The genuine lsass.exe file is a software component of Microsoft Windows by .
If «lsass.exe» resides in «C:\Windows\System32», it is the Microsoft Windows Operating System’s Local Security Authority Subsystem Service. Six critical Windows services involved in the computer’s security management are dynamic link library (.dll) files which are called by «lsass.exe». These include «vaultsvc.dll», which controls access to credentials of users and applications; «efssvc.dll», central to storage of encrypted files on NTFS-type disk volumes; and «samsrv.dll», the Security Accounts Manager. If the real «lsass.exe» is forcibly stopped the machine is forced into a restart because the Welcome screen loses its account(s). It also cannot be uninstalled. In other locations, assume «lsass.exe» is disguised malware, which may include extremely dangerous Trojans or worms. A spyware or malware removal program may be needed to remove such files.
LSASS stands for Local Security Authority Subsystem Service
The .exe extension on a filename indicates an executable file. Executable files may, in some cases, harm your computer. Therefore, please read below to decide for yourself whether the lsass.exe on your computer is a Trojan that you should remove, or whether it is a file belonging to the Windows operating system or to a trusted application.
Click to Run a Free Scan for lsass.exe related errors
Lsass.exe file information

The process known as Local Security Authority Process or LSA Shell (Export Version) or LSA Shell or pikachu or Bonjour or Windows host process (Rundll32) or CNG Key Isolation, Security Accounts Manager or igfxCUIService Module
belongs to software Microsoft Windows Operating System or IPSEC Services, Protected Storage, Security Accounts Manager or CNG Key Isolation, Security Accounts Manager or Encrypting File System (EFS), CNG Key Isolation, Security Accounts Manager or CNG Key Isolation, Security Accounts Manager, Credential Manager or Project1 or CNG Key Isolation, Protected Storage, Security Accounts Manager or NT LM Security Support Provider, IPSEC Services, Protected Storage, Security Accounts Manager
by Microsoft (www.microsoft.com) or www.microsoft.com or Blackburn Laocoon or Nenad Hrg (SoftwareOK.com) or qYpbf or NETGATE Technologies s.r.o (www.netgate.sk) or Ci78JjFt5o9WNk.
Description: The original lsass.exe from Microsoft is an important part of Windows, but often causes problems. The lsass.exe file is located in the C:\Windows\System32 folder.
Known file sizes on Windows 10/11/7 are 13,312 bytes (68% of all occurrences), 22,528 bytes and 18 more variants.
The program is not visible. It is a Microsoft signed file. The process uses ports to connect to or from a LAN or the Internet.
Therefore the technical security rating is 13% dangerous, however you should also read the user reviews.
Recommended: Identify lsass.exe related errors
Viruses with the same file name
Is lsass.exe a virus? No, it is not. The true lsass.exe file is a safe Microsoft Windows system process, called «Local Security Authority Process».
However, writers of malware programs, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans deliberately give their processes the same file name to escape detection. Viruses with the same file name are for instance Trojan.Gen or W32.Imaut (detected by Symantec), and TROJ_GEN.R47C3LG or Mal_OtorunN (detected by TrendMicro).
To ensure that no rogue lsass.exe is running on your PC, click here to run a Free Malware Scan.
How to recognize suspicious variants?
- If lsass.exe is located in a subfolder of C:\Windows, the security rating is 87% dangerous. The file size is 1,591,808 bytes (13% of all occurrences), 3,902,464 bytes and 25 more variants.
The lsass.exe file is not a Windows core file. The program is not visible. The lsass.exe file is located in the Windows folder, but it is not a Windows core file. The program has no file description.
Lsass.exe is able to monitor applications, record keyboard and mouse inputs and manipulate other programs. - If lsass.exe is located in a subfolder of C:\, the security rating is 62% dangerous. The file size is 551,669 bytes (15% of all occurrences), 552,448 bytes and 23 more variants.
The lsass.exe file is not a Windows system file. There is no description of the program. The program has no visible window. The process starts when Windows starts (see Registry key: MACHINE\Run, Run, Userinit, User Shell Folders, Winlogon\Shell, TaskScheduler).Lsass.exe is able to record keyboard and mouse inputs, manipulate other programs and monitor applications.
- If lsass.exe is located in a subfolder of the user’s profile folder, the security rating is 63% dangerous. The file size is 42,687 bytes (12% of all occurrences), 212,992 bytes and 24 more variants.
- If lsass.exe is located in a subfolder of «C:\Program Files», the security rating is 75% dangerous. The file size is 4,606,976 bytes (39% of all occurrences), 196,919 bytes and 11 more variants.
- If lsass.exe is located in the C:\Windows folder, the security rating is 80% dangerous. The file size is 13,179,660 bytes (25% of all occurrences), 528,398 bytes, 185,344 bytes or 983,552 bytes.
- If lsass.exe is located in the Windows folder for temporary files, the security rating is 90% dangerous. The file size is 6,790,656 bytes (33% of all occurrences), 24,064 bytes or 1,591,808 bytes.
- If lsass.exe is located in a subfolder of C:\Windows\System32, the security rating is 96% dangerous. The file size is 471,040 bytes (50% of all occurrences) or 460,288 bytes.
- If lsass.exe is located in the user’s profile folder, the security rating is 76% dangerous. The file size is 473,001 bytes.
- If lsass.exe is located in the C:\Windows\System32\drivers folder, the security rating is 72% dangerous. The file size is 32,768 bytes.
- If lsass.exe is located in the «C:\Program Files\Common Files» folder, the security rating is 40% dangerous. The file size is 32,256 bytes.
External information from Paul Collins:
There are different files with the same name:
- «MicrosoftSourceSafe» definitely not required. Added by the WEBUS.B TROJAN! Note — this is not the legitimate lsass.exe process, which should not appear in Msconfig/Startup!
- «lsass» definitely not required. Added by the RATSOU.B TROJAN! Note — this is not the legitimate Lsass.exe system file should normally NOT figure in Msconfig/Startup!
- «Microsoft UPDATER32» definitely not required. Added by the RANDEX.AR WORM! Note — this is not the legitimate Lsass.exe system file should normally NOT figure in Msconfig/Startup!
- «System Handler» definitely not required. Added by the NIMOS WORM! Note — this is not the legitimate Lsass.exe system file should normally NOT figure in Msconfig/Startup!
- «Traybar» definitely not required. Added by the MYDOOM.L WORM! Note — this is not the legitimate Lsass.exe system file should normally NOT figure in Msconfig/Startup!
Important: Some malware disguises itself as lsass.exe, particularly when not located in the C:\Windows\System32 folder. Therefore, you should check the lsass.exe process on your PC to see if it is a threat. We recommend Security Task Manager for verifying your computer’s security. This was one of the Top Download Picks of The Washington Post and PC World.
Best practices for resolving lsass issues
A clean and tidy computer is the key requirement for avoiding problems with lsass. This means running a scan for malware, cleaning your hard drive using 1cleanmgr and 2sfc /scannow, 3uninstalling programs that you no longer need, checking for Autostart programs (using 4msconfig) and enabling Windows’ 5Automatic Update. Always remember to perform periodic backups, or at least to set restore points.
Should you experience an actual problem, try to recall the last thing you did, or the last thing you installed before the problem appeared for the first time. Use the 6resmon command to identify the processes that are causing your problem. Even for serious problems, rather than reinstalling Windows, you are better off repairing of your installation or, for Windows 8 and later versions, executing the 7DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth command. This allows you to repair the operating system without losing data.
To help you analyze the lsass.exe process on your computer, the following programs have proven to be helpful: ASecurity Task Manager displays all running Windows tasks, including embedded hidden processes, such as keyboard and browser monitoring or Autostart entries. A unique security risk rating indicates the likelihood of the process being potential spyware, malware or a Trojan. BMalwarebytes Anti-Malware detects and removes sleeping spyware, adware, Trojans, keyloggers, malware and trackers from your hard drive.
Other processes
hkcmd.exe task.vbs ascplugin_protection.dll lsass.exe csrss.exe skypehost.exe steam.exe hostappserviceupdater.exe armsvc.exe googleupdate.exe igfxtray.exe [all]
The June 2020 update contained multiple bugs, prompting Microsoft to issue a warning against version 2004 and impose a compatibility hold on affected Windows 10/11 devices. The bulletin highlighted various errors, such as Bluetooth, printer, unexpected restarts, and DISM errors.
However, Windows 10/11 users have recently discovered another error that is related to the June 2020 update, which Microsoft also confirmed. According to reports, some users with machines running Windows 10 version 1809 and later are experiencing forced reboots, due to the lsass.exe process.
This error has left the affected users very frustrated because the reboot happens right after installing the update.
What is C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe Failed in Windows 10/11?
Windows 10/11 C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe failed is a critical error that involves the lsass.exe process or the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) file. According to Microsoft, this error is triggered by the installation of the Windows 10/11 Patch Tuesday updates, resulting in unexpected crashes. The bug affects devices running Windows 10 versions 1809 (KB4561608), 1903, 1909 (KB4560960), and version 2004 (KB4557957). The LSASS failure also affects the June 16 out-of-band update.
When users get this error, a message notification in the following format may appear:
- A critical system process, C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe, failed with status code c0000008. The machine must now be restarted.
- A critical system process, C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe, failed with status code c0000354. The machine must now be restarted.
- A critical system process, C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe, failed with status code 80000003. The machine must now be restarted.
The status code might vary, but these errors all involve the LSASS file. The Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) is in charge of enforcing security policies on Windows systems. It is also used by the Windows system to add new entries to the security log, handle user logins, initiate password changes, and create access tokens.
When the LSASS process fails, the user will automatically lose access to all of the accounts on the device, and an error message will be displayed. The computer will be forced to restart and you’ll see a warning prompt displayed on the desktop, saying that the computer will soon restart.
There is no known cause that triggers this bug when the update is being installed and Microsoft is still investigating the issue. Microsoft is still working on a fix for this box but there is no definite delivery timeline yet. However, the company is resuming the delivery of optional non-security update releases.
So, if you’re getting this error when you install the updates, there is nothing you can do but look for a workaround. Lucky for you, we’ve listed down the most effective methods to deal with the C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe failed in Windows 10/11. Check out the methods listed below.
How to Fix “A critical system process C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe failed” in Windows 10/11
When you encounter the “A critical system process C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe failed” in Windows 10/11, waiting for Microsoft to launch the fix is not a viable solution because we don’t know when it will be released. You won’t be able to use your computer effectively when this error appears, so you might as well give the methods below a try.
But before you do, here are some basic troubleshooting steps you need to clear:
- Restart your computer and try reinstalling the update. If it goes through, then the error might have been caused by a temporary glitch. If a simple restart won’t do, boot into Safe Mode instead.
- Disable your security software temporarily while installing. A hyperactive security program might interfere with installing the updates. If this doesn’t help, try disabling your firewall temporarily too.
- Make sure your internet connection is stable when downloading and installing the update to avoid file corruption. Use a wired connection if possible, to avoid disruptions.
If the above methods don’t work, then refer to our solutions listed below.
Fix #1: Uninstall the update.
The first step you need to try when you are getting the C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe failed in Windows 10/11 is to uninstall the problematic update from your computer. Then, you can choose to wait for a cumulative update before trying again, to make sure that you’re not being plagued by this error all the time. You need to block the Update from the Windows Update service as well, to prevent any of the installation files from being re-downloaded and re-installed on your computer.
To uninstall recently installed updates, follow the steps below:
- Click Start, then choose Settings.
- Click Update & Security.
- From the list in the middle of the screen, click on View update history.
- Click Uninstall updates in the top-left corner of the window.
A Control Panel window will open listing all the recently installed updates on that device. The entries will be filtered into groups and according to the date. The most recent update installed will be at the top of the list.
Scroll down to the Microsoft Windows menu, then highlight the update at the top of the list and with the most recent install date. Click Uninstall. When you’re asked to confirm the action, click Uninstall again. You might need to restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Fix #2: Disable Fast Startup
The second option is to disable the Fast Startup feature on Windows 10/11. This feature is enabled by default and is designed to help your device boot up faster when you shut down your computer. Instead of completely shutting down, your computer simply enters a hibernation state to make it easier for you to pick up where you left.
To disable this feature, follow the steps below:
- Click Start and search for Control Panel from the search dialog.
- Open Control Panel and click on the Power Option.
- Click on Choose what the power buttons do.
- Choose Change settings that are currently unavailable.
- Uncheck Turn on fast startup.
- Close the window.
Computers with the Fast Startup option enabled often encounter issues when installing updates, so disabling it this time might help.
Summary
The June 2020 Update is a real headache for most Windows 10/11 users, that is why even Microsoft is discouraging those who are affected by the issues from downloading and installing this update. If you’re getting the C:\WINDOWS\system32\lsass.exe failed in Windows 10/11 and the above tricks won’t work, then you can only wait for Microsoft to release the patch in the coming weeks.
Give us some love and rate our post!
Генерация программного кода стала одной из сфер, где ИИ уже внедрен достаточно широко, — по некоторым оценкам, за минувший год около 40% нового кода было написано ИИ. CTO Microsoft считает, что через пять лет эта цифра достигнет 95%. Этот код еще предстоит научиться правильно сопровождать и защищать.
Безопасность ИИ-кода эксперты пока оценивают как невысокую, в нем систематически встречаются все классические программные дефекты: уязвимости (SQL-инъекции, вшитые в код токены и секреты, небезопасная десериализация, XSS), логические дефекты, использование устаревших API, небезопасные алгоритмы шифрования и хеширования, отсутствие обработки ошибок и некорректного пользовательского ввода и многое другое. Но использование ИИ-ассистента в разработке ПО добавляет еще одну неожиданную проблему — галлюцинации. В новом исследовании авторы подробно изучили, как на ИИ-код влияют галлюцинации больших языковых моделей. Оказалось, что некоторых сторонних библиотек, которые ИИ пытается использовать в своем коде, просто не существует в природе.
Вымышленные зависимости в open source и коммерческих LLM
Для изучения фантомных библиотек исследователи сгенерировали 576 тысяч фрагментов кода на Python и JavaScript с помощью 16 популярных LLM.
Модели выдумывали зависимости с разной частотой: реже всего галлюцинировали GPT4 и GPT4 Turbo (вымышленные библиотеки встретились менее чем в 5% образцов кода), у моделей DeepSeek этот показатель уже превышает 15%, а сильнее всего ошибается Code Llama 7B (более 25% фрагментов кода ссылаются на несуществующие библиотеки). При этом параметры генерации, которые снижают вероятность проникновения случайных токенов в выдачу модели (температура, top-p, top-k), все равно не могут снизить частоту галлюцинаций до незначительных величин.
Код на Python содержал меньше вымышленных зависимостей (16%) по сравнению с кодом на JavaScript (21%). Результат также зависит от того, насколько стара тема разработки. Если при генерации пытаться использовать пакеты, технологии и алгоритмы, ставшие популярными за последний год, несуществующих пакетов становится на 10% больше.
Самая опасная особенность вымышленных пакетов — их имена не случайны, а нейросети ссылаются на одни и те же библиотеки снова и снова. На втором этапе эксперимента авторы отобрали 500 запросов, которые ранее спровоцировали галлюцинации, и повторили каждый из них 10 раз. Оказалось, что 43% вымышленных пакетов снова возникают при каждой генерации кода.
Интересна и природа имен вымышленных пакетов. 13% были типичными «опечатками», отличающимися от настоящего имени пакета всего на один символ, 9% имен пакетов были заимствованы из другого языка разработки (код на Python, пакеты из npm), еще 38% были логично названы, но отличались от настоящих пакетов более значительно.
View the full article
Что такое LSASS на Windows
Сервис проверки подлинности локальной системы безопасности (Local Security Authority Server Service, LSASS) — это процесс, который управляет политикой безопасности компьютера. LSASS проверяет логины, изменения паролей, токены доступа и административные привилегии у пользователей системы или сервера.
LSASS можно сравнить с охранником, который проверяет документы на входе в ночной клуб. Без него в заведение смог бы попасть любой человек с поддельными документами.
LSASS выполняется как процесс под названием lsass.exe. При запуске lsass.exe хранит в памяти такие аутентификационные данные, как зашифрованные пароли, НТ-хэши, LM-хэши и билеты Kerberos. Благодаря этому пользователи могут работать с файлами во время активных сеансов Windows, не вводя учетные данные каждый раз, когда нужно выполнить какую-либо задачу.
При краже учетных данных злоумышленники удаляют, перемещают, редактируют или заменяют настоящий файл lsass.exe. Для этого обычно используются такие инструменты, как Mimikatz, Crackmapexec и Lsassy.
Как происходит кража учетных данных через LSASS
Для этого злоумышленники обычно получают удаленный доступ к компьютеру жертвы — это можно сделать несколькими способами.
Во-первых, хакеру нужно получить права администратора, чтобы изменять LSASS. Так он сможет установить вредоносное ПО, чтобы скопировать данные процесса LSASS, скачать эту копию и локально извлечь из нее учетные данные.
Читайте по теме:
11 параметров безопасности в Windows 11, о которых следует знать
Однако, поскольку антивирус Microsoft Defender обнаруживает и удаляет вредоносное ПО все эффективнее, хакеры все чаще применяют тактику Living off the Land, при которой атаки совершаются через предустановленные программы.
Признаки кражи учетных данных
Эти пять способов помогут выяснить, не стали ли вы жертвой хакерской атаки.
Lsass.exe использует много аппаратных ресурсов
Откройте «Диспетчер задач» и проверьте, сколько CPU и памяти использует этот процесс. В обычных условиях он потребляет 0% CPU и около 5 МБ памяти. Стоит насторожиться, если он сильно нагружает CPU и задействует более 10 МБ, а вы за последнее время не выполняли никаких действий, связанных с безопасностью, например не меняли данные для входа.
В таком случае завершите процесс через «Диспетчер задач». Затем откройте местоположение файла и удалите его. В отличие от поддельного, реальный процесс отобразит ошибку. Помимо этого, стоит заглянуть в «Историю файлов» и проверить, не сохранила ли Windows резервную копию процесса.
В названии процесса есть ошибки
Хакеры часто переименовывают взломанные процессы так, чтобы они выглядели как настоящие. В таком случае злоумышленник может использовать заглавную «i», чтобы имитировать «L» в аббревиатуре LSASS. Обнаружить такое название можно с помощью конвертера регистров.
В названии также могут присутствовать лишние «a» и «s». Если вы встретили подобный файл, то удалите его (а также его резервные копии из «Истории файлов»).
Lsass.exe находится в другой папке
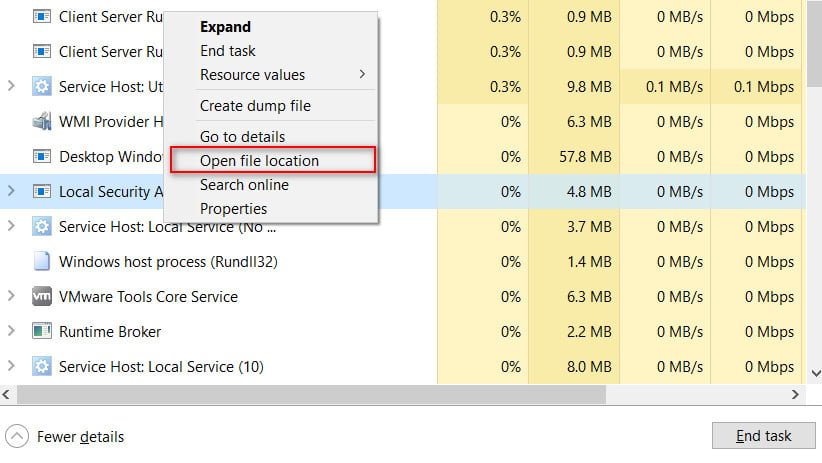
Снова откройте «Диспетчер задач», пролистайте до «Процессы Windows» и найдите Local Security Authority Process. Затем нажмите на него правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Открыть расположение файла».
Настоящий файл lsass.exe находится в папке C:\Windows\System32. Если он расположен в любом другом месте, то это, скорее всего, вредоносное ПО, и его стоит удалить.
В «Диспетчере задач» есть более одного процесса Lsass
В «Диспетчере задач» должен отображаться лишь один Local Security Authority Process. При открытии выпадающего меню, расположенного слева от названия процесса, появляется список активных служб — это тоже нормально.
Однако если вы обнаружили несколько процессов LSASS, а также более одного lsass.exe при открытии расположения файла, то велика вероятность, что ваш компьютер подвергся атаке хакеров. Попробуйте удалить эти файлы — если это настоящий lsass.exe, появится ошибка.
Файл Lsass.exe весит слишком много
Объем файлов lsass.exe небольшой: примерно 83 КБ на компьютере на базе Windows 11 и 60 КБ — на Windows 10. Конечно, хакеры понимают, что большой lsass.exe сразу привлечет внимание владельца устройства, поэтому обычно стараются этого избегать. Тем не менее, если учесть приведенные выше сигналы, вредоносное ПО все равно удастся обнаружить.
Способы предотвратить кражу учетных данных через LSASS
Безопасность на компьютерах Windows постепенно улучшается, но кража учетных данных остается серьезной угрозой. Особенно это актуально для старых устройств, работающих на устаревших операционных системах, и новых, не получающих обновления ПО.
Ниже представлены три простых способа избежать этой угрозы.
Установите последние обновления системы безопасности
Такие обновления исправляют уязвимости, которые злоумышленники могут использовать для атаки на компьютер. Поддержание устройств в актуальном состоянии снижает риск взлома. Для этого подключите автоматическую загрузку и установку обновлений для Windows, а также сторонних программ, установленных на ПК.
Используйте Credential Guard в Защитнике Windows
Credential Guard или Диспетчер учетных данных — это механизм безопасности, создающий изолированный процесс LSASS (LSAIso), который безопасно хранит все учетные данные и взаимодействует с основным LSASS для проверки пользователей. Этот механизм защищает целостность личной информации и предотвращает ее кражу.
Credential Guard доступен на корпоративной и профессиональной версиях Windows 10 и 11, а также на некоторых версиях серверных ОС Windows Server. Устройства также должны соответствовать строгим требования, таким как наличие протокола Secure Boot и поддержка 64-разрядной виртуализации. Эта функция не активирована по умолчанию — ее нужно устанавливать вручную.
Отключите удаленный доступ к рабочему столу
С помощью удаленного доступа вы и другие авторизованные пользователи можете использовать компьютер, находясь в другом физическом месте. Эта функция позволяет вам переносить файлы с рабочего на домашнее устройство, а сотрудникам техподдержки — удаленно устранять неполадки. Это удобно, но делает компьютер уязвимым для хакерских атак.
Чтобы отключить удаленный доступ, нажмите клавишу «Пуск» и введите в поисковую строку «удаленный доступ». Выберите «Разрешить удаленные подключения к этому компьютеру» и уберите галочку у пункта «Разрешить подключение удаленного помощника к этому компьютеру».
Помимо этого, можно удалить ПО для удаленного доступа, такое как TeamViewer, AeroAdmin и AnyDesk. Эти программы повышают риски, в том числе, атак в стиле Living off the Land.
Источник.
Фото на обложке: Unsplash
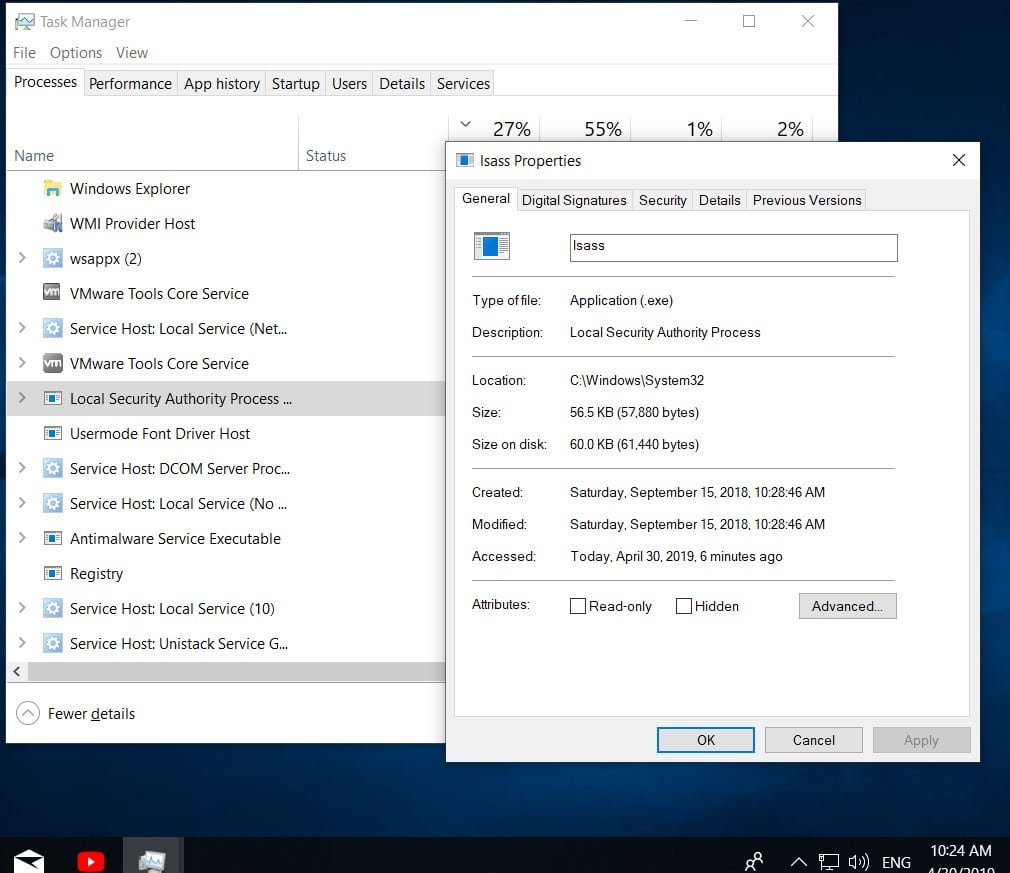
You may have seen a service in the Task Manager in the Local Security Authority Process, with properties named lsass.exe. This is an important executable file in Windows 10 that handles many operations performed under the Windows operating system (OS) and serves for system security. Sometimes you may misinterpret this as a virus due to the .exe extension. Let’s look at the details associated with lsass.exe and its working principle.
Lsass.exe means the local security subsystem service, where .exe indicates that it is an executable file. It works as a component of the Windows 10 security policy, such as checking the user on the server, changing the password, and authenticating the user during login or logout. lsass.exe is activated when winlogon.exe starts, and if the password is correct, it transmits permissions, or shows a message that the password does not match. The location of the Lsass.exe file is always the path C: \ Windows \ System32.
Is lsass.exe a virus?
No, lsass.exe is not a virus, it is an official file from Microsoft Corporation. You do not need to worry about any damage from this process if it is not damaged. Details lsass.exe following:
File description – Local Security Authority Process (Local Security Center).
The product name of the application is Microsoft Windows operating system.
Copyright – Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
The size is 56.6 KB.
English language.
The original file name is lsass.exe.

Related posts :
WINLOGON.EXE – WHAT IS THIS PROCESS IN WINDOWS 10/7
SIHOST.EXE IN WINDOWS 10 – WHAT IS IT AND HOW IT WORKS
How does lsass.exe work in Windows 10?
lsass.exe in Windows 10 is the main system file that participates in root. If your system reboots again, this is due to damage to the lsass.exe file or there may be a password error. The executable is known to work in four different ways in your computer.
File System Encryption (EFS) – This file helps in processing and storing the encrypted file on your desktop. Encryption is a means of encoding information so that only an authorized user can enter it. You can read more about EFS encryption.
CNG key isolation (keyiso) – Works as a data protection process for private keys and a cryptographic file. If the CNG key isolation does not work, the Extensible Authentication Protocol cannot be initialized.
Security Account Manager (SamSs) —It helps to reduce data crash when transferring a signal from one server to another.
Credential Manager – Software also works to control the Internet Protocol when it is connected to a network.
How to recognize lsass.exe virus or not?
Sometimes malware developers create a file with the same name for the purpose of cheating, but you can easily distinguish the original lsass.exe file from the questionable one. If the file with the name lsass.exe is not in the path C: \ Windows \ System32, then this is already a big doubt about its originality, and you should delete it. To check this, simply open the Task Manager and go to the “Processes” tab. Here you can view a list of all executable files. Find the Local Security Authority Process, right click on it, and then click Open File Location. You will be transferred to the C: \ Windows \ System32 directory, and you will see lsass.exe there. If you are transferred to another place, then most likely this is malware. A virus similar to the lsass.exe service can heavily load the processor.
Should I disable lsass.exe in Windows 10?
As mentioned above, lsass.exe is a Windows security management program; there is no need to deactivate this file. You simply can not delete this file in Windows 10, as this may cause damage to the system.
