В современных версиях Windows уже есть встроенный SSH сервер на базе пакета OpenSSH. В этой статье мы покажем, как установить и настроить OpenSSH сервер в Windows 10/11 и Windows Server 2022/2019 и подключиться к нему удаленно по защищенному SSH протоколу (как к Linux).
Содержание:
- Установка сервера OpenSSH в Windows
- Настройка SSH сервера в Windows
- Sshd_config: Конфигурационный файл сервера OpenSSH
- Подключение по SSH к Windows компьютеру
- Логи SSH подключений в Windows
Установка сервера OpenSSH в Windows
Пакет OpenSSH Server включен в современные версии Windows 10 (начиная с 1803), Windows 11 и Windows Server 2022/2019 в виде Feature on Demand (FoD). Для установки сервера OpenSSH достаточно выполнить PowerShell команду:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like ‘OpenSSH.Server*’ | Add-WindowsCapability –Online
Или при помощи команды DISM:
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
Если ваш компьютер подключен к интернету, пакет OpenSSH.Server будет скачан и установлен в Windows.
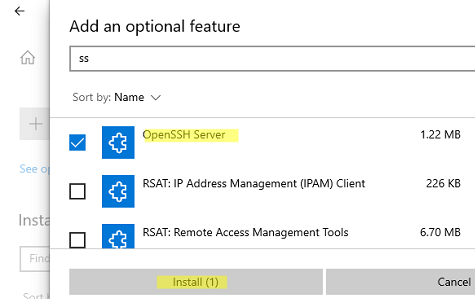
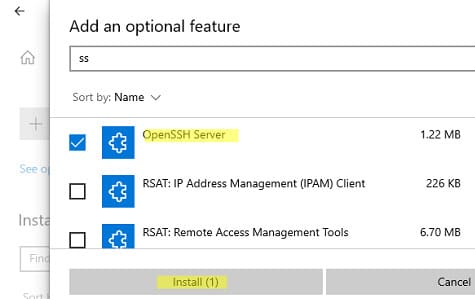
Также вы можете установить сервер OpenSSH в Windows через современную панель Параметры (Settings -> Apps and features -> Optional features -> Add a feature, Приложения -> Управление дополнительными компонентами -> Добавить компонент. Найдите в списке OpenSSH Server и нажмите кнопку Install).
На изолированных от интернета компьютерах вы можете установить компонент с ISO образа Features On Demand (доступен в личном кабинете на сайте Microsoft: MSDN или my.visualstudio.com). Скачайте диск, извлеките его содержимое в папку c:\FOD (достаточно распаковать извлечь файл
OpenSSH-Server-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~.cab
), выполните установку из локального репозитория:
Add-WindowsCapability -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0 -Online -Source c:\FOD
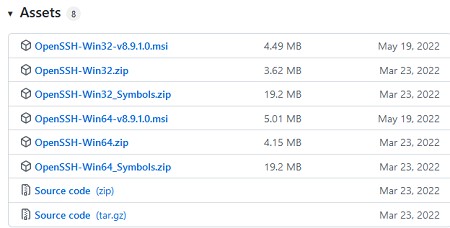
Также доступен MSI установщик OpenSSH для Windows в официальном репозитории Microsoft на GitHub (https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/). Например, для Windows 10 x64 нужно скачать и установить пакет OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi. Следующая PowerShell команда скачает MSI файл и установит клиент и сервер OpenSSH:
Invoke-WebRequest https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/download/v8.9.1.0p1-Beta/OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -OutFile $HOME\Downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -UseBasicParsing
msiexec /i c:\users\root\downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi
Также вы можете вручную установить OpenSSH сервер в предыдущих версиях Windows (Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2016/2012R2). Пример установки Win32-OpenSSH есть в статье “Настройка SFTP сервера (SSH FTP) в Windows”.
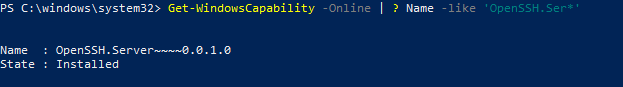
Чтобы проверить, что OpenSSH сервер установлен, выполните:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like 'OpenSSH.Ser*'
State : Installed
Настройка SSH сервера в Windows
После установки сервера OpenSSH в Windows добавляются две службы:
- ssh-agent (OpenSSH Authentication Agent) – можно использовать для управления закрытыми ключами если вы настроили SSH аутентификацию по ключам;
- sshd (OpenSSH SSH Server) – собственно сам SSH сервер.
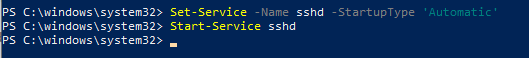
Вам нужно изменить тип запуска службы sshd на автоматический и запустить службу с помощью PowerShell:
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Start-Service sshd
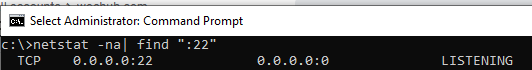
С помощью nestat убедитесь, что теперь в системе запущен SSH сервер и ждет подключений на порту TCP:22 :
netstat -na| find ":22"
Проверьте, что включено правило брандмауэра (Windows Defender Firewall), разрешающее входящие подключения к Windows по порту TCP/22.
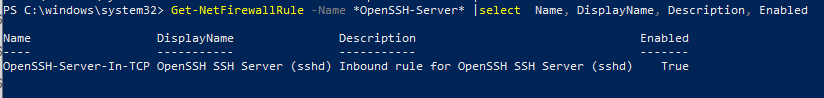
Get-NetFirewallRule -Name *OpenSSH-Server* |select Name, DisplayName, Description, Enabled
Name DisplayName Description Enabled ---- ----------- ----------- ------- OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) Inbound rule for OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) True
Если правило отключено (состоянии Enabled=False) или отсутствует, вы можете создать новое входящее правило командой New-NetFirewallRule:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
Рассмотрим, где храниться основные компоненты OpenSSH:
- Исполняемые файлы OpenSSH Server находятся в каталоге
C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\
(sshd.exe, ssh.exe, ssh-keygen.exe, sftp.exe и т.д.) - Конфигурационный файл sshd_config (создается после первого запуска службы):
C:\ProgramData\ssh - Файлы authorized_keys и ssh ключи можно хранить в профиле пользователей:
%USERPROFILE%\.ssh\
Sshd_config: Конфигурационный файл сервера OpenSSH
Настройки сервере OpenSSH хранятся в конфигурационном файле %programdata%\ssh\sshd_config. Это обычный текстовый файл с набором директив. Для редактирования можно использовать любой текстовый редактор (я предпочитаю notepad++). Можно открыть с помощью обычного блокнота:
start-process notepad C:\Programdata\ssh\sshd_config
Например, чтобы запретить SSH подключение для определенного доменного пользователя (и всех пользователей указанного домена), добавьте в конце файле директивы:
DenyUsers winitpro\[email protected] DenyUsers corp\*
Чтобы разрешить подключение только для определенной доменной группы:
AllowGroups winitpro\sshadmins
Либо можете разрешить доступ для локальной группы:
AllowGroups sshadmins
По умолчанию могут к openssh могут подключаться все пользователи Windows. Директивы обрабатываются в следующем порядке: DenyUsers, AllowUsers, DenyGroups,AllowGroups.
Можно запретить вход под учетными записями с правами администратора, в этом случае для выполнения привилегированных действий в SSH сессии нужно делать runas.
DenyGroups Administrators
Следующие директивы разрешают SSH доступ по ключам (SSH аутентификации в Windows с помощью ключей описана в отдельной статье) и по паролю:
PubkeyAuthentication yes PasswordAuthentication yes
Вы можете изменить стандартный SSH порт TCP/22, на котором принимает подключения OpenSSH в конфигурационном файле sshd_config в директиве Port.
После любых изменений в конфигурационном файле sshd_config нужно перезапускать службу sshd:
restart-service sshd
Подключение по SSH к Windows компьютеру
Теперь вы можете попробовать подключиться к своей Windows 10 через SSH клиент (в этом примере я использую putty).
Вы можете использовать встроенный SSH клиентом Windows для подключения к удаленному хосту. Для этого нужно в командной строке выполнить команду:
ssh [email protected]
В этом примере
alexbel
– имя пользователя на удаленном Windows компьютере, и 192.168.31.102 – IP адрес или DNS имя компьютера.
Обратите внимание что можно использовать следующие форматы имен пользователей Windows при подключении через SSH:
-
alex@server1
– локальный пользователь Windows -
[email protected]@server1
–пользователь Active Directory (в виде UPN) или аккаунт Microsoft/ Azure(Microsoft 365) -
winitpro\alex@server1
– NetBIOS формат имени
В домене Active Directory можно использовать Kerberos аутентификацию в SSH. Для этого в sshd_config нужно включить параметр:
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
После этого можно прозрачно подключать к SSH сервер с Windows компьютера в домене из сессии доменного подключается. В этом случае пароль пользователя не указывается и выполняется SSO аутентификация через Kerberos:
ssh -K server1
При первом подключении появится стандартный запрос на добавление узла в список известных SSH хостов.
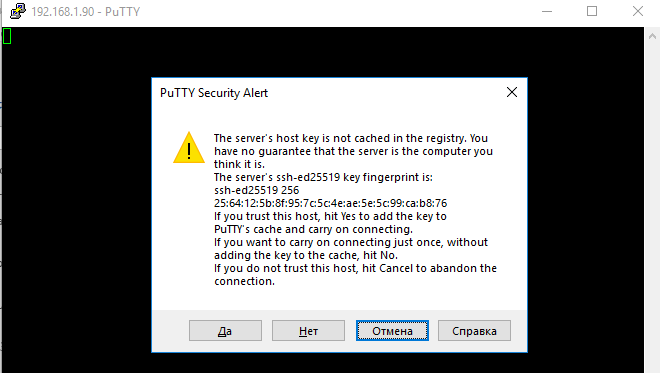
Нажимаем Да, и в открывшееся окне авторизуемся под пользователем Windows.
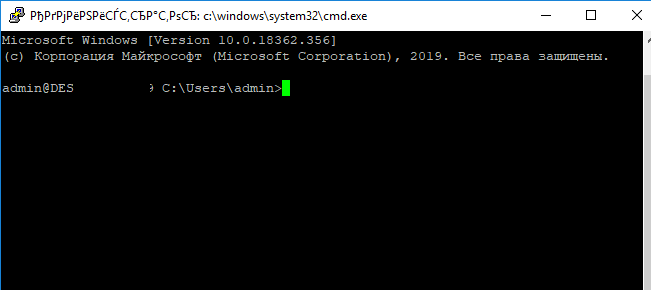
При успешном подключении запускается командная оболочка cmd.exe со строкой-приглашением.
admin@win10tst C:\Users\admin>
В командной строке вы можете выполнять различные команды, запускать скрипты и программы.
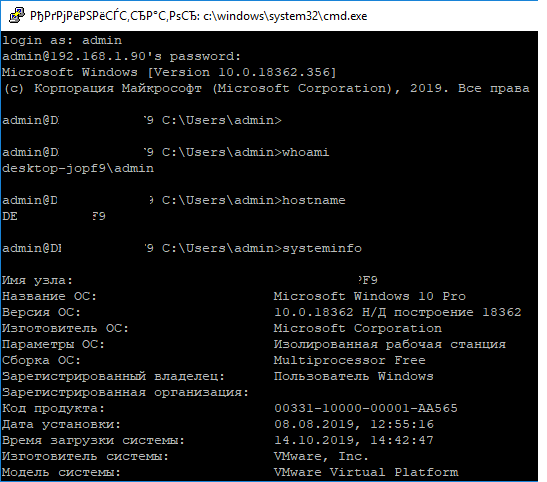
Я предпочитаю работать в командной строке PowerShell. Чтобы запустить интерпретатор PowerShell, выполните:
powershell.exe
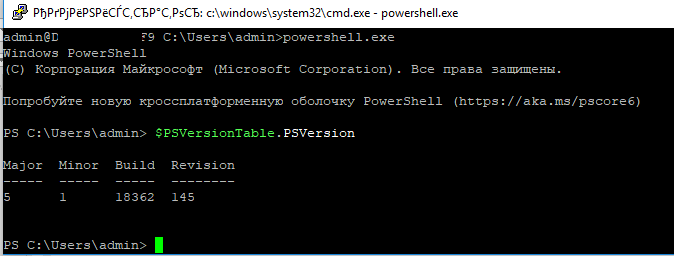
Чтобы изменить командную оболочку (Shell) по умолчанию в OpenSSH с cmd.exe на PowerShell, внесите изменение в реестр такой командой:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\OpenSSH" -Name DefaultShell -Value "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -PropertyType String –Force
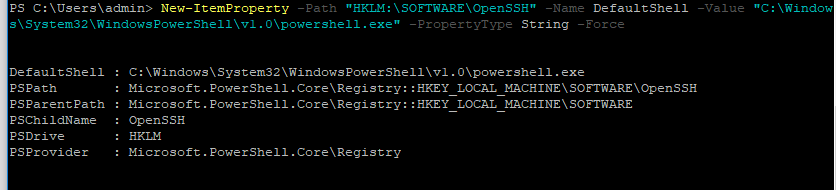
Осталось перезапустить SSH подключение и убедиться, что при подключении используется командный интерпретатор PowerShell (об этом свидетельствует приглашение
PS C:\Users\admin>
).
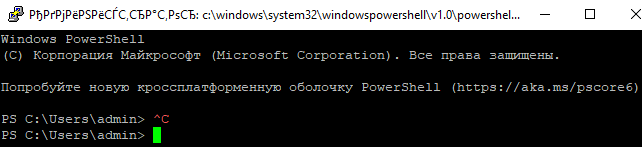
В SSH сессии запустилась командная строка PowerShell, в которой работают привычные функции: авто дополнение, раскраска модулем PSReadLine, история команд и т.д. Если текущий пользователь входит в группу локальных администраторов, то все команды в его сессии выполняются с повышенными правами даже при включенном UAC.
Логи SSH подключений в Windows
В Windows логи подключений к SSH серверу по-умолчанию пишутся не в текстовые файлы, а в отдельный журнал событий через Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). Откройте консоль Event Viewer (
eventvwr.msc
>) и перейдите в раздел Application and services logs -> OpenSSH -> Operational.
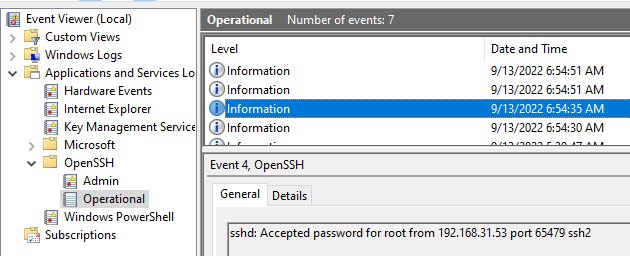
При успешном подключении с помощью к SSH серверу с помощью пароля в журнале появится событие:
EventID: 4 sshd: Accepted password for root from 192.168.31.53 port 65479 ssh2
Если была выполнена аутентификация с помощью SSH ключа, событие будет выглядеть так:
sshd: Accepted publickey for locadm from 192.168.31.53 port 55772 ssh2: ED25519 SHA256:FEHDEC/J72Fb2zC2oJNb45678967kghH43h3bBl31ldPs
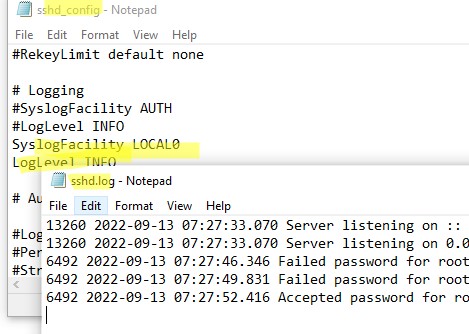
Если вы хотите, чтобы логи писались в локальный текстовый файл, нужно в файле sshd_config включить параметры:
SyslogFacility LOCAL0 LogLevel INFO
Перезапустите службу sshd и провеьте, что теперь логи SSH сервера пишутся в файл C:\ProgramData\ssh\logs\sshd.log
The latest builds of Windows 10 and Windows 11 include a build-in SSH server and client that are based on OpenSSH.
This means now you can remotely connect to Windows 10/11 or Windows Server 2019 using any SSH client, like Linux distros.
Let’s see how to configure OpenSSH on Windows 10 and Windows 11, and connect to it using Putty or any other SSH client.
OpenSSH is an open-source, cross-platform version of Secure Shell (SSH) that is used by Linux users for a long time.
This project is currently ported to Windows and can be used as an SSH server on almost any version of Windows.
In the latest versions of Windows Server 2022/2019 and Windows 11, OpenSSH is built-in to the operating system image.
How to install SSH Server on Windows 10?
Make sure our build of Windows 10 is 1809 or newer. The easiest way to do this is by running the command:
Note. If you have an older Windows 10 build installed, you can update it through Windows Update or using an ISO image with a newer version of Windows 10 (you can create an image using the Media Creation Tool). If you don’t want to update your Windows 10 build, you can manually install the Win32-OpenSSH port for Windows with GitHub.
Enable feature
We can enable OpenSSH server in Windows 10 through the graphical Settings panel:
-
Go to the
Settings>Apps>Apps and features>Optional features(or run thecommand ms-settings:appsfeatures) -
Click Add a feature, select
OpenSSH Server(OpenSSH-based secure shell (SSH) server, for secure key management and access from remote machines), and clickInstall
Install using PowerShell
We can also install sshd server using PowerShell:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Server*
Install using DISM
Or we can also install sshd server using DISM:
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
If you want to make sure the OpenSSH server is installed, run the following PS command:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like 'OpenSSH.Server*'
How to uninstall SSH Server?
Use the following PowerShell command to uninstall the SSH server:
Remove-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
How to Install SSH Server on Windows 11?
Also, you can add the OpenSSH Server on Windows 11.
- Go to Settings > Apps > Optional features;
- Click View Features;
Select OpenSSH Server from the list and click Next > Install;
Wait for the installation to complete.
The OpenSSH binaries are located in the C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\ folder.
Configuring SSH Service on Windows 10 and 11
Check the status of ssh-agent and sshd services using the PowerShell command Get-Service:
As we can see, both services are in a Stopped state and not added to the automatic startup list. To start services and configure autostart for them, run the following commands:
Start-Service sshd Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic' Start-Service 'ssh-agent' Set-Service -Name 'ssh-agent' -StartupType 'Automatic'
We also need to allow incoming connections to TCP port 22 in the Windows Defender Firewall. We can open the port using netsh:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SSHD service” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=22
Or we can add a firewall rule to allow SSH traffic using PowerShell:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
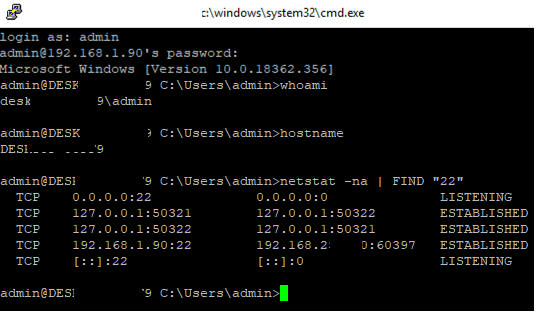
Now we can connect to Windows 10 using any SSH client. To connect from Linux, use the command:
ssh -p 22 admin@192.168.1.90
Here, the admin is a local Windows user under which we want to connect. 192.168.1.90 is an IP address of your Windows 10 computer.
After that, a new Windows command prompt window will open in SSH session.
Hint. To run the PowerShell.exe cli instead of cmd.exe shell when logging in via SSH on Windows 10, we need to run the following command in Windows 10 (under admin account):
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\OpenSSH" -Name DefaultShell -Value "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -PropertyType String -Force
Now, we change the default OpenSSH shell. From here, when connecting to Windows via SSH, you will immediately see PowerShell prompt instead of cmd.exe.
If you want to use key-based ssh authentication instead of password authentication, you need to generate a key using ssh-keygen on your client.
Then, the contents of the id_rsa.pub file must be copied to the c:\users\admin\.ssh\authorized_keys file in Windows 10.
After that, you can connect from your Linux client to Windows 10 without a password. Use the command:
ssh -l admin@192.168.1.90
Configuration
We can configure various OpenSSH server settings in Windows using the %programdata%\ssh\sshd_config configuration file.
For example, we can disable password authentication and leave only key-based auth with:
PubkeyAuthentication yes PasswordAuthentication no
Here we can also specify a new TCP port (instead of the default TCP 22 port) on which the SSHD will accept connections. For example:
Using the directives AllowGroups, AllowUsers, DenyGroups, DenyUsers, you can specify users and groups who are allowed or denied to connect to Windows via SSH:
DenyUsers theitbros\jbrown@192.168.1.15— blocks connections to username jbrown from 192.168.1.15 hostsжDenyUsers theitbros\*— prevent all users from theitbros domain to connect host using sshжAllowGroups theitbros\ssh_allow— only allow users from theitbtos\ssh_allow connect hostю- The allow and deny rules of sshd are processed in the following order:
DenyUsers,AllowUsers,DenyGroups, andAllowGroups.
After making changes to the sshd_config file, you need to restart the sshd service:
Get-Service sshd | Restart-Service –force
In previous versions of OpenSSH on Windows, all sshd service logs were written to the text file C:\ProgramData\ssh\logs\sshd.log by default.
On Windows 11, SSH logs can be viewed using the Event Viewer console (eventvwr.msc). All SSH events are available in a separate section Application and Services Logs > OpenSSH > Operational.
For example, the screenshot shows an example of an event with a successful connection to the computer via SSH. You can see the ssh client’s IP address (hostname) and the username used to connect.
sshd: Accepted password for jbrown from 192.168.14.14. port 49833 ssh2
В этой статье рассмотрим, как установить и настроить встроенный SSH сервер на базе OpenSSH в Windows 10/11 и Windows Server 2022/2019. Вы узнаете, как подключиться к системе по защищенному SSH протоколу, как это делается в Linux.
Приобрести оригинальные ключи активации Windows Server можно у нас в каталоге от 1190 ₽
Установка OpenSSH сервера в Windows
OpenSSH сервер включен в современные версии Windows 10 (начиная с 1803), Windows 11 и Windows Server 2022/2019 как Feature on Demand (FoD). Установить его можно несколькими способами.
1. Установка через PowerShell:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like 'OpenSSH.Server*' | Add-WindowsCapability -Online
2. Установка через DISM:
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
3. Через панель «Параметры»:
— Перейдите в Настройки -> Приложения -> Дополнительные компоненты -> Добавить компонент.
— Найдите OpenSSH Server и нажмите Установить.
4. Установка с помощью MSI пакета:
Вы можете установить OpenSSH с помощью MSI установщика, доступного на GitHub:
Invoke-WebRequest https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/download/v8.9.1.0p1-Beta/OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -OutFile $HOME\Downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -UseBasicParsing
msiexec /i c:\users\root\downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi
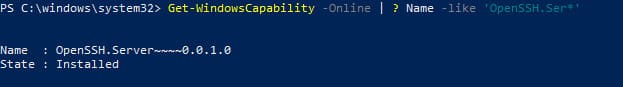
Чтобы проверить, что OpenSSH сервер установлен, выполните:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like 'OpenSSH.Ser*'
State : Installed
Настройка SSH сервера в Windows
После установки OpenSSH на Windows появляются две службы:
— ssh-agent (для управления ключами если вы настроили SSH аутентификацию по ключам)
— sshd (собственно сам SSH сервер)
1. Настройка автозапуска SSH службы:
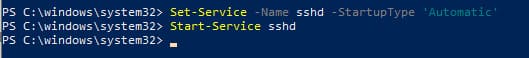
Выполните команду PowerShell для включения автозапуска SSH сервера:
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Start-Service sshd
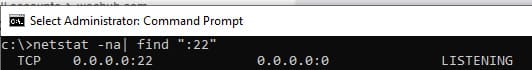
2. Проверка порта SSH:
Убедитесь, что сервер слушает на порту TCP:22:
netstat -na | find ":22"
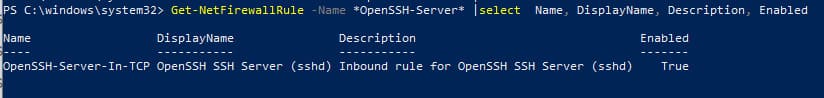
3. Настройка брандмауэра:
Убедитесь, что брандмауэр разрешает подключения по SSH:
Get-NetFirewallRule -Name *OpenSSH-Server* |select Name, DisplayName, Description, Enabled
Если правило отключено, включите его:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
Если правило отключено (состоянии Enabled=False) или отсутствует, вы можете создать новое входящее правило командой New-NetFirewallRule:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
Конфигурация файла sshd_config
Конфигурационный файл OpenSSH сервера находится по пути C:\ProgramData\ssh\sshd_config. Вы можете отредактировать его через любой текстовый редактор. Например, откройте файл с помощью блокнота:
start-process notepad C:\ProgramData\ssh\sshd_config
1. Запрет подключения для пользователей/групп:
— Запретить подключение для определенного пользователя:
DenyUsers softcomputers\[email protected]
DenyUsers corp\*
— Разрешить доступ только для локальной группы:
AllowGroups sshadmins
2. Изменение порта SSH:
Для смены порта измените значение директивы Port.
После изменений не забудьте перезапустить службу:
Restart-Service sshd
3. Чтобы разрешить подключение только для определенной доменной группы:
AllowGroups softcomputers\sshadmins
По умолчанию могут к openssh могут подключаться все пользователи Windows. Директивы обрабатываются в следующем порядке: DenyUsers, AllowUsers, DenyGroups,AllowGroups.
4. Можно запретить вход под учетными записями с правами администратора, в этом случае для выполнения привилегированных действий в SSH сессии нужно делать runas.
DenyGroups Administrators
Следующие директивы разрешают SSH доступ по ключам и по паролю
PubkeyAuthentication yes
PasswordAuthentication yes
5. Вы можете изменить стандартный SSH порт TCP/22, на котором принимает подключения OpenSSH в конфигурационном файле sshd_config в директиве Port.
6. После любых изменений в конфигурационном файле sshd_config нужно перезапускать службу sshd:
restart-service sshd
Подключение по SSH к Windows компьютеру
Для подключения к Windows через SSH можно использовать любые SSH клиенты (например, PuTTY или встроенный клиент Windows). Пример команды для подключения:
ssh [email protected]
В этом примере alexbel – имя пользователя на удаленном Windows компьютере, и 192.168.31.102 – IP адрес или DNS имя компьютера.
Обратите внимание что можно использовать следующие форматы имен пользователей Windows при подключении через SSH:
alex@server1 – локальный пользователь Windows
[email protected]@server1 – пользователь Active Directory (в виде UPN) или аккаунт Microsoft/ Azure(Microsoft 365)
softcomputers\alex@server1 – NetBIOS формат имени
Если используется аутентификация по Kerberos в домене, включите ее в конфигурационном файле:
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
После этого можно прозрачно подключать к SSH серверу с Windows компьютера в домене из сессии доменного подключения. В этом случае пароль пользователя не указывается и выполняется SSO аутентификация через Kerberos:
ssh -K server1
При первом подключении появится стандартный запрос на добавление узла в список известных SSH хостов.
Нажимаем — «Да»
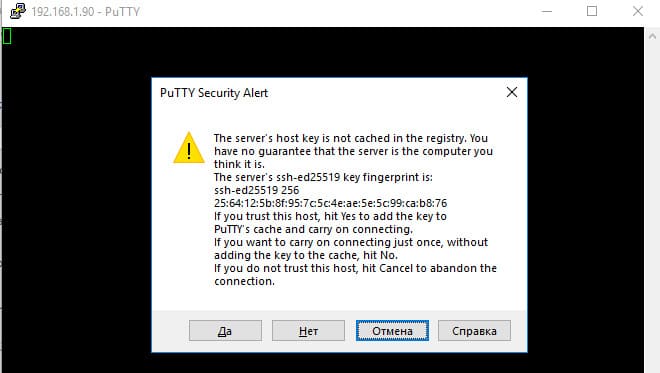
В открывшееся окне авторизуемся под пользователем Windows.
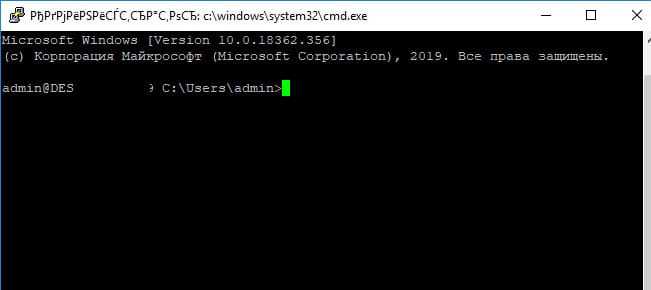
При успешном подключении запускается командная оболочка cmd.exe со строкой-приглашением.
admin@win10tst C:\Users\admin>
В командной строке вы можете выполнять различные команды, запускать скрипты и приложения.

Чтобы запустить интерпретатор PowerShell, выполните:
powershell.exe
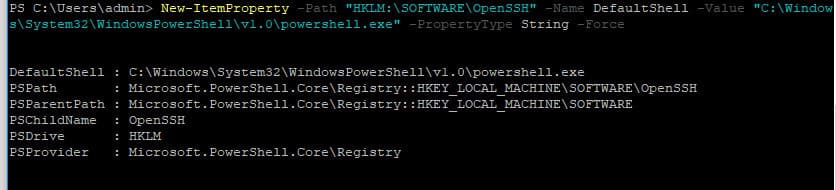
Чтобы изменить командную оболочку (Shell) по умолчанию в OpenSSH с cmd.exe на PowerShell, внесите изменение в реестр следующей командой:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\OpenSSH" -Name DefaultShell -Value "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -PropertyType String –Force
Осталось перезапустить SSH подключение и убедиться, что при подключении используется командный интерпретатор PowerShell
(об этом свидетельствует приглашение PS C:\Users\admin>).
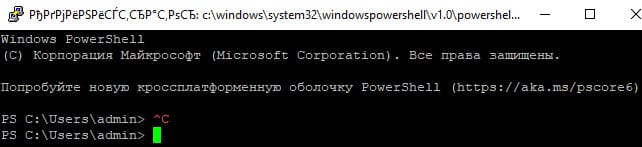
В SSH сессии запустилась командная строка PowerShell, в которой работают привычные функции: авто дополнение, раскраска модулем PSReadLine, история команд и т.д. Если текущий пользователь входит в группу локальных администраторов, то все команды в его сессии выполняются с повышенными правами даже при включенном UAC.
Логи SSH подключений в Windows
Логи SSH подключений пишутся в журнал событий Windows через Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). Чтобы просмотреть логи:
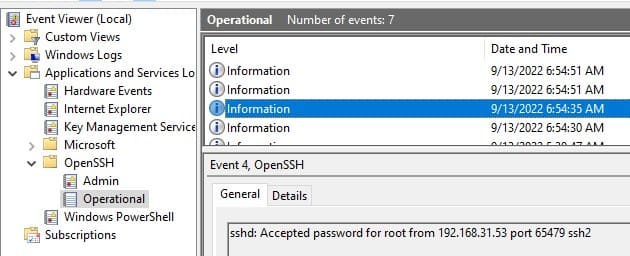
1. Откройте Event Viewer (eventvwr.msc).
2. Перейдите в Application and Services Logs -> OpenSSH -> Operational.
Пример события успешного подключения по паролю:
EventID: 4
sshd: Accepted password for user1 from 192.168.31.102 port 55432 ssh2
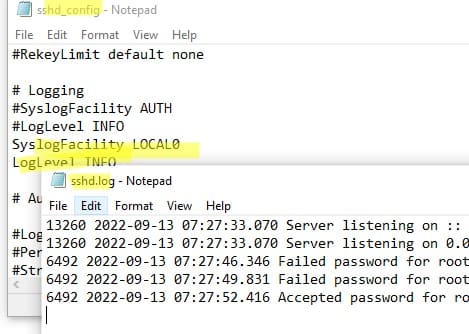
Если необходимо, вы можете настроить запись логов в текстовый файл. Для этого добавьте в файл sshd_config директивы:
SyslogFacility LOCAL0
LogLevel INFO
Перезапустите службу sshd для применения изменений и проверьте, что теперь логи SSH сервера пишутся в файл C:\ProgramData\ssh\logs\sshd.log
Теперь вы знаете, как настроить и использовать OpenSSH сервер на Windows для удаленного подключения по защищенному протоколу SSH.
In this article I’m going to show you can use SSH on Windows machines. We’ll go over the installation of OpenSS, basic SSH configuration, as well as connecting to and from a Windows and Linux machine.
The Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol is a network protocol that allows secure access to interact with remote network resources over port 22. SSH is commonly used for remote login and command-line execution for administrative purposes. Microsoft Windows uses an implementation of OpenSSH to implement the SSH protocol and actively maintains this software project on GitHub under the openssh-portable repository.
Did you know that you can even use SSH to mount a filesystem with SSHFS, create a transparent proxy with SSHuttle, and copy files back and forth between systems using SCP? There are many amazing uses that includes the SSH protocol! If you’re curious about more implementations of the SSH protocol you can learn more here.
Installation
In order to use OpenSSH we need to first install the Microsoft.OpenSSH.Beta package using Microsoft Package Manager (winget). For those unfamiliar with the Windows Package Manager, I wrote a blog post on winget.
Searching For the OpenSSH Package
In order to find the OpenSSH package to install we are going to use the Windows Package Manager through a PowerShell terminal to search for available packages.

winget search openssh
Once we have the name of the package, Microsoft.OpenSSH.Beta we can verify this package by showing package details using winget.
Is OpenSSH Already Installed?
We can check if OpenSSH is installed or not using the winget list command.
winget list Microsoft.OpenSSH.Beta

winget list Microsoft.OpenSSH.Beta
If OpenSSH is already installed we can skip the installation process.
OpenSSH Package Metadata
When searching for applications and packages using Microsoft winget it’s a good idea to show the package metadata before installing, especially if this package is not something you’re familiar with.
winget show Microsoft.OpenSSH.Beta

winget show Microsoft.OpenSSH.Beta
Using the show command allows us to see critical information regarding this package including: publisher, source, release notes, and security fixes. Keeping up with package security is essential!
Installing the OpenSSH Package
Once we’ve found and verified the OpenSSH package we can move on to installing the package using winget. During the installation we can verify the Installer Url is indeed the URL we saw from the previous show command. The Windows Package Manager will also verify the hash for us!
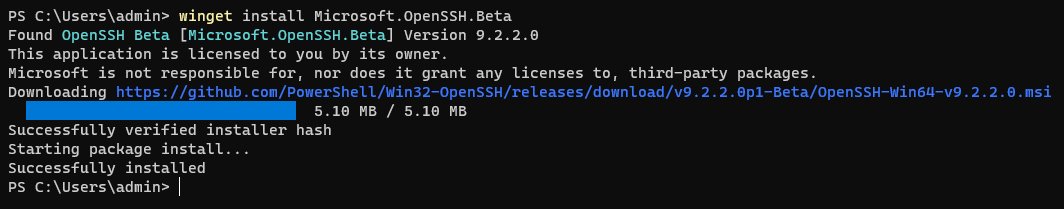
winget install Microsoft.OpenSSH.Beta
Enabling the ssh-agent Service
Once installed we can ensure that the ssh-agent service is enabled and started on our Windows machine using a powershell terminal. It’s important to note that this must be done through an Administrator terminal.
Elevate Terminal
I suggest using gsudo to elevate the current terminal. The tool gsudo is the Windows equivalent of the Linux sudo command. If you don’t have gsudo already installed you can use this guide to setup gsudo.
If gsudo is already installed we can elevate the current terminal window with the following command.
Enable ssh-agent Service
Once the current terminal is elevated with Administrator privileges we can run use the Set-Service command to enable the ssh-agent service to be a persistent service which starts up automatically.
Set-Service ssh-agent -StartupType Automatic
Start ssh-agent Service
Once we have our ssh-agent enabled as a persistent service we can start this service directly with the Start-Service command.
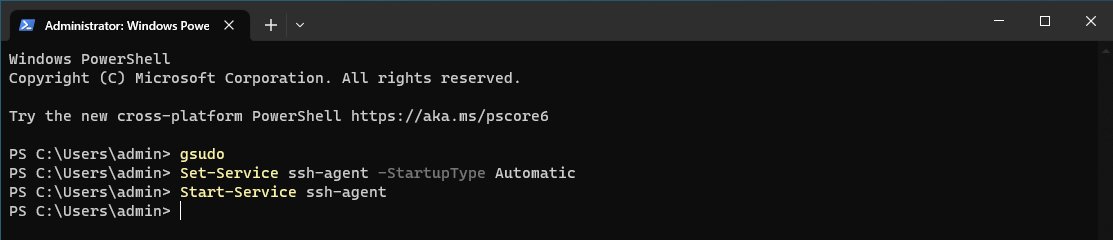
Sequence of commands to enable & start ssh-agent service
Generate SSH Keys
After we have enabled and started the ssh-agent service we can move onto generating an ssh keypair. This can be accomplished using the ssh-keygen command. In our terminal run the following command.
This command will generate a new ssh key-pair for us and will ask us to provide the file to save the key as. Additionally, we will be asked to provide a key password, we can hit enter twice to use a passwordless key.
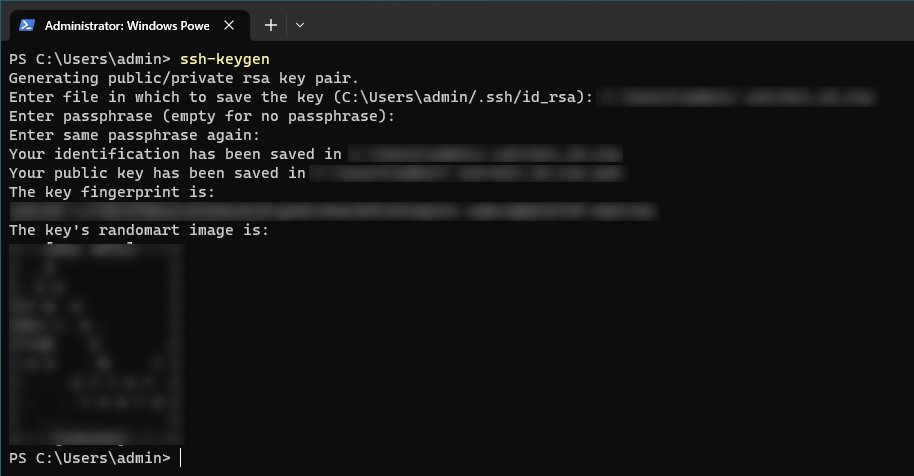
Generating a new ssh key-pair using the ssh-keygen command
Adding the SSH Key to the Authentication Agent
Once our ssh key-pair has been generated we can move onto adding our private key to the ssh agent using the ssh-add command. This important step adds our key to the authentication agent which we need in order to authenticate with our key-pair.
ssh-add 'C:\Users\admin\.ssh\win_id_rsa'
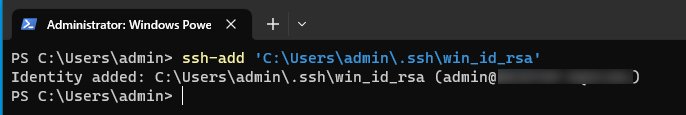
Connecting to Windows From Linux
After we’ve successfully added our ssh key to the authentication agent with ssh-add we are ready to test ssh authentication using our .pub public key.
In this example I’m going to connect to my Windows machine from my Linux machine. First we need to ensure that the public key we just generated is on the machine we want connect from. Since I’m using virtual machines I’ll simply move my key over using a shared folder from my host.
The Windows public ssh key located on my Linux machine
We also need to know the IP address of our Windows machine, we can find this information out easily with PowerShell with the Get-NetIPAddress command.
Get-NetIPAddress -AddressFamily IPv4 | Format-Table
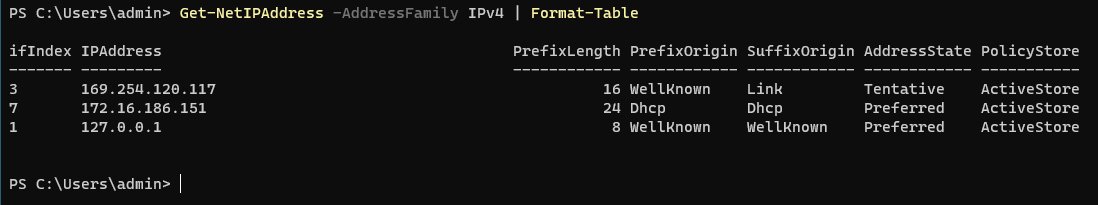
Get-NetIPAddress command output
Once we have our public key on our Linux machine and the IP address of our Windows machine we are ready ssh to our Windows machine.
To confirm we are on a Linux machine we can use the uname -a command.
Running the uname -a command
To ssh to our Windows machine we can run the following command providing our username, IP address, as well as public key.
ssh admin@172.16.186.151 -i win_id_rsa.pub
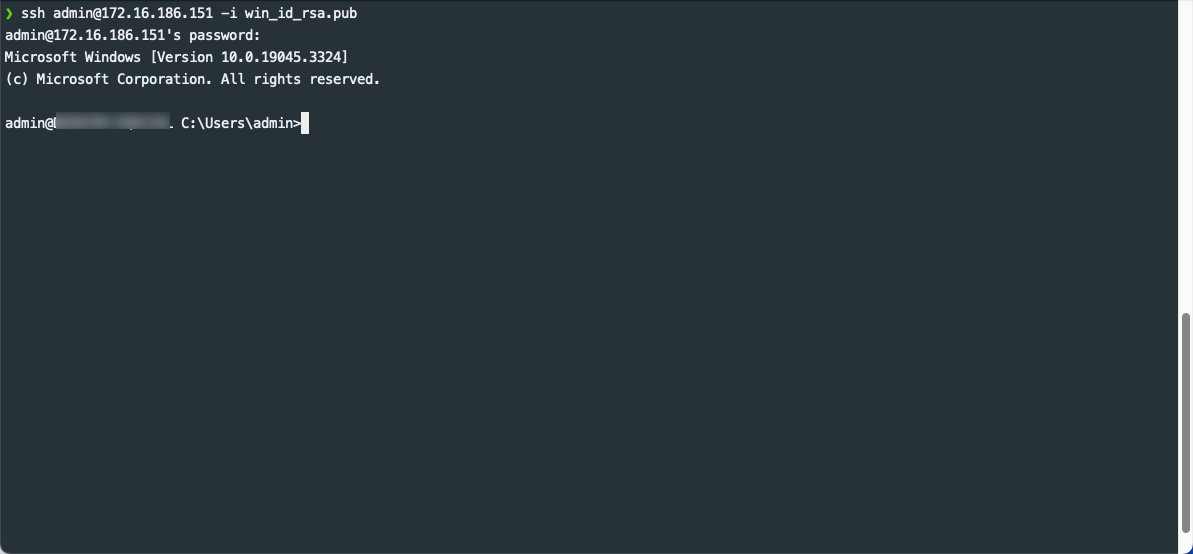
Running the SSH command to connect to Windows from Linux
If successful you’ll see a Microsoft Windows command-line terminal from your Linux.
Connecting to Linux From Windows
If we would like to connect to our Linux machine from our Windows machine we can perform the opposite steps. Similar to the above we need to do the following (if you already have a key-pair for your Linux machine setup feel free to skip the “Ensuring SSH Is Installed on Linux” section).
Ensuring SSH Is Installed on Linux
In this section I will use an Ubuntu Desktop as my Linux machine. We need to perform some administrative tasks to ensure that we are able to connect to our Linux machine from Windows
Install SSH
If SSH is not already installed we can install using apt install.
Running the sudo apt install -y ssh
Start & Enable the SSH Service
Once the ssh package as well as dependant packages are installed we can start the ssh service using the following the systemctl command.
You can also ensure that the ssh starts in a persistent manner when the Ubuntu machine boots.
sudo systemctl enable ssh
Generate SSH keys
Similar to how we generated a key-pair on Windows, we can use the same command on Linux to generate a new SSH key-pair. We can do so with the ssh-keygen command.
Like when we did with Windows we’ll be required to give the output location of our key-pair as well as provide an optional password.
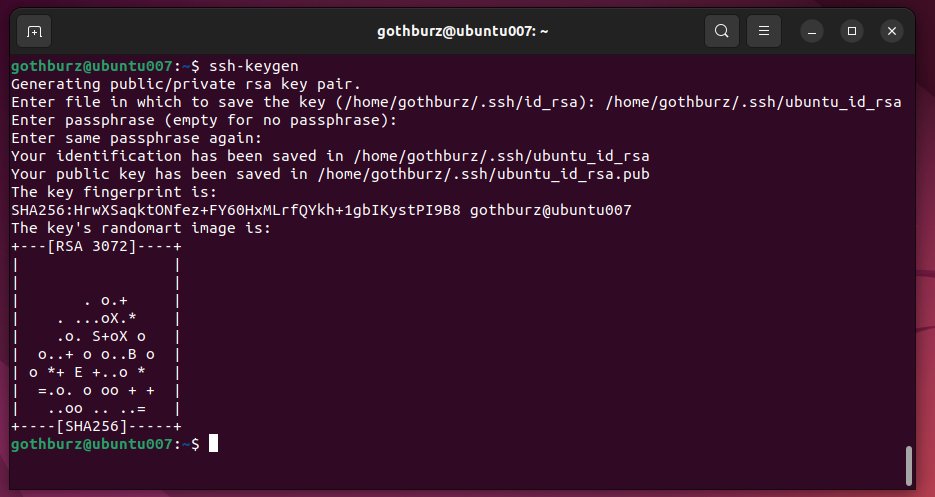
Running the ssh-keygen command
Adding the SSH Key with ssh-add
Once we’ve generated the ssh key we can proceed to add the private key to the ssh authentication agent using ssh-add command by running.
ssh-add /home/gothburz/.ssh/ubuntu_id_rsa
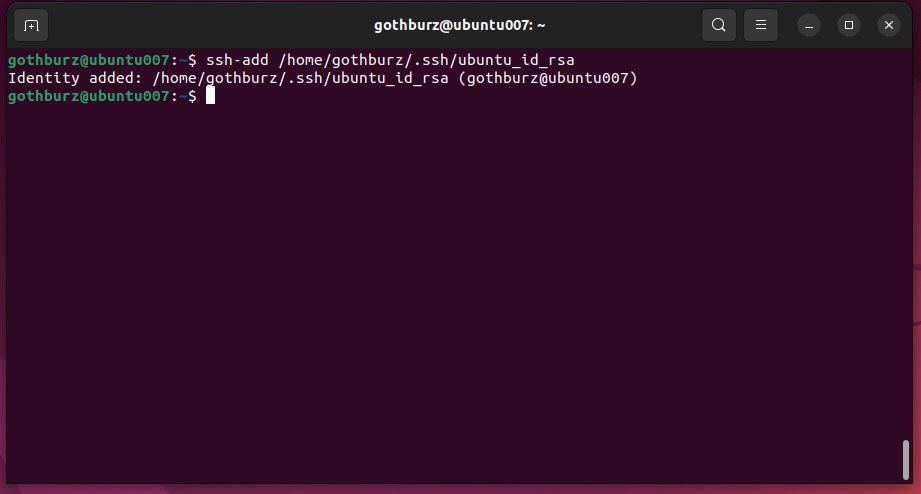
Running the ssh-add command
Copy SSH Public Key to Windows Machine
Once we have ensured that ssh is properly up and running including adding our key-pair to the ssh authentication agent we need to ensure we copied our public key over to our Windows machine
Since I’m using virtual machines I’ll simply move my key over using a shared folder from my host.
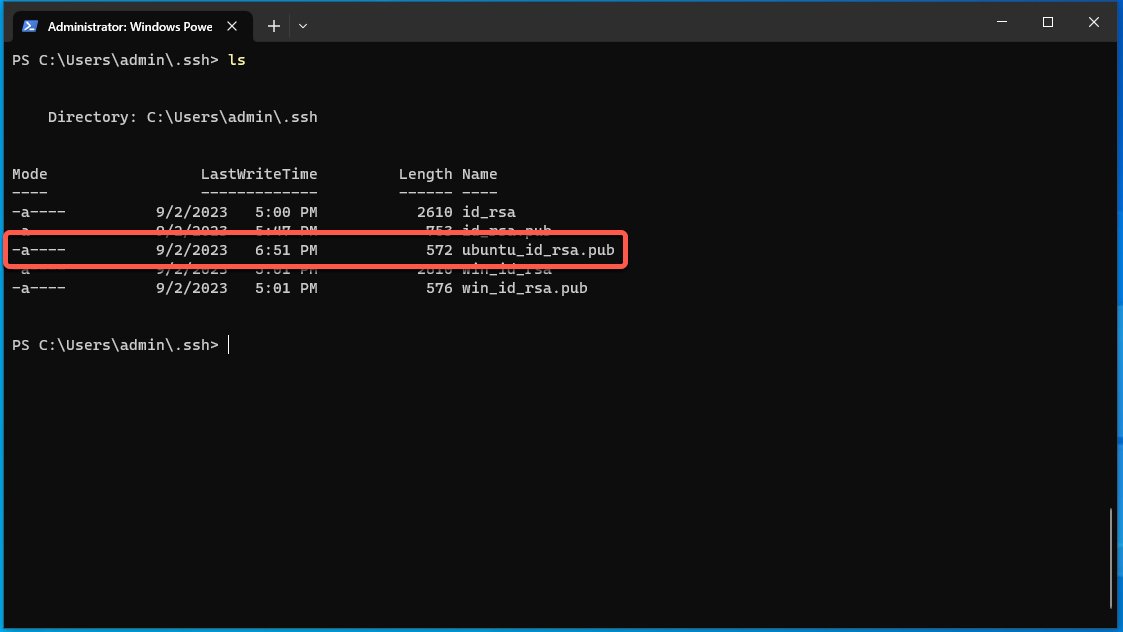
Verifying the Linux SSH public key with the ls command
Connecting to Linux from Windows Machine
Once we have ensured that our Linux machine is properly configured with SSH and that our public ssh key is on our Windows machine we can go ahead and initiate an SSH connection.
We can use the ssh command to initiate the connection from Windows to Linux using powershell.
Be sure to change your username@host as well as the path to the public key.
ssh gothburz@172.16.186.163 -i .\ubuntu_id_rsa.pub

Connecting to our Linux machine from Windows with the ssh command
Depending on your configuration you might be asked for a password as well. Once you’ve ran the ssh command and entered the correct password you should enter a new Linux terminal from Windows. Congrats!
Learn More About SSH
If you’d like to add a definitive guide to SSH to your library then I highly recommend the following book. Written for a wide audience, this book covers the Secure Shell (SSH) in great detail by providing a comprehensive guide for a plethora of use cases, features, and even contains in-depth case studies on large, sensitive computer networks.
Conclusion
In this blog post we looked at how to use the SSH protocol on Microsoft Windows using OpenSSH. We went through the following:
-
The OpenSSH installation process with the Windows Package Manager (WinGet)
-
The SSH configuration process
-
How to connect to Windows from Linux
-
How to connect to Linux from Windows
I hope you found this post insightful and useful in your day-to-day operations.
Let me know if you have any questions regarding SSH and happy connecting! 
SSH-server based on the OpenSSH package is part of the operating system in all modern versions of Windows. In this article, we’ll show you how to install and configure the OpenSSH server on Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2022/2019 and connect to it remotely via a secure SSH connection (just like in Linux 🙂).
Contents:
- How to Install OpenSSH Server on Windows
- Configuring SSH Server on Windows
- Sshd_config: OpenSSH Server Configuration File
- How to Connect to a Remote Windows Computer via SSH?
- Checking SSH Connection Logs in Windows
How to Install OpenSSH Server on Windows
The OpenSSH Server package is a part of all modern versions of Windows 10 (starting with 1803), Windows 11, and Windows Server 2022/2019 as a Feature on Demand (FoD). To install the OpenSSH server, open the elevated PowerShell prompt and run the command:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like ‘OpenSSH.Server*’ | Add-WindowsCapability –Online
Or using DISM:
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
If your computer is directly connected to the Internet, the OpenSSH.Server package will be downloaded and installed on Windows.
You can also install OpenSSH on Windows 10/11 through the modern Settings panel (Settings -> Apps and features -> Optional features -> Add a feature). Find Open SSH Server in the list and click Install.
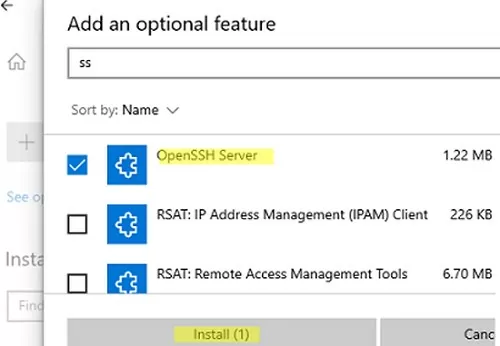
On computers in disconnected (offline) environments, you can install the OpenSSH Server from the Feature on Demand ISO image (available in your account on the Microsoft websites: MSDN or my.visualstudio.com). Download the ISO and extract its contents to the E:\FOD folder (you can only extract the file OpenSSH-Server-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~.cab) and install the Windows feature from the local repository:
Add-WindowsCapability -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0 -Online -Source E:\FOD
An MSI installer for OpenSSH for Windows is also available in the official Microsoft repository on GitHub (https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/). For example, for Windows 10 x64, you need to download and install the OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi package. The following PowerShell command will download the MSI file and install the OpenSSH client and server on your computer:
Invoke-WebRequest https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/download/v8.9.1.0p1-Beta/OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -OutFile $HOME\Downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -UseBasicParsing
msiexec /i $HOME\Downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi
You can install an OpenSSH server in previous Windows versions as well (Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2016/2012R2/2012). Check the example on how to install and configure Win32-OpenSSH in the article “How to Configure SFTP Server (SSH FTP) on Windows?”.
To make sure the OpenSSH server has been installed, run the command:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like 'OpenSSH.Ser*'
State : Installed

Configuring SSH Server on Windows
After installing the OpenSSH server on Windows, two services are added:
- ssh-agent (OpenSSH Authentication Agent) – can be used to manage private keys if you have configured SSH key authentication;
- sshd (OpenSSH SSH Server).
You need to change the startup type of the sshd service to automatic and start the service using PowerShell:
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Start-Service sshd

Use the netstat command to make sure that the SSH server is running and waiting for the connections on TCP port 22:
netstat -na| find ":22"

Make sure that Windows Defender Firewall allows inbound connections to Windows through TCP port 22:
Get-NetFirewallRule -Name *OpenSSH-Server* |select Name, DisplayName, Description, Enabled
Name DisplayName Description Enabled ---- ----------- ----------- ------- OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) Inbound rule for OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) True
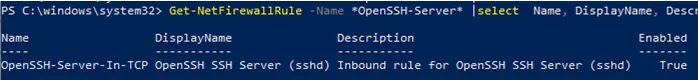
If the rule is disabled (Enabled=False) or missing, you can create a new inbound rule using the New-NetFirewallRule cmdlet:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
By default, key OpenSSH components are located in these folders:
- OpenSSH Server executables:
C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\(sshd.exe, ssh.exe, ssh-keygen.exe, sftp.exe, etc.) - The sshd_config file (created after the first service start of the service):
C:\ProgramData\ssh - The authorized_keys file and keys can be stored in the user profile folder:
%USERPROFILE%\.ssh\
Sshd_config: OpenSSH Server Configuration File
You can change your OpenSSH server settings in the config file: %programdata%\ssh\sshd_config. This is a plain text file with a set of directives. You can use any text editor for editing:
start-process notepad C:\Programdata\ssh\sshd_config
For example, to deny SSH connection for a specific domain user account (or all users in the specified domain), add these directives to the end of the file:
DenyUsers woshub\[email protected] DenyUsers corp\*
To allow SSH connection to the specific domain security group only:
AllowGroups woshub\sshadmins
You can allow access to a local user group:
AllowGroups sshadmins
By default, all Windows users can connect to OpenSSH. Directives in the sshd_config files are processed in the following order: DenyUsers, AllowUsers, DenyGroups, AllowGroups.
You can deny SSH login for the accounts with administrator privileges. In this case, if you need to perform any privileged actions in your SSH session, you will have to use runas.
DenyGroups Administrators
The following directives allow you to access Windows using SSH private keys or a password.
PubkeyAuthentication yes PasswordAuthentication yes
You can change the default TCP/22 port on which OpenSSH Server connections are accepted in the sshd_config configuration file using the Port directive.
After making any changes to the sshd_config file, you need to restart the sshd service
restart-service sshd
How to Connect to a Remote Windows Computer via SSH?
Now you can try to connect to your Windows 10 computer using the SSH client (I’m using putty in this example).
You can use the built-in Windows SSH client to connect to a remote host. To do this, open the command prompt and run the following command:
ssh [email protected]
In this example, max is the username on the remote Windows computer, and 192.168.13.12 is the IP address or DNS name of the computer.
Note that you can use the following username formats when connecting to Windows via SSH:
max@server1– local Windows user[email protected]@server1– Active Directory user or Microsoft/Azure account (use the UserPrincipalName format)woshub\max@server1– NetBIOS name format
In an Active Directory domain, you can use Kerberos authentication in SSH. To do this, you need to enable the following directive in sshd_config:
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
You can now transparently connect to an SSH server from a domain-joined Windows machine with a domain user session. In this case, the user’s password will not be requested, and SSO authentication via Kerberos will be performed:
ssh -K server1
The first time you connect, you will be prompted to add the host to the list of known SSH hosts (C:\Users\your_user\.ssh\known_hosts).
Click Yes, and login under your Windows user account.
If the SSH connection is successful, you will see the cmd.exe shell prompt.
admin@win10pc C:\Users\admin>
You can run different commands, scripts, and apps in the SSH command prompt.
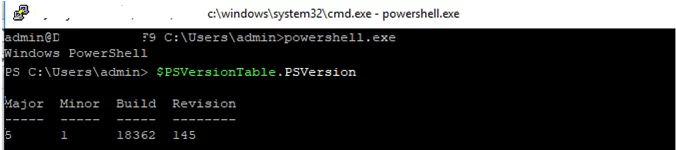
I prefer working in the PowerShell console. To start it, run:
powershell.exe
In order to change the default cmd.exe shell in OpenSSH to PowerShell, make changes to the registry using the following PowerShell command:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\OpenSSH" -Name DefaultShell -Value "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -PropertyType String –Force

Restart your SSH connection and make sure that PowerShell is now used as a default SSH shell (this is indicated by the prompt PS C:\Users\admin>).
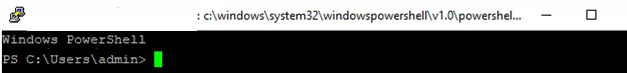
The PowerShell prompt has been started in my SSH session, where the usual functions work: tab autocomplete, PSReadLine syntax highlighting, command history, etc. If the current user is a member of the local administrators’ group, all session commands are executed elevated even if UAC is enabled.
OpenSSH server on Windows can be used in various SSH tunneling scenarios.
Checking SSH Connection Logs in Windows
By default in Windows SSH server connection logs are written not to text files, but to a separate event log via Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). Open the Event Viewer console (eventvwr.msc ) and navigate to Application and services logs -> OpenSSH -> Operational.
If you successfully connect to the SSH server using a password, an event will appear in the log:
EventID: 4 sshd: Accepted password for root from 192.168.1.53 port 65749 ssh2
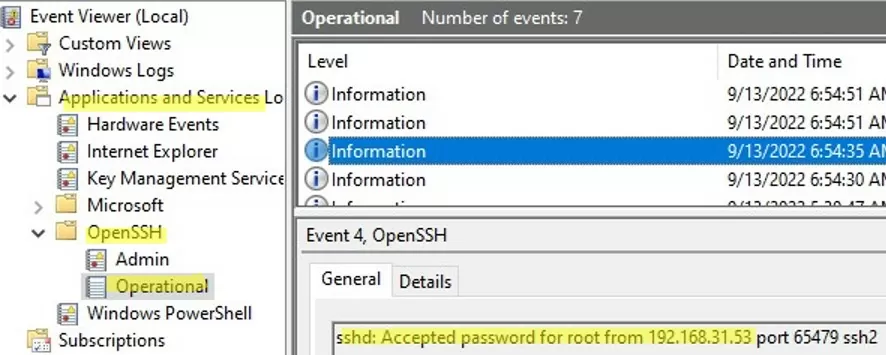
If SSH key authentication was performed, you will see the following event:
sshd: Accepted publickey for locadm from 192.168.1.53 port 61426 ssh2: ED25519 SHA256:FEHDEC/G42FS23209C2KMb4335923pigN31s3qMK322lGibD
If you want the SSH connection logs to be written to a local text file, you need to enable the following parameters in the sshd_config file:
SyslogFacility LOCAL0 LogLevel INFO
Restart the sshd service and make sure that the SSH server logs are now written to a plain text file C:\ProgramData\ssh\logs\sshd.log
You can use a secure SSH connection with PSRemoting to manage remote computers via WinRM.
