Парольная политика в домене Active Directory задает базовые требования безопасности к паролям учетных записей пользователей такие как сложность, длину пароля, частоту смены пароля и т.д. Надежная политика паролей AD позволяет снизить возможность подбора или перехвата паролей пользователей.
Содержание:
- Настройка политики паролей в Default Domain Policy
- Основные параметры политики паролей в домене
- Управление параметрами политики паролей AD с помощью PowerShell
- Несколько парольных политик в домене Active Directory
Настройка политики паролей в Default Domain Policy
Настройки политика паролей пользователей в домене AD по умолчанию задаются через групповую политику Default Domain Policy. Вы можете просмотреть и изменить настройки парольной политики в домене с помощью консоли управления консоль управления доменными GPO
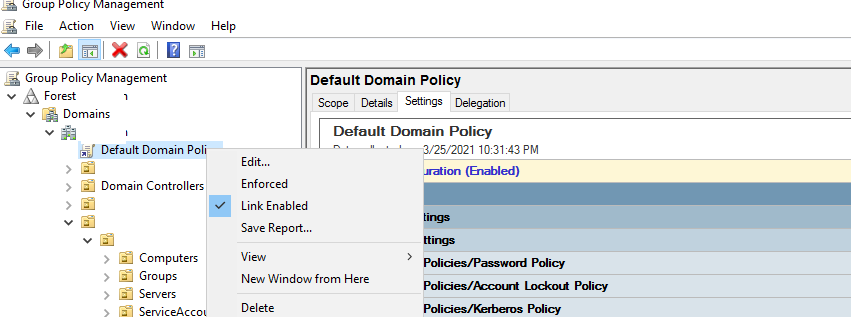
- Откройте консоль
gpmc.msc
и выберите Default Domain Policy, которая назначена на корень домена; - Щелкните правой кнопкой по Default Domain Policy и выберите Edit;
- Разверните Конфигурация компьютера -> Политики -> Конфигурация Windows -> Параметры безопасности -> Политики учетных записей -> Политика паролей (Computer configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Account Policies -> Password Policy
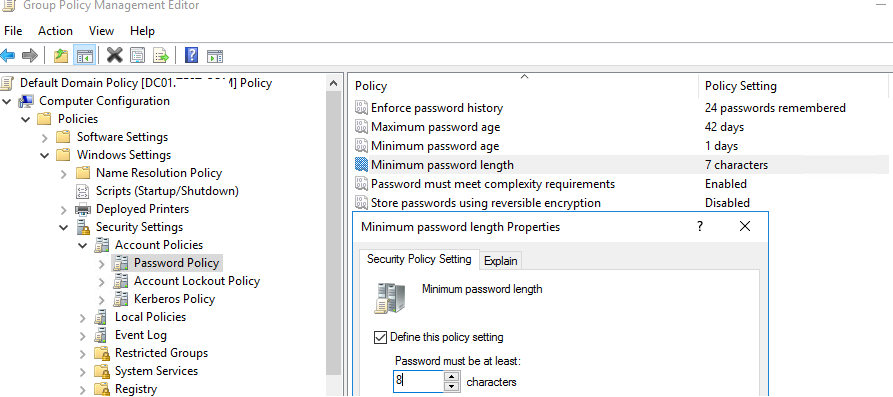
- В этом разделе есть шесть параметров политики паролей (описаны ниже);
- Чтобы изменить настройки параметра, дважды щелкните по ней. Чтобы включить политику, отметьте галку Define this policy settings и укажите необходимую настройку (в примере на скриншоте я задал минимальную длину пароля пользователя 8 символов). Сохраните изменения;
- Новые настройки парольной политики применяться ко всем пользователям домена после обновления настроек GPO на контролере домена с FSMO ролью PDC Emulator.
Основные параметры политики паролей в домене
Всего доступно шесть параметров политики паролей:
- Вести журнал паролей (Enforce password history) – задать количество старых паролей, которые хранятся в AD. Пользователь не сможет повторно использовать старый пароль (однако администратор домена или пользователь, которому делегированы права на сброс пароля в AD, может вручную задать для аккаунта старый пароль);
- Максимальный срок действия пароля (Maximum password age) – срок действия пароля в днях. После истечения срока действия пароля Windows потребует у пользователя сменить его. Обеспечивает регулярность смены пароля пользователями;
- Минимальный срок жизни пароля (Minimum password age) – как часто пользователи могут менять пароль. Этот параметр не позволит пользователю несколько раз подряд сменить пароль, чтобы вернуться к старому паролю, перезатерев пароли в журнале Password History. Как правило тут стоит оставить 1 день, чтобы пользователь мог самостоятельно сменить пароль в случае его компрометации;
- Минимальная длина пароля (Minimum password length) – не рекомендуется делать пароль короче, чем 8 символов (если указать тут 0 – значит пароль не требуется);
- Пароль должен отвечать требование сложности (Password must meet complexity requirements) – при включении этой политики пользователю запрещено использовать имя своей учетной записи в пароле (не более чем два символа подряд из
username
или
Firstname
). Также в пароле должны использоваться 3 типа символов из следующего списка: цифры (0 – 9), символы в верхнем регистре, символы в нижнем регистре, спец символы ($, #, % и т.д.).Чтобы исключить использование пользователями простых паролей (из словаря популярных паролей) рекомендуется периодически выполнять аудит паролей в домене.
- Хранить пароли, использую обратимое шифрование (Store passwords using reversible encryption) – пароли пользователей в базе AD хранятся в зашифрованном виде, но иногда нужно предоставить доступ некоторым приложениям к паролю. При включении этой политики пароли хранятся в менее защищенной виде (по сути, в открытом виде), что небезопасно (можно получить доступ к базе паролей при компрометации DC). При включении этой опции нужно дополнительно защищать пароли привилегированных пользователей на удаленных площадках с помощью внедрения Read-Only контроллеров домена (RODC).
Если пользователь попытается задать пароль, которые не соответствует политике паролей в домене, Windows выдаст ошибку:
Не удается обновить пароль. Введенный пароль не обеспечивает требований домена к длине пароля, его сложности или истории обновления.
Unable to update the password. The value provided for the new password does not meet the length, complexity, or history requirements of the domain.

Обычно вместе с политикой паролей нужно настроить параметры блокировки пользователей при неправильном введении пароля. Эти настройки находятся в разделе GPO: Политика блокировки учетной записи (Account Lockout Password):
- Пороговое значение блокировки (Account Lockout Threshold) – через сколько попыток набрать неверный пароль учетная запись пользователя будет заблокирована;
- Продолжительность блокировки учетной записи (Account Lockout Duration) – длительность блокировки учетной записи, в течении которой вход в домен будет невозможен;
- Время до сброса счетчика блокировки (Reset account lockout counter after) – через сколько минут счетчик неверных паролей (Account Lockout Threshold) будет сброшен.
Если учетные записи блокируются слишком часто, вы можете найти компьютер/сервер источник блокировки так.
Настройки парольных политик домена Active Directory по-умолчанию перечислены в таблице:
| Политика | Значение по-умолчанию |
| Enforce password history | 24 пароля |
| Maximum password age | 42 дня |
| Minimum password age | 1 день |
| Minimum password length | 7 |
| Password must meet complexity requirements | Включено |
| Store passwords using reversible encryption | Отключено |
| Account lockout duration | Не определено |
| Account lockout threshold | 0 |
| Reset account lockout counter after | Не определено |
Управление параметрами политики паролей AD с помощью PowerShell
Для просмотра настроек и изменения конфигурации политики паролей в AD можно использовать командлеты PowerShell из модуля Active Directory:
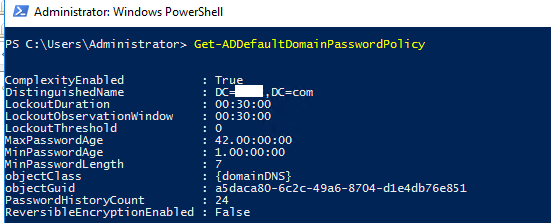
Вывести настройки дефолтной политики паролей:
Get-ADDefaultDomainPasswordPolicy
ComplexityEnabled : True
DistinguishedName : DC=winitpro,DC=ru
LockoutDuration : 00:30:00
LockoutObservationWindow : 00:30:00
LockoutThreshold : 0
MaxPasswordAge : 42.00:00:00
MinPasswordAge : 1.00:00:00
MinPasswordLength : 7
objectClass : {domainDNS}
objectGuid :
PasswordHistoryCount : 24
ReversibleEncryptionEnabled : False
Или с помощью команды:
net accounts
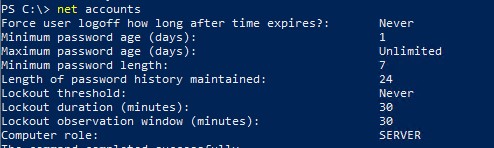
Также вы можете узнать текущие настройки политики паролей AD на любом компьютере в отчете результирующей политики, сгенерированном с помощью консольной утилиты gpresult.
Вывести информацию о том, когда пользователь менял пароль последний раз, и когда истекает его пароль:
net user aivanov /domain
Изменить параметры политики паролей AD:
Set-ADDefaultDomainPasswordPolicy -Identity winitpro.ru -MinPasswordLength 14 -LockoutThreshold 10
Несколько парольных политик в домене Active Directory
С помощью групповых политик на домен можно назначить только одну политику, которая будет действовать на всех пользователей без исключения. Даже если вы создадите новую GPO с другими парольными настройками и примените ее к OU с пользователями, эти настройки фактически не применяться.
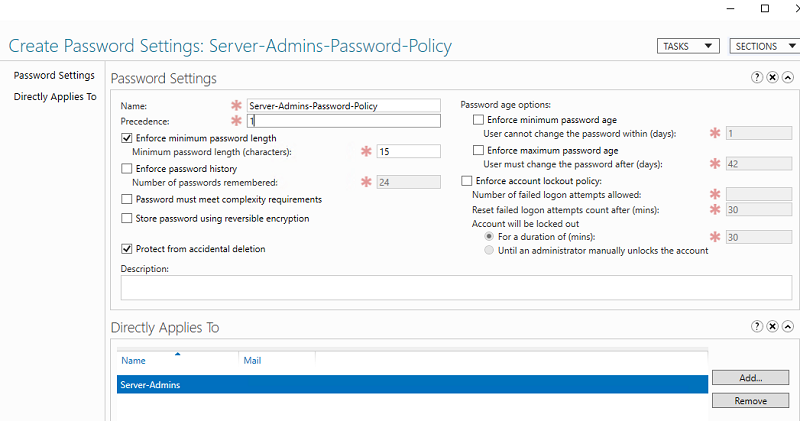
Начиная с версии Active Directory в Windows Server 2008 с помощью гранулированных политик паролей Fine-Grained Password Policies (FGPP) можно применять индивидуальный параметры политики паролей для конкретных пользователей или групп. Например, вы хотите, чтобы пользователи из группы Server-Admins использовали пароли с минимальной длиной 15 символов.
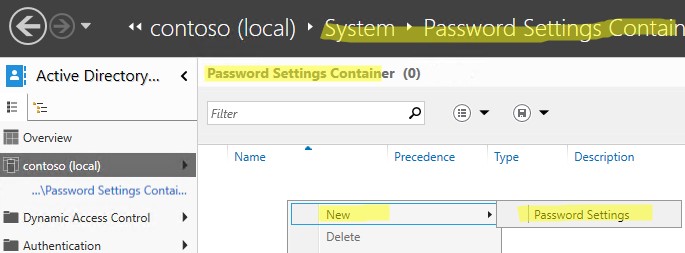
- Откройте консоль Active Directory Administrative Center (
dsac.exe
); - Перейдите в раздел System -> Password Settings Container и создайте новый объект PSO (Password Settings Object);
- В открывшемся окне укажите название политики паролей и ее приоритет. Включите и настройте параметры парольной паролей, которые вы хотите применить. В разделе Directly Applies to нужно добавить группы или пользователей, для которых должны применяться ваши особые настройки политики паролей.
Чтобы проверить, применяются ли к конкретному пользователю особая политика паролей, выполните команду:
Get-ADUserResultantPasswordPolicy -Identity aivanov
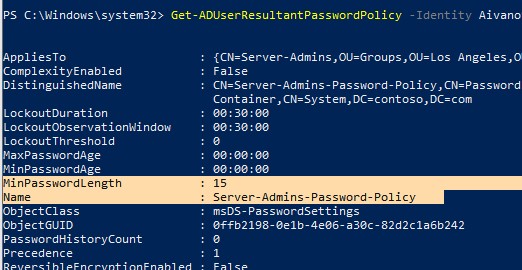
Команда выведет результирующие настройки политики паролей, которые дейсвтуиют на пользователя.
Прошу прощения за рекламу на сайте. Я постарался сделать это максимально ненавязчиво и по минимуму. При чтении заинтересовавших вас статей она не будет вам мешать.
И если есть возможность поставить мой сайт в исключения у блокировщика рекламы, я буду очень признателен вам.

Ниже приведена небольшая инструкция об изменении политики паролей в Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2.
По умолчанию политика паролей определена таким образом, что все пароли учетных записей пользователей должны удовлетворять следующим требованиям:
1. Не содержать имени учетной записи пользователя или частей полного имени пользователя длиной более двух рядом стоящих знаков.
2. Иметь длину не менее 6 знаков.
3. Содержать знаки трех из четырех перечисленных ниже категорий:
4. Латинские заглавные буквы (от A до Z)
5. Латинские строчные буквы (от a до z)
6. Цифры (от 0 до 9)
7. Отличающиеся от букв и цифр знаки (например, !, $, #, %)
Все параметры политики паролей задаются в локальных групповых политиках.
Для запуска Редактора Локальных Групповых Политик (Local Group Policy Editor) необходим выполнить команду gpedit.msc (для этого необходимо нажать комбинацию клавиш Win + R, в окне «Выполнить» (Run) в поле «Открыть:» (Open:) ввести имя команды и нажать «ОК»)
В запустившейся оснастке в дереве групповых политик последовательно раскрываем группы:
_ «Конфигурация компьютера» (Computer Configuration)
__ «Конфигурация Windows» (Windows Settings)
___ «Параметры безопасности» (Security Settings)
____ «Политики учетных записей» (Account Policies)
_____ «Политика паролей» (Password Policy)
Здесь мы можем изменить необходимую нам политику.
В частности, политику сложности паролей. Для этого два раза кликаем по строке «Пароль должен отвечать требованиям сложности» (Password must meet complexity requirements) и в окне свойства политики устанавливаем переключатель в «Отключен» (Disabled)
Для всех политик доступно довольно подробное описание, для доступа к которому необходимо перейти на вкладку «Объяснение» (Explain).
Изменив необходимые параметры, сохраняем настройки и закрываем окна, нажав «ОК» .
В этой же ветке можно изменить Политику блокировки учетных записей (Account Lockout Policy) в случае неверного ввода паролей.
Все политики редактируются аналогичным образом.
Необходимо понимать, что изменение политики паролей может сильно снизить безопасность сервера.
Вот и всё упрощение политики.
Пароли в Windows Server 2012 R2, упрощение пароля
18 октября 2017, 10:59
Александр
Windows
0
1563
0
Из этой категории
-
Windows не грузится после переноса на RAID
WINDOWS SERVER 2012/2016/2019: Изменение размера шрифта при подключении по RDP
Mukeydrv не работает. Обнаружена обновленная политика цифровых подписей
Проблемы с печатью из RDP
Разрешаем этому приложению вносить изменения на вашем устройстве
Очистка RDP подключения
Перенос папки пользователя и администратора на другой диск windows server
Показать скрытые устройства в диспетчере устройств Windows 7
Этому файлу не сопоставлена программа для выполнения этого действия
Исчезла служба Диспетчер печати в Windows Server 2012
Estimated reading: 3 minutes
1270 views
Using password policy can enhance password’s security. It requires users to set password length, password age, password history, etc. Via password policy, you can set a more complicated password that’s hard to be guessed or cracked.
In this article, we will guide you to Set Password Policy on Windows server 2019.
Step 1: Press “Win” + “R” key to open “Run” window. Type in: secpol.msc then click “OK”.

Step 2: After you open “Local Security Policy”, select them in order: “Security Settings” > “Account Policies” > “Password Policy”.

Step 3: In the right pane, double click any policy and change the setting according to your needs.

Explanation of Setting Each Password Policy
Password Must Meet Complexity Requirements
Requirements as below:
1. More than two contiguous characters from user name cannot be contained in password.
2. Be at least six characters in length and three of following four types of character need to be included in password.
• English uppercase characters (A through Z)
• English lowercase characters (a through z)
• Base 10 digits (0 through 9)
• Non-alphabetic characters (for example, !, $, #, %)
Minimum Password Length
The longer the password, the safer it will be. A password should at least contain the minimum number of characters for a user account.

Minimum Password Age
This security setting determines the period of time (in days) that a password must be used before the user can change it. For example, if you set 10 days, then your password can be changed after 10 days. Besides, password can be changed anytime if the minimum password age is set to be 0.
Maximum Password Age
This security setting determines the period of time (in days) that a password can be used before the system requires the user to change it. For example, if you set 90 days, your password will expire in 90 days then system will require you to change it. But the password will not expire if the maximum password age is set to 0.

Enforce Password History
This security setting determines the number of unique new passwords that have to be associated with a user account before an old password can be reused. It can ensure the old passwords are not reused continually. For example, if you keep 9 passwords remembered, then you need to change new passwords nine times before an old password can be reused.

Store Passwords Using Reversible Encryption
This security setting determines whether the operating system stores passwords using reversible encryption. If this policy is enabled, some bad guys may easily crack the password and access users’ PCs. It’s suggested to disable it unless application requirements are more important than the protection of password information.
Conclusion
So we have guided you through the steps set Password Policy on Windows server 2019 this will help increase security on your VPS.

Hello, how are you doing? In this opportunity, we will talk about password policies on Windows Server 2019. Once we have managed users through Active Directory, we need to set the valid date of the passwords. Indeed, sometimes we need to restrict access to certain users due to the security policies of the organization.
Please keep in mind that when working with servers, security is a fundamental aspect. For this reason, there are several reasons for modifying the duration of passwords. For this reason, there are several reasons for modifying the duration of passwords. According to the type of use, it is convenient to establish passwords with security time. For example, to temporary users, test users or those who are practicing in the company.
Now, we have two options for modifying password expiration policies on Windows Server 2019. Group Policy: Apply for when the computer is included in a corporate domain with Windows Server Domain Controller. Local Security Policy: Applies when our group is not in a domain, but is in a workgroup or is managed locally. Here’s how to change a password or change the expiration date of a password within Windows Server 2019 step by step.
Changing password expiration through Local Security Policy on Windows Server 2019
Below we will detail the process for entering the password policy configuration.
Step 1. Open Local Group Policy Editor
First, we need to enter Group Policy Management by clicking Windows+R and typing gpedit.msc

Once there, we must follow the next route: Local Computer Policy>Computer Configuration>Windows Settings>Security Settings>Password Policy

Step 2. Editing password policies
The editor allows you to configure different aspects of the password:
Enforce password history. This security setting determines the number of unique new passwords that have to be associated with a user account before an old password can be reused. The value must be between 0 and 24 passwords.
Maximum password age. This security setting determines the period of time (in days) that a password can be used before the system requires the user to change it. You can set passwords to expire after a number of days between 1 and 999, or you can specify that passwords never expire by setting the number of days to 0.
Minimum password age. This security setting determines the period of time (in days) that a password must be used before the user can change it. You can set a value between 1 and 998 days, or you can allow changes immediately by setting the number of days to 0.
Minimum password length. This security setting determines the least number of characters that a password for a user account may contain. It can set a value of between 1 and 20 characters, or you can establish that no password is required by setting the number of characters to 0.
Password must meet complexity requirements. This security setting determines whether passwords must meet complexity requirements.
Password Requirements
If it enabled, the password must meet the following minimum requirements:
Not contain the user’s account name or parts of the user’s full name that exceed two consecutive characters
Be at least six characters in length
Contain characters from three of the following four categories:
English uppercase characters (A through Z)
English lowercase characters (a through z)
Base 10 digits (0 through 9)
Non-alphabetic characters (for example, !, $, #, %)
Store passwords using reversible encryption. This security setting determines whether the operating system stores passwords using reversible encryption. This policy provides support for applications that use protocols that require knowledge of the user’s password for authentication purposes.
Changing password expiration through Local Active Directory on Windows Server 2019
To access the domain password policy editor, we need to open the Server Manager. Next, click on the Active Directory Administrative Center tool.

In the next window, select the forest and then follow the following path: Domains>nameofdomain>Default Domain Policy. Where nameofdomain is the name of our domain, in my case telematic.local. Next, double click on Default Domain Policy to edit the values.

Once the window opens, follow this path: Default Domain Policy>Compuer Configuration>Policies>Windows Settings>Security Settings>Password policy

As we see we have the same options as in the local directives, the only difference is that if we open the local policies with our computer in a domain we cannot make any change in the directives. On the other hand, from a computer in a domain using this option if we will be able to make adjustments in the policies.
Changing or unlocking administrator password on Windows Server 2019
Sometimes it happens that we want to change the administrator password, or the account has been blocked. Sometimes it happens that we want to change the administrator password, or the account has been blocked. To do this, we must enter the Server Manager and select Active Directory Administrative Center.

Once there, all you have to do is select Reset Password, and enter the new password or unblock the account if it is locked.

As has been noted, the process for changing password policies is not that complicated. However, we must be careful when modifying these values, as it will affect the entry of users. In conclusion, Windows Server 2019 is a very friendly system and has wizards that facilitate the changes desired by the server administrator.
Well, this is all for now, before saying goodbye I would like to invite you to review our tutorial on installing Apache on Windows Server 2019.
— Advertisement —
Everything Linux, A.I, IT News, DataOps, Open Source and more delivered right to you.
Subscribe
«The best Linux newsletter on the web»
Introduction
Table of Contents
Password complexity is a security feature that enhances the strength and resilience of passwords used to access computer systems, applications, and accounts. In Windows Server 2022, you can configure password complexity settings through Group Policy, which enforces specific criteria that passwords must meet. While password complexity is a valuable security measure, there may be instances where administrators need to relax these requirements. In this article we will provide an overview of password complexity, its benefits, and how to remove or adjust it in Windows Server 2022.
Understanding Password Complexity
Typically, several rules define password complexity, and network administrators enforce these rules to make it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to guess or crack passwords. The primary components of password complexity requirements in Windows Server 2022 include:
Length: Passwords must be a minimum number of characters in length, which is often set by administrators.
Character Variety: Passwords should contain a mix of character types, including uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
History: Password history rules can prevent users from reusing their previous passwords for a specified number of iterations.
Expiration: Passwords may be set to expire after a defined period, prompting users to change them regularly.
Lockout Policy: After a certain number of failed login attempts, an account can be locked to prevent further access.
Complexity Requirements: Passwords should meet complexity requirements, which typically mandate a combination of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Why password complexity is important?
Password complexity is crucial for several reasons:
Security: Complex passwords are harder to guess or crack, enhancing the security of sensitive systems and data.
Compliance: Many regulatory standards, such as HIPAA and PCI DSS, require the use of complex passwords.
Protection Against Dictionary Attacks: Password complexity rules make it difficult for attackers to use dictionary attacks to guess passwords.
Reducing the Risk of Brute Force Attacks: Complex passwords help protect against brute force attacks where attackers try every possible combination.
How to Remove Password Complexity in Windows Server 2022
Log in to your Windows Server with an account that has administrative privileges. Open the Group Policy Management Editor. Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
Type gpedit.msc and press Enter.

Navigate to the Password Policy Settings
In the Group Policy Management Editor, navigate to the following path: Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Account Policies -> Password Policy.
Edit Password Policy
In the right pane, you will see various password policy settings, including Password must meet complexity requirements.
Double-click on Password must meet complexity requirements to edit the policy.
windows server password complexity
Modify the Password Complexity Settings:
By default, the Password must meet complexity requirements setting is enabled. To disable password complexity requirements, select the Disabled option.

Apply Changes
Clicok OK to save your changes. Force a Group Policy Update:
Open a Command Prompt with administrative privileges by right clicking the Start button and selecting Windows Terminal (Admin).
Run the command: gpupdate/force
Restart the Server (Optional)
In some cases, it may be necessary to restart the server for the changes to take effect. This step is optional but can be helpful in ensuring consistent policy application.
After following these steps, your Windows Server 2022 should no longer enforce password complexity requirements. Users will be able to set less complex passwords. Keep in mind that relaxing password complexity requirements may pose security risks, so consider alternative security measures if necessary, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) or strong password policies in conjunction with regular password changes.
Conclusion
Password complexity is an essential aspect of securing your Windows Server 2022 environment. While it enhances security, there may be circumstances where it is necessary to remove or adjust password complexity requirements. By following the steps outlined above, administrators can configure password policies to meet their specific security needs while balancing usability for users. It is crucial to carefully consider the implications of relaxing these requirements and to implement alternative security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, as necessary to maintain the security of your systems.
-
Design