JupyterLab can be installed as a terminal-launched application accessible via a web browser (default), or as a desktop application which is running in its own window and can be opened by clicking on a desktop shortcut (JupyterLab Desktop). This page describes installation of the default (terminal-launched) JupyterLab application using conda, mamba, pip, pipenv or docker and assumes basic knowledge of the terminal. For JupyterLab Desktop instructions see the Installation section in the JupyterLab Desktop repository.
Warning
New versions of JupyterLab may break backwards compatibility with extensions and other
Jupyter customizations. As noted in Backwards Compatibility, Versions and Breaking Changes, JupyterLab development and
release cycles follow semantic versioning, so we recommend planning your installation and
upgrade procedures to account for possible breaking changes that may disrupt your usage
of JupyterLab and any related tools that are critical to your workflows.
conda#
If you use conda, you can install it with:
conda install -c conda-forge jupyterlab
mamba#
If you use mamba, you can install it with:
mamba install -c conda-forge jupyterlab
pip#
If you use pip, you can install it with:
If installing using pip install --user, you must add the user-level
bin directory to your PATH environment variable in order to launch
jupyter lab. If you are using a Unix derivative (FreeBSD, GNU/Linux,
macOS), you can do this by running export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH".
pipenv#
If you use pipenv, you can install it as:
pipenv install jupyterlab pipenv shell
or from a git checkout:
pipenv install git+git://github.com/jupyterlab/jupyterlab.git#egg=jupyterlab pipenv shell
When using pipenv, in order to launch jupyter lab, you must activate the project’s virtualenv.
For example, in the directory where pipenv’s Pipfile and Pipfile.lock live (i.e., where you ran the above commands):
Alternatively, you can run jupyter lab inside the virtualenv with
Docker#
If you have Docker installed, you can install and use JupyterLab by selecting one
of the many ready-to-run Docker images
maintained by the Jupyter Team. Follow the instructions in the Quick Start Guide
to deploy the chosen Docker image.
Ensure your docker command includes the -e JUPYTER_ENABLE_LAB=yes flag to ensure
JupyterLab is enabled in your container.
Usage with JupyterHub#
Read the details on our JupyterLab on JupyterHub documentation page.
Usage with Jupyverse#
Jupyverse is a next-generation Jupyter server based on
FastAPI. It can be used instead of
jupyter-server, the Jupyter server installed by default with JupyterLab.
Note that jupyter-server extensions won’t work with jupyverse (for which there might be equivalent plugins).
You can install jupyverse with pip:
pip install "jupyverse[auth,jupyterlab]"
or with conda:
conda install -c conda-forge jupyverse fps-auth fps-jupyterlab
or with mamba:
mamba install -c conda-forge jupyverse fps-auth fps-jupyterlab
And run it with:
Supported browsers#
The latest versions of the following browsers are currently known to work:
-
Firefox
-
Chrome
-
Safari
-
Edge
Earlier browser versions may also work, but come with no guarantees.
Installation problems#
If your computer is behind corporate proxy or firewall,
you may encounter HTTP and SSL errors due to the proxy or firewall blocking connections to widely-used servers. For example, you might see this error if conda cannot connect to its own repositories:
CondaHTTPError: HTTP 000 CONNECTION FAILED for url <https://repo.anaconda.com/pkgs/main/win-64/current_repodata.json>
Here are some widely-used sites that host packages in the Python and JavaScript open-source ecosystems. Your network administrator may be able to allow http and https connections to these domains:
-
pypi.org
-
pythonhosted.org
-
continuum.io
-
anaconda.com
-
conda.io
-
github.com
-
githubusercontent.com
-
npmjs.com
-
yarnpkg.com
Alternatively, you can specify a proxy user (usually a domain user with password),
that is allowed to communicate via network. This can be easily achieved
by setting two common environment variables: HTTP_PROXY and HTTPS_PROXY.
These variables are automatically used by many open-source tools (like conda) if set correctly.
# For Windows set HTTP_PROXY=http://USER:PWD@proxy.company.com:PORT set HTTPS_PROXY=https://USER:PWD@proxy.company.com:PORT # For Linux / MacOS export HTTP_PROXY=http://USER:PWD@proxy.company.com:PORT export HTTPS_PROXY=https://USER:PWD@proxy.company.com:PORT
In case you can communicate via HTTP, but installation with conda fails
on connectivity problems to HTTPS servers, you can disable using SSL for conda.
Warning
Disabling SSL in communication is generally not recommended and involves potential security risks.
# Configure npm to not use SSL conda config --set ssl_verify False
You can do a similar thing for pip.
The approach here is to mark repository servers as trusted hosts,
which means SSL communication will not be required for downloading Python libraries.
# Install pandas (without SSL) pip install --trusted-host pypi.org --trusted-host files.pythonhosted.org pandas
Using the tips from above, you can handle many network problems
related to installing Python libraries.
Many Jupyter extensions require having working npm and jlpm (alias for yarn) commands,
which is required for downloading useful Jupyter extensions or other JavaScript dependencies. If npm cannot connect to its own repositories, you might see an error like:
ValueError: "@jupyterlab/toc" is not a valid npm package
You can set the proxy or registry used for npm with the following commands.
# Set proxy for NPM npm config set proxy http://USER:PWD@proxy.company.com:PORT npm config set proxy https://USER:PWD@proxy.company.com:PORT # Set default registry for NPM (optional, useful in case if common JavaScript libs cannot be found) npm config set registry http://registry.npmjs.org/ jlpm config set npmRegistryServer https://registry.yarnpkg.com/
In case you can communicate via HTTP, but installation with npm fails
on connectivity problems to HTTPS servers, you can disable using SSL for npm.
Warning
Disabling SSL in communication is generally not recommended and involves potential security risk.
# Configure npm to not use SSL npm set strict-ssl False
Project Jupyter’s tools are available for installation via the Python Package Index, the leading repository of software created for the Python programming language.
This page uses instructions with pip, the recommended installation tool for Python. If you require environment management as opposed to just installation, look into conda, mamba, pipenv, and Homebrew.
JupyterLab
Install JupyterLab with pip:
Note: If you install JupyterLab with conda or mamba, we recommend using the conda-forge channel.
Once installed, launch JupyterLab with:
Jupyter Notebook
Install the classic Jupyter Notebook with:
To run the notebook:
Voilà
Install Voilà with:
Once installed, launch Voilà with:
Homebrew
Homebrew is a package manager for macOS and Linux.
You can use it to install Jupyter by running:
Note
Installation steps assume that you have administrator rights on your system.
If you don’t have administrator rights, follow the steps without selecting “for all users”
options and install software packages to your user account only.
Install Python
Skip this step if you have Python 3.x already installed on your system.
-
Open your web browser and go to https://www.python.org/
-
Click
Downloadson the top menu and clickPython 3.9.7button.
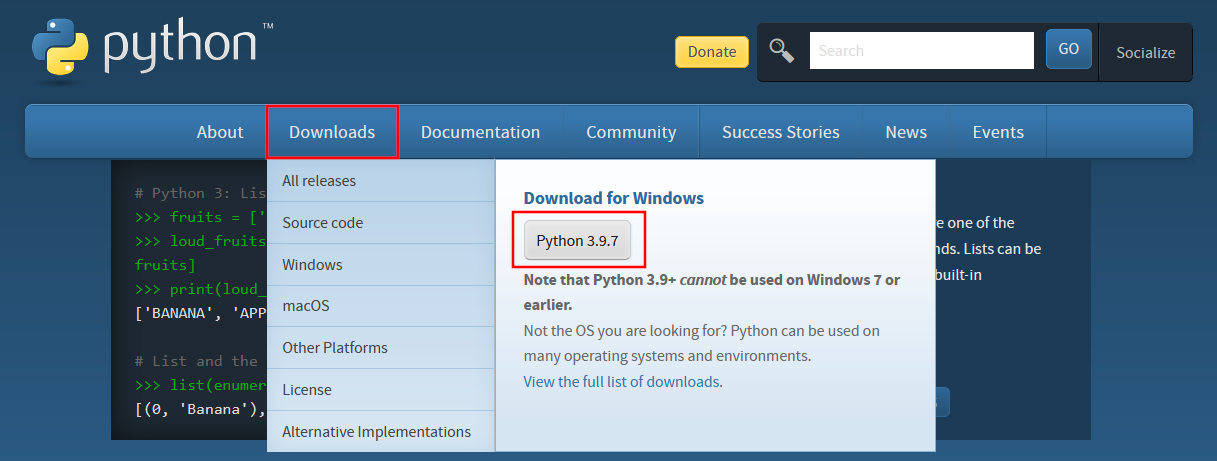
-
Save installation file.
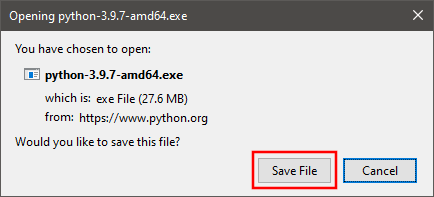
-
Run installation file.
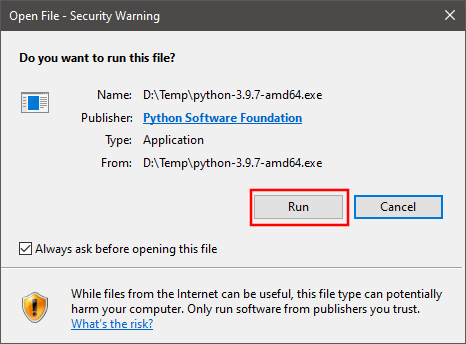
-
You can choose
Install Nowoption to complete installation with default options. For the suggested custom installation please follow steps 6 – 8. -
Check
Install launcher for all usersandAdd Python 3.9 to PATHboxes. ClickCustomize Installation.
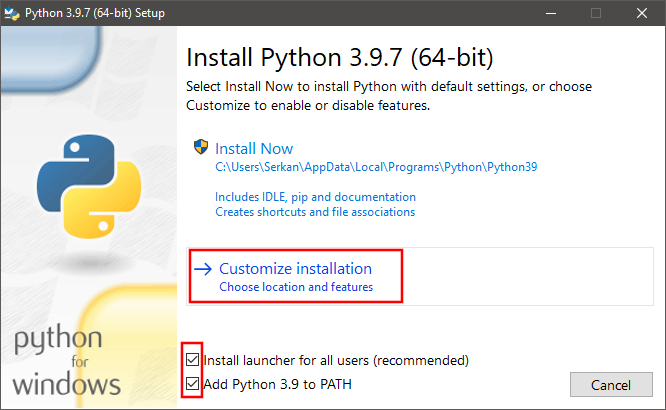
-
Uncheck
Documentation,tcl/tk and IDLE, andPython test suiteoptions. Checkpip,py launcher, andfor all usersoptions. ClickNext.
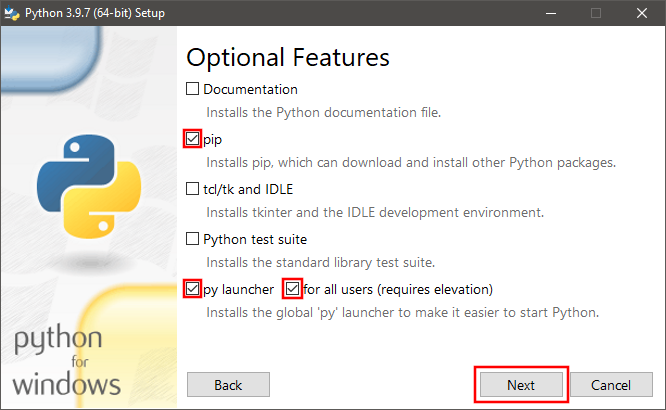
8. Check Install for all users, Associate files with Python, Create shortcuts for installed applications, Add Python to environment variables,
and Precompile standard library options. Uncheck Download debugging symbols and Download debug binaries options. Click Install.
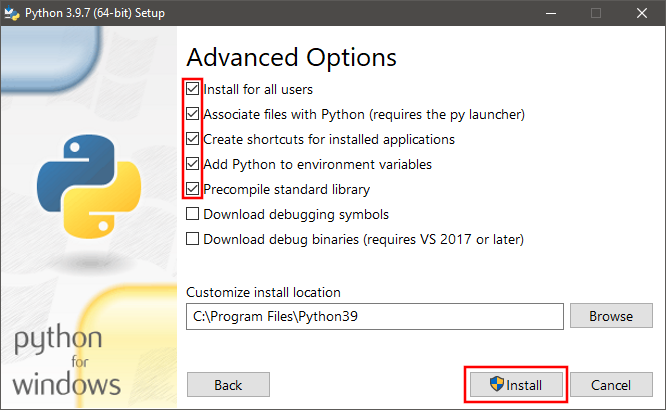
9. Once installation is finished, open a command prompt and test Python by entering python
command. Python command line interface should be available with >>> prompt.
Install node.js
Skip this step if you have node.js 14.x or newer already installed on your system.
Note
Installation steps assume that you have administrator rights on your system.
If you don’t have administrator rights, follow the steps without selecting “for all users”
options and install software packages to your user account only.
-
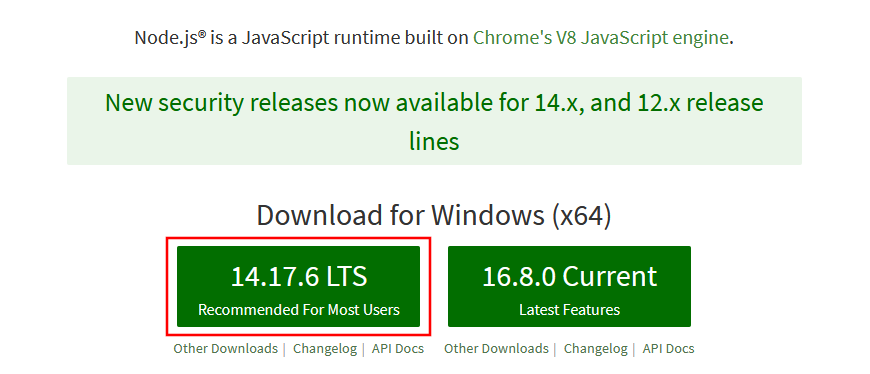
Open your web browser and go to https://nodejs.org/en/
-
Click LTS (Long Term Support) version
downloadbutton.
-
Save installation file.
-
Run installation file.
-
Complete installation by following the wizard accepting the terms and the default options.

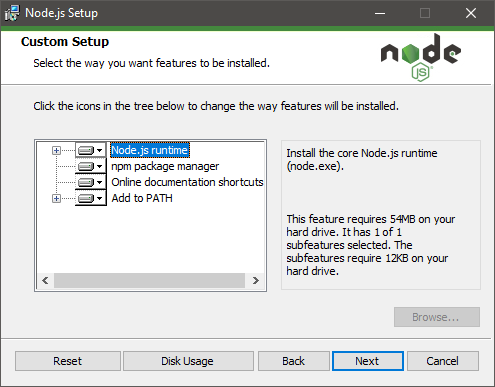
6. Once installation is finished, open a command prompt and test node.js by entering npm
command. Help on its usage should be displayed.
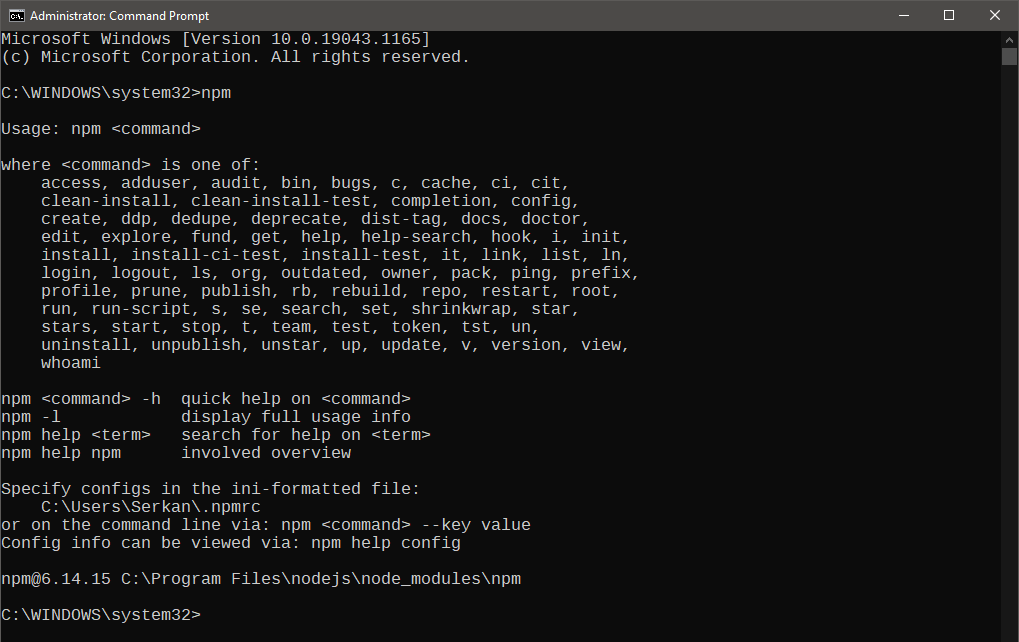
Install JupyterLab
-
Open a command prompt and enter
pip install jupyterlabcommand.

-
Python package manager (pip) will install JupyterLab and all other required packages.
-
Once installation is finished, enter
jupyter labcommand to start JupyterLab.

-
By default, JupyterLab automatically opens a web browser tab to display the user interface.
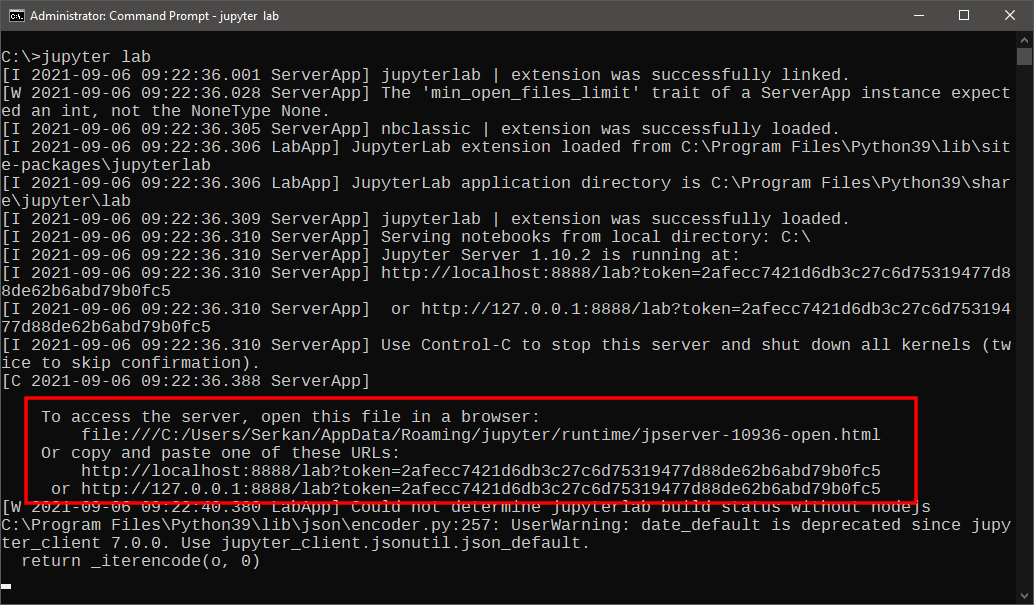
5. JupyterLab will also display some information on the terminal, including the URL address to
access the user interface. You can copy-paste the URL address to your web browser to access
the user interface if it is not displayed automatically.
-
Enjoy your JupyterLab!
Working with the ‘jupyter’ Notebook is familiar to everybody who is engaged in developing through Python. This is an ‘iPython’ console which is regarded as the best for carrying out data analysis and machine learning related work. The notebook provides easy code execution and displays various graphs and glyphs within the console. Also, it provides the provision to download Python packages within its console and allows users to carry out web scraping related activities. But, what if I tell you that there is more to it that is; there is one cooler version of this ‘jupyter’ that provides more no. of features than this obsolete one.
Yes, the name of this advanced jupyter is jupyter Lab. It is an extension to the normal jupyter Notebook as it allows users to work in multiple files. This can be elaborated as jupyter Lab provides much functionality that users can access at the same time while working with a notebook like opening the text editor that is provided within jupyter lab, opening Markdown editor, opening the command prompt, python console. This makes jupyter lab more robust and acceptable by Python developers out there. We can even replicate our present iPython notebook into many to view our work more easily.
All the work that we have done can either be saved to our local system or can be saved within the Jupyter lab. So, it acts as a vault in saving our work to access it in the future. Also, this lab comes with a provision to set different themes we like (Dark and White) and also increase and decrease the UI size as per our comfort. These things make this a powerful tool when it comes to performing data analytics related work as well as general Python related development.
So, how to download jupyter Lab for our Windows operating system and how to open the same??? The answer to this question is given below:
Pre Requisites
- Python
- Pip should be installed within the system.(mostly it will be installed while installing python)
- Good internet connection.
Installing Jupyter Lab via Python Through Terminal:
The installation steps of this tool are just like other packages that is can be installed through pip.
- Just open your terminal (if your using windows open cmd)
- Just type in the command prompt:
pip install jupyterlab
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
After the installation finishes type command within the command prompt and wait for the browser to open jupyter lab for you.
jupyter lab
(or)
python -m jupyterlab
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode

We can install jupyterlab through anaconda, and desktop version also available.
click here to try the jupyterlab
Conclusion
We can conclude that Jupyter lab dominates over the normal Jupyter and one must prioritize this rather than going with the Jupyter installation..
JupyterLab Desktop
JupyterLab Desktop is the cross-platform desktop application for JupyterLab. It is the quickest and easiest way to get started with Jupyter notebooks on your personal computer, with the flexibility for advanced use cases.

Installation
Install JupyterLab Desktop using one of the methods listed below for your system.
| Windows (10, 11) | Mac (macOS 10.15+) | Linux |
|---|---|---|
| x64 Installer | arm64 Installer (Apple silicon) | Snap Store [recommended] |
| x64 Installer (Intel chip) | .deb x64 Installer (Debian, Ubuntu) | |
| .rpm x64 Installer (Red Hat, Fedora, SUSE) |
Additionally, JupyterLab Desktop can be installed on Windows via winget: winget install jupyterlab.
If you need to remove a previous JupyterLab Desktop installation, please follow the uninstall instructions.
Launching JupyterLab Desktop
JupyterLab Desktop can be launched from the GUI of your operating system by clicking the application’s icon or by using jlab command from the command line. Double clicking .ipynb files is also supported and it will launch JupyterLab Desktop and load the notebook file.
JupyterLab Desktop sets File Browser’s root directory based on the launch method.
- If launched from the application icon on GUI or by using
jlabcommand without any arguments, then the default working directory is set as the root directory. The default working directory is user home directory but it can be customized from the Settings dialog. - If launched by double clicking
.ipynbfile orjlabcommand with a file path as the argument, then file’s parent directory is set as the root directory. Similarly, if a file is opened using theOpen...orOpen File...links in the Start section or by using drag & drop, then file’s parent directory is set as the root directory. - If
jlabcommand is used with a directory path as the argument or with the--working-dirargument then the directory in the argument is set as the root directory. Similarly, if a folder is opened using theOpen Folder...link in the Start section or by using drag & drop, then the opened directory is set as the root directory
Sessions and Projects
Sessions represent local project launches and connections to existing JupyterLab servers. Each JupyterLab UI window in the app is associated with a separate session and sessions can be restored with the same configuration later on.
Each launch of JupyterLab in a different working directory is a separate project and projects can have their own configuration such as Python environment and UI layout.
Session start options
You can start a new session by using the links at the Start section of the Welcome Page.
New notebook...creates a new notebook in the default working directory.New session...launches a new JupyterLab session in the default working directory.Open...starts a new JupyterLab session in the selected working directory. If files are chosen, selected files’ parent directory becomes the working directory and selected files are opened in the session. On Windows and LinuxOpen Folder...andOpen Files...options are presented as separate items.Connect...creates a session by connecting to an existing JupyterLab server running locally or remotely. Locally running JupyterLab servers are automatically detected and listed in the Connect dialog.
Similarly, CLI launches of the application, dropping files and folders, and double clicking to open files create new sessions as well.
Previously opened sessions are stored as part of application data and they are listed on Welcome Page. Clicking an item in the Recent sessions list restores the selected session.
jlab command-line launch examples
- Open directories using relative or absolute path
jlab .launch in current directoryjlab ../notebookslaunch with relative pathjlab /Users/username/notebookslaunch with absolute path
- Open notebooks and other files using relative or absolute path
jlab /Users/username/notebooks/test.ipynblaunch notebook with absolute pathjlab ../notebooks/test.ipynblaunch notebook with relative pathjlab ../test.pylaunch python file with relative path
- Open with a custom Python environment
jlab --python-path /Users/username/custom_env/bin/python ../notebooks/test.ipynblaunch notebook with custom Python environment
- Connect to existing JupyterLab server
jlab https://example.org/lab?token=abcde
See CLI documentation for more CLI commands and options.
JupyterLab Extension support
JupyterLab Desktop currently supports user-friendly prebuilt extensions. Source extensions which require rebuilding are not supported.
Guides and Help
-
See user guide for configuration options
-
Python environment management guide for managing Python environments on your system using JupyterLab Desktop
-
See CLI documentation for CLI commands and options
-
See troubleshooting guide for troubleshooting issues
-
For contributing, see developer documentation
