To run a Bash script on Windows, you can use the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) or Git Bash to execute your script directly from the command line.
Here’s a code snippet to run a Bash script:
bash your_script.sh
Understanding Bash Scripts
What is a Bash Script?
A Bash script is a file that contains a series of commands that the Bash interpreter can execute. These scripts enable you to automate tasks that you would normally perform in the command line interface, making repetitive tasks easier and more efficient. Common use cases for Bash scripts include automating backups, running scheduled tasks, and managing system resources.
The Benefits of Using Bash Scripts
Using Bash scripts has several advantages:
- Efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks through scripts, you save time and reduce the possibility of human error.
- Flexibility: Bash scripts can be used in conjunction with various tools and commands available in a Unix-like environment, extending their capabilities.
- Cross-Platform Nature: Bash scripts can often be run on different operating systems, allowing for more versatile development and deployment options.

Bash Script Options: A Quick Guide to Mastering Choices
Prerequisites for Running Bash Scripts on Windows
Setting Up the Environment
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) enables you to run a Linux distribution alongside your Windows operating system. This allows you to execute Bash scripts natively within a Linux environment. To enable WSL on Windows 10 or 11, follow these steps:
- Open PowerShell as Administrator.
- Run the command:
wsl --install
- Restart your computer.
After installation, you can choose a Linux distribution like Ubuntu from the Microsoft Store.
Installing a Bash Shell
Using Ubuntu / Debian on WSL
Once WSL is enabled, install a Linux distribution from the Microsoft Store. Simply search for «Ubuntu» or «Debian» and click the «Install» button. Upon successful installation, launch the application to complete the setup.
Alternatives
If you prefer not to use WSL, you can opt for Git Bash or Cygwin. Both environments provide a Bash-like experience on Windows.

Run Bash Script: Your Quick-Start Guide to Success
Executing Bash Scripts on Windows
Creating a Bash Script
Writing a Bash script begins with a text editor. Here’s how to create a simple Bash script called `hello.sh` that prints «Hello, World!».
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello, World!"
The first line, known as the shebang (`#!/bin/bash`), indicates which interpreter should be used to run the script.
Running Bash Scripts in WSL
Navigating the Terminal
To run Bash scripts within WSL, you must first open your chosen Linux distribution terminal and navigate to the directory where your script is saved. You can use basic terminal commands such as `cd` (change directory) and `ls` (list files).
Execution Commands
There are two main methods to execute your Bash script in WSL:
- Basic Execution: You can run the script directly by typing:
bash hello.sh
- Making it Executable: To run the script without having to prefix it with `bash`, you can make it executable:
chmod +x hello.sh
After this, you can execute it using:
./hello.sh
Running Bash Scripts in Git Bash
Setting Up Git Bash
To use Git Bash, you first need to install Git for Windows. You can find the installer on the [official Git website](https://git-scm.com/download/win). During installation, you can choose the relevant options to set up your Bash environment.
Executing Scripts in Git Bash
Just like in WSL, create the `hello.sh` script in Git Bash. To run the script, you simply navigate to its directory and execute the following command:
bash hello.sh
Running Bash Scripts in Cygwin
Cygwin Setup
Cygwin provides a large collection of GNU and Open Source tools which provide functionality similar to a Linux distribution on Windows. To install Cygwin, navigate to the [Cygwin website](https://www.cygwin.com/) and download the installer. Follow the setup instructions, selecting the packages you wish to install.
Executing Scripts in Cygwin
After creating your Bash script in the Cygwin terminal, the execution process is similar. Use the `bash` command or mark the script as executable before running it.

Run Bash Script on Mac: A Simple Guide
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Handling Script Errors
When running Bash scripts, you may encounter common error messages, such as «command not found» or «permission denied.» These can be addressed through basic troubleshooting steps—ensure that the command is correctly spelled, the script file exists, and you have the necessary permissions.
Performance Issues
If your Bash script runs slowly, investigate any potential bottlenecks, such as infinite loops or redundant function calls. Optimizing your scripts can lead to better performance and faster execution times.

Mastering Bash for Windows: A Quick Guide for Beginners
Best Practices for Writing and Running Bash Scripts on Windows
Script Organization
For clarity, ensure that your scripts are well-organized. Use comments to document sections of code and explain the purpose of specific commands. This practice not only benefits you but also helps anyone else who may need to use or modify your scripts in the future.
Testing Scripts
Before deploying any scripts, it’s essential to test them thoroughly. Run your scripts in a safe environment and use tools like ShellCheck to check for syntax errors and coding best practices.

Bash Script Closure: Quick Guide to Mastering It
Conclusion
Being able to run Bash scripts on Windows significantly enhances your productivity and allows you to harness the power of automation. By following the steps outlined above, you can easily set up your environment, write and execute Bash scripts effectively. The combination of WSL, Git Bash, and Cygwin provides robust options for integrating Bash into your workflow.

Bash Script Beginner: Your Quick Start to Shell Mastery
Further Reading and Resources
For those looking to deepen their knowledge, check out recommended books, websites, and forums for Bash scripting. Explore tutorials and resources on WSL, Git Bash, and Cygwin to continue your journey into the world of Bash scripting.
- To run shell scripts on Windows, you must enable WSL and Virtual Machine Platform, install a WSL distro, and use “Bash Script.sh” to execute it.
- Alternatively, use third-party tools like Cygwin, Cmder to run Linux commands on top of Windows OS.
If you have worked with Linux distributions and repositories, you would know what shell scripts are. To run shell scripts on top of a Windows computer can be challenging, as the process is not quite straightforward.
Shell scripts are a piece of code written in plain text but have the “.SH” file extension. These are usually used to automate tasks and execute Linux or Unix packages. These are written in Bash and start with “#! /bin/sh“.
You do not need to install a Linux or Unix distribution alongside your Windows operating system to run a shell script. In this article, we’ll show you how to run a shell script on a Windows PC.
Table of Contents
What are Shell (.SH) Files
The Linux/Unix operating system uses shell or .SH script files to perform certain tasks. In comparison, it can be substituted by Windows batch files for the Windows operating systems, which are used to execute commands on a computer.
The Batch language is a simple and interpreted programming language, unlike C++ or C#. However, you do not have to translate a shell script file to batch to perform similar tasks on a Windows computer, as you do on a Linux PC.
There are different methods to run the same .SH file on a Windows computer as on a Linux system. Let us show you how to run a shell file on a Windows PC.
Run Shell Script (.SH) File on Windows
There are both native and third-party methods to run shell files on a Windows computer. You can use Cygwin, or a third-party tool of your choice, to run a shell script on Windows OS. Alternatively, you can install the Windows Subsystem for Linux feature on Windows and then execute the shell script file through it.
Below you’ll find the methods to run the file using both methods.
Run Shell Script File using Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
This section has been divided into 3 steps to make the process easier to understand. You must do the following 3 things to run a shell script file in the given order:
- Install WSL
- Install a Linux distro
- Run the shell script file
Note: If you are performing these steps on a Virtual Machine, then you will need to enable Nested Virtualization.
Install WSL
Use the following steps to install WSL on your computer:
-
Press the Windows Key + R shortcut keys to open the Run Command box.
-
Type in “optionalfeatures” and press Enter.
Open the Optional Features applet -
Select “Windows Subsystem for Linux” and “Virtual Machine Platform,” and then click Ok.
Enable WSL and Virtual Machine Platform The wizard will now install WSL.
-
When the installation is completed, click “Restart now.”
Restart computer
Once the computer restarts, it is time to install a Linux distro.
Install a Linux Distribution
Use the following steps to install a Linux distribution:
-
When it restarts, press Windows Key + R again to open Run.
-
Type in “cmd” and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to run Command Prompt as administrator.
-
Run the following command to obtain a list of available Linux distros:
wsl --list --onlineGet list of all available Linux distros in Command Prompt Note down the name of the distro you want to install.
-
Use the following command to install the preferred distro while substituting its name:
wsl --install -d [DistributionName]Install a Linux distro in WSL The distro will now begin to download and install.
-
Set up a username and password.
Set up username and password -
Restart the computer.
Now, the next step is to simply run the shell script file.
Run the Shell Script File
Follow the simple steps below to run the shell script file on a Windows PC:
-
Press the Windows Key + R again to open Run.
-
Type in “cmd” and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to run Command Prompt as administrator.
-
Use the CD cmdlet to change the directory to the location of the shell script file.
CD [PathToShellScriptFile]Change directory to the shell script file location -
Now, use the following command to run the shell script file while substituting [ShellFileName] with the complete and correct name of the shell file:
Bash [ShellFileName].shRun the shell script file using Windows Subsystem for Linux
This is how you run a shell script (.SH) file on a Windows computer using WSL.
If this seems like a lengthy process for you, then you can also use the alternative method given below.
Run Shell Script File using Third-Party Tools
You can also run a shell script file on a Windows computer using a third-party tool. In the steps below, we have used Cygwin.
Follow these steps to run a .SH file on a Windows PC:
-
First, download and install Cygwin from their official website.
-
Once installed, run the Cygwin app.
-
In the Cygwin terminal, use the
CDcommand to change the directory to the shell script file location.Note: In Cygwin, the syntax to change the directory is different from Command Prompt or PowerShell. Use the following command syntax and example in the image to change your directory in Cygwin.
CD /cygdrive/[driveLetter]/[Subfolder1]/[Subfolder2]Change directory to the shell script file location in Cygwin -
Now, make the shell script file executable through this command:
chmod +x [ShellFileName].shMake the shell script file executable -
Now, use the following syntax to run the shell script file:
./[ShellFileName].shRun shell script file on Windows using Cygwin
These are the two methods to run shell script files (.SH) on a Windows PC. Of course, there are many other third-party tools available that allow you to run Linux and Unix files on a Windows computer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to create a shell script (.SH) file?
I you know what you want to write inside the shell script file, all you need to do is follow these simple rules:
– Create a new notepad file
– Start the script with “#! /bin/sh”
– Write the code below it
– Save the file with a “.sh” extension
– To run the script, type “bash [FileName].sh” after navigating to the folder.
Can I run shell scripts on Windows?
Yes, shell script files can be executed on a Windows computer using Windows Subsystem for Linux, or third-party tools like Cygwin, kiTTY, ConEmu, Cmder, etc.
Why use shell scripts on Windows?
Shell scripts are used to perform repetitive tasks to save time and resources. They are also used to automate tasks. With the WSL feature, Microsoft has opened doors to natively run shell scripts on Windows operating systems.
Are you interested in working with shell scripts on Windows? Thanks to a recent addition by Microsoft, you can now use Windows Subsystem for Linux to make this happen.
Once you enable shell scripts in Windows 10, you can start creating shell scripts of your own. Shell scripts are great for automating simple tasks. You can also work on open-source Linux-based projects if that’s an area of interest to you. Finally, you’ll learn how to execute shell scripts on Windows 10. Continue reading to learn more.
What is Linux?
Linux is an open-source operating system that is highly popular among computer enthusiasts. Linux competes with other computer operating systems like Microsoft’s Windows, Apple’s macOS, and mobile operating systems like Android and iOS.
The Linux operating system was originally developed by Linus Torvalds back in 1991. The Linux kernel was designed as a Unix-like operating system. Unix was an early operating system created by Bell Labs in 1969. Today, modern Linux distributions are still Unix-like, meaning they retain the basic structure and properties that Unix had. An example of a non-Unix operating system would be Microsoft Windows.
The top Linux distributions have changed over the years, but as of 2022, Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Fedora, and Red Hat rank as the top 5 most popular options.
What is Bash?
When Linus Torvalds created Linux, he included a Unix shell called Bash. Bash had been created just two years before, in 1989 by Brian Fox. Bash has been the longtime default for Linux and was also the default for Apple macOS until it was replaced by Z shell in 2019.
Until 2016, Windows users could not use the Linux kernel or Bash at all. Windows first introduced the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) beta with Windows 10 version 1607 update. About a year later, in October 2017, WSL was fully released in Windows 10 version 1709. Microsoft developed WSL for hobbyists and developers who want to work on open-source Linux-based projects.
It’s important to note that WSL is not preinstalled on Windows 10. If you would like access to create and run shell scripts on Windows 10, you will need to manually install WSL or join the Windows insider program.
What is a shell script?
A Shell script is a type of script that cannot be run without a Unix shell. Further, a shell script is a series of commands that are executed line by line by the command line.
You can use shell scripts to automate processes and avoid repetitive tasks. Instead of manually completing each step in a series, you can execute a script, and the command line will handle the rest.
For example, if you find yourself regularly stopping processes that are hogging your CPU, you can automate this process with a script. When you execute the script, it may be designed to find a set of processes using CPU resources and request to kill them.
Enabling shell scripts in Windows 10
- Click on the Start (Windows) button and enter “Control Panel” into the search bar. Click Open on the Control Panel result on the right-hand side.

- Within the Control Panel window, find and click on Programs.

- Now, from the Programs window, find Click Turn Windows features on or off underneath the Programs and Features header.

- In the Windows Features window, scroll to the very bottom of the window. Check the Windows Subsystem for Linux option. Then click OK.

- Windows will automatically install the necessary files. When the installation is complete, select Restart Now.

- When your computer restarts, you need to install Ubuntu from the Microsoft store.

- After installation, make sure you open Ubuntu and see it up. You are now ready to use scripts on your Windows 10 machine.
If you encounter any issues with Ubuntu or bash commands not working correctly, you may want to check that Virtualization is turned on in your BIOS. The most updated WSL version, WSL 2, runs the Linux kernel using virtualization technology. This means a virtual machine needs to be able to run on your system.
Now that Windows Subsystem for Linux and Ubuntu has been installed, you are ready to start creating shell scripts in Windows 10. You may be tempted to write bash scripts with Notepad, but this is not recommended. Because Notepad is designed for Windows/DOS systems, the line endings will differ from those that are found at the end of Unix/Linux line endings.
Text editors for shell scripts
You should use software that is designed to convert to Unix/OSX end-of-line characters. The best open-source software available for this is Notepad++. Amazingly, Notepad++ is lovingly maintained and developed by a single individual, Don Ho.
If you try Notepad++ and don’t like it, you can try another fan favorite, nano. Nano is a text editor for Unix/Linux systems. You can easily create shell scripts that will run in bash, using nano. Download nano to get started.
Example shell scripts
Let’s look at some basic shell scripts, so you can learn more about what you are going to be coding and see how some formatting and syntax work.
1. Hello World!
echo "Hello World!"This script will print out the infamous Hello World! Notice that echo can be used as a print command when not combined with any other modifiers. It will print the string on a new line. If you add the -n modifier, the output will print on the same line.
2. Sum two numbers
If you want to do some basic arithmetic, you might have a script that looks like:
# Add two numbers together
((sum=25+35))
# Print the sum of the numbers
echo $sum
Note that the # symbol is used to make comments that are not expressed. The output of this script will print the sum of 25+35, which is 60.
3. Take user input
The following script will ask for the user’s name and then use the read command to take the user’s input. Then the user’s name is passed into the following expression, ultimately welcoming you to Windows Subsystem for Linux.
echo "What is your name?"
read name
echo "Welcome $name to Windows Subsystem for Linux."
Write basic shell scripts in Windows 10
Continue reading to learn how to write basic shell scripts in Windows 10 using Notepad++.
- Click the Start button and search for “Notepad++” and click Run as administrator on the right-hand side.

- Now you can create your script.

- Once your script is complete, you need to use the EOL Conversion option available in Notepad++. Click Edit and locate EOL Conversion from the dropdown menu. Hover over this option and then select UNIX/OSX Format from the next dropdown menu.

- Now select File and then Save As. Make sure to name your file something you will recognize and add .sh to make it a shell script file.

- Once the shell script is saved, continue to the next section to learn how to run your own shell scripts.
How to run shell scripts (.sh files) on Windows 10
You’ve created your first shell scripts, and it’s time to execute the sh file. Remember that when using WSL, you can only use Linux commands and utilities. Windows 10 programs will not work in bash scripts. To execute a script file, follow these step-by-step instructions:
- Click on the Start (Windows) button and enter “Command Prompt” into the search bar. Click Run as administrator on the Command Prompt result on the right-hand side.
- Navigate to the folder where the script file is saved. You move around in the command prompt using the cd command. For example, if you want to access the Documents folder, you would enter the following and press Enter:
cd C:\Users\Username\OneDrive\Documents
Note: Username would be the username that you set up for yourself when you registered your computer.

- Now enter bash file-name.sh, where file-name is the whatever you’ve named your script file.
bash file-name.sh
The script will execute, and if there are any outputs or print statements included in the script, the output will be returned.
Bash scripts running on Windows 10
You’ve made it far and learned a ton of information in one go. Command-line utilities, different operating systems, and learning to write and execute shell scripts can be difficult topics. In fact, these topics will take time to master. You have a ton of learning to do for scripting, but resources are available to help you all over the internet.
Within this guide, you learned the basics of Linux and Bash. You learned what shell scripts are and that you need to specifically enable Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) to use them. You learned how to create shell scripts using Notepad++ and how to execute the scripts in bash. Enjoy experimenting!
Download Windows Speedup Tool to fix errors and make PC run faster
Shell Scripts or .SH files are like batch files of Windows which can be executed in Linux or Unix. It is possible to run .sh or Shell Script files in Windows 11 or Windows 10 using Windows Subsystem for Linux. In this post, we will show you how to run a Shell Script file in Windows 11/10.
BASH is a Unix shell and command language which can run Shell Script files. You do not need to install Ubuntu or any other Linux Distros unless your scripts need the support of the real Linux kernel. We will share both methods.
- Execute Shell Script file using WSL
- Execute Shell Script using Ubuntu on Windows 11/10
1] Execute Shell Script file using WSL
Install WSL or Windows Subsystem for Linux
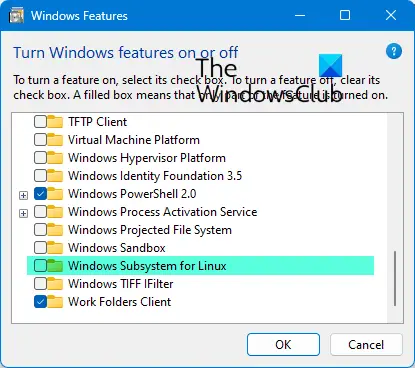
Go to Settings > Update & Security > For Developers. Check the Developer Mode radio button. And search for “Windows Features”, choose “Turn Windows features on or off”.
Scroll to find Windows Subsystem for Linux, check the box, and then install it. Once done, one has to reboot to finish installing the requested changes. Press Restart now. BASH will be available in the Command Prompt and PowerShell.
Execute Shell Script Files
- Open Command Prompt and navigate to the folder where the script file is available.
- Type Bash script-filename.sh and hit the enter key.
- It will execute the script, and depending on the file, you should see an output.
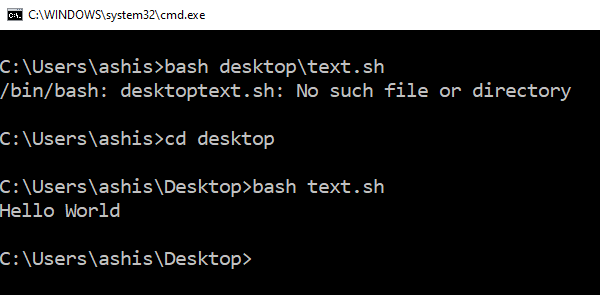
On a Linux platform, you usually use SH, but here you need to use BASH. That said, BASH in Windows has its limitations, so if you want to execute in a Linux environment, you need to install Ubuntu or anything similar.
2] Execute Shell Script using Ubuntu on Windows 11/10
Make sure you have Ubuntu or any other Linux distros installed. Ubuntu will mount or make all your Windows directories available under /mnt. So the C drive is available at /mnt/C. So if the desktop will be available at /mnt/c/users/<username>/desktop.
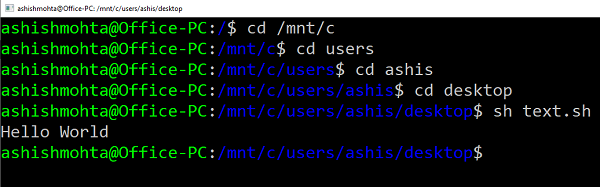
Now follow these steps
- Type Bash in the Run prompt, and it will launch the distro prompt.
- Navigate to the folder using “cd” command to the folder where the scripts are available.
- Type “sh script.sh” and hit Enter.
It will execute the script and if they have a dependency on any of the core Linux features.
Since Linux is now available in Windows, you need not use any third-party applications like Cygwin. WSL should be enough for most of the scenarios to help you run a shell script in Windows 11/10.
How do I create a .SH file?
The steps to create a shell script file are:
- Create a file using an editor
- Name script file with extension . sh
- Start the script with #! /bin/sh
- Write the desired code
- Save the script file as ABC.sh
- To execute the script type bash ABC.sh.
Can we run shell script on Windows?
Yes, now with Bash Shell in Windows 11 and Windows 10, you can now create and run Bash shell scripts and incorporate Bash commands into a Windows batch file or PowerShell script.
How do I run a script in Windows?
To run a script in Windows, you can use the wscript.exe command followed by the path to the script file. Open Command Prompt, navigate to the location of your script and type wscript.exe name.vbs to execute the script. You have to make sure that you have the Windows Script Host enabled or installed on your system.
How do I run bash on Windows?
To run bash on Windows, press Win + X and select Command Prompt (Admin). Then, type “bash” and hit Enter. To access the local file system, choose Command Prompt (Admin) and enter “bash” at the prompt. Running bash on Windows allows you to use Linux command-line tools and scripts seamlessly.
How do I run a sh file in Windows PowerShell?
To run a .sh file in PowerShell, you can use the following command: bash script.sh. This command executes the shell script within PowerShell.
Ashish holds a Bachelor’s in Computer Engineering and is a veteran Windows. He has been a Microsoft MVP (2008-2010) and excels in writing tutorials to improve the day-to-day experience with your devices.
To those who are not deeply immersed in the world of programming or system administration, the concept of executing .sh files might feel intimidating at first. However, understanding how to handle these files can unlock the ability to run scripts that automate tasks, configure environments, and even set up applications. This article will walk you through the details surrounding .sh files, their purpose, and how to execute them on a Windows operating system.
What are SH Files?
The .sh file extension denotes a shell script, which is a text file containing a sequence of commands that are executed within a shell, or command line interpreter. The shell is a program that provides the user interface for the operating system, allowing users to execute commands, manage files, and launch applications. When executed, the commands within an .sh file are run in sequence, automating various tasks that could otherwise be performed one at a time.
Shell scripts are commonly used in Unix-like operating systems, including various distributions of Linux, macOS, and even Android. However, Windows traditionally uses cmd.exe, PowerShell, or Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) to interact with commands, making direct execution of .sh files on Windows a little different. Yet, with the right tools and methods, executing these files can easily be accomplished.
Prerequisites
Before executing an .sh file on Windows, ensure that you have the following prerequisites:
-
Windows 10 or later: While older versions may still allow for some degree of compatibility, the latest features and enhancements available in Windows 10 or later makes it easier to work with Linux-based files and applications.
-
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL): This is one of the most efficient ways to run
.shfiles on your Windows machine. The WSL allows you to run a Linux distribution alongside your Windows operating system. -
Git Bash: This is another popular option that provides a Bash emulation environment on Windows, allowing you to run
.shscripts seamlessly. -
An installed Linux distribution: If you chose WSL, you need to have a Linux distribution installed (such as Ubuntu or Debian) and properly set up.
-
Text Editor: Having a text editor will help you view and modify your
.shfiles if needed.
Setting Up Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
Step 1: Enable WSL
-
Open PowerShell as Administrator: Search for PowerShell in the start menu, right-click it, and select «Run as administrator».
-
Run the WSL Installation Command: Enter the following command:
wsl --install -
Restart Your Computer: Once the installation completes, restart your system to apply changes.
Step 2: Install a Linux Distribution
-
Open Microsoft Store: Search for a Linux distribution like Ubuntu, Debian, or Kali Linux.
-
Install Your Preferred Distribution: Click install and wait for the installation process to complete.
-
Launch the Distribution: Open the newly installed Linux app to complete the setup. You’ll be prompted to create a user account and password.
Step 3: Execute SH Files via WSL
-
Open WSL: Search for your installed distribution (e.g., Ubuntu) in the start menu.
-
Navigate to Your SH File: Use the
cdcommand to change directories to where your.shfile is located. If your file is in the C drive, you can access it as follows:cd /mnt/c/Path/To/Your/File -
Execute the SH File: Once you are in the correct directory, run the following command:
bash script.sh
Step 4: Make the SH File Executable (if necessary)
If you encounter issues, it may be necessary to change the file permissions to make it executable:
chmod +x script.sh
./script.shUsing Git Bash to Execute SH Files
Git Bash is an alternative solution for users who prefer not to enable WSL. Here’s how to use it:
Step 1: Install Git for Windows
-
Download Git: Visit the official Git website (git-scm.com) and download the latest version for Windows.
-
Install Git: Run the installer and ensure you select the option to use Git Bash as your terminal.
Step 2: Launch Git Bash
- After installation, right-click on your desktop or in any folder and select “Git Bash Here” to launch the terminal.
Step 3: Execute SH Files
-
Navigate to the Directory: Use the
cdcommand to navigate to the folder containing your.shfile. -
Run the Script: Just as in WSL:
bash script.sh
Or if it has executable permissions:
./script.shExecuting SH Files via Cygwin
Cygwin is another tool that allows you to run a Linux-like environment on Windows, providing a more comprehensive suite of tools:
Step 1: Download and Install Cygwin
-
Download Cygwin Installer: Visit the official Cygwin website and download the setup.
-
Run the Installer: During installation, you can choose optional packages you’d like to add.
Step 2: Launch Cygwin Terminal
Step 3: Execute your SH file
-
Navigate to your File: Similar to previous methods, use:
cd /cygdrive/c/Path/To/Your/File -
Run the Script: Using:
bash script.sh
Troubleshooting Common Issues
As with any setup, problems may arise when attempting to run .sh files. Here are some common issues and solutions.
Issue 1: Permission Denied
This typically occurs when the script does not have the necessary execute permissions. Utilize the chmod +x script.sh command to resolve this.
Issue 2: Command Not Found
If you encounter a command not found error, ensure that you are in the correct directory and that the command you attempt to execute exists in the .sh file.
Issue 3: Line Ending Issues
When transferring scripts between different operating systems, you might run into issues related to line endings. Unix uses LF (Line Feed), while Windows uses CRLF (Carriage Return Line Feed). If your script appears illegible, run it through a Unix-compatible text editor such as Visual Studio Code or Notepad++ and convert line endings.
Issue 4: Missing Dependencies
SH files may require external tools or scripts to execute fully. Always read the script or accompanying documentation to check for prerequisites.
Conclusion
Executing .sh files on Windows is versatile and straightforward when armed with the right tools and knowledge. Whether you prefer to leverage the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), use Git Bash, or employ Cygwin, each option allows you to maximize the capabilities and functionality of your Windows operating system.
By embracing these tools, you not only simplify the execution of shell scripts, but you also enhance your workflow and productivity. Take the time to explore these environments further to develop a deeper understanding of shell scripting, and soon you’ll be on your way to creating custom scripts tailored to automate your tasks or improve your development processes.
The ability to run .sh files is just one piece of a much larger puzzle. As you delve deeper into programming and automation, you will find that scripts can serve you in countless ways, allowing you to weave efficiency seamlessly into your daily computing tasks. Happy scripting!










