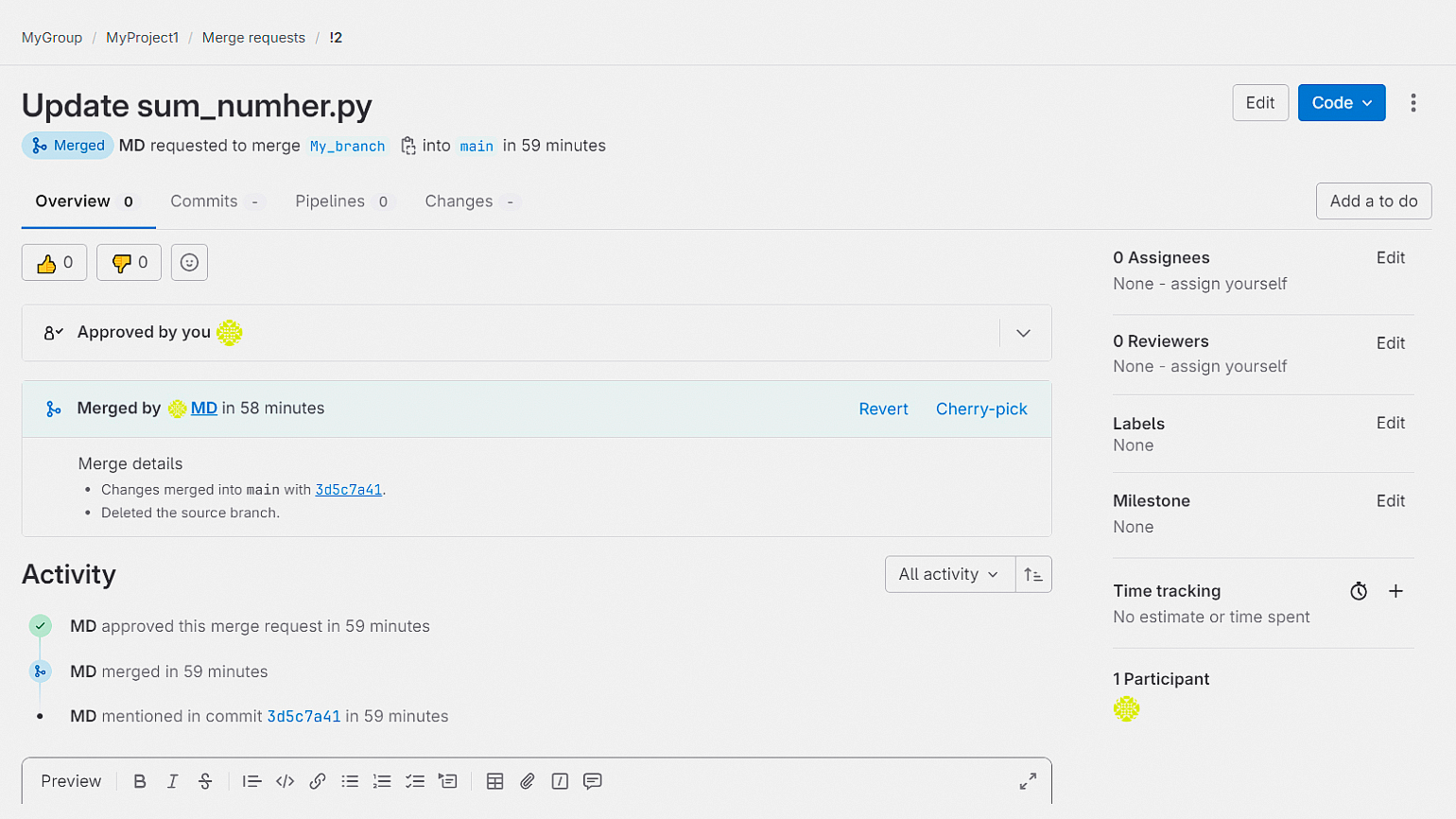
На практике согласовывать и производить слияние, скорее всего, будет кто-то другой, например ваш тимлид.
Когда слияние веток будет выполнено, информация о нём появится в описании:
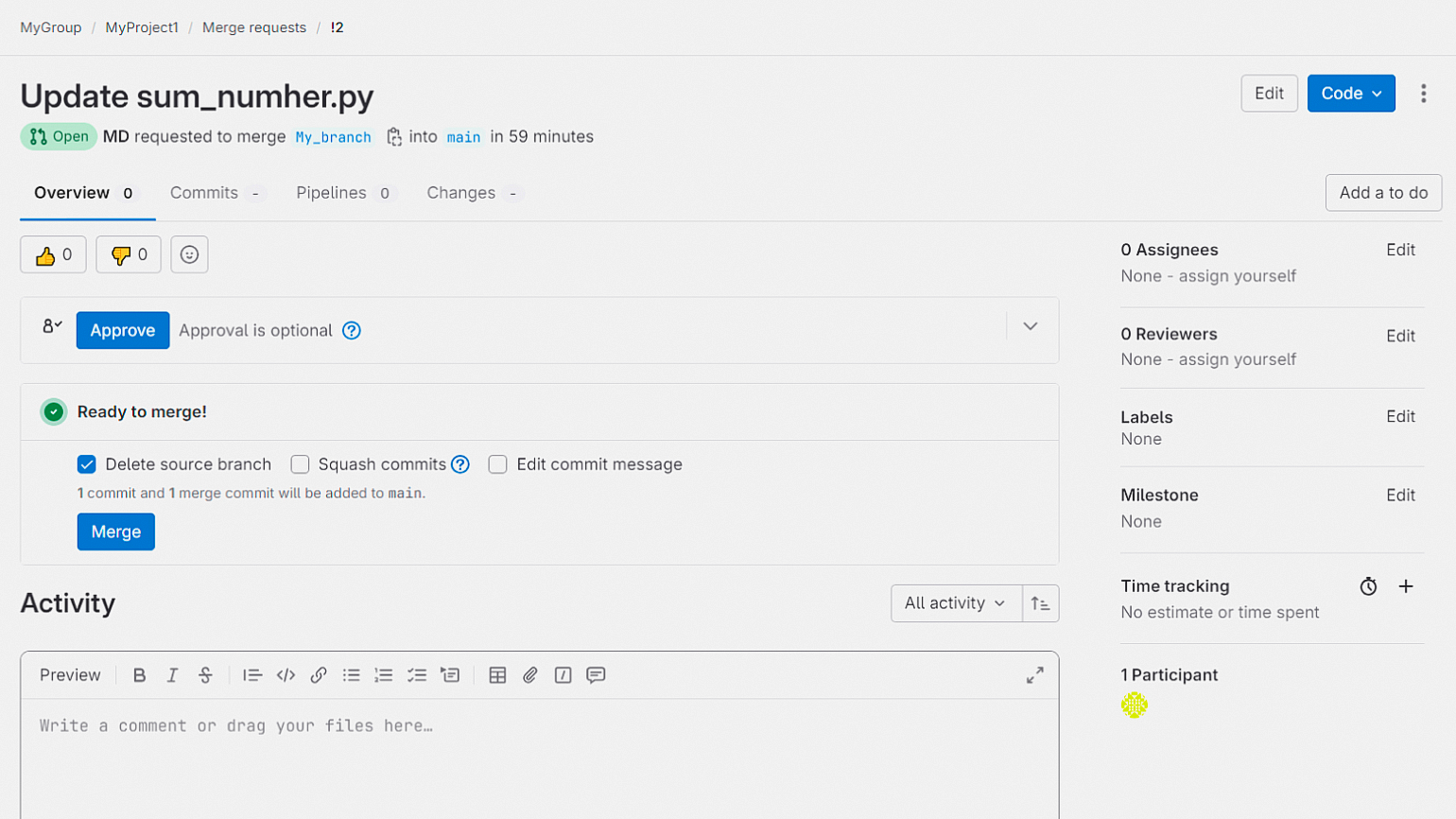
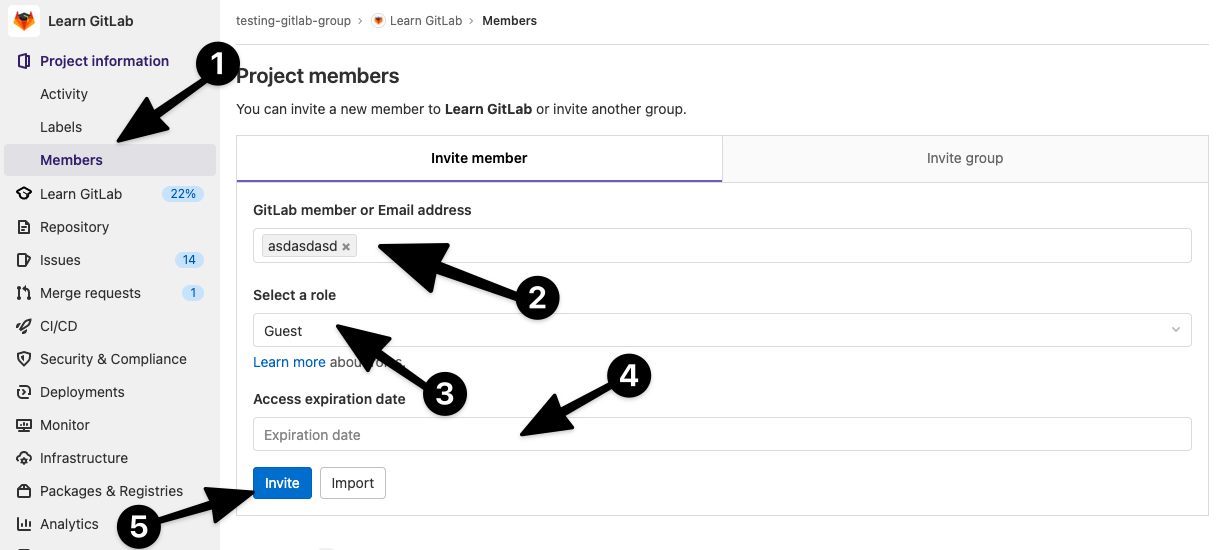
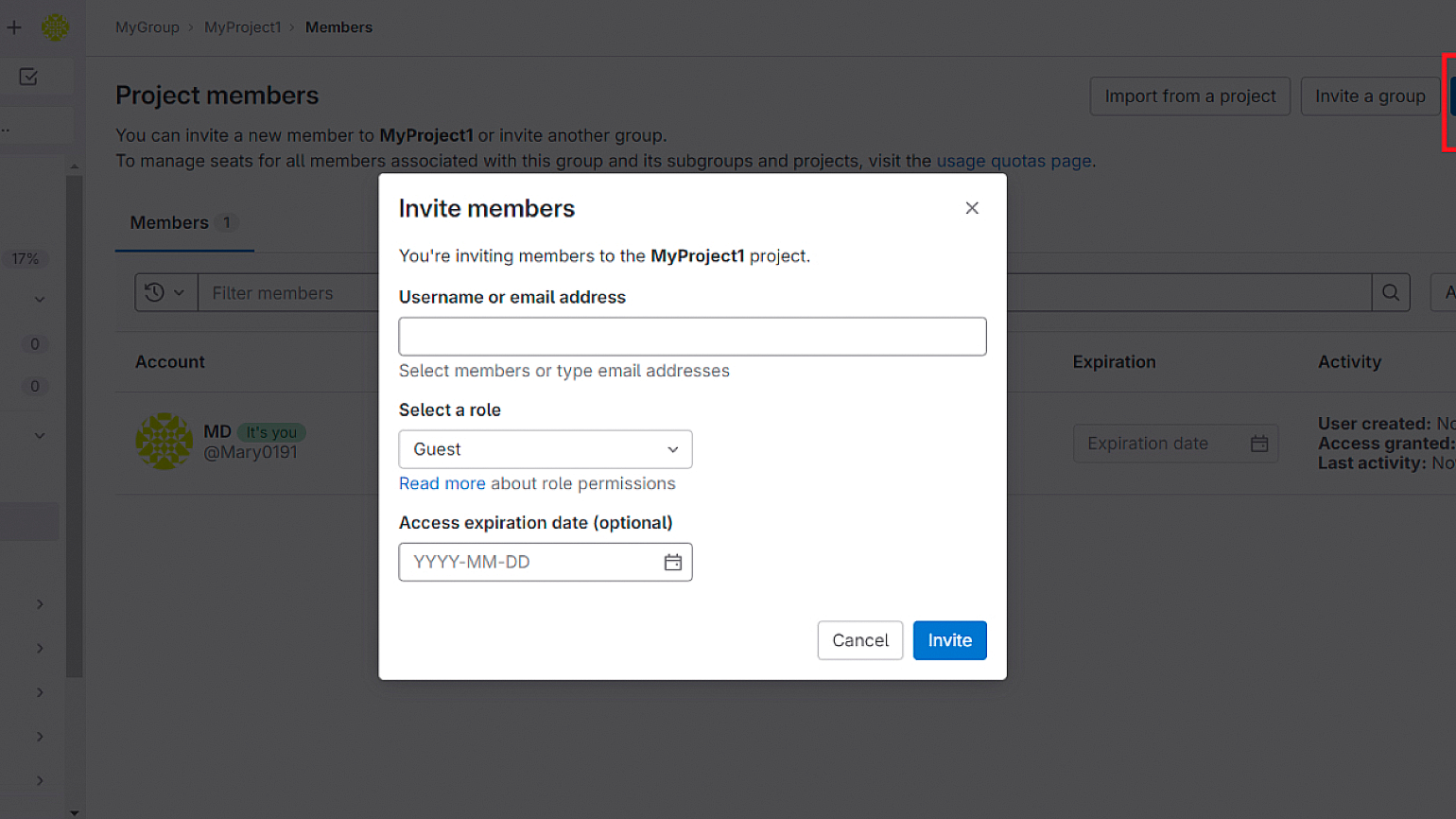
Вы можете добавлять к своему проекту участников с разными уровнями доступа. Для этого выберите на панели слева пункт Members.
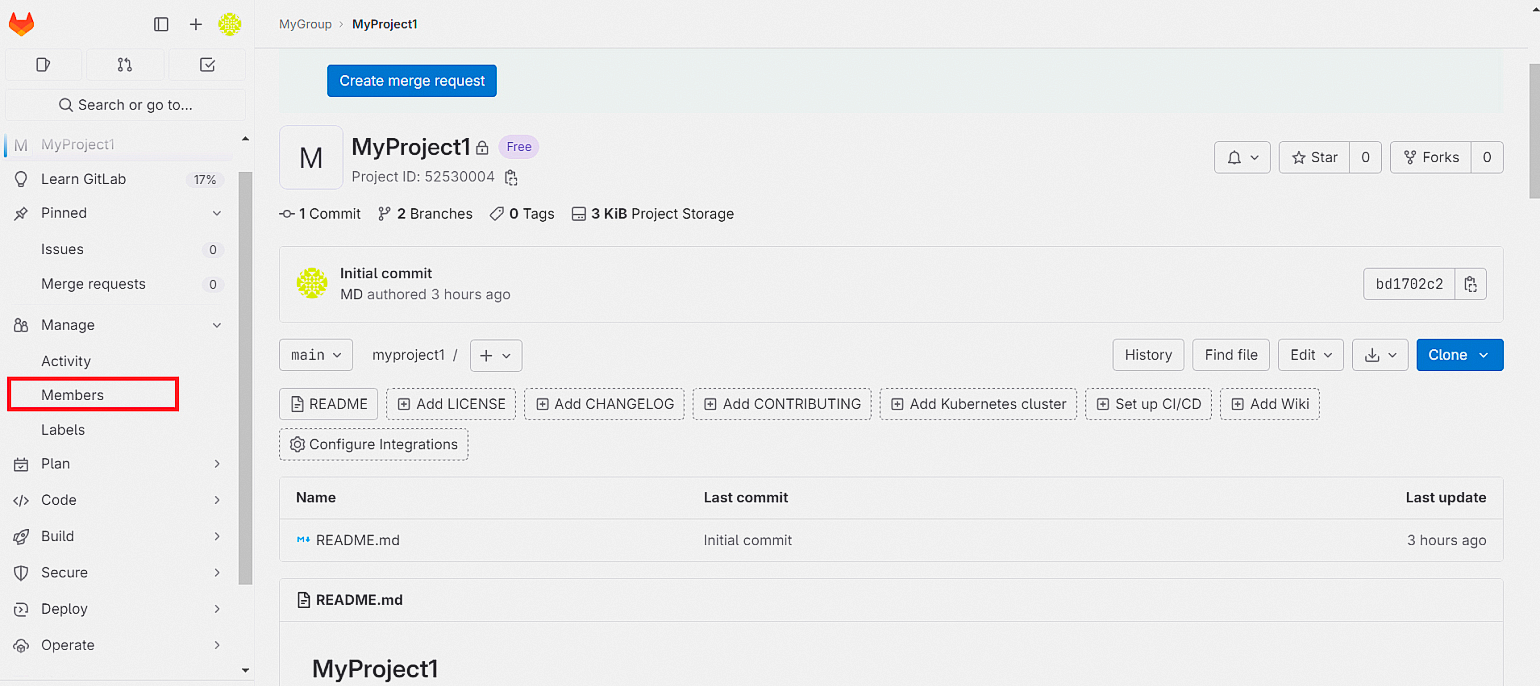
В новом окне нажмите Invite members, введите никнейм или адрес электронной почты пользователя, выберите для него роль и нажмите кнопку Invite.
Большую часть времени вы будете писать код локально, в любимом редакторе или IDE, а не в панели GitLab. Для этого нужно будет клонировать репозиторий — после завершения работы его также можно будет слить с основным репозиторием.
Как работать локально:
- Скопируйте URL репозитория. На своём компьютере откройте командную строку или терминал и выполните команду git clone <URL репозитория> для загрузки репозитория на локальную машину.
- В созданном клоне репозитория вносите изменения в файлы проекта или добавляйте новые.
- После завершения работы с кодом откройте командную строку или терминал в папке вашего проекта. Выполните команду git add ., чтобы добавить все изменения в стейдж. Стейдж (staging area) в Git — это место, где собираются изменения перед коммитом. Если вы хотите добавить только конкретные файлы, используйте команду git add <имя_файла>.
- Чтобы посмотреть, какие файлы находятся в стейдже и какие изменения готовы к коммиту, используйте команду git status.
- Для создания коммита наберите команду git commit -m «Ваш комментарий к изменениям». В кавычках можете написать короткий комментарий, например: «Добавлены новые функции» или «Исправлены ошибки».
- Чтобы отправить коммит на сервер, используйте команду git push.
Удалить проект в GitLab может администратор проекта или пользователь с соответствующими правами доступа.
Войдите в GitLab и перейдите в проект, который хотите удалить. Откройте раздел Settings и выберите General. Прокрутите страницу вниз до раздела Advanced и откройте его. Внизу вы увидите кнопку Delete project. Нажмите на неё и подтвердите, что вы действительно хотите удалить проект.
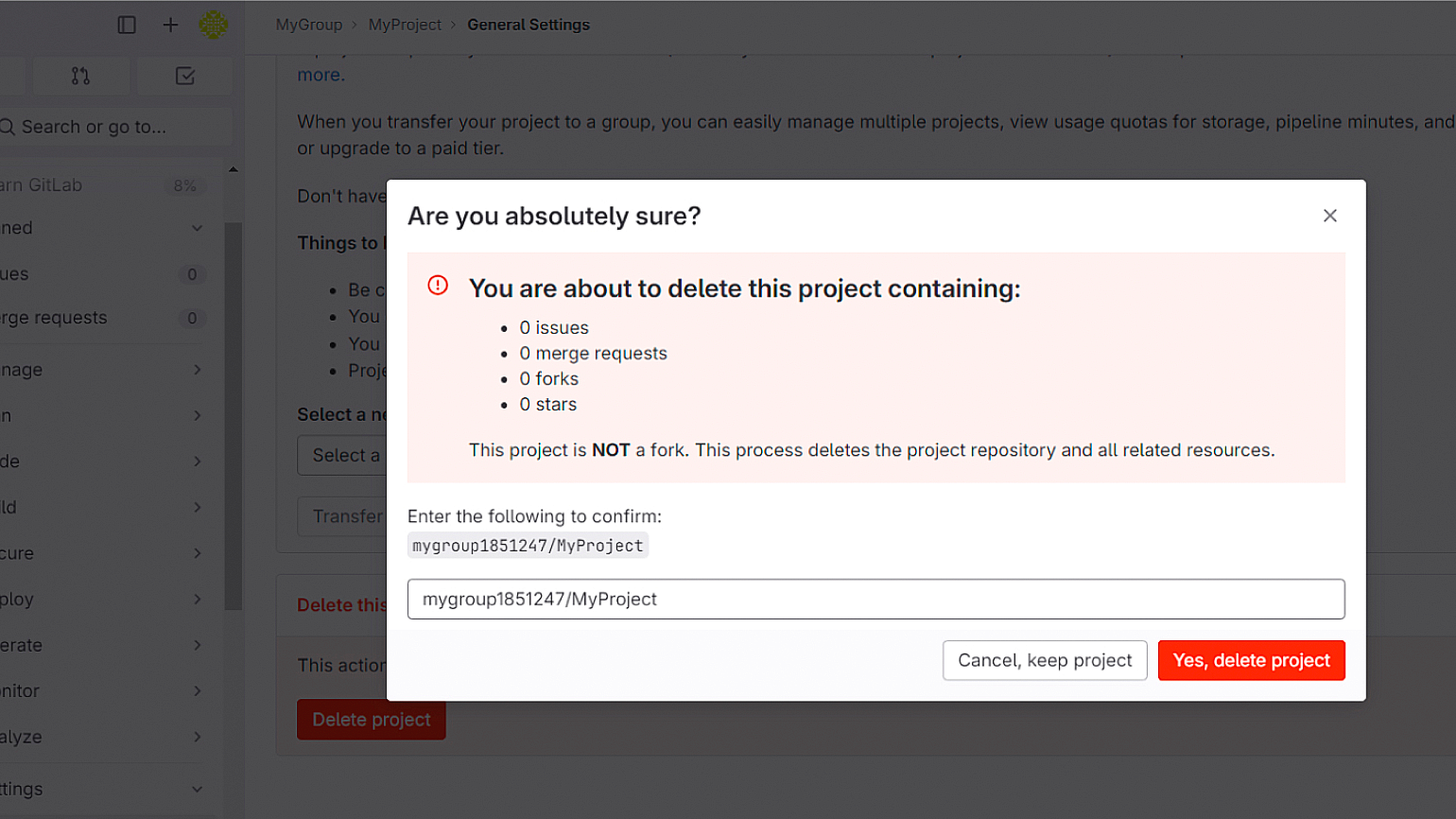
Всё. Проект безвозвратно удалён.
Пробежимся по тому, что узнали сегодня:
- GitLab — удобный и полезный инструмент для команд, занимающихся разработкой программного обеспечения. Он позволяет совместно работать над кодом и сохранять его промежуточные версии, к которым можно вернуться при необходимости.
- Разработчики, которые используют GitLab, пишут код в отдельных ветвях или клонах репозитория на своих компьютерах. После дополнения, изменения или удаления кода они создают коммит, содержащий все изменения, которые будут внесены в основной репозиторий. Сеньор или тимлид проверяют их и принимают или отправляют на доработку.
- GitLab включает в себя встроенные средства continuous integration (CI) и continuous deployment (CD), которые автоматизируют процессы тестирования, сборки приложения и развёртывания.
- GitLab отличается от GitHub встроенным инструментом для CI/CD, возможностью развёртывания сервиса на собственном сервере и отсутствием ограничений на число групп пользователей с разным уровнем доступа.

Научитесь: Профессия Специалист по кибербезопасности
Узнать больше
If you’re new to GitLab, get started learning about how GitLab works.
| Get started with Git Learn Git basics. |
Get started with GitLab Duo Use AI as part of your workflow. |
Get started organizing work with projects Use projects as a starting point. |
| Get started planning work Organize your backlog. |
Get started managing code Use merge requests to iterate on code. |
Get started with GitLab CI/CD Build your application. |
| Get started securing your application Secure your application. |
Get started deploying and releasing your application Get your app out to customers. |
Get started managing your infrastructure Manage your infrastructure. |
| Get started with monitoring your application in GitLab Monitor performance. |
Get started extending GitLab Work with the API or integrate with third-party applications. |
Docs
Edit this page
to fix an error or add an improvement in a merge request.
Create an issue to suggest an improvement to this page.
Product
Create an issue if there’s something you don’t like about this feature.
Propose functionality by submitting a feature request.
Feature availability and product trials
View pricing to see all GitLab tiers and features, or to upgrade.
Try GitLab for free with access to all features for 30 days.
Get help
If you didn’t find what you were looking for,
search the docs.
If you want help with something specific and could use community support, post on the GitLab forum.
For problems setting up or using this feature (depending on your GitLab subscription).
Request support
Сегодня поговорим об азах взаимодействия с одной из самых популярных git-систем.
Что такое GitLab
Сейчас почти никто не пишет код в одиночку. Команды инженеров и разработчиков растут, как на дрожжах. Работая в группах, программисты используют системы управления исходным кодом на базе git, специального инструмента, позволяющего хранить данные разрабатываемого проекта в сети и совместно редактировать его с учетом определенных правил и методик взаимодействия. Самый известный подобный сервис – GitHub. А GitLab – это его собрат, выполняющий те же функции, но устроенный несколько иначе.
GitLab позволяет управлять репозиториями с кодом, отслеживать ошибки в разрабатываемых программах, публиковать код и тестировать его. Это незаменимый инструмент для каждого, кто программирует не в одиночку.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Разница между GitLab и GitHub
Оба сервиса – системы управления репозиториями на базе git. Принципиальных отличий между ними нет. GitHub появился раньше и стал чуть ли не синонимом git, поэтому он популярнее и для многих является единственной системой для управления репозиториями.
Но GitLab есть что предложить с точки зрения функциональности, поэтому все чаще наблюдается переход пользователей с GitHub на GitLab. В частности, это касается разработчиков-новичков, которые пока еще не «приросли» к GitHub.
В связи с растущей популярностью GitLab я и решил познакомить вас с этим сервисом поближе.
Инструкция по использованию GitLab
Перед началом работы с сервисом, нужно создать учетную запись. Процедура эта весьма тривиальна:
-
Заходим на официальный сайт GitLab.
-
В верхнем левом углу находим кнопку Login и жмем по ней.
-
Через пару секунд перед вам откроется форма входа в систему, а под ней будет ссылка на форму регистрации (Register now). Переходим по ней.
-
Заполняем данные для регистрации (классические данные: адрес электронной почты, пароль, логин и т.п.). Жмем на кнопку Register.
-
В течение пары минут на указанную при регистрации почту «упадет» сообщение со ссылкой для подтверждения создания аккаунта. Переходим по ней.
Учетная запись готова. Теперь можно переходить непосредственно к знакомству с GitLab.
Как создать проект
Проектом в GitLab считается глобальное рабочее пространство, в котором будет размещен репозиторий с файлами ваших сайтов и приложений. А также в нем можно взаимодействовать с коллегами и использовать другие возможности сервиса.
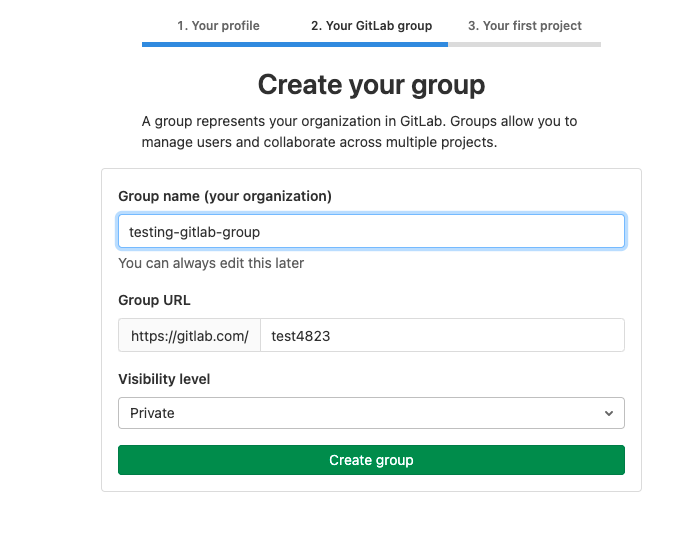
Поэтому при первом входе под своей учетной записью GitLab попросит вас указать род деятельности, наличие или отсутствие команды, имя рабочей группы и название проекта.
После формирования проекта можно переходить непосредственно к созданию репозиториев, загрузке программ в GitLab и т.п.
Как создать репозиторий
Чтобы воспользоваться репозиторием, нужно создать новый проект:
-
Кликаем по иконке со значком + в панели управления.
-
Выбираем пункт New project/repository.
-
Затем кликаем по Create blank project.
-
Указываем его имя и другие запрашиваемые параметры (можно указать, публичным будет репо или приватным) и нажимаем на кнопку Create Project.
Вместе с проектом сформируется новый git-репозиторий. Теперь можно с ним взаимодействовать, то есть загружать файлы, делать коммиты, создавать различные ветки для разработки продукта и мерджить их при необходимости.
Как загрузить файлы сайта/приложения в GitLab
Тут есть 3 пути.
Первый – используем веб-интерфейс GitLab
-
На главной странице проекта ищем строку The repository for this project is empty, а под ней кнопку Upload File и нажимаем на нее.
-
GitLab предложит выбрать файлы проекта для загрузки и последующей работы с ними. Выбираем все файлы, что используем при разработке и выгружаем.
Также можно использовать WebIDE, встроенную в GitLab, чтобы прямо в браузере писать код и создавать файлы для своего приложения/сайта.
Второй – используем командную строку
Тут все сложнее, но на самом GitLab опубликована короткая и доходчивая инструкция по подключению к сервису через командную строку, используя классический git-клиент.

Третий – используем сторонний git-клиент
Существуют приложения в духе Tower и Sublime Merge, позволяющие управлять репозиториями, делать коммиты и пушить изменения в проекты при помощи удобного графического интерфейса. Можно подключиться к GitLab с помощью одной из таких программ.
Как добавить SSH-ключ для подключения к репозиторию
SSH-ключи можно использовать для авторизации в GitLab и для управления репозиториями по протоколу Secure Shell. Чтобы это сделать:
-
Генерируем ключ с помощью команды ssh-keygen (вводим ее в терминал).
-
Генератор предложит сохранить получившийся ключ. Менять директорию, куда сохраняется ключ, необязательно.
-
Затем утилита попросит ввести пароль. Его тоже можно не вводить. Просто жмем на Enter.
-
В указанной на втором этапе папке появится файл с ключом в формате .pub. В нем лежит ключ. Нужно скопировать его.
-
Возвращаемся на сайте GitLab. Открываем раздел SSH-keys, вставляем ключ в специально отведенное для этого поле и нажимаем на кнопку Add key.
Как работать с ветками
Ветки – это инструмент для создания дополнительных вариаций приложения/сайта, которые позволяют вести разработку новых функций, не затрагивая при этом основное приложение, доступное для пользователей.
По умолчанию в GitLab доступна только одна ветка – master. Но ее чаще используют не для разработки, а для публикации готовых сборок проекта, которые нестрашно превратить в релиз для масс.
Поэтому принято создавать новые ветки для разработки дополнительных функций, а уже потом объединять их с основной.
Как создавать ветки
Ветки – не уникальная для GitLab функция. Это часть git, поэтому, как и в случае с репозиториями, тут можно пойти тремя путями:
-
На сайте GitLab в окне управления репозиторием нажать на кнопку + справа от названия ветки, а потом выбрать пункт New branch в выпадающем меню.
-
Можно создать новую ветку через git-клиент в терминале с помощью команды git checkout -b [название новой ветки].
-
Или воспользоваться аналогичной функций в используем графическом git-клиенте (Tower, Sublime Merge, GitFox и т.п.).
Любой из способов позволит создавать новую ветку, в которую после этого можно будет отправлять коммиты и делать пуши.
Мерджинг веток
Мерджинг (или объединение) веток – это механизм слияния двух наборов функций одной программы, позволяющий переносить функции из дополнительных веток в основную ветку разработки, где лежит приложение. Результат увидят еще и пользователи, а не только разработчики.
Запрос на объединение веток будет появляться на сайте GitLab каждый раз, когда вы будете вносить изменения в код одной или нескольких веток.
Выглядит это следующим образом:
-
На сайте появляется большая синяя кнопка Create merge request. Кликаем по ней.
-
Затем рассказываем о своем запросе (поясняем, для чего он делается).
-
Указываем автор запроса в поле Assignee.
-
Указываем человека, который будет проверять запрос в поле Reviewer.
-
Потом указываем Milestone (если используете их).
-
Ставим теги.
-
И нажимаем на Create merge request.
-
Если с запросом все ок, то проверяющий нажмет на кнопку Merge, и весь код перекочует в основную ветку проекта (ну или ту, которую указал автор запроса).
Как добавлять пользователей в проект
К разработке своего приложения/сайта всегда можно привлечь людей со стороны:
-
Для этого кликаем по кнопке Project information в боковой панели GitLab.
-
Выбираем пункт Members.
-
В графу GitLab member or Email address вписываем ник GitLab-пользователя или его email-адрес.
-
Выбираем для него роль (гость, наблюдатель, разработчик).
-
Также указываем время действия приглашения (в указанный день приглашенный будет исключен из проекта).
-
А потом кликаем на Invite.
Если выбранный человек согласится присоединиться, то ваша команда расширится.
Как создавать баг-репорты
В git-системах есть инструменты, помогающие оповещать разработчиков об ошибках и обсуждать их как с пользователями, так и с коллегами.
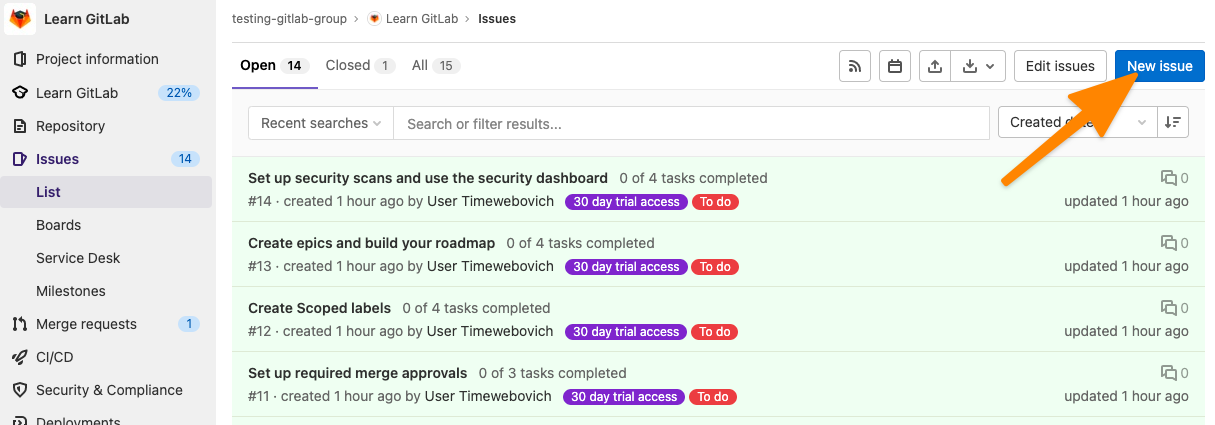
Речь идет о разделе Issues. Если возникла проблема, то нужно сообщить о ней тут. Для этого:
-
Открываем раздел Issues в боковой панели управления.
-
Затем нажимаем на кнопку New issue.
-
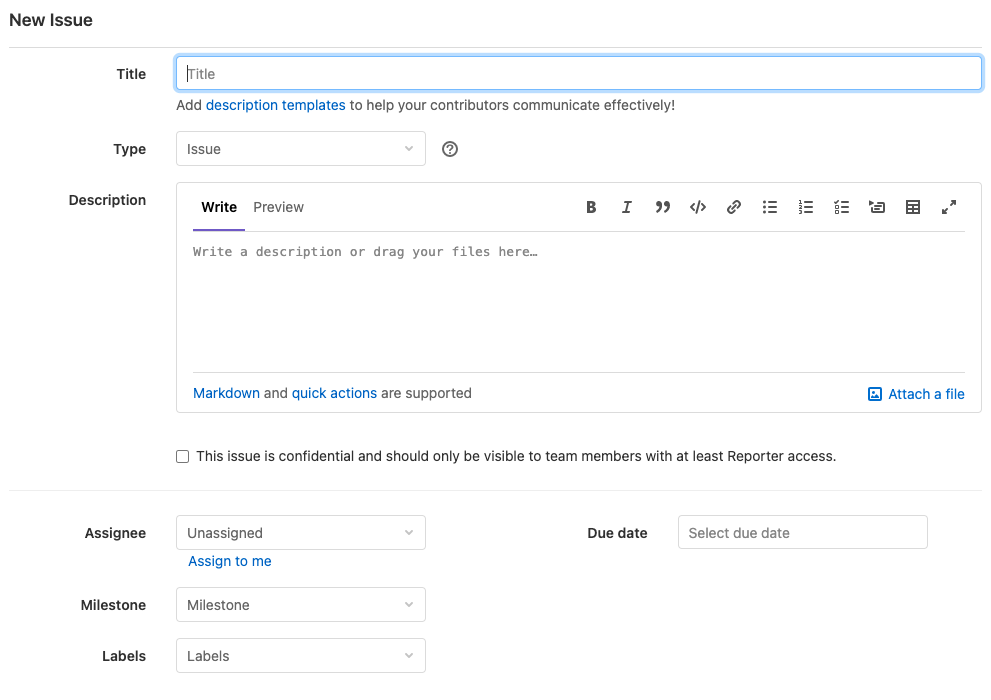
Даем имя обнаруженной проблеме, а затем подробно описываем ее в разделе Description.
-
Затем назначаем ответственного в пункте Assignee и срок, в течение которого нужно найти решение найденной проблемы.
-
А потом нажимаем на кнопку Create issue.
Как удалить проект
-
Открываем настройки проекта и переходим во вкладку General.
-
Листаем ее до пункта Advanced и справа от него ищем кнопку Expand, которая откроет доступ к дополнительным параметрам.
-
Вновь пролистываем появившееся меню до упора вниз, пока не наткнемся на кнопку Delete project.
-
Нажимаем на нее и вписываем название проекта, чтобы его удалить.
Вместо заключения
На этом все. Я рассмотрел базовые возможности GitLab и намеренно не затрагивал аналитические инструменты, интеграцию с Kubernetes и дополнительные функции, пытаясь сконцентрироваться на важнейших концептах GitLab и git. Это то, что вам необходимо для старта, независимо от того, пользовались вы ранее другими системами управлениями репозиториями или нет.
Last Updated :
16 Sep, 2024
GitLab is a popular DevOps platform that provides a robust solution for source code management, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD), and other development workflows. While GitLab is typically hosted on Linux servers, it can also be installed on Windows using a virtual machine or Docker.
In this article, we will walk you through the steps to install GitLab on Windows using Docker, which provides a manageable and efficient way to run GitLab without needing to configure a full Linux environment.
Prerequisites
Before installing GitLab on Windows, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, or Education: Required for Docker Desktop.
- Docker Desktop: A platform that allows you to run Docker containers on Windows.
- Sufficient System Resources: At least 4 CPU cores and 4GB of RAM for GitLab to run smoothly. Higher specifications are recommended for production environments.
Installing Docker on Windows
To run GitLab on Windows, you’ll need to install Docker Desktop, which enables running containers on Windows systems.
Step 1: Download Docker Desktop
Go to the Docker Desktop website and download the installer for Windows.
Step 2: Install Docker Desktop
- Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
- When prompted, enable the option for Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL 2) for better performance.
Step 3: Start Docker Desktop
- Once installed, launch Docker Desktop and ensure it is running. You should see the Docker icon in the system tray.
Step 4: Verify Docker Installation
Open Command Prompt or PowerShell and type:
docker --version
You should see the version of Docker installed, confirming that Docker is set up correctly.
Downloading and Running GitLab Using Docker
With Docker installed, you can now download and run GitLab using Docker containers.
Step 1: Pull the GitLab Docker Image
Open PowerShell or Command Prompt and pull the GitLab image from Docker Hub:
docker pull gitlab/gitlab-ee:latest
This command pulls the latest version of GitLab Enterprise Edition. If you prefer the Community Edition, use gitlab/gitlab-ce:latest.
Step 2: Run GitLab in a Docker Container
Create a new directory on your Windows system to store GitLab configuration and data. This ensures data persists even if the container is removed:
mkdir C:\gitlab\data
mkdir C:\gitlab\logs
mkdir C:\gitlab\config
Step 3: Start the GitLab container:
docker run --detach `
--hostname gitlab.local `
--publish 443:443 --publish 80:80 --publish 22:22 `
--name gitlab `
--restart always `
--volume C:\gitlab\config:/etc/gitlab `
--volume C:\gitlab\logs:/var/log/gitlab `
--volume C:\gitlab\data:/var/opt/gitlab `
gitlab/gitlab-ee:latest
Options:
- —hostname: Sets the hostname for GitLab (e.g., gitlab.local).
- —publish: Maps ports from the container to the host (HTTP, HTTPS, and SSH).
- —name: Names the container gitlab.
- —restart always: Ensures GitLab restarts automatically if the container stops or the host reboots.
- —volume: Maps local directories to container directories for persistent storage.
Step 3: Wait for GitLab to Initialize:
It may take several minutes for GitLab to initialize. You can monitor the process using:
docker logs -f gitlab
Wait until you see the message indicating that GitLab is ready.
Configuring GitLab
After GitLab starts, you can configure it through the GitLab interface:
Step 1: Access GitLab
- Open a web browser and navigate to http://localhost.
- You should see the GitLab login screen.
Step 2: Set Up the Root Password
The first time you access GitLab, you’ll be prompted to set the root password. Enter a secure password and save it.
Step 3: Log In:
Log in using the username root and the password you just set.
Step 4: Configure GitLab Settings
Navigate to the Admin area to configure GitLab settings, such as email notifications, user management, and project settings.
Accessing GitLab
To access GitLab, simply navigate to the hostname you set during the Docker run command (e.g., http://localhost if using the default setup). If you mapped the ports differently or used a different hostname, adjust the URL accordingly.
Setting Up GitLab Runner (Optional)
GitLab Runner is a tool used for running CI/CD jobs on your GitLab instance. Installing GitLab Runner on Windows allows you to leverage GitLab’s powerful CI/CD pipelines.
Step 1: Download GitLab Runner
Visit the GitLab Runner downloads page and download the binary for Windows.
Step 2: Install GitLab Runner:
- Extract the binary to a directory, for example, C:\GitLab-Runner.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator and register the runner:
C:\GitLab-Runner\gitlab-runner.exe register
- Follow the prompts to configure the runner with your GitLab instance, including:
- GitLab URL.
- Registration token (found in GitLab’s Admin area under Runners).
- Runner description, tags, and executor type (use shell for simplicity on Windows).
Step 3: Start the Runner
Install and start GitLab Runner as a service:
C:\GitLab-Runner\gitlab-runner.exe install
C:\GitLab-Runner\gitlab-runner.exe start
In the last article, we saw the various parts of GitLab, its architecture and how GitLab works. If you haven’t already, I suggest reading the previous article first before reading this one. Here is the link
GitLab, A Complete Beginner’s Guide!
In this article lets look at how to set it up locally on your Windows PC, so that you can have your very own GitLab setup running right at your home or organization!
If you are using Mac or Linux, you can follow the links below.
Complete Guide To Setting Up GitLab Locally On Mac.
Complete Guide To Setting Up GitLab Locally On Linux PC..!!
So let’s begin!
Things you will need
All you need are a computer running Windows OS with enough resources (CPU, memory, and disk space) for running the GitLab Server and GitLab Runner. How much resources is enough depends on how much performance you need, the more you have the better it is!
You can also set it up on the cloud over at Gitlab.com, but
- the free plans have some limitations in terms of processing power and hard disk space.
- Also doing it locally gives you more control over the setup and
- it will also be an opportunity to learn you more about GitLab
Hence I suggest taking this route of a local installation.
If you are part of a larger organization, and you wish to install it on the cloud, then you can always take a look at the paid plans of GitLab here link
Approach to install GitLab on Windows
Okay, let’s get back to the task in hand.
As we saw in the previous article GitLab consists of 2 parts.
- GitLab Server and
- GitLab Runner
Also, we have learned in the previous article that it is preferable to set the GitLab server and runners on separate computers. But I am going for a home set up, so I will be setting them both upon the same Windows computer.
The GitLab Server relies heavily on Linux technologies and hence it cannot be installed in our Windows PC natively. If you do some research, there are ways you can do it through the Linux subsystem in windows, but we are not going to take that approach.
The
problem with these workarounds are
- The installation process is a bit complicated and is not recommended for beginners.
- They are only guaranteed to work on a version to version basis. What I mean by that is you need to have a particular version of Windows and a particular version of GitLab for everything to run smoothly. If you update your Windows or if you wish to upgrade your GitLab then you might break your GtiLab set up. Since both Windows and GitLab updates come frequently, it is not such a good idea to waste time trying to fix things every few months.
- It is unofficial and hence support for future versions cannot be guaranteed.
- These unofficial methods will bring their own limitations as opposed to running natively on Linux
Due to these above reasons, we are going to go for a more stable approach of installing the GitLab server in a virtual environment. We will also see in this article the ways to make it run as smoothly and efficiently as possible while making sure it consumes as few resources as possible.
So this
is what we are going to do
- Install the GitLab Server on a Virtual Box running Ubuntu server
- Install GitLab runner natively on Windows.
This approach takes away the cons of using unofficial hacks, as it will work on all versions of you Windows and GitLab and you don’t need to worry too much while updating your software either!
By following the step by step guide shown below you should be able to set everything up and running in an hour or 2 (depending upon how good your internet connection is, it can take longer!)
GitLab Installation Process
STEP#1: Download and install VirtualBox
You can download and install VirtualBox from this link
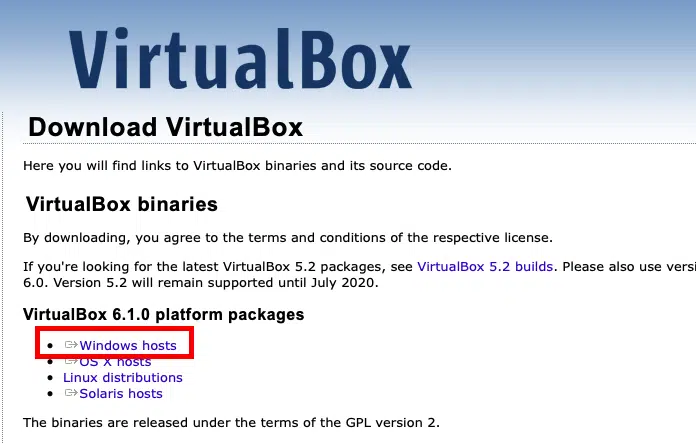
Just click on the Windows hosts and the download should start automatically. The installation process is pretty straightforward, you can just accept the default options and click through to complete the process.
Once the installation is completed you can open VirtualBox from the Start menu in Windows.
STEP#2: Install Ubuntu Server as a Virtual Machine in your Windows PC.
The next step is to get a Linux distro to install our GitLab server. For this purpose, I recommend Ubuntu Server. I chose this particular distro for 2 reasons.
- Ubuntu is known for its stability.
- GitLab Server software has support for Ubuntu
- The server edition is chosen so that it will consume fewer resources on your computer.
For this first, you need the Ubuntu Server image. You can download it from this link.
Ubuntu usually offers 2 sets of packages for us to choose from.
- Long term support version: Has a support period of 5 years
- Latest Version: has all the latest features.
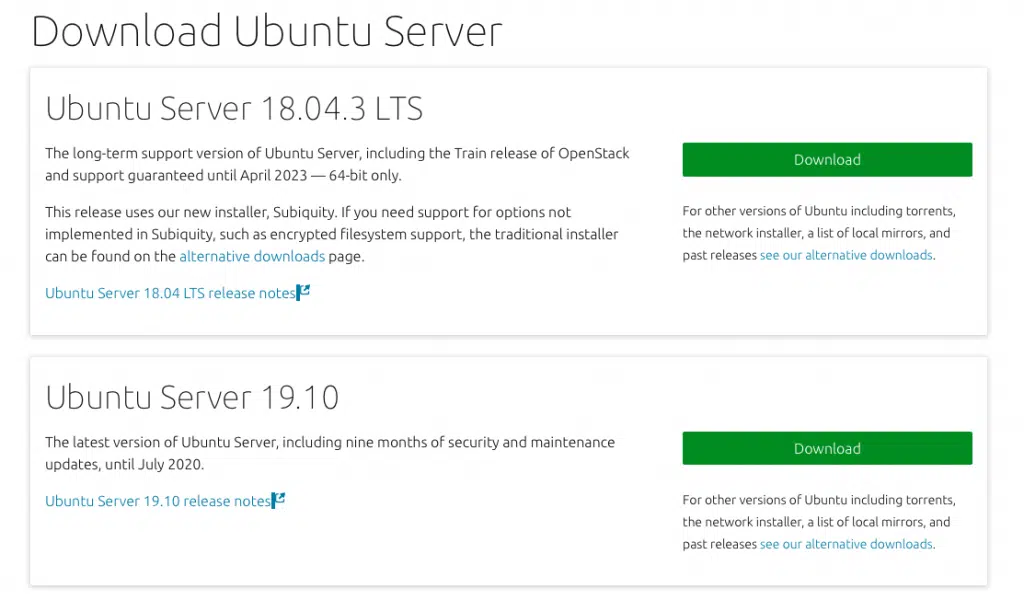
I suggest you go for the LTS one, but then the latest version should also work just fine. So click on a “Download” button and your download should start automatically. It will take some time to complete as the iso is around 900MB.
Once the download is complete you can proceed to the installation process on VirtualBox.
STEP#3: Install Ubuntu Server on VirtualBox
Open VirtualBox Application and click on the “New” button

A window like this should pop up
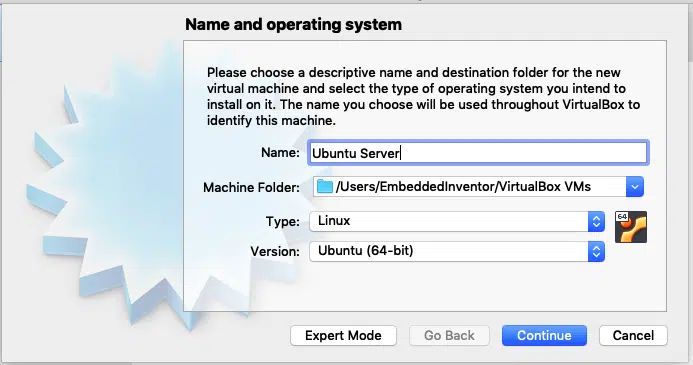
Give your virtual machine a name and choose Linux for type and ubuntu 64 bit for version and click “Continue”.
The next screen usually asks for RAM. GitLab recommends 8GB for a GitLab system with 100 users, I suggest a minimum of 2GB RAM for a home set up, you can give more if you can, just make sure you don’t allot more than 50% of your total available RAM.
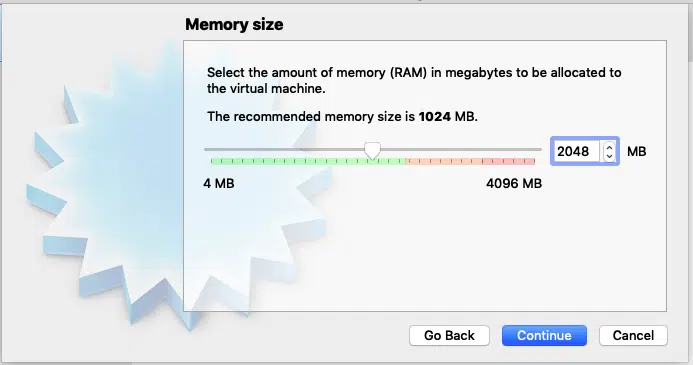
Once you have allocated RAM space, Click “Continue” to the next page.
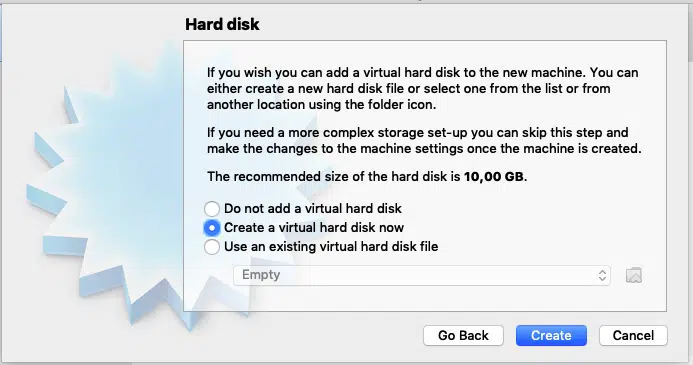
Next, you will be prompted for hard disk. Make sure “Create a virtual hard disk now” is selected and click “Create”
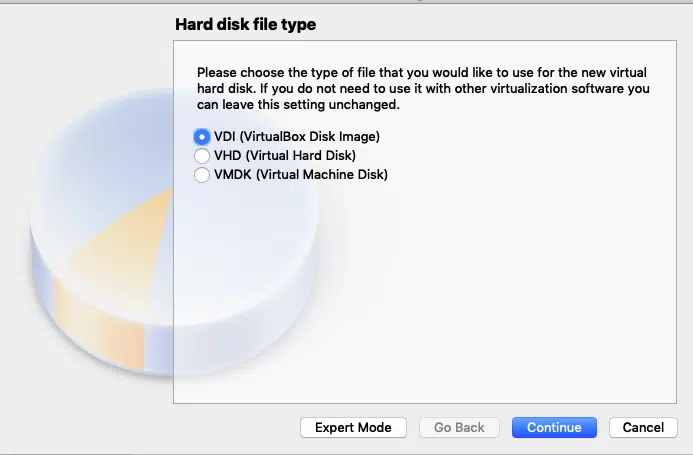
Accept
the default “VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image)” and click
“Continue”
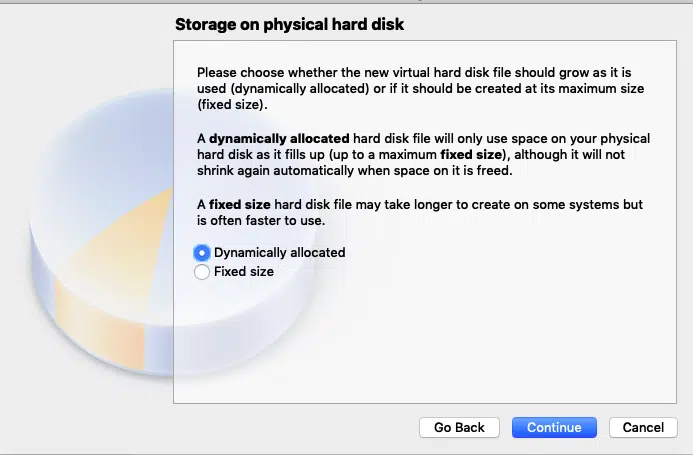
Accept “Dynamically Allocated” and Press continue. This option allocates hard disk space to the virtual machine on the run, so that as you use the more space, more will be allocated.
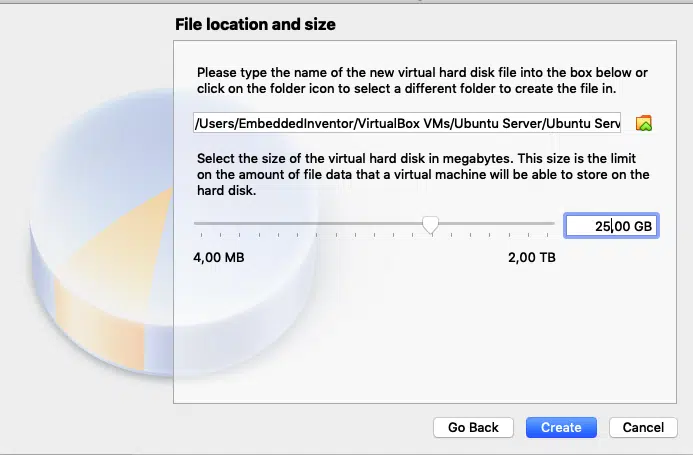
I suggest you allocate at least 25GB of space to the virtual machine, you can allot more if you can. Once you have chosen the disk space click create
Once you have done this, you should be taken back to the main window of VirtualBox and you should see the virtual machine you just created on the left pane of the window as shown in the screenshot below.

Next click on the “Settings”

And click on storage -> empty -> disk icon -> “Choose a disk file”

Select the ubuntu server iso image you have just downloaded and press ok. This is equivalent to inserting the Ubuntu disk in a real machine.

Next, go to settings->Network and choose “Bridged Adapter” in the “Attached to:” drop-down menu and press “OK”
I have explained the reason behind using these network settings in detail in this article, you can go ahead and read that if you are into computer networks.
The short explanation is, we will not be able to access the GitLab server from our other machines on the network unless we choose this option.
That’s it, the configuration is done!
You can now go ahead and click the start button!

Now the installation process will start. Since we have chosen to go with “Ubuntu server” in order to minimize the resource consumption (so that GitLab can take up as many resources as it needs) we don’t get a fancy Graphical UI, like in the desktop version of Ubuntu. You need to navigate the menus during installation only using Keyboard (tab, enter and arrow keys) since the Ubuntu server doesn’t come with mouse support. So go through the process and get it done.
STEP#4: Get the IP address of your ubuntu server
Okay now
once you got the Ubuntu server up and running, you need to find its IP address
and make a note of it.
To do that, use the “ifconfig” command on your Ubuntu server’s terminal

STEP#5: Download and install GitLab server
To download GitLab server, go to the official link on the Gitlab’s Website
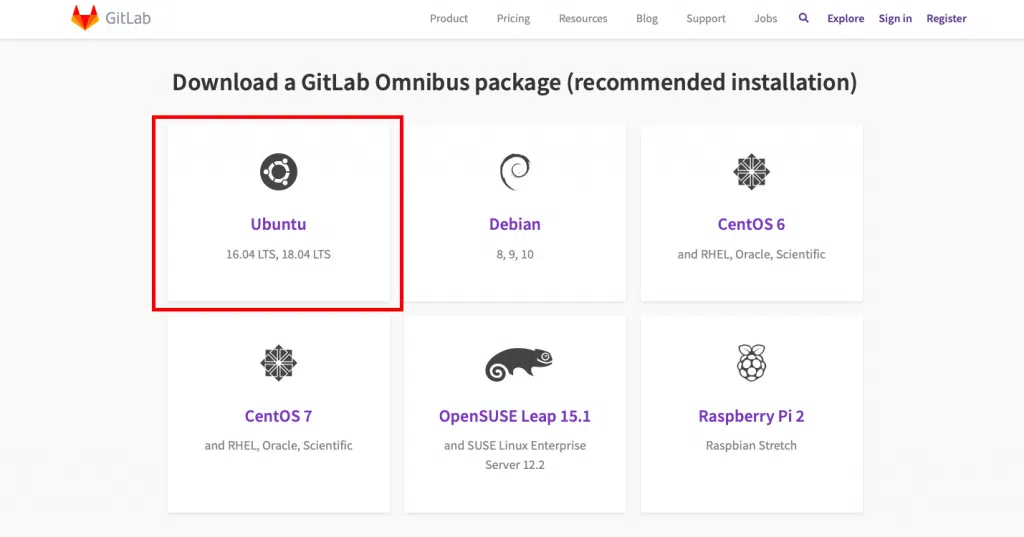
As you can see GitLab official supports several Linux distros, even a Raspberry Pi 2’s Raspbian! We are interested in Ubuntu, so click on the Omnibus Ubuntu Link on as shown in the screenshot above.
Once you click on Ubuntu, the commands you need to enter to install GitLab server will be shown to you.
I am not showing each instruction here since GitLab updates the information presented on their website all the time and that can make this section of the article outdated. Just follow the step by step instructions given in the link to install the GitLab Server on your VM.
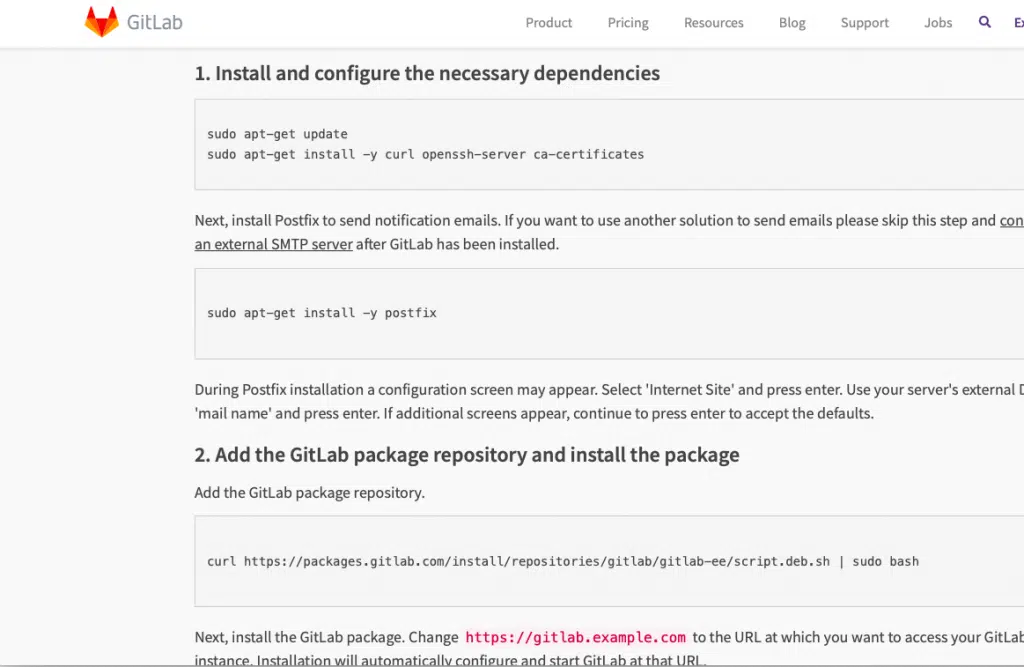
Just type in the commands shown there on you Ubuntu server’s terminal one by one to get GitLab Server installed.
A couple of tips on the GitLab installation instructions
Tip#1
In the postfix installation step (step 1 last command on the GitLab website)
sudo apt-get install -y postfix
you can skip the mail option by choosing the “no configuration” option as shown in the screenshot below.

Tip#2
In the last command of step 2 at GitLab website
sudo EXTERNAL_URL="https://gitlab.example.com" apt-get install gitlab-ee
Make sure you replace the URL with the IP address of the VM that we have made a note of in Step 5 above like this
sudo EXTERNAL_URL="192.168.0.116" apt-get install gitlab-ee
Or to be more precise just place the VM’s IP address that we obtained in Step#4 in its appropriate place
sudo EXTERNAL_URL=”<Your VM’s IP address>” apt-get install gitlab-ee
This step will take a while, so be patient. In my machine it took 4 minutes 48 seconds as shown in the screenshot below, yours can vary depending on the processing power it has.
Once done it will show u something like in the screenshot below.

Once it’s done, you can go ahead to your favorite browser and type in the IP address of your VM and check if the installation has succeeded.

And voila! GitLab server installation has succeeded!
Go ahead and follow the onscreen instructions to set up your password, accounts and everything else!
STEP#6: Download GitLab runners
Before installing GitLab runners you need to install Git on your Windows PC. You can download the latest version of Git in this link.
Now that we have set up the Gitlab server and Git, the next step is to set up the GitLab runner!
At the time of writing this article, the installation process goes like this:
Make a folder on your computer and go to either this link for 32bit version or this link for 64bit version to download the binaries and put them in the folder you created
For getting the most up to date instruction, I am gonna ask you to follow the process given in the GitLab website
STEP#7: Connect the GitLab server to the GitLab runner
GitLab
calls this process of connecting the Server to Runner as “Registering the
GitLab Runner to the Server”
You can follow the instructions for Windows in this link to do the same.
Scroll down to the windows section and you will see something similar to this

Step# 7.1: Start the registration process
To enter these commands you need to open a command prompt with administrator privileges. For this just type cmd on the search menu, right-click on Command prompt and choose run as administrator

After that, just go to the folder to which you have downloaded the Gitlab Runner to and copy the path to that folder

Next, go back to the command line and give the following command
cd <path you copied>
Run the following command to start the registration process
gitlab-runner-windows-amd64.exe register

As shown in the screenshots above, enter your Virtual Machine’s IP address when prompted. Make sure you add “http://” before the IP address.
Once the IP address is entered, the next prompt appears asking you to enter a token, so let’s first go get a token from our GitLab server.
Step#7.2: Obtain token from GitLab Server
Go to your browser and enter the GitLab Server’s IP address. Once you have logged in you can create your first project by clicking on the respective pane as shown in the screenshot below.
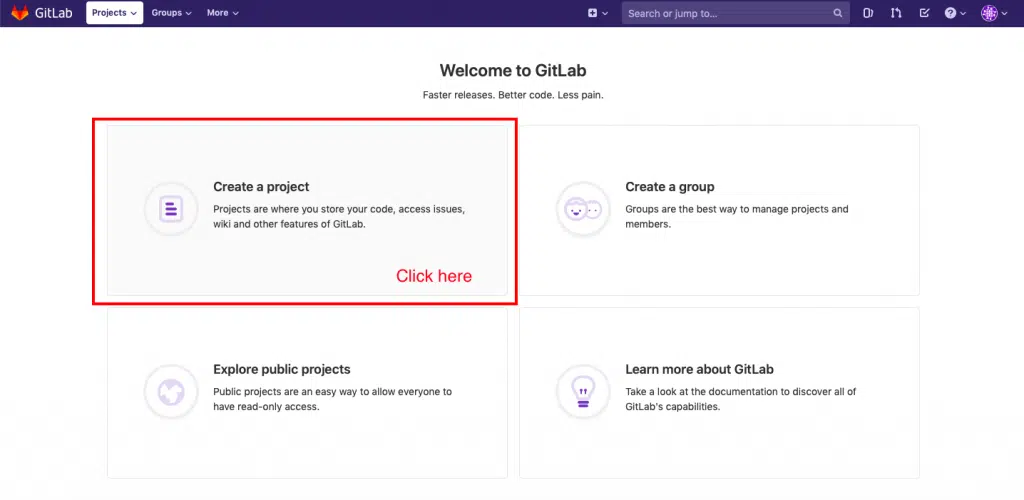
Just give the project a name and click on the create project button. The other field should get populated automatically.
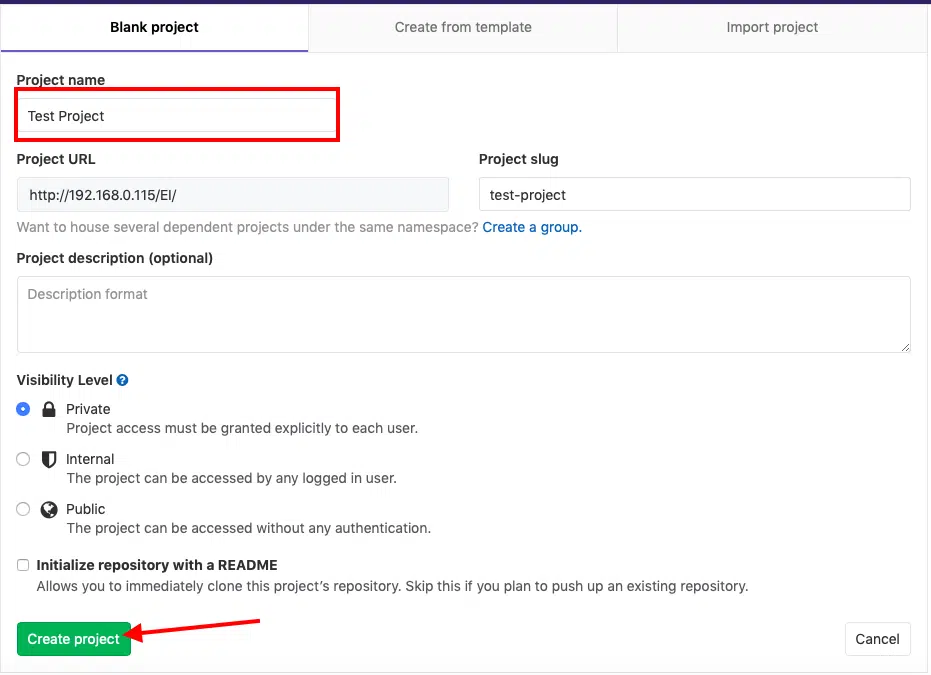
Once you click the button as shown in the screenshot above, you will be taken to your project page.
From there just click on Settings->CI/CD and scroll down a bit and click the “Expand” button next to “Runners” and you will find the token you need as shown in the screenshot below.
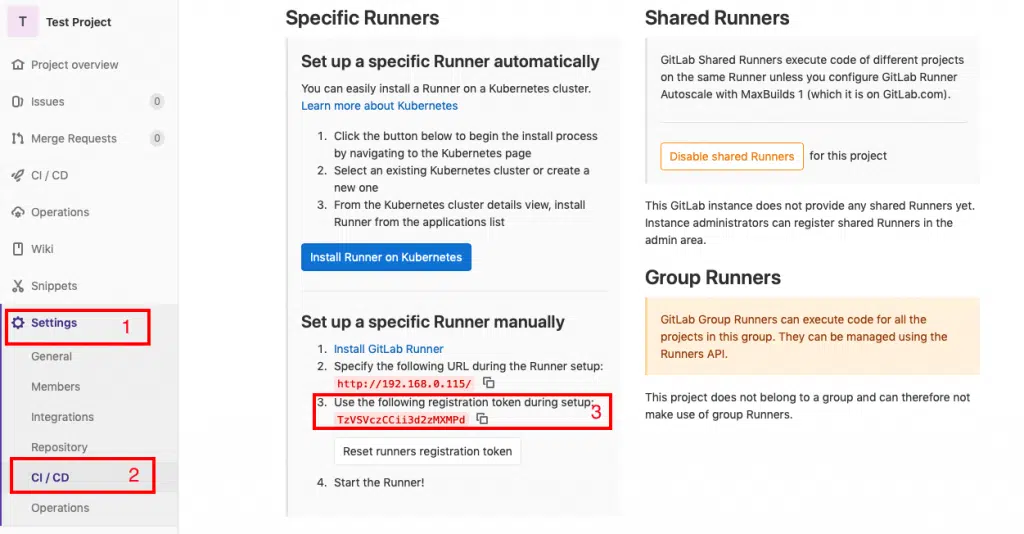
This token basically connects your project on the GitLab Server to the GitLab runner.
Step#7.3: Enter the token
Now that we have the token let’s enter it on the Command prompt

Once
entering the token, you will be prompted to give the runner a description, go
ahead and do that.
After that, you will be asked to enter some tags.
What are tags? Why are they needed for GitLab runners?
The
better term for tags can be capabilities.
Consider
this scenario.
Assume you are working in a large team of 1000 developers, who are doing say 50 different projects and your GitLab system has 100 different runners set up with several capabilities to do specific tasks. Some projects may need C compilers, while others may need python interpreters.
Now in order to connect a given project with a free-runner, we need some sort of parameter to tell the GitLab server that this particular free runner is capable of running the scripts needed for that particular job.
This is where tags come into the picture. By giving tags like “C” or “Python” a single runner can be connected to multiple projects and a single project can execute its jobs on several runners to ensure the best possible performance.
Using
these tags the Gitlab server can find a runner with the specific capability to
use for a given job. So give some suitable tags that will imply the
capabilities of your runner.
Once that is done, you will be prompted to enter “executor”.
Executors are programs that run our CI/CD scripts. Type shell and press enter

This will end the registration process the Runner to the server
Once registered you can start the GitLab runner as a Service (background task) by issuing the commands
gitlab-runner-windows-amd64.exe install gitlab-runner-windows-amd64.exe start

As you can see in the screenshot below, in the task manager app we can see that our gitlab-runner service is running!

Test to see if everything works
By following the 7 steps above, you should have a set up with GitLab Server and Runner running on your system. Its time to test and see if everything works the way it is supposed to work!
First, let’s test the GitLab server by creating a repo and pushing it to the server.
Testing GitLab Server
STEP#1: Make a test git repo
Let’s make a simple git repo on a new folder on our Desktop and push it to the GitLab server.
So open your Git-Bash app, which got installed as you were installing git.

Once opened type in the following commands
cd cd Desktop mkdir test_project cd test_project touch test.c
The above lines of command are just the fancy way of creating a folder named test_project on your Desktop and a file named test.c inside it. You can also do it through the Graphical User Interface if you want to.
So next, please open the C file using your favorite text editor and type in a simple program for testing, something like the following.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello Embedded Inventors!");
return 0;
}
Next, let’s initialize a git repository on our test_project folder. So go back to the terminal cd into the test_project folder and type in the following command
You should receive a reply saying “Initialized empty Git repository”
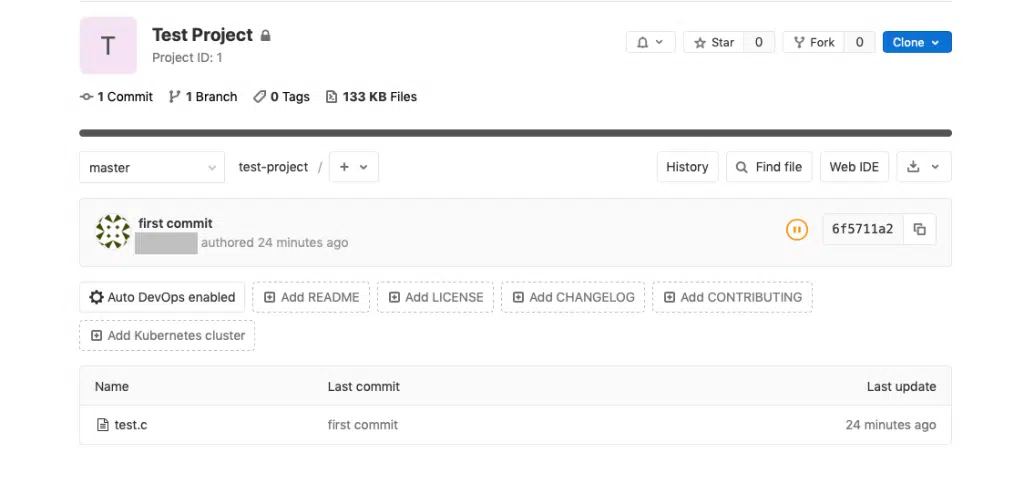
STEP#2: Push it to the server
Now that we have our git repo ready, let’s push it to our git server. To do that login to your GitLab and go to the project we created earlier. There GitLab shows us the commands needed to push our repo to the server.
First, let’s configure our name and email on the git repository to the ones set on the GitLab server
So enter
the following command.
git config --global user.name "<enter your name here>" git config --global user.email "<enter your email here>"
Next, we need to connect our server and our repository. To do that just enter the following commands
git remote add origin <your project URL>.git
In my case it is
git remote add origin http://192.168.0.115/EI/test-project.git
To find your project URL, just copy the address bar of your browser while you are on your project’s page in GitLab
Then add our test.c file and commit the changes using the following commands
git add . git commit -m"first commit"
Then push
your git repo onto the GitLab using the command
git push -u origin master
You will be prompted to enter the user name and password of your GitLab account, once done go to your browser and just refresh the page and you should be able to see your test project page in GitLab!
Testing GitLab Runner
STEP#3: Make a simple bash script to build the test.c
file
Create a bash script on your project folder
cd cd Desktop/test_project touch build.ps1
Edit it so that it looks something like this
gcc test.c -o test echo "Build completed"
STEP#4: Create and edit .gitlab_ci.yml to run the
above script
What is .gitlab-ci.yml and why it is needed? This is the file that contains the instructions for the GitLab runners to execute the CI/CD tasks. It should be present in the project’s root folder. It can be used to test if a commit builds correctly, passes some unit tests and if it needs packaging and deployment.
You can
learn more about how to configure it from the official quick start tutorial
here
For the
purpose of testing our installation let’s create a file named .gitlab-ci.yml in
the test_project folder and put the following lines in there.
Make sure you are in the right directory
cd cd Desktop/test_project
Create the file using the command
Open it with your favorite text editor and type the following lines into it.
build:
script:
- powershell -File build.ps1
tags:
- test
The last line tells the GitLab server to use the GitLab runner with the tag named “test”. If you gave your GitLab runner installation a different tag, make sure you make the appropriate change to the above lines.
Also,
make sure you use spaces instead of tabs at the beginning of the above lines.
Now add it to the git repository and push it to the Gitlab server
git add . git commit -m"gitlab yml added" git push
Now let’s get back to our GitLab server’s URL and see if it worked. Go to the project page and click on CI/CD
You will
be taken to the pipeline page which shows the result of your latest commit.
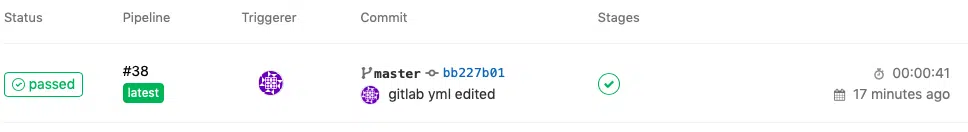
It will
take a minute or so before it completes the pipeline and as you can see in the
screenshot above, mine took 41 seconds to complete and the status is
“passed”
If you
click on “jobs” under the CI/CD menu, you will be taken to another
page which shows you more information about the execution of our yml file
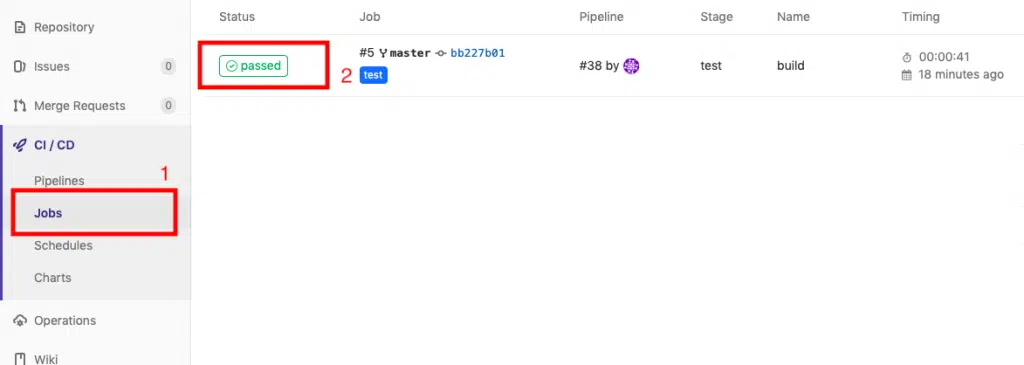
Next click on “passed” as shown in the screenshot above, this will take you to another page which will look something like this.

As you can see, our build.ps1 gets executed by the GitLab runner and it succeeds to compile our project.
And with that, I will conclude this tutorial!
I leave the rest to you to play, explore, experiment and learn GitLab!
I hope you guys enjoyed this article and learned something useful.
You can email us or contact us through this link if you have any questions or suggestions.
If you liked the post, feel free to share this post with your friends and colleagues!