Загрузить PDF
Загрузить PDF
В этой статье рассказывается, как перейти в другую папку (каталог) в командной строке Windows. Чтобы работать с командной строкой, необходимо использовать учетную запись администратора.
-
Для этого щелкните по логотипу Windows в нижнем левом углу экрана или нажмите клавишу ⊞ Win на клавиатуре.
- В Windows 8 переместите указатель мыши в верхний правый угол экрана и щелкните по отобразившемуся значку в виде лупы.
-
Значок утилиты командной строки отобразится над строкой поиска.
-
Он имеет вид черного квадрата. Откроется контекстное меню.
-
Эта опции находится в верхней части раскрывшегося меню. Откроется командная строка с правами администратора.
- В открывшемся окне с предложением подтвердить ваши действия нажмите «Да».
- Нельзя запустить командную строку от имени администратора, если вы работаете на компьютере, у которого есть ограничения, который находится в публичном месте или подключен к локальной сети (например, в библиотеке или в школе), то есть в том случае, когда вы пользуетесь гостевой учетной записью.
Реклама
-
После «cd» обязательно добавьте пробел. Эта команда, которая представляет собой сокращение от «change directory» (изменить каталог), является основной командой для перехода в другой каталог.
- Не нажимайте клавишу ↵ Enter.
- Альтернативный вариант — ввести chdir. Эта команда действует точно так же, как «cd».[1]
-
Путь к каталогу — своего рода маршрут, ведущий к определенной папке. Например, если нужным каталогом является папка «System32», которая находится в папке «WINDOWS» на системном диске, путь будет таким: «C:\WINDOWS\System32\».
- Чтобы выяснить путь к папке, перейдите в нее в Проводнике, а затем скопируйте информацию из адресной строки Проводника (сверху).
- Вы можете отобразить список всех каталогов внутри текущего каталога с помощью комадной строки, набрав dir и нажав «Enter».
-
Сделайте это после команды «cd». Убедитесь, что между «cd» и путем к каталогу есть пробел.
- Например, команда может выглядеть так: cd Windows\System32.
- Также можно перетащить папку из Проводника в командную строку.
- По умолчанию местоположением всех папок считается жесткий диск (например, «C:»), поэтому букву жесткого диска вводить не нужно.
-
Так вы перейдете в нужный каталог. Текущий каталог отображается рядом с текстовым курсором (например, «C:\Windows\System32>».)
Реклама
-
и нажмите ↵ Enter, чтобы подняться на один каталог выше. Если вы хотите перейти на один каталог назад (например, из «C:\Windows\System32» в «C:\Windows»), просто наберите «cd..» с двумя точками и нажмите «Enter».
-
Если вы хотите перейти в корневой каталог диска (например, из «C:\Windows\System32» to «C:\»), наберите «cd\» с обратным слешем и нажмите «Enter».
-
Если вы попробуете переместиться в каталог, находящийся на другом диске, с помощью команды «cd», то увидите, что это не сработает. Вам нужно сначала изменить диск. Для этого введите букву, которой обозначен диск, с двоеточией (например, «D:») и нажмите «Enter».
- В качестве альтернативы можете ввести cd /d, а затем полный (включая букву диска) путь к каталогу на другом диске, чтобы непосредственно перейти к нужному каталогу на нем (например, «cd /d D:\Документы».)
-
Введите dir и нажмите ↵ Enter, чтобы отобразить список каталогов внутри текущего. Если вы не уверены, какие каталоги находятся в вашем текущем каталоге, вы можете просмотреть их полный список, набрав «dir» и нажав «Enter».
Реклама
-
Если вы получите сообщение об ошибке «Системе не удается найти указанный путь», проверьте написание имени каталога. Чтобы увидеть список всех каталогов внутри текущего, можете ввести dir и нажать «Enter».
-
Если вы набираете имя верно, но по-прежнему получаете сообщение о той же ошибке, откройте Проводник и проверьте, действительно ли каталог, к которому вы пытаетесь перейти, существует и находится там, где вы думаете.
- Если каталог не существует, вы можете создать новый, введя mkdir, пробел и имя создаваемого каталога. Затем нажмите «Enter».
-
Убедитесь, что каталог расположен на том диске, где вы находитесь в настоящий момент. Команда «cd» не позволяет перейти к каталогу на другом диске. Если ваш текущий диск — это диск C, а каталог, к которому вы хотите переместиться, находится на диске D, вам сначала нужно изменить диск. Для этого введите букву диска и нажмите «Enter».
-
Убедитесь, что вы запустили командную строку от имени администратора. Если командная строка запущена не от имени администратора, набор действий, выполняемых с ее помощью, будет ограничен. Войдите в Windows как администратор, затем щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по значку командной строк в меню «Пуск» и выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
Реклама
Советы
- Изменить каталог необходимо, чтобы отредактировать или удалить файл.
- Чтобы увидеть полный список команд, выполняемых с помощью командной строки, введите help и нажмите «Enter».
Реклама
Предупреждения
- Попытка запустить из одного каталога команду, связанную с определенным файлом или папкой, находящимися в другом каталоге, приведет к ошибке.
Реклама
Об этой статье
Эту страницу просматривали 834 028 раз.
Была ли эта статья полезной?
Навигация
—
Основы командной строки
- Как проверить, в какой директории мы находимся
- Как посмотреть список файлов
- Как переместиться в другую директорию
После запуска операционной системы с графической оболочкой мы попадаем в специальную рабочую область, которую часто называют рабочий стол. Это центральная точка входа, откуда через разные пункты меню начинается работа, запускаются разные задачи. Например, для навигации по файловой системе понадобится проводник.
В командной строке все устроено иначе: после загрузки системы мы попадаем в режим ожидания ввода команды. Этот режим привязан к файловой системе. Можно сказать, что мы всегда находимся внутри какой-то директории, которую называют рабочей директорией (working directory).
В этом уроке мы поговорим о навигации по директориям через командную оболочку.
Как проверить, в какой директории мы находимся
Начнем с самого основного. Проверить, в какой директории мы сейчас находимся, можно командой pwd:
pwd
/Users/guest
Кстати, название команды pwd — это сокращение, которое расшифровывается как print working directory. Похожим образом устроены имена многих команд, что позволяет легче и быстрее их запомнить.
По умолчанию новая сессия командной оболочки открывается внутри домашней директории пользователя. У каждого пользователя своя домашняя директория, поэтому в вашем случае путь будет отличаться.
В приведенном примере есть две неожиданности для тех, кто привык пользоваться Windows:
- В начале указан не диск, а единый корневой каталог
/. Это вершина файловой системы, внутри которой лежат все остальные файлы и директории - Вместо обратных слэшей
\используются прямые слэши/
Подробнее о различиях и файловой структуре мы поговорим в одном из следующих уроков, а сейчас сосредоточимся на навигации.
Как посмотреть список файлов
Изучим команду ls (сокращение от list). Она выводит список файлов и директорий в текущей рабочей директории:
ls
Desktop Documents Downloads Library Movies Music Pictures Public
Как переместиться в другую директорию
Еще одна полезная команда — cd (сокращение от change directory). С помощью нее мы перемещаемся по файловой структуре. Для этого ей нужно передать аргумент — директорию, в которую необходимо переместиться:
# Входим в директорию
cd Music
# Смотрим ее содержимое
ls
iTunes
# Смотрим текущую рабочую директорию
pwd
/Users/guest/Music
# Если имя директории содержит пробел, то его нужно экранировать с помощью `\`
cd Best\ music
Остановимся на этом моменте подробнее. Возможно, вы знаете, что есть два способа обозначить путь до файла:
- Абсолютный путь начинается от корня
- Относительный путь начинающийся от текущей рабочей директории
Выше мы указали относительный путь. Отличить их друг от друга очень легко:
- Абсолютный — первым символом в пути идет
/ - Относительный — во всех остальных случаях
Когда мы используем относительный путь, команда cd считывает его и внутри себя пытается вычислить абсолютный путь. Она берет текущую рабочую директорию /Users/guest/ и присоединяет к ней Music. В итоге получается /Users/guest/Music.
Команда cd понимает и абсолютные, и относительные пути. Поэтому передавать ей можно что угодно:
# Неважно, в каком месте
cd /Users/guest/Music # Абсолютный путь
Еще раз проговорим, что абсолютный путь однозначно определяет адрес файла или директории в файловой системе, а относительный — нет.
Поэтому относительный путь стоит использовать только вместе с текущей рабочей директорией, относительно которой он считается. При передаче абсолютного пути не имеет никакого значения, какая сейчас рабочая директория. Если путь существует, то переход произойдет.
Теперь рассмотрим другую задачу. Предположим, что мы находимся в директории /Users/guest/Music. Как выйти из нее и попасть снова в /Users/guest? Мы уже знаем один способ — указать абсолютный путь и сделать cd:
cd /Users/guest
Но есть путь проще. Можно указать специальное значение .. и перейти на директорию уровнем выше:
# В директории /Users/guest/Music
cd ..
pwd
/Users/guest
Более того, с помощью этого заполнителя можно выходить на любое количество уровней, указывая .. через разделитель:
# В директории /Users/guest/Music
# Выходим на два уровня вверх
cd ../..
pwd
/Users
Иногда в пути используется одинарная точка, которая означает текущую директорию. Например, вместо cd Music можно писать cd ./Music — разницы между этими выражениями нет.
Есть и третий вариант возврата в /Users/guest из директории /Users/guest/Music. Можно выполнить команду cd без аргументов, тогда мы перейдем в домашнюю директорию текущего пользователя:
# Из любого места
cd
pwd
/Users/guest
Ну и, наконец, четвертый вариант. Домашняя директория пользователя имеет специальное обозначение — ~ (тильда). В момент выполнения команды тильда заменяется на абсолютный путь. Поэтому из любого места можно напрямую перейти в любую поддиректорию домашней директории:
# Из любого места
cd ~/Music
pwd
/Users/guest/Music
Допустим, вы находитесь в домашней директории и хотите посмотреть файлы в поддиректории Music. Один способ вы уже знаете — для этого нужно перейти в директорию Music и выполнить программу ls.
Как обычно, есть другой способ. Команда ls также может принимать на вход аргумент — директорию, которую нужно проанализировать:
ls Music
iTunes
Как и в случае с командой cd, к аргументу ls применимы понятия абсолютных и относительных путей. Впрочем, это правило распространяется на большинство случаев, где передаются пути.
Команда cd - возвращает в предыдущую директорию. Другими словами, последовательный вызов этой команды переключает между двумя последними посещенными директориями.
Команды cd, ls и pwd вместе составляют основу навигации по файловой структуре. Зная их, вы никогда не потеряетесь и не запутаетесь.
Со временем набирать пути становится все более лениво. Тогда можно дважды нажать Tab и воспользоваться автокомплитом — функцией, которая автоматически завершает имена.
Самостоятельная работа
Изучите содержимое директорий своей файловой системы. При перемещении между разделами с помощью команды cd используйте клавишу Tab для автозаполнения.
Открыть доступ
Курсы программирования для новичков и опытных разработчиков. Начните обучение бесплатно
-
130 курсов, 2000+ часов теории -
1000 практических заданий в браузере -
360 000 студентов
Наши выпускники работают в компаниях:
In this article, let’s learn how to navigate through directories in Command Prompt — The Command Prompt (CMD) in Windows is a powerful tool for executing commands, managing files, and navigating your system. One of the most common tasks you’ll perform in CMD is changing directories, which allows you to move between folders to access and manage files. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, knowing how to change directories in Command Prompt is essential for effective system navigation.
This guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of changing directories in Windows 11 and Windows 10 using basic commands like cd (change directory) and dir (list contents), along with helpful tips to make your file management easier. Whether you’re navigating through your system’s folders, opening a project folder, or accessing a specific directory for troubleshooting, changing directories is a fundamental task in CMD.

Understanding Directories in Windows
When working with Windows, you’ve likely encountered the term «directory.» But what exactly is a directory in Windows? In this article, we’ll delve into the world of directories, exploring their definition, types, and importance in the Windows operating system.
What is a Directory in Windows?
A directory, also known as a folder, is a container used to store and organize files and subdirectories on a computer. It’s a way to categorize and structure your files, making it easier to locate and access them. Think of a directory as a physical file folder, where you can store related documents, images, or other files.
Types of Directories in Windows
- Root Directory: The root directory, denoted by a backslash (), is the topmost directory on a hard drive or storage device. It contains all other directories and files.
- Subdirectories: Subdirectories are directories within directories. They help further organize files and can be nested multiple levels deep.
- System Directories: System directories, such as Windows, System32, and Program Files, are created by the operating system and contain essential files and programs.
- User Directories: User directories, such as Documents, Pictures, Music, and Videos, are created by the operating system for each user account. They serve as default locations for storing personal files.
- Program Directories: Program directories, such as Program Files (x86) and Program Files, contain installed applications and their associated files.
- Temporary Directories: Temporary directories, such as Temp and %temp%, store temporary files created by applications and the operating system.
- System Volume Information: The System Volume Information directory contains system files, such as restore points and indexing data.
- Recycle Bin: The Recycle Bin is a special directory that stores deleted files until they are permanently erased or restored.
- Hidden Directories: Hidden directories, such as AppData and Local Settings, contain configuration files and data used by applications and the operating system. They are hidden by default to prevent accidental modification or deletion.
- Network Directories: Network directories, such as shared folders and network drives, provide access to files and resources on other computers or devices over a network.
- Virtual Directories: Virtual directories, such as those created by subst or mklink commands, are symbolic links that map a directory to a different location on the same or another drive.
- Mount Points: Mount points are directories that serve as entry points for mounted volumes, such as USB drives or network shares.
- Reparse Points: Reparse points are directories that contain reparse data, which allows the operating system to redirect file system requests to a different location.
- Junction Points: Junction points are directories that link to another directory on the same volume, allowing multiple paths to access the same files.
- Symbolic Links: Symbolic links are directories that link to a file or directory on the same or another volume, allowing multiple paths to access the same file or directory.
How to Change Directories in CMD at Different Levels (With Examples)
Before moving ahead with Changing Directories to Windows Folders, we have to understand Directory Changing to Different Levels. Let us discuss all the methods for Changing Directories in CMD at different levels in Windows 10 or 11.
1. Root Level Directory
Open Command Prompt to change to a directory in the root directory (such as»C:\» on Windows), you can use the `cd` command followed by the directory name.
Example:
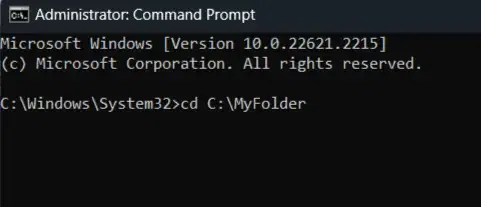
2. Parent Level Directory
Open Command Prompt to move to a directory within the parent directory (like going from «Documents» to «Users»), simply use the `cd` command followed by `..` to go up one level, and then the name of the parent directory.
Example:
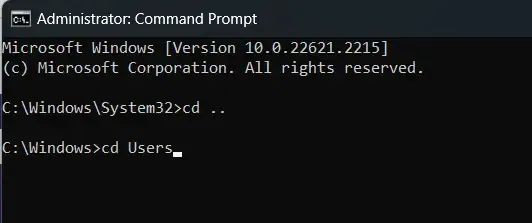
3. Subdirectories Level Directory
Open CMD or Command Prompt to enter a subdirectory within your current directory (such as going from «Documents» to «Photos»), use the `cd` command followed by the name of the subdirectory.
Example:
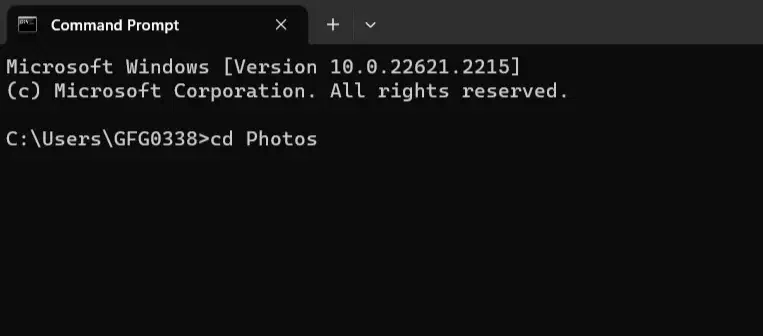
4. Nested Subdirectories Level
Open CMD to navigate to a deeply nested subdirectory (like going from «Documents» to «Work > Projects»), use the `cd` command with each subdirectory name, separated by a backslash (\).
Example:
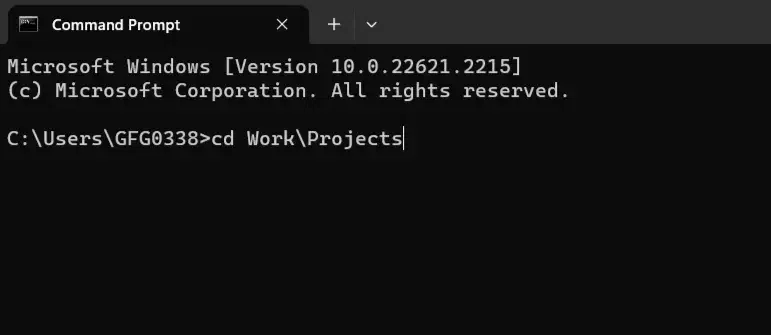
5. Leaf Level Directory
Open Command Prompt in Windows 10 or 11 to enter a directory that doesn’t contain any subdirectories (like going to a folder with just files), use the `cd` command followed by the leaf directory’s name.
Example:
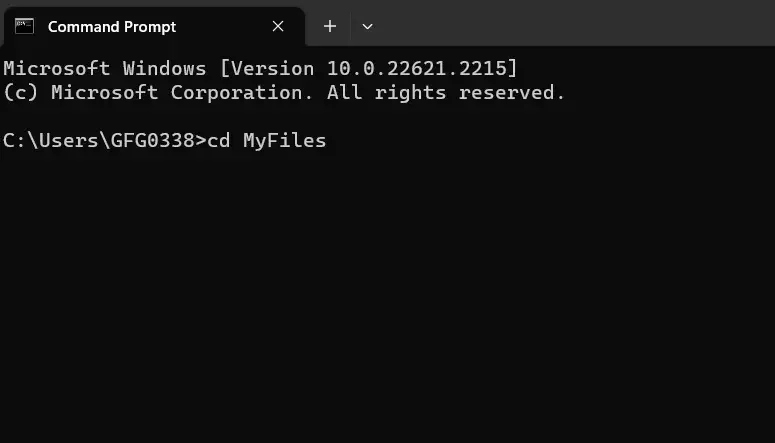
Note: Remember, you can always type `cd ..` to go up one level and explore different directories easily.
Changing Directories in Command Prompt to Different Folders
Now, after discussing Directory Change in Different Levels, we will discuss all the possible methods that are required to Change Directories to Folders in the Windows Command Line Tool.
Method 1: Using Drag and Drop
For those who prefer a graphical approach, changing directories using drag and drop is simple. You can open File Explorer, locate the desired directory, and drag it to the Command Prompt window. This action automatically populates the Command Line with the directory path.

Method 2: Using Commands
Changing directories using commands may seem tricky at first, but it’s essential to get the hang of it in Command Prompt. Here are some easy methods to do it:
1. Absolute Paths
This is like using a full address to find a place. In Command Prompt, you can use the full path to a folder to get there directly. This will take you straight to your «Documents» folder. For instance:
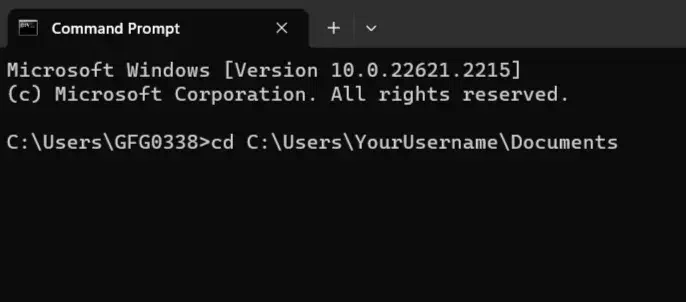
2. Relative Paths
Think of this as giving directions from where you are. You can use `..` to move up one level and the folder name to go into a subfolder. This will take you up one level from where you are right now. For example:
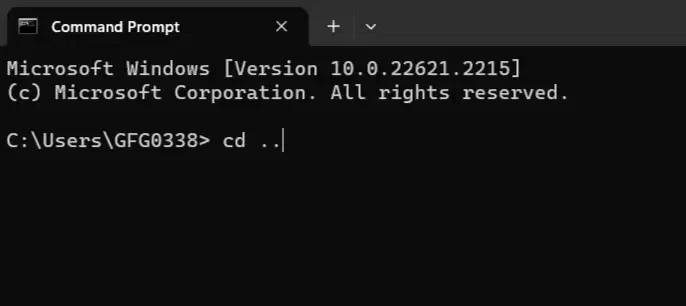
3. Drive Letters
Imagine switching between different drives as changing streets. To switch to a different drive, just type its letter and a colon. This will take you to the D: drive. For example:
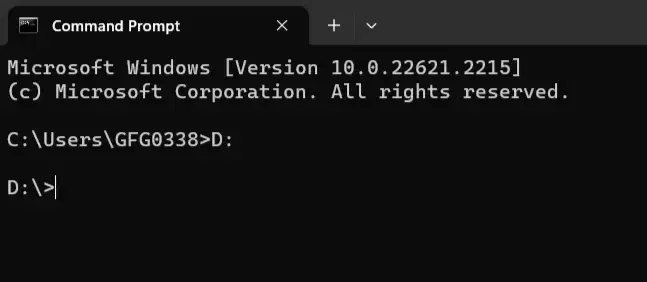
4. Environment Variables
These are like shortcuts to important places. You can use names like `%USERPROFILE%` to go to common folders without typing the whole path. This will take you to your user profile folder. For example:
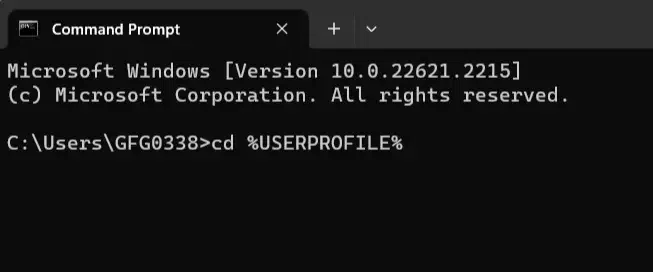
5. Tab Auto-Completion
Think of this as your Command Prompt assistant. When you start typing a folder name and press Tab, Command Prompt will try to finish it for you. If there’s more than one option, it will show you a list.
6. Previous Directory (`cd ..`)
This is like having a «go back» button. If you want to return to the folder you were in before, just type `cd ..`. It’s like a quick way to backtrack.
7. Using Wildcards
Wildcards are like search filters. You can use `*` to find folders based on patterns. This will take you to a folder with a name starting with «sep». For example:
cd C:\Users\GFG0338\Desktop\mystuff\my_Sep_Doc>dir sep*.*
8. Using the «dir» command
It lists all Windows Files and Directories (folders) in the current directories. This helps the users to quickly see what Files and Directories are present in a particular location
For example, if you want to list the content of » C:\Users\GFG0338\Desktop\mystuff\my_Doc «, you would type the following:
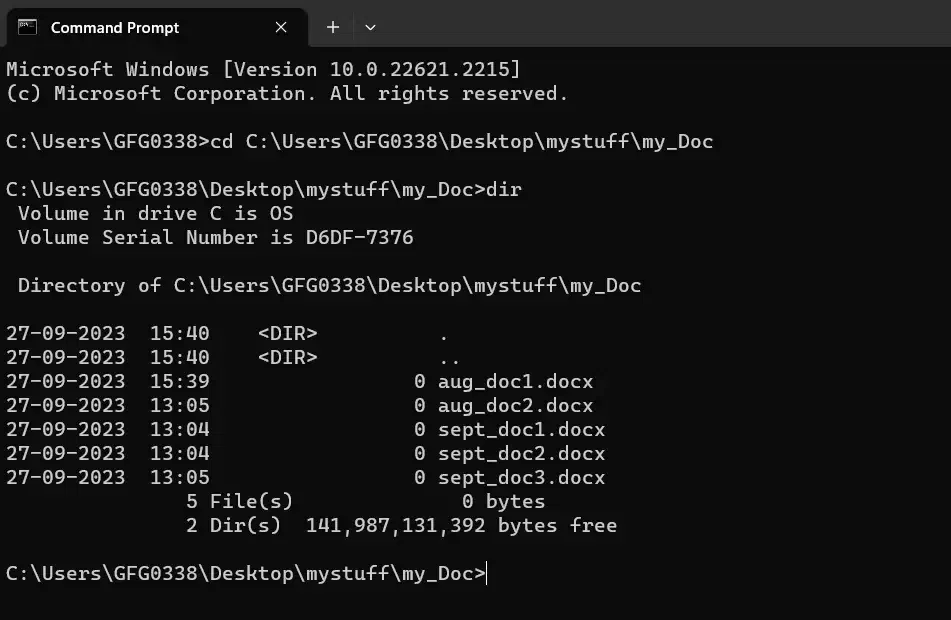
This will give you a list of Files and Directories in that folder along with respective attributes.
How to Navigate to a Folder in Command Prompt
When you want to navigate to a different folder in the Command Prompt, it’s like giving your computer directions. Here’s how to do it in simple steps:
- Open Command Prompt: First, you need to open Command Prompt in Windows 10 or 11. You can do this by pressing the Windows key, typing «Command Prompt,» and hitting Enter.
- Understand Your Starting Point: Before you start, it’s good to know where you are. Command Prompt opens in a default location, usually your user folder.
- Type ‘cd’ and Space: To tell Command Prompt you want to change the folder, type `cd` (which stands for «change directory») followed by a space.
- Enter the Folder Name: Now, type the name of the folder you want to go to. If your folder name has spaces, put it in double-quotes. For example, if you want to go to a folder named «My Stuff,» you’d type: cd «My Stuff»
- Hit Enter: Press the Enter key on your keyboard. This tells Command Prompt to follow your directions and take you to the folder.
- Check Your Location: To make sure you’re in the right place, you can type `cd` without any folder name and press Enter. Command Prompt will show you the full path of where you are.
Note: Remember, you can always use the `cd ..` command to go up one level if you ever want to backtrack.
Tips for Navigating Directories in Command Prompt
Below we have highlighted a few tips and tricks to make directory navigation in the Command Prompt much easier, let’s check them out:
1. The dir Command
The dir command is being used in CMD to list down all the files and directories in the current folder, here’s a quick example for this:
Example:
dir
2. The cd .. Command
The cd .. command helps in navigating back to the previous directory instantly, here’s a quick example for this:
Example:
cd ..
3. Drag & Drop
You can also choose to simply drag a folder from File Explorer into the Command Prompt. This woll automatically insert the entire path of that directory into CMD.
Tips and Tricks while Changing Directory
There could be five possible reasons if you’re unable to change directory in CMD (command prompt). Let’s identify them in segregated format:
1. Incorrect Syntax
If you are not using the correct command, it might led to throw Syntax error. For example,
cd C:\Path\To\Directory (no quotes unless the path contains spaces)2. Permission Issues
Since, normal users have the limited access so there are high chances that you might not beable to access to certain directories. So, it’s recommended to run CMD as an administrator.
3. Non-Existent Directory
Sometimes, we do try to access to a certain directory that might not exist. So, it’s better to verify the path using dir to list down all the available directories.
4. Special Characters or Spaces
If the path contains spaces or special characters, enclose the path in double quotes, For example,
cd "C:\My Folder"5. Drive Mismatch
If you’re trying to change to a directory on a different drive, make sure to switch drives first by typing the drive letter. For example D: before using cd.
D: cd
Best Practices for Directory Management
To ensure efficient directory management, follow these best practices:
- Use Clear and Concise Names: Use descriptive names for directories and files to facilitate easy identification.
- Avoid Deep Nesting: Limit the number of subdirectories within directories to prevent confusion and disorganization.
- Regularly Clean Up Directories: Periodically review and remove unnecessary files and directories to maintain a clutter-free file system.
Conclusion
Changing directories in Command Prompt is an important skill that simplifies file system navigation and task management. Whether you’re working with relative paths, absolute paths, or switching between drives, mastering these commands ensures a smoother and more efficient CMD experience.
Also Read
- Most Useful CMD Commands in Windows
- 10 Ways to Open the Command Prompt in Windows 10
- How to Change Colours in Command Prompt in Windows?
Understanding how to access the home directory, often known as the user profile directory, is fundamental for efficient navigation and management of the individual files, settings, and configurations on a Windows system. The home directory serves as a centralized hub where the personalized data resides, encompassing documents, downloads, desktop items, app settings, and much more. This tutorial provides 2 methods how to get home directory on Windows.
Method 1 — CMD
To obtain the home directory using Command Prompt (CMD), we can utilize the echo command along with the %USERPROFILE% environment variable, which holds the path to the user’s home directory.
echo %USERPROFILE%Output example:
C:\Users\JohnMethod 2 — PowerShell
To retrieve the home directory using PowerShell, we can utilize the $HOME automatic variable, which holds the path to the current user’s home directory.
$HOME















