Skip to content
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to restart MySQL Server on Windows and Linux.
Restart MySQL Server on Windows
If you install MySQL as a Windows service, you can follow these steps to restart the MySQL Server.
First, press the Windows+R to open the Run dialog.
Second, type services.msc and press Enter to open the Services window.
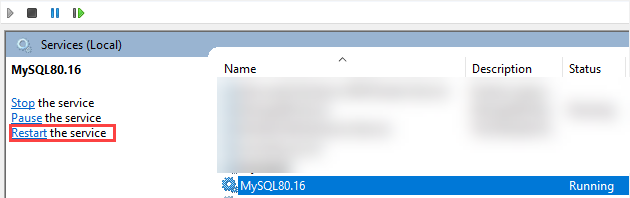
Third, in the Services window, look for the MySQL service name, select it, and click the Restart the service button as shown in the following picture:
If you want to use commands, you can stop and start the MySQL service.
Restart MySQL Server on Linux
You use the following command to restart the MySQL Server on Linux:
First, open the Terminal program.
Second, run the following command to restart the MySQL service:
sudo systemctl restart mysql.serviceCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this command, you need to replace the mysql.serivce service name with the actual one in your server.
Third, check the status and confirm the mysql service has restarted successfully, you run the following command:
sudo systemctl status mysql.serviceCode language: CSS (css)If the service has restarted successfully, you should see “Active: active (running)“.
Summary
- Use the
Servicesapp to restart the MySQL Service on Windows. - Use the
sudo systemctl restart mysqlcommand to restart MySQL Service on Linux.
Was this tutorial helpful?
Перезапуск MySQL можно выполнить несколькими способами, в зависимости от операционной системы, на которой вы работаете. Ниже приведены инструкции для перезапуска MySQL на Linux, Windows и macOS:
- Linux:
-
Для большинства дистрибутивов Linux команда для перезапуска MySQL выглядит следующим образом:
sudo systemctl restart mysqlили
sudo service mysql restart -
Windows:
-
Для Windows вы можете перезапустить MySQL через службы Windows. Пройдите к «Службы» через Панель управления или через поиск Windows. Найдите службу MySQL и выберите «Перезапустить».
-
macOS:
-
Для macOS вы можете перезапустить MySQL через терминал. Запустите Terminal и выполните следующую команду:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server restart
После выполнения одной из указанных выше команд, MySQL будет перезапущен и доступен для использования.
There are several ways to start, stop and restart the MySQL server depending upon the operating system you are using. In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to start-stop and restart MySQL servers in windows, mac, and Linux operating systems.
There are 3 ways by which you can perform these tasks on the MySQL server on Windows:
- Using services.msc
- Using Command Prompt
- Using MySQL Workbench
We’ll learn all three methods one by one:
Using services.msc
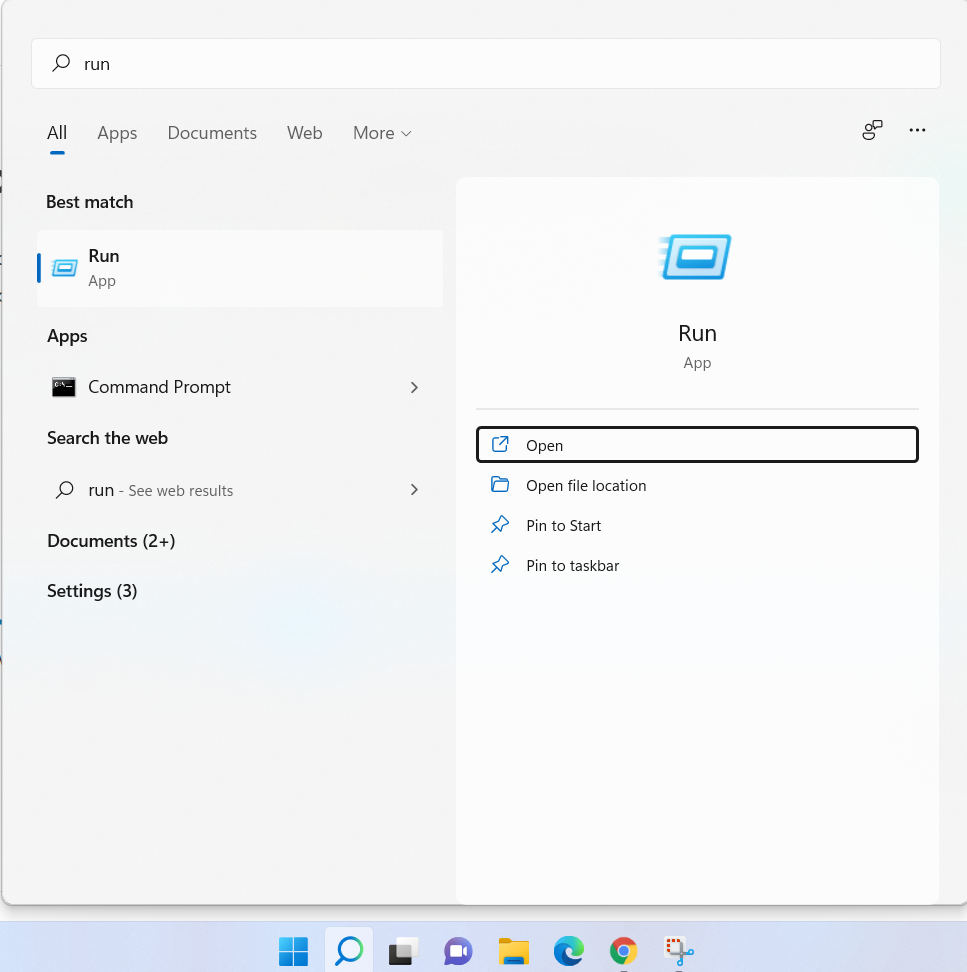
Step 1: On the keyboard press Windows, Type run on the search area, and click on open:
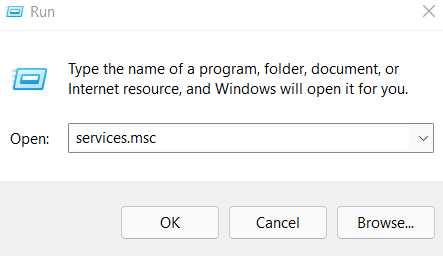
Step 2: Type Services.msc on run and click on OK:
Step 3: Search for MySQL under the name column, Please keep in mind that the numeric extension after MySQL, as in the below example is MySQL80 may vary depending on the version of MySQL installed on your desktop. You can click on the MySQL80 section and a section on the left-hand side will be available to you with all the operations you can perform on that service.
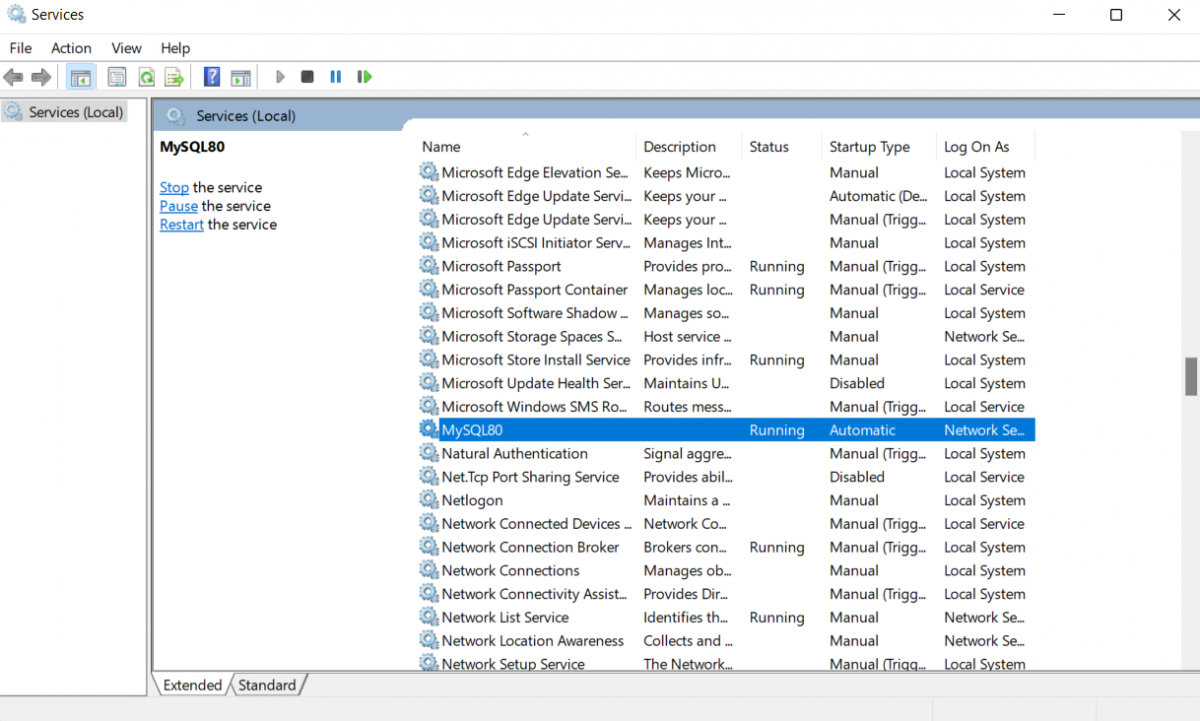
Step 4: Currently MySQL server is running, you can either choose to start, stop and restart the service from the left-hand side panel by selecting any of the options, or you can right-click on MySQL80 service and restart or stop the MySQL server from there.
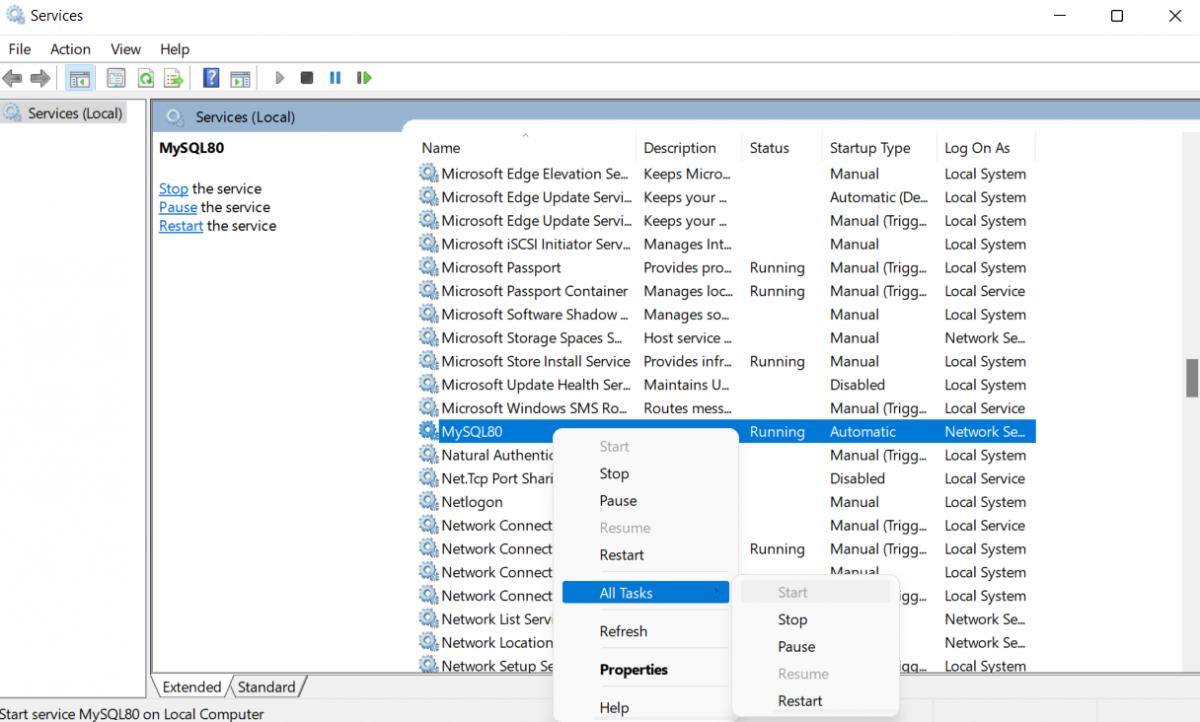
That’s how you can start, stop or restart the MySQL server in windows using services.
Using Windows Command Line
Step 1: Open Command Prompt, you can open it by pressing the Windows key on your keyboard and typing cmd on the search area.
Step 2: Start, stop or restart the MySQL server.
To stop the MySQL server you can type the following command:
net stop MySQL80Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To start the MySQL server you can type the following command:
net start MySQL80Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Using MySQL Workbench
Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard, type MySQL Workbench on the search bar, and open MySQL Workbench.
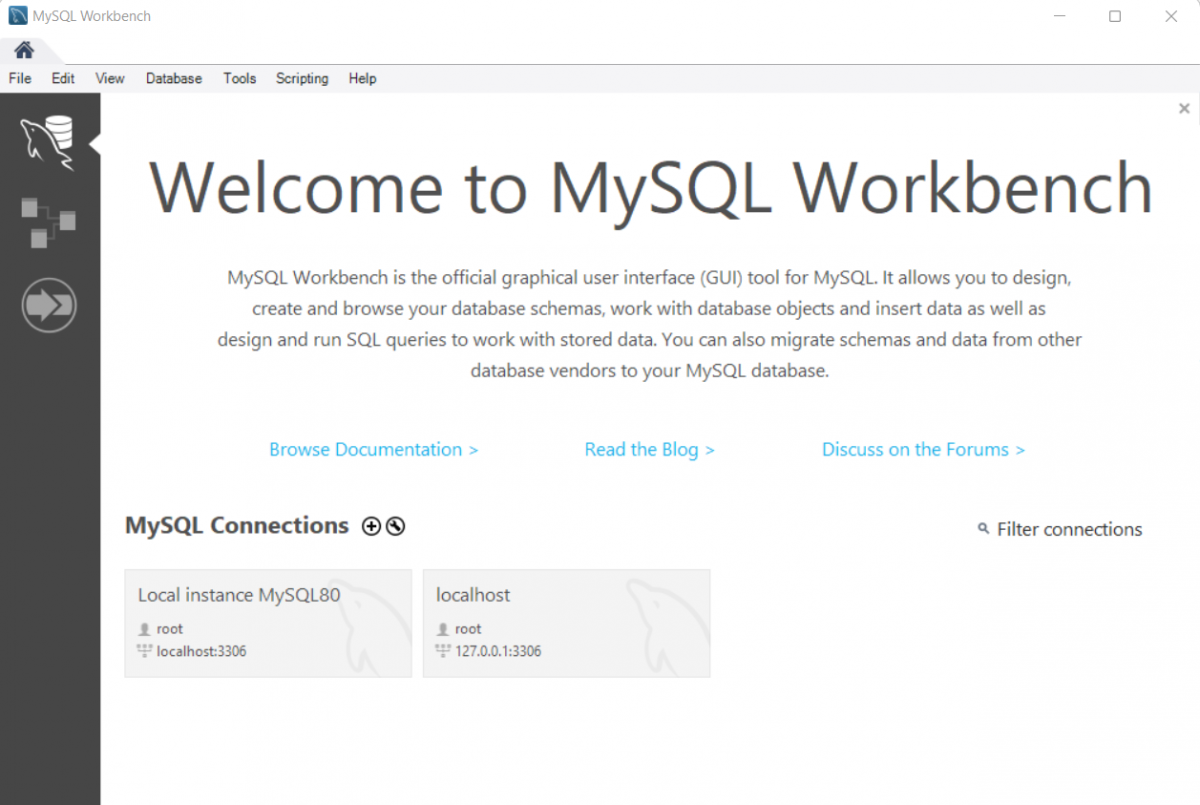
Step 2: Select the Administrator tab, in the Instances section select the Startup/Shutdown section.
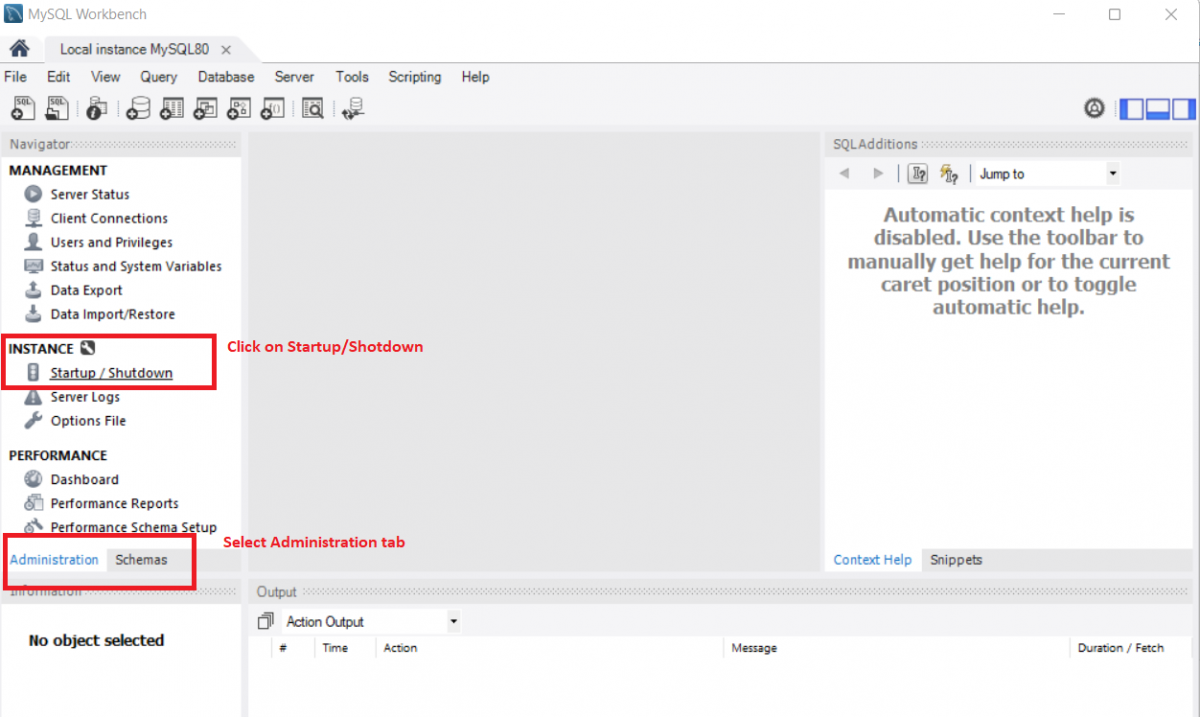
Step 3: You can start or stop the server in this window.
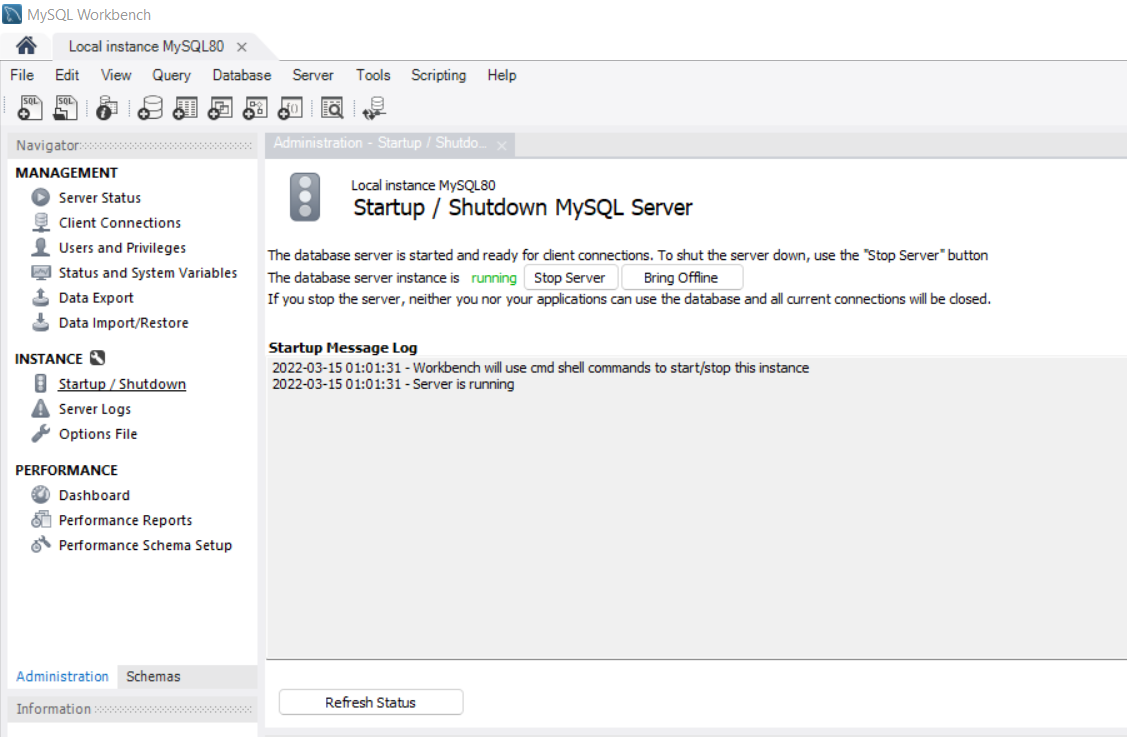
These are the three ways, you can use to start or stop of MySQL server.
Start, Stop and restart MySQL Server on Linux
For performing these activities on Linux, you must be a superuser as only the superuser has these privileges.
Step 1: Open your Linux terminal and we need to check if MySQL is running on your operating system or not. To do so, we’ll need to type the following command:
service mysqld statusCode language: Bash (bash)If MySQL is properly configured on your OS then the command will return Active status as Active(running) which means that MySQL is running on your operating system.
Step 2: Start, stop or restart MySQL
There will be two commands, service and sudo, both should work properly, but it depends if you have the privilege to use the service or sudo command on Linux. Make sure that you are a root user or a super user to perform the activity on MySQL.
To stop the MySQL server on Linux, use the following command:
service mysqld stop
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stopCode language: Bash (bash)The above command will stop the MySQL server. Now if you will try to check again for the MySQL status it will show inactive(dead) on the active status.
To Start the MySQL server on Linux, use the following command:
service mysqld start
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql startCode language: Bash (bash)The above command will start the MySQL server. Now, if you will try to check again for the MySQL status it will again be active(running) on the active status.
To restart the MySQL server on Linux, use the following command:
service mysqld restart
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql restartCode language: Bash (bash)The above command will restart the MySQL server. Now, if you will try to check again for the MySQL status it will again be active(running) on the active status because we restarted the server.
Start, Stop or Restart MySQL Server on macOS
Open terminal on your Mac, we’ll be using the Sudo command to start, stop or restart the MySQL server.
For MySQL versions which are newer than 5.7:
To start MySQL server on Mac:
sudo launchctl load -F /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.oracle.oss.mysql.mysqld.plistCode language: Bash (bash)To Stop MySQL server on Mac:
sudo launchctl unload -F /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.oracle.oss.mysql.mysqld.plistCode language: Bash (bash)For versions older than MySQL 5.7:
To Start MySQL server on Mac:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server startCode language: Bash (bash)To Stop MySQL server on Mac:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server stopCode language: Bash (bash)To Restart MySQL server on Mac:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server restartCode language: Bash (bash)Conclusion
Mysql is a powerful database management system. In order to use it effectively, you need to be familiar with the different ways to start, stop and restart it. By following the instructions in this article, you should be able to do just that. Thank you for reading!
-
Method 1: Using the Command Line
-
Method 2: Using MySQL Workbench
-
Method 3: Using Python Scripts
-
Conclusion
-
FAQ

Restarting your MySQL server on Windows can seem daunting, especially if you’re new to database management. However, it’s a straightforward process that can resolve various issues, such as performance glitches or configuration changes. Whether you’re a developer, a database administrator, or just someone curious about managing MySQL, this tutorial will guide you through the necessary steps. We will explore multiple methods, including using Python scripts, to ensure you have a solid understanding of how to effectively restart your MySQL server. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to handle MySQL restarts with confidence.
Method 1: Using the Command Line
One of the simplest ways to restart your MySQL server on Windows is through the Command Prompt. This method is quick and effective, especially if you prefer working with command-line tools. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open the Command Prompt as an administrator. You can do this by searching for “cmd” in the Start menu, right-clicking, and selecting “Run as administrator.”
- Type the following command to stop the MySQL service:
Output:
The MySQL service is stopping.
The MySQL service was stopped successfully.
- Next, restart the MySQL service with this command:
Output:
The MySQL service is starting.
The MySQL service was started successfully.
This method is straightforward and effective for those who are comfortable with the command line. By stopping and then starting the MySQL service, you can ensure that any changes made to the configuration files take effect. Additionally, if MySQL is running into issues, this restart can often resolve them without needing further intervention.
Method 2: Using MySQL Workbench
If you prefer a graphical interface, MySQL Workbench provides a user-friendly way to manage your MySQL server. Restarting the server through MySQL Workbench is quite simple. Here’s how to do it:
- Open MySQL Workbench and connect to your database server.
- Navigate to the “Server” menu at the top of the window.
- Click on “Startup/Shutdown.”
In the Startup/Shutdown panel, you will see options to stop and start the server.
- Click “Stop Server” to halt the MySQL service. Wait for the process to complete.
- After stopping the server, click “Start Server” to restart it.
Using MySQL Workbench allows you to manage your MySQL server visually, making it easier for those who may not be as familiar with command-line operations. This method is particularly useful for database administrators who prefer a more intuitive approach to server management. The graphical interface also provides additional features for monitoring and configuring your MySQL server.
Method 3: Using Python Scripts
For those who prefer automation or need to restart MySQL servers programmatically, using Python is an excellent option. Below is a simple Python script that utilizes the os module to restart the MySQL server.
import os
os.system("net stop mysql")
os.system("net start mysql")
This script first stops the MySQL service and then starts it again.
When you run this script, it executes the same commands you would use in the Command Prompt, but from within Python. This method is particularly useful if you’re looking to integrate MySQL server management into a larger Python application or automate routine tasks.
Before running the script, ensure you have the necessary permissions, as administrative rights are required to stop and start services on Windows. Additionally, you might want to add error handling to manage any issues that arise during the restart process.
Conclusion
Restarting your MySQL server on Windows is a crucial skill for anyone involved in database management. Whether you prefer using the command line, a graphical interface like MySQL Workbench, or even automating the process with Python, there are several effective methods to achieve this. Each method has its unique advantages, allowing you to choose the one that best fits your workflow. With this knowledge, you can ensure your MySQL server runs smoothly and efficiently, ready to handle your data needs.
FAQ
-
how often should I restart my MySQL server?
It’s generally recommended to restart your MySQL server if you make significant changes to the configuration or if you encounter performance issues. Regular restarts are not usually necessary. -
can I restart MySQL server without losing data?
Yes, restarting the MySQL server should not cause any data loss, as long as all transactions are completed before the restart. -
what should I do if MySQL fails to restart?
Check the MySQL error logs for any issues that may have occurred during the restart process. Additionally, ensure that you have appropriate permissions to start and stop the service.
-
is there a way to automate MySQL restarts?
Yes, you can use scripts in languages like Python or batch files to automate the restart process based on specific conditions or schedules. -
are there any risks associated with restarting MySQL?
Restarting MySQL can temporarily disrupt service, so it’s best to perform this action during off-peak hours or maintenance windows to minimize impact.
Enjoying our tutorials? Subscribe to DelftStack on YouTube to support us in creating more high-quality video guides. Subscribe
In this post, we are going to see how to start, stop, and restart MySQL Server on macOS, Linux, and Windows.
1. On Mac
You can start/stop/restart MySQL Server via the command line.
- For the version of MySQL older than 5.7:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server stop
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server restart
- For the MySQL version 5.7 and newer:
sudo launchctl load -F /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.oracle.oss.mysql.mysqld.plist
sudo launchctl unload -F /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.oracle.oss.mysql.mysqld.plist
- Or you can turn it on/off via the macOS Preference Panel
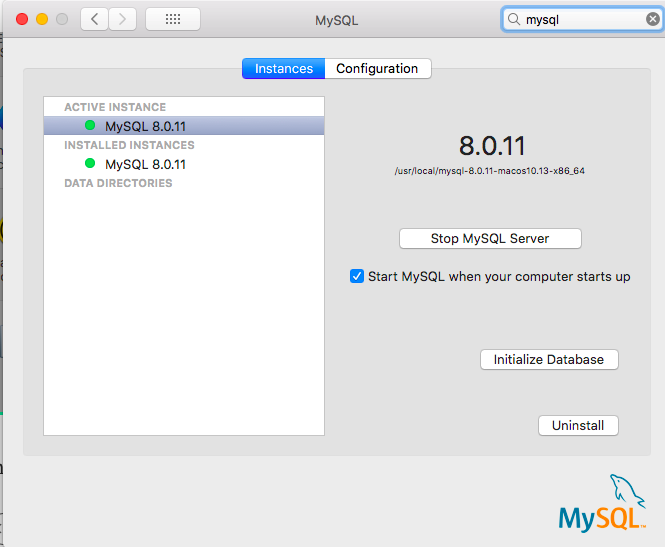
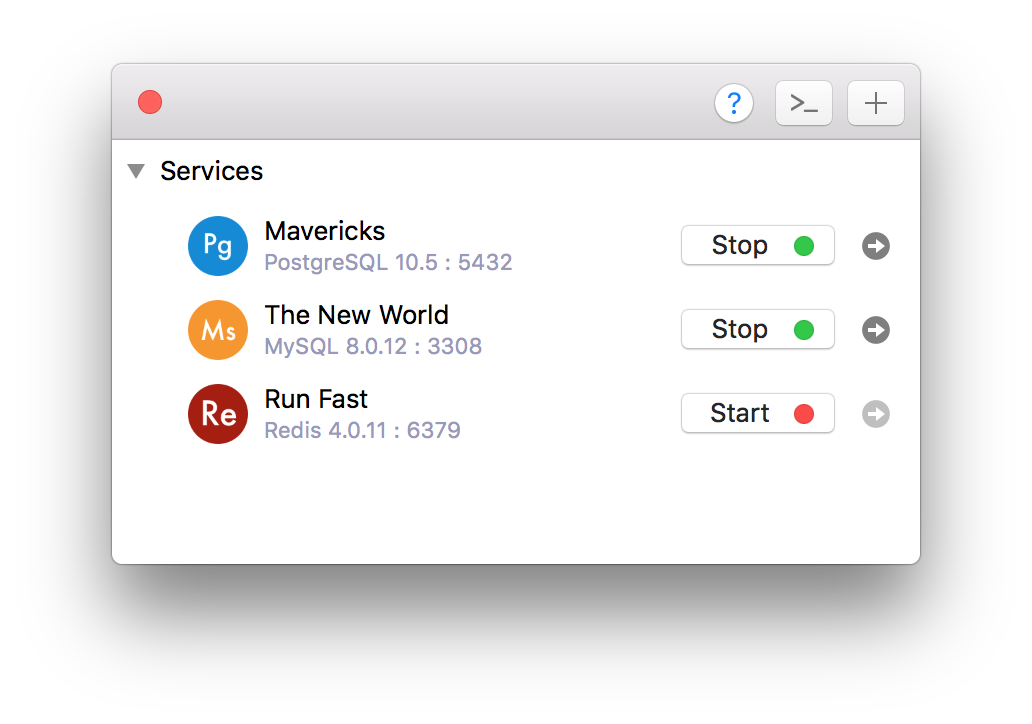
There’s another way which you can use DBngin, an free utility to install and manage multiple database servers on Mac.
- To turn on/off, it’s just one click away from the server control panel:
2. On Linux
- On Linux start/stop from the command line:
/etc/init.d/mysqld start
/etc/init.d/mysqld stop
/etc/init.d/mysqld restart
- Some Linux flavours offer the service command too
service mysqld start
service mysqld stop
service mysqld restart
- or
service mysql start
service mysql stop
service mysql restart
3. On Windows
- Open Run Window by
Winkey + R - Type
services.msc - Search MySQL service based on version installed.
- Click stop, start or restart the service option.
Or you can start/stop MySQL from the command prompt:
C:\> "C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin\mysqld"
C:\> "C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin\mysqladmin" -u root shutdown
Need a good GUI tool for MySQL on MacOS and Windows? TablePlus is a modern, native tool with an elegant GUI that allows you to simultaneously manage multiple databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server and more.
Download TablePlus for Mac. It’s free anyway!
Not on Mac? Download TablePlus for Windows.