The latest Intel graphics driver v15.46.02.4729 for HD Graphics 500 / 600 comes with the following new features:
- OpenGL 4.5 support
- Vulkan 1.0.38 support
- Enabled additional OpenCL media extensions: cl_intel_device_side_avc_motion_estimation, cl_intel_media_block_io, cl_intel_planar_yuv (details: here)
- Enabled Programmable Sample Positions in Direct3D 12
- Added support for Computer Vision SDK and Deep Learning Deployment Toolkits (details: here)
- Windows 10 Creators Update features enabled (7th Gen Intel® Core Processors only)
You can download the Intel graphics driver v15.46.02.4729 from the following links:
- Intel HD Graphics driver v15.46.02.4729 (zip) @ Geeks3D
- Intel Graphics Driver for Windows* [15.46] @ Intel
Here is the partial report from GPU Caps Viewer for OpenGL, Vulkan and OpenCL:
OpenGL
- OpenGL vendor: Intel - OpenGL renderer: Intel(R) HD Graphics 630 - OpenGL Version: 4.5.0 - Build 22.20.16.4729 - OpenGL Extensions: 241 extensions (GL=220 and WGL=21) - GL_3DFX_texture_compression_FXT1 - GL_AMD_depth_clamp_separate - GL_AMD_vertex_shader_layer - GL_AMD_vertex_shader_viewport_index - GL_ARB_ES2_compatibility - GL_ARB_ES3_1_compatibility - GL_ARB_ES3_compatibility - GL_ARB_arrays_of_arrays - GL_ARB_base_instance - GL_ARB_bindless_texture - GL_ARB_blend_func_extended - GL_ARB_buffer_storage - GL_ARB_cl_event - GL_ARB_clear_buffer_object - GL_ARB_clear_texture - GL_ARB_clip_control - GL_ARB_color_buffer_float - GL_ARB_compatibility - GL_ARB_compressed_texture_pixel_storage - GL_ARB_compute_shader - GL_ARB_conditional_render_inverted - GL_ARB_conservative_depth - GL_ARB_copy_buffer - GL_ARB_copy_image - GL_ARB_cull_distance - GL_ARB_debug_output - GL_ARB_depth_buffer_float - GL_ARB_depth_clamp - GL_ARB_depth_texture - GL_ARB_derivative_control - GL_ARB_direct_state_access - GL_ARB_draw_buffers - GL_ARB_draw_buffers_blend - GL_ARB_draw_elements_base_vertex - GL_ARB_draw_indirect - GL_ARB_draw_instanced - GL_ARB_enhanced_layouts - GL_ARB_explicit_attrib_location - GL_ARB_explicit_uniform_location - GL_ARB_fragment_coord_conventions - GL_ARB_fragment_layer_viewport - GL_ARB_fragment_program - GL_ARB_fragment_program_shadow - GL_ARB_fragment_shader - GL_ARB_fragment_shader_interlock - GL_ARB_framebuffer_no_attachments - GL_ARB_framebuffer_object - GL_ARB_framebuffer_sRGB - GL_ARB_geometry_shader4 - GL_ARB_get_program_binary - GL_ARB_get_texture_sub_image - GL_ARB_gpu_shader5 - GL_ARB_gpu_shader_fp64 - GL_ARB_half_float_pixel - GL_ARB_half_float_vertex - GL_ARB_indirect_parameters - GL_ARB_instanced_arrays - GL_ARB_internalformat_query - GL_ARB_internalformat_query2 - GL_ARB_invalidate_subdata - GL_ARB_map_buffer_alignment - GL_ARB_map_buffer_range - GL_ARB_multi_bind - GL_ARB_multi_draw_indirect - GL_ARB_multisample - GL_ARB_multitexture - GL_ARB_occlusion_query - GL_ARB_occlusion_query2 - GL_ARB_pixel_buffer_object - GL_ARB_point_parameters - GL_ARB_point_sprite - GL_ARB_post_depth_coverage - GL_ARB_program_interface_query - GL_ARB_provoking_vertex - GL_ARB_query_buffer_object - GL_ARB_robust_buffer_access_behavior - GL_ARB_robustness - GL_ARB_robustness_isolation - GL_ARB_sample_shading - GL_ARB_sampler_objects - GL_ARB_seamless_cube_map - GL_ARB_seamless_cubemap_per_texture - GL_ARB_separate_shader_objects - GL_ARB_shader_atomic_counters - GL_ARB_shader_bit_encoding - GL_ARB_shader_draw_parameters - GL_ARB_shader_image_load_store - GL_ARB_shader_image_size - GL_ARB_shader_objects - GL_ARB_shader_precision - GL_ARB_shader_stencil_export - GL_ARB_shader_storage_buffer_object - GL_ARB_shader_subroutine - GL_ARB_shader_texture_image_samples - GL_ARB_shading_language_100 - GL_ARB_shading_language_420pack - GL_ARB_shading_language_packing - GL_ARB_shadow - GL_ARB_stencil_texturing - GL_ARB_sync - GL_ARB_tessellation_shader - GL_ARB_texture_barrier - GL_ARB_texture_border_clamp - GL_ARB_texture_buffer_object_rgb32 - GL_ARB_texture_buffer_range - GL_ARB_texture_compression - GL_ARB_texture_compression_bptc - GL_ARB_texture_compression_rgtc - GL_ARB_texture_cube_map - GL_ARB_texture_cube_map_array - GL_ARB_texture_env_add - GL_ARB_texture_env_combine - GL_ARB_texture_env_crossbar - GL_ARB_texture_env_dot3 - GL_ARB_texture_float - GL_ARB_texture_gather - GL_ARB_texture_mirror_clamp_to_edge - GL_ARB_texture_mirrored_repeat - GL_ARB_texture_multisample - GL_ARB_texture_non_power_of_two - GL_ARB_texture_query_levels - GL_ARB_texture_query_lod - GL_ARB_texture_rectangle - GL_ARB_texture_rg - GL_ARB_texture_rgb10_a2ui - GL_ARB_texture_stencil8 - GL_ARB_texture_storage - GL_ARB_texture_storage_multisample - GL_ARB_texture_swizzle - GL_ARB_texture_view - GL_ARB_timer_query - GL_ARB_transform_feedback2 - GL_ARB_transform_feedback3 - GL_ARB_transform_feedback_instanced - GL_ARB_transpose_matrix - GL_ARB_uniform_buffer_object - GL_ARB_vertex_array_bgra - GL_ARB_vertex_array_object - GL_ARB_vertex_attrib_64bit - GL_ARB_vertex_attrib_binding - GL_ARB_vertex_buffer_object - GL_ARB_vertex_program - GL_ARB_vertex_shader - GL_ARB_vertex_type_10f_11f_11f_rev - GL_ARB_vertex_type_2_10_10_10_rev - GL_ARB_viewport_array - GL_ARB_window_pos - GL_ATI_separate_stencil - GL_EXT_abgr - GL_EXT_bgra - GL_EXT_blend_color - GL_EXT_blend_equation_separate - GL_EXT_blend_func_separate - GL_EXT_blend_minmax - GL_EXT_blend_subtract - GL_EXT_clip_volume_hint - GL_EXT_compiled_vertex_array - GL_EXT_direct_state_access - GL_EXT_draw_buffers2 - GL_EXT_draw_range_elements - GL_EXT_fog_coord - GL_EXT_framebuffer_blit - GL_EXT_framebuffer_multisample - GL_EXT_framebuffer_object - GL_EXT_geometry_shader4 - GL_EXT_gpu_program_parameters - GL_EXT_gpu_shader4 - GL_EXT_multi_draw_arrays - GL_EXT_packed_depth_stencil - GL_EXT_packed_float - GL_EXT_packed_pixels - GL_EXT_polygon_offset_clamp - GL_EXT_rescale_normal - GL_EXT_secondary_color - GL_EXT_separate_specular_color - GL_EXT_shader_framebuffer_fetch - GL_EXT_shader_integer_mix - GL_EXT_shadow_funcs - GL_EXT_stencil_two_side - GL_EXT_stencil_wrap - GL_EXT_texture3D - GL_EXT_texture_array - GL_EXT_texture_compression_s3tc - GL_EXT_texture_edge_clamp - GL_EXT_texture_env_add - GL_EXT_texture_env_combine - GL_EXT_texture_filter_anisotropic - GL_EXT_texture_integer - GL_EXT_texture_lod_bias - GL_EXT_texture_rectangle - GL_EXT_texture_sRGB - GL_EXT_texture_sRGB_decode - GL_EXT_texture_shared_exponent - GL_EXT_texture_snorm - GL_EXT_texture_storage - GL_EXT_texture_swizzle - GL_EXT_timer_query - GL_EXT_transform_feedback - GL_IBM_texture_mirrored_repeat - GL_INTEL_conservative_rasterization - GL_INTEL_fragment_shader_ordering - GL_INTEL_framebuffer_CMAA - GL_INTEL_map_texture - GL_INTEL_multi_rate_fragment_shader - GL_INTEL_performance_query - GL_KHR_blend_equation_advanced - GL_KHR_blend_equation_advanced_coherent - GL_KHR_context_flush_control - GL_KHR_debug - GL_KHR_texture_compression_astc_hdr - GL_KHR_texture_compression_astc_ldr - GL_NV_blend_square - GL_NV_conditional_render - GL_NV_primitive_restart - GL_NV_texgen_reflection - GL_SGIS_generate_mipmap - GL_SGIS_texture_edge_clamp - GL_SGIS_texture_lod - GL_SUN_multi_draw_arrays - GL_WIN_swap_hint - WGL_EXT_depth_float - WGL_ARB_buffer_region - WGL_ARB_extensions_string - WGL_ARB_make_current_read - WGL_ARB_pixel_format - WGL_ARB_pbuffer - WGL_EXT_extensions_string - WGL_EXT_swap_control - WGL_ARB_multisample - WGL_ARB_pixel_format_float - WGL_ARB_framebuffer_sRGB - WGL_ARB_create_context - WGL_ARB_create_context_profile - WGL_EXT_pixel_format_packed_float - WGL_EXT_create_context_es_profile - WGL_EXT_create_context_es2_profile - WGL_NV_DX_interop - WGL_INTEL_cl_sharing - WGL_NV_DX_interop2 - WGL_ARB_create_context_robustness - WGL_ARB_context_flush_control
Vulkan
- Instance extensions: 9
- VK_EXT_debug_report (version: 6)
- VK_EXT_display_surface_counter (version: 1)
- VK_KHR_get_physical_device_properties2 (version: 1)
- VK_KHR_surface (version: 25)
- VK_KHR_win32_surface (version: 5)
- VK_KHX_device_group_creation (version: 1)
- VK_KHX_external_memory_capabilities (version: 1)
- VK_KHX_external_semaphore_capabilities (version: 1)
- VK_NV_external_memory_capabilities (version: 1)
- Instance layers: 1
- VK_LAYER_NV_optimus (version: 1.0.46, impl: 1)
- Physical devices: 1
- [Vulkan device 0]: Intel(R) HD Graphics 630 ------------------
- API version: 1.0.38
- vendorID: 32902
- deviceID: 22811
- driver version: 65538
- memory heap count: 2
- heap1: 3660MB
- heap2: 3660MB
- memory type count: 3
- mem type 0 - heap index : 0 - property flag : 1
> mem property: VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_DEVICE_LOCAL_BIT
- mem type 1 - heap index : 1 - property flag : 7
> mem property: VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_DEVICE_LOCAL_BIT
> mem property: VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_VISIBLE_BIT
> mem property: VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_COHERENT_BIT
- mem type 2 - heap index : 1 - property flag : 15
> mem property: VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_DEVICE_LOCAL_BIT
> mem property: VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_VISIBLE_BIT
> mem property: VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_COHERENT_BIT
> mem property: VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_CACHED_BIT
- extensions: 4
- VK_KHR_swapchain (version: 68)
- VK_KHR_sampler_mirror_clamp_to_edge (version: 1)
- VK_KHR_maintenance1 (version: 1)
- VK_KHR_shader_draw_parameters (version: 1)
- device layers: 1
- VK_LAYER_NV_optimus (version: 1.0.46, impl: 1)
- device features:
- robustBufferAccess: true
- fullDrawIndexUint32: true
- imageCubeArray: true
- independentBlend: true
- geometryShader: true
- tessellationShader: true
- sampleRateShading: true
- dualSrcBlend: true
- logicOp: true
- multiDrawIndirect: true
- drawIndirectFirstInstance: true
- depthClamp: true
- depthBiasClamp: true
- fillModeNonSolid: true
- depthBounds: false
- wideLines: true
- largePoints: true
- alphaToOne: true
- multiViewport: true
- samplerAnisotropy: true
- textureCompressionETC2: true
- textureCompressionASTC_LDR: true
- textureCompressionBC: true
- occlusionQueryPrecise: true
- pipelineStatisticsQuery: true
- vertexPipelineStoresAndAtomics: true
- fragmentStoresAndAtomics: true
- shaderTessellationAndGeometryPointSize: true
- shaderImageGatherExtended: true
- shaderStorageImageExtendedFormats: true
- shaderStorageImageMultisample: true
- shaderStorageImageReadWithoutFormat: false
- shaderStorageImageWriteWithoutFormat: true
- shaderUniformBufferArrayDynamicIndexing: true
- shaderSampledImageArrayDynamicIndexing: true
- shaderStorageBufferArrayDynamicIndexing: true
- shaderStorageImageArrayDynamicIndexing: true
- shaderClipDistance: true
- shaderCullDistance: true
- shaderFloat64: true
- shaderInt64: true
- shaderInt16: true
- shaderResourceResidency: true
- shaderResourceMinLod: true
- sparseBinding: true
- sparseResidencyBuffer: true
- sparseResidencyImage2D: true
- sparseResidencyImage3D: true
- sparseResidency2Samples: true
- sparseResidency4Samples: true
- sparseResidency8Samples: true
- sparseResidency16Samples: true
- sparseResidencyAliased: true
- variableMultisampleRate: true
- inheritedQueries: true
- device limits
- maxImageDimension1D: 16384
- maxImageDimension2D: 16384
- maxImageDimension3D: 2048
- maxImageDimensionCube: 16384
- maxImageArrayLayers: 2048
- maxTexelBufferElements: 134217728
- maxUniformBufferRange: 65536
- maxStorageBufferRange: 134217728
- maxPushConstantsSize: 256
- maxMemoryAllocationCount: 1874157
- maxSamplerAllocationCount: 4000
- bufferImageGranularity: 1
- sparseAddressSpaceSize: 17592186044416
- maxBoundDescriptorSets: 8
- maxPerStageDescriptorSamplers: 16
- maxPerStageDescriptorUniformBuffers: 200
- maxPerStageDescriptorSampledImages: 200
- maxPerStageDescriptorStorageImages: 16
- maxPerStageDescriptorInputAttachments: 8
- maxPerStageResources: 200
- maxDescriptorSetSamplers: 96
- maxDescriptorSetUniformBuffers: 1200
- maxDescriptorSetUniformBuffersDynamic: 16
- maxDescriptorSetStorageBuffers: 1200
- maxDescriptorSetStorageBuffersDynamic: 16
- maxDescriptorSetSampledImages: 1200
- maxDescriptorSetStorageImages: 96
- maxDescriptorSetInputAttachments: 8
- maxVertexInputAttributes: 16
- maxVertexInputBindings: 16
- maxVertexInputAttributeOffset: 2047
- maxVertexInputBindingStride: 4095
- maxVertexOutputComponents: 128
- maxTessellationGenerationLevel: 64
- maxTessellationPatchSize: 32
- maxTessellationControlPerVertexInputComponents: 128
- maxTessellationControlPerVertexOutputComponents: 128
- maxTessellationControlPerPatchOutputComponents: 120
- maxTessellationControlTotalOutputComponents: 4096
- maxTessellationEvaluationInputComponents: 128
- maxTessellationEvaluationOutputComponents: 128
- maxGeometryShaderInvocations: 32
- maxGeometryInputComponents: 128
- maxGeometryOutputComponents: 128
- maxGeometryOutputVertices: 256
- maxGeometryTotalOutputComponents: 1024
- maxFragmentInputComponents: 128
- maxFragmentOutputAttachments: 8
- maxFragmentDualSrcAttachments: 1
- maxFragmentCombinedOutputResources: 16
- maxComputeSharedMemorySize: 32768
- maxComputeWorkGroupCount: [65536; 65536; 65536]
- maxComputeWorkGroupInvocations: 1024
- maxComputeWorkGroupSize: [1024; 1024; 64]
- subPixelPrecisionBits: 8
- subTexelPrecisionBits: 8
- mipmapPrecisionBits: 8
- maxDrawIndexedIndexValue: 4294967295
- maxDrawIndirectCount: 4294967295
- maxSamplerLodBias: 16.000000
- maxSamplerAnisotropy: 16.000000
- maxViewports: 16
- maxViewportDimensions: [32768; 32768]
- viewportBoundsRange: [-65536.000000 ; 65535.000000]
- viewportSubPixelBits: 8
- minMemoryMapAlignment: 64
- minTexelBufferOffsetAlignment: 16
- minUniformBufferOffsetAlignment: 32
- minStorageBufferOffsetAlignment: 16
- minTexelOffset: 4294967288
- maxTexelOffset: 7
- minTexelGatherOffset: 4294967264
- maxTexelGatherOffset: 31
- minInterpolationOffset: -0.500000
- maxInterpolationOffset: 0.437500
- subPixelInterpolationOffsetBits: 4
- maxFramebufferWidth: 16384
- maxFramebufferHeight: 16384
- maxFramebufferLayers: 2048
- framebufferColorSampleCounts: 31
- framebufferDepthSampleCounts: 31
- framebufferStencilSampleCounts: 31
- framebufferNoAttachmentsSampleCounts: 31
- maxColorAttachments: 8
- sampledImageColorSampleCounts: 31
- sampledImageIntegerSampleCounts: 31
- sampledImageDepthSampleCounts: 31
- sampledImageStencilSampleCounts: 31
- storageImageSampleCounts: 31
- maxSampleMaskWords: 1
- timestampComputeAndGraphics: 1
- timestampPeriod: 83.000000
- maxClipDistances: 16
- maxCullDistances: 16
- maxCombinedClipAndCullDistances: 16
- discreteQueuePriorities: 2
- pointSizeRange: [0.125000 ; 255.875000]
- lineWidthRange: [0.000000 ; 7.992188]
- pointSizeGranularity: 0.125000
- lineWidthGranularity: 0.007813
- strictLines: 0
- standardSampleLocations: 1
- optimalBufferCopyOffsetAlignment: 16
- optimalBufferCopyRowPitchAlignment: 16
- nonCoherentAtomSize: 1
OpenCL
- CL_PLATFORM_NAME: Intel(R) OpenCL
- CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR: Intel(R) Corporation
- CL_PLATFORM_VERSION: OpenCL 2.1
- CL_PLATFORM_PROFILE: FULL_PROFILE
- Num devices: 2
- CL_DEVICE_NAME: Intel(R) HD Graphics 630
- CL_DEVICE_VENDOR: Intel(R) Corporation
- CL_DRIVER_VERSION: 22.20.16.4729
- CL_DEVICE_PROFILE: FULL_PROFILE
- CL_DEVICE_VERSION: OpenCL 2.1
- CL_DEVICE_TYPE: GPU
- CL_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID: 0x8086
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_COMPUTE_UNITS: 24
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_CLOCK_FREQUENCY: 1100MHz
- CL_DEVICE_ADDRESS_BITS: 32
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_MEM_ALLOC_SIZE: 1524534KB
- CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_SIZE: 1488MB
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_PARAMETER_SIZE: 1024
- CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_CACHELINE_SIZE: 64 Bytes
- CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_CACHE_SIZE: 512KB
- CL_DEVICE_ERROR_CORRECTION_SUPPORT: NO
- CL_DEVICE_LOCAL_MEM_TYPE: Local (scratchpad)
- CL_DEVICE_LOCAL_MEM_SIZE: 64KB
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_CONSTANT_BUFFER_SIZE: 1524534KB
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_DIMENSIONS: 3
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_SIZES: [256 ; 256 ; 256]
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_GROUP_SIZE: 256
- CL_EXEC_NATIVE_KERNEL: 2125540
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE_SUPPORT: YES
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_READ_IMAGE_ARGS: 128
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WRITE_IMAGE_ARGS: 128
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE2D_MAX_WIDTH: 16384
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE2D_MAX_HEIGHT: 16384
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE3D_MAX_WIDTH: 16384
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE3D_MAX_HEIGHT: 16384
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE3D_MAX_DEPTH: 2048
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_SAMPLERS: 16
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_CHAR: 16
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_SHORT: 8
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_INT: 4
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_LONG: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_FLOAT: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_DOUBLE: 1
- CL_DEVICE_EXTENSIONS: 37
- Extensions:
- cl_intel_accelerator
- cl_intel_advanced_motion_estimation
- cl_intel_d3d11_nv12_media_sharing
- cl_intel_device_side_avc_motion_estimation
- cl_intel_driver_diagnostics
- cl_intel_dx9_media_sharing
- cl_intel_media_block_io
- cl_intel_motion_estimation
- cl_intel_planar_yuv
- cl_intel_packed_yuv
- cl_intel_required_subgroup_size
- cl_intel_simultaneous_sharing
- cl_intel_subgroups
- cl_intel_subgroups_short
- cl_khr_3d_image_writes
- cl_khr_byte_addressable_store
- cl_khr_d3d10_sharing
- cl_khr_d3d11_sharing
- cl_khr_depth_images
- cl_khr_dx9_media_sharing
- cl_khr_fp16
- cl_khr_fp64
- cl_khr_gl_depth_images
- cl_khr_gl_event
- cl_khr_gl_msaa_sharing
- cl_khr_global_int32_base_atomics
- cl_khr_global_int32_extended_atomics
- cl_khr_gl_sharing
- cl_khr_icd
- cl_khr_image2d_from_buffer
- cl_khr_local_int32_base_atomics
- cl_khr_local_int32_extended_atomics
- cl_khr_mipmap_image
- cl_khr_mipmap_image_writes
- cl_khr_spir
- cl_khr_subgroups
- cl_khr_throttle_hints
- CL_DEVICE_NAME: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7700HQ CPU @ 2.80GHz
- CL_DEVICE_VENDOR: Intel(R) Corporation
- CL_DRIVER_VERSION: 7.2.0.10
- CL_DEVICE_PROFILE: FULL_PROFILE
- CL_DEVICE_VERSION: OpenCL 2.1 (Build 10)
- CL_DEVICE_TYPE: CPU
- CL_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID: 0x8086
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_COMPUTE_UNITS: 8
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_CLOCK_FREQUENCY: 2800MHz
- CL_DEVICE_ADDRESS_BITS: 32
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_MEM_ALLOC_SIZE: 524256KB
- CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_SIZE: 511MB
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_PARAMETER_SIZE: 3840
- CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_CACHELINE_SIZE: 64 Bytes
- CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_CACHE_SIZE: 256KB
- CL_DEVICE_ERROR_CORRECTION_SUPPORT: NO
- CL_DEVICE_LOCAL_MEM_TYPE: Global
- CL_DEVICE_LOCAL_MEM_SIZE: 32KB
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_CONSTANT_BUFFER_SIZE: 128KB
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_DIMENSIONS: 3
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_SIZES: [8192 ; 8192 ; 8192]
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_GROUP_SIZE: 8192
- CL_EXEC_NATIVE_KERNEL: 2125536
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE_SUPPORT: YES
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_READ_IMAGE_ARGS: 480
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WRITE_IMAGE_ARGS: 480
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE2D_MAX_WIDTH: 16384
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE2D_MAX_HEIGHT: 16384
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE3D_MAX_WIDTH: 2048
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE3D_MAX_HEIGHT: 2048
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE3D_MAX_DEPTH: 2048
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_SAMPLERS: 480
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_CHAR: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_SHORT: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_INT: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_LONG: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_FLOAT: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_DOUBLE: 1
- CL_DEVICE_EXTENSIONS: 16
- Extensions:
- cl_khr_icd
- cl_khr_global_int32_base_atomics
- cl_khr_global_int32_extended_atomics
- cl_khr_local_int32_base_atomics
- cl_khr_local_int32_extended_atomics
- cl_khr_byte_addressable_store
- cl_khr_depth_images
- cl_khr_3d_image_writes
- cl_intel_exec_by_local_thread
- cl_khr_spir
- cl_khr_dx9_media_sharing
- cl_intel_dx9_media_sharing
- cl_khr_d3d11_sharing
- cl_khr_gl_sharing
- cl_khr_fp64
- cl_khr_image2d_from_buffer
via
Jun. 23, 2022 / Updated by
Bessie Shaw to
Windows Driver Solutions
Can’t find the name of Intel ICD OpenGL driver? To fix the Intel ICD OpenGL driver error, you just need to update your Intel OpenGL driver. Here are top 2 ways to download and update Intel ICD OpenGL driversfor Windows 10.
1. Manually Download Intel ICD OpenGL Driver for Windows 10
You could manually search for and download the Intel ICD OpenGL driver from your PC manufacturer’s website,
Step 1. Go to Intel’s Drivers & Software page.
Step 2. In the top right corner of the page, enter your model number in the search box.
Step 3. Select your operating system. The related Intel ICD OpenGL driver will show up below.
Step 4. Click on the driver name and you will go to the download page.
Step 5. Click the .exe file to download it directly.
Step 6. Once the driver download is complete, install it on your PC.
Step 7.Reboot your PC.
2. Update Intel ICD OpenGL Driver for Windows 10 with Driver Update Utility
If you are a novice computer user and don’t want to manually download the Intel ICD OpenGL driver yourself, you could adopt a reliable driver update utility to do it, and Driver Talent is highly recommended, which could automatically download and install the best-matched Intel ICD OpenGL driver for your Windows 10 PC.
Click the button below to download Driver Talent directly.
Download Now
Here are 3 easy steps to download and update Intel ICD OpenGL drivers for Windows 10, both 64 bit and 32 bit.
Step 1. Scan Your PC
Launch Driver Talent. Click the “Scan” button to scan all Windows 10 drivers, including the Intel ICD OpenGL driver.
Note: You could go to “Settings” to set Driver Talent to the automatic scanning mode.
Step 2. Download and Update Intel ICD OpenGL Driver
Click “Update” to update your Intel ICD OpenGL driver to the latest version. Click “Repair” to fix the outdated or missing Intel ICD OpenGL driver problem. Driver Talent will download and install the right driver automatically in the background.
Step 3. Reboot Your PC
Reboot your PC to make the Intel ICD OpenGL driver update take effect.
In addition to the Intel ICD OpenGL driver update, Driver Talent provides further features, such as drivers backup, drivers restore, drivers uninstall, system restore, drivers pre-download for another PC, PC Repair (no sound, no video, no Wi-Fi available, etc.), DLL files repair, hardware detection, VR support check and PC speed up, etc.
You may also like to check out:
-
How to Tell If Your Computer Has Bluetooth
-
How to Determine If Windows 10 Is 32-bit or 64-bit
-
How to Remove Test Mode Watermark in Windows 10
-
How to Enter Safe Mode in Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7, Vista, XP
-
How to Launch Command Prompt on Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7, Vista, XP
If you think this article is useful, please share it on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Google+, Reddit or Digg to help your friends solve the similar issues.
If you have any questions about downloading and updating Intel ICD OpenGL drivers for Windows 10, welcome to leave comments below. Any other drivers download and update, like network driver, mouse driver, Bluetooth driver, 802.11n WLAN driver, Dolby audio driver, USB Type-C driver, please check the Windows Driver Solutions section.
Recommended Download
|
ExplorerMax |
Driver Talent for Network Card | |||
| Smart and advanced file explorer tool for Windows platforms | Download & Install Network Drivers without Internet Connection | |||
|
30-day Free Trial |
Free Download |
About Save Legacy Intel OpenGL
This repository is intended to be a catalog of fixes to get OpenGL working on Windows 10 for programs coded to advertise Window 10 compatibility on old Intel graphics controllers. The following graphics controllers generations are affected by this issue:
- 3rd generation Graphics Media Accelerators except GMA 910 and 915 series; [1]
- 4th generation Graphics Media Accelerators;
- PowerVR edition Graphics Media Accelerators;
- 1st and 2nd generations Intel HD Graphics.
Note [1]: Intel GMA 910 and 915 series released in 2004 and 2005 respectively didn’t get WDDM driver which means they only work with Windows XP, Vista and 7 according to Wikipedia.
End-user guide
- download the whole code as ZIP and extract it;
- double-click the .cmd file intended for the program you want to fix OpenGL for [2].
[2] Some program fixes included are for software runtimes like Java. If your program is using such runtime make sure you apply the fix for the runtime first and see if the issue goes away. You don’t want to waste both mine and your time with an invalid contribution like the individual from here did.
If a program has both 32-bit and 64-bit versions and you have only one of them installed, the one you don’t have gets fixed in advance in case you install it at a later date see #1.
You don’t need Application Compatibility Toolkit to install fixes. You only need the affected program and a copy of this repository codebase.
Why we have this issue
In order to fix any problem we must understand its root cause. In the early days of Windows 10 development Microsoft decided to change the Windows major version from 6 to 10. However Microsoft thought it is enough to provide software developers APIs to advertise Windows 10 compatibility. Programs that advertise compatibility get current OS version when they ask for it, others get the old 6.3 format. When implementing this Microsoft forgot about dynamic link libraries or maybe was unable to do anything about them. There is no similar mechanism(s) for DLLs as far as I know, they always inherit Windows version received by the programs that loads them. As a result of this, things go south when a program advertising Windows 10 compatibility loads a DLL that is not ready for current Windows 10 major version. Anything can happen but most likely the DLL just unloads right away. Intel OpenGL driver for iGPU generations listed above is the perfect example and as a result it unloads immediately.
Determine if a program is affected without running it (for advanced users)
It is possible to determine if a program is affected by inspecting its manifest if exists as shown in this video
Ways to fix this problem
Patch Intel OpenGL driver to recognize Windows 10 major version
Done by Marcinosoft for various Intel GPU generations. DLLs are scattered throughout this issue thread.
Pros:
- it fixes all affected programs at once if enough effort is put into overcoming the cons.
Cons:
- breaks digital signature of the OpenGL driver which needs fixing by removing it and replacing it with new code signature to retain compatibility with protected processes like Virtualbox;
- if you are downloading a pre-patched copy from Internet (not recommended) it must be for your Intel GPU generation;
- this is the riskiest method.
Alter or remove the manifest of programs lacking OpenGL support (remove the tag that contains {8 unique identifier from the manifest)
Pros:
- less risky than OpenGL driver patching.
Cons:
- can only fix affected programs individually;
- basic usage of binary editing tools is needed for embedded manifests [3];
- it is still a manual process that is not mass deployment friendly;
- basic HTML and XML knowledge is needed [3];
- cannot fix protected processes like Virtualbox.
[3]: WTFI tool eliminates these complexity relared cons.
Use Mesa3D as an alternative to Windows inbox OpenGL 1.1 software renderer. Install Mesa3D desktop OpenGL drivers using system-wide deployment tool.
Pros:
- supports OpenGL 4.5 in core profile while OpenGL supported by affected drivers even when fixed barely get to OpenGL 3.1;
- it fixes all affected programs at once;
- included software rasterizers work through RDP, GPU OpenGL only works through RDP on currently supported hardware;
- can be installed even if GPU OpenGL is working correctly, e.g. just to get RDP OpenGL support.
Cons:
- not digitally signed but you can sign it with an Ascertia Free Try code signing certificate if you want;
- far slower than the GPU since it is still a software renderer.
Create a compatibility shim with Win81RTMVersionLie fix for Intel OpenGL driver applied to affected programs individually (this is the method used by this project)
Pros:
- cleanest method (it doesn’t touch the program directly);
- it is mass deployment friendly (we can create a repository of fixes with people picking the ones they need);
- using its internal version of Compatibility Administrator Microsoft can create a master fix that works for all affected programs, it might even work in kernel mode and for programs using protected process APIs like Virtualbox. Feedback suggesting this enhancement is filed here.
Cons:
- public version of Compatibility Administrator cannot fix kernel mode and protected processes like Virtualbox;
- public version of Compatibility Administrator can only fix affected programs individually;
- creation of fixes requires decent knowledge in using Compatibility Administrator tool.
Video tutorial on creating a compatibility shim with Win81RTMVersionLie fix is below
Sometimes, you will suddenly run into OpenGL error when playing games, for instance, can’t find the name of Intel ICD OpenGL driver. Or for the better gaming experience, there is much need to make sure the Intel, AMD, and NVIDIA OpenGL driver are updated.
But for many of you, what this OpenGL means and how to update the OpenGL on Windows and Mac.
What is OpenGL? What is OpenGL Driver?
OpenGL, short for Open Graphics Library, is the standard 3D Graphics API and is often required in some games or software. It will provide these programs with graphics and images. It is worth noting that OpenGL aims to communicate with the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) to improve the performance of the hardware.
On another hand, the OpenGL driver ensuring OpenGL is installed with the graphics card driver, like Intel, AMD, and NVIDIA HD graphics drivers.
How to Download and Update OpenGL Drivers?
It is said that if not updating the OpenGL drivers, your PC will automatically set the OpenGL to its default version, namely, OpenGL 1.1. In this way, there is a high probability that you can’t enjoy the maximized gaming experience.
While in order to get the OpenGL drivers updated, you need only update the display driver as OpenGL driver will come along with the driver you download. For instance, if you are using Intel HD graphics card, try to update the Intel driver so as to get the latest OpenGL driver installed.
Methods:
- 1: Update the OpenGL Driver Automatically
- 2: Update OpenGL Drivers Manually
- 3: Update OpenGL Driver in Device Manager
Method 1: Update the OpenGL Driver Automatically
More often than not, users find it difficult to locate the right OpenGL drivers even on OpenGL official site. If it is the case, why not try an automatic tool to download the recent driver for OpenGL? Here Driver Booster can be the top one driver updater available for you.
Whatever display card on your PC, Driver Booster is able to detect the outdated or corrupted graphics driver for you.
1. Download, install and run Driver Booster.
2. Hit the Scan button. Immediately Driver Booster will search for all the missing, outdated and even faulty drivers for you.
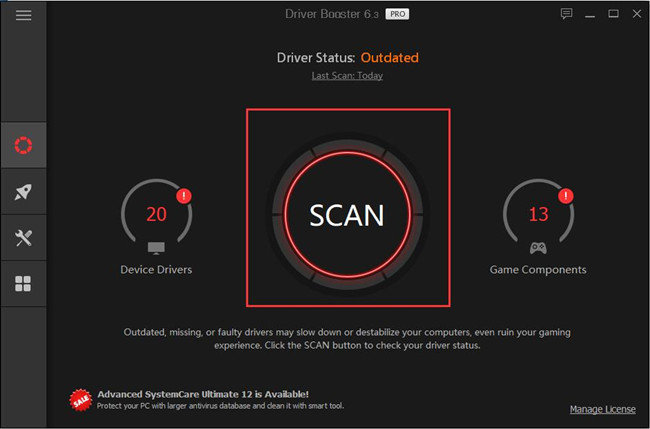
3. Pinpoint Display adapters and then Update the graphics driver.
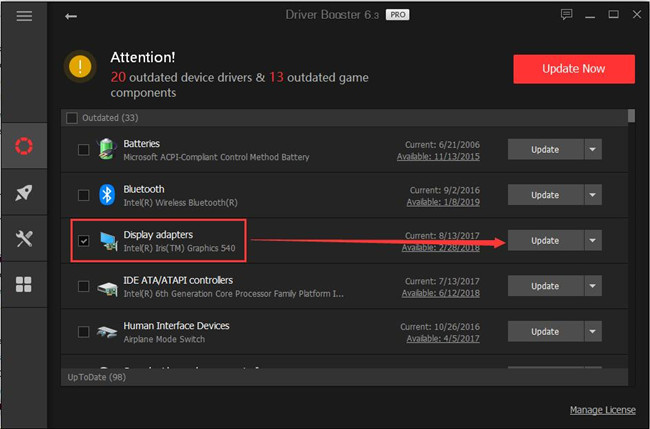
Driver Booster will automatically install the display driver on your PC, like Intel ICD OpenGL driver. In doing so, you will notice the OpenGL driver has been updated as well. Start and enjoy your game, such as Minecraft.
Method 2: Update OpenGL Driver Manually
Due to the fact that OpenGL driver is embedded with the Intel graphics card, the time you feel like finding the driver on your own, you just need to get the latest graphics driver.
Here for different display card, be it AMD, Intel, and NVIDIA card, you are supposed to their individual official site.
Here take the example of updating Intel ICD OpenGL driver as an example. Of course, it is accessible to download AMD OpenGL or NVIDIA OpenGL driver on AMD or NVIDIA site.
1. Navigate to Intel official site.
2. On Intel site, click Graphics driver.
3. Choose your Intel model and then filter by Drivers, Windows 10 64 bit. You need to enter your Windows type, like Windows 10 32-bit, Windows 8, 7, etc.
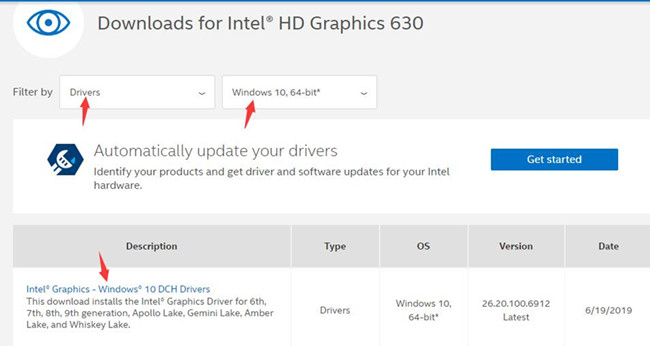
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to finish installing the Intel HD graphics driver.
On the basis of that, you will have also updated Intel ICD OpenGL driver for Windows 10. In this case, you may as well open your game to check whether OpenGL driver error will pop up again.
Method 3: Update OpenGL Driver in Device Manager
Otherwise, it makes sense to get the OpenGL driver from the graphics driver within Windows 10. That is to say, you can attempt to let Windows device manager find the driver you need.
1. Open Device Manager.
2. Expand Display adapters and then right-click the graphics driver to Update driver. Here your display card may be AMD, Intel, or NVIDIA or any other ones with different brands.
3. Try to Search automatically for the updated driver software.
If possible, the Device Manager will locate the latest graphics driver for you. You can install it on Windows 10 in the hope that the OpenGL driver can be updated. In a large sense, can’t find the name of Intel ICD OpenGL driver or any other OpenGL driver issue in games will disappear.
In a word, if you are to download the recent OpenGL driver, you are to install the most updated graphics driver for Windows 11, 10, 8, 7.
More Articles:
Download Intel HD Graphics 4600 Drivers for Windows 11, 10, 8 and 7
3 Ways to Download AMD Drivers on Windows 11, 10, 8 and 7
What is OpenAL? Should I Remove it?
Learn how to enable OpenGL 3.3 driver by downloading and installing the correct drivers for graphics cards. Follow our troubleshooting guide for a seamless installation.

OpenGL is a powerful graphics library used to render 2D and 3D vector graphics, making it a crucial tool for everything from gaming to scientific visualization. Programs that require OpenGL to render graphics, particularly 3D visuals, may sometimes prompt you with errors, particularly when the version of OpenGL installed does not meet the program’s requirements. For instance, some programs may need OpenGL 3.3 or higher to function smoothly.
Understanding OpenGL 3 and Beyond
Before we dive into the installation process, let’s first understand why OpenGL 3.3 or higher is required for many modern programs. OpenGL 3.3 was released on March 11, 2010, and offered several improvements over its predecessors, allowing more efficient rendering of complex graphics. The requirement for OpenGL 3.3 has become standard due to its ability to handle high-quality graphics, making it essential for programs related to 3D modeling, gaming, and other GPU-intensive applications.
The main advantage of OpenGL 3.3 is its improved performance in rendering 3D images compared to older versions. However, to fully utilize OpenGL 3.3 or higher, your graphics card and driver must be compatible with this version of OpenGL.
Key Features of OpenGL 3.3:
- Enhanced texture and shader management
- Support for more advanced features in graphical applications
- Better performance and stability compared to older OpenGL versions
Enabling OpenGL 3 requires updating or installing the correct graphics card drivers that support OpenGL 3.3 or higher. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide on how to do this:
Step 1: Check Your Graphics Card Compatibility
The first step in enabling OpenGL 3 is to check whether your current graphics card supports OpenGL 3.3 or higher. Different manufacturers support various versions of OpenGL, and you must ensure that your graphics card meets the necessary requirements.
How to Check Your Graphics Card on Windows
- Press Start and type
dxdiagin the search bar. - Hit Enter to open the DirectX Diagnostic Tool.
- Navigate to the Display tab. Here, you’ll find information about your graphics card and its capabilities, including the supported version of OpenGL.
- If your card does not support OpenGL 3.3 or higher, you will need to update your graphics driver or, in some cases, consider replacing the graphics card.
Step 2: Download and Install the OpenGL Driver
Once you’ve determined which graphics card you have, the next step is to download and install the appropriate OpenGL driver for your system. Below are the download links for OpenGL drivers from the most popular graphics card manufacturers:
1. Intel OpenGL Driver Download
Intel provides OpenGL drivers for a wide range of integrated graphics solutions, such as the Intel HD Graphics and Intel Iris Graphics. To enable OpenGL 3.3 support for Intel graphics, follow these steps:
Intel HD Graphics OpenGL 3.3 Driver Download: For Intel users, the most recent drivers for Intel HD Graphics support OpenGL 3.3 or higher. You can download the drivers directly from the Intel website.
For Windows 10, use the Intel OpenGL Driver Download for Windows 10 to ensure compatibility.
2. NVIDIA OpenGL Driver Download
NVIDIA is known for its high-performance graphics cards, and its drivers typically support the latest versions of OpenGL. If you have an NVIDIA graphics card, here’s how to download and install OpenGL drivers:
- NVIDIA GeForce OpenGL Driver Download: NVIDIA drivers for GeForce and Quadro series GPUs support OpenGL 3.3 or higher. Use the NVIDIA Driver Download page to download the latest drivers.
Make sure to select the appropriate operating system version (Windows 7, Windows 10, or Windows 11) when downloading drivers.
3. AMD OpenGL Driver Download
AMD graphics cards, such as the AMD Radeon series, also support OpenGL 3.3 and above. To enable OpenGL 3 on AMD systems, follow these steps:
- AMD OpenGL Driver Download Windows 10: For AMD users on Windows 10, you can download the drivers from AMD’s official website. Choose your specific GPU model to get the correct driver.
4. Microsoft OpenGL Driver Download
If you’re using a Microsoft graphics card (often integrated in laptops or tablets), you may also need to download the necessary OpenGL drivers from Microsoft’s update center or the manufacturer’s website.
- Microsoft OpenGL Driver Download: If your device uses a Microsoft-provided GPU, you may find OpenGL drivers in Windows updates or through the manufacturer’s support page.
Step 3: Install OpenGL Drivers
Once you’ve downloaded the correct drivers for your system, follow these installation steps:
- Run the Setup: Open the downloaded file and follow the on-screen instructions to install the OpenGL driver.
- Restart Your Computer: After the installation is complete, restart your system to ensure the new drivers take effect.
- Verify Installation: After rebooting, repeat the process of checking your graphics card via
dxdiagto verify that OpenGL 3.3 or higher is now supported.
Step 4: Switching Graphics Cards (Optional)
If your computer has multiple graphics cards (such as integrated and discrete GPUs), you may want to switch to the high-performance card for better OpenGL support. This is particularly useful for systems with both Intel integrated graphics and NVIDIA or AMD discrete graphics.
To do this:
- Open your system’s Graphics Settings or Control Panel.
- Select the program (e.g., your 3D modeling software) and assign it to use the high-performance GPU.
- Save and restart the application to use the new GPU.
Step 5: Troubleshooting OpenGL Installation Issues
Even after installing the correct OpenGL drivers, you may run into problems. Here are some common troubleshooting tips:
1. “Does My Driver Support OpenGL?”
If you encounter the error “Does my driver support OpenGL?”, it likely means that your current driver doesn’t meet the minimum requirements. To resolve this, make sure you download the latest driver for your system using the links provided earlier.
2. OpenGL Driver Not Accelerated Error
Sometimes, you may get an error saying “OpenGL Driver Not Accelerated”. This can happen if your hardware doesn’t support hardware acceleration for OpenGL. In this case, check if your graphics card supports OpenGL 3.3 or higher, and consider upgrading your graphics card if necessary.
3. OpenGL Driver Download Issues
If you’re unable to download the drivers, check your internet connection or try using a different browser. In rare cases, specific drivers may be temporarily unavailable on the manufacturer’s website.
Additional Information and Resources
If you’re using a system with older graphics cards, it’s important to note that certain models may not support OpenGL 3.3 or higher. If none of your graphics cards support OpenGL 3.3, you may need to upgrade to a newer model. NVIDIA’s GeForce and AMD’s Radeon series are known for supporting the latest OpenGL versions.
Additionally, for Android users, you can find OpenGL drivers by searching for “OpenGL driver download for Android” or downloading directly through your device’s settings if it supports OpenGL versions higher than 3.3.
Conclusion
Enabling OpenGL 3 drivers on your system is essential for running modern applications, from 3D modeling software to games. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your graphics drivers support OpenGL 3.3 or higher. Whether you use Intel, AMD, or NVIDIA graphics, updating your drivers and ensuring compatibility will help optimize your system’s performance and resolve any OpenGL-related issues.
If you continue facing issues with OpenGL, don’t hesitate to contact the manufacturer’s support team for further assistance.
Visit Our Post Page: Blog Page
