Linux wget: ваш загрузчик командной строки
Wget — это открыто распостраняемая утилита для загрузки файлов из интернет.
Он поддерживает HTTP, FTP, HTTPS и другие протоколы, а также средство аутентификации и множество других опций.
Если вы пользователь Linux или Mac, WGET либо уже включен в пакет, который вы используете, либо это простой случай установки из любого репозитория, который вы предпочитаете, с помощью одной команды.
Как установить команду wget в Linux
Используйте команду apt / apt-get, если вы работаете в Ubuntu / Debian / Mint Linux:
$ sudo apt install wget
Пользователь Fedora Linux должен ввести команду dnf
$ sudo dnf install wget
Пользователь RHEL / CentOS / Oracle Linux должен ввести команду yum :
$ sudo yum install wget
Пользователь SUSE / OpenSUSE Linux должен ввести команду zypper:
$ zypper install wget
Пользователь Arch Linux должен ввести команду pacman:
$ sudo pacman -S wget
К сожалению, в Windows все не так просто (хотя не так сложно!).
Для запуска WGET вам необходимо скачать, распаковать и установить утилиту вручную.
Установите WGET в Windows 10
Загрузите классическую 32-разрядную версию 1.14 здесь или перейдите в эту коллекцию двоичных файлов Windows на сайте Eternal Bored здесь, чтобы получить более поздние версии и более быстрые 64-разрядные сборки.
Вот загружаемый zip-файл для 64-разрядной версии 1.2.
Если вы хотите иметь возможность запускать WGET из любого каталога в терминале, вам нужно будет узнать о переменных пути в Windows, чтобы решить, куда копировать новый исполняемый файл. Если вы это сделаете, то сможете сделать WGET командой, которую можно запускать из любого каталога в командной строке, это отдельная тема по настройке Windows.
Запуск WGET из любого места
Во-первых, нам нужно определить, куда копировать WGET.exe.
Мы собираемся переместить wget.exe в каталог Windows, который позволит запускать WGET из любого места.
После того, как вы загрузили wget.exe (или распаковали связанные с ним zip-файлы дистрибутива), откройте командный терминал, набрав «cmd» в меню поиска и запустите командную строку.
Во-первых, нам нужно выяснить, в каком каталоге это должно быть. В командную строку введите:
path
Вы должны увидеть что-то вроде этого:
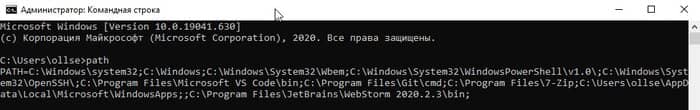
Благодаря переменной окружения “Path” мы знаем, что нам нужно скопировать wget.exe в папку c:\Windows\System32.
Скопируйте WGET.exe в каталог System32 и перезапустите командную строку.
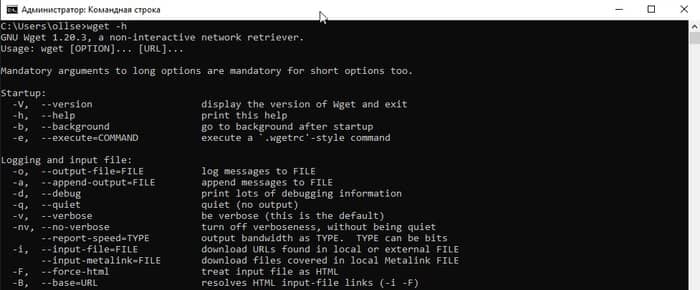
Если вы хотите проверить правильность работы WGET, перезапустите терминал и введите:
wget -h
Если вы скопировали файл в нужное место, вы увидите файл справки со всеми доступными командами.
Итак, вы должны увидеть что-то вроде этого:
Начнем работать с WGET
Мы будем работать в командной строке, поэтому давайте создадим каталог загрузок только для загрузок WGET.
Чтобы создать каталог, воспользуемся командой md («создать каталог»).
Перейдите в корневой каталог c: / и введите команду:
md wgetdown
Затем перейдите в новый каталог и введите «dir», и вы увидите (пустое) содержимое.

После того, как вы установили WGET и создали новый каталог, все, что вам нужно сделать, это изучить некоторые тонкости аргументов WGET, чтобы убедиться, что вы получаете то, что вам нужно.
Руководство Gnu.org WGET — особенно полезный ресурс для тех, кто действительно хочет узнать подробности.
Вот несколько советов, как извлечь из этого максимум пользы:
Linux wget примеры команд
Синтаксис:
wget url
wget [options] url
Давайте посмотрим на некоторые распространенные примеры команд Linux wget, синтаксис и использование.
WGET можно использовать для:
Скачать один файл с помощью wget
$ wget https://cyberciti.biz/here/lsst.tar.gz
Загрузить несколько файлов с помощью wget
$ wget https://cyberciti.biz/download/lsst.tar.gz ftp://ftp.freebsd.org/pub/sys.tar.gz ftp://ftp.redhat.com/pub/xyz-1rc-i386.rpm
Можно прочитать URL из файла
Вы можете поместить все URL в текстовый файл и использовать опцию -i, чтобы wget загрузил все файлы. Сначала создайте текстовый файл:
$ xed /temp/download.txt
Добавить список URL:
https://cyberciti.biz/download/lsst.tar.gz
ftp://ftp.freebsd.org/pub/sys.tar.gz
ftp://ftp.redhat.com/pub/xyz-1rc-i386.rpm
Введите команду wget следующим образом:
$ wget -i /temp/download.txt
Можно ограничить скорость загрузки
$ wget -c -o /temp/susedvd.log —limit-rate=50k ftp://ftp.novell.com/pub/suse/dvd1.iso
Используйте wget с сайтами, защищенными паролем
Вы можете указать http имя пользователя / пароль на сервере следующим образом:
$ wget —http-user=vivek —http-password=Secrete http://cyberciti.biz/vivek/csits.tar.gz
Другой способ указать имя пользователя и пароль — в самом URL.
$ wget ‘http://username:password@cyberciti.biz/file.tar.gz
Скачать все mp3 или pdf файлы с удаленного FTP сервера
$ wget ftp://somedom-url/pub/downloads/*.mp3
$ wget ftp://somedom-url/pub/downloads/*.pdf
Скачать сайт целиком
$ wget -r -k -l 7 -p -E -nc https://site.com/
Рассмотрим используемые параметры:
-r — указывает на то, что нужно рекурсивно переходить по ссылкам на сайте, чтобы скачивать страницы.
-k — используется для того, чтобы wget преобразовал все ссылки в скаченных файлах таким образом, чтобы по ним можно было переходить на локальном компьютере (в автономном режиме).
-p — указывает на то, что нужно загрузить все файлы, которые требуются для отображения страниц (изображения, css и т.д.).
-l — определяет максимальную глубину вложенности страниц, которые wget должен скачать (по умолчанию значение равно 5, в примере мы установили 7). В большинстве случаев сайты имеют страницы с большой степенью вложенности и wget может просто «закопаться», скачивая новые страницы. Чтобы этого не произошло можно использовать параметр -l.
-E — добавлять к загруженным файлам расширение .html.
-nc — при использовании данного параметра существующие файлы не будут перезаписаны. Это удобно, когда нужно продолжить загрузку сайта, прерванную в предыдущий раз.
По умолчанию wget загружает файл и сохраняет его с оригинальным именем в URL — в текущем каталоге.
Здесь я перечислил набор инструкций для WGET для рекурсивного зеркалирования вашего сайта, загрузки всех изображений, CSS и JavaScript, локализации всех URL-адресов (чтобы сайт работал на вашем локальном компьютере) и сохранения всех страниц как .html файл.
Чтобы скачать ваш сайт, выполните эту команду:
wget -r https://www.yoursite.com
Чтобы скачать сайт и локализовать все URL:
wget —convert-links -r https://www.yoursite.com
Чтобы создать полноценное оффлайн зеркало сайта:
wget —mirror —convert-links —adjust-extension —page-requisites —no-parent https://www.yoursite.com
Чтобы скачать сайт и сохранить файлы как .html:
wget —html-extension -r https://www.yoursite.com
Чтобы скачать все изображения в формате jpg с сайта:
wget -A «*.jpg» -r https://www.yoursite.com
Дополнительные сведения об операциях, связанных с конкретным типом файлов, можно найти в этой полезной ветке на Stack .
Установите другой пользовательский агент:
Некоторые веб-серверы настроены так, чтобы запрещать пользовательский агент WGET по умолчанию — по очевидным причинам экономии полосы пропускания. Вы можете попробовать изменить свой пользовательский агент, чтобы обойти это. Например, притворившись роботом Google:
wget —user-agent=»Googlebot/2.1 (+https://www.googlebot.com/bot.html)» -r https://www.yoursite.com
Wget режим «паук»:
Wget может получать страницы без их сохранения, что может быть полезной функцией, если вы ищете неработающие ссылки на веб-сайте. Не забудьте включить рекурсивный режим, который позволяет wget сканировать документ и искать ссылки для перехода.
wget —spider -r https://www.yoursite.com
Вы также можете сохранить это в файл журнала, добавив эту опцию:
wget —spider -r https://www.yoursite.com -o wget.log
wget -m -l 10 -e robots=off -p -k -E —reject-regex «wp» —no-check-certificate -U=«Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/68.0.3440.106 Safari/537.36» site-addr.com
Как найти неработающие ссылки на вашем сайте
wget —spider -r -nd -nv -H -l 2 -w 2 -o run1.log https://site.by
Наслаждайтесь использованием этого мощного инструмента, и я надеюсь, что вам понравился мой урок.

Что такое wget?
Это утилита командной строки для получения файлов с использованием HTTP, HTTPS и FTP протоколов.
Как установить wget на компьютер с ОС Windows?
Вариант, которым пользуюсь сам, это скачать архив с уже скомпилированными бинарными файлами GNU Wget 0

После того как скачали архив, в любом месте создаём папку wget, например в C:\Program Files\wget и в эту папку распаковываем всё содержимое скачанного архива.
Чтобы программа свободно вызывалась отовсюду нужно добавить путь в переменную среды Path операционной системы Windows. Для этого заходим в Панель управления > Система

В зависимости какая разрядность у вашей установленной Windows, запускайте 32-битную либо 64-битную версию программы, wget либо wget64 соответственно.
Обратите внимание, что начиная с версии wget 1.20 прекращена поддержка Windows XP.
Примеры команд для wget:
Скачать файл с докачкой по протоколу http
wget -c http://ftp.byfly.by/pub/CentOS/8/isos/x86_64/CentOS-8.3.2011-x86_64-boot.iso
Скачать файл по протоколу https
wget --no-check-certificate https://www.linux.org.ru/images/7626/original.jpg
Скачать файл с докачкой по протоколу ftp
wget -c ftp://ftp.byfly.by/pub/CentOS/8/isos/x86_64/CentOS-8.3.2011-x86_64-boot.iso
Скачать с докачкой файлы по списку ссылок (в текстовом файле)
wget -c -i spisok.txt
Скачать рекурсивно указанный сайт
wget -rkx URL
Описание прочих команд смотрите во встроенной в программу помощи
wget -h
GNU Wget 1.20.3, программа для загрузки файлов из сети в автономном режиме.
Использование: wget [ПАРАМЕТР]... [URL]...
Обязательные аргументы для длинных параметров являются обязательными и для коротких параметров.
Запуск:
-V, --version показать версию Wget и завершить работу
-h, --help показать эту справку
-b, --background после запуска перейти в фоновый режим
-e, --execute=КОМАНДА выполнить команду в стиле <.wgetrc>
Журналирование и входной файл:
-o, --output-file=ФАЙЛ записывать сообщения в ФАЙЛ
-a, --append-output=ФАЙЛ дописывать сообщения в конец ФАЙЛА
-d, --debug показать много отладочной информации
-q, --quiet ничего не выводить
-v, --verbose показывать подробные сведения (по умолчанию)
-nv, --no-verbose отключить вывод подробных сведений (не полностью)
--report-speed=ТИП единицы измерения пропускной способности
определить ТИПОМ. ТИП может быть равно bits
-i, --input-file=ФАЙЛ загрузить URL-ы согласно локальному
или внешнему ФАЙЛУ
--input-metalink=ФАЙЛ скачать файлы, перечисленные в локальном
ФАЙЛЕ Metalink
-F, --force-html считать, что входной файл - HTML
-B, --base=URL считать, что ссылки из входного файла (-i -F)
указаны относительно URL
--config=ФАЙЛ задать файл настроек
--no-config не читать файлы настроек
--rejected-log=ФАЙЛ протоколировать причины отброса URL в ФАЙЛ
Загрузка:
-t, --tries=ЧИСЛО установить ЧИСЛО повторных попыток
(0 без ограничения)
--retry-connrefused повторять, даже если в подключении отказано
-O, --output-document=ФАЙЛ записывать документы в ФАЙЛ
-nc, --no-clobber пропускать загрузки, которые приведут к
загрузке уже существующих файлов
(и их перезаписи)
--no-netrc don't try to obtain credentials from .netrc
-c, --continue возобновить загрузку частично загруженного
файла
--start-pos=СМЕЩЕНИЕ начинать загрузку со СМЕЩЕНИЯ (считается с 0)
--progress=ТИП выбрать тип индикатора выполнения
--show-progress показывать индикатор выполнения в любом
режиме подробности
-N, --timestamping не загружать повторно файлы, только если они
не новее, чем локальные
--no-use-server-timestamps не использовать проверку
if-modified-since для запросов в режиме учёта
меток времени
--no-use-server-timestamps не устанавливать метку времени локальному
файлу, полученную с сервера
-S, --server-response вывод ответа сервера
--spider ничего не загружать
-T, --timeout=СЕКУНДЫ установка значений всех тайм-аутов равными
числу СЕКУНД
--dns-servers=АДРЕСА список запрашиваемых серверов DNS
(через запятую)
--bind-dns-address=АДРЕС привязать определитель DNS к АДРЕСУ
(имя компьютера или IP) локального компьютера
--dns-timeout=СЕК установка тайм-аута поиска в DNS в СЕК
--connect-timeout=СЕК установка тайм-аута подключения в СЕК
--read-timeout=СЕК установка тайм-аута чтения в СЕК
-w, --wait=СЕКУНДЫ пауза в СЕКУНДАХ между загрузками
--waitretry=СЕКУНДЫ пауза в 1..СЕКУНДЫ между повторными
попытками загрузки
--random-wait пауза в 0.5*WAIT...1.5*WAIT секунд
между загрузками
--no-proxy явно выключить прокси
-Q, --quota=ЧИСЛО установить величину квоты загрузки в ЧИСЛО
--bind-address=АДРЕС привязать АДРЕС (имя компьютера или IP)
локального компьютера
--limit-rate=СКОРОСТЬ ограничить СКОРОСТЬ загрузки
--no-dns-cache отключить кэширование DNS-запросов
--restrict-file-names=ОС использовать в именах файлов символы,
допустимые в ОС
--ignore-case игнорировать регистр при сопоставлении
файлов и/или каталогов
-4, --inet4-only подключаться только к адресам IPv4
-6, --inet6-only подключаться только к адресам IPv6
--prefer-family=СЕМЕЙСТВО подключаться сначала к адресам указанного
семейства (может быть IPv6, IPv4 или ничего)
--user=ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬ установить и ftp- и http-пользователя в
ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬ
--password=ПАРОЛЬ установить ftp- и http-пароль в ПАРОЛЬ
--ask-password запрашивать пароли
--use-askpass=КОМАНДА указать обработчик мандатов для запроса
имени пользователя и пароля. Если
КОМАНДА не указана, то используется
переменная окружения WGET_ASKPASS
или SSH_ASKPASS.
--no-iri выключить поддержку IRI
--local-encoding=КДР использовать КДР как локальную кодировку
для IRI
--remote-encoding=КДР использовать КДР как удалённую кодировку
по умолчанию
--unlink удалить файл перед затиранием
--keep-badhash оставлять файлы с неправильными
контрольными суммами (добавляя .badhash)
--metalink-index=НОМЕР порядковый НОМЕР metaurl
Metalink application/metalink4+xml
--metalink-over-http использовать метаданные Metalink из
заголовка ответов HTTP
--preferred-location предпочитаемое расположение ресурсов Metalink
Каталоги:
-nd, --no-directories не создавать каталоги
-x, --force-directories принудительно создавать каталоги
-nH, --no-host-directories не создавать каталоги как на узле
--protocol-directories использовать имя протокола в каталогах
-P, --directory-prefix=ПРЕФИКС сохранять файлы в ПРЕФИКС/..
--cut-dirs=ЧИСЛО игнорировать ЧИСЛО компонентов удалённого
каталога
Параметры HTTP:
--http-user=ПОЛЬЗОВ. установить http-пользователя в ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬ
--http-password=ПАРОЛЬ установить http-пароль в ПАРОЛЬ
--no-cache отвергать кэшированные сервером данные
--default-page=ИМЯ изменить имя страницы по умолчанию (обычно
это )
-E, --adjust-extension сохранять документы HTML/CSS с надлежащими
расширениями
--ignore-length игнорировать поле заголовка
--header=СТРОКА вставить СТРОКУ между заголовками
--compression=TYPE choose compression, one of auto, gzip and none. (default: none)
--max-redirect максимально допустимое число перенаправлений
на страницу
--proxy-user=ПОЛЬЗОВ. установить ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЯ в качестве имени
пользователя для прокси
--proxy-password=ПАРОЛЬ установить ПАРОЛЬ в качестве пароля для
прокси
--referer=URL включить в HTTP-запрос заголовок
--save-headers сохранять HTTP-заголовки в файл
-U, --user-agent=АГЕНТ идентифицировать себя как АГЕНТ вместо
Wget/ВЕРСИЯ
--no-http-keep-alive отключить поддержание активности HTTP
(постоянные подключения)
--no-cookies не использовать кукисы
--load-cookies=ФАЙЛ загрузить кукисы из ФАЙЛА перед сеансом
--save-cookies=ФАЙЛ сохранить кукисы в ФАЙЛ после сеанса
--keep-session-cookies загрузить и сохранить кукисы сеанса
(непостоянные)
--post-data=СТРОКА использовать метод POST; отправка СТРОКИ в
качестве данных
--post-file=ФАЙЛ использовать метод POST; отправка содержимого
ФАЙЛА
--method=HTTPMethod использовать метод в заголовке
--body-data=СТРОКА отправка СТРОКИ в качестве данных;
ДОЛЖЕН быть указан параметр --method
--body-file=ФАЙЛ отправка содержимого ФАЙЛА;
ДОЛЖЕН быть указан параметр --method
--content-disposition учитывать заголовок Content-Disposition
при выборе имён для локальных файлов
(ЭКСПЕРИМЕНТАЛЬНЫЙ)
--content-on-error выводить принятые данные при ошибках сервера
--auth-no-challenge отправлять информацию об аутентификации
Basic HTTP не дожидаясь первого ответа
сервера
Параметры HTTPS (SSL/TLS):
--secure-protocol=PR choose secure protocol, one of auto, SSLv2,
SSLv3, TLSv1, TLSv1_1, TLSv1_2 and PFS
--https-only переходить только по безопасным ссылкам HTTPS
--no-check-certificate не проверять сертификат сервера
--certificate=FILE файл сертификата пользователя
--certificate-type=ТИП тип сертификата пользователя: PEM или DER
--private-key=ФАЙЛ файл секретного ключа
--private-key-type=ТИП тип секретного ключа: PEM или DER
--ca-certificate=ФАЙЛ файл с набором CA
--ca-directory=КАТ каталог, в котором хранится список CA
--crl-file=ФАЙЛ файл с набором CRL
--pinnedpubkey=ФАЙЛ/ХЭШИ Файл с открытым ключом (PEM/DER) или любое
количество хэшей sha256 в виде base64,
начинающихся с и разделённых <;>,
по которым проверяется ответный узел
Параметры HSTS:
--no-hsts отключить HSTS
--hsts-file путь к базе данных HSTS (заменит значение
по умолчанию)
Параметры FTP:
--ftp-user=ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬ установить ftp-пользователя в ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬ
--ftp-password=ПАРОЛЬ установить ftp-пароль в ПАРОЛЬ
--no-remove-listing не удалять файлы <.listing>
--no-glob выключить маски для имён файлов FTP
--no-passive-ftp отключить <пассивный> режим передачи
--preserve-permissions сохранять права доступа удалённых файлов
--retr-symlinks при рекурсии загружать файлы по ссылкам
(не каталоги)
Параметры FTPS:
--ftps-implicit безусловно использовать FTPS (порт
по умолчанию - 990)
--ftps-resume-ssl возобновлять сеанс SSL/TLS, начатый
в канале управления, при открытии
канала данных
--ftps-clear-data-connection шифровать только канал управления;
данные не шифруются
--ftps-fallback-to-ftp вернуться к FTP, если FTPS не
поддерживается сервером
Параметры WARC:
--warc-file=ФАЙЛ записать данные запроса/ответа в файл .warc.gz
--warc-header=СТРОКА вставить СТРОКУ в запись warcinfo
--warc-max-size=ЧИСЛО максимальный размер файлов WARC равен ЧИСЛУ
--warc-cdx записать индексные файлы CDX
--warc-dedup=ФАЙЛ не сохранять записи, перечисленные в файле CDX
--no-warc-compression не сжимать файлы WARC с помощью GZIP
--no-warc-digests не вычислять дайджесты SHA1
--no-warc-keep-log не сохранять файл журнала в записи WARC
--warc-tempdir=КАТАЛОГ расположение для временных файлов,
создаваемых процедурой записи WARC
Рекурсивная загрузка:
-r, --recursive включение рекурсивной загрузки
-l, --level=ЧИСЛО глубина рекурсии (inf и 0 - бесконечность)
--delete-after удалять локальные файлы после загрузки
-k, --convert-links делать ссылки локальными в загруженном
HTML или CSS
--convert-file-only преобразовывать только файловую часть URL
(базовую часть имени)
--backups=N перед записью файла X, ротировать до N
резервных файлов
-K, --backup-converted перед преобразованием файла X делать резервную
копию в виде X.orig
-m, --mirror короткий параметр, эквивалентный
-N -r -l inf --no-remove-listing
-p, --page-requisites загрузить все изображения и проч., необходимые
для отображения HTML-страницы
--strict-comments включить строгую (SGML) обработку комментариев
HTML
Разрешения/запреты при рекурсии:
-A, --accept=СПИСОК список разрешённых расширений
через запятую
-R, --reject=СПИСОК список запрещённых расширений,
разделённых запятыми.
--accept-regex=РЕГВЫР регулярное выражение для разрешённых URL
--reject-regex=РЕГВЫР регулярное выражение для запрещённых URL
--regex-type=ТИП тип регулярного выражения (posix|pcre)
-D, --domains=СПИСОК список разрешённых доменов,
через запятую
--exclude-domains=СПИСОК список запрещённых доменов,
через запятую
--follow-ftp следовать по ссылкам FTP в HTML-документах
--follow-tags=СПИСОК список используемых тегов HTML,
через запятую
--ignore-tags=СПИСОК список игнорируемых тегов HTML,
через запятую
-H, --span-hosts заходить на чужие узлы при рекурсии
-L, --relative следовать только по относительным ссылкам
-I, --include-directories=СПИСОК список разрешённых каталогов
--trust-server-names использовать имя, указанное в перенаправляющем URL,
в качестве последнего компонента.
-X, --exclude-directories=СПИСОК список исключаемых каталогов
-np, --no-parent не подниматься в родительский каталог
The Command Prompt in Windows 10 doesn’t compare to the terminal on Linux. To make up for its shortcomings, tools like wget and Cygwin can be installed on Windows to get more out of the Command Prompt. Here’s how you can install and use wget in Windows 10.
Wget is a free tool but downloading the correct file is oddly tricky. It’s hard to tell just which one you should download and one of the more popular mirrors for the EXE is notorious for crashing on Windows 10. In order to install wget, (https://sourceforge.net/projects/gnuwin32/files/wget/1.11.4-1/wget-1.11.4-1-setup.exe/download?use_mirror=excellmedia) download this file from Sourceforge.
Extract the file, and run the EXE inside it. The installation is pretty straightforward. Except the EULA, and don’t change anything else.
Using Wget
There are two ways to use Wget on Windows 10. This is a command line tool so it doesn’t have a GUI. You access it via the Command Prompt. To use it from the Command Prompt, you can either add it as an environment variable, or you can manually go to the directory the Wget app is in, and use it from there. The second method isn’t convenient if you intend to use this tool often but we’re going to detail both methods and you can chose whichever suits you best.
CD To Wget
This is the less convenient method. Open File Explorer and go to the following location. There will be a Wget.exe file here. You really only need the path to this file. Copy it to your clipboard.
C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\bin
Next, open Command Prompt and enter the following command to move to the above location.
cd C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\bin
Once you’re in this folder, you can type wget and use any of its functions and switches.
Add Environment Variable
To have to move to the bin folder the Wget.exe is in every single time you want to use the tool is time consuming. If you add it as an environment variable though, you can simply type wget from any directory and use it. You will need admin rights to do this.
To add wget as an environment variable, open File Explorer and paste the following in the location bar.
Control Panel\System and Security\System
On the left column, click Advanced System Settings. In the window that opens, click Environment Variables. In the Environment Variables window, select ‘Path’ in the section at the top, and click Edit.
In the window that opens, click New, then click the browse button. Enter this location;
C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\bin
Click Ok on each window to exit.
Now, when you open Command Prompt, you can type wget regardless of which directory/folder you’re in and you will be able to access this app and use its commands.

Fatima Wahab
Fatima has been writing for AddictiveTips for six years. She began as a junior writer and has been working as the Editor in Chief since 2014.
Fatima gets an adrenaline rush from figuring out how technology works, and how to manipulate it. A well-designed app, something that solves a common everyday problem and looks
Have you ever lost an essential asset at a crucial moment on your website? It is frightening to even think about it, isn’t it? Perhaps if you have used Linux, then you might have heard of WGET. Yay! WGET is also available for Windows. Thank GNU for coming up with a compatible version of WGET for Windows 10. From the starting of this article, you will understand how to download and install WGET for Windows 10. Also, you will learn how to use WGET command with examples provided for improving your understanding. Keep on reading to gain comprehensive knowledge about WGET.

Table of Contents
WGET has been available for Linux users for a long time. Learners can even refer to the different articles and guides available on the web to better their comprehension. But when it comes to the Windows version, even the scarce amount of articles cannot give you the information you need. However, do not lose hope. From this point on, you will know things about WGET on Windows that you’ve never heard or read. So why not start with answering the most asked question: What is WGET?
What is WGET?
WGET is a free tool to download files and crawl websites using the command line. Before learning to download WGET and how to use WGET command with examples, check out the points given below to know more about its features:
- WGET can retrieve contents from web pages.
- It even allows you to download from any web pages (FTP, HTTP) in any format (PDF, XML).
- It’s known to provide operational anonymity to keep users’ location or activities a secret.
- WGET works perfectly in bad network conditions too.
- Apart from these features, WGET can overwrite correct domain name in links.
- Moreover, it can perform recursive downloads, where the link present in the downloading document gets automatically downloaded further.
Also Read: What is a Command Line Interpreter?
How to Install WGET for Windows 10
Using WGET for Windows 10 will seamlessly download and extract information from any webpage by using commands. Implement the steps below to download GnuWin first to create a Windows environment and use WGET.
1. Download GnuWin WGET from here. The download process will start and finish automatically in a few seconds.
2. Click the downloaded WGET setup.exe folder to open it, as shown below.

3. Click Yes when prompted.
Note: Make sure to close already running applications before starting WGET installation.
4. To install WGET for Windows, click on Next, as depicted below.

5. Select the I accept the agreement radio button and click the Next option as highlighted below to continue the installation process.

6. Click on Browse to select the Destination Location. Choose a folder where you want to set up WGET and click on Next as shown.
Note: It is recommended to use default path: C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\bin

7. Select the components you want to install among Binaries and Documentation. Click Next to proceed further.

8. Here, click on Browse and select a Destination Folder to create the program shortcut in the start menu. Then, click on Next.
Note: If you don’t want to create a shortcut, select the checkbox Don’t create a Start Menu folder.

9. Select the Additional icons you need and click Next as illustrated below:
- Create document shortcuts in Start Menu folder
- Download Sources
10. Scroll down the review tab and check if all the desired options are present. Click Install to begin installing WGET on your system.
Note: You can select Back to change any setting you need to modify.

11. Wait for the WGET installation process to complete in your Windows 10 desktop/laptop and click Finish to exit the setup.

Also Read: Fix error 1500 Another Installation is in Progress
How to Use WGET for Windows 10
There are two ways to use WGET on your system.
- First, it is accessed directly via Command Prompt using a single path.
- Second, you need to manually go to the directory page where the app is present, and then proceed to the command prompt procedure.
You can implement any of these methods to use WGET on your system at your convenience. So, now you will see both methods in action below:
Method 1: Add CD to WGET Path
Once you install WGET for Windows 10, ensure that the wget.exe folder exists in the path given in this method.
Note: If not, copy and paste the respective folder in the location shown in the below File Explorer navigation, as you are about to use only this path.
1. Press Windows + E keys simultaneously to open File Explorer.
2. Navigate to C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\bin and copy the location.

3. Type Command Prompt in the Windows search bar and click Open to launch it, as shown below.

4. Type cd C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\bin and press Enter.
5. Then type wget and hit Enter. If the command is executed, it shows that WGET is running properly.

6A. Type the required WGET for Windows 10 command to download any file in the given format:
wget [OPTION] … [URL]…
6B. Or, view help from WGET by typing ‘wget –help’
Also Read: Fix File Explorer Not Responding in Windows 10
Method 2: Add Environment Variable
Once you download WGET for Windows 10, you must change the environmental variable set in the system settings. This is a long process. Follow the steps below carefully to set up WGET for Windows 10:
1. Press the Windows key from the keyboard and type Control Panel. Click the Open option to launch it.

2. Choose View by: Large icons from the top right corner. Click on the System option.
3. Scroll down and click on the Advanced system settings as illustrated below.

4. In the Advanced tab, click the Environment Variables button as shown.

5. Environmental Variables pop-up window will appear. Select the Path under the User variables for GREEN category and click on Edit as depicted below.

6. In the Edit environmental variable window, select the Browse option.

7. Select C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\bin path and click OK as shown.

8. Then, click OK as shown.

9. Again, click OK in the System Properties window.

10. Now, open Command Prompt as explained in Method 1.
11. Type wget and press Enter on the keyboard. Once the Environment Variable is set, you will be able to run WGET regardless of any folder you are currently in.

Also Read: How to Fix Git Merge Error
How to Check the Functioning of WGET App and Commands
To check if you can access WGET for Windows 10 regardless of any folder or directory that is present, follow the steps given below:
1. Type Command Prompt on the start menu search bar and click Open to launch it.

2. Type wget and press Enter to check whether the application runs.
Note: If you receive unrecognized command error, you have downloaded the WGET Setup from the wrong source. So, ensure to use only the link given above for the download process and try again.

3A. If the test worked, then it’s great. You have done a good job!
3B. If it is not working, do not worry. Check if you have followed the steps in an orderly manner, from downloading GnuWin, installing WGET Setup, then adding WGET environment variable. Try once again and restart the command line.
Also Read: Fix ERR_EMPTY_RESPONSE in Google Chrome
How to Use WGET Command with Examples
There are thousands of WGET commands to perform specific tasks. Run WGET for Windows 10 using any of the methods given above and type any of the commands listed below in Command Prompt.
Note: You need to enter the command correctly to obtain desired results.
1. To get list of commands, use the command wget -h.

2. To download a single file, use the command wget [URL]. For instance, enter the command wget https://wordpress.org/latest.zip. Here, WordPress is chosen as an example.
3. To download to a specific folder, use the command wget ‐P [wanted directory] [URL]. For instance, wget -P /temp https://github.com/git/git/archive/master.zip.
4. To resume an interrupted download, use the command wget ‐c [URL]. For instance, wget -c https://wordpress.org/latest.zip.
5. To set the download speed, use the command wget ‐‐limit-rate [wanted speed] [URL]. For instance, wget –limit-rate 1m https://wordpress.org/latest.zip.
6. To mirror a single webpage, use the command wget -m [URL]. For instance, wget -m https://cereal.guru/.
7. To know the version of installed WGET, then use the command wget -V.

8. To download and save under a specific name, use the command wget -o [file name] [URL]. For instance, wget -o file.docx https://cereal.guru/.
9. To download a web page in the background, use the command wget -b [URL]. For instance, wget -b https://cereal.guru/.
10. To download multiple URLs, use the command wget -i [File name]. For instance, wget -i URL.txt. Before executing this command, place all the URLs in one file and include that file name in the command.
11. To download via FTP, use the command wget –ftp-user=[ftp_username] –ftp-password=[ftp_password] ftp://… For instance, wget –ftp-user=sofiftp –ftp-password=TopSecretPassword ftp://123.456.7890.
12. To change the number of retry attempts, use the command wget –tries=[number_of_tries] [URL]. For instance, wget –tries=inf https://cereal.guru/. In this example, inf denotes infinity. The default number of retries is 20.
This is how to use WGET command with examples. Click here to know about more commands and their uses.
Recommended:
- Fix Windows 10 Update Error 0x80070103
- How to Enable Telnet in Windows 10
- Complete List of Windows 11 Run Commands
- Discord Commands List
We hope that this guide was helpful and you could learn how to download, install & use WGET for Windows 10. If you have any queries or suggestions, feel free to drop them in the comments section below.
WGET is a free tool to crawl websites and download files via the command line.
In this wget tutorial, we will learn how to install and how to use wget commands with examples.

What is Wget?
Wget is free command-line tool created by the GNU Project that is used todownload files from the internet.
- It lets you download files from the internet via FTP, HTTP or HTTPS (web pages, pdf, xml sitemaps, etc.).
- It provides recursive downloads, which means that Wget downloads the requested document, then the documents linked from that document, and then the next, etc.
- It follows the links and directory structure.
- It lets you overwrite the links with the correct domain, helping you create mirrors of websites.
What Is the Wget Command?
The wget command is a tool developed by the GNU Project to download files from the web. Wget allows you to retrieve content and files from web servers using a command-line interface. The name “wget” comes from “World Wide Web” and “get”. Wget supports downloads via FTP, SFTP, HTTP, and HTTPS protocols.
Wget is used by developers to automate file downloads.

Install Wget
To install wget on Windows, install the executable file from eternallybored.org. To install wget on Mac, use the brew install wget command on Mac. Make sure that it is not already installed first by running the wget -V command in the command line interface. For more details on how to install Wget, read one of the following tutorials.
- Install Wget on Mac
- Install Wget on Windows
- Install Wget on Linux
Downloading Files From the Command Line (Wget Basics)
Let’s look at the wget syntax, view the basic commands structure and understand the most important options.
Wget Syntax
Wget has two arguments: [OPTION] and [URL] .
wget [OPTION]... [URL]...
- [OPTION] tells what to do with the [URL] argument provided after. It has a short and a long-form (ex:
-Vand--versionare doing the same thing). - [URL] is the file or the directory you wish to download.
- You can call many OPTIONS or URLs at once.
View WGET Arguments
To view available wget Arguments, use the wget help command:
The output will show you an exhaustive list of all the wget command parameters.

Here are the 11 best things that you can do with Wget:
- Download a single file
- Download a files to a specific directory
- Rename a downloaded files
- Define User Agent
- Extract as Googlebot
- Extract Robots.txt when it changes
- Convert links on a page
- Mirror a single page
- Extract Multiple URLs from a list
- Limit Speed
- Number of attempts
- Use Proxies
- Continue Interrupted Downloads
- Extract Entire Website
Download a single file with Wget
$ wget https://example.com/robots.txt
Download a File to a Specific Output Directory
Here replace <YOUR-PATH> by the output directory location where you want to save the file.
$ wget ‐P <YOUR-PATH> https://example.com/sitemap.xml
Rename Downloaded File when Retrieving with Wget
To output the file with a different name:
$ wget -O <YOUR-FILENAME.html> https://example.com/file.html
Define User Agent in WGET
Identify yourself. Define your user-agent.
$ wget --user-agent=Chrome https://example.com/file.html
Extract as Googlebot with Wget Command
$ wget --user-agent="Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 6.0.1; Nexus 5X Build/MMB29P) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.198 Mobile Safari/537.36 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html)" https://example.com/path
Let’s extract robots.txt only if the latest version in the server is more recent than the local copy.
First time that you extract use -S to keep a timestamps of the file.
$ wget -S https://example.com/robots.txt
Later, to check if the robots.txt file has changed, and download it if it has.
$ wget -N https://example.com/robots.txt
Wget command to Convert Links on a Page
Convert the links in the HTML so they still work in your local version. (ex: example.com/path to localhost:8000/path)
$ wget --convert-links https://example.com/path
Mirror a Single Webpage in Wget
To mirror a single web page so that it can work on your local.
$ wget -E -H -k -K -p --convert-links https://example.com/path
Add all urls in a urls.txt file.
https://example.com/1 https://example.com/2 https://example.com/3
To be a good citizen of the web, it is important not to crawl too fast by using --wait and --limit-rate.
--wait=1: Wait 1 second between extractions.--limit-rate=10K: Limit the download speed (bytes per second)
Define Number of Retry Attempts in Wget
Sometimes the internet connection fails, sometimes the attempts it blocked, sometimes the server does not respond. Define a number of attempts with the -tries function.
$ wget -tries=10 https://example.com
How to Use Proxies With Wget?
To set a proxy with Wget, we need to update the ~/.wgetrc file located at /etc/wgetrc.
You can modify the ~/.wgetrc in your favourite text editor.
$ vi ~/.wgetrc # VI $ code ~/.wgetrc # VSCode
And add these lines to the wget parameters:
use_proxy = on http_proxy = http://username:password@proxy.server.address:port/ https_proxy = http://username:password@proxy.server.address:port/
Then, by running any wget command, you’ll be using proxies.
Alternatively, you can use the -e command to run wget with proxies without changing the environment variables.
wget -e use_proxy=yes -e http_proxy=http://proxy.server.address:port/ https://example.com
How to remove the Wget proxies?
When you don’t want to use the proxies anymore, update the ~/.wgetrc to remove the lines that you added or simply use the command below to override them:
Continue Interrupted Downloads with Wget
When your retrieval process is interrupted, continue the download with restarting the whole extraction using the -c command.
$ wget -c https://example.com
Recursive mode extract a page, and follows the links on the pages to extract them as well.
This is extracting your entire site and can put extra load on your server. Be sure that you know what you do or that you involve the devs.
$ wget --recursive --page-requisites --adjust-extension --span-hosts --wait=1 --limit-rate=10K --convert-links --restrict-file-names=windows --no-clobber --domains example.com --no-parent example.com
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
| –recursive | Follow links in the document. The maximum depth is 5. |
| –page-requisites | Get all assets (CSS/JS/images) |
| –adjust-extension | Save files with .html at the end. |
| –span-hosts | Include necessary assets from offsite as well. |
| –wait=1 | Wait 1 second between extractions. |
| –limit-rate=10K | Limit the download speed (bytes per second) |
| –convert-links | Convert the links in the HTML so they still work in your local version. |
| –restrict-file-names=windows | Modify filenames to work in Windows. |
| –no-clobber | Overwrite existing files. |
| –domains example.com | Do not follow links outside this domain. |
| –no-parent | Do not ever ascend to the parent directory when retrieving recursively |
| –level | Specify the depth of crawling. |
$ wget --spider -r https://example.com -o wget.log
Wget VS Curl
Wget’s strength compared to curl is its ability to download recursively. This means that it will download a document, then follow the links and then download those documents as well.
Use Wget With Python
Wget is strictly command line, but there is a package that you can import the wget package that mimics wget.
import wget url = 'http://www.jcchouinard.com/robots.txt' filename = wget.download(url) filename
Debugging: What to Do When Wget is Not Working
Wget Command Not Found
If you get the -bash: wget: command not found error on Mac, Linux or Windows, it means that the wget GNU is either not installed or does not work properly.
Go back and make sure that you installed wget properly.
Wget is not recognized as an internal or external command
If you get the following error
'wget' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file
It is more than likely that the wget package was not installed on Windows. Fix the error by installing wget first and then start over using the command.
Otherwise, it may also mean that the wget command is not not found in your system’s PATH.
Adding Wget to the System’s Path (Windows)
Adding the wget command to the system’s path will allow you to run wget from anywhere.
To add wget to the Windows System ‘s Path you need to copy the wget.exe file to the right directory.
- Download the wget file for Windows
- Press
Windows + Eto open File Explorer. - Find where you downloaded
wget.exe(e.g. Downloads folder) - Copy the
wget.exefile - Paste into the System Directory (System32 is already in your system’s path)
- Go to
C:\Windows\System32. - Paste your
wget.exefile into your System32 folder
- Go to
wget: missing URL
The “wget: missing URL” error message occurs when you run the wget command without providing a URL to download.
One of the use cases that I have seen this is when users used flags without the proper casing.
$ wget -v # wget: missing URL
Above the casing of the v flag should not be lowercase, but uppercase.
Or use the verbose way of calling it with the double-dash and full name.
$ wget --version # No error
Alternatives to Wget on Mac and Windows
You can use cURL as an alternative of Wget command line tool. It also has to be installed on Mac, Linux and Windows.
Wget for Web Scraping
By allowing you to download files from the Internet, the wget command-line tool is incredibly useful in web scraping. It has a set of useful features that make web scraping easy:
- Batch Downloading:
wgetallows you to download multiple files or web pages in a single command. - Recursive Downloading: the
--recursiveflag inwgetallows you to follow links and download an entire website - Retries:
wgetis designed to handle unstable network connections and interruptions and retry failed extractions - Command-line options: Options are available to improve scraping capabilities (download speed, User-Agent headers, cookies for authentication, etc.).
- Header and User-Agent Spoofing: To avoid being blocked by websites when web scraping,
wgetallows you to change the User-Agent header to make your requests appear more regular users. - Limiting Server Load: By using the
--waitand--limit-rateoptions, you can control the speed at whichwgetfetches data.
About Wget
| Wget was developed by | Hrvoje Nikšić |
| Wget is Maintained by | Tim Rühsen and al. |
| Wget Supported Protocols | HTTP(S), FTP(S) |
| Wget was Created In | January 1996 |
| Installing Wget | brew install wget |
| Wget Command | wget [option]…[URL]… |
Wget FAQs
What is Wget Used For?
Wget is used to download files from the Internet without the use of a browser. It supports HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP protocols, as well as retrieval through HTTP proxies.
How Does Wget Work?
Wget is non-interactive and allows to download files from the internet in the background without the need of a browser or user interface. It works by following links to create local versions of remote web sites, while respecting robots.txt.
What is the Difference Between Wget and cURL?
Both Wget and cURL are command-line utilities that allow file transfer from the internet. Although, Curl generally offers more features than Wget, wget provide features such as recursive downloads.
Can you Use Wget With Python?
Yes, you can run wget get in Python by installing the wget library with $pip install wget
Does Wget Respect Robots.txt?
Yes, Wget respects the Robot Exclusion Standard (/robots.txt)
Is Wget Free?
Yes, GNU Wget is free software that everyone can use, redistribute and/or modify under the terms of the GNU General Public License
What is recursive download?
Recursive download, or recursive retrieval, is the capacity of downloading documents, follow the links within them and finally downloading those documents until all linked documents are downloaded, or the maximum depth specified is reached.
How to specify download location in Wget?
Use the -P or –directory-prefix=PREFIX. Example: $ wget -P /path <url>
Conclusion
This is it.
You now know how to install and use Wget in your command-line.
SEO Strategist at Tripadvisor, ex- Seek (Melbourne, Australia). Specialized in technical SEO. Writer in Python, Information Retrieval, SEO and machine learning. Guest author at SearchEngineJournal, SearchEngineLand and OnCrawl.
