В случае, если вам потребовался доступ из Windows к данным на разделе диска с файловой системой Linux — ext4/ext3/ext2, встроенными средствами системы сделать это не получится. Однако, возможности есть, причем реализовать это можно встроенными средствами системы или с помощью сторонних инструментов.
В этой инструкции подробно о способах подключить раздел диска в файловой системе Linux в Windows 11 и Windows 10 для доступа к данным на этом разделе как для чтения, так и для записи.
Ext2 File System Driver (Ext2Fsd) — самый простой способ открыть раздел ext4/ext3/ext2 в Windows
Ext2 File System Driver или Ext2Fsd — сторонний и полностью бесплатный драйвер для подключения разделов Linux во всех версиях Windows начиная с XP. Несмотря на название, поддерживаются не только разделы не только с файловой системой ext2, но и более новые ext4 и ext3.
Порядок использования Ext2 File System Driver для доступа к дискам Linux будет следующим:
- Загрузите установщик Ext2Fsd с сайта https://sourceforge.net/projects/ext2fsd/
- Установите драйвер, в параметрах установки как правило не требуется ничего изменять.
- По завершении установки вам будет предложено запустить Ext2 Volume Manager (менеджер томов), запустите его.
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по разделу Linux ext4, ext3, ext2 и выберите пункт «Assign Drive Letter» — назначить букву диска.
- Для раздела будет автоматически назначена буква диска, и вы увидите раздел в Проводнике Windows с возможностью чтения и записи файлов на нём.
В дальнейшем вы тем же способом сможете удалить букву диска с раздела (опция «Change letter» — «Remove»).
Доступ к разделам Linux средствами Подсистемы Windows для Linux (WSL)
Подсистема Windows для Linux (WSL) также может быть использована для подключения дисков Linux в Windows таким образом, чтобы доступ к ним был возможен из проводника. Шаги будут следующими:
- Запустите командную строку, Терминал или PowerShell от имени администратора и по порядку введите команды
wsl --install wsl --set-default-version 2 dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart wsl --install -d Ubuntu
- После выполнения последней команды откроется окно консоли Linux (командную строку при этом не закрывайте, она еще пригодится) с предложением настроить имя пользователя и пароль, сделайте это. Если в окне консоли вы увидите сообщение об ошибке, скачайте и установите обновление WSL, перезагрузите компьютер и запустите Ubuntu из меню «Пуск».
- В консоли Ubuntu введите команду
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/ext-drives/
для создания папки, к которой будут монтироваться диски.
- В консоли Windows (командная строка, терминал, Powershell) введите команду
wmic diskdrive list brief
- Обратите внимание на DeviceID диска, который нужно подключить и введите команду (так же в консоли Windows) указав соответствующий номер в имени PHYSICALDRIVE
wsl --mount \\.\PHYSICALDRIVE
- В консоли Ubuntu введите команду lsblk — это отобразит список подключенных дисков, разделов на них и их размер. В следующей команде используем имя нужного раздела для монтирования:
sudo mount /dev/sdИМЯ /mnt/ext-drives/
- После успешного выполнения всех указанных шагов вы можете зайти в Проводник Windows, выбрать пункт «Linux» в панели быстрого доступа, перейти в папку mnt\ext-drives и получить доступ к файлам на подключенном разделе Linux с возможностью записи и чтения.
В дальнейшем для отключения диска от WSL можно использовать ту же команду, которая использовалась на 5-м шаге, заменив mount на unmount.
Есть и другие программы (драйверы) для доступа к разделам Linux из Windows, но не полностью бесплатные. Среди них:
- DiskInternals Linux Reader — в бесплатной версии доступно только чтение данных с разделов.
- Paragon Linux File Systems for Windows — бесплатная работа в течение пробной версии, затем необходимо приобретать лицензию.
In this article, we will be discussing five different ways to access Linux files from Windows. We’ll work on Ubuntu in this article, but you can use any distribution. Just identify the partition type that you’re using on your system and download the appropriate tool from this list.
Ubuntu supports Windows NTFS partitions but Windows can’t access Ubuntu partitions i.e. Ext4, Ext3, Ext2, etc. To access these partitions from windows when dual-booted with Ubuntu, this can only be done using third-party software. We will discuss some of the software to read and write Linux partitions.
Here are some free tools to access Linux files from windows without booting into Linux:
1. ext2fsd
ext2fsd can read Ext4, Ext3, Ext2 file systems and can even provide write access on enabling write support during the setup. You have to start it manually in Tools > Service Management and click on Start or you can set it to start automatically when the system boots. It is free and easy to install.
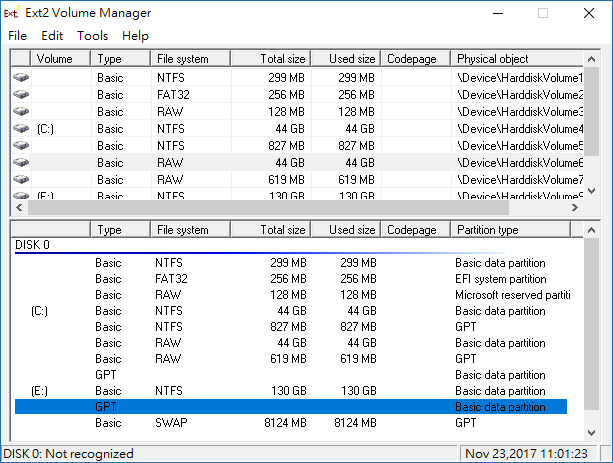
It assigns a drive letter to the Linux partitions or you can set it manually using Ext2 Volume Manager and can change ext2fsd’s settings. You can choose to assign the drive letter automatically in Tools > Service Management. Assigning a drive letter to Linux partitions allows apps to directly access Linux Files on Windows!
2. DiskInternals Linux Reader
Unlike ext2fsd, Linux Reader also supports ReiserFS, Reiser 4, HFS, HFS+(Apple’s file system), APFS, XFS, etc along with Ext4, Ext3, Ext2. It provides read-only access to keep the original files secure. It previews the contents of the files and bypasses the security policies of files which gives you access to any file on your Linux partition. It is free software for non-commercial use and works on Windows 7, 8, and 10.
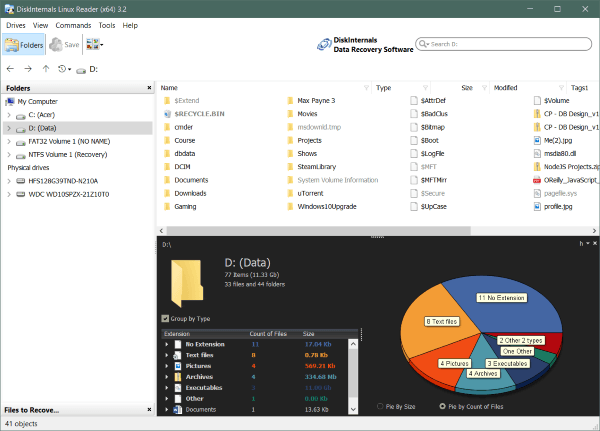
It also has a pro version i.e. Linux Reader Pro which provides some extra features such as remote access via SSH, Exporting files to an FTP server. You can download it through this link. Instead of assigning a drive letter, it shows the files in its application window. You can save the files to windows which you want to use.
3. Ext2Read
Ext2read is a free and open-source utility that works the same as the Linux Reader. It provides read-only access only to Ext4, Ext3, Ext2, and Ext4 Extents. It does not need to be installed, It is just a .exe file that should be run as an administrator. You can copy folders and even whole directories from Linux partitions. You can download the .exe file through this link.
4. Explore2fs
Explore2fs is a tool that gives you access to Ext2 and Ext3 file systems. It supports all versions of windows, especially the older versions. This tool is used for the old hardware as it supports Floppy disks, CD-ROM, Jazz Disk and can export files as binary, text, or even directories. While not the best option, if you need to access Linux files on Windows on a old device, go for this one. You can download it from here.
5. Ext2 IFS
Ext2 IFS is a tool used to access the Ext2 file system with read and write access. You can read, write, rename, move and delete files or directories. It works on Windows 7 and 8, Windows Server 2003, 2008, 2012, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and other old versions.
During installation, it will give the option to choose a drive letter for your Linux partition and after the installation, you will find the Linux file system in your file explorer.
Unlike other software discussed above, this tool can only access Ext2 file systems. You can download it through this link.
FAQs
What are some tools to access Linux files on Windows?
You can use tools like DiskInternals Linux Reader, Ext2Fsd, Explore2fs, WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux), and Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon to access Linux files on Windows.
How can I access Linux partitions from Windows?
You can use tools like Ext2Fsd or Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon to access Linux partitions from Windows. These tools allow you to browse and save files from Linux partitions on your Windows system.
Can I access Ext4 partitions from Windows?
Yes, you can access Ext4 partitions from Windows using tools like Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon which supports the Ext4 file system and allows you to access files from Ext4 partitions on your Windows PC.
Does Windows 10 have built-in support for accessing Linux files?
Windows 10 does not have built-in support for accessing Linux files. However, you can use third-party tools like DiskInternals Linux Reader or Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon to access Linux files from Windows 10.
How can I transfer files between Windows and Linux systems?
You can transfer files between Windows and Linux systems by using tools like WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) or third-party applications like DiskInternals Linux Reader or Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon.
Conclusion
So, We discussed different ways to access Ubuntu files from Windows without shutting windows and booting into Linux. Explore2fs and Ext2 IFS can be used for older versions of windows and can access old hardware as discussed.
Всякий человек, совершающий побег из семьи Windows, некоторое время непременно будет жить на два дома, перескакивая то туда, то сюда. И если в семействе Linux относятся к такому положению вполне благосклонно, предоставляя полный доступ к разделам Windows, то Windows, наоборот, как ревнивая жена на корню пресекает все попытки добраться до своего имущества. Однако с помощью утилиты Ext2Fsd можно такое положение вещей изменить и с легкостью получить доступ к Linux-разделам.

Утилита Ext2Fsd служит для быстрого и удобного доступа к папкам и файлам, расположенным на разделах операционной системы Linux. В процессе установки программы инсталлируется специальный драйвер, обеспечивающий прозрачный доступ к томам в форматах Ext2, Ext3, Ext4. При этом linux-раздел может автоматически монтироваться при старте системы и становится, таким образом, доступным для работы из любой программы в Windows.
Для начала необходимо скачать инсталляционный файл программы и установить на свой компьютер. Программа работает в Windows 2k, XP, Vista и Win7, однако и в восьмерке при соответствующих опциях совместимости чувствует себя прекрасно. В процессе установки следует обратить внимание на одно из диалоговых окон.
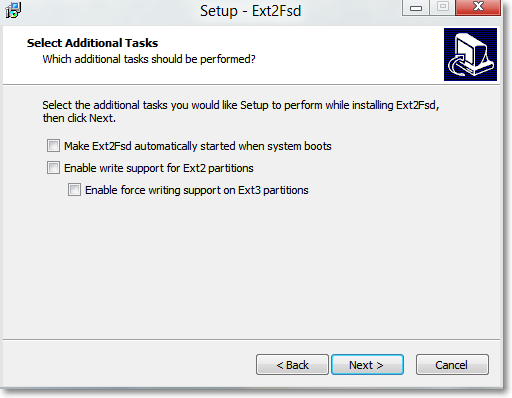
Здесь верхний пункт предлагает включить опцию автоматического монтирования дисков при старте системы, что очень удобно, поэтому этот пункт лучше включить. А вот следующие два пункта лучше не активировать — они включают возможность записи на подключаемые диски, что с большой долей вероятности может привести к различным проблемам.
После установки и запуска программы перед нами появляется окно с перечнем всех разделов. Здесь мы видим таблицу, содержащую обозначение разделов, файловую систему, общее и занятое место.
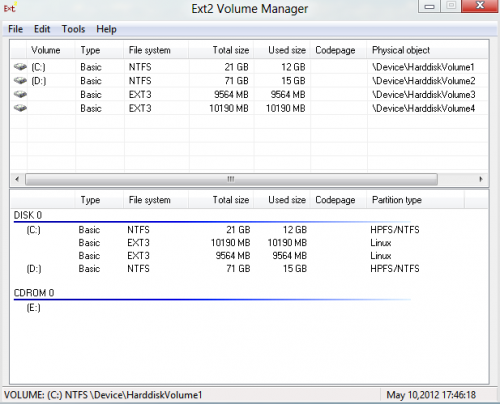
Следующим действием необходимо найти раздел, который вы хотите присоединить, и сделать по нему двойной щелчок, после чего откроется дополнительное окно его свойств.
В этом окне нас интересует кнопка Mount Points, которая вызывает ещё одно диалоговое окошко, в котором следует задать букву диска и отметить галочкой пункт Create a permament MountPoint via Session Manager. Теперь последовательно закрываем всю стопку открытых диалоговых окон и собственно окно программы. После этого необходимо перезагрузить компьютер, и в файловом менеджере появляется новый диск, представляющий собой подключенный вами linux-раздел.
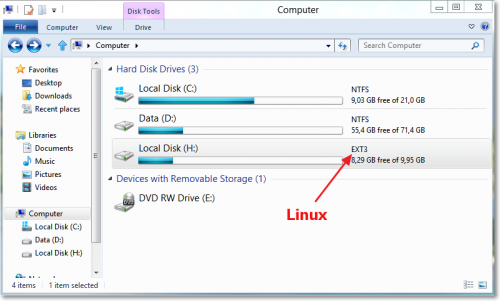
Теперь вы легко сможете прямо из Windows без всяких перезагрузок получить доступ ко всем своим данным, хранящимся, например, в Ubuntu. В том числе вы сможете проигрывать музыку виндовым проигрывателем, просматривать фотографии, редактировать документы и так далее. Совместная жизнь налажена!
Ext2Fsd
What’s a Linux file system? Can I read Linux drive on Windows? How to access Linux files from Windows 10? A lot of users are confused about these questions. In the article, MiniTool will explore them one by one together with you.
If you have a Linux distribution alongside a Windows system on the laptop or desktop, you may need to access Linux files from Windows 10. After analyzing lots of user reports on forums, we conclude the following questions that are frequently talked about. Let’s start exploring them in detail.
What’s Linux File System
In order to access Linux files from Windows successfully, the first thing you should figure out is what file system is supported by Linux. The common Linux Files Systems are Ext2, Ext3, and Ext4.
At present, Ext4 has become the default file system for most Linux distributions including Debian and Ubuntu. This is because the Ext4 provides more flexibility for storing large files than other extended file systems. It’s reported that the Ext4 can support storing a file up to 16TB and creating a partition up to 1EB.
Top recommendation: How to Install Linux (Ubuntu) on Windows 10 [Ultimate Guide 2021]
Can I Access Linux Files from Windows 10
There are a lot of users who have Windows 10 plus Linux dual boot or a hard drive formatted with Ext4. So, here comes a new question. Can I access Linux files from Windows 10? As discussed above, the most common Linux file system is Ext4. That is to say, you have to read Ext4 from Windows if you want to access Linux files.
However, the Ext4 file system is not supported by Windows. When right-clicking the Ext4 partition, you will find the Open and other function menus become greyed out. Obviously, you can’t access Ubuntu files from Windows directly. What can I do if I have to read Linux drive on Windows? Please keep reading the following part.
How to Access Linux Files from Windows 10
Since Windows 10 doesn’t offer any direct methods to access Ext4, you need to utilize some professional tools to access Linux files from Windows. Here we summarize top 4 Ext4 partition readers on Windows.
Method 1. Use Ext4 Partition Manager – MiniTool Partition Wizard
MiniTool Partition Wizard is an all-in-one partition manager that supports many file systems including FAT16/32, NTFS, exFAT, and Ext2/3/4, Linux Swap. With this powerful software, you can format a hard drive, convert NTFS to FAT, convert MBR to GPT, recover lost data, migrate OS to SSD/HD, rebuild MBR, and so forth.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
In order to access Ext4 from Windows smoothly, you can make it accessible by formatting it to NTFS. Although formatting will delete the data on the hard drive, MiniTool can help you restore the Ext4 partition data so that you can access Linux files from Windows 10.
Part 1. Read Linux Drive on Windows
Follow the steps below to format the Ext4 partition to NTFS or other file systems that are supported by Windows 10.
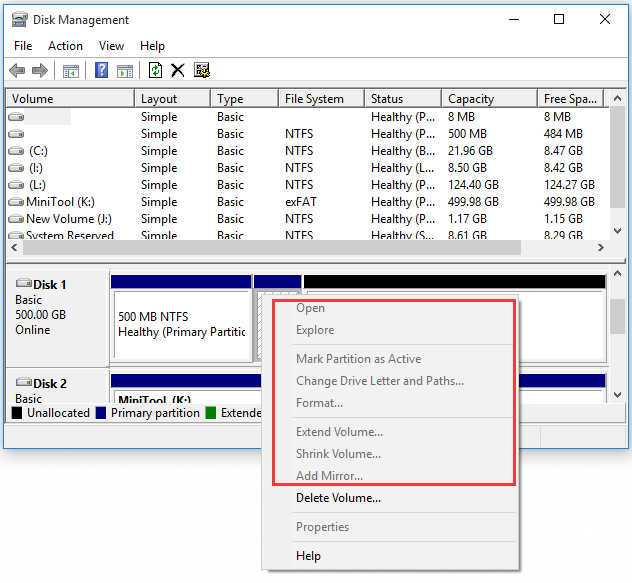
Step 1. Launch the MiniTool Partition Wizard to enter its main interface, and then right-click the Ext4 partition from the disk map and select Format.
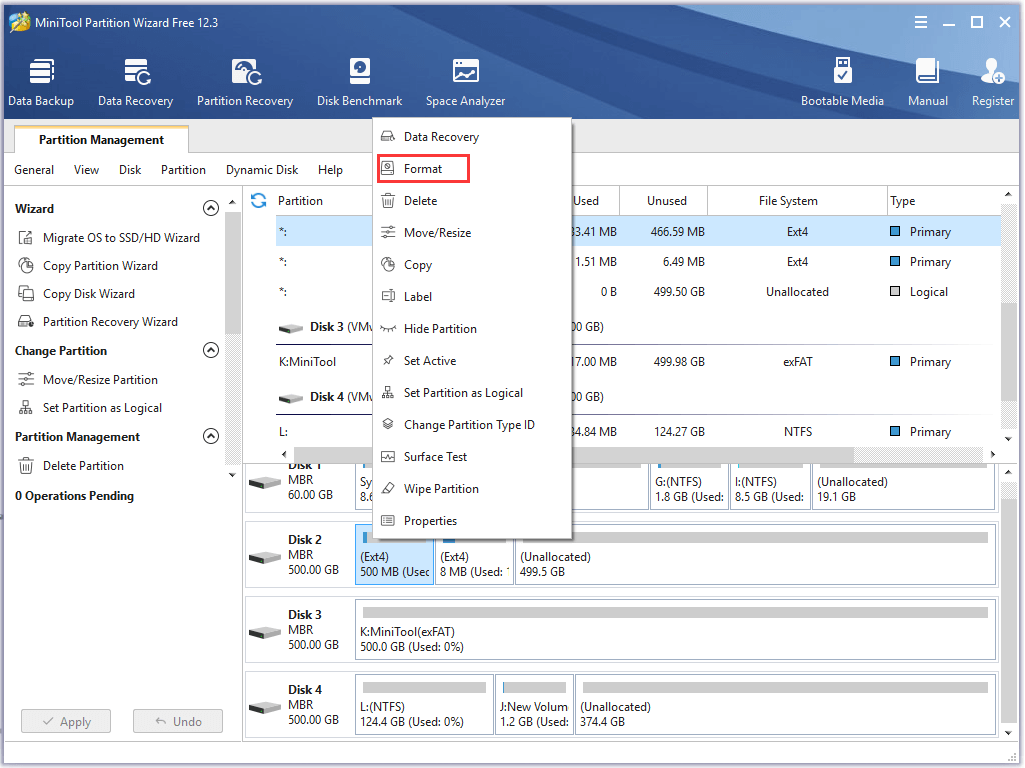
Step 2. In the pop-up window, select NTFS from the drop-down menu and click on OK to continue.
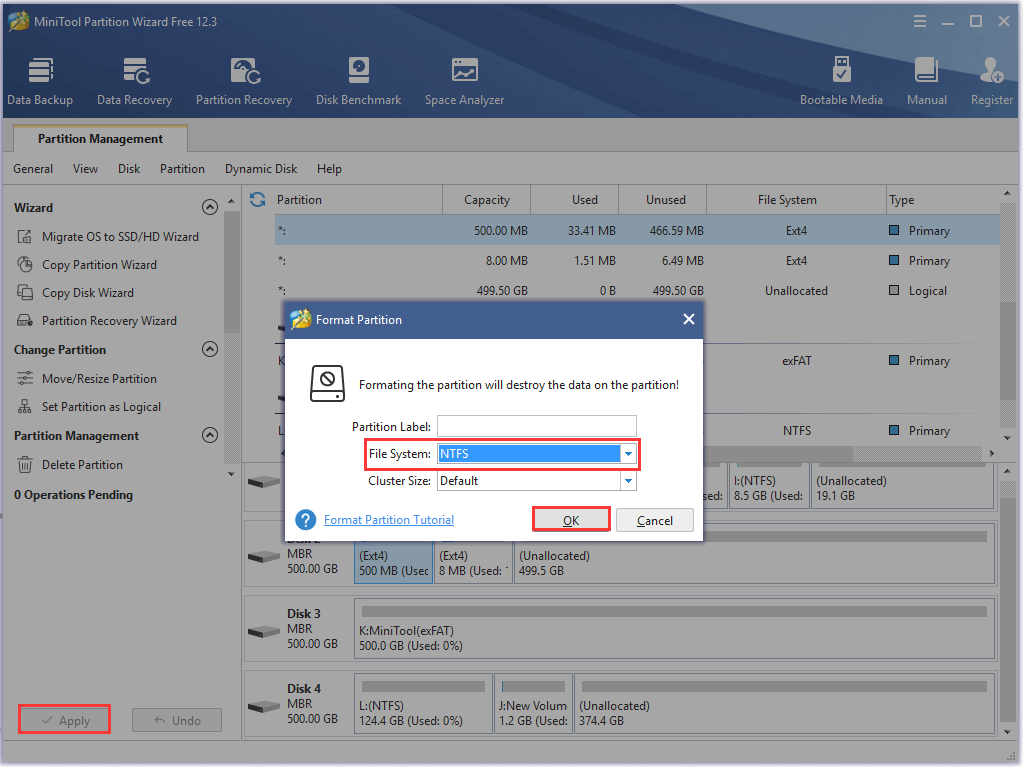
Step 3. Click on Apply button to execute the operation.
Part 2: Restore Data from the Ext4 Partition
Now, you should make the Ext4 accessible on Windows 10. Another question is how to regain data from the formatted partition. Here MiniTool Partition Wizard is capable of restoring Ext4 partition data. Please continue with the following steps.
Tip: MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition doesn’t support data recovery. You need to install a professional edition or a more advanced edition to recover the lost partition.
Step 1. In the main interface, select the partition that you just formatted to NTFS and click on Partition Recovery from the top toolbar. Click on Next in the pop-up window.
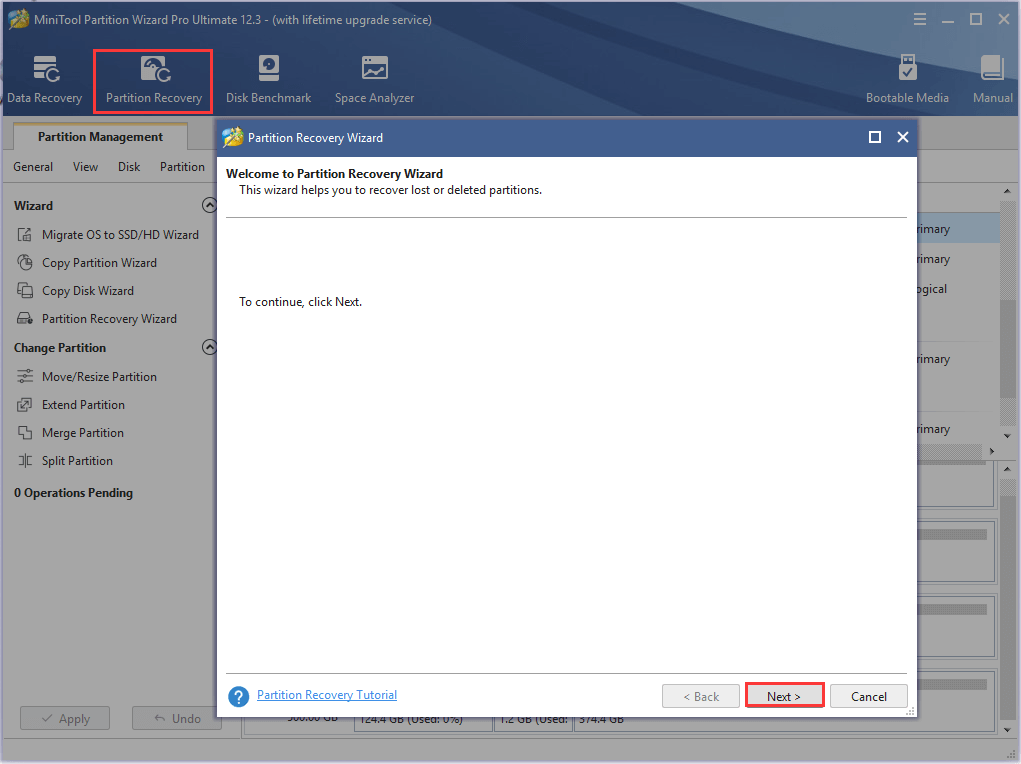
Step 2. Choose a scanning range based on your needs. There are 3 ranges to scan the disk including Full Disk, Unallocated Space, and Specified Range. Here we take Full Disk for example and click on Next to go on.
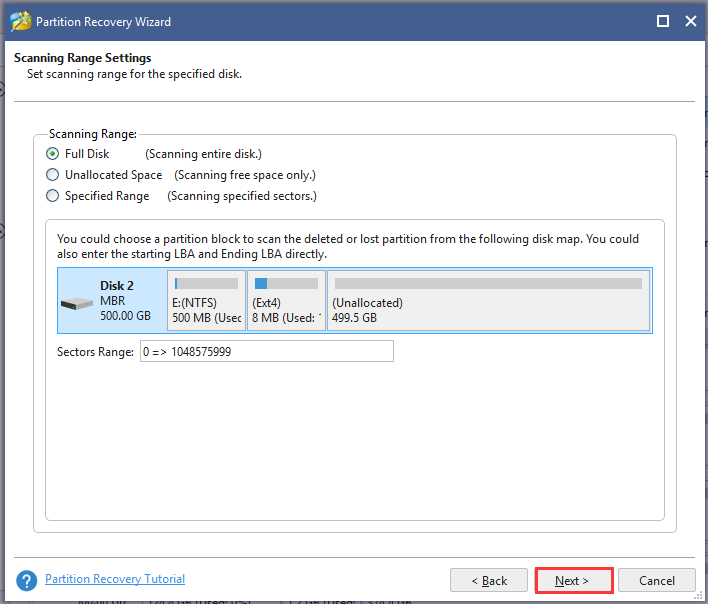
Step 3. Select a scanning method to scan the disk and click Next to continue.
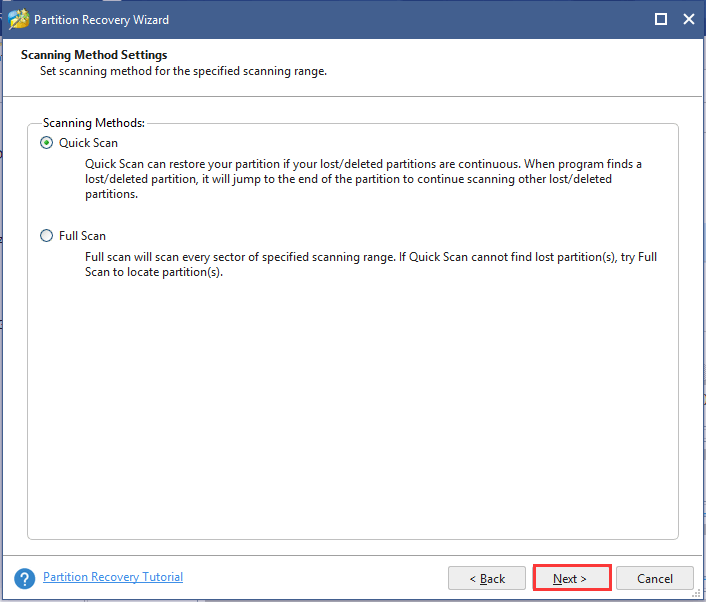
Step 4. Make sure that you check all partitions including existing partitions and deleted/formatted partitions. Wait for some time until the scanning completes and click on the Finish button.
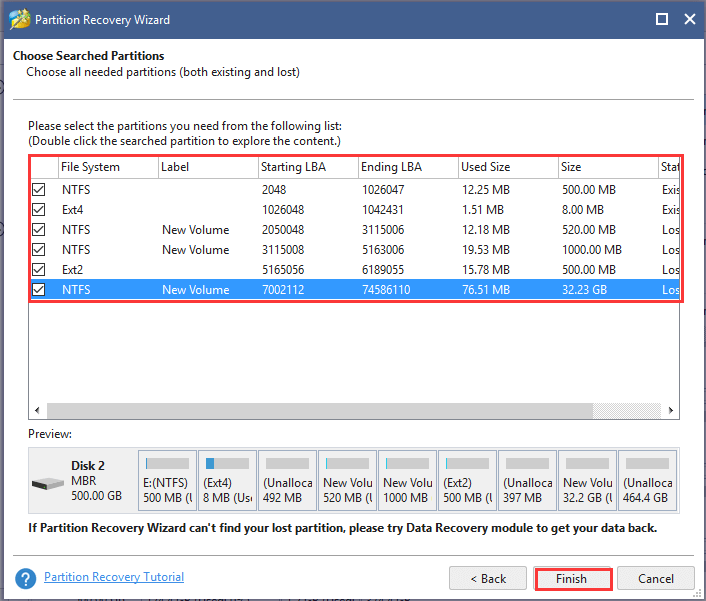
Step 5. Click on Apply button to recover the formatted partition on the hard disk.
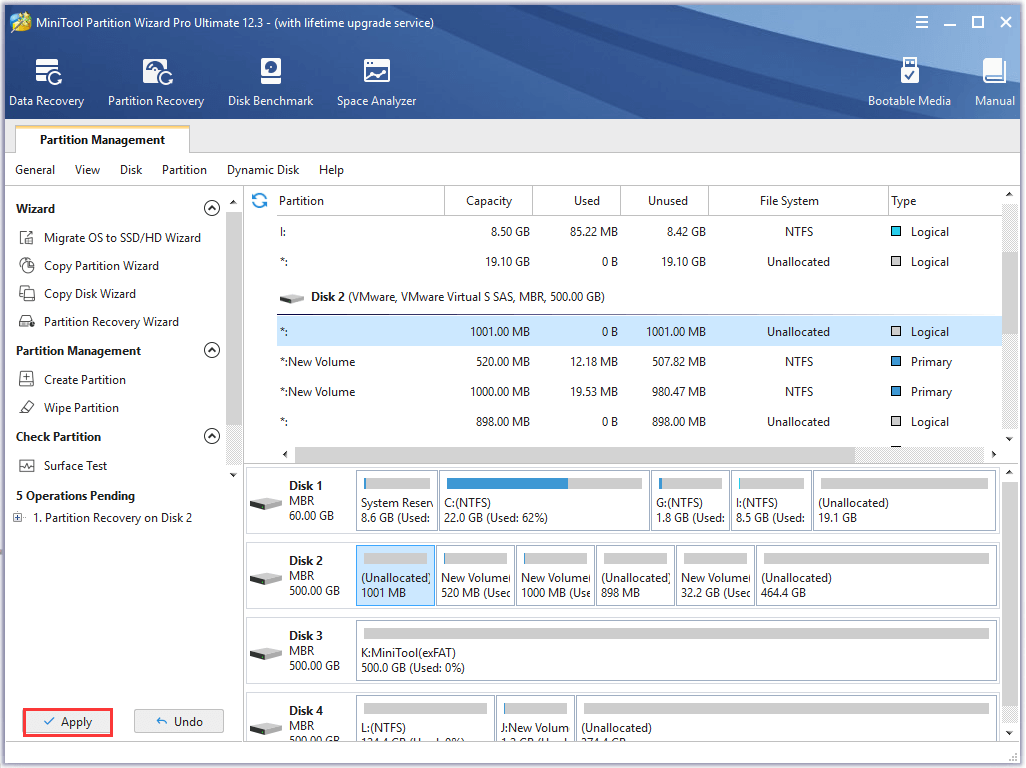
Up till now, the formatted partition should be recovered, and then you can read Linux partition Windows 10 and access its files.
Also, you can try the other three utilities to access Ext4 from Windows 10. Let’s keep reading!
Method 2. Use Ext2Fsd
Ext2Fsd is a Windows file system driver that supports the Ext2/3/4 file system. It allows you to read Linux partition Windows 10 and access Ubuntu files by mounting the Ext4 partition and assigning a drive letter. You can lunch the Ext2Fsd at every boot or only open it when you need it.
To access Ext4 from Windows, follow the steps below:
Step 1. Install this tool on your Windows 10 PC and launch the driver.
Note: If you don’t want to automatically launch the software at every boot, don’t tick the checkbox for Make Ext2Fsd automatically started when system boots.
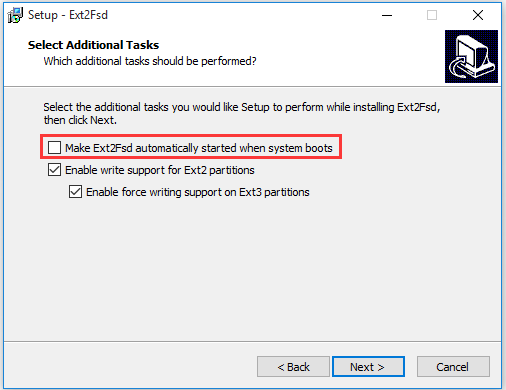
Step 2. In the main interface of Ext2Fsd, navigate to the Tools tab and select Service Management from the context menu.
Tip: If you haven’t set Ext2Fsd to automatically start at boot, you need to select Tools > Service Management > Start Ext2Fsd service before you access Linux files from Windows 10.
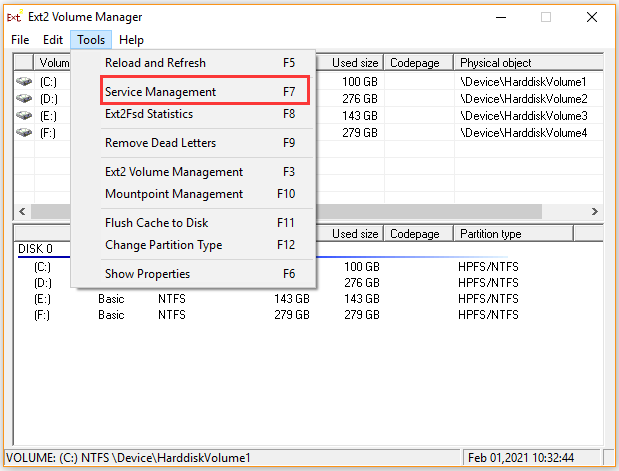
Step 3. In the Ext2Fsd Service Management window, select the checkboxes for Mount all volumes in read-only mode and Assign drive letter automatically. Then click on Apply to execute the operation. After that, this tool will automatically mount and assign drive letters to the Linux partitions.
Step 4. Press Win + E keys to open File Explorer, and then you will find the Ext4 partitions are mounted with their own drive letters and you can directly access Ubuntu files from Windows.
Method 3. Use DiskInternals Linux Reader
DiskInternals Linux Reader is a free utility to access Linux files from Windows 10. This tool can not only support the Ext4 file system but ReFS, HFS, and HFS+ file systems. Different from Ext2Fsd, this program allows you to read Linux drive on Windows within this application.
Step 1. Install DiskInternals Linux Reader on your Windows PC and launch it to enter the main interface.
Step 2. After the Linux Reader detects all partitions on your hard drive, navigate to the Ext4 partition from the list of drives.
Step 3. Double click the Ext4 partition to open it and then you can preview and access the saved data on the drive.
Step 4. If you want to make full use of the Linux files on Windows, you have to transfer the files from the Ext4 partition to another location that is supported by the Windows file system. Here right-click the file that you need and click on Save from the context menu.
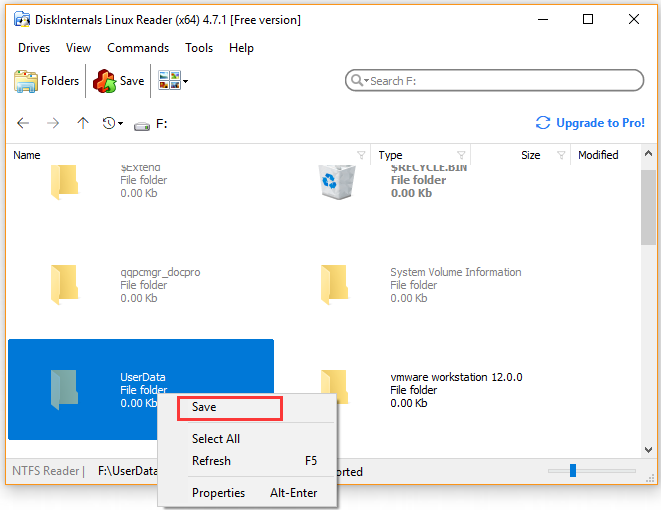
Step 5. Select the Save Files option and click on Next button.
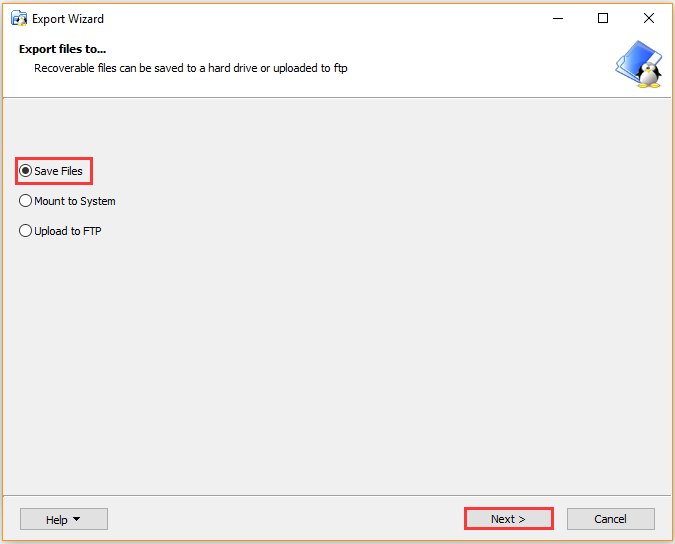
Step 6. Click on Browse button to select a location where you save the file and click on OK. Then click on Next. Wait for some time until the file is saved to your selected location.
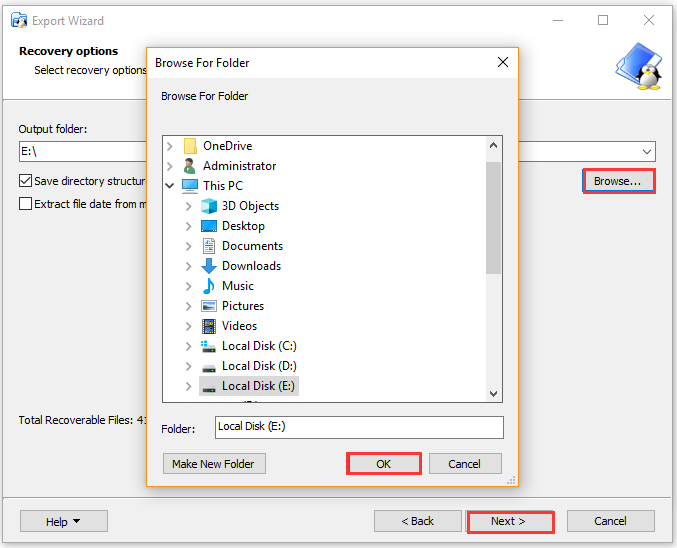
Method 4. Use Ext2explore
Ext2explore is a practical explorer that can access Ext2/3/4 files on Windows 10. It works similarly to DiskInternals Linux Reader, but it doesn’t allow you to preview files using Ext2explore. This utility doesn’t have to be installed and you can run the .exe file directly.
Bear in mind that you must run the Ext2explore.exe program as an administrator, or you will receive an error message.
Step 1. Right-click the Ext2explore.exe file that you download to Windows PC and select Run as administrator.
Tip: Also, you can right-click the Ext2explore.exe and select Properties. Then go to the Compatibility tab and select the checkbox for Run this program as an administrator > OK.
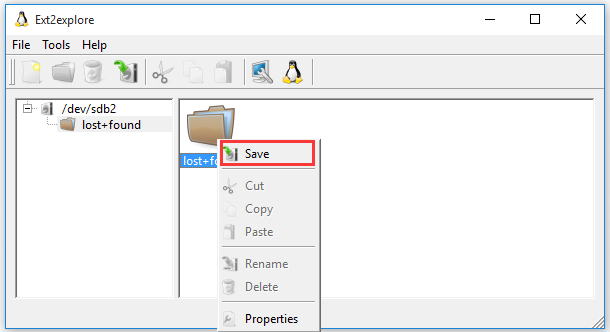
Step 2. Now, you can access the Ext4 partition and its Linux files. To open the files in the Windows system, you need to save them to the Windows partition. Right-click on the file and select Save, then navigate to another location to save files on the Windows system.
I have Windows 10 and Linux a dual boot system. Although Linux distribution has built-in support for Windows NTFS partition, Windows can’t read Linux drive. Fortunately, I found 4 effective methods to access Linux files from Windows 10. Probably you also need this post. Click to Tweet
What’s Your Opinion
This post mainly focuses on how to access Linux files from Windows 10. You can choose one from the top 4 utilities to access Ext4 from Windows. If you have any better ideas on this topic, please share them in the comment area. Also, you can send us an email via [email protected] if you have any questions about the MiniTool software.
Access Linux Files from Windows 10 FAQ
How to transfer files from Windows to Linux?
After analyzing lots of user reports and references, we summarize the following 5 methods to transfer files between Windows and Linux.
- Use the Share network folders.
- Transfer files from Windows to Linux via FTP.
- Securely copy the files or folders to Linux via SSH.
- Share the files via sync software.
- Use the shared folder in Linux virtual machine.
How to mount a Linux folder in Windows?
Here are detailed steps to mount a Linux folder in Windows.
- Press Win + E keys to open the File Explorer, and then map your Linux home folder or directory on Windows.
- Click on Tools at the top menu and select Map network drive.
- Select the drive letter from the drop-down menu and click on Browse to select the folder that you want to mount.
- Click on Finish
How to access a network drive in Linux?
- Open a terminal on your Linux, and then type sudo apt-get install smbfs in it and hit Enter.
- Type the sudo yum install cifs-utils line in terminal and press Enter.
- Execute the sudo chmod u+s /sbin/mount.cifs /sbin/umount.cifs
- Use the cifs utility to map a network drive to storage.
How to access a shared folder in Linux?
The first and simplest method is to press Alt + F2 keys to open the Run dialog box, and then type smb:// followed by the IP address of your Linux sever and the folder name. Then click on the Run button.







