Что такое Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop — это инструмент для работы с Docker-контейнерами на локальной машине. Он упрощает процесс разработки, тестирования и развертывания приложений, позволяя взаимодействовать с контейнерами как через консоль, так и через удобный интерфейс.
Ключевые особенности:
- понятный графический интерфейс,
- удобное управление образами и контейнерами,
- встроенные инструменты для мониторинга,
- возможность разработки и тестирования без привязки к серверу,
- поддержка работы с Docker Compose.
Если вы только начинаете изучение Docker и хотите разобраться в основах, рекомендуем ознакомиться с отдельным вводным обзором. В нем разобрали принципы работы Docker, его основные компоненты и решаемые задач. Из текста вы узнаете, как создать и запустить контейнер, а также какую роль играет Kubernetes в связке c Docker.
О системных требованиях
Перед установкой Docker Desktop важно выбрать подходящий бэкенд для работы с контейнерами: WSL 2 или Hyper-V. Оба имеют свои особенности, так что от выбора будут зависеть и системные требования. Далее в тексте разберемся, когда и какой бэкенд подойдет лучше.
Когда нужен WSL
WSL 2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux 2) — это усовершенствованная версия подсистемы Windows для Linux, которая использует виртуальную машину с реальным Linux-ядром. В отличие от первой версии, WSL 2 обеспечивает лучшую совместимость с Linux-инструментами, технологиями и приложениями, а также более высокую производительность.
Преимущества использования WSL 2 с Docker Desktop
Работа с Linux-контейнерами. Docker изначально разрабатывали для работы в Linux-среде, поэтому большинство контейнеров в Docker Hub — это образы, ориентированные на Linux. Использование WSL 2 предоставляет Docker Desktop полноценную Linux-среду на Windows.
Повышенная производительность. WSL 2 значительно ускоряет выполнение контейнеров, что особенно заметно в сравнении с WSL 1 или Hyper-V, о котором мы расскажем дальше. Это преимущество обеспечивает полноценное Linux-ядро, которое позволяет Docker работать гораздо быстрее и с меньшими накладными расходами.
Работа с файловой системой Linux. В WSL 2 можно монтировать файловую систему Linux, что позволяет работать с кодом и данными в нативной Linux-среде. Это особенно важно при разработке приложений, которые будут запускаться в Linux-контейнерах и требуют специфической настройки среды — например, прав доступа или структуры каталогов.
Когда нужен Hyper-V
Рассмотрим ключевые сценарии, в которых предпочтительнее использовать Hyper-V.
Если система не поддерживает WSL 2
Некоторые сборки системы не позволяют включать необходимые компонентов для работы WSL 2 В частности, это касается старых версий Windows, а также устройств, которые не поддерживают Windows 10 Pro или 11 Pro, — WSL 2 для них недоступна, так как требует включенной виртуализации на уровне системы. В таких случаях можно использовать Hyper-V для виртуализации контейнеров и запуска Docker Desktop.
Для работы с Windows-контейнерами
Docker Desktop поддерживает как Linux-, так и Windows-контейнеры. Однако последние требуют прямого взаимодействия с ядром Windows, а WSL 2 предоставляет только Linux-среду. Hyper-V позволяет запускать Windows-контейнеры благодаря виртуализации Windows-системы.
Для изоляции и обеспечения безопасности
Hyper-V создает полноценные виртуальные машины, обеспечивая строгую изоляцию контейнеров друг от друга и от хост-системы. Это может быть важно в корпоративной среде или при работе с чувствительными данными.
Разница между WSL 2 и Hyper-V
Если вам нужны Linux-контейнеры и высокая производительность — выбирайте WSL 2. Если же требуется строгая изоляция или работа с Windows-контейнерами, Hyper-V будет предпочтительнее. Подробнее о разнице по ключевым критериям — в таблице:
| Критерий | WSL 2 | Hyper-V |
| Производительность | Высокая (нативное Linux-ядро) | Низкая (работа через полноценную ВМ) |
| Изоляция | Относительно низкая | Высокая (контейнеры изолированы) |
| Типы контейнеров | Только Linux-контейнеры | Linux- и Windows-контейнеры |
Системные требования Docker Desktop
При использовании WSL 2 в качестве бэкенда
- WSL версии 1.1.3.0 или новее.
- Windows 11 64-bit Home / Pro / Enterprise / Education, версия 22H2 или новее.
- Windows 10 64-bit Home / Pro / Enterprise / Education, версия 22H2 (сборка 19045) или новее.
- Включенная функция WSL 2 в Windows. Подробная инструкция есть в документации Microsoft;
- 4 ГБ ОЗУ.
- Включенная аппаратная виртуализация в BIOS на вашей локальной машине.
При использовании Hyper-V в качестве бэкенда
- Windows 11 64-разрядная Enterprise / Pro / Education, версия 22H2 или новее.
- Windows 10 64-разрядная Enterprise / Pro / Education, версия 22H2 (сборка 19045) или новее.
- Включенная функция Hyper-V. Подробнее об установке — в документации Microsoft;
- 4 ГБ ОЗУ.
- Включенная аппаратная виртуализация в BIOS на вашей локальной машине.
Установка WSL 2
1. Откройте PowerShell от имени администратора и введите команду wsl —install. Она выполняет следующие действия:
- включает дополнительные компоненты WSL и платформы виртуальных машин;
- скачивает и устанавливает последнюю версию ядра Linux;
- задает WSL 2 в качестве среды по умолчанию;
- скачивает и устанавливает дистрибутив Ubuntu Linux.
2. После успешной установки всех компонентов перезапустите компьютер.
Первичная настройка
1. Откройте установленный дистрибутив с помощью меню Пуск — найдите установленный дистрибутив (Ubuntu).
2. При первом запуске системы нужно создать имя пользователя и пароль для дистрибутива Linux.
3. Первичная настройка завершена, можно приступать к использованию WSL 2.
Альтернативный вариант — запустить WSL через PowerShell. Для этого введите команду wsl и система предложит произвести первичную настройку.
Установка Hyper-V
Для установки компонентов Hyper-V откройте PowerShell от имени администратора и выполните команду:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All
Она установит все компоненты для работы Hyper-V, после чего нужно будет перезапустить компьютер.
Проверить корректность установки Hyper-V можно с помощью команды:
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName *hyper*|ft
Установка Docker с бэкендом WSL 2
- Скачайте дистрибутив Docker Desktop с официального сайта и запустите установщик. Галочки оставьте на всех пунктах.
- После установки перезайдите в учетную запись и откройте ярлык Docker Desktop.
- Если все прошло успешно, вы увидите интерфейс инструмента:
Установка Docker с бэкендом Hyper-V
1. Скачайте дистрибутив Docker Desktop с официального сайта и запустите установщик. В инсталляционном окне уберите галочку Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V.
2. После установки перезайдите в учетную запись и откройте ярлык Docker Desktop.
3. Если установка выполнена корректно, программа запустится без ошибок и вы увидите интерфейс:
Запуск контейнера
Рассмотрим запуск первого контейнера на примере самого популярного образа — hello-world.
Поиск и скачивание образа
Поскольку вы только установили Docker Desktop, в системе нет образов контейнеров, которые можно запустить. Исправим это.
- Перейдите в раздел Images и нажмите кнопку Search images to run.
- Введите hello-world. В текущем окне на выбор есть две кнопки: Pull и Run. Если планируете для начала просто скачать образ, то выбирайте Pull. Если скачать и сразу запустить — Run.
- Оставляем стандартные настройки для запуска.
Проверка работы контейнера
Чтобы посмотреть запущенные контейнеры, перейдите во вкладку Containers и выберите созданный на прошлом этапе. В нашем примере для него было автоматически сгенерировано имя determined_jennings. Открыв контейнер, вы увидите сообщение, если настройка установка прошла успешно.
Как настроить запуск Docker при старте Windows
Для автозапуска Docker Desktop при авторизации на компьютере достаточно поставить галочку в настройках: Settings → General → Start Docker Desktop when you sign in to your computer.
После этого Docker Desktop будет запускаться автоматически при включении устройства.
Запуск Docker в облаке
Docker Desktop — удобный инструмент для локальной работы, но в ряде случаев может потребоваться облачная инфраструктура:
- если мощности вашего ПК не хватает для работы с контейнерами;
- если нужна среда для тестирования без нагрузки на локальную машину;
- если вы работаете с ML/AI и нужны видеокарты для обучения моделей.
1. В панели управления в верхнем меню перейдем в раздел Продукты → Облачные серверы.
2. Нажмем кнопку Создать сервер.
3. Выберем имя, регион и сегмент пула. Важно учесть, что от сегмента зависят доступные конфигурации и стоимость. После создания сервера менять сегмент пула нельзя.
4. В качестве источника выберите готовый образ, приложение, свой образ, сетевой диск или снапшот. В нашем случае — приложение Containers Ready с настроенной Ubuntu 22.04. Оно содержит:
- Docker версии 27.0.3;
- плагины для запуска Docker Compose версии 2.11.1;
- Portainer версии 2.20.3 — графический интерфейс для мониторинга и управления Docker-контейнерами, образами и сетью Docker.
5. Конфигурацию для примера возьмем базовую — 2 vCPU и 2 ГБ RAM, а в поле Диски выберем SSD Быстрый на 20 ГБ. Важно: это минимальные требования. Рекомендуем выбирать параметры серверы, исходя из ваших задач.
Помимо прочего, на этапе создания сервера или позже вы можете добавить GPU. При этом объем ОЗУ, который выделяется серверу, может быть меньше указанного в конфигурации — ядро ОС резервирует ее часть. Выделенный объем на сервере можно посмотреть с помощью команды sudo dmesg | grep Memory.
6. Для работы Containers Ready сервер должен быть доступен из интернета. Для этого создадим приватную подсеть и подключим публичный IP-адрес. В поле Сеть выберем Приватная подсеть и добавим новый публичный адрес. Подробнее о настройке подсети можно узнать в документации.
6. Добавьте SSH-ключ в поле Доступ. Подробнее о его генерации можно узнать в отдельной инструкции.
7. Ознакомьтесь с ценой и нажмите кнопку Создать сервер.
Сервер готов к использованию! Подробности о создании сервера с Сontainers Ready вы можете найти в документации. Если вам нужно запускать контейнеры с ML-моделями на мощных видеокартах, развернуть облачные серверы с GPU можно за несколько минут. Они помогут ускорить обучение нейросетей без закупки дорогого оборудования.
Читайте другие тексты о Docker
Данная публикация является разбором особенностей контейнерной виртуализации Docker под системой Windows.
Она не претендует на роль исчерпывающей и по мере необходимости будет обновляться и дополняться.
За практическим руководством с нуля советую обратиться к этой публикации.
Содержание
- Предварительные настройки
- Выбор между Docker Toolbox on Windows или Docker for Windows
- Windows контейнеры и Linux контейнеры
- Особенности монтирования папок
- Монтирование с хост-машины или volume
- Особенности разметки диска GPT и MBR
- Docker Toobox to Windows
- Docker Swarm
- Проблемы с кодировкой
- Полезные ссылки
- Заключение
Предварительные настройки
Контейнерная виртуализация или виртуализация на уровне операционной системы Docker нативно работает только на дистрибутивах Linux и FreeBSD (экспериментально).
На Windows вам понадобится гостевая Linux система либо специальная минималистичная виртуальная машина с ядром Linux от разработчиков Docker, которая и ставится из коробки.
Само собой разумеется, что вы включили виртуализацию у себя в BIOS/UEFI
Пункт настройки может называться по-разному: VT-x, VT-d, Intel VT, AMD-V, Virtualization Technology.
Еще одним минимальным системным требованием будет разрядность системы x64 и версия не ниже Windows 7 Pro.
Выбор между Docker Toolbox on Windows или Docker for Windows
Появление Docker Toolbox on Windows и Docker Toolbox on Mac было большим событием.
Сборка включается в себя сам docker, утилиту docker-compose, утилиту для работы с виртуальной машиной docker-machine и клиент Kitematic.
Используется виртуальная машина (по умолчанию на VirtualBox) с минималистичным Linux окружением.
Позже для новых операционных систем выпустили Docker for Windows и Docker for Mac, которая на текущий момент является актуальной версией и продолжает развиваться.
Выбор между версиями не сложный:
— Если у вас Windows 10 x64 Pro, Enterprise или Education то включаем службу Hyper-V и ставим Docker for Windows.
Заметьте, что после включения службы Hyper-V пропадет возможность запускать и создавать x64 виртуальные машины на VirtualBox.
— Если же у вас другая версия Windows(7 Pro, 8, 8.1, 10 Home) то ставим VirtualBox и Docker Toolbox on Windows.
Несмотря на то, что Docker Toolbox разработчиками признан устаревшим работа с ним слабо отличается от Docker for Windows.
Вместе с установкой Docker Toolbox будет создана виртуальная машина.
В самом VirtualBox можно будет добавить оперативной памяти и ядер процессора на ваше усмотрение.
Windows контейнеры и Linux контейнеры
Docker for Windows предоставляет возможность переключать контейнеризацию между Linux и Windows версией.
В режиме Windows контейнеризации вы можете запускать только Windows приложения.
Замечу, что на май 2018 года в официальном Docker Hub существует всего 13 образов для Windows.
После включения Windows контейнеризации не забудьте добавить внешнюю сеть.
В конфигурационном файле docker-compose.yml это выглядит так:
networks:
default:
external:
name: nat
Особенности монтирования папок
На примонтированных volume-ах не кидаются события файловой системы, поэтому inotify-tools не работает.
Спасибо пользователю eee
Если вы разрабатываете свой проект и пользуетесь docker-compose вне домашней папки то вам нужно будет проделать некоторые манипуляции.
Используя Docker for Windows для монтирования нового диска у вашего локального пользователя обязательно должен стоять пароль, который будет использоваться для доступа к shared папки.
Особенность заключается в том, что монтируемые внутрь контейнера диск будет монтироваться как от удаленной машины //10.0.75.1/DISK_DRIVE по протоколу SMB.
Для Docker Toolbox диски монтируются в самом VirtualBox на вкладке «Общие папки»
Пример для диска «D»:

Права доступа к монтируемым файлам и папкам
Как бы вам не хотелось, но для всех примонтированных из хост-машины файлов и папок будут стоять права 755 (rwx r-x r-x) и поменять их вы не сможете.
Остро встает вопрос при монтировании внутрь файла закрытого SSH ключа, права на который должны быть только у владельца(например 600).
В данном случае либо генерируют ключ при создании образа, либо прокидывают сокет ssh-agent с хост-машины.
Монтирование с хост-машины или volume
Монтирование внутрь контейнера происходит с использованием сети и протокола SMB, следовательно, внутри контейнера диск «D:\» будет примонтирован из источника //10.0.75.1/D
Использование volume внутри контейнера отображается как монтирование локального диска /dev/sda1, что влияет на скорость работы.
Простым тестом копирование файла на обычном HDD скорость работы получилась следующая:
Такая разница в скорости скорее всего связана с тем, что в volume данные сбрасываются на диск постепенно, задействуя кеш в ОЗУ.
Особенности разметки диска GPT и MBR
Данный пункт не является истинной так как опровергающей или подтверждающей информации в интернете найти не смог.
Если на хост-машине таблица разделов MBR, то контейнер с MySQL/MariaDB может упасть с ошибкой:
InnoDB: File ./ib_logfile101: ‘aio write’ returned OS error 122. Cannot continue operation
По умолчанию в базе данных включеён параметр innodb_use_native_aio, отвечающий за асинхронный ввод/вывод и его надо будет выключить.
Данная проблема также встречается на некоторых версиях MacOS.
Docker Toobox to Windows
Главное правило: начинать работу с запуска ярлыка на рабочем столе «Docker Quickstart Terminal», это решает 80% проблем.
— Бывает возникают проблемы с отсутствия переменных окружения, решается командой:
eval $(docker-machine env default)
— Если все же возникают проблемы из разряда «docker: error during connect», необходимо выполнить:
docker-machine env --shell cmd default
@FOR /f "tokens=*" %i IN ('docker-machine env --shell cmd default') DO @%i
Название Docker Machine по умолчанию default.
Docker Swarm
Ни в Docker for Mac, ни в Docker for Windows — нет возможности использовать запущенные демоны в качестве клиентов кластера (swarm members).
Спасибо пользователю stychos
Проблемы с кодировкой
Используя Docker Toolbox(на Docker for Windows не удалось воспроизвести) нашлась проблема с тем, что русские комментарии в docker-compose.yml файле приводили к ошибке:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "docker-compose", line 6, in <module>
File "compose\cli\main.py", line 71, in main
File "compose\cli\main.py", line 124, in perform_command
File "compose\cli\command.py", line 41, in project_from_options
File "compose\cli\command.py", line 109, in get_project
File "compose\config\config.py", line 283, in find
File "compose\config\config.py", line 283, in <listcomp>
File "compose\config\config.py", line 183, in from_filename
File "compose\config\config.py", line 1434, in load_yaml
File "site-packages\yaml\__init__.py", line 94, in safe_load
File "site-packages\yaml\__init__.py", line 70, in load
File "site-packages\yaml\loader.py", line 24, in __init__
File "site-packages\yaml\reader.py", line 85, in __init__
File "site-packages\yaml\reader.py", line 124, in determine_encoding
File "site-packages\yaml\reader.py", line 178, in update_raw
File "c:\projects\compose\venv\lib\encodings\cp1251.py", line 23, in decode
UnicodeDecodeError: 'charmap' codec can't decode byte 0x98 in position 1702: character maps to <undefined>
[4176] Failed to execute script docker-compose
Полезные ссылки
Docker Toolbox on Windows
Docker for Windows
Практическое руководство по Docker
Заключение
Особенности работы с Docker контейнеризацией на системе Windows не отличается от работы на Linux за исключение разобранных выше.
В статье я умышленно не упомянул заметно низкую скорость работы контейнеров и overhead используя систему Windows как само собой разумеющееся.
Буду рад услышать ваши отзывы. Не стесняйтесь предлагать улучшения или указывать на мои ошибки.
Только зарегистрированные пользователи могут участвовать в опросе. Войдите, пожалуйста.
Какой версией Docker вы пользуетесь?
32% Docker Toolbox on Windows88
68% Docker for Windows187
Проголосовали 275 пользователей. Воздержались 196 пользователей.
Docker is a powerful platform that allows you to develop, ship, and run applications inside lightweight containers. Install Docker on Windows to create consistent development environments, streamline deployment processes, and enhance system efficiency.
This guide will provide step-by-step instructions for installing Docker on Windows using the GUI or the command line.

Prerequisites
- A machine running Windows 10 22H2 or Windows 11.
- At least 4GB of RAM.
- A user account with administrator privileges.
- WSL 2 enabled.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows via GUI
Installing Docker via a GUI is simple, with a full desktop app, and it is great for beginners and GUI users. It involves downloading the Docker Desktop Installer from the official website and installing the program through a wizard.
Follow the steps in the sections below.
Step 1: Download Docker Desktop Installer
Download the Docker Desktop Installer for Windows x86/x64 from the official Docker website.
Note: A paid subscription is required if you plan to use Docker Desktop in large enterprises with over 250 employees or if your annual revenue exceeds $10 million USD. Docker is free for personal use, small businesses, and education. Refer to the official page for pricing details.
Step 2: Install Docker Desktop
The steps below will guide you through the installation process:
1. Find and double-click the downloaded installer to start the installation.
2. The installer initializes, and the configuration screen appears, allowing you to customize your setup.
Keeping the default options checked is recommended, as WSL 2 offers faster performance, better integration with the Windows filesystem, and uses fewer system resources compared to Hyper-V.
Uncheck the box to use Hyper-V instead if you need to run traditional Windows-based virtual machines or if you require stricter isolation and security controls than WSL’s.
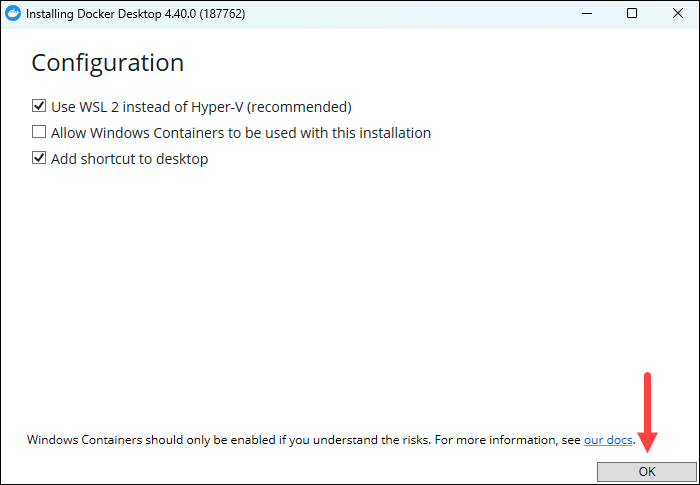
Click OK to start the installation.
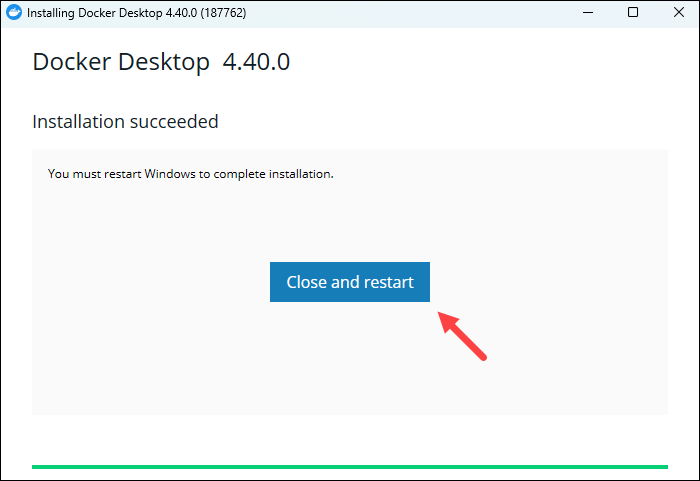
3. When the process completes, click the Close and restart button to close the installer and reboot Windows for the changes to take effect:
Step 3: Start Docker Desktop
After installation, start the Docker tool manually:
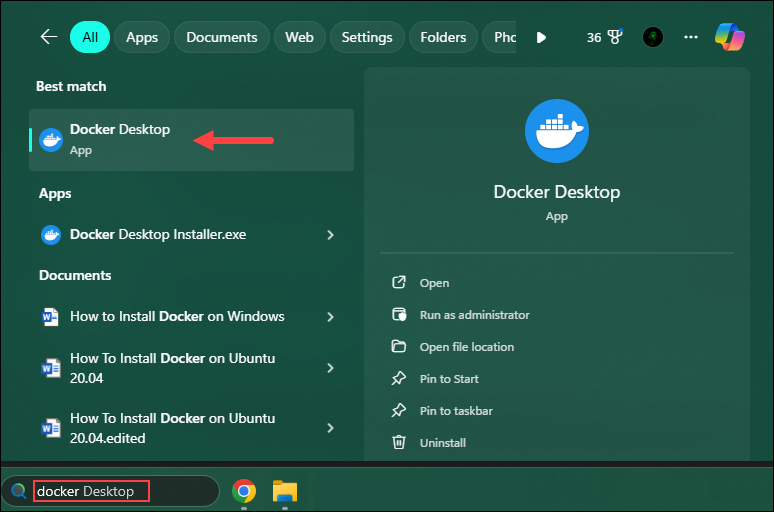
1. Press the Windows button and type Docker desktop to find the app.
2. Open the Docker Desktop app from the search results.
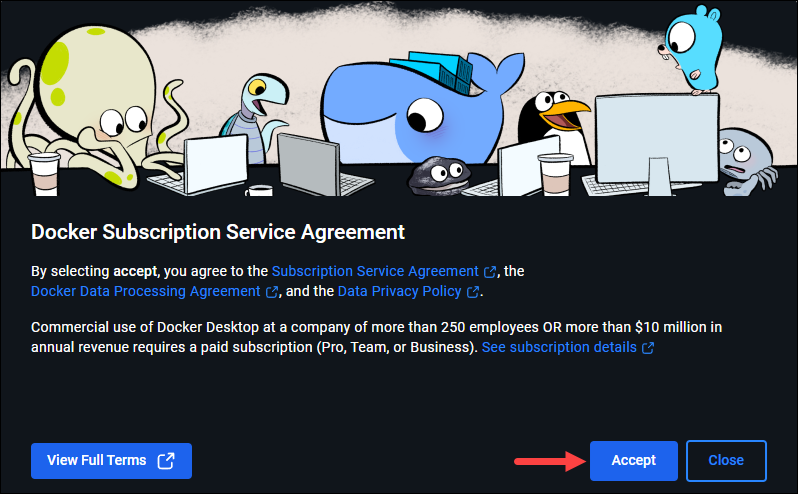
3. The app requires you to accept the Docker Subscription Service Agreement first. If you agree with the terms, click Accept to proceed.
4. The app presents a Welcome survey. The survey is optional, and you can click Skip in the top right corner to move on to the sign-in step.
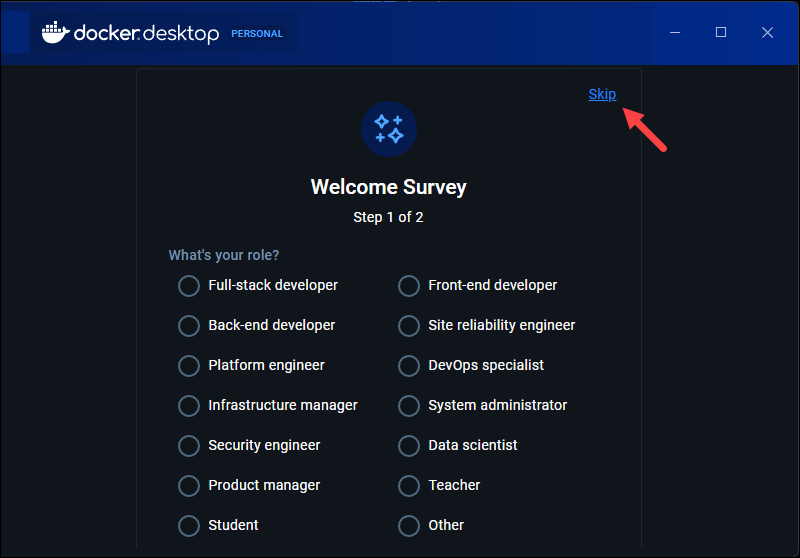
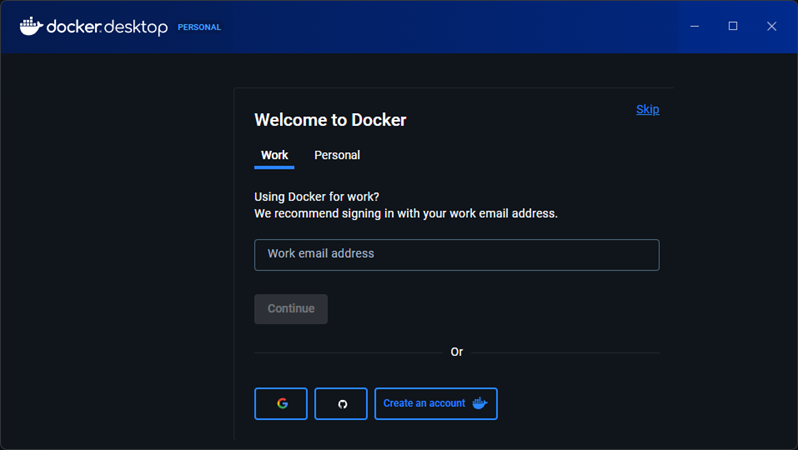
5. The Welcome to Docker screen appears, where you can sign in to Docker if you already have an account or create a new account. Complete the sign-in process to finish the installation.
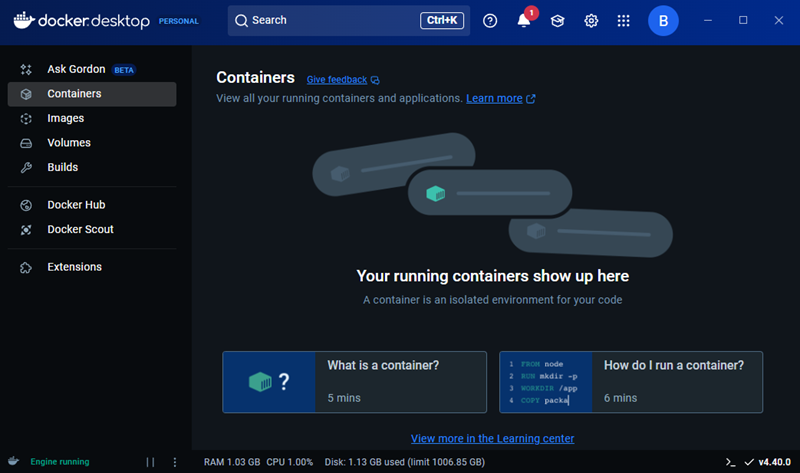
6. After signing in, the Docker Desktop dashboard opens, which means Docker Desktop is successfully running on Windows.
Install Docker Desktop via CLI
This method shows a terminal-based, manual setup that installs Docker in a Linux environment inside Windows, without using the GUI installer. The installation is silent, via PowerShell, and it is ideal for sysadmins or DevOps users who want automation or script-based installs.
Note that Docker still runs on Windows through the Docker Desktop app (with GUI components), even if it is installed and started via the terminal.
Step 1: Download the Installer
Download the Docker Desktop Installer and save it in an easily accessible location. Remember the path as you will need it in the following step.
Step 2: Install Docker
After you download the installer, there are two ways to install Docker Desktop, depending on which command line option you want to use:
Windows PowerShell
1. Open PowerShell as an administrator and use the cd command to navigate to the folder in which you downloaded the installer.
2. Run the command below to install Docker Desktop:
Start-Process 'Docker Desktop Installer.exe' -Wait --quiet install3. If prompted, click OK to complete the installation.
Command Prompt
1. Open Windows Command Prompt as an administrator and navigate to the installer location.
2. Run the command below to start the installation:
start /w "" "Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install3. When prompted, click OK to finish the installation.
The default installation location for Docker Desktop is C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker.
Step 3: Add User Account
If your admin account and user account are not the same, use the syntax below to add user accounts to Docker user groups:
net localgroup docker-users [user] /addReplace [user] with the respective username.
Step 4: Start Docker Desktop
Open the Docker Desktop app and sign in to your account to enable the Docker engine. Follow the steps outlined in Step 3: Start Docker Desktop section above, and when you finish, you can start using Docker.
Step 5: Verify Docker Installation
To verify that Docker installed correctly, pull a sample image. In PowerShell or the Command Prompt, run the command below:
docker pull nginx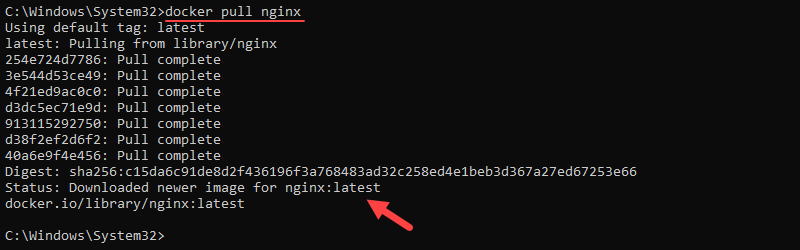
If the image pulls successfully, Docker Desktop has been installed correctly.
Install Docker on Windows via Command Line
This method shows how to bypass Docker Desktop completely and install the Docker Engine inside a Linux environment (Ubuntu on WSL). Installing Docker inside a Linux environment is closer to how Docker works natively on Linux systems. It is ideal for developers who want a lightweight, GUI-free, native-Linux experience or dislike Docker Desktop’s licensing or resource overhead.
Follow the steps in the sections below.
Step 1: Enable WSL
If you do not have WSL enabled, you must first install it. Open PowerShell or Windows Command Prompt as an administrator and run the following command:
wsl --installThe command enables the required features for running WSL and installs the default Linux distro (Ubuntu).
If you want a specific Linux distribution, you can specify it using the -d flag. In this tutorial, we will use Ubuntu 24.04:
wsl --install -d Ubuntu-24.04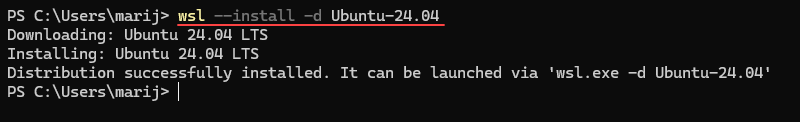
Step 2: Initialize Distro and Create User
After the installation, it is time to set up the Linux distribution.
1. Press the Windows button and type Ubuntu to find the distribution. Press Enter to initialize it.
2. After the instance initializes, it prompts you to create a new default user account. Provide the username and password to start using Ubuntu within WSL.
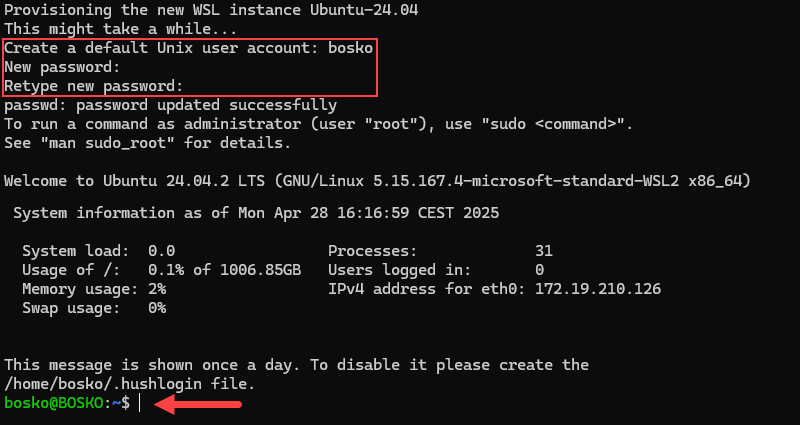
Step 3: Install Docker
After initialization, the system is ready for Docker installation. Follow the steps below:
1. Update the system package index with:
sudo apt update2. Install the dependencies:
sudo apt install ca-certificates curl3. Set the permissions for the /etc/apt/keyrings directory that will hold the GPG key:
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings4. Download the GPG key:
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc5. Change the key permissions:
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc6. Add the Docker repository to apt sources:
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo "${UBUNTU_CODENAME:-$VERSION_CODENAME}") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null7. Refresh the package index one more time to pull information from the Docker repository:
sudo apt update8. Install Docker and all required packages:
sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin docker-buildx-pluginWait for the installation to complete. For more detailed instructions on enabling non-root access and a QuickStart guide on using Docker in Ubuntu, refer to our tutorial for installing Docker on Ubuntu.
If you have installed a different distribution on WSL, refer to our guides for installing Docker on Raspberry Pi, Rocky Linux and CentOS, or Debian.
9. After you set up and customize the installation to your needs, verify the installation with:
docker --versionThe output should print the Docker version if the installation completed successfully:

Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to install Docker on Windows using the GUI or the CLI. Installing Docker on Windows allows users to benefit from streamlined development processes, reliable application deployment, and greater operational efficiency.
Next, learn how to check and reduce Docker image size or set up and use a private Docker registry. If you already use Docker, download our handy Docker commands cheat sheet.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
Last Updated :
14 Apr, 2022
In this article, we are going to see how to install Docker on Windows.
On windows if you are not using operating system Windows 10 Pro then you will have to install our docker toolbox and here docker will be running inside a virtual machine and then we will interact with docker with a docker client
To understand this let us look at the left side of the below image where you can see on Linux operating system docker is installed directly on the operating system but if you look at the right side on Windows operating system docker is installed inside a Linux virtual machine and we use a docker client to interact with docker.
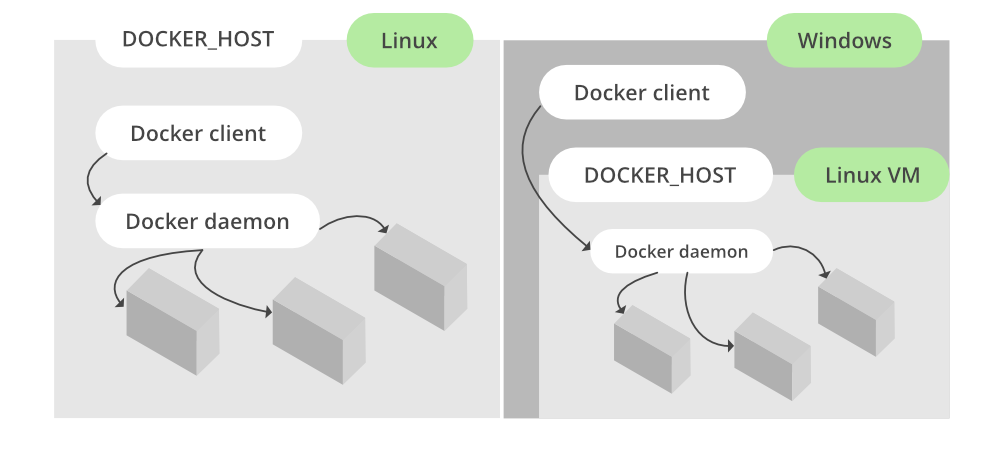
Prerequisites:
- Windows 7 or higher
- 64-bit Operating System
- Download and Install Linux kernel update package
Installation:
Follow the below steps to install Docker on Windows operating system:
Step 1: Visit this website and click on the «Docker Desktop for Windows» button.
Step 2: The installer will ask you to install WSL2, so click on the tick box next to it and click on ok. This will download and install WSL2 for you as shown below:
Step 3: Then we will need to restart our system, so click on «Close and restart» button in the Docker installer window.
After you restart the computer it will open up the Docker windows as shown below:
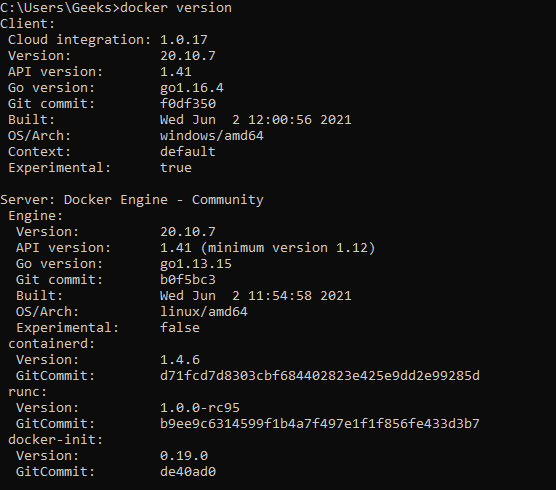
At this point we have successfully installed docker on our Windows operating system. We can verify this using the below command:
docker version
This will result in the following informations:
How to Use Docker on Windows: An Advanced Guide
Docker has revolutionized software development, making it faster and more efficient to build, ship, and run«RUN» refers to a command in various programming languages and operating systems to execute a specified program or script. It initiates processes, providing a controlled environment for task execution…. applications. Using Docker on Windows can streamline your development process, allowing for a consistent experience across different environments. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of using Docker on Windows, covering installation, configuration, advanced usage, and troubleshooting.
What is Docker?
Before we dive into the usage of Docker on Windows, it’s essential to understand what Docker is. Docker is an open-source platform that allows developers to automate the deployment of applications inside lightweight containers. These containers package the application with all its dependencies, ensuring that it runs consistently across various environments.
Why Use Docker on Windows?
Running Docker on Windows offers several advantages:
- Consistency: Containers ensure that the application behaves the same on all systems, eliminating the «works on my machine» syndrome.
- Isolation: Docker containers are isolated from one another and the host system, providing a clean environment for each application.
- Scalability: Containers can be easily scaled up or down to meet demand.
- Resource Efficiency: Docker containers share the host OS kernel, making them more lightweight compared to traditional virtual machines.
System Requirements
Before you install Docker on Windows, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
- Windows 10 64-bit: Pro, Enterprise, or Education versions are supported.
- Windows 11: Supported with the latest updates.
- Hyper-V: Enabled on your system. It is used to run containers on Windows.
- WSL 2: The Windows Subsystem for Linux version 2 is required for the latest Docker DesktopDocker Desktop is a comprehensive development environment for building, testing, and deploying containerized applications. It integrates Docker Engine, Docker CLI, and Kubernetes, enhancing workflow efficiency…. functionality.
Installing Docker on Windows
Step 1: Install Docker Desktop
-
Download Docker Desktop: Visit the official Docker website to download the latest version of Docker Desktop for Windows.
-
Run the Installer: After downloading, run the installer. You may need to grant administrative privileges.
-
Enable WSL 2: During installation, Docker will prompt you to enable WSL 2. Ensure you check this box if you haven’t set it up yet.
-
Complete Installation: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
-
Start Docker Desktop: Once installed, launch Docker Desktop from your Start menu. It may take a few moments to initialize.
Step 2: Verify Installation
After launching Docker Desktop, verify that it is running correctly:
- Open a command prompt or PowerShell window.
-
Run the following command:
docker --version
If installed correctly, you should see the version of Docker that you have installed.
Step 3: Configure Docker Desktop
-
Settings: Access Docker settings by right-clicking on the Docker icon in the system tray and selecting ‘Settings.’
-
Resources: You can adjust CPU, Memory, and Disk usage for your Docker containers under the ‘Resources’ tab. This is particularly useful for ensuring optimal performance, especially if you are running resource-intensive applications.
-
WSL Integration: Ensure that WSL integration is enabled for your preferred Linux distributions under the ‘Resources > WSL Integration’ tab.
-
Docker EngineDocker Engine is an open-source containerization technology that enables developers to build, deploy, and manage applications within lightweight, isolated environments called containers….: You can customize the Docker daemonA daemon is a background process in computing that runs autonomously, performing tasks without user intervention. It typically handles system or application-level functions, enhancing efficiency…. settings under the ‘Docker Engine’ tab. This is an advanced feature for users who wish to modify default configurations.
Using Docker on Windows
Now that you have Docker installed, let’s explore how to use it effectively.
Creating Your First Docker Container
To create a simple Docker containerContainers are lightweight, portable units that encapsulate software and its dependencies, enabling consistent execution across different environments. They leverage OS-level virtualization for efficiency…., follow these steps:
-
Pull an ImageAn image is a visual representation of an object or scene, typically composed of pixels in digital formats. It can convey information, evoke emotions, and facilitate communication across various media….: Docker images serve as the template for your containers. For example, to pull an official Nginx image, run:
docker pull nginx -
Run a Container: After pulling the image, you can run a container. Use the command below to run Nginx:
docker run -d -p 8080:80 nginxThe
-dflag runs the container in detached mode, and-p 8080:80maps portA PORT is a communication endpoint in a computer network, defined by a numerical identifier. It facilitates the routing of data to specific applications, enhancing system functionality and security…. 80 of the container to port 8080 of your host. -
Access the Application: Open a web browser and go to
http://localhost:8080. You should see the Nginx welcome page.
Managing Docker Containers
Once you start working with Docker, managing your containers becomes crucial. Here are some essential commands:
-
List Running Containers:
docker ps -
Stop a Container:
docker stop -
Start a Stopped Container:
docker start -
Remove a Container:
docker rm -
View Logs:
docker logs
Building Custom Docker Images
Creating your own Docker images can be a powerful feature. Here’s how to build a custom image:
-
Create a DockerfileA Dockerfile is a script containing a series of instructions to automate the creation of Docker images. It specifies the base image, application dependencies, and configuration, facilitating consistent deployment across environments….: A Dockerfile is a script containing a series of commands to assemble an image. Below is a simple example of a Dockerfile for a NodeNode, or Node.js, is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 engine, enabling server-side scripting. It allows developers to build scalable network applications using asynchronous, event-driven architecture…..js application:
# Use the official Node.js image FROM node:14 # Set the working directory WORKDIR /usr/src/app # Copy package.json and install dependencies COPY package*.json ./ RUN npm install # Copy the rest of the application code COPY . . # Expose the application port EXPOSE 3000 # Run the application CMD ["node", "app.js"] -
Build the Image: Navigate to the directory containing your Dockerfile and build the image using the following command:
docker build -t my-node-app . -
Run Your Custom Image: After building the image, run it like so:
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 my-node-app
Networking in Docker
Docker provides robust networking capabilities. By default, Docker runs containers in a bridge networkBridge Network facilitates interoperability between various blockchain ecosystems, enabling seamless asset transfers and communication. Its architecture enhances scalability and user accessibility across networks…., but you can create custom networks for more complex applications.
-
Create a NetworkA network, in computing, refers to a collection of interconnected devices that communicate and share resources. It enables data exchange, facilitates collaboration, and enhances operational efficiency….:
docker network createThe `docker network create` command enables users to establish custom networks for containerized applications. This facilitates efficient communication and isolation between containers, enhancing application performance and security.... my-network -
Run Containers on a Custom Network:
docker run -d --name app1 --network my-network my-node-app docker run -d --name app2 --network my-network nginx
This setup allows containers to communicate with each other using their names as hostnames.
Using Docker Compose
For managing multi-container Docker applications, Docker ComposeDocker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications using a YAML file. It simplifies deployment, configuration, and orchestration of services, enhancing development efficiency…. More is an invaluable tool. With Docker Compose, you define and run multi-container applications using a YAMLYAML (YAML Ain’t Markup Language) is a human-readable data serialization format commonly used for configuration files. It emphasizes simplicity and clarity, making it suitable for both developers and non-developers…. file.
Example: Running a Node.js and MongoDB Application
-
Create a
docker-compose.ymlFile:version: '3' services: app: build: . ports: - "3000:3000" depends_on: - mongo mongo: image: mongo ports: - "27017:27017" -
Build and Run the Application:
Navigate to the directory containing your
docker-compose.ymlfile and run:docker-compose up -d
This command will start both the Node.js application and MongoDB container in the background.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While Docker on Windows is generally stable, users may encounter issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Issue: Docker Daemon Not Running
If you receive an error indicating that the Docker daemon is not running:
- Ensure that Docker Desktop is running.
- Restart Docker Desktop from the system tray icon.
Issue: WSL 2 Issues
If you experience problems related to WSL 2:
- Verify that WSL 2 is installed correctly and that your distributions are set to use WSL 2.
-
You can check WSL version with:
wsl -l -v
Issue: Insufficient Resources
If containers are crashing due to resource constraints:
- Adjust CPU and memory limits in Docker Desktop settings.
- Ensure that no other resource-intensive applications are running concurrently.
Best Practices for Docker on Windows
-
Keep Docker Updated: Ensure that you regularly update Docker Desktop to take advantage of the latest features and fixes.
-
Use .dockerignore: Create a
.dockerignorefile to exclude unnecessary files from being added to your Docker images, keeping image sizes smaller. -
Leverage VolumeVolume is a quantitative measure of three-dimensional space occupied by an object or substance, typically expressed in cubic units. It is fundamental in fields such as physics, chemistry, and engineering…. Mounts: Use volumes to persist data between container restarts and to share files between your host and containers.
-
Optimize Dockerfile: Write efficient Dockerfiles by minimizing the number of layers and using multi-stage builds when appropriate.
-
Automate with CI/CD: Integrate Docker into your CI/CD pipeline for streamlined deployment and testing processes.
Conclusion
Using Docker on Windows can significantly enhance your development workflow, providing consistency, efficiency, and scalability. With the steps outlined in this article, you can install Docker Desktop, create and manage containers and images, and troubleshoot common issues. By employing best practices and advanced features like Docker Compose, you ensure that your applications are robust and easy to maintain. As you continue to explore Docker, you’ll find that it opens up new possibilities for developing and deploying applications more effectively.
Related posts:
- Challenges of Using Docker in Windows Server Environments
- Common Issues and Solutions for Installing Docker on Windows
- Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Docker on Windows, Mac, and Linux
- How do I use Docker with CircleCI?
