В случае, если вам потребовался доступ из Windows к данным на разделе диска с файловой системой Linux — ext4/ext3/ext2, встроенными средствами системы сделать это не получится. Однако, возможности есть, причем реализовать это можно встроенными средствами системы или с помощью сторонних инструментов.
В этой инструкции подробно о способах подключить раздел диска в файловой системе Linux в Windows 11 и Windows 10 для доступа к данным на этом разделе как для чтения, так и для записи.
Ext2 File System Driver (Ext2Fsd) — самый простой способ открыть раздел ext4/ext3/ext2 в Windows
Ext2 File System Driver или Ext2Fsd — сторонний и полностью бесплатный драйвер для подключения разделов Linux во всех версиях Windows начиная с XP. Несмотря на название, поддерживаются не только разделы не только с файловой системой ext2, но и более новые ext4 и ext3.
Порядок использования Ext2 File System Driver для доступа к дискам Linux будет следующим:
- Загрузите установщик Ext2Fsd с сайта https://sourceforge.net/projects/ext2fsd/
- Установите драйвер, в параметрах установки как правило не требуется ничего изменять.
- По завершении установки вам будет предложено запустить Ext2 Volume Manager (менеджер томов), запустите его.
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по разделу Linux ext4, ext3, ext2 и выберите пункт «Assign Drive Letter» — назначить букву диска.
- Для раздела будет автоматически назначена буква диска, и вы увидите раздел в Проводнике Windows с возможностью чтения и записи файлов на нём.
В дальнейшем вы тем же способом сможете удалить букву диска с раздела (опция «Change letter» — «Remove»).
Доступ к разделам Linux средствами Подсистемы Windows для Linux (WSL)
Подсистема Windows для Linux (WSL) также может быть использована для подключения дисков Linux в Windows таким образом, чтобы доступ к ним был возможен из проводника. Шаги будут следующими:
- Запустите командную строку, Терминал или PowerShell от имени администратора и по порядку введите команды
wsl --install wsl --set-default-version 2 dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart wsl --install -d Ubuntu
- После выполнения последней команды откроется окно консоли Linux (командную строку при этом не закрывайте, она еще пригодится) с предложением настроить имя пользователя и пароль, сделайте это. Если в окне консоли вы увидите сообщение об ошибке, скачайте и установите обновление WSL, перезагрузите компьютер и запустите Ubuntu из меню «Пуск».
- В консоли Ubuntu введите команду
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/ext-drives/
для создания папки, к которой будут монтироваться диски.
- В консоли Windows (командная строка, терминал, Powershell) введите команду
wmic diskdrive list brief
- Обратите внимание на DeviceID диска, который нужно подключить и введите команду (так же в консоли Windows) указав соответствующий номер в имени PHYSICALDRIVE
wsl --mount \\.\PHYSICALDRIVE
- В консоли Ubuntu введите команду lsblk — это отобразит список подключенных дисков, разделов на них и их размер. В следующей команде используем имя нужного раздела для монтирования:
sudo mount /dev/sdИМЯ /mnt/ext-drives/
- После успешного выполнения всех указанных шагов вы можете зайти в Проводник Windows, выбрать пункт «Linux» в панели быстрого доступа, перейти в папку mnt\ext-drives и получить доступ к файлам на подключенном разделе Linux с возможностью записи и чтения.
В дальнейшем для отключения диска от WSL можно использовать ту же команду, которая использовалась на 5-м шаге, заменив mount на unmount.
Есть и другие программы (драйверы) для доступа к разделам Linux из Windows, но не полностью бесплатные. Среди них:
- DiskInternals Linux Reader — в бесплатной версии доступно только чтение данных с разделов.
- Paragon Linux File Systems for Windows — бесплатная работа в течение пробной версии, затем необходимо приобретать лицензию.
Position : Tips — How to Read and Write EXT4, EXT3 and EXT2 Drives in Windows 10/11?
This guide shows how to read and write data of Linux Ext2/Ext3/Ext4 partitions in Windows 11/10/8/7/Vista/XP. If you dual boot your computer with Windows and Linux, you’ll be able to access NTFS or FAT32 partitions under Linux, but you cannot access Linux partitions directly under Windows. If you need to read Ext4, Ext3 or Ext2 partitions under Windows 10/11 without booting into Linux, here is the tutorial that can help you.
Overview on reading Ext4/3/2 drives in Windows
«My computer is in a dual-boot environment with Windows 10 and Ubuntu. They are installed on one hard drive which is divided into two partitions C and D. Sometimes I want to grab files from Linux partition while computer has booted into Windows 10. It’s way too trouble to restart into Linux and copy files to a FAT32 partition and reboot back into Windows 10. Anyone here knows how to access Ext4 partitions from Windows 10?»
If your computer is dual-booting with Windows and Linux, you must have trouble in accessing files and folder stored in Linux partitions while Windows is running. The default file system type used on Windows and Linux are different, Windows users NTFS, exFAT, or FAT32, while Linux employs Ext2, Ext3, or Ext4 file systems. Besides, Linux has support for NTFS and FAT32 file system, which enables users to access files on Windows partitions. However, on the other hand Windows does not have inbuilt support for Linux partitions.
Therefore, you may come across such a situation that if you are using Windows and Linux together on a computer. You may need to use some files you downloaded in Linux, and you are logged into Windows OS already. Since you cannot access Linux partition directly, you’ll have to restart computer and boot to Linux, copy these files to a NTFS or FAT32 partition and then reboot computer to Windows. Wouldn’t it be better if you can access Linux partitions from Windows?
Nowadays, many users would like to dual boot Linux and Windows on one PC, and they often need to transfer data between two systems. Since Windows does not provide built-in tools to mount Linux partitions, we need to use third-party software to read & write data in Ext4/3/2 partitions. This article will introduce an effective tool to solve the problem. Keep reading the guide, you’ll be able to know how to mount and access files in Linux partitions under Windows 10/11.
Windows & Linux file systems
Some readers may wonder what a file system is. A file system is the tool for operating system to control, store, retrieve and organize files on a storage device. Why are there so many file system types? Different operating systems use and support specific types of file systems, for they target different users. For instance, Windows NT targets enterprise users and uses NTFS file system which enhanced security greatly; Windows 9X targets ordinary users and uses FAT file system which has less security but more performance.
As we all know that Windows and Linux uses different file systems: Windows uses NTFS, exFAT, and FAT32 file system, whereas Linux uses Ext2, Ext3 and Ext4. Thus, users cannot copy a file from Linux to Windows directly. It is quite complicated for an OS to add the support of a particular file system, especially adding support for proprietary file system. For example, the structure of data on disk, encryption algorithm and so on of NTFS file system are not known to the public, and it is very challenging to fully support NTFS in Linux.
Windows does not have native support for Linux file system like Ext2, Ext3 and Ext4. However, some tools have been created to solve this issue. Such software supports Linux file system and allows users to access Linux partitions under Windows. The follow section will introduce a Windows partition manager that can mount and access Linux partition from Windows.
Ext4/3/2 reader for Windows
If you have Windows and Linux on the same PC and want to access data of an EXT4 partition under Windows 10/11, then you need to use third-party software to read & write data in EXt4 partitions. Here we recommend DiskGenius Professional Edition to solve the problem. DiskGenius Professional Edition (formerly known as PartitionGuru) is advanced Windows partition manager and data recovery software. It can handle partitions formatted as NTFS, FAT32, FAT12, FAT16, exFAT, ReFS, Ext2, Ext3 and Ext4 file system from Windows.
Download DiskGenius
With this tool you can do following operations:
- Full access (write & read) to Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4 partitions under Windows
- Create Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4 partitions under Windows 11/10/8/7
- Format a drive to Ext4/3/2 in Windows 11/10/8/7
- Resize, shrink, extend, or split Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4 partitions without deleting data
- Partition recovery — recover lost or deleted Ext4/3/2 partitions in Windows
- File recovery – recover deleted or lost files from Ext4/3/2 partitions in Windows
- Clone or back up Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4 partitions
- Edit hex data of Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4 partitions
- Check and repair disk bad sectors
Guide 1. How to mount Ext4/Ext3/Ext2 partitions in Windows 10/11?
Mounting Ext4 partitions in Windows is the first step before we can read or write data in the volume. Now we can use DiskGenius to open the Ext4 partition.
Step 1. Connect the disk that contains Ext4 partitions to your computer and boot your PC into Windows 10.
Step 2. Download and install DiskGenius Professional Edition on your PC and then launch it.
Step 3. Once DiskGenius is launched, you can view all disks and partitions attached to this computer. Select the Ext4 partition and you can browse files and folders in it.
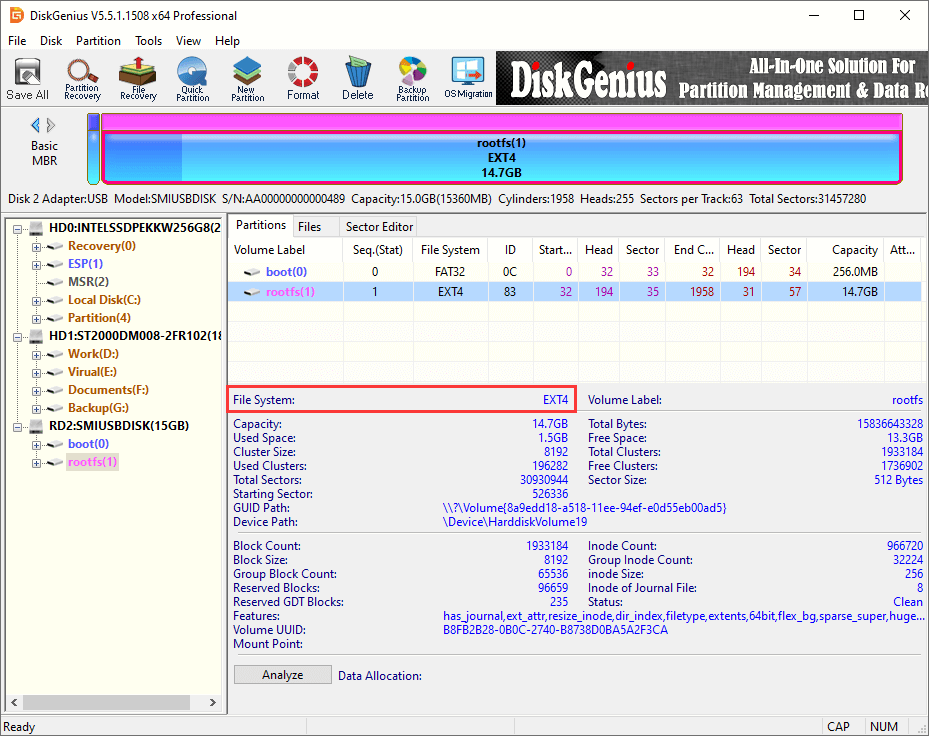
Step 4. Select the Ext4 partition and click Files tab, and you can see data in the root directory. Then you can double click a folder to open it and view files in it.
Guide 2. How to read files of Ext4 partitions in Windows 10/11?
Once the Ext4 partition is recognized by DiskGenius, you can read & write files in the partition.
File paths and directories are listed in the left pane like Windows File Explorer, and you can click path and view files on the right pane. Click a file on the right pane, and you can see the thumbnail preview, as follows.
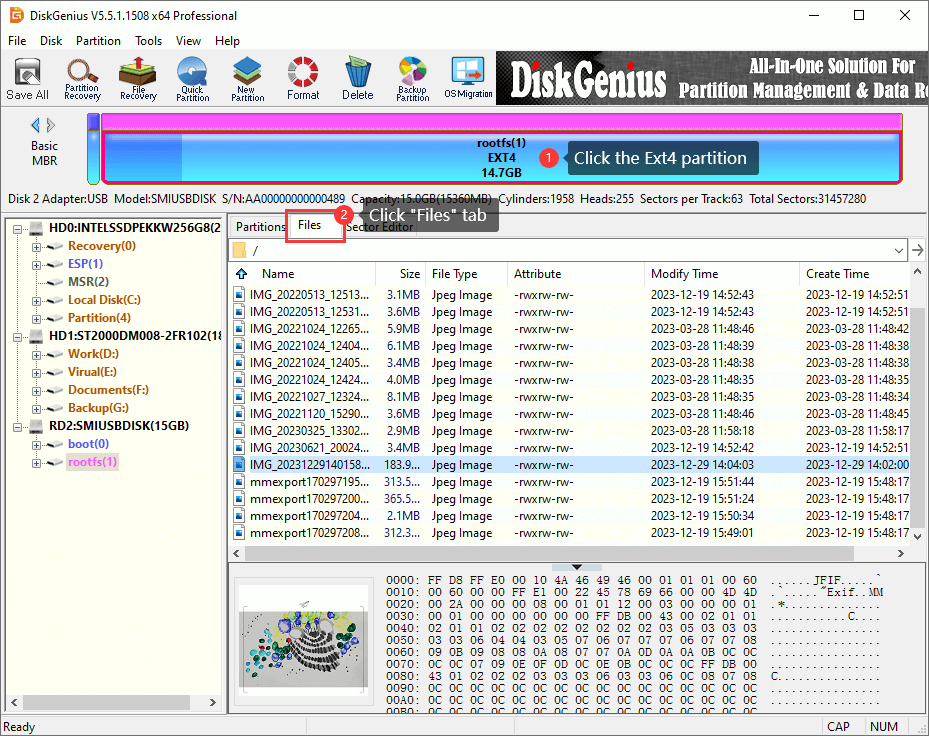
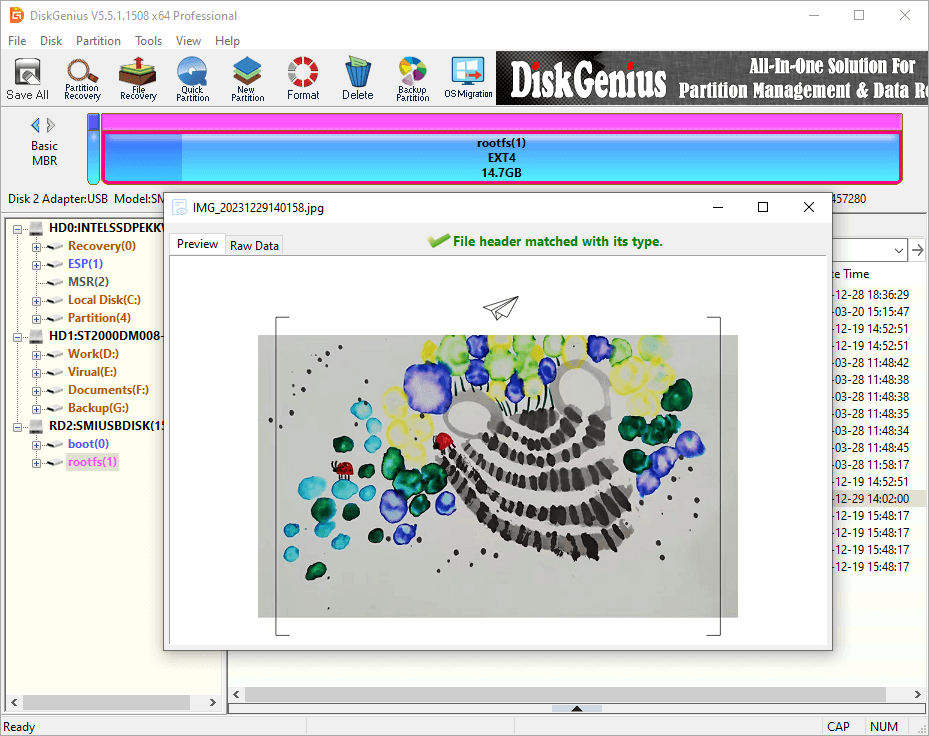
You can double-click the file to open it and view file content in its original size. This tool supports to preview photos, audio, video, Microsoft Office documents, PDF files, and text files.
Guide 3. How to write data into Ext4 partitions in Windows 10/11?
With DiskGenius Professional Edition, you can create new folders in the Ext4 partition, write files to this Ext4 partition, rename files and folder, delete files, export files of the Ext4 partition to another drive, etc. Here are some examples:
Example 1: Write files to Ext4 partitions
Step 1. Open the folder where you want to add data and right-click empty space on the right pane to choose «Copy Files To Current Partition«.
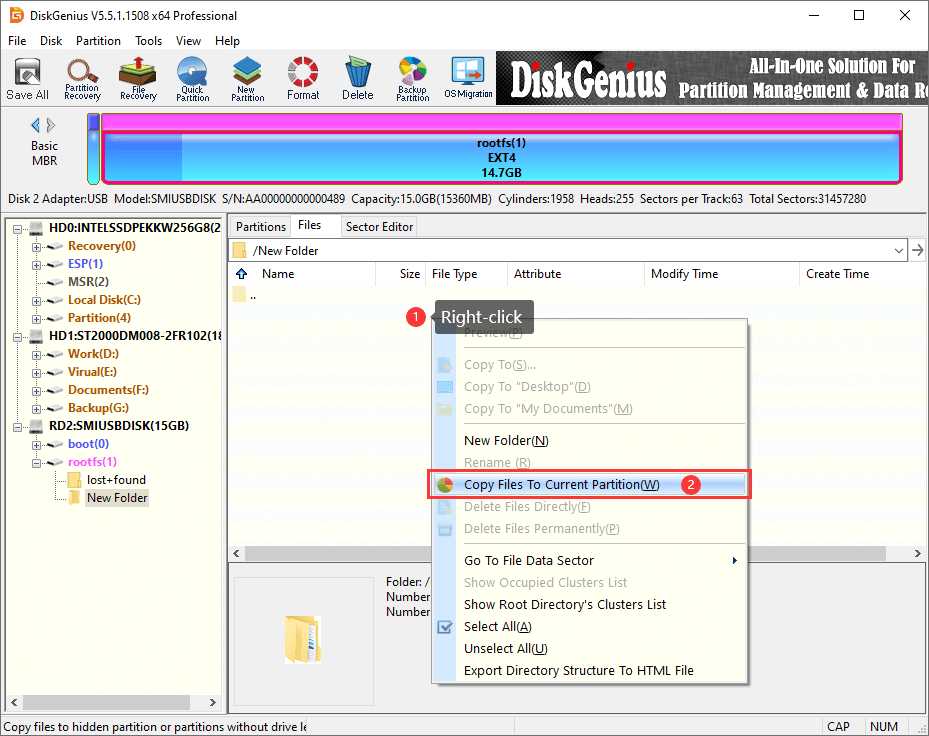
Step 2. Select files from other partitions or hard drives on your computer and Open. Wait for a while, and files will be write into this Ext4 partition.
Tip: This software also allows users to export files from the Ext4 partition to another partition on this computer: Select files you want to output -> right-click files and select «Copy To» -> select target location — > begin outputting files.
Example 2: Permanently delete files from Ext4 partitions
This feature is able to delete files permanently so that they cannot be recovered by any means, as the software overwrites the disk space while deleting files. If you just want to delete files, you can use Delete Files Directly
Step 1. Select and right-click files you want to delete and select «Delete Files Permanently» option from context menu.
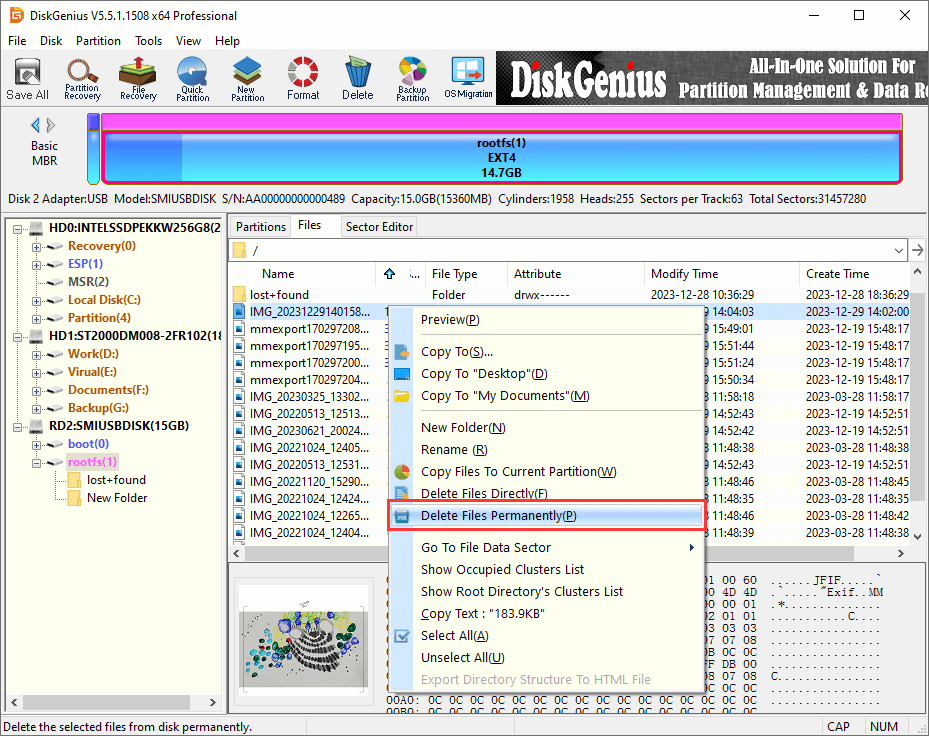
Step 2. Click «Permanently Delete» button on the popup window. Then the selected file will be deleted permanently.
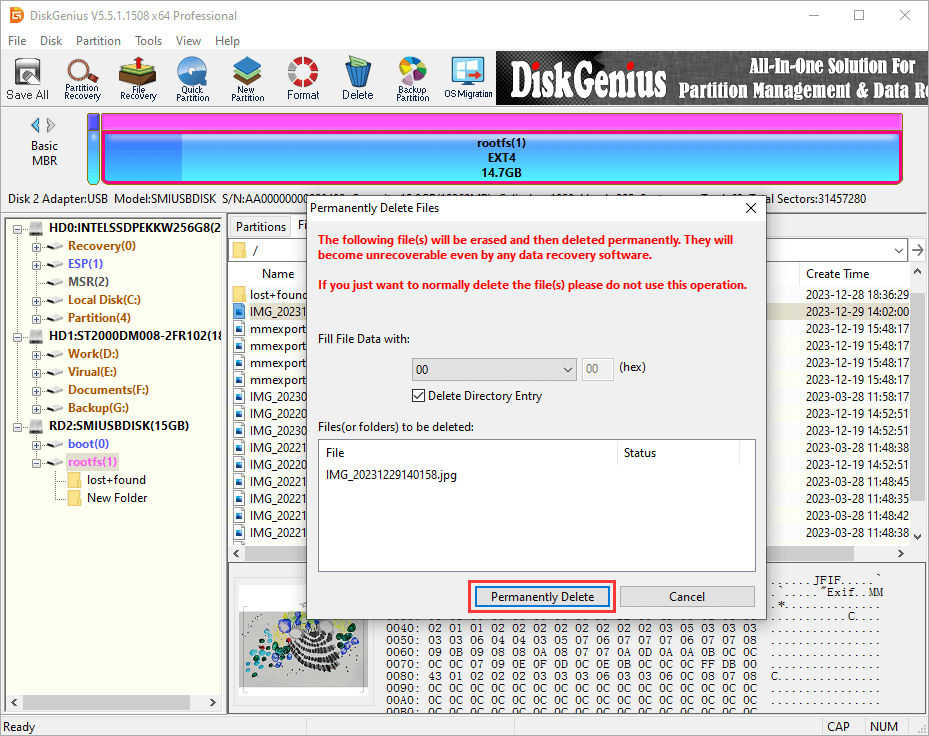
Example 3: Rename files or folders in Ext4 partitions
In addition to creating new folders, you can also rename files or folders in the software as follows:
Step 1. Right-click on a file or folder you want to change name and select «Rename«.
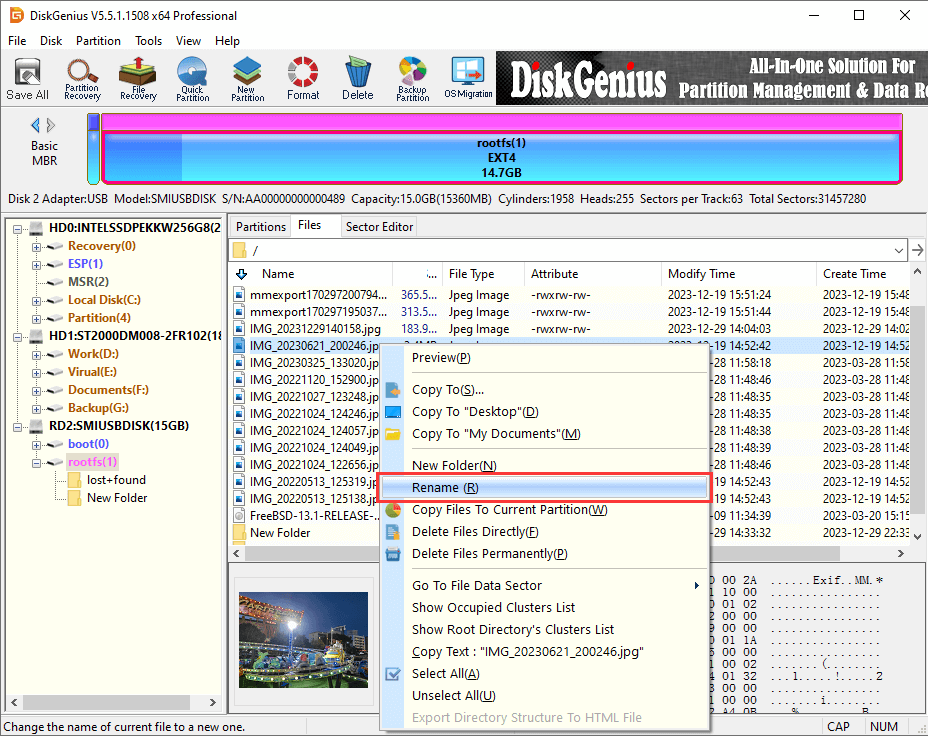
Step 2. Put in the desired name and click «OK» button.
Guide 4. How to resize Ext4 partitions without losing data in Windows 10/11?
The feature of resizing Ext4 partition without losing data is available for the DiskGenius Free Edition, and you can free download the free edition to resize, extend, or split an Ext4, Ext3 or Ext2 partition without deleting existing data in Windows 11/10/8/7.
Step 1. After launch DiskGenius, you can easily locate the Ext4 partition. Right-click it and choose «Resize Partition».
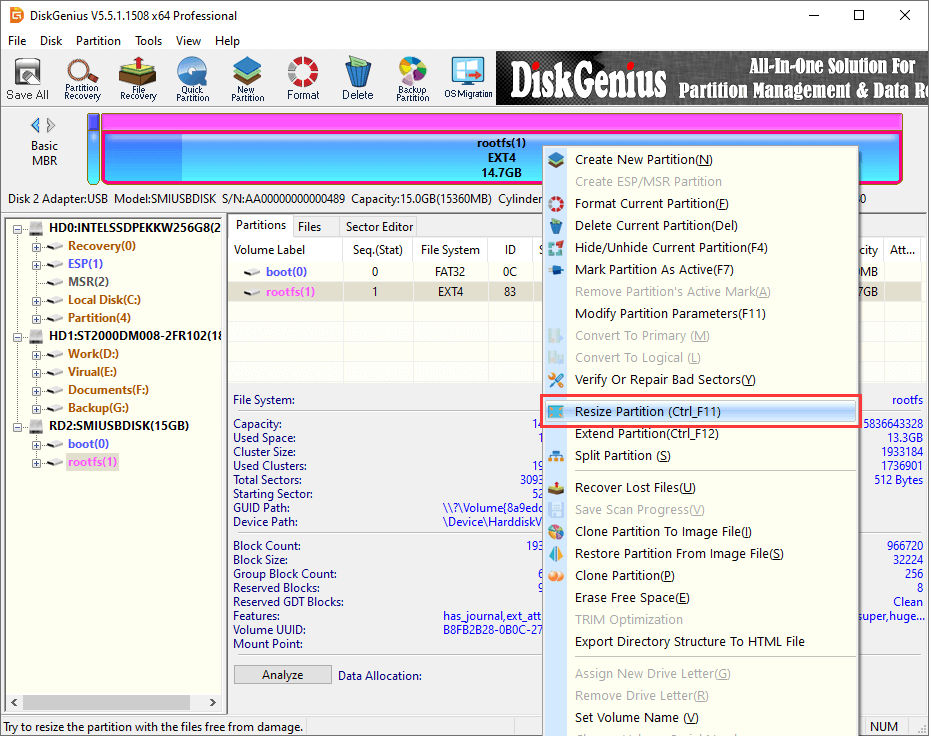
Step 2. Adjust partition size based on your needs. You can change partition size either by manually inputting the size or by dragging the partition boundaries.
The free disk space gained from the partition can be left as unallocated or created as a new partition.
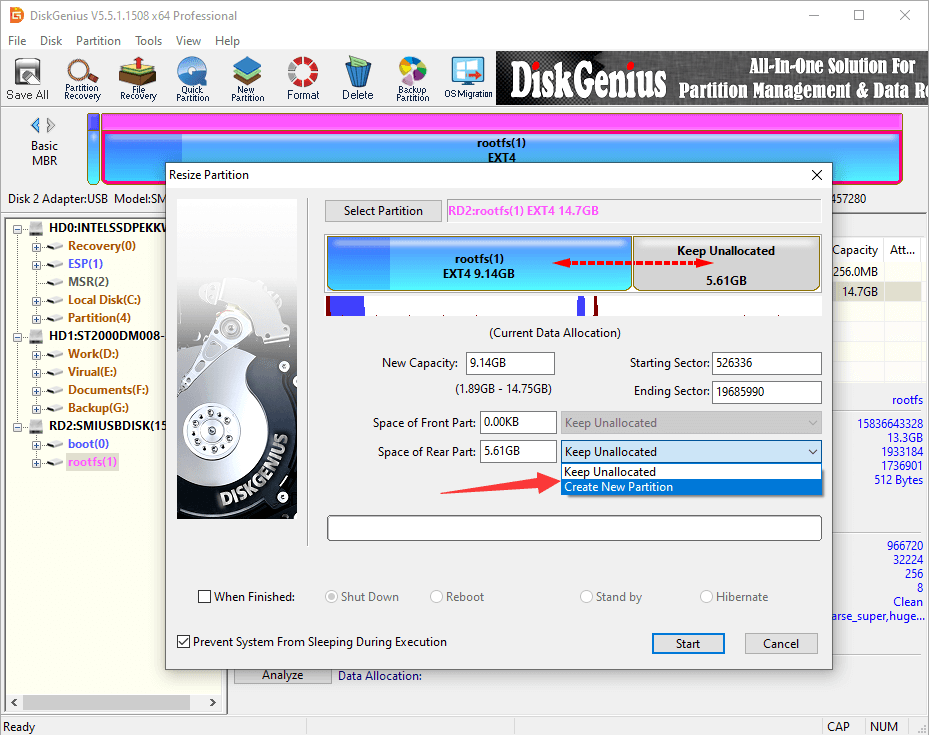
Step 3. Carefully read the notes. Click «Yes» to confirm and continue.
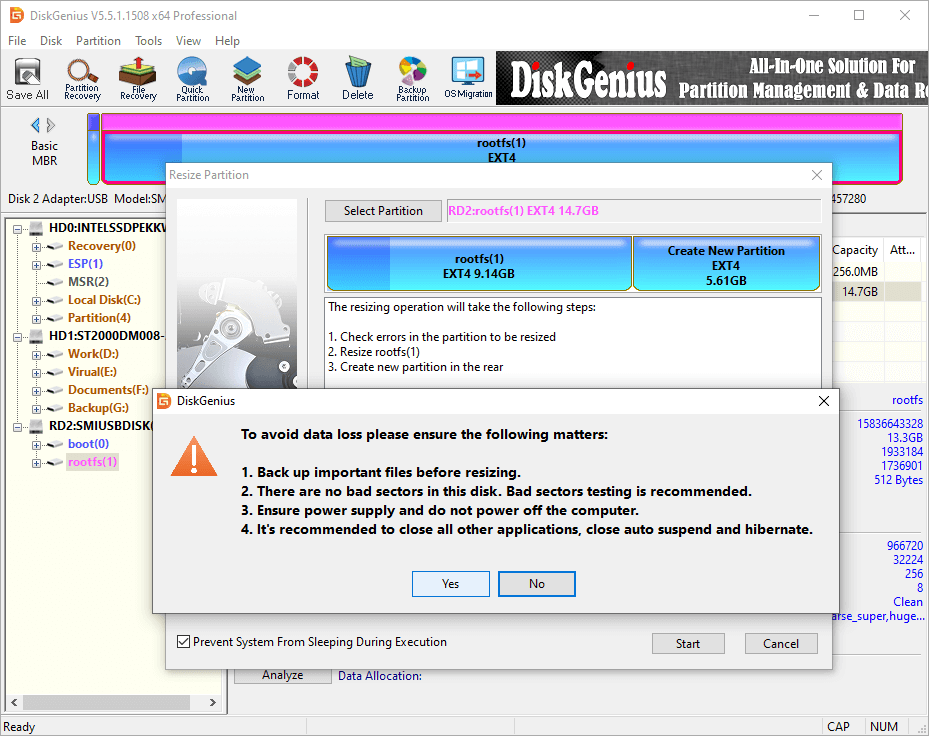
Step 4. DiskGenius is resizng the partition. The process might take some time depending on the size of the partition and the amount of data stored on it. Please be patient.
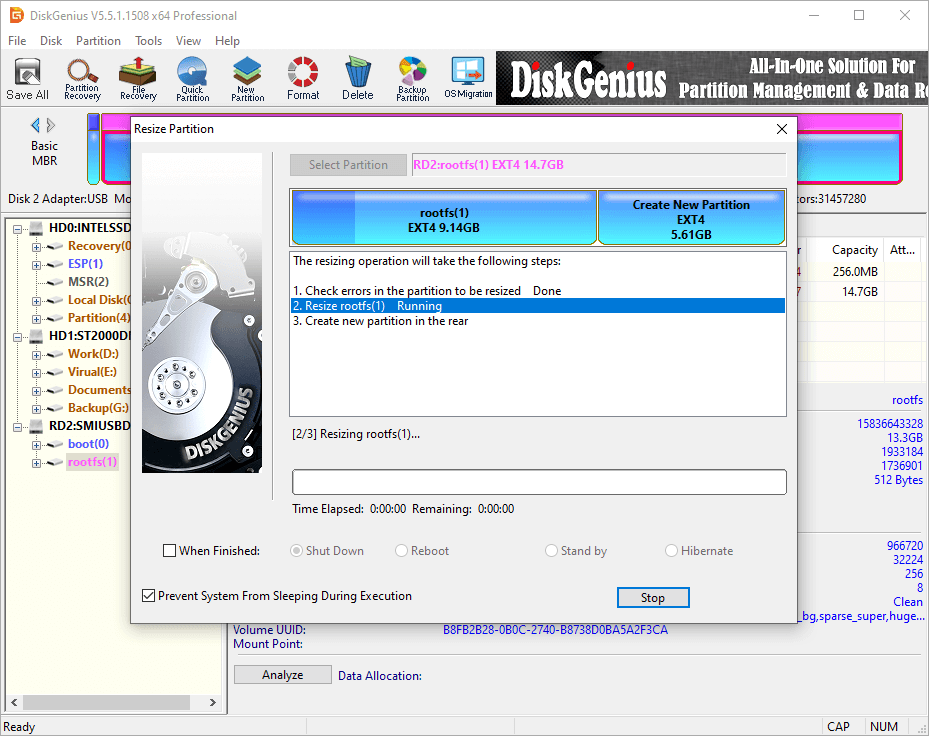
Guide 5. How to format a drive to Ext4/3/2 in Windows 10/11?
DiskGenius Free Edition support creating or formatting Linux-specific file systems like ext4, ext3, or ext2 within Window. The following steps shows how to format a partition to Ext4 using DiskGenius Free Edition in Windows 10.
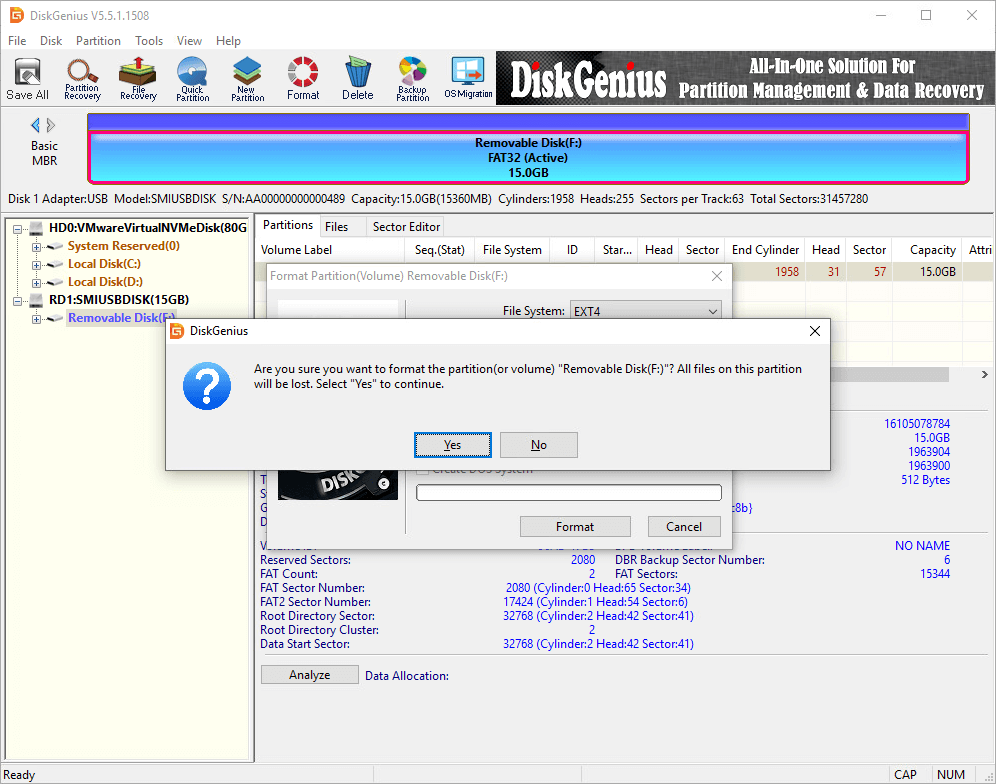
Step 1. After launching DiskGenius Free Edition, you can select the partition to be formatted, click «Format» button. Then you can choose Ext4 as the file system and click «Format» button.
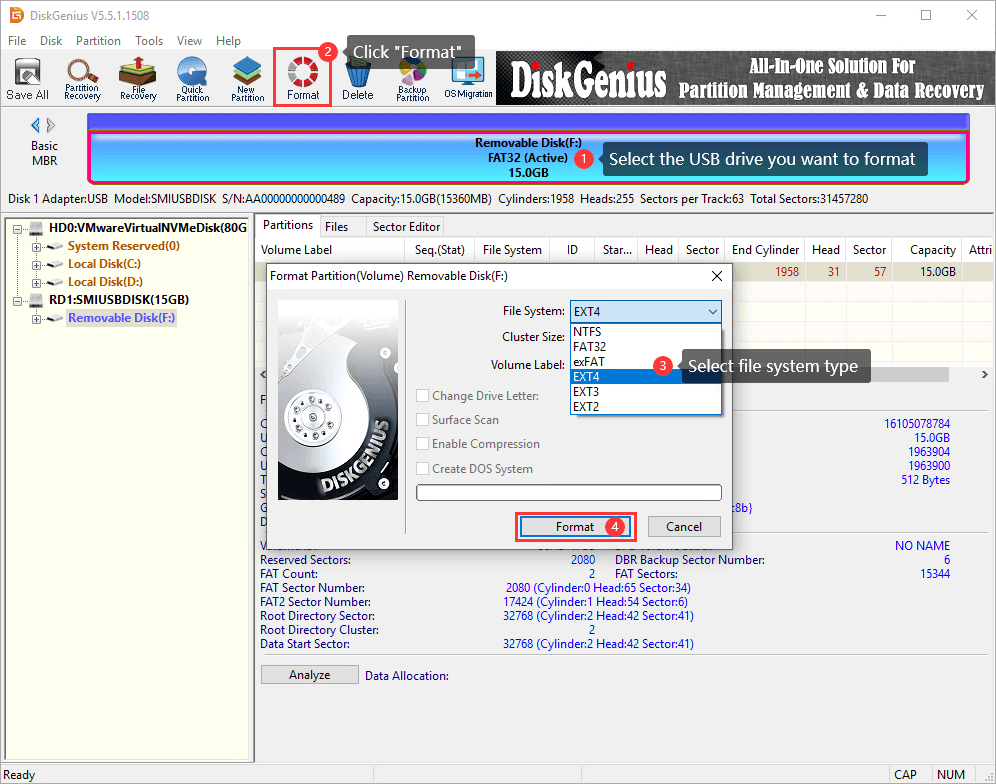
Step 2. A warning message pops up, saying all data on the drive will be erased by the formatting. If you don’t have any important data on the drive, click «Yes» to continue. Then DiskGenius starts to format the drive.
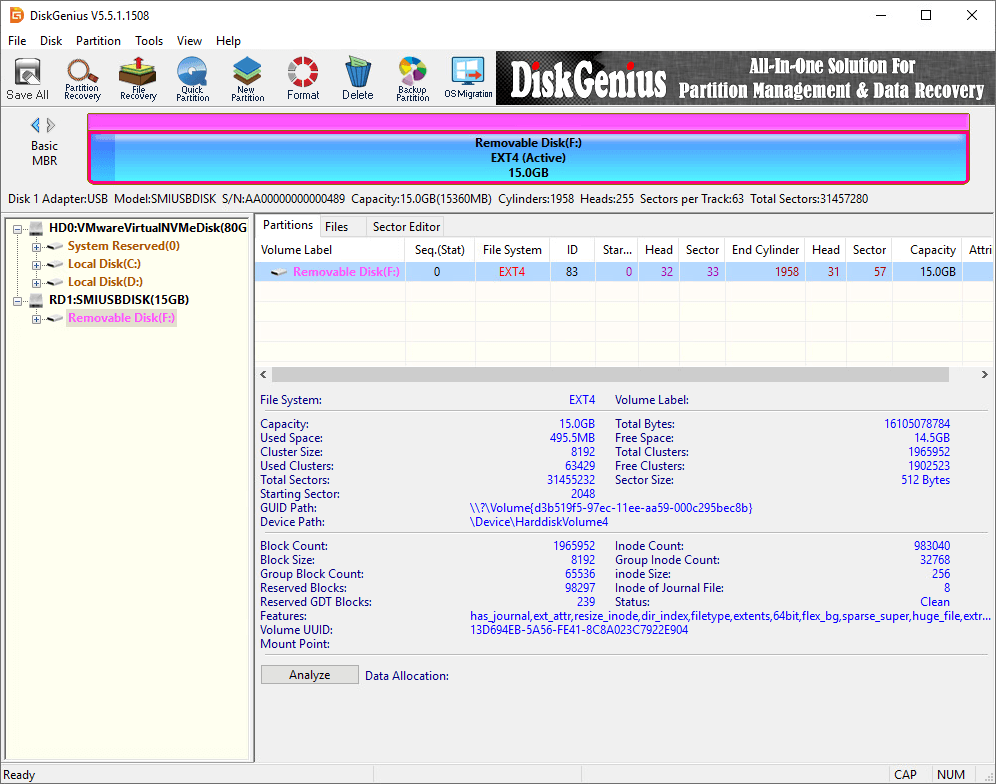
The drive is formatted as Ext4 successfully.
Here’s the video guide on how to format a partition to Ext4 file system in Windows 10:
Conclusion
DiskGenius is a handy and versatile Linux reader for Windows users. By using the software, you can easily read or write your Ext4, Ext3, and Ext2 partitions from Windows 11/10/8/7. Moreover, it also supports to manage Ext4/3/2 partitions to help you get the best use of disk space. If you are one of the dual-boot users, DiskGenius Professional Edition will be your best assistance.
Содержание статьи:
- Как «прочитать» информацию на разделах с файловыми системами Ext2, Ext3, Ext4
- Способ 1 (через спец. драйвер)
- Способ 2 (через дополнения к TC)
- Способ 3 (с помощью LiveCD)
- Вопросы и ответы: 4
Доброго дня!
К сожалению «обычная» версия Windows не позволяет работать с дисками, отформатированными в файловые системы (ФС) Ext2, Ext3, Ext4 (используются в Linux). Всё, что доступно — это узнать о их существовании в управлении дисками, а вот скопировать файл — уже проблема…
Что делать?
Наиболее сподручный и самый удобный вариант (на мой взгляд) — установить в Windows спец. драйвер, который позволит ОС работать с дисками Ext2/3/4 также, как если бы они были отформатированы в NTFS (скажем). Т.е. любая программа в Windows (тот же проводник) сможет в обычном режиме работать с диском. Удобно?
Теперь о том, «что» выбрать…
*
Как «прочитать» информацию на разделах с файловыми системами Ext2, Ext3, Ext4
Способ 1 (через спец. драйвер)
Подобные «драйверы» есть от нескольких производителей. Я бы выделил продукт от Paragon (ссылка на офиц. сайт с драйвером). Почему:
- поддержка ФС: Ext2, Ext3, Ext4 (чтение + запись); Btrfs, XFS (только чтение);
- после установки драйвера — ничего «делать» не нужно: просто Windows начинает видеть накопители с Ext4+;
- совместим с ОС Windows 7/8/10 (плюс есть пробный период, которого хватает для возникшей задачи (обычно)).

Драйвер от Paragon
Обратите внимание, что «ненужные» разделы диска можно откл. и не монтировать. Настройка драйвера позволяет это сделать.
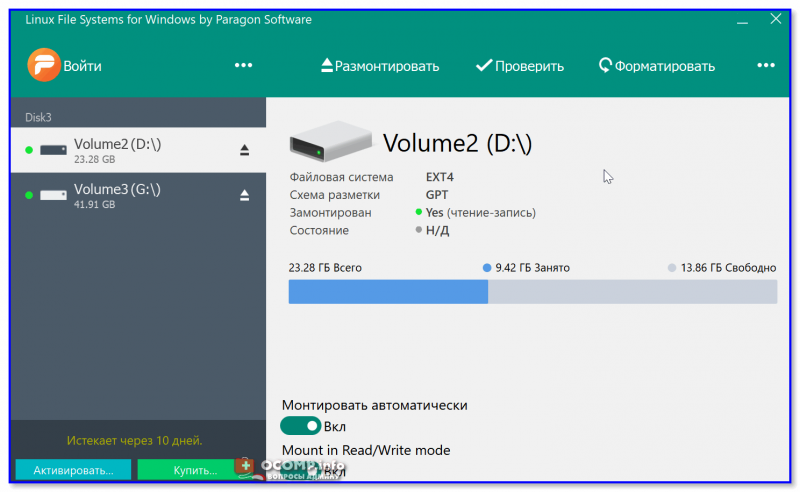
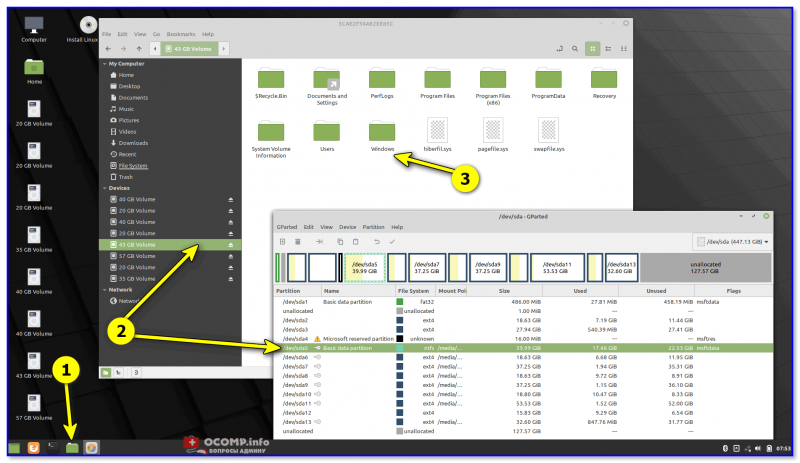
Главное окно (Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon Software)
На скрине ниже привел окно проводника: как видите, раздел отображает как «обычный» — на него также можно что-нибудь скопировать / удалить.
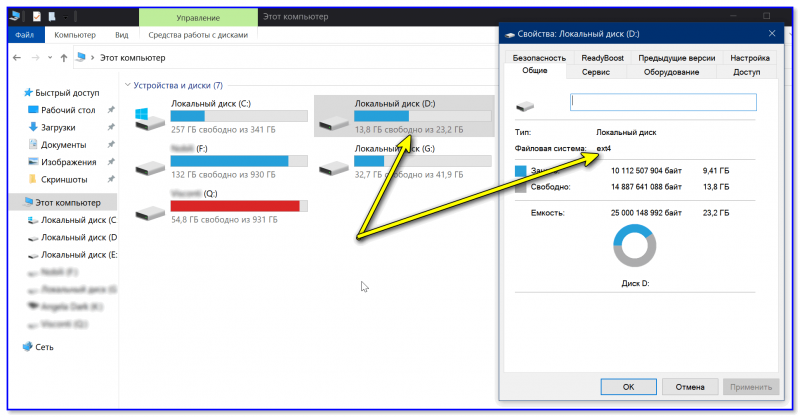
Этот компьютер — диски с ФС EXT4 появились в проводнике
👉 Дополнение!
На Sourceforge можно также найти бесплатный драйвер файловой системы Ext2/3/4 для Windows 7/8/10* (ориг. название: Ext2Fsd).
Сразу отмечу, что на некоторых ОС Windows 10 — драйвер этот ведет себя нестабильно, и не позволяет прочитать информацию с нужного раздела…
Продукт от Paragon, конечно, выигрывает…
*
Способ 2 (через дополнения к TC)
TC — это сокращенное название файлового коммандера Total Commander (некая замена проводнику). К этой программе есть очень много плагинов, и, разумеется, для чтения Ext2/3/4 ФС тоже есть!
Покажу по шагам, как в нем открыть подобный раздел диска…
1) Сначала устанавливаем сам Total Commander. Ссылка на офиц. сайт.
2) Далее необходимо загрузить плагин DiskInternals Reader с офиц. сайта (он идет в архиве ZIP — извлекать не нужно).
3) После необходимо запустить TC от имени администратора (просто кликните правой кнопкой мыши по значку…). 👇
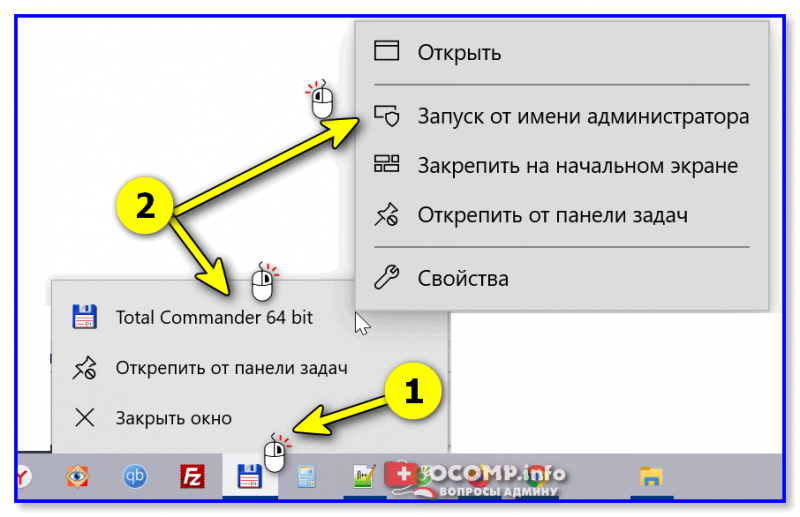
Запуск TC от имени админа
4) Затем необходимо открыть архив ZIP с плагином DiskInternals Reader в Total Commander — тогда он предложит вам установить плагин. Разумеется, соглашаетесь! 👌
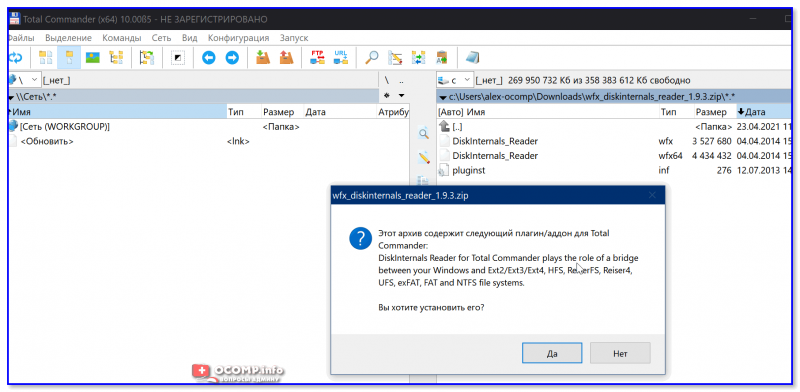
Установка плагина
5) Далее необходимо закрыть TC и снова его запустить от имени админа. В меню выбора диска укажите вариант «Сеть / FS-плагины» — далее кликните по значку DiskInternals Reader (см. стрелки 1, 2 на скрине ниже 👇).
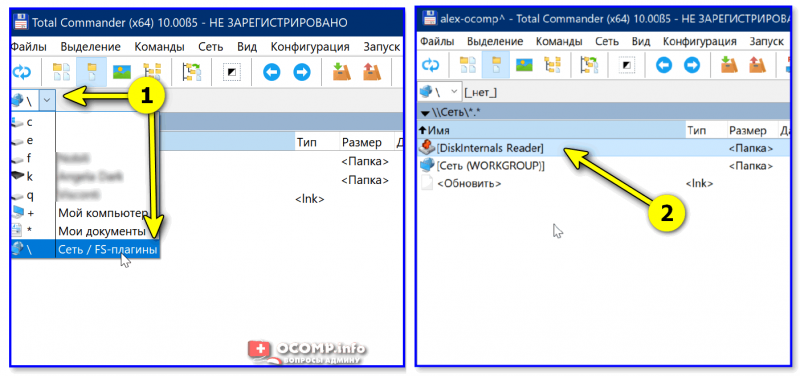
DiskInternals Reader
6) Собственно, далее появиться список всех дисков (в том числе и Ext2/3/4) — их можно открыть и скопировать с них нужную информацию. Задача решена?! 👌
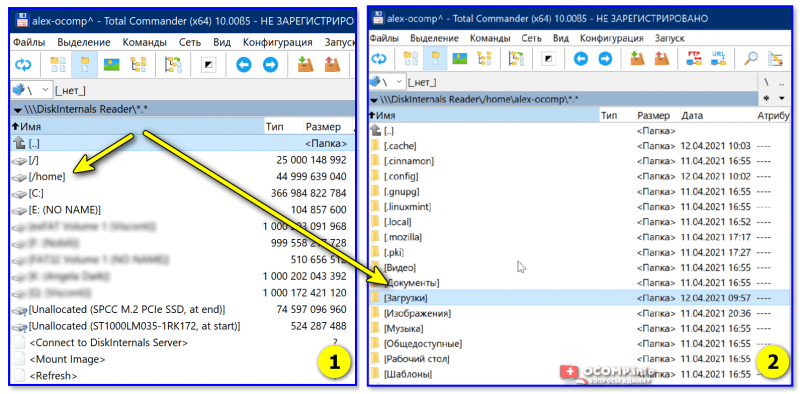
Файлы читаются, можно копировать
*
Способ 3 (с помощью LiveCD)
Вообще, этот вариант, конечно, не относится к работе из-под Windows… Однако, он вполне себе годен для какой-то разовой работы (например, для копирования и переноса папки с файлами). К тому же аварийный LiveCD с Linux никогда не помешает — вдруг чего… 👌
1) Дистрибутивы Linux с поддержкой работы LiveCD — 👉 можете найти в моей подборке
2) Загруженный ISO-файл с нужной версией дистрибутива Linux необходимо правильно записать на флешку.
3) Далее останется только загрузиться с этой флешки с помощью Boot Menu (вызывается сразу после вкл. ПК). Если вы выберите дистрибутив Linux для новичка — то работать с ним весьма просто (ничуть не сложнее, чем с проводником Windows).
Linux Mint загружена с LiveCD
*
Дополнения приветствуются!
Успехов!
👌
How to access ext2, ext3 and ext4 filesystems in windows 10
Dual boot with Windows and Linux leads to the access of files in other Operating Systems. Viewing a windows partition on a Linux OS is not a big task. One can simply mount the OS and can see the files of windows within Linux.
But accessing Linux EXT2, EXT3 and EXT4 files within Windows can be done only through an external software.
EXt2FSD is a software that does this job. you can download the software from this link
Once installed, its as easy as possible to “assign a drive letter ” to the partition. Figure below shows that.

|
| Ext2FSD |

|
| Ext2FSD |
Its just a simple process to access the linux files within windows. This is really helpful for the machines with UEFI partition. When Linux Boot loader is deleted, this will help to retrieve the files.
Any other info, please comment below.
Popular posts from this blog
In this post, we are going to see how to install ns-3.36.1 in Ubuntu 22.04. You can follow the video for complete details Tools used in this simulation: NS3 version ns-3.36.1 OS Used: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Installation of NS3 (ns-3.36.1) There are some changes in the ns3 installation procedure and the dependencies. So open a terminal and issue the following commands Step 1: Prerequisites $ sudo apt update In the following packages, all the required dependencies are taken care and you can install all these packages for the complete use of ns3. $ sudo apt install g++ python3 python3-dev pkg-config sqlite3 cmake python3-setuptools git qtbase5-dev qtchooser qt5-qmake qtbase5-dev-tools gir1.2-goocanvas-2.0 python3-gi python3-gi-cairo python3-pygraphviz gir1.2-gtk-3.0 ipython3 openmpi-bin openmpi-common openmpi-doc libopenmpi-dev autoconf cvs bzr unrar gsl-bin libgsl-dev libgslcblas0 wireshark tcpdump sqlite sqlite3 libsqlite3-dev libxml2 libxml2-dev libc6-dev libc6-dev-i386 libc…
NS-2.35 installation in Ubuntu 22.04 This post shows how to install ns-2.35 in Ubuntu 22.04 Operating System Since ns-2.35 is too old, it needs the following packages gcc-4.8 g++-4.8 gawk and some more libraries Follow the video for more instructions So, here are the steps to install this software: To download and extract the ns2 software Download the software from the following link http://sourceforge.net/projects/nsnam/files/allinone/ns-allinone-2.35/ns-allinone-2.35.tar.gz/download Extract it to home folder and in my case its /home/pradeepkumar (I recommend to install it under your home folder) $ tar zxvf ns-allinone-2.35.tar.gz or Right click over the file and click extract here and select the home folder. $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install build-essential autoconf automake libxmu-dev gawk To install gcc-4.8 and g++-4.8 $ sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list make an entry in the above file deb http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic main universe $ sudo apt update Since, it…
Design a User-defined robot of your choice (or you can use the URDF file) and enable the LIDAR Scanner so that any obstacle placed on the path of the light scan will cut the light rays. Visualize the robot in the Gazebo workspace, and also show the demonstration in RViz. (NB: Gain knowledge on wiring URDF file and .launch file for enabling any user-defined robot to get launched in the gazebo platform.) SLAM : One of the most popular applications of ROS is SLAM(Simultaneous Localization and Mapping). The objective of the SLAM in mobile robotics is to construct and update the map of an unexplored environment with the help of the available sensors attached to the robot which will be used for exploring. URDF: Unified Robotics Description Format, URDF, is an XML specification used in academia and industry to model multibody systems such as robotic manipulator arms for manufacturing assembly lines and animatronic robots for amusement parks. URDF is especially popular with users of the …
This article guides you on how you can access Linux File-system Ext2, Ext3 and Ext4 partitions in Windows 10 and automatically keep them mounted in Explorer like other NTFS or FAT32 partitions. You can even read or write to those partitions.
While Windows uses NTFS and FAT32 file-system, Linux (such as Ubuntu) uses extended file-system architectures Ext 3, Ext4, etc. Though Linux can access, read and write to Windows file-systems, Windows can’t access Linux file-systems. I mean, Windows has no support to read or access Ext3 or Ext4 partitions.

Thus, if you have a dual-boot or multi-boot system where you can switch between Windows and Linux from boot menu, you may sometimes need access to Linux drives/partitions. Or suppose, you are on Windows and you have an HDD or removable drive which is formatted in Ext3 and now you need to read files inside it. Or your Linux system is crashed and you need to recover your important files using Windows. In such cases your need to read those file-systems without switching from Windows.
Though Windows had never interest on Linux file-systems, fortunately there are third-party drives and tools to open and read Linux partitions from Windows. We will review multiple tools in a future article. However, here we will use an opensource Linux file-system driver called Ext2Fsd which is solely made to bring Ext2/3/4 support in Microsoft Windows. With this you can automatically mount Ext partitions on boot or mount just when you need.
Mount Linux Ext4/3/2 Partitions in Windows Explorer using Ext2Fsd
- Download Ex2Fsd from sourceforge.net/projects/ext2fsd/.
- While installing, mark “Make Ext2Fsd automatically started when system boots” and hit Next and finish the setup. It will auto-start Ex2Fsd driver with Windows from next reboot.
- Start Ext2Fsd Volume Manager. With this, you can set mount point and settings.
- To assign a volume latter, double-click on the partition (or choose the partition and select Tools > Ex2 Volume Management), enable “Mountpoint for fixed disk” and assign a drive letter. Hit Apply then.
- On next reboot of Windows, you will see your desired Linux partition is mounted in Explorer as other standard partitions.
- You can also set your custom name by renaming the default name “Local Disk”. That’s it.
Note 1: Keeping your Linux partitions read-only is recommended so that you or your system cannot introduce any harm to the Linux system.
Note 2: If you don’t want Ext2Fsd automatically mount a disk in Explorer on boot, you can mark “Automatically mount via Ex2Mgr”. With this, your partition will only mount when you open Ex2Fsd Volume Manager as below:

Note 3: At the installation time of Ext2Fsd, if you didn’t set Ex2Fsd service to automatically start with windows, you need to manually start the service from Tools > Service Management > Start as below:

Recovering Personal Files
If you are looking for accessing your personal files that your stored when you were on Linux, head to home\name\ as below:

Though this guide is made on Windows 7, I have tested it on Windows 10 and should also work on Windows 8.x according to its authors. Being able to view and read all partitions from both OS is obviously a cool feature for those who use both Linux and Windows on same machine.
Author: Jaber Al Nahian
Jaber is a Programmer and Tech Enthusiast Geek from Dhaka, Bangladesh. He is the founder and Chief-Editor of TechGainer. While he is away from his keyboard, either he’s fishing or messing with wildlife. In case, you can contact him at rijans[at]techgainer[dot]com.











