-
Home
-
Partition Magic
- How to Uninstall Docker from Windows/Mac Completely? [Full Guide]
By Ariel | Follow |
Last Updated
A lot of users don’t know how to Uninstall Docker completely from Windows and Mac. If you are also trying to figure it out, this post on MiniTool is worth reading. It provides a full Docker uninstall guide for different platforms.
Docker is a widely used open-source platform for developing, publishing, and running applications on Windows, macOS, and Linux. It allows developers to decouple your apps from your infrastructure so that they can deliver software quickly. With this tool, developers can manage their infrastructure easily just like applications.
However, this tool also comes with some limitations such as a lack of security, provide no cross-platform compatibility, etc. So, lots of people want to uninstall Docker. how to uninstall Docker from Windows and Mac? Let’s keep reading.
Tips:
Experience a faster system with MiniTool System Booster – your solution to effortless program uninstallation.
MiniTool System Booster TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Uninstall Docker Windows 10/11
When it comes to the Docker uninstall Windows, most of us may want to use Control Panel or Settings. Of course, you can do that easily but some Docker files are leftover. To clean uninstall Docker Windows 10/11, you can follow the guide below:
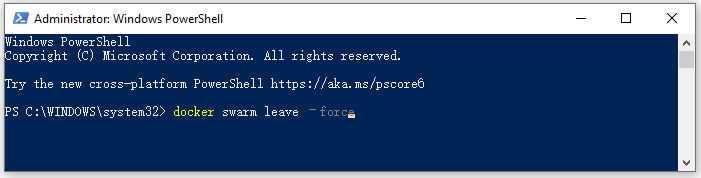
Step 1. Make sure no containers are running on your system
- Type PowerShell in the Windows search bar, and then Windows PowerShell and select Run as administrator. Then click on Yes to continue.
- In the elevated PowerShell window, type the following cmdlets in order and hit Enter after each one to remove all running containers.
docker swarm leave –force
docker ps –quiet | ForEach-Object {docker stop $_}
docker system prune –volumes –all
Step 2. Remove Docker from Windows 10/11
- Press Win + I keys to open the Settings app and select Apps.
- With Apps & features selected from the left panel, locate Docker Desktop and click on Uninstall. Then click on Uninstall/Remove to confirm this operation.
Step 3. Clear the leftover Docker data and system components
1. Open the elevated PowerShell window, type the following cmdlet, and hit Enter to remove the default networks of Docker.
Get-HNSNetwork | Remove-HNSNetwork
2. Run the following cmdlet to clear the program date of Docker from Windows.
Remove-Item “C:\ProgramData\Docker” -Recurse
3. Run the following command to reboot your system to execute the uninstallation and cleanup.
Restart-Computer -Force
Uninstall Docker macOS
Although Docker comes with a built-in uninstaller, it only can remove the program but leave some data. To clean uninstall Docker MacOS, we recommend you use the Finder.
Step 1. Completely quit the Docker Desktop app
- Open the Spotlight search by pressing the Command and Space keys together.
- Enter “Activity Monitor” into the search box and then open the Activity Monitor
- In the Process Name tab, highlight all Docker Desktop processes and click on the Stop icon from the top toolbar, and select Quit or Force Quit.
Step 2. Uninstall Docker desktop Mac
- Press the Option + Command + Space keys to open the Finder app and select Applications.
- Find and select the Docker icon and drag it to the Trash.
Tips:
Alternatively, you can launch the App Cleaner & Uninstaller and select Applications, tick the checkbox next to Docker and select all cache files from the right panel, and click on Remove to confirm the uninstallation.
Step 3. Clean up all Docker’s program data
- Open the Finder app, select the File menu and click on Go to Folder.
- Navigate to the following paths and delete all files under the paths. Then you can empty your Trash.
- ~/Library/Logs/Docker Desktop
- ~/Library/Group Containers/group.com.docker
- ~/Library/Caches/com.docker.docker
- ~/Library/Cookies/com.docker.docker.binarycookies
- ~/Library/Preferences/com.docker.docker.plist
- ~/Library/Preferences/com.electron.docker-frontend.plist
- ~/Library/Saved Application State/com.electron.docker-frontend.savedState
- ~/.docker
- /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.docker.vmnetd.plist
- /Library/PrivilegedHelperTools/com.docker.vmnetd
- /usr/local/lib/docker
How to uninstall Docker desktop Mac/Windows? All the detailed steps have been illustrated. Now, it’s your turn to have a try.
Further reading: If you enter some issues like file system corruption and low disk space on Windows, don’t worry. MiniTool Partition Wizard can help you fix them easily by checking file system errors, extending/resizing partitions, analyzing disk space, upgrading to a larger hard disk, etc.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Ariel has been working as a highly professional computer-relevant technology editor at MiniTool for many years. She has a strong passion for researching all knowledge related to the computer’s disk, partition, and Windows OS. Up till now, she has finished thousands of articles covering a broad range of topics and helped lots of users fix various problems. She focuses on the fields of disk management, OS backup, and PDF editing and provides her readers with insightful and informative content.
Docker is an essential tool for developers and system administrators who want to manage multi-container applications. However, whether it’s to solve problems, free up disk space, or simply start with a clean installation, it may be necessary to uninstall Docker from your device.
You want to uninstall Docker from your computer but don’t know how? Don’t worry, with the right method, there’s nothing very complicated. And it just so happens that Debugbar has prepared a little step-by-step tutorial to uninstall Docker on Windows, Mac, and Ubuntu.
Uninstall Docker on Windows in a few clicks
On Windows, uninstalling Docker is done through the control panel:
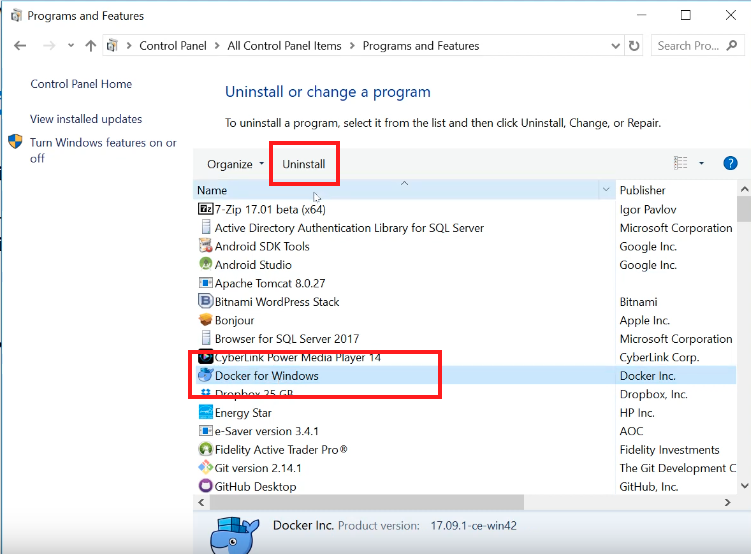
- Go to Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features.
- Right-click on Docker Desktop in the list of installed applications.
- Select Uninstall and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Once the uninstallation is complete, delete the C:\ProgramData\DockerDesktop folder if it still exists.
- Restart your PC to finalize the uninstallation.
And there you have it, no more trace of Docker on your Windows device! If you had installed Docker Toolbox (the old method of installing Docker on Windows), you’ll need to uninstall it separately following exactly the same method.
Clean up by uninstalling Docker on Mac
The procedure to get rid of Docker on a Mac is a bit more manual but still very simple:
- Quit Docker Desktop if it is running.
- Open the Finder and click on the “Applications” tab in the left column.
- Find and drag the Docker icon from your Applications folder to the trash.
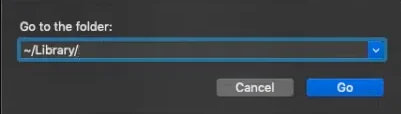
- Launch the quick search window: “Finder > Go > Go to Folder”.
- Type: ~/Library/ then press Enter.
- In the search field of the window, type “Docker”. All remaining Docker files will then appear.
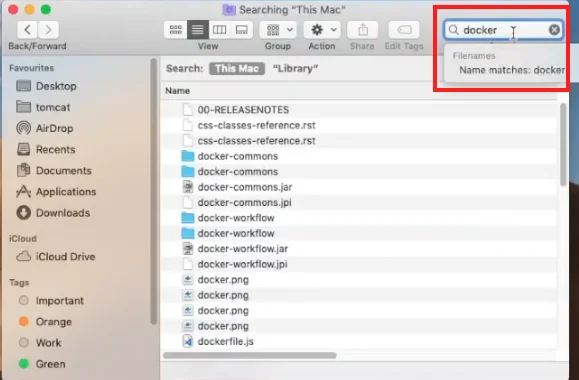
- Make sure they are Docker files, then delete them (right-click > Delete or Select > Drag and drop into the trash).
- Empty the trash and restart your Mac
After these steps, no Docker components will remain on your system. If needed, you can also manually delete the com.docker.vmnetd.plist file in ~/Library/LaunchAgents and the ~/Library/Group Containers/group.com.docker folder.
Uninstall Docker from Ubuntu from A to Z
The complete uninstallation of Docker Engine on a Linux distribution like Ubuntu requires being a bit more thorough. Here’s how to do it step by step:
- Launch the command prompt and stop the Docker daemon with : sudo systemctl stop docker
- Remove all installed Docker packages by using the package manager:
- sudo apt-get purge -y docker-engine docker docker.io docker-ce docker-ce-cli
- sudo apt-get autoremove -y –purge docker-engine docker docker.io docker-ce docker-ce-cli
- Remove Docker images, containers, volumes, and networks:
- sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker /etc/docker
- sudo rm /etc/apparmor.d/docker
- sudo groupdel docker
- sudo rm -rf /var/run/docker.sock
- sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerd
- Remove any remaining Docker configuration and data files:
- sudo find / -name “*docker*” -exec rm -rf {} \;
After all these steps, your Ubuntu system will be completely purged of Docker and all its components. Feel free to restart your machine to finalize the uninstallation.
Clean up your system by uninstalling Docker Compose
If you were using Docker Compose, you’ll also need to uninstall it properly. Here’s how to remove it on Linux:
- sudo rm /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
- sudo find / -name “*docker-compose*” -delete
On Mac and Windows, Docker Compose is integrated with Docker Desktop. Its uninstallation will therefore be done at the same time as Docker Desktop.
Uninstall tools associated with Docker
In addition to Docker itself, you may have installed other tools from the Docker ecosystem that you’ll also need to uninstall if you want to start fresh:
- Docker Machine: sudo rm $(which docker-machine)
- Kitematic: Drag the app from /Applications to the trash on Mac. On Windows, go through the control panel.
- Docker Toolbox: Use the uninstaller provided with the installer.
Don’t forget to delete any images, Dockerfiles, and configuration files that you may have downloaded or created manually on your machine.
By carefully following the steps above according to your OS, you can completely uninstall Docker and all its components from your system. This clean uninstallation will allow you to start on a good basis if you decide to reinstall Docker later or migrate to another containerization solution.
Uninstalling Docker Desktop may seem daunting, but with the help of this simple guide, you’ll be able to remove it from your system in no time.
Key Takeaways:
- Uninstalling Docker Desktop is a straightforward process that requires a few steps.
- For Windows users, the process involves stopping running containers, removing Docker from the system, and clearing any leftover data and components.
- On macOS, you can uninstall Docker by using the Docker Desktop app itself or manually removing all Docker files using Finder or Terminal.
- Following the provided steps will help you successfully uninstall Docker Desktop from your Windows or macOS machine.
- Consider alternative solutions if you no longer wish to use Docker or experience issues with it.
There are various reasons why you might want to remove Docker Desktop from your computer. Whether you need to free up valuable disk space or resolve any compatibility issues, uninstalling Docker Desktop can be a practical solution. By removing Docker and its associated components, you can declutter your system and ensure smooth operation.
Free up Disk Space
Docker Desktop can occupy a significant amount of disk space, especially if you have been using it to run multiple containers or images. By uninstalling Docker Desktop, you can reclaim this space and use it for other purposes, such as storing important files or installing other software.
Troubleshoot Issues
If you have been experiencing any issues or conflicts with Docker Desktop, uninstalling it can help resolve these problems. Removing Docker and reinstalling it can sometimes be an effective troubleshooting step, allowing you to start with a clean slate and potentially fix any underlying issues.
Switch to an Alternative Solution
While Docker Desktop is widely used and offers a range of features, you may find that another containerization solution better suits your needs. Uninstalling Docker Desktop allows you to explore alternative options and find a tool that aligns with your requirements and preferences.
| Reasons to Uninstall Docker Desktop: |
|---|
| Free up disk space |
| Troubleshoot issues |
| Switch to an alternative solution |
Stopping Running Containers
Before you begin the uninstallation process, it’s important to stop any running containers in Docker Desktop to prevent any potential issues during the removal.
To stop running containers, follow these steps:
- Open Docker Desktop on your system.
- In the Docker Dashboard, navigate to the “Containers/Apps” section.
- Locate the running containers and click on the “Stop” button next to each container.
- Wait for the containers to stop completely before proceeding with the uninstallation process.
Stopping the running containers ensures that there are no active processes that could interfere with the removal of Docker Desktop.
Table 1: Steps to Stop Running Containers
| Step Number | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Open Docker Desktop on your system. |
| Step 2 | Navigate to the “Containers/Apps” section in the Docker Dashboard. |
| Step 3 | Locate the running containers and click on the “Stop” button next to each container. |
| Step 4 | Wait for the containers to stop completely before proceeding with the uninstallation process. |
By following these steps, you can ensure a smooth uninstallation process and avoid any potential issues that may arise from running containers.
Uninstalling Docker Desktop on Windows
If you’re using a Windows machine, follow these easy steps to uninstall Docker Desktop and remove all its components from your system. To ensure a clean uninstallation, it’s important to stop any running containers in Docker Desktop before proceeding. Here’s how:
- Open Docker Desktop on your Windows machine.
- In the system tray, right-click on the Docker icon.
- From the drop-down menu, select “Stop Docker Desktop”.
Once you have stopped the running containers, you can proceed with uninstalling Docker Desktop:
- Go to the Start menu and click on the Settings icon.
- In the Settings window, select “Apps”.
- Scroll down and find “Docker Desktop” in the list of installed apps.
- Click on “Docker Desktop” and select “Uninstall”.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the uninstallation process.
After uninstalling Docker Desktop, it’s recommended to clear any leftover data and components to ensure a thorough removal. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open File Explorer and navigate to the following location:
1
C:UsersYourUsernameAppDataRoamingDocker
.
- Delete the “Docker” folder.
- Next, navigate to the following location:
.
- Delete the “Docker” folder from here as well.
By following these steps, you should be able to successfully uninstall Docker Desktop from your Windows machine and remove all its associated components.
| Step | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stop running containers in Docker Desktop by right-clicking on the Docker icon in the system tray and selecting “Stop Docker Desktop”. | ||
| 2 | Go to the Start menu, click on the Settings icon, and select “Apps”. | ||
| 3 | Scroll down and find “Docker Desktop” in the list of installed apps. Click on it and select “Uninstall”. | ||
| 4 | Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the uninstallation process. | ||
| 5 | Open File Explorer and delete the “Docker” folder located in
. |
||
| 6 | Delete the “Docker” folder located in
. |
Clearing Leftover Data and Components (Windows)
To ensure a thorough uninstallation of Docker Desktop on Windows, it’s important to clear any leftover data and components from your system. This step helps to free up disk space and ensures a clean removal of Docker Desktop.
Here is a step-by-step guide to clearing leftover data and components after uninstalling Docker Desktop on Windows:
- Open the File Explorer on your Windows machine.
- Navigate to the following location:
.
- Delete the entire
folder.
- Next, press
on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
- Type
and click OK to open the Registry Editor.
- In the Registry Editor, navigate to
1
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareDocker Desktop
and delete the
folder.
- Finally, empty your Recycle Bin to permanently delete the Docker files.
By following these steps, you can ensure that all the leftover data and components of Docker Desktop are removed from your Windows system.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Open File Explorer |
| 2 | Navigate to C:Program FilesDocker |
| 3 | Delete Docker folder |
| 4 | Press Win + R |
| 5 | Type regedit and click OK |
| 6 | Delete HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareDocker Desktop folder in Registry Editor |
| 7 | Empty Recycle Bin |
Uninstalling Docker Desktop on macOS
If you’re using a macOS machine, follow these step-by-step instructions to remove Docker Desktop from your system either through the Docker Desktop app or manually using Finder or Terminal.
- Uninstalling Docker Desktop using the Docker Desktop app:
- Open the Docker Desktop app on your macOS machine.
- Navigate to the top menu and click on “Docker” (next to the Apple icon).
- From the dropdown menu, select “Preferences.”
- In the Preferences window, go to the “Uninstall” tab.
- Click the “Uninstall” button.
- Follow the prompts to complete the uninstallation process.
- Manually removing Docker Desktop files using Finder or Terminal:
- Open Finder and click on “Go” in the top menu.
- From the dropdown menu, select “Go to Folder.”
- Type
and press Enter.
- Locate the “Application Support” folder and delete the “Docker” folder.
- Go back to the “Library” folder and open the “Preferences” folder.
- Delete the files or folders associated with Docker (e.g.,
).
- Open Terminal and execute the following command to remove Docker-related files:
.
By following these instructions, you can successfully uninstall Docker Desktop from your macOS machine, freeing up disk space and removing all associated components. Remember to carefully follow the steps and ensure all files and folders related to Docker are deleted to complete the uninstallation process.
Clearing Leftover Data and Components (macOS)
After uninstalling Docker Desktop on macOS, it’s essential to clear any remaining data and components to fully remove it from your system. This ensures a clean uninstallation and frees up disk space. Here are two methods you can use to clear leftover data and components:
Method 1: Using the Docker Desktop app
If you chose to uninstall Docker Desktop using the Docker Desktop app, follow these steps to clear any remaining data:
- Open the Finder on your macOS system.
- Navigate to the “Applications” folder.
- Locate and open the “Docker” folder.
- Drag the “Docker.app” file to the Trash.
- Right-click on the Trash icon and select “Empty Trash” to permanently delete the Docker app.
Method 2: Manually removing Docker files
If you want to manually remove Docker files using Finder or Terminal, follow these steps:
- Open the Finder on your macOS system.
- Click on the “Go” menu in the menu bar and select “Go to Folder…”.
- Type “/usr/local” and click “Go”.
- Locate and delete the “docker” folder, if it exists.
- Open Terminal and run the following command to remove additional Docker files:
1
<a class=»wpil_keyword_link» href=»https://www.howto-do.it/what-is-sudo-superuser-do/» title=»sudo» data-wpil-keyword-link=»linked»>sudo</a> rm -rf ~/.docker
- Enter your administrator password when prompted.
By following these methods, you can ensure that all Docker-related files and components are removed from your macOS system. This will free up valuable disk space and ensure a complete uninstallation of Docker Desktop.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While uninstalling Docker Desktop is generally straightforward, you may encounter some issues along the way. Here are some common problems and their solutions to help you successfully complete the uninstallation.
1. Error: “Docker Desktop is still running.”
If you receive this error message, it means that Docker Desktop is still running in the background. To resolve this issue, you need to manually stop Docker Desktop by following these steps:
- Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- In the Processes or Details tab, locate the Docker Desktop process.
- Right-click on the process and select “End Task” or “End Process”.
2. Unable to uninstall Docker Desktop on Windows.
If you’re having trouble uninstalling Docker Desktop on Windows, you can try the following steps to resolve the issue:
- Restart your computer and try uninstalling Docker Desktop again.
- If the issue persists, open the Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
- Type the command “wmic product where name=’Docker Desktop’ call uninstall” and press Enter.
- Follow the prompts to complete the uninstallation process.
3. Leftover Docker files and components.
After uninstalling Docker Desktop, you may find that there are still leftover files and components on your system. To remove them completely, follow these steps:
- Open File Explorer and navigate to the following directories:
- C:Program FilesDocker
- C:Users{your_username}AppDataRoamingDocker
- C:Users{your_username}AppDataLocalDocker
- Delete all Docker-related files and folders.
- Empty the Recycle Bin to permanently delete the files.
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Error: “Docker Desktop is still running.” | Manually stop Docker Desktop process in Task Manager. |
| Unable to uninstall Docker Desktop on Windows. | Restart computer and try uninstalling again. If it persists, use Command Prompt with administrative privileges. |
| Leftover Docker files and components. | Delete files and folders in specific directories. |
By following these troubleshooting steps, you should be able to overcome any common issues and successfully uninstall Docker Desktop from your Windows or macOS machine.
Reinstalling Docker Desktop (Optional)
If you ever decide to reinstall Docker Desktop, here are the steps to guide you through the installation process after successful uninstallation:
- Visit the official Docker website and download the latest version of Docker Desktop for your operating system.
- Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
- Once the installation is complete, launch Docker Desktop from your applications or desktop shortcut.
- Sign in to your Docker account or create a new one if you don’t have an existing account.
- Configure Docker Desktop settings according to your preferences, such as resource allocation and network settings.
- Click on the “Apply & Restart” button to save the changes and restart Docker Desktop.
- You have now successfully reinstalled Docker Desktop and can begin using it for your containerization needs.
Remember to follow any additional instructions provided by the installer to ensure a smooth reinstallation process. If you encounter any issues or errors during the installation, refer to Docker’s official documentation or reach out to their support team for assistance.
| Operating System | Installation Steps |
|---|---|
| Windows |
|
| macOS |
|
If you ever decide to reinstall Docker Desktop, here are the steps to guide you through the installation process after successful uninstallation.
Alternative Solutions
If Docker Desktop isn’t meeting your needs or you’re seeking alternative solutions, here are some popular options you can explore:
- Kubernetes: A widely-used open-source container orchestration platform that allows you to manage and deploy containers at scale. Kubernetes offers advanced features for managing containerized applications and provides a flexible and scalable solution.
- Podman: An alternative to Docker that enables you to run and manage containers without requiring a separate daemon. Podman is compatible with Docker images and offers a secure and lightweight container runtime.
Additionally, you may consider the following:
- VirtualBox: A powerful virtualization tool that allows you to create and manage virtual machines. VirtualBox provides a complete operating system environment and is suitable for running different operating systems on a single machine.
- Vagrant: A tool for creating and managing reproducible development environments. Vagrant simplifies the process of setting up and sharing development environments across different machines.
These alternatives offer different features and functionalities, so it’s important to assess your specific needs and requirements before making a decision. Remember to research each option and consider factors such as ease of use, community support, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes | A popular open-source container orchestration platform for managing and deploying containers at scale. |
| Podman | An alternative container runtime to Docker that offers compatibility with Docker images and a lightweight architecture. |
| VirtualBox | A virtualization tool for creating and managing virtual machines with different operating systems. |
| Vagrant | A tool for creating and managing reproducible development environments across different machines. |
Removing Docker Images and Containers (Optional)
If you want to completely remove all Docker images and containers from your system, here’s how you can do it as an additional step after uninstalling Docker Desktop.
The first step is to open a command prompt or terminal window. On Windows, you can do this by pressing the Windows key, typing “cmd,” and selecting the Command Prompt app. On macOS, you can use the Terminal app, which can be found in the Utilities folder within the Applications folder.
Once you have the command prompt or terminal open, you can use the following commands to remove Docker images and containers:
| Command | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Removes all stopped containers. | ||
|
Removes all images. |
Note: These commands will remove all containers and images from your system, so make sure you have backups or copies of any important data before running them.
By running these commands, you’ll ensure that no remnants of Docker, such as unused images or containers, are left on your system. This can help free up disk space and ensure a clean removal of Docker from your machine.
Remember, this step is optional and should only be performed if you want to completely remove all Docker-related files from your system. If you plan on reinstalling Docker or using it in the future, these commands will erase all your images and containers.
Conclusion
Uninstalling Docker Desktop can be a simple and effective process if you follow the steps outlined in this guide. By removing Docker Desktop properly, you can free up disk space and address any issues that may arise, ensuring a smooth transition or alternative solution.
For Windows users, the uninstallation process involves stopping any running containers in Docker Desktop, accessing the Control Panel to remove Docker from the system, and clearing any leftover data and components. This comprehensive approach ensures a complete removal of Docker Desktop from your Windows machine.
If you’re using a macOS system, you have the option of uninstalling Docker Desktop using the Docker Desktop app itself or manually removing all Docker files using Finder or Terminal. Regardless of your preferred method, it’s important to follow the steps carefully to ensure a clean uninstallation.
In conclusion, by following the steps provided in this guide, you can successfully uninstall Docker Desktop from your Windows or macOS machine. This not only frees up disk space but also allows you to troubleshoot any issues and consider alternative solutions. Remember, proper uninstallation is key to maintaining the performance and functionality of your system.
FAQ
How do I uninstall Docker Desktop?
Uninstalling Docker Desktop is a straightforward process that involves stopping running containers, removing Docker from the system, and clearing any leftover data and components. Detailed instructions can be found in the article.
Why would I want to uninstall Docker Desktop?
There are several reasons why someone may want to uninstall Docker Desktop, such as freeing up disk space, troubleshooting issues, or switching to an alternative solution. The article provides more information on this topic.
How do I stop running containers before uninstalling Docker Desktop?
Stopping running containers is an important step in the uninstallation process to ensure a clean removal. The article provides instructions on how to perform this step.
How do I uninstall Docker Desktop on Windows?
Uninstalling Docker Desktop on Windows involves accessing the Control Panel and removing Docker from the system. The article provides step-by-step instructions for this process.
How do I clear leftover data and components after uninstalling Docker Desktop on Windows?
Clearing any leftover data and components after uninstalling Docker Desktop on Windows ensures a complete removal. The article provides details on how to perform this additional step.
How do I uninstall Docker Desktop on macOS?
Uninstalling Docker Desktop on macOS can be done using the Docker Desktop app itself or by manually removing Docker files using Finder or Terminal. The article provides step-by-step instructions for both methods.
How do I clear leftover data and components after uninstalling Docker Desktop on macOS?
Clearing any leftover data and components after uninstalling Docker Desktop on macOS is essential for a clean uninstallation. The article provides guidance on how to perform this task.
What should I do if I encounter any issues during the uninstallation process?
The article offers troubleshooting steps to address common issues that may arise during the uninstallation of Docker Desktop. Following these steps should help overcome any problems.
Is reinstalling Docker Desktop an optional step?
Yes, reinstalling Docker Desktop is an optional step. The article provides guidance for those who may want to reinstall Docker Desktop in the future.
Are there alternative solutions to Docker Desktop?
Yes, there are alternative solutions to Docker Desktop. The article explores some options that users can consider if they no longer wish to use Docker or experience issues with it.
Is removing Docker images and containers after uninstalling Docker Desktop optional?
Yes, removing Docker images and containers after uninstalling Docker Desktop is an optional step for those who want to further clean up their system. The article provides information on how to perform this step.
- About the Author
- Latest Posts
Mark is a senior content editor at Text-Center.com and has more than 20 years of experience with linux and windows operating systems. He also writes for Biteno.com

Docker is an open-source containerization platform that enables developers to package apps into containers and standardized executable components combining application source code with the operating system (OS) libraries and dependencies required to run that code in any environment. The Docker Engine and client aren’t included with Windows and need to be installed and configured individually. You need Docker in order to work with Windows Containers. Docker consists of the Docker Engine (dockerd.exe), and the Docker client (docker.exe). In this article, you’ll explore how to install and uninstall Docker Desktop in Windows.
To run containers on Windows Server, you need a physical server or virtual machine running Windows Server 2022, Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2019, or Windows Server 2016 as of the time of writing this article. More on this later. Kindly refer to these related guides: How to create and deploy a local Registry Server with Docker Image, how to Pull your first Nginx Container Image from Docker Hub and deploy it to your local machine, Azure DevOps and GitHub integration for Docker and Kubernetes deployment, how to create a static pod in Kubernetes, and how to install, register and start GitLab Runner on Windows.
Windows Requirements
GitLab Runner only supports the following versions of Windows as of the time of writing this piece which follows the support lifecycle for Windows. You can use the following hyperlink for more information.
- Windows Server 20H2.
- Windows Server 2004.
- Windows Server 1809.
This means that Docker only supports Docker Desktop on Windows for those versions of Windows 10 that are still within Microsoft’s servicing timeline:
- Long-Term Servicing Channel, versions for 5 years after their release date. Note that we don’t support versions that are on extended support.
- Furthermore, Semi-Annual Channel versions for 18 months after their release date. We don’t support these versions after mainstream support ends.
This is the case for both the Windows binaries that we distribute and also for the Docker executor.
You can create a free Docker account for personal or small business users, however, for larger businesses, there is a monthly fee. For more details, see the
- However, Our Docker Subscription Service Agreement includes a change to the terms of use for Docker Desktop
- It remains free for small businesses (fewer than 250 employees AND less than $10 million in revenue), personal use, education, and non-commercial open-source projects.
- It requires a paid subscription for professional use in larger enterprises.
- The effective date of these terms is August 31, 2021. There is a grace period until January 31, 2022 for those that will require a paid subscription to use Docker Desktop.
- Moreover, The existing Docker Free subscription has been renamed Docker Personal and we have introduced a Docker Business subscription .
- The Docker Pro, Team, and Business subscriptions include commercial use of Docker Desktop.
Key Features of Docker Desktop
Some of the key features of Docker Desktop include:
- In addition, Ability to containerize and share any application on any cloud platform, in multiple languages and frameworks
- Easy installation and setup of a complete Docker development environment
- Includes the latest version of Kubernetes
- Automatic updates to keep you up to date and secure
- Nonetheless, On Windows, the ability to toggle between Linux and Windows Server environments to build applications
- Consequently, Fast and reliable performance with native Windows Hyper-V virtualization
- Similarly, Ability to work natively on Linux through WSL 2 on Windows machines
- Volume mounting for code and data, including file change notifications and easy access to running containers on the localhost network
- In-container development and debugging with supported IDEs.
System requirements for Installing and Uninstalling Docker Desktop on Windows
Below are the hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run Client Hyper-V on Windows 10:
– Nevertheless, 64-bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT),
– 4GB system RAM, and
– BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in the BIOS settings. And, If this is not done, you will be prompted with the following error “Please enable the Virtual Machine Platform Windows Feature and ensure Virtualization is enabled in the BIOS“.
Your Windows machine must meet the following requirements to successfully install and uninstall Docker Desktop on Windows.
1: Therefore, Windows 10 64-bit: Pro 2004 (build 19041) or higher, or Enterprise or Education 1909 (build 18363) or higher.
2: For the WSL2 backend, please enable the WSL 2 feature on Windows. Additionally, For detailed instructions, refer to these guides: What is Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), how to install WSL on Windows Server via Server Manager and PowerShell, and how to install WSL on Windows 10. You can install WSL with the following command wsl --install by entering the command either in PowerShell or the Command Prompt.

Alternatively, you can use the following command to install it very quickly as well.
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
3: Download and install the WSL2 Linux kernel update package for x64 machines. You can also see this guide for more information Linux kernel update package.



4: Hyper-V and Containers Windows features must be enabled. Here is a similar guide to work you through how to install RSAT on Windows 10 via Windows features, and on a server, see how to install RSAT on Windows Server. You may also want to see this very detailed guide discussing “how to enable or disable DotNet Framework (NetFx3) via PowerShell, Control Panel, and DISM in Windows“.
5: To do this, launch the Windows Control Panel and click on Programs, and then on “Turn Windows features on or Off”.


Note:
As you can see, we already have the Hyper-V feature installed. We will have to check the “Container” feature as shown below.

Ensure both the Hyper-V and Containers Windows features must be enabled. When you are done, click on OK.

After these steps, Windows will search and apply the settings and you will be required to restart afterward.


Windows Server Containers use Hyper-V isolation by default on Windows 10 in order to provide developers with the same kernel version and configuration that will be used in production.
You need Docker in order to work with Windows Containers. Docker consists of the Docker Engine (dockerd.exe), and the Docker client (docker.exe). You can install Docker on Windows 10 Professional and Enterprise editions by using the following steps.
The Docker Desktop can be downloaded from the following link as shown below.

It typically downloads to your Downloads folder, or you can run it from the recent downloads bar at the bottom of your web browser.
– To install the Docker Desktop, double-click on the Docker Desktop Installer.exe to run the installer.
Ensure you install the latest version of the Docker engine to avoid vulnerabilities
Accept the User Account Control. You may want to learn how to turn UAC on or off in Windows.

When prompted, ensure the install required Windows components for WSL 2 option is selected on the Configuration page.


This will unpack and install as shown below


As you can see below, the installation has succeeded. Just Close and Logout

If you get this window close and restart, you may run into issues which means, the prerequisites defined above were not correctly follwed. I just had to simulate this on a different PC in my Lab. You have to click on close and restart and ensure you install WSL, the package update etc as defined above.
Note: If your admin account is different from your user account, you must add the user to the docker-users group. Run Computer Management as an administrator and navigate to Local Users and Groups > Groups > docker-users. Right-click to add the user to the group. Log out and log back in for the changes to take effect.

Start Docker Desktop
The Docker Desktop does not start automatically after installation. To start Docker Desktop, search for Docker, and select Docker Desktop in the search results.
Note: You can just click on the Docker Desktop available on the desktop of your PC because we selected to have it installed on the Desktop.

The Docker menu displays the Docker Subscription Service Agreement window. It includes a change to the terms of use for Docker Desktop. Please refer to the 3rd paragraph above for more information.

As you can see, Docker is now installed and started.

You may want to sign into Docker Hub with your Docker IDas shown below

If you wish to check for updates after logging in, please navigate to the Software Updates and click on Check for Updates.

Now, let’s run some Docker commands. Below are some possible commands that you can run.


Currently, this is the version of Docker Desktop we are running

Before you can use Docker, you will need to install the container images. For more information, see docs for our container base images.
Containers and images created with Docker Desktop are shared between all user accounts on machines where it is installed. This is because all Windows accounts use the same VM to build and run containers. Note that it is not possible to share containers and images between user accounts when using the Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend. Nested virtualization scenarios, such as running Docker Desktop on a VMWare or Parallels instance might work, but there are no guarantees [Reference: Docker Docs].
Uninstall Docker Desktop
While you’ve learned how to install, let’s discuss how to uninstall Docker Desktop on Windows. Uninstalling Docker Desktop destroys Docker containers, images, volumes, and other Docker-related data local to the machine, and removes the files generated by the application. To uninstall Docker Desktop from your Windows machine, please follow the steps discussed below.
From the Windows Start menu, select Settings > Apps > Apps & features as shown below
– Select Docker Desktop from the Apps & features list and then select Uninstall.
Alternatively, you could also launch Windows Control Panel, click on programs and Features and have the Docker Desktop uninstalled. Click Uninstall to confirm your selection.

To uninstall Docker on Windows Server 2016
From an elevated PowerShell session, use the Uninstall-Package and Uninstall-Module cmdlets to remove the Docker module and its corresponding Package Management Provider from your system, as shown in the following example:
Uninstall-Package -Name docker -ProviderName DockerMsftProvider
Uninstall-Module -Name DockerMsftProviderYou can find the Package Provider that you used to install Docker with PS C:\> Get-PackageProvider -Name *Docker*
Clean up Docker data and system components
After you uninstall Docker, you’ll need to remove Docker’s default networks so their configuration won’t remain on your system after Docker is gone. You can do this by running the following cmdlet:
Get-HNSNetwork | Remove-HNSNetworkTo remove Docker’s default networks on Windows Server 2016.
Get-ContainerNetwork | Remove-ContainerNetworkRun the following cmdlet to remove Docker’s program data from your system:
Remove-Item "C:\ProgramData\Docker" -RecurseRemove features associated with Docker/containers on Window
This includes the “Containers” feature, which is automatically enabled on any Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016 when Docker is installed. It may also include the “Hyper-V” feature, which is automatically enabled on Windows 10 when Docker is installed but must be explicitly enabled on Windows Server 2016.
Note: The Hyper-V feature is a general virtualization feature that enables much more than just containers. Before disabling the Hyper-V feature, make sure there are no other virtualized components on your system that require Hyper-V.
To remove Windows features on Windows 10:
- Go to Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features > Turn Windows features on or off.
- Find the name of the feature or features you want to disable—in this case, Containers and (optionally) Hyper-V.
- Uncheck the box next to the name of the feature you want to disable.
- Select “OK”.
To remove Windows features on Windows Server 2016: From an elevated PowerShell session, run the following cmdlets to disable the Containers and (optionally) Hyper-V features from your system:
Remove-WindowsFeature Containers
Remove-WindowsFeature Hyper-VReboot your system
To finish uninstallation and cleanup, run the following cmdlet from an elevated PowerShell session to reboot your system:
Restart-Computer -ForceI hope you found this blog post helpful. By now, you should have ample knowledge on how to install and uninstall Docker Desktop on Windows. If you have any questions, please let me know in the comment session.
Skip to content

Docker is the leading containerization platform that simplifies the deployment and administration of applications.
However, there are situations where you might want to uninstall Docker, such as concerns over its licensing terms, which have raised issues about potential costs and compliance for some organizations.
This has prompted users to look for alternative container platforms.
Let’s go through how to uninstall Docker on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
- Uninstall Docker on Widows
- Uninstall Docker on Mac
- Uninstall Docker on Linux
Uninstall Docker on Widows
To uninstall Docker on Windows, you can follow these steps:[1][2]
- First, let’s remove all Docker containers, images, and networks created or used by Docker:
- To stop all running containers, run this command in a CMD prompt or Powershell terminal:
docker stop $(docker ps -a -q) - To delete all containers, images, and networks, run this command:
docker system prune -a
- To stop all running containers, run this command in a CMD prompt or Powershell terminal:
- Next, go to the Windows Start menu, search for “Add or remove programs” and open it.
- Find “Docker Desktop” in the list of installed applications then click the “Uninstall” button.
- You can optionally remove any lingering files and folders that Docker may leave such as its installation directory which is
C:\ProgramData\Dockerby default. - Docker for Windows may have enabled Hyper-V and related features. To disable these features, you can open “Control Panel,” navigate to “Programs and Features,” click on “Turn Windows features on or off,” and then uncheck the features related to Hyper-V and virtualization.
After uninstalling Docker and disabling related features, it’s a good idea to reboot your computer.
To uninstall Docker on Mac, you can follow these steps:[3]
- First, let’s remove all Docker containers, images, and networks created or used by Docker:
- To stop all running containers, run this command in a CMD prompt or Powershell terminal:
docker stop $(docker ps -a -q) - To delete all containers, images, and networks, run this command:
docker system prune -a
- To stop all running containers, run this command in a CMD prompt or Powershell terminal:
- Click on the “Docker Desktop” icon in the menu bar and select “Quit Docker Desktop” to stop the Docker application.
- Open Finder, go to your Applications folder, and find “Docker”. Drag the Docker application to the Trash.
- Docker may leave behind some data, including containers, images, and configurations. To remove this data, open Terminal and run the following commands:
rm -rf ~/.dockerrm -rf ~/Library/Containers/com.docker.docker
- If you’ve set up shell completions for Docker (e.g., using Zsh or Bash), you can remove them by deleting the relevant configuration files. For example, if you’re using Zsh, you might remove the Docker completions with:
rm -f ~/.zsh/completion/_docker
It’s a good practice to restart your Mac at this point.
Uninstall Docker on Linux
The exact steps to uninstall Docker on Linux can vary depending on your Linux distribution. Here are general instructions for some common Linux distributions: Ubuntu, CentOS, and Fedora. Be sure to adapt these commands to your specific distribution:[4][5]
- First, let’s remove all Docker containers, images, and networks created or used by Docker:
- To stop all running containers, run this command in a CMD prompt or Powershell terminal:
docker stop $(docker ps -a -q) - To delete all containers, images, and networks, run this command:
docker system prune -a
- To stop all running containers, run this command in a CMD prompt or Powershell terminal:
- Uninstall Docker’s packages:
- For Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get remove docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io - For CentOS:
sudo yum remove docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io - For Fedora:
sudo dnf remove docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
- For Ubuntu:
- To remove all Docker-related configuration files, you can use the following command:
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
- To ensure there are no remaining Docker files or directories, run:
sudo rm -rf /etc/docker
References
- “Uninstall docker desktop.” (2023, December 5). Docker Documentation. https://docs.docker.com/desktop/uninstall/ ↩︎
- Ariel. (2023, November 3). How to Uninstall Docker from Windows/Mac Completely? [Full Guide] – MiniTool Partition Wizard. MiniTool. https://www.partitionwizard.com/partitionmagic/uninstall-docker.html ↩︎
- Lanman, J. (2023, July 4). How to safely uninstall Docker desktop from a Mac. MUO. https://www.makeuseof.com/how-to-uninstall-docker-desktop-mac/ ↩︎
- Nek, D. (2023, October 18). How to uninstall Docker on Ubuntu. Linux Tutorials for Beginners. https://webhostinggeeks.com/howto/how-to-uninstall-docker-on-ubuntu/ ↩︎
- Uninstall Docker from Linux (CentOS 7, RedHat 7). (n.d.). https://www.learn-it-with-examples.com/development/virtualization/docker/uninstallation-docker-from-linux.html ↩︎
