Windows позволяет подключить любую общую сетевую папку с файлового сервера или NAS хранилища в виде отдельного диска с назначенной ему буквой диска. Такие подключенные сетевые папки называются сетевыми дисками. Сетевые диски удобно использовать для удобства доступа пользователей к часто используемым общим ресурсам на файловом сервере.
Сетевой диск в Windows можно подключить несколькими способами:
- Из проводника Windows
- Из командной строки или PowerShell
- С помощью групповых политик
Чтобы подключить сетевой диск в Windows 11, откройте проводник, нажмите кнопку с тремя точками в верхнем меню и выберите пункт Map network drive.
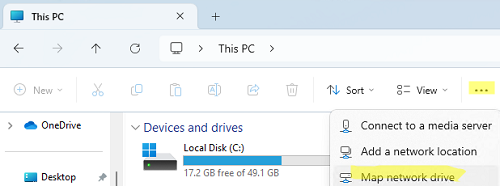
- Выберите букву диска, которую нужно назначить сетевой папке,
- Укажите путь к папке на файловом сервере (в UNC формате, например
\\fs01\Docs\IT
). Если у вас настроено отображение компьютеров в сетевом окружении, можно воспользоваться кнопкой Browse для ручного выбора компьютера и общей сетевой папки на нем. - Если нужно автоматически подключать этот диск пользователю при входе в Windows, включите опцию Reconnect at sign-in (Восстанавливать подключение при входе в систему).
- Если вы не хотите использовать учетные данные текущего пользователя, с помощью опции Connect using different credentials можно указать имя пользователя и пароль, который будут использоваться для подключения (будут сохранены в диспетчер учетных данных Windows).
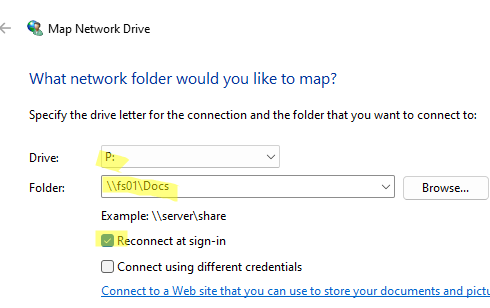
После этого в проводнике Windows появится новый сетевой диск. Пользователь теперь сможет быстро и удобно открывать общей файлы на сетевом диске.
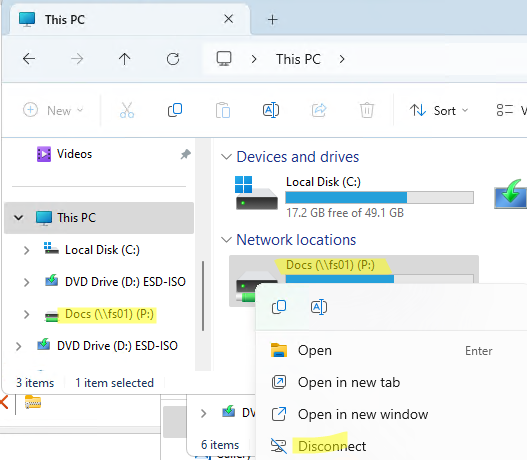
Чтобы отключить сетевой диск, щелкните по нему и выберите Disconnect.
Для подключения/отключения сетевых дисков из командной строки можно использовать команду
net use
. Например:
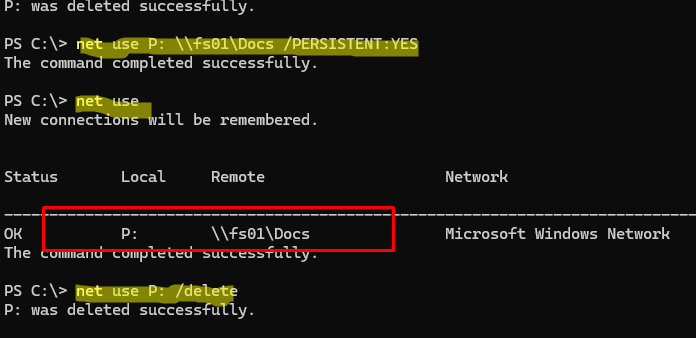
net use P: \\fs01\Docs /PERSISTENT:YES
где:
-
P:
— буква диска, которую нужно назначить сетевой папке -
\\fs01\Docs
— полный UNC путь к папке -
/PERSISTENT:YES
— сделать сетевой диск постоянным. Без использования этой опции сетевой диск автоматически удаляется при перезагрузке компьютера. - Если нужно указать учетную запись пользователя для подключения к папке, добавьте:
/USER:WINITPRO\kbuldogov *
(пароль будет запрошен интерактивно). Либо вы можете указать пароль в открытом виде:
/USER:WINITPRO\kbuldogov Password1
Вывести все подключенные сетевые диски в сессии пользователя:
net use
Удалить сетевой диск:
net use P: /delete
Также для подключения сетевого диска можно использовать PowerShell.
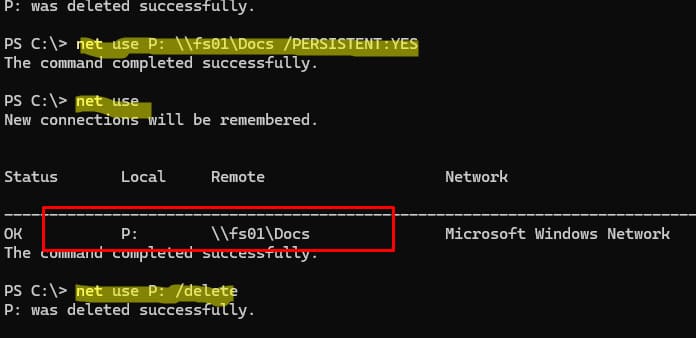
Вывести список сетевых папок на удаленном компьютере:
Get-SmbShare -CimSession "FS01"
Создать постоянное подключение к сетевой папке в виде сетевого диска:
New-SmbMapping -LocalPath P: -RemotePath \\fs01\docs –Persistent $true
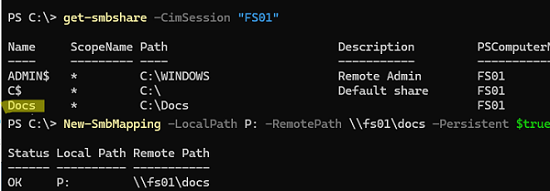
Удалить сетевую папку:
Remove-SmbMapping P: -UpdateProfile
В этой статье расскажем, как подключить сетевой диск или папку в Windows. Сетевые диски позволяют пользователям получать удобный доступ к общим ресурсам, таким как файлы на файловом сервере или NAS хранилище, напрямую через проводник Windows, как к обычному диску.
Приобрести оригинальные ключи активации Windows всегда можно у нас в каталоге от 1099 ₽
Способы подключения сетевого диска:
1. Из проводника Windows
2. Из командной строки или PowerShell
3. С помощью групповых политик
Подключение сетевого диска через проводник Windows 11
1. Откройте проводник Windows.
2. Нажмите на три точки в верхнем меню и выберите Map network drive (Подключить сетевой диск).
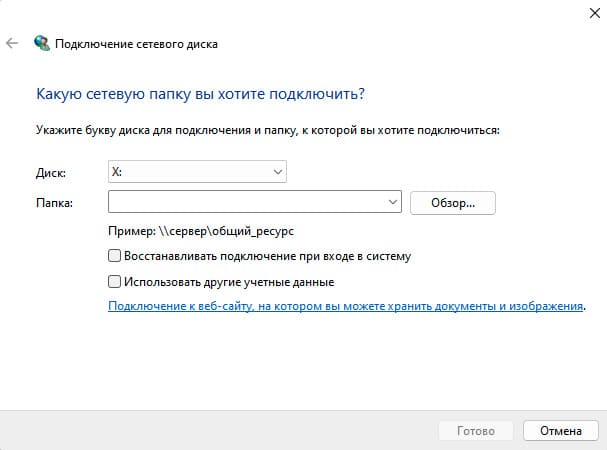
3. Выберите букву диска, которую хотите назначить сетевой папке.
4. Укажите путь к папке на файловом сервере в формате UNC (например, \\fs01\Docs\IT). Если вы не знаете путь, можно воспользоваться кнопкой Browse, чтобы выбрать папку вручную.
5. Если необходимо автоматически подключать диск при входе в систему, включите эту опцию.
6. Если нужно использовать другие учетные данные для подключения, включите эту опцию, после чего введите логин и пароль.
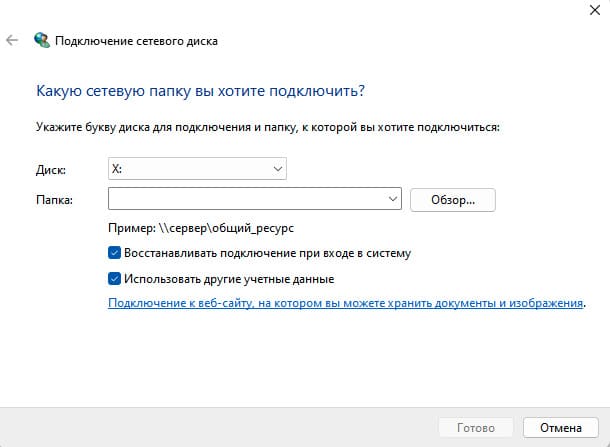
После этого сетевой диск появится в проводнике Windows и будет доступен для использования.
Чтобы отключить сетевой диск, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по диску и выберите Отключить (Disconnect).
Подключение сетевого диска через командную строку
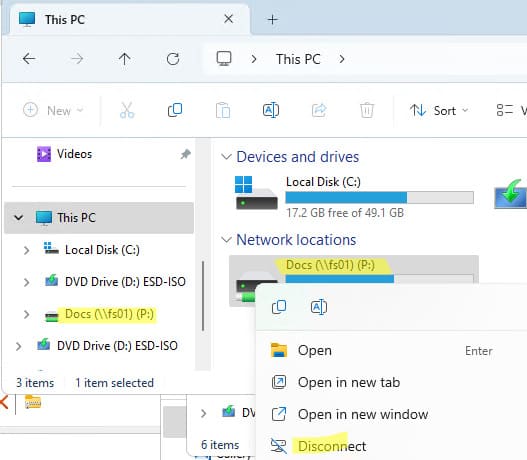
Подключить сетевой диск можно с помощью команды net use. Пример:
net use P: \\fs01\Docs /PERSISTENT:YES
Где:
— P: — буква диска для сетевой папки.
— \\fs01\Docs — UNC путь к папке на сервере.
— /PERSISTENT:YES — делает подключение постоянным, сетевой диск не будет удален при перезагрузке.
Чтобы использовать учетную запись для подключения:
net use P: \\fs01\Docs /USER:WINITPRO\kbuldogov *
Где:
— /USER — указывает учетную запись.
— Звездочка (*) означает, что система запросит пароль интерактивно.
Удалить сетевой диск:
net use P: /delete
Подключение сетевого диска через PowerShell
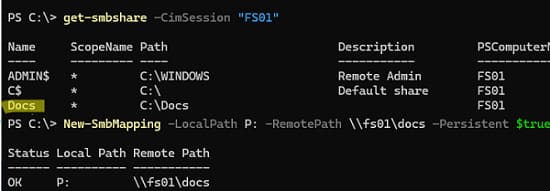
Для подключения сетевого диска через PowerShell используйте команду New-SmbMapping. Пример:
New-SmbMapping -LocalPath P: -RemotePath \\fs01\docs -Persistent $true
Чтобы удалить сетевую папку:
Remove-SmbMapping P: -UpdateProfile
Вывести список сетевых папок на удаленном компьютере можно командой:
Get-SmbShare -CimSession "FS01"
Подключение сетевого диска с помощью групповых политик
Администраторы домена могут использовать групповые политики для автоматического подключения сетевых дисков всем пользователям сети. Это особенно полезно для централизованного управления общими ресурсами и упрощения доступа к ним для пользователей.
Теперь вы знаете, как подключить сетевой диск в Windows несколькими способами, будь то через проводник, командную строку или PowerShell. Выбирайте тот метод, который подходит вам больше всего.
Лицензионный ключ активации Windows от
One of the most ubiquitous commands in a senior Windows admin’s arsenal is probably the Windows net command. This command has a lot of functionality. In this article, you’re going to learn about net use.
Not a reader? Watch this related video tutorial!
Not seeing the video? Make sure your ad blocker is disabled.
The net use command is a legacy, yet still completely functional command to create, remove and manage SMB Windows mapped connections and drives.
Let’s dig into the net use command and cover what it’s capable of and how to use it in this tutorial.
Prerequisites
To follow along with any examples in this tutorial, ensure you have at least:
- A Windows client computer (any version will work) in an Active Directory domain. This tutorial will use Windows 10.
The
net usecommand will work in non-domain environments. If not though, you’ll always need to pass a username and password to authenticate to the remote file share.
- One or more available file shares on an accessible server part of an Active Directory domain. This tutorial will be connecting to an administrative file share called C$ on a server called DEVSRV.
- A user account with read access to the file share and NTFS read permissions to the folder the share is pointing to
Getting Started with Net Use
The net use command enables you to work with files on network file shares. It does this using various parameters and switches as shown below.

The net use command can view device connections, create new connections and remove them. Throughout this tutorial, you’re going to learn about each parameter and see in what use case each parameter fits.
Much of the content you’ll see around
net userefers to the endpoints it works with as ‘connections’ instead of ‘drives’. This command is capable of connecting to printers and other devices but for this tutorial, you’re going to focus on remote file shares.
Creating Remote Connections
Creating new connections is one of the most common reasons to use the net use command. This command allows you to connect to remote file shares to copy files to, remove from, etc just like if the folder you’re connecting to was local.
To create a new remote file share connection, you have two options with net use. You can either create what Microsoft calls a “deviceless” connection which is simply a file share connection without a drive letter or a mapped drive.
Mapping Network Drives Using Logged-In Credentials
Mapping network drives is one of the most common uses of the net use command. This command allows you to map a network drive on the command line much like you would via File Explorer.
Assuming you’re on a Windows 10 PC in a domain environment with a Windows server hosting a file share:
1. Open a command prompt or PowerShell console as administrator.
2. Let’s map the drive letter F: to the DEVSRV server file share C$. To do so, specify the drive letter to map the network drive to followed by the UNC path of the remote file share.
You can use any letter to map the network drive to if it’s not already in use.
If the file share has spaces in it, always be sure to surround it in quotes e.g.
\\DEVSRV\"My File Share".

3. Now run net use with no parameters to confirm Windows mapped the drive correctly.

4. Open File Explorer and you’ll also now notice a new network location.

If you don’t care what device (drive letter) to map the drive to, you can also use an asterisk (*) for the drive letter. Doing so will tell Windows to find the next available drive letter.

Mapping Network Drives Using Alternate Credentials
If you went through the demo above and mapped a network drive, you did so authenticating as the logged on user. But what if you need to authenticate to the remote file share using alternate credentials?
Mapping a network drive authenticating as a non-logged-in user account is nearly the same as with a logged-in account. The only difference is using a couple more parameters.
To map a network drive with alternate credentials, open a command prompt or PowerShell console as an administrator.
Run net use providing:
- The drive letter to map to
- The UNC path of the file share
- The username to authenticate with (
/u) - The password
In the below example, Windows will map the F: drive to the \\DEVSRV\c$ file share authenticating as the test_user account in the domain domain using the password of passwordhere.
net use f: \\DEVSRV\c$ /u:domain\\test_user passwordhereSpecify a local user account on the remote computer by removing the domain from the username parameter e.g.
/u:test_user.
Use the
/savecredparameter to save the credentials to prevent being prompted the password later.
Create “Deviceless” Connections (No Drive Letter)
Perhaps you need to use a remote file share but you don’t want to map a drive letter to it. In that case, simply remove the drive letter.
Let’s create a file share connection without a drive letter known as a “deviceless” connection. Assuming you’re on a Windows 10 PC in a domain environment with a Windows server hosting a file share:
1. Open a command prompt or PowerShell console as administrator.
2. Create the “deviceless” connection by specifying the UNC path to the remote file share a username and password to authenticate and hitting Enter.
net use \DEVSRV\c$ /u:domain\test_user passwordhereIf your client computer and remote Windows server are in an Active Directory domain and you’re logged into your client computer with a domain user account, it doesn’t typically make sense to use
net usein this situation. You can already access these resources with no extra steps. But when you need to authenticate with an alternate user account, that’s where it comes in handy.
The connection has been made but if you look in File Explorer, you’ll see no connection. This connection is “deviceless”.

3. Now, confirm the connection has been made by running net use with no parameters. You can see below that Windows knows a connection is there.

At this point you can now navigate and work with the file share just as if it was local to you using the alternate user account credentials.

Persistent Connections
Whenever you establish new connections, Windows can keep those connections around after a reboot or not called persistence. The net use command has a parameter called /persistent that defines whether or not a connection remains after a reboot.
To ensure a connection stays around, add the /persistent parameter to any attempt to create a new connection like:
net use \\DEVSRV\c$ /persistent:yesMapped drives are not persistent, by default.
Windows will remember the last created connection’s persistence setting. If you set
/persistenttoyesfor a connection, all subsequent connections will be persistent if you do not explicitly set/persistenttono. To ensure all connections are persistent in the current session, usenet use /persistent:yes.
Advanced Connection Parameters
Most of the time, you’ll only need the parameters discussed earlier to create a connection. But, you may run into situations where you’ll need to perform some advanced connection tasks
Mapping Drives with Write Through (Forced Unit Access)
Added in Windows 10 build 1809, you can use the /writethrough parameter to map a drive bypassing all OS caches and forcing I/Os through to disk.
Increasing Security
The net use command also has two advanced parameters that increase security; /reguireintegrity and /requireprivacy through a feature called UNC Hardened Access. This feature “tags” information on these shares to inform Multiple UNC Provide (MUP) and UNC providers of additional security requirements
Using the /requireintegrity parameter ensures additional integrity checks to block tampering attacks.
The /requireprivacy parameter instructs net use to use encryption to prevent third parties from seeing any sensitive information in the file share communication.
Removing Network Connections
Finally, if you’ve set up some connection and need to get rid of them, the /delete parameter is your friend. To remove a non-persistent connection, provide the /delete parameter and the UNC path to the network share as shown below.
net use /delete \\devsrv\c$
To remove a mapped drive, provide the drive letter and the mapped drive
net use f: \\devsrv\c$ /delete Conclusion
You should now have a good idea of just about everything you can do with the net use command. This old-school yet handy command is still in use today and can still help you map network drives in Windows.
How are you going to use net use?
The Net Use command is a pretty old command that is still commonly used to connect network drives in Windows. The advantage of the Net Use command is that it allows you to quickly add, view, and delete network resources from your computer.
The command is capable of connecting to all kinds of network resources. But most of the time it’s used to connect to network shares.
In this article
In this article, we are going to take a closer look at the Net Use command. I will explain how you can view, add, and delete network shares from the cmd line.
Before we are going to take a look at how to add a network drive, we first going to list the existing connections. If you simply type the command Net Use you will get an overview of all existing network connections and their status.
Now you could also open explorer to see all network drivers. But the advantage of Net Use is that it will also list any hidden network connections that are created with a group policy.
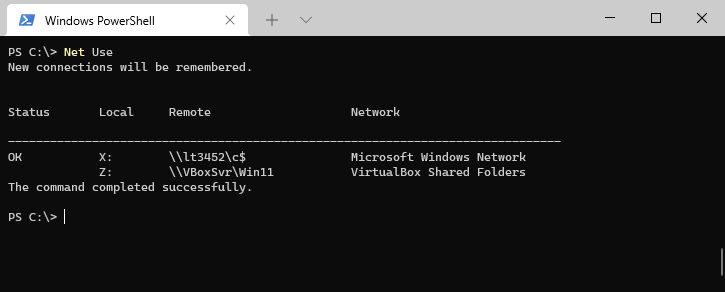
Open the command prompt or PowerShell and type:
Net Use
This will show a list of all connections and the status of the connection:
We can also view the details of each connection with net use <driveletter>. This is really handy if you want to check if a particular network drive is currently used or if you want to know more about the resource type.
# Type Net use followed by the drive letter Net Use X:
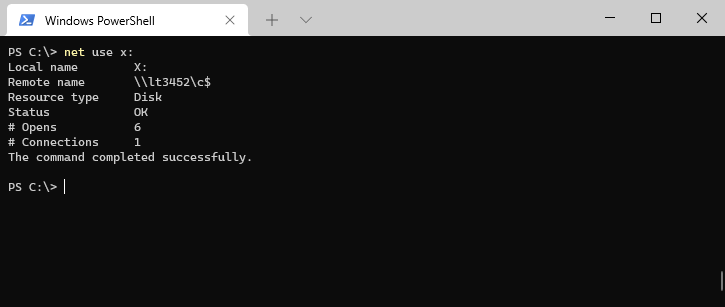
Add Network Connection with Net Use
The Net Use command is commonly used to add or remove network connections from a computer. One of the advantages of using a command for this is that you can add a drive letter after somebody logs in. Or easily create a script that will add the network connection on multiple computers.
Let’s start with simply adding a network drive to the computer. We are going to make a connection to the \\VBoxSvr\Win11\Documents and assign the drive letter H: to it. \\VBoxSvr is the name of the computer or server. Win11 is the shared folder and Documents is a subfolder.
Net use h: \\VBoxSvr\Win11\Documents
After you have run the command you will see the drive mapping in the explorer.
You can choose any available drive letter from A to Z (c is often taken for your system drive) for shared folders and LTP1: to LTP3: for printers. It’s also possible to automatically assign a drive letter by using * . This way the Net Use command will automatically select the highest available drive letter, starting with Z:
# Pick the first available drive letter: Net use * \\VBoxSvr\Win11\Documents
Net Use Persistent
By default, the network resources that you add with Net Use are only temporary. After you log off or reboot the mapping will be gone. However, most of the time you want the drive mapping to be persistent.
To make a drive mapping persistent we will need to add the parameter /persistent:yes to the command:
Net use h: \\VBoxSvr\Win11\Documents /persistent:yes # or in short: Net use h: \\VBoxSvr\Win11\Documents /p:yes
Note
All other drive mappings that you add in the same session after you have used
/persistent:yeswill also be persistent. So to make a temporarily drive mapping after a persisitent one, you will need to use/persistent:no
Mapping Network Drive with different credentials
Your computer will use your current credentials when mapping a shared network folder. But often you will need to supply different credentials for the network resource. With Net Use we can supply the username and password that needs to be used to open the network resource.
It’s possible to enter the password as plain text in the command:
# Authenticate with the username VboxSrv\user1 and password Passwrd123 Net use h: \\VBoxSvr\Win11\Documents /user:VboxSrv\user1 Passwrd123 /p:yes
But another option is to use a * symbol, after which you will be prompted to enter the password:
Net use h: \\VBoxSvr\Win11\Documents /user:VboxSrv\user1 * /p:yes
The only problem with this is that the password is forgotten after a reboot. So you will need to reenter the password every time you open the network connection. We can solve this by using the parameter /savecred.
There is one catch, however, to use /savecred you must not supply the username and password. Otherwise, you get the error “A command was used with conflicting switches”. The /savecred parameter will use the stored credentials on your computer. If it doesn’t find credentials for the connection it will ask for it:
PS C:\> net use * \\VBoxSvr\Win11 /savecred /p:yes Enter the user name for 'VBoxSvr': lazyadmin\user01 Enter the password for VBoxSvr: Drive Y: is now connected to \\VBoxSvr\Win11. The command completed successfully.
Unmap Network Drive
We can also use the Net Use command to unmap a network drive in Windows. The first step is to list the existing connections by simply typing net use in the command prompt or PowerShell window.
Next, we can type net use followed by the drive letter that we want to remove. Instead of a drive letter, you can also supply the remote target path:
Net use Y: /delete # Or Net use \\VboxSvr\Win11 /delete
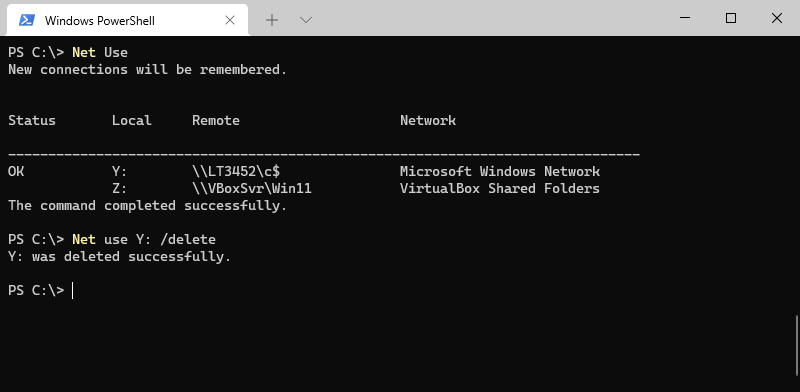
Mapping users home directory
When the user’s home directories are stored on a network share then you can easily map their home folder with the net use command. For this, you will need to have a domain with the home directory path configured in the Active Directory.
To map the user’s home folder you use the following command:
Net Use h: /home
Wrapping Up
The Net Use command is an old but useful command. I still use it often to get a quick overview of the mapped (hidden) network drives on computers or in local home networks to map a NAS for example.
When using the command, make sure that you use the /persistent:yes parameter so the mapping stays in place after a reboot.
If you have any questions, just drop a comment below.
Если вы часто пользуетесь общими папками на компьютерах, расположенных в вашей локальной сети, то вы можете подключить эти папки как сетевые диски. После этого данные папки появятся в окне «Этот компьютер» и работать с ними станет намного проще. В этом материале мы рассмотрим два способа подключения сетевых дисков на компьютере с Windows 10.
Подключение сетевого диска в Windows 10
Самый простой способ подключения сетевого диска – это подключение через Проводник. Для этого откройте папку «Этот компьютер», где у вас расположены все диски, перейдите на вкладку «Компьютер» и нажмите на кнопку «Подключить сетевой диск».
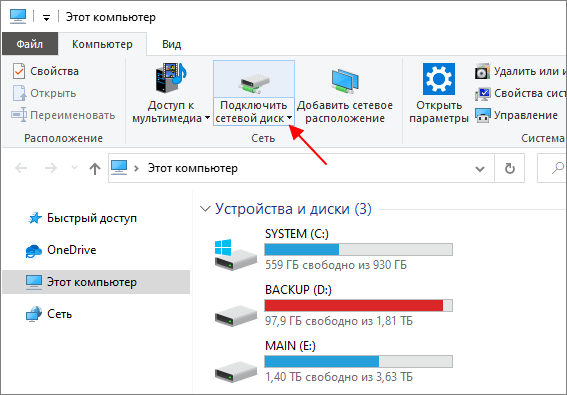
После этого отроется окно с настройками подключения сетевого диска. Здесь нужно указать букву, которой будет обозначаться сетевой диск после подключения, а также указать путь к общей папке, которую нужно подключить как сетевой диск.
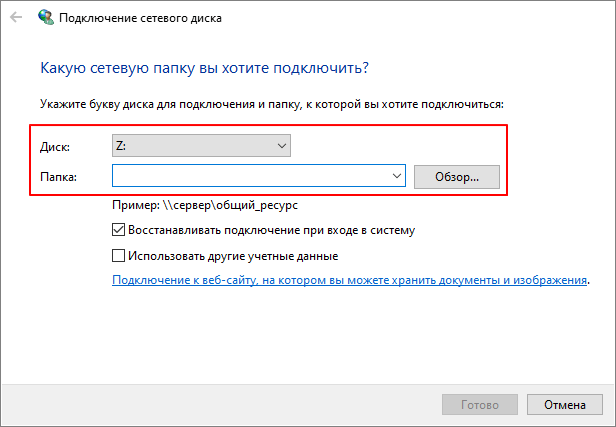
Путь к сетевой папке должен иметь следующий формат:
\\IP адрес или имя компьютера\имя папки
Например, нам нужно подключить общую папку «test», которая находится на компьютере с IP-адресом «192.168.1.235», то путь будет выглядеть следующим образом:
\\192.168.1.235\test
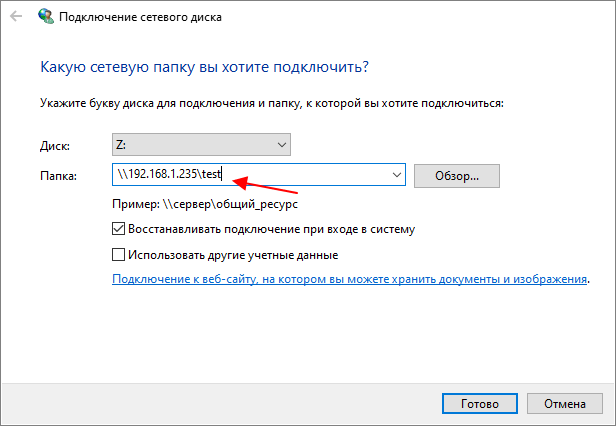
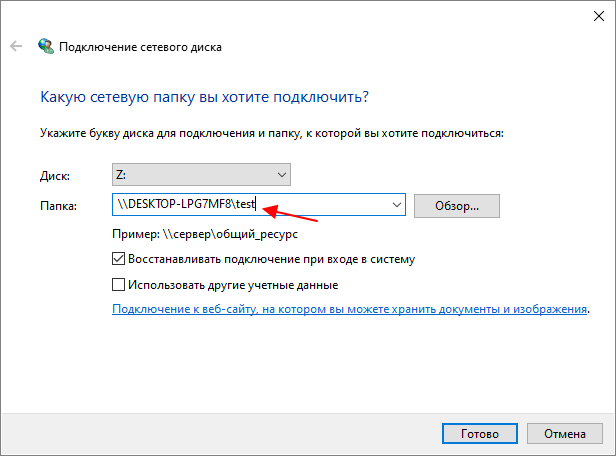
Также вместо IP-адреса можно ввести имя компьютера. Например, если имя компьютера «DESKTOP-LPG7MF8», то путь к сетевой папке будет выглядеть так:
\\DESKTOP-LPG7MF8\test
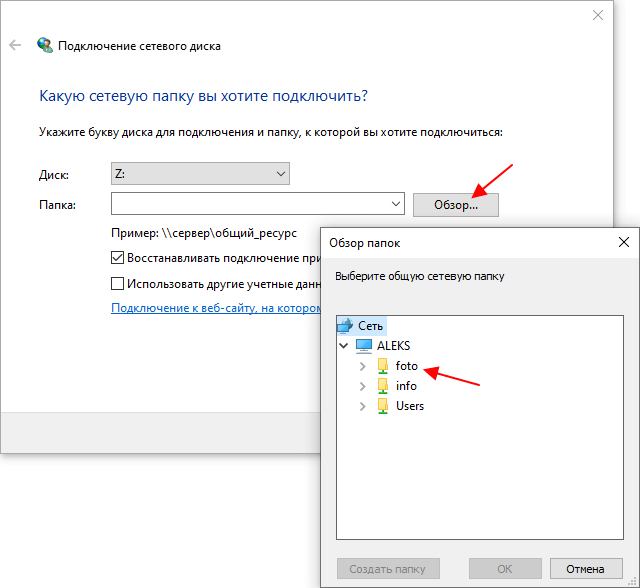
Кроме этого, компьютер и общую папку можно найти с помощью кнопки «Обзор». Но, этот способ работает не всегда, во многих случаях нужный компьютер просто не отображается. В таких случаях нужно указывать IP-адрес или имя компьютера, так как это описано выше.
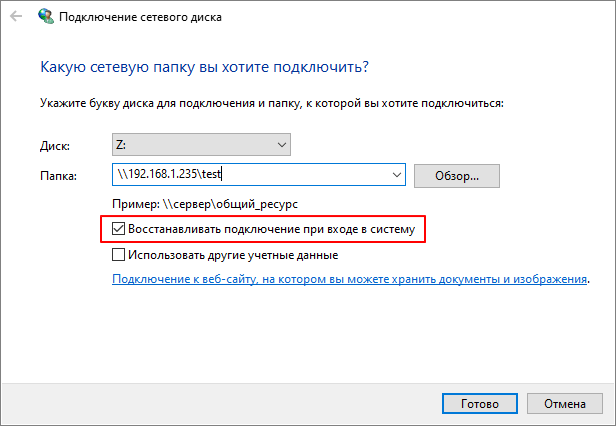
Еще один важный момент – опция «Восстанавливать подключение при входе в систему». Если она включена, то сетевой диск будет автоматически подключаться каждый раз при включении компьютера.
После того как все нужные настройки указаны, нужно нажать на кнопку «Готово».
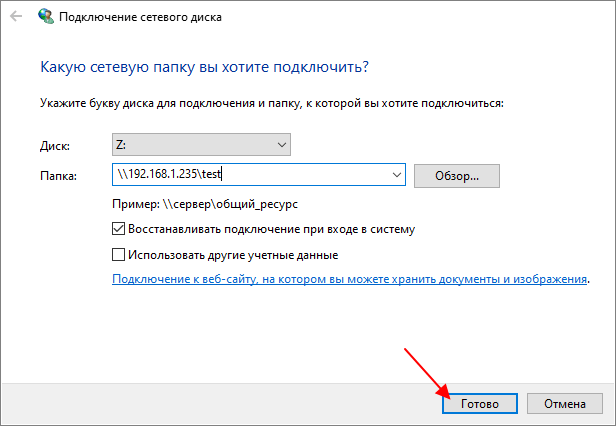
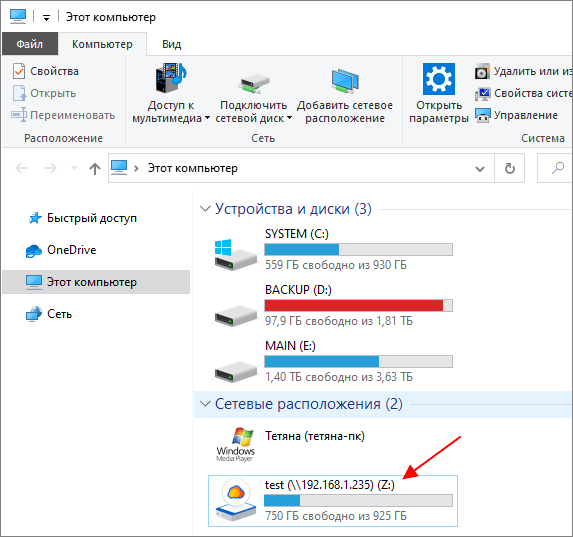
Если все было сделано правильно, то в окне «Этот компьютер» в блоке «Сетевые расположения», должен появиться подключенный сетевой диск.
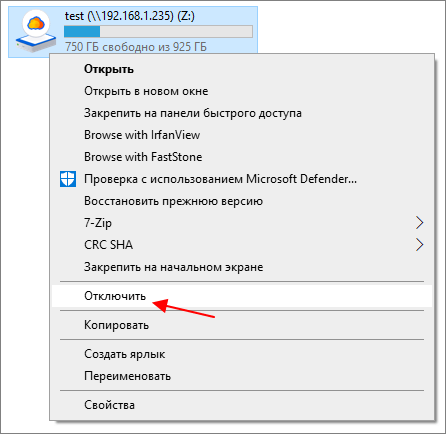
Для отключения сетевого диска нужно кликнуть по нему правой кнопкой мышки и выбрать пункт «Отключить».
Подключение сетевого диска через командную строку
Также сетевой диск можно подключить через командную строку при помощи команды «net use». Данная команда имеет множество параметров, с которыми можно ознакомиться на сайте Майкрософт. Здесь же мы рассмотрим только самые простые варианты, которые будут полезны обычным пользователям.
Самый простой вариант использования команды «net use» выглядит так:
net use <буква:> <путь>
Где «буква» — это буква диска, которая будет присвоена сетевому диску после подключения, а «путь» — это путь к сетевой папке, которую нужно подключить как диск. Формат пути к папке точно такой же, как это было описано выше.
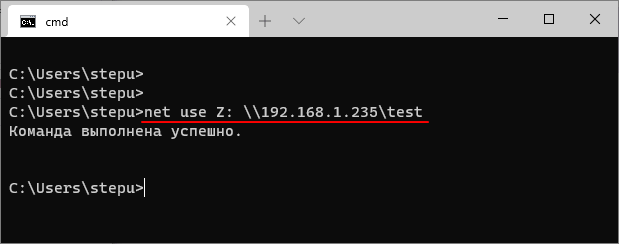
Например, для того чтобы подключить общую папку «test», на компьютере с IP-адресом «192.168.1.235», нужно выполнить следующую команду:
net use Z: \\192.168.1.235\test
Для того чтобы подключенные сетевые диски восстанавливались после перезагрузки нужно выполнить:
net use /Persistent:Yes
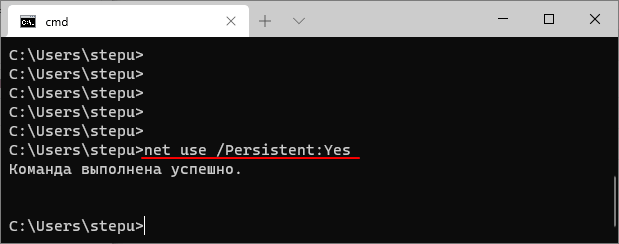
Для отключения сетевого диска с буквой «Z:» нужно выполнить:
net use z: /delete
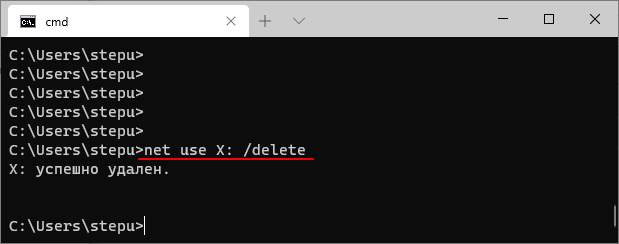
Для просмотра доступных общих папок на удаленном компьютере с IP-адресом «192.168.1.235» нужно выполнить:
net view 192.168.1.235
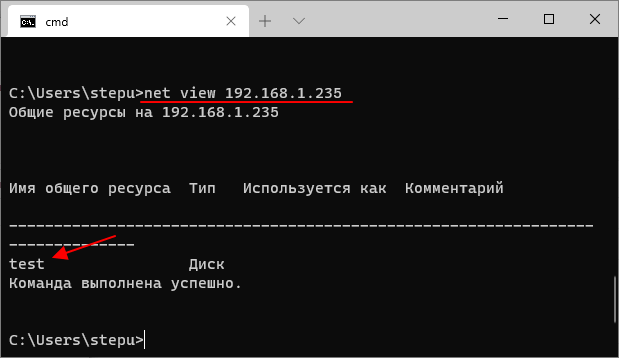
Если сетевой диск не подключается, то нужно проверять доступность компьютера и общей папки. Попробуйте выполнить команду «PING» с указанием IP-адреса компьютера с общей папкой и повторно открыть общий доступ к папке. О том, как это делается можно прочитать в наших статьях:
- Как открыть общий доступ к папке на Windows 10
- Как проверить Ping на Windows 10
Посмотрите также:
- Схема обжима витой пары
- Как узнать какая сетевая карта стоит на компьютере
- Как узнать MAC адрес компьютера на Windows 10
- Как найти все папки с общим доступом на Windows 10 или Windows 7
- Как расшарить принтер по сети в Windows 10
Автор
Александр Степушин
Создатель сайта comp-security.net, автор более 2000 статей о ремонте компьютеров, работе с программами, настройке операционных систем.
Остались вопросы?
Задайте вопрос в комментариях под статьей или на странице
«Задать вопрос»
и вы обязательно получите ответ.
