В случае, если вам потребовался доступ из Windows к данным на разделе диска с файловой системой Linux — ext4/ext3/ext2, встроенными средствами системы сделать это не получится. Однако, возможности есть, причем реализовать это можно встроенными средствами системы или с помощью сторонних инструментов.
В этой инструкции подробно о способах подключить раздел диска в файловой системе Linux в Windows 11 и Windows 10 для доступа к данным на этом разделе как для чтения, так и для записи.
Ext2 File System Driver (Ext2Fsd) — самый простой способ открыть раздел ext4/ext3/ext2 в Windows
Ext2 File System Driver или Ext2Fsd — сторонний и полностью бесплатный драйвер для подключения разделов Linux во всех версиях Windows начиная с XP. Несмотря на название, поддерживаются не только разделы не только с файловой системой ext2, но и более новые ext4 и ext3.
Порядок использования Ext2 File System Driver для доступа к дискам Linux будет следующим:
- Загрузите установщик Ext2Fsd с сайта https://sourceforge.net/projects/ext2fsd/
- Установите драйвер, в параметрах установки как правило не требуется ничего изменять.
- По завершении установки вам будет предложено запустить Ext2 Volume Manager (менеджер томов), запустите его.
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по разделу Linux ext4, ext3, ext2 и выберите пункт «Assign Drive Letter» — назначить букву диска.
- Для раздела будет автоматически назначена буква диска, и вы увидите раздел в Проводнике Windows с возможностью чтения и записи файлов на нём.
В дальнейшем вы тем же способом сможете удалить букву диска с раздела (опция «Change letter» — «Remove»).
Доступ к разделам Linux средствами Подсистемы Windows для Linux (WSL)
Подсистема Windows для Linux (WSL) также может быть использована для подключения дисков Linux в Windows таким образом, чтобы доступ к ним был возможен из проводника. Шаги будут следующими:
- Запустите командную строку, Терминал или PowerShell от имени администратора и по порядку введите команды
wsl --install wsl --set-default-version 2 dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart wsl --install -d Ubuntu
- После выполнения последней команды откроется окно консоли Linux (командную строку при этом не закрывайте, она еще пригодится) с предложением настроить имя пользователя и пароль, сделайте это. Если в окне консоли вы увидите сообщение об ошибке, скачайте и установите обновление WSL, перезагрузите компьютер и запустите Ubuntu из меню «Пуск».
- В консоли Ubuntu введите команду
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/ext-drives/
для создания папки, к которой будут монтироваться диски.
- В консоли Windows (командная строка, терминал, Powershell) введите команду
wmic diskdrive list brief
- Обратите внимание на DeviceID диска, который нужно подключить и введите команду (так же в консоли Windows) указав соответствующий номер в имени PHYSICALDRIVE
wsl --mount \\.\PHYSICALDRIVE
- В консоли Ubuntu введите команду lsblk — это отобразит список подключенных дисков, разделов на них и их размер. В следующей команде используем имя нужного раздела для монтирования:
sudo mount /dev/sdИМЯ /mnt/ext-drives/
- После успешного выполнения всех указанных шагов вы можете зайти в Проводник Windows, выбрать пункт «Linux» в панели быстрого доступа, перейти в папку mnt\ext-drives и получить доступ к файлам на подключенном разделе Linux с возможностью записи и чтения.
В дальнейшем для отключения диска от WSL можно использовать ту же команду, которая использовалась на 5-м шаге, заменив mount на unmount.
Есть и другие программы (драйверы) для доступа к разделам Linux из Windows, но не полностью бесплатные. Среди них:
- DiskInternals Linux Reader — в бесплатной версии доступно только чтение данных с разделов.
- Paragon Linux File Systems for Windows — бесплатная работа в течение пробной версии, затем необходимо приобретать лицензию.
На чтение 4 мин Просмотров 13.2к. Опубликовано Обновлено
В этой статье рассказывается о том, как вы можете получить доступ к разделам файловой системы Linux Ext2, Ext3 и Ext4 в Windows 10 и автоматически сохранить их в проводнике, как все другие разделы NTFS или FAT32. Вы даже можете копировать файлы и записывать новый файлы на эти разделы.
Хотя Windows использует файловую систему NTFS и FAT32, Linux (например, Ubuntu) использует расширенные архитектуры файловой системы Ext 3, Ext4 и т. д. Самое интересное то, что Linux может получать доступ, читать и записывать файлы в файловые системы Windows, а Windows не может получить доступ к файлу Linux — системы. Я имею в виду, что Windows не имеет поддержки для чтения или доступа к разделам Ext3 или Ext4.
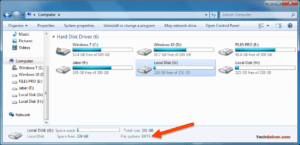
Таким образом, если у вас есть система с двойной загрузкой или более, в которой вы можете переключаться между Windows и Linux из меню загрузчика, иногда вам может понадобиться доступ к Linux-дискам / разделам. Или предположим, что вы находитесь в Windows, и у вас есть съемный / жесткий диск, который отформатирован в Ext3, и теперь вам нужно открыть файл внутри него. Или ваша система Linux «зависла», и вам необходимо восстановить важные файлы с помощью Windows. В таких случаях вам необходимо прочитать эти файловые системы без переключения с Windows.
Хотя Windows никогда не интересовалась файловыми системами Linux, к счастью, существуют сторонние диски и инструменты для открытия и чтения разделов Linux из Windows. Мы рассмотрим несколько инструментов в этой статье. Однако здесь мы будем использовать драйвер файловой системы Linux с открытым исходным кодом под названием Ext2Fsd, который предназначен исключительно для поддержки Ext2/3/4 в Microsoft Windows. При этом вы можете автоматически монтировать разделы Ext при загрузке диска, когда вам нужно.
- Размонтируйте разделы Linux Ext4/3/2 в проводнике Windows
- Загрузите Ex2Fsd из sourceforge.net/projects/ext2fsd/.
Содержание
- Подключение EXT4 в Windows 7/8/8.1/10
- Восстановление личных файлов
- Выводы
Подключение EXT4 в Windows 7/8/8.1/10
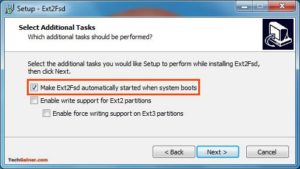
При установке отметьте «Make Ext2Fsd автоматически запускается при загрузке системы» и нажмите «Далее» и завершите настройку. Он будет автоматически запускать драйвер Ex2Fsd с Windows после следующей перезагрузки.
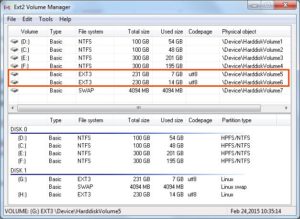
Запустите диспетчер томов Ext2Fsd. С помощью этого вы можете установить точку монтирования и настройки.
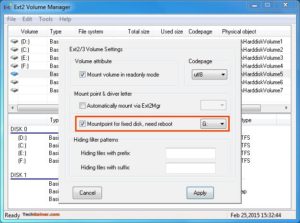
Чтобы назначить последний том, дважды щелкните раздел (или выберите раздел и выберите «Инструменты»> «Управление томами Ex2»), включите «Mountpoint for fixed disk» и назначьте букву диска. Затем нажмите Применить.
При следующей перезагрузке Windows вы увидите, что ваш желаемый раздел Linux монтируется в Проводнике в качестве других стандартных разделов.
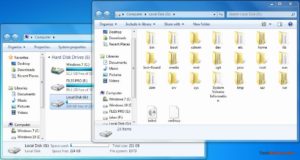
Вы также можете указать свое имя, переименовав имя по умолчанию «Локальный диск». Готово!
Примечание 1: Рекомендуется хранить ваши разделы Linux только для чтения, чтобы вы или ваша система не могли повредить системе Linux.
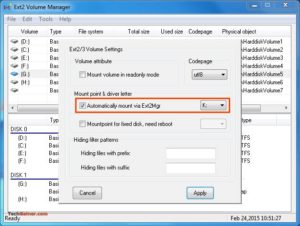
Примечание 2: Если вы не хотите, чтобы Ext2Fsd автоматически монтировал диск в проводнике при загрузке, вы можете отметить «Автоматически монтировать через Ex2Mgr». При этом ваш раздел будет монтироваться только при открытии диспетчера томов Ex2Fsd, как показано ниже:
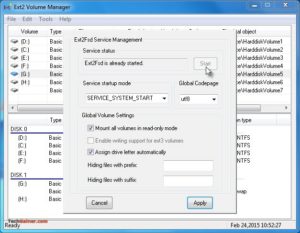
Примечание 3: Во время установки Ext2Fsd, если вы не устанавливали службу Ex2Fsd для автоматического запуска с Windows, вам необходимо вручную запустить службу из меню «Сервис»> «Управление службами»> «Пуск», как показано ниже:
Восстановление личных файлов
Про подключение EXT4 в Windows поговорили, теперь узнаем что делать дальше. Если вы ищете доступ к своим личным файлам, хранящимся в Linux, перейдите в home\name\, как показано ниже:
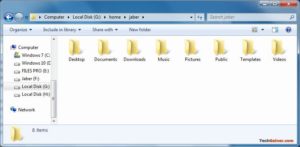
Хотя это руководство сделано в Windows 7, я протестировал его на Windows 10 и способ должен также работать с Windows 8.x в соответствии с его редакциями. Возможность просмотра и чтения всех разделов в обеих ОС — это, безусловно, классная функция для тех, кто использует Linux и Windows на одной машине.
Выводы
Подключение EXT4 в Windows является очень простым. Надеемся, Вам была интересна наша статья об этом — расскажите нам в комментариях.
Также, не забудьте поделится ссылкой на статью в Google+, Facebook, Twitter, Одноклассники или, например, ВКонтакте.
Подключение ext4 в Windows
Подключение ext4 в Windows
Если вы используете Windows рядом с Linux, рано или поздно может возникнуть необходимость скопировать файлы из одной операционной системы в другую. При копировании с Windows в Linux проблем не возникнет так как Linux отлично открывает файловые системы семейства NTFS, но вот открыть файловую систему ext4 в операционной системе от майкрософт будет не так то просто.
В этой инструкции я опишу несколько способов подключения ext4 в Windows. Вы можете либо добавить поддержку этой файловой системы в Windows либо просто извлечь из неё файлы с помощью специальной программы.
Подключение ext4 в Windows 10
Сообществом открытого программного обеспечения был разработан открытый драйвер ext4 для windows под названием ext2fsd.
1. Установка драйвера ext2fsd
Загрузить установщик для вашей версии ОС можно с официального сайта программы. Процесс установки не должен вызвать никаких трудностей и сводиться к нажиманию кнопки Далее в мастере установки, как обычно при установке программ в Windows. Интерес представляет только это окно:

Здесь:
- Make Ex2Fsd automatically started when system boots — автоматическая загрузка драйвера во время загрузки системы, желательно включить.
- Enable write support for ext2 partitions — поддержка записи в файловую систему ext2
- Enable force writing support on Ext3 partitions — поддержка записи в файловую систему ext3
Установите необходимые галочки и еще несколько раз нажмите кнопку Далее.
2. Подключение ext4
Главное окно программы выглядит вот так:

Здесь в в списке показаны все доступные разделы, их размер и файловая система. Для того чтобы примонтировать любой из разделов выполните на нем двойной щелчок:

Здесь есть два варианта монтирования:
- Automaticly mount via Ext2Mgr — раздел будет подключен сейчас, но только до перезагрузки
- Mountpoint for fixed disk — постоянное автоматическое подключение раздела при старте системы.
С права от поля способа монтирования можно выбрать букву диска для монтирования.
Также в поле Hiding files with prefix можно указать с какими префиксами файлы нужно считать скрытыми, как вы знаете в Linux считаются скрытыми файлы с префиксом точка. Когда укажите все необходимые параметры нажмите кнопку Apply.
Теперь открыв Мой компьютер вы увидите подключенный диск:

С помощью драйвера Ext2fsd вы можете работать с вашими разделами Linux как с обычными NTFS или FAT.
Извлечение файлов из Ext4 в Windows
Это самый простой способ открыть ext4 в windows 10. С помощью программы DiskInternals Linux Reader вы можете извлечь файлы из раздела с файловой системой Linux не добавляя её поддержку в ядро системы. Скачать программу можно на официальном сайте. Установка программы аналогично предыдущей сводится к нажатию кнопки Далее:

Главное окно программы выглядит вот так:

Здесь вы можете выбрать нужный раздел с файловой системой ext4 и просмотреть все файлы, что там есть:

Чтобы извлечь любой из файлов или папку, кликните по ней правой кнопкой мыши и выберите Save As, затем выберите папку, в которую будет сохранен ваш файл:

Чтобы сохранить структуру папок нужно отметить флажок Save directory structure. Затем дождитесь завершения процесса копирования и можете делать с полученными файлами все что нужно уже в проводнике.
Source
Position : Tips — How to Read and Write EXT4, EXT3 and EXT2 Drives in Windows 10/11?
This guide shows how to read and write data of Linux Ext2/Ext3/Ext4 partitions in Windows 11/10/8/7/Vista/XP. If you dual boot your computer with Windows and Linux, you’ll be able to access NTFS or FAT32 partitions under Linux, but you cannot access Linux partitions directly under Windows. If you need to read Ext4, Ext3 or Ext2 partitions under Windows 10/11 without booting into Linux, here is the tutorial that can help you.
Overview on reading Ext4/3/2 drives in Windows
«My computer is in a dual-boot environment with Windows 10 and Ubuntu. They are installed on one hard drive which is divided into two partitions C and D. Sometimes I want to grab files from Linux partition while computer has booted into Windows 10. It’s way too trouble to restart into Linux and copy files to a FAT32 partition and reboot back into Windows 10. Anyone here knows how to access Ext4 partitions from Windows 10?»
If your computer is dual-booting with Windows and Linux, you must have trouble in accessing files and folder stored in Linux partitions while Windows is running. The default file system type used on Windows and Linux are different, Windows users NTFS, exFAT, or FAT32, while Linux employs Ext2, Ext3, or Ext4 file systems. Besides, Linux has support for NTFS and FAT32 file system, which enables users to access files on Windows partitions. However, on the other hand Windows does not have inbuilt support for Linux partitions.
Therefore, you may come across such a situation that if you are using Windows and Linux together on a computer. You may need to use some files you downloaded in Linux, and you are logged into Windows OS already. Since you cannot access Linux partition directly, you’ll have to restart computer and boot to Linux, copy these files to a NTFS or FAT32 partition and then reboot computer to Windows. Wouldn’t it be better if you can access Linux partitions from Windows?
Nowadays, many users would like to dual boot Linux and Windows on one PC, and they often need to transfer data between two systems. Since Windows does not provide built-in tools to mount Linux partitions, we need to use third-party software to read & write data in Ext4/3/2 partitions. This article will introduce an effective tool to solve the problem. Keep reading the guide, you’ll be able to know how to mount and access files in Linux partitions under Windows 10/11.
Windows & Linux file systems
Some readers may wonder what a file system is. A file system is the tool for operating system to control, store, retrieve and organize files on a storage device. Why are there so many file system types? Different operating systems use and support specific types of file systems, for they target different users. For instance, Windows NT targets enterprise users and uses NTFS file system which enhanced security greatly; Windows 9X targets ordinary users and uses FAT file system which has less security but more performance.
As we all know that Windows and Linux uses different file systems: Windows uses NTFS, exFAT, and FAT32 file system, whereas Linux uses Ext2, Ext3 and Ext4. Thus, users cannot copy a file from Linux to Windows directly. It is quite complicated for an OS to add the support of a particular file system, especially adding support for proprietary file system. For example, the structure of data on disk, encryption algorithm and so on of NTFS file system are not known to the public, and it is very challenging to fully support NTFS in Linux.
Windows does not have native support for Linux file system like Ext2, Ext3 and Ext4. However, some tools have been created to solve this issue. Such software supports Linux file system and allows users to access Linux partitions under Windows. The follow section will introduce a Windows partition manager that can mount and access Linux partition from Windows.
Ext4/3/2 reader for Windows
If you have Windows and Linux on the same PC and want to access data of an EXT4 partition under Windows 10/11, then you need to use third-party software to read & write data in EXt4 partitions. Here we recommend DiskGenius Professional Edition to solve the problem. DiskGenius Professional Edition (formerly known as PartitionGuru) is advanced Windows partition manager and data recovery software. It can handle partitions formatted as NTFS, FAT32, FAT12, FAT16, exFAT, ReFS, Ext2, Ext3 and Ext4 file system from Windows.
Download DiskGenius
With this tool you can do following operations:
- Full access (write & read) to Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4 partitions under Windows
- Create Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4 partitions under Windows 11/10/8/7
- Format a drive to Ext4/3/2 in Windows 11/10/8/7
- Resize, shrink, extend, or split Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4 partitions without deleting data
- Partition recovery — recover lost or deleted Ext4/3/2 partitions in Windows
- File recovery – recover deleted or lost files from Ext4/3/2 partitions in Windows
- Clone or back up Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4 partitions
- Edit hex data of Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4 partitions
- Check and repair disk bad sectors
Guide 1. How to mount Ext4/Ext3/Ext2 partitions in Windows 10/11?
Mounting Ext4 partitions in Windows is the first step before we can read or write data in the volume. Now we can use DiskGenius to open the Ext4 partition.
Step 1. Connect the disk that contains Ext4 partitions to your computer and boot your PC into Windows 10.
Step 2. Download and install DiskGenius Professional Edition on your PC and then launch it.
Step 3. Once DiskGenius is launched, you can view all disks and partitions attached to this computer. Select the Ext4 partition and you can browse files and folders in it.
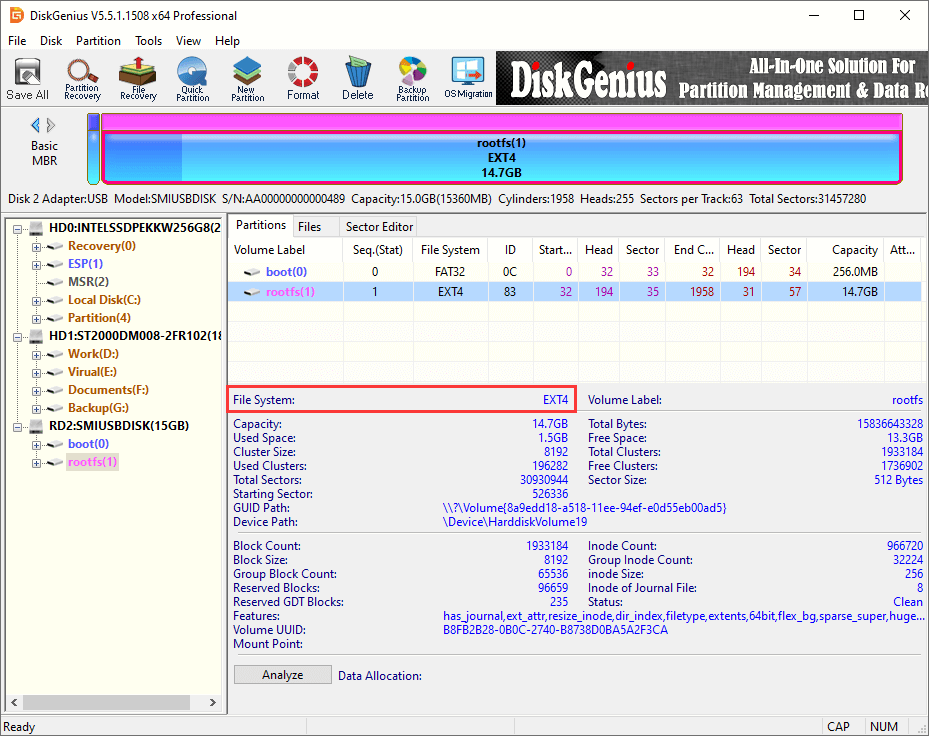
Step 4. Select the Ext4 partition and click Files tab, and you can see data in the root directory. Then you can double click a folder to open it and view files in it.
Guide 2. How to read files of Ext4 partitions in Windows 10/11?
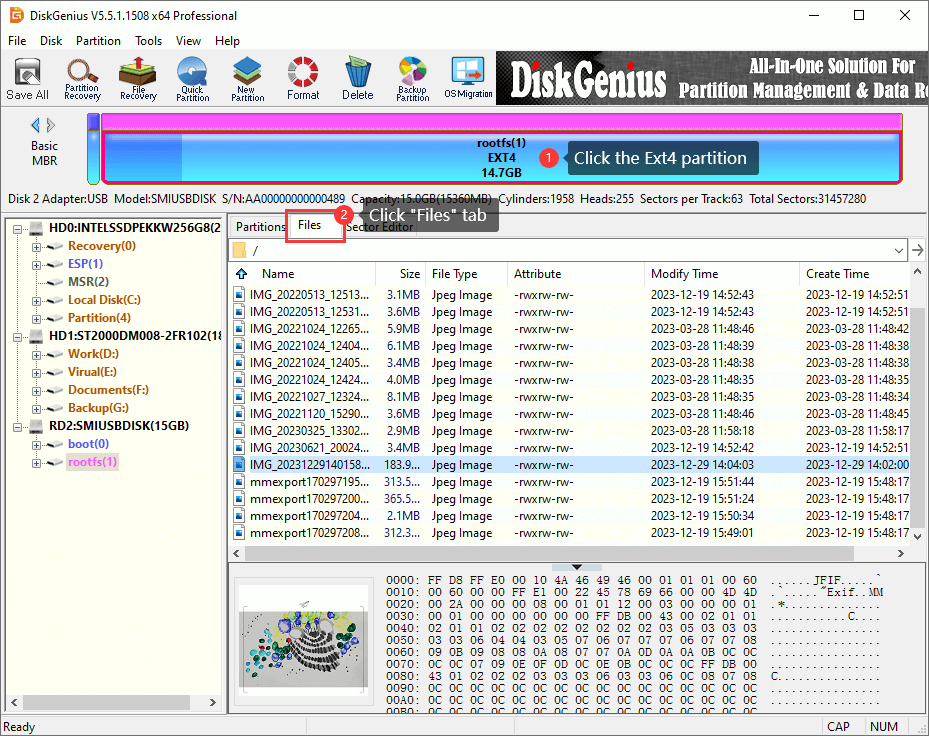
Once the Ext4 partition is recognized by DiskGenius, you can read & write files in the partition.
File paths and directories are listed in the left pane like Windows File Explorer, and you can click path and view files on the right pane. Click a file on the right pane, and you can see the thumbnail preview, as follows.
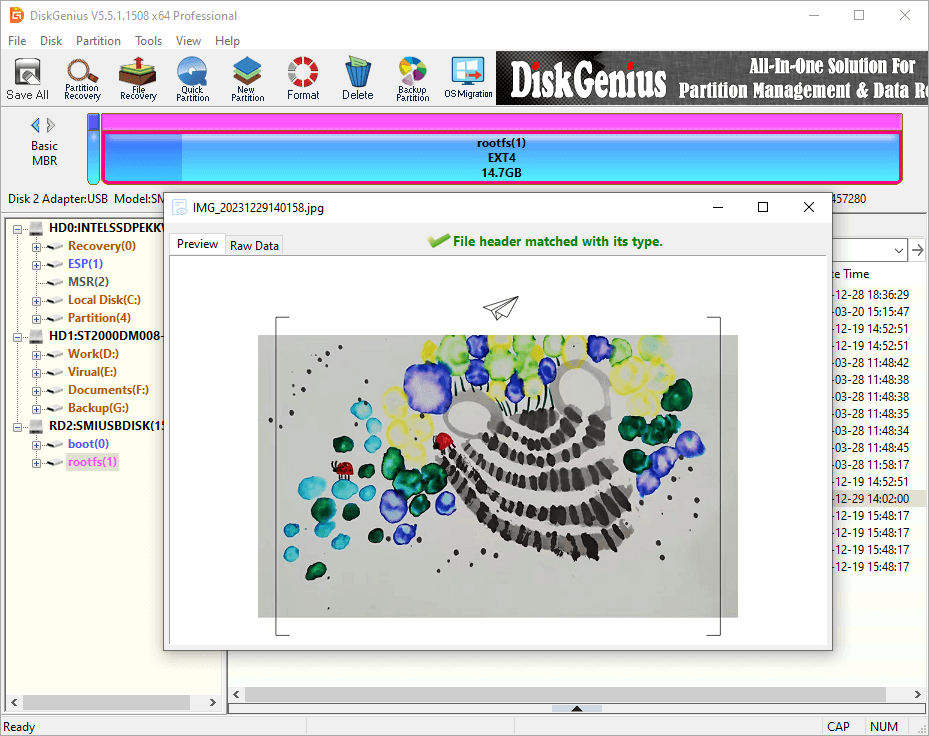
You can double-click the file to open it and view file content in its original size. This tool supports to preview photos, audio, video, Microsoft Office documents, PDF files, and text files.
Guide 3. How to write data into Ext4 partitions in Windows 10/11?
With DiskGenius Professional Edition, you can create new folders in the Ext4 partition, write files to this Ext4 partition, rename files and folder, delete files, export files of the Ext4 partition to another drive, etc. Here are some examples:
Example 1: Write files to Ext4 partitions
Step 1. Open the folder where you want to add data and right-click empty space on the right pane to choose «Copy Files To Current Partition«.
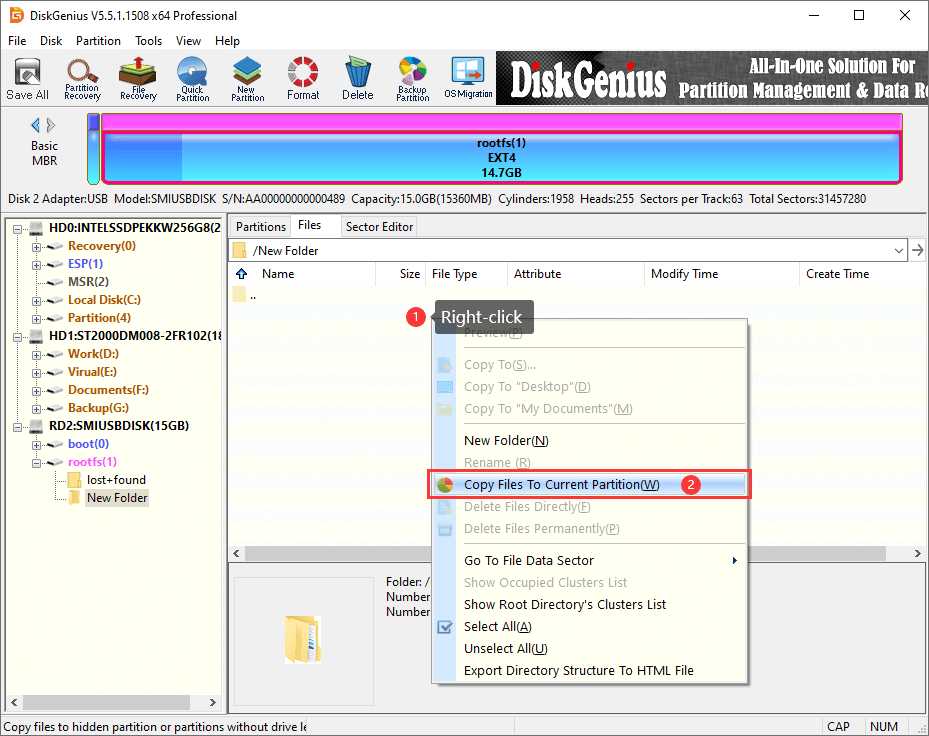
Step 2. Select files from other partitions or hard drives on your computer and Open. Wait for a while, and files will be write into this Ext4 partition.
Tip: This software also allows users to export files from the Ext4 partition to another partition on this computer: Select files you want to output -> right-click files and select «Copy To» -> select target location — > begin outputting files.
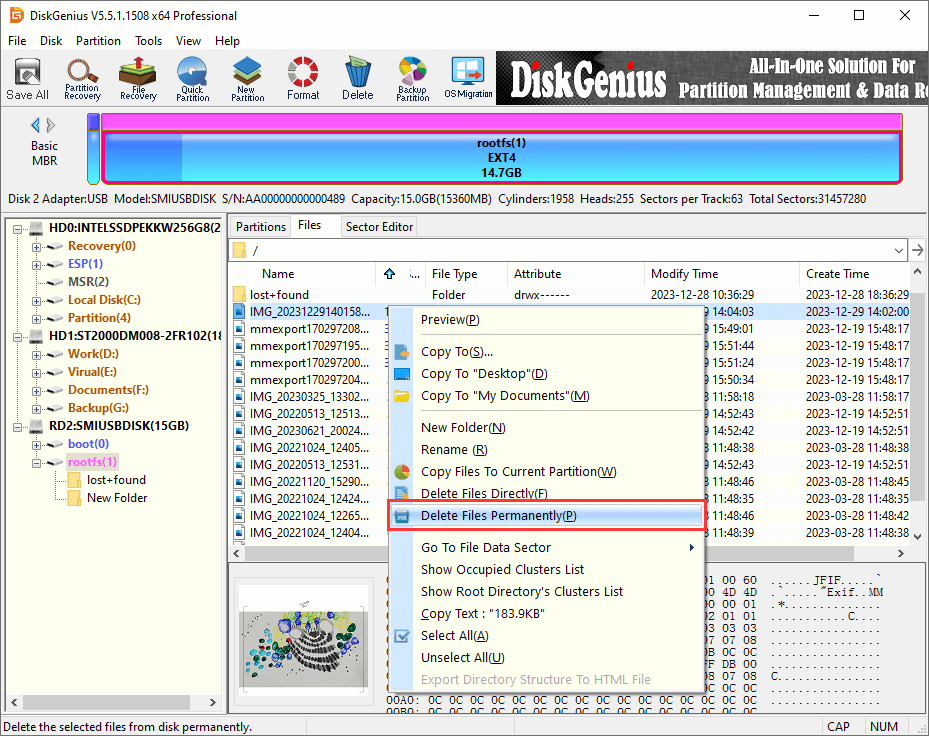
Example 2: Permanently delete files from Ext4 partitions
This feature is able to delete files permanently so that they cannot be recovered by any means, as the software overwrites the disk space while deleting files. If you just want to delete files, you can use Delete Files Directly
Step 1. Select and right-click files you want to delete and select «Delete Files Permanently» option from context menu.
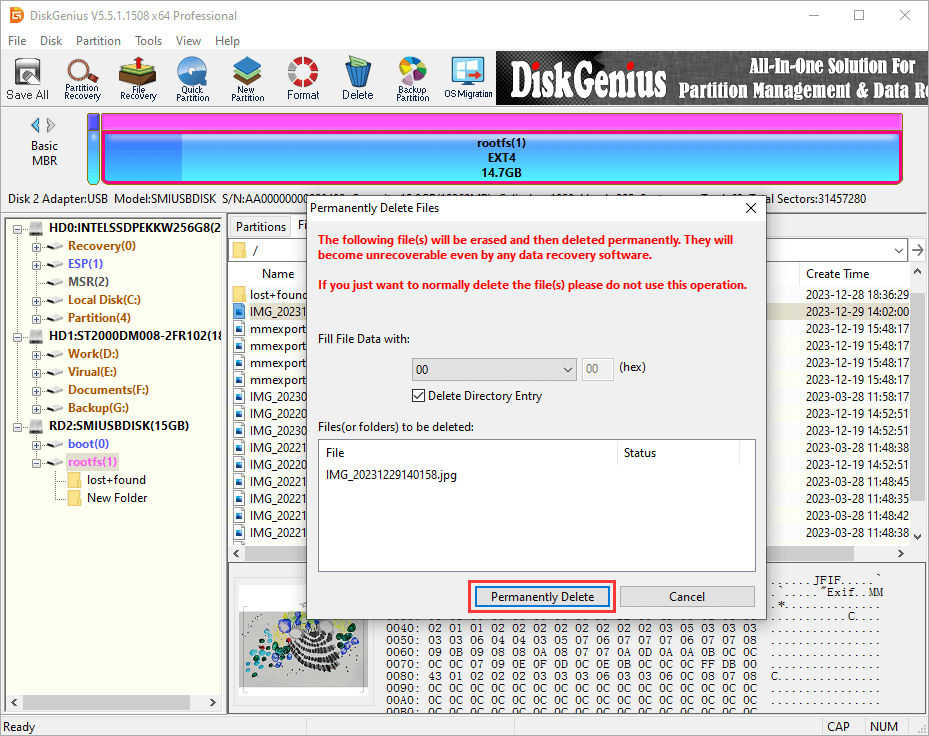
Step 2. Click «Permanently Delete» button on the popup window. Then the selected file will be deleted permanently.
Example 3: Rename files or folders in Ext4 partitions
In addition to creating new folders, you can also rename files or folders in the software as follows:
Step 1. Right-click on a file or folder you want to change name and select «Rename«.
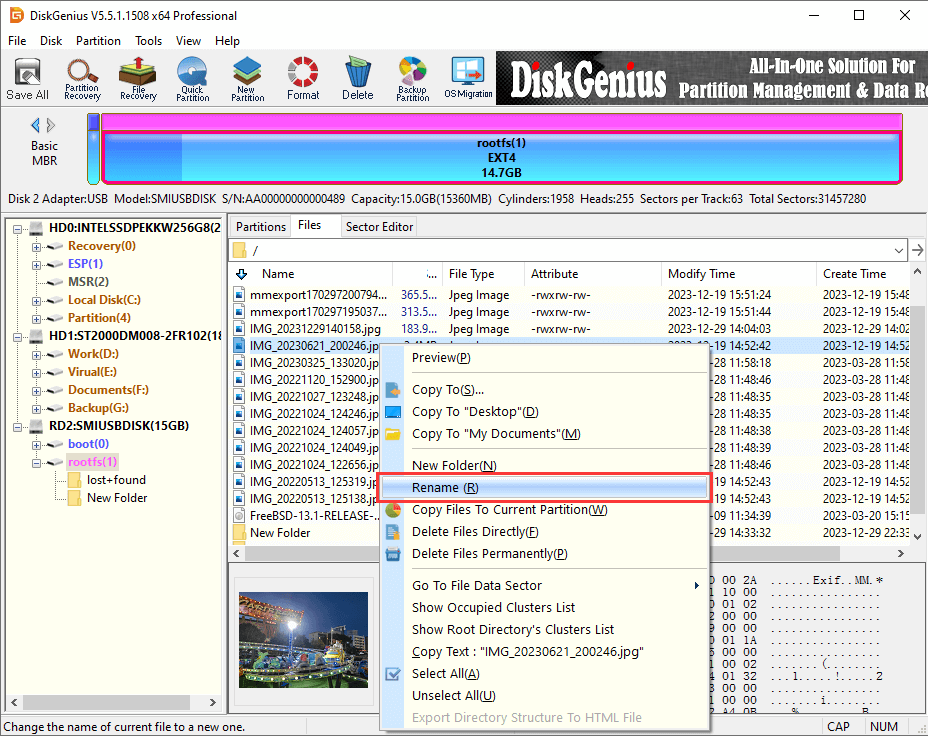
Step 2. Put in the desired name and click «OK» button.
Guide 4. How to resize Ext4 partitions without losing data in Windows 10/11?
The feature of resizing Ext4 partition without losing data is available for the DiskGenius Free Edition, and you can free download the free edition to resize, extend, or split an Ext4, Ext3 or Ext2 partition without deleting existing data in Windows 11/10/8/7.
Step 1. After launch DiskGenius, you can easily locate the Ext4 partition. Right-click it and choose «Resize Partition».
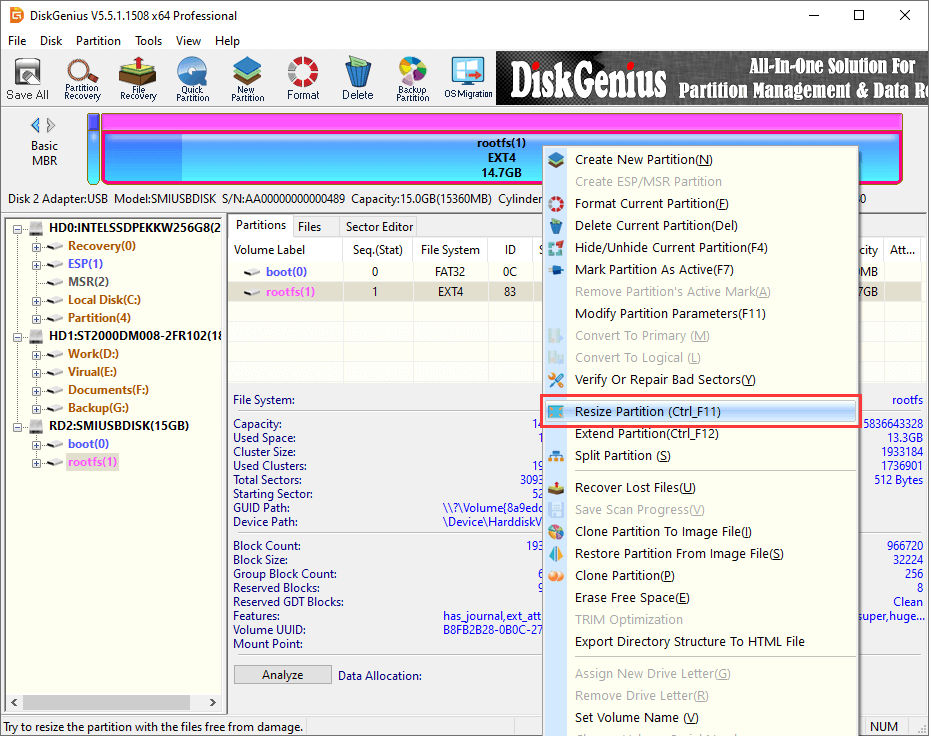
Step 2. Adjust partition size based on your needs. You can change partition size either by manually inputting the size or by dragging the partition boundaries.
The free disk space gained from the partition can be left as unallocated or created as a new partition.
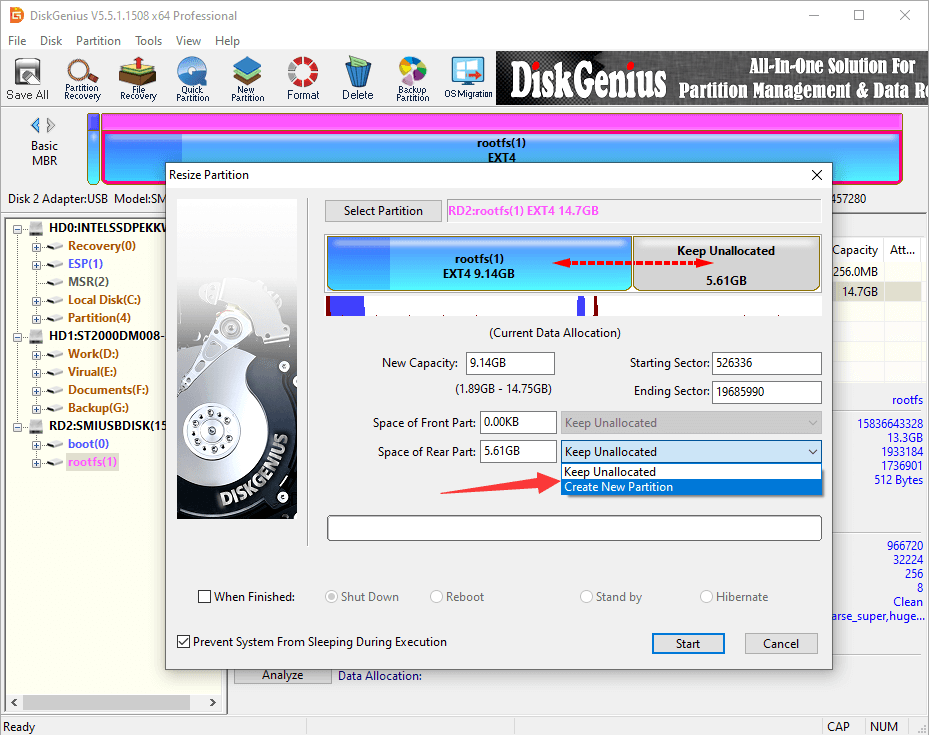
Step 3. Carefully read the notes. Click «Yes» to confirm and continue.
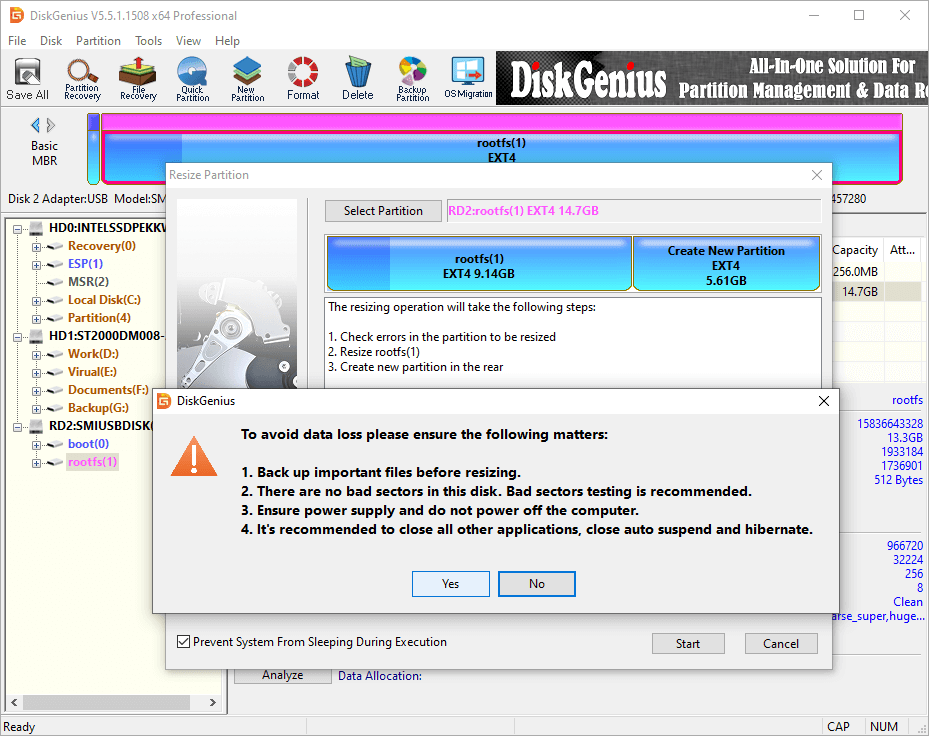
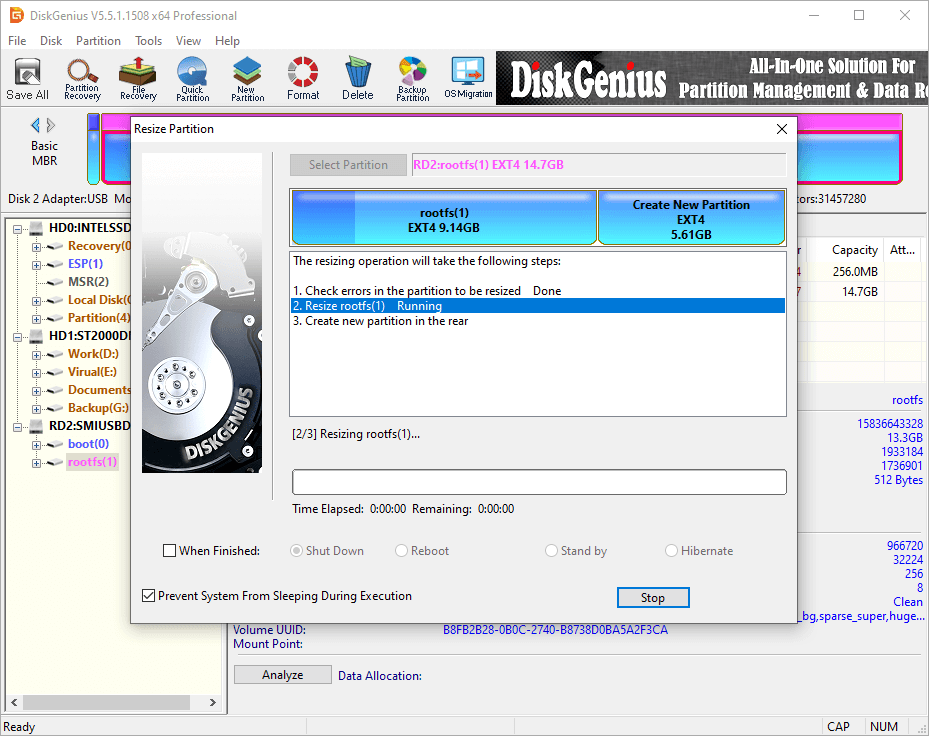
Step 4. DiskGenius is resizng the partition. The process might take some time depending on the size of the partition and the amount of data stored on it. Please be patient.
Guide 5. How to format a drive to Ext4/3/2 in Windows 10/11?
DiskGenius Free Edition support creating or formatting Linux-specific file systems like ext4, ext3, or ext2 within Window. The following steps shows how to format a partition to Ext4 using DiskGenius Free Edition in Windows 10.
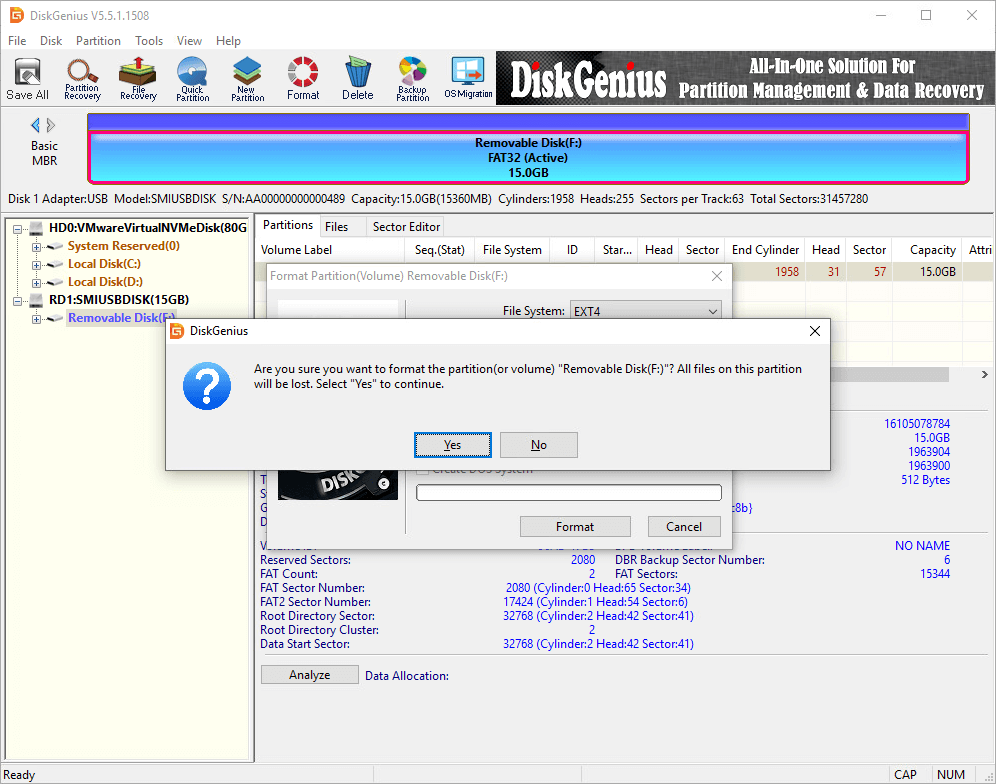
Step 1. After launching DiskGenius Free Edition, you can select the partition to be formatted, click «Format» button. Then you can choose Ext4 as the file system and click «Format» button.
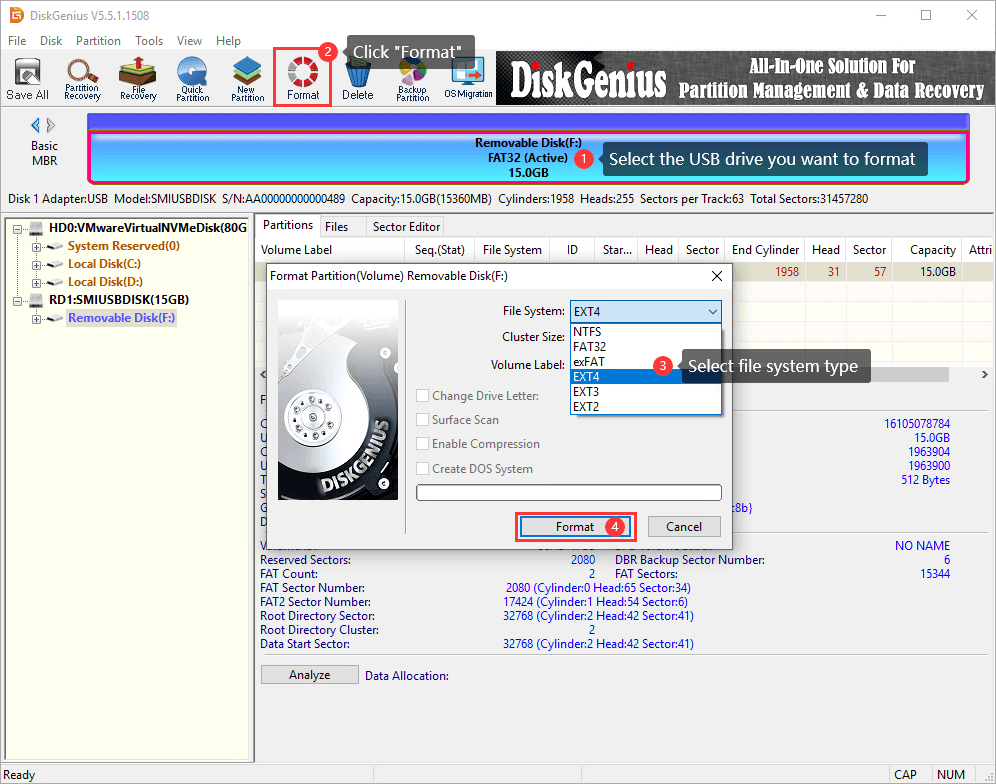
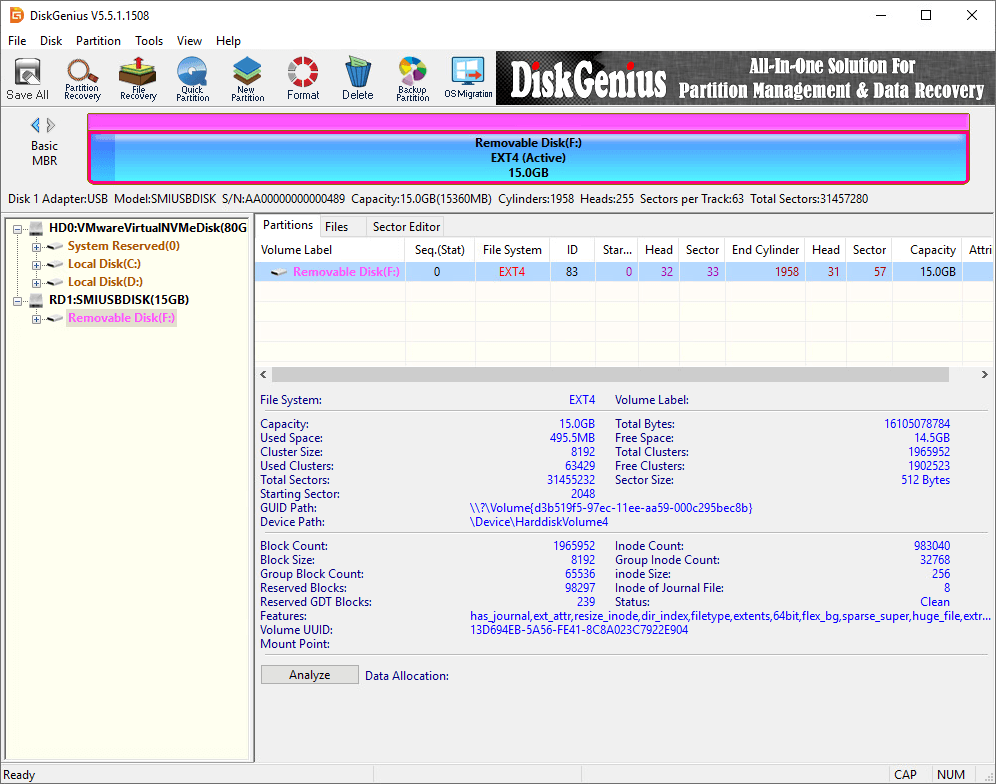
Step 2. A warning message pops up, saying all data on the drive will be erased by the formatting. If you don’t have any important data on the drive, click «Yes» to continue. Then DiskGenius starts to format the drive.
The drive is formatted as Ext4 successfully.
Here’s the video guide on how to format a partition to Ext4 file system in Windows 10:
Conclusion
DiskGenius is a handy and versatile Linux reader for Windows users. By using the software, you can easily read or write your Ext4, Ext3, and Ext2 partitions from Windows 11/10/8/7. Moreover, it also supports to manage Ext4/3/2 partitions to help you get the best use of disk space. If you are one of the dual-boot users, DiskGenius Professional Edition will be your best assistance.
Updated on May 09, 2024
On this page, you’ll discover 6 practical ways to access EXT4 partitions from Windows 11/10/8/7 in two parts. Continue reading to learn how to easily access and read data from Linux EXT4 partitions on Windows:
Part 1: Accessing EXT4 Partition with Software Solutions
1. **EXT2FSD**: This is a free file system driver that allows Windows to read EXT2, EXT3, and EXT4 partitions. Download and install it, then mount the partition to access your files.
2. **Paragon ExtFS for Windows**: A commercial tool that provides full read and write support for EXT4 partitions. Install it, and you can directly open and modify files on the Linux partition.
3. **Linux Reader by Diskinternals**: This software enables you to view and copy files from EXT4 partitions without needing any additional software or drivers. Simply download and run it to access your data.
Part 2: Using Command Prompt or PowerShell
4. **Using FUSE for Windows**: Install the FUSE for Windows and the ext2fuse package, which allows you to mount EXT4 partitions via the command line. After installation, use the `mount` command to mount the partition and explore the files.
5. **Virtual Machines (VMware or VirtualBox)**: Create a Linux virtual machine and install a distribution like Ubuntu. Share the EXT4 partition with the virtual machine, and you can access it from within the Linux environment.
6. **SSH into a Linux System**: If you have access to a remote Linux system, you can use SSH to connect and transfer files from the EXT4 partition. Use tools like PuTTY for Windows to establish the connection.
By using these methods, you can effectively work with Linux EXT4 partitions on your Windows system. Choose the one that suits your needs best.
If you’re running a dual-boot setup with Windows and Linux on your laptop or desktop, you might need to access files from your Linux partition, such as EXT4, on Windows at some point. For this purpose, you can utilize the Explore feature in Partition Master Professional, which enables immediate visibility of your drive data. Let’s explore how to easily access and open EXT4 partition files on your Windows PC.

The tools featured on this page also allow you to access EXT2/3 Linux partitions on Windows. So, feel free to share this article on your social media to help more people in need.
1. 中文 (Chinese): Chinese
2. 英文 (English): English
3. 日本語 (Japanese): Japanese
4. 韩国语 (Korean): Korean
5. 法语 (French): French
6. 德语 (German): German
7. 西班牙语 (Spanish): Spanish
8. 意大利语 (Italian): Italian
9. 俄语 (Russian): Russian
10. 阿拉伯语 (Arabic): Arabic
11. 葡萄牙语 (Portuguese): Portuguese
12. 荷兰语 (Dutch): Dutch
13. 希腊语 (Greek): Greek
14. 土耳其语 (Turkish): Turkish
15. 波兰语 (Polish): Polish
16. 越南语 (Vietnamese): Vietnamese
17. 印度尼西亚语 (Indonesian): Indonesian
18. 泰语 (Thai): Thai
19. 菲律宾语 (Filipino): Filipino
20. 丹麦语 (Danish): Danish
21. 瑞典语 (Swedish): Swedish
22. 挪威语 (Norwegian): Norwegian
23. 芬兰语 (Finnish): Finnish
24. 印地语 (Hindi): Hindi
25. 乌尔都语 (Urdu): Urdu
26. 波斯语 (Persian): Persian
27. 希伯来语 (Hebrew): Hebrew
28. 马来语 (Malay): Malay
29. 斯洛伐克语 (Slovak): Slovak
30. 匈牙利语 (Hungarian): Hungarian
Remember, there are many more languages spoken worldwide, but this list includes some of the most widely spoken.
How to Access Ext4 on Windows 11/10/8/7
To use the Linux hard drive as a data disk on Windows and make the EXT4 partition accessible in Windows, you’ll first need to check if there’s any important data saved on the drive by using an EXT4 viewer tool.
- 1. Please note that if you don’t concern about the data, proceed to the EXT4 Formatter for assistance.
2. If you have crucial data saved, it is recommended to use a reliable EXT4 reader to access and recover the data from the partition first. After that, you can format and convert the EXT4 partition to NTFS using a professional EXT4 formatter. This way, no data loss will happen.
Follow the complete process below to make EXT4 readable on Windows 10/8/7:
#1. View and Explore EXT4 Partition Content
- Here are the translations:
- ?Applies to: Viewing EXT4 partition content and data on Windows
- ?Important Tool: Linux EXT4 partition management software — Partition Master tool
If you wish to view and examine the saved content within the EXT4 volume on Windows prior to conversion, the tool Partition Master, equipped with its Explore feature, can assist. Here’s how to view the contents of your EXT4 partition on a Windows PC using the EXT4 partition management software:
1. Download and install the Partition Master software on your Windows computer.
2. Launch the software and it will display an overview of all the disks and partitions present on your system.
3. Locate the EXT4 partition that you want to view and select it.
4. From the main menu, click on the «Explore» or «Browse» option (the exact term may vary depending on the software version).
5. A new window will open, allowing you to navigate through the files and folders within the EXT4 partition just like you would in a regular Windows explorer.
6. You can now view, open, and even copy files from the EXT4 partition to your Windows system for safekeeping.
7. After you’ve examined the content and made any necessary backups, proceed with converting the EXT4 partition to a Windows-compatible file system if needed.
Remember that while this method allows you to access the files, the partition will still not be natively readable by Windows without the use of such tools.
Step 1. Launch AOMEI Partition Assistant and locate the EXT4 partition.
Step 2. Right-click on the EXT4 partition and select «Explore».
Step 3: Expand the folders on the left pane to check the contents of the EXT4 partition.
Explore partition with tools Partition Master
If the Linux EXT4 partition has some valuable files, proceed to the next stage, where you’ll learn how to access and recover data from a Linux partition on Windows.
#2. Access EXT4 Partition Data from Windows 10/8/7
- Here are the translations for the provided text:
- ?Applies to: Read and access data on EXT partition, enabling the opening and usability of EXT4 partitions in Windows.
- ?Important Tools: 1. EXT4 Reader; 2. EXT4 Formatting Tool.
To prevent unintended data loss, it’s advisable to use a reliable EXT4 reader to access the stored data beforehand before converting the EXT4 partition. Here’s how to make the EXT4 partition accessible without losing any data:
< strong > First, use EXT4 Reader to read and restore EXT4 partition data < /strong >
To access and restore data from the EXT4 partition on Windows, you’ll need a reliable EXT4 reader for assistance. Tools like Data Recovery Wizard, as a professional hard drive data recovery software, are capable of helping.
This software will promptly scan and recover all your lost data from EXT2/EXT3 partitions, FAT32 USB drives, or exFAT external hard disks. To use this software to scan, preview, and restore files stored in the EXT4 partition, follow this guide page:
Remember to save the recovered EXT4 partition data to another secure location on your Windows hard drive.
Next, Use EXT4 Formatter to Make EXT4 Partition Accessible on Windows
Since Windows does not support Linux-based file systems, Windows users cannot view or make any changes to the EXT4/3/2 partitions on a Windows PC without professional tools.
Fortunately, a reliable EXT4 formatter — AOMEI Partition Assistant allows you to change the file system of Linux partition from EXT4/3/2 to a Windows-supported one — NTFS or FAT32. By doing so, you can fully access and make use of an EXT4/3/2 partition on Windows.
Here’s how you can easily format EXT4 partition to NTFS with just a few simple clicks:
Step 1. Launch AOMEI Partition Assistant, right-click the partition you plan to format and choose “Format”.
Step 2. In the new window, enter the Partition label, select the FAT32/EXT2/EXT3/EXT4 file system, and set the cluster size as needed, then click «OK».
Step 3. A warning window will appear; click «Yes» to proceed.
Step 4. Click the «Execute 1 Task(s)» button in the top-left corner to review the changes, then click «Apply» to start formatting the partition to FAT32/EXT2/EXT3/EXT4.
Once you’re done with that, you should be able to fully access and make use of the EXT4 partition on your PC. If you liked this method, feel free to share it online to help more of your friends:
1. Chinese: Chinese
2. English: English
3. French: French
4. Spanish: Spanish
5. German: German
6. Japanese: Japanese
7. Korean: Korean
8. Arabic: Arabic
9. Russian: Russian
10. Italian: Italian
11. Portuguese: Portuguese
12. Thai: Thai
13. Hindi: Hindi
14. Vietnamese: Vietnamese
15. Turkish: Turkish
16. Greek: Greek
17. Dutch: Dutch
18. Polish: Polish
19. Danish: Danish
20. Swedish: Swedish
21. Finnish: Finnish
22. Norwegian: Norwegian
23. Indonesian: Indonesian
24. Malay: Malay
25. Filipino: Filipino
26. Hebrew: Hebrew
27. Urdu: Urdu
28. Persian: Persian
29. Ukrainian: Ukrainian
30. Hungarian: Hungarian
31. Romanian: Romanian
32. Croatian: Croatian
33. Slovenian: Slovenian
34. Serbian: Serbian
35. Bulgarian: Bulgarian
36. Lithuanian: Lithuanian
37. Latvian: Latvian
38. Estonian: Estonian
39. Georgian: Georgian
40. Azerbaijani: Azerbaijani
You May Also Like:
How to Partition Hard Drive in Windows 10
After formatting the EXT4 partition to a normal file system, you may also like to repartition the volume. Follow this guide to learn how to partition a hard drive on your own.
How to Mount EXT4 on Windows 11/10/8/7
If you plan to keep Linux and Windows on the same computer and access EXT4 files from Windows, you can try mounting the EXT4 partition in Windows 10/8/7. But how do I mount a Linux drive in Windows 10? If you have the same question, stay tuned.
In this part, we’ll introduce you to 3 reliable Linux readers that can help you mount EXT4 on Windows 10/8/7:
- Here are the translations of the given text into English:
- #1. EXT2Fsd
- #2. DiskInternals Linux Reader
- #3. Ext2explore
These are actually already in English. They appear to be list items with anchor links, referring to software names for accessing or reading Linux file systems on Windows computers:
1. EXT2Fsd: A software that allows Windows to read and write to EXT2, EXT3, and EXT4 file systems.
2. DiskInternals Linux Reader: A tool that enables users to view and access files from Linux file systems on a Windows environment.
3. Ext2explore: A utility for exploring and managing EXT2, EXT3, and EXT4 file systems on Windows.
Grab one of the tools below and follow the tutorials to mount EXT4 on your Windows machine right now:
#1. Mount EXT4 on Windows using Ext2Fsd
Ext2Fsd is a Windows file system driver developed for EXT4/3/2 file systems. It allows Windows users to read and access Linux file systems, such as EXT4, by mounting the EXT4 partition in Windows. Here are the steps:
Step 1. Install and launch the Ext2Fsd driver on your Windows PC.
Step 2. Go to Tools > Service Management > Start Ext2Fsd service before accessing Linux files.
Step 3. Check the «Mount all volumes in read-only mode» and «Assign drive letter automatically» boxes, and click «Apply».

From here on, you can find your EXT4 partitions with their own drive letters in File Explorer. You can even directly access files on the EXT4 partition.
#2. Mount EXT4 Partition on Windows 10 using DiskInternals Linux Reader
DiskInternals Linux Reader supports the EXT4, ReFS, HFS, and HFS+ file systems. Unlike Ext2Fsd, DiskInternals Linux Reader allows Windows users to access and explore Linux partitions directly within the app.
Step 1. Install and launch DiskInternals Linux Reader on your Windows PC.
Step 2. Locate the EXT4 partition on this application.

Step 3: Double-click to open the EXT4 partition and view/check the saved data on the partition.
Access EXT 4 partition data via DiskIntrnals Linux Reader

Step 4. To make use of the files on the EXT4 partition, select the files and click «Save» to store them in another secure location on your Windows PC.
#3. Mount EXT4 on Windows using Ext2explore
Ext2explore is an open-source application that functions similarly to DiskInternals Linux Reader. It allows users to access the contents of an EXT4 partition exclusively within this software.
Here are the steps you can follow to access EXT4 from Windows using Ext2explore:
Step 1. Download Ext2explore.exe and run this program on a Windows PC.
Step 2. Once launched, right-click on it and select «Run as administrator».
You can also right-click on ext2explore.exe and select «Properties» > Compatibility > Check «Run this program as an administrator» > «OK».
Step 3. After this, you can then browse the Linux EXT4 partition and its contents.
To use the files, right-click on them and select «Save» > Navigate to another secure location to save the files on a Windows computer.
Access EXT4 partition data via Ext2Explore
Q&A: Can I Read EXT4 on Windows
«Hello, I recently transferred my old Linux computer’s hard drive to my current Windows 10 laptop. I’m considering using the Linux hard drive as a data storage drive. Can anyone advise on how to read and access an EXT4 partition from Windows 10?»
Are you facing a similar issue that blocks you from accessing or mounting a Linux EXT4 partition on Windows 10/8/7? To proceed, you need to address the following two questions:
< strong >1. What is EXT4?< /strong >
EXT4, known as the fourth extended file system, succeeding EXT3, is one of the most contemporary file systems utilized by Linux users. It serves as the default file system for numerous Linux distributions, such as Debian and Ubuntu.
< strong >2. Can Windows 10 or Windows 8/7 read EXT4?< /strong >
While EXT4 is the most prevalent Linux file system, it isn’t natively supported by Windows. Hence, the answer to «Can Windows read EXT4?» is no. You can readily access a Windows NTFS partition from Linux, but Windows cannot directly read Linux partitions.
But that doesn’t mean there’s no way to open or access EXT4 from Windows. You’ll just need some third-party tools and solutions to help you out.
By following the methods provided above on this page, you can fully access and read Linux EXT4 partition data on Windows.
Conclusion
On this page, you’ve learned what EXT4 is and two different methods to access and open an EXT4 partition on Windows.
To utilize a Linux EXT4 partition as a data drive on Windows, you need to first extract and recover the data from the EXT4 partition using a tool like Data Recovery Wizard. After that, format the partition with Partition Master to convert it into a file system recognizable by Windows, such as NTFS or FAT32.
To maintain both Linux and Windows on your computer and access EXT4 files from Windows, you’ll need to mount the Linux partition in Windows. To accomplish this, you can utilize recommended tools for assistance. For the most straightforward approach, we suggest giving Ext2Fsd a try.
If you have further questions about EXT4 or Linux file systems, check the FAQs below; you may get the desired answer.
Frequently Asked Questions about EXT4 Partition
Windows operating systems do not support the Linux file system, including EXT4. Consequently, Windows is unable to directly read or recognize an EXT4 partition or device. However, if you wish to access EXT4 from Windows, you can try the methods outlined on this page. They will enable you to achieve this.
2. Which is better, NTFS or EXT4?
Which file system is superior, NTFS or EXT4?
Since NTFS and EXT4 are two distinct file systems designed for two separate operating systems, to accurately test their performance, you would need to conduct the tests within their respective native operating systems.
- As tested, NTFS is significantly faster than EXT4 when used in Windows.
Additionally, in a Linux environment, EXT4 outperforms NTFS in terms of speed.
< strong >3. Can Windows write to EXT4?< /strong >
In fact, if you are running both Windows and Linux on the same computer, it is impossible to access EXT4 file systems directly from Windows, meaning you cannot perform any operations on an EXT4 partition or storage device.
In a nutshell, Windows is incapable of writing to the EXT4 file system. If you genuinely require writing capabilities on an EXT4 partition under the Windows operating system, you’ll need to convert the EXT4 file system to an NTFS or FAT32-based one first. You can utilize a tool like Partition Master and its Format feature to assist you, as demonstrated in Part 2 on this page.
< strong > 4. How do I open a Linux drive in Windows? < /strong >
To access a Linux drive in Windows, you can use a tool called «Linux File System for Windows» or a similar software. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. **Download Software**: First, download and install a utility like [Ext2Fsd](http://www.ext2fsd.com/) or [VirtualBox Guest Additions](https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch04.html#idp5274880) if you’re using a virtual machine.
— For Ext2Fsd, visit the website and download the latest version. Install it following the on-screen instructions.
— For VirtualBox Guest Additions, ensure you have VirtualBox installed, then launch your Linux virtual machine. Go to `Devices` in the menu bar, click `Insert Guest Additions CD Image`, and follow the installation instructions.
2. **Mount the Drive**: After installing the software, follow these steps:
— For Ext2Fsd:
— Open the Ext2Fsd application.
— In the main window, you should see a list of drives. Locate the Linux drive you want to access (usually labeled as `/dev/sdX`, where `X` is a letter).
— Right-click on the drive and select «Assign Drive Letter» or «Mount.» Choose a drive letter that is not currently in use by Windows.
— For VirtualBox:
— Within your Linux virtual machine, the shared folder should automatically appear after installing Guest Additions. If not, you may need to configure the settings manually. Access the shared folder through your file manager.
3. **Access the Drive**: Now you should be able to access the Linux drive in Windows File Explorer by navigating to the assigned drive letter.
Remember that reading is usually supported, but writing might be read-only depending on the software used and the Linux file system type. Be cautious when modifying files to avoid data loss.
Similar to the methods shown on this page, to open a Linux drive in Windows, you can either attempt to change its file system to NTFS/FAT32 or mount the Linux drive in Windows.
If you prefer to change the Linux drive file system to make it readable and writable, format it to NTFS or FAT32 using the solutions in Part 2 on this page.
If you only want to visit or access files saved on the Linux drive from Windows, mount it on Windows using applications recommended in Part 3.







