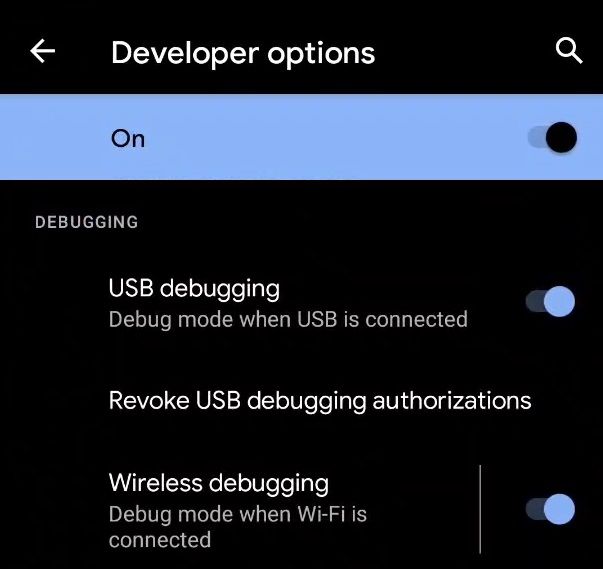
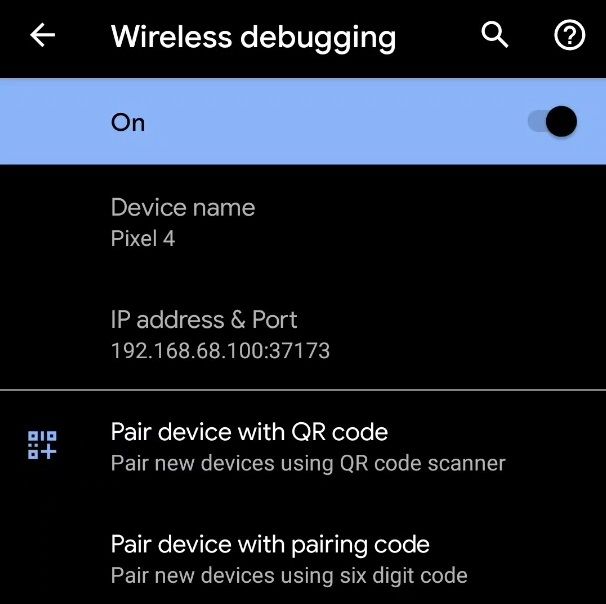
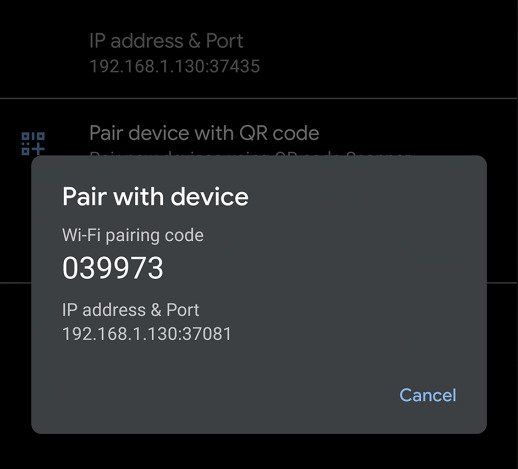
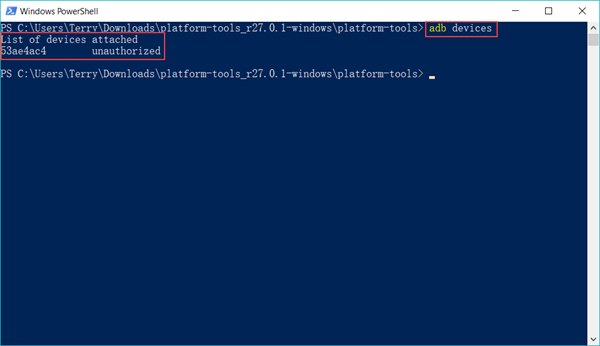
Все способы:
- Шаг 1: Скачивание и установка
- Шаг 2: Запуск утилиты ADB
- Способ 1: «Командная строка» Windows
- Способ 2: Windows PowerShell
- Дополнительно. Подключение Android-устройства к ADB на ПК
- Вопросы и ответы: 3
Шаг 1: Скачивание и установка
Прежде чем запуск консольной утилиты ADB станет возможным, конечно же, необходимо загрузить и инсталлировать её на компьютер. В действительности, существует множество вариантов получения и развёртывания софта, который обеспечивает функционирование Android Debug Bridge на ПК под управлением Windows 10, а следующая инструкция демонстрирует, как это сделать задокументированным разработчиками технологии Android Debug Bridge, а значит, самым надёжным и эффективным способом.
Скачать SDK Platform Tools (ADB и Fastboot) с официального сайта
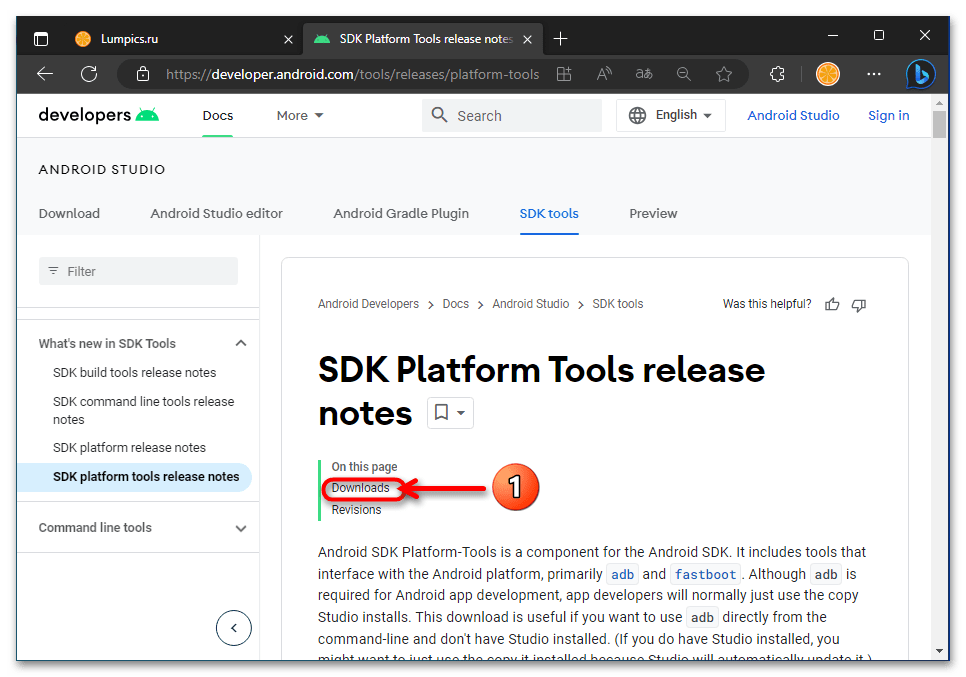
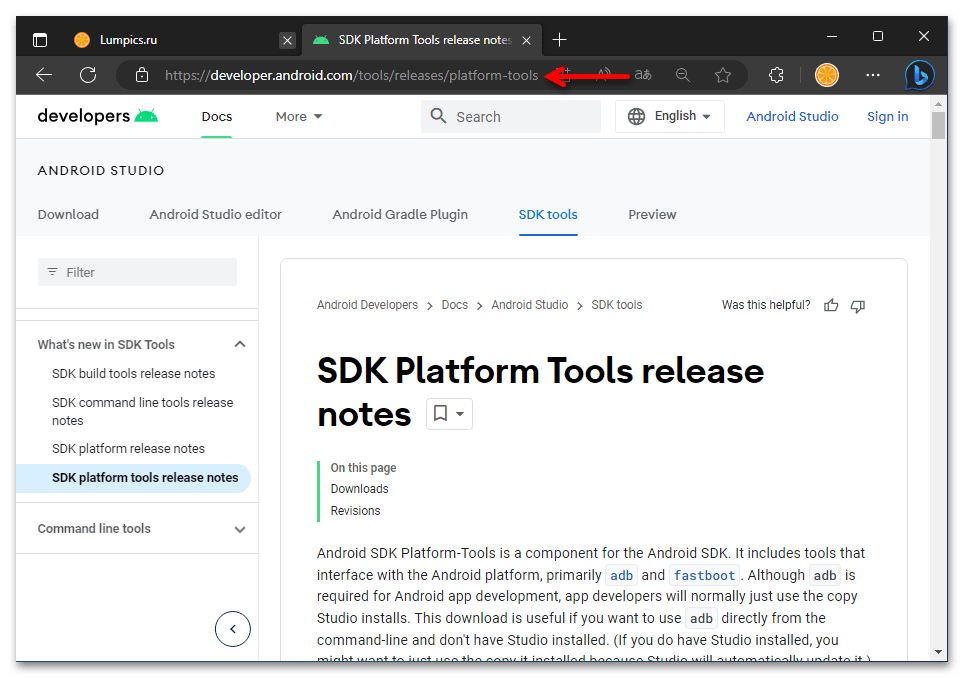
- Перейдите по представленной перед этой инструкцией ссылке. В результате откроется веб-страница с описанием и возможностью загрузки включающего ADB пакета SDK Platform Tools на интернет-ресурсе Android Developers от Google.
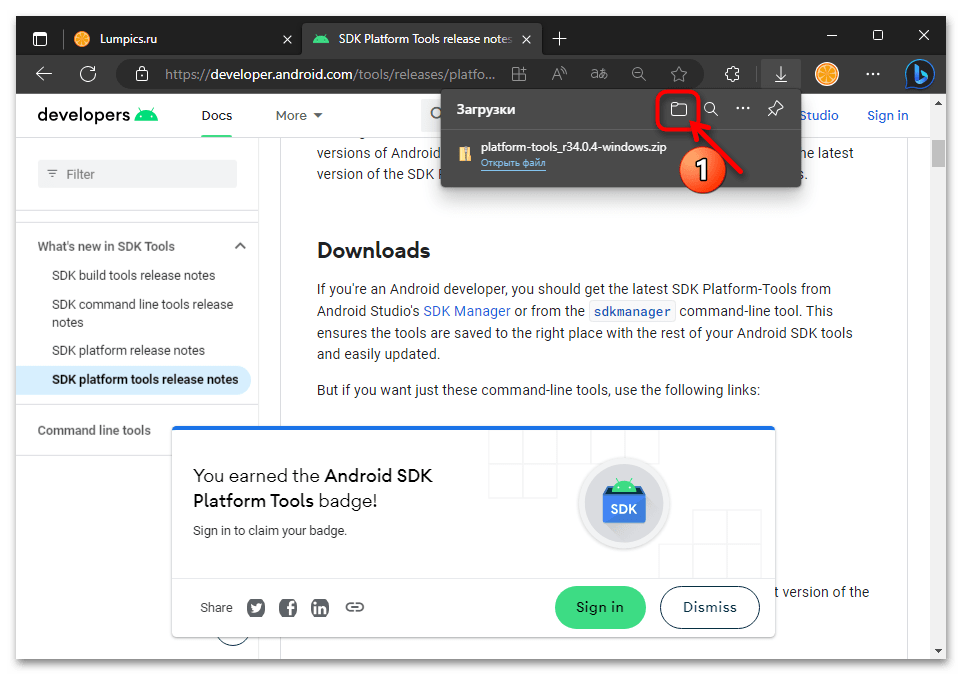
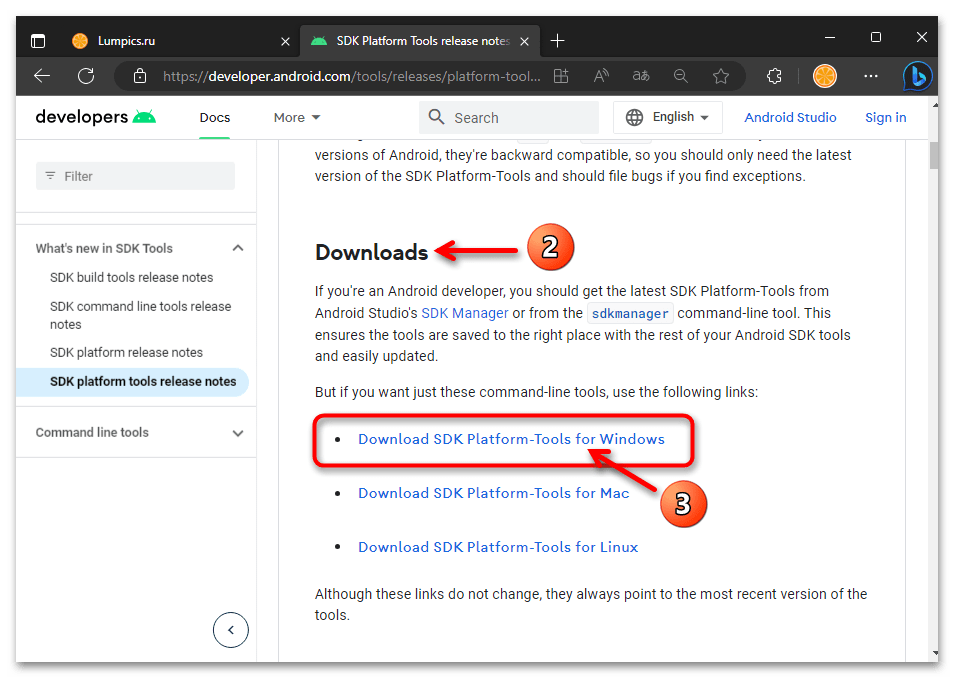
- Переместитесь в раздел веб-страницы «Downloads»,
щёлкните по имеющейся здесь ссылке «Download SDK Platform-Tools for Windows».
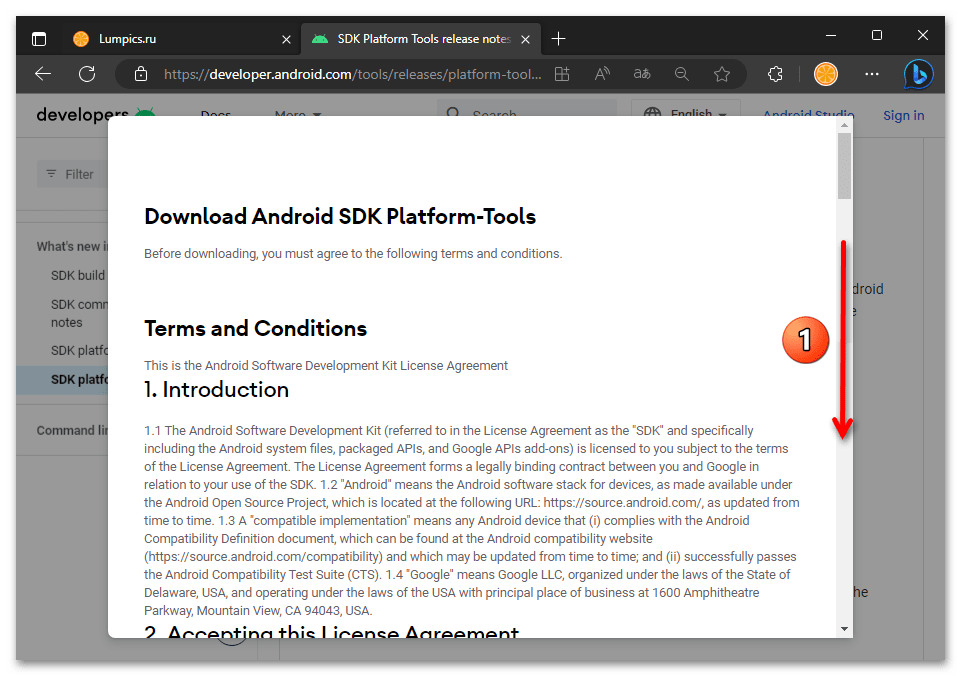
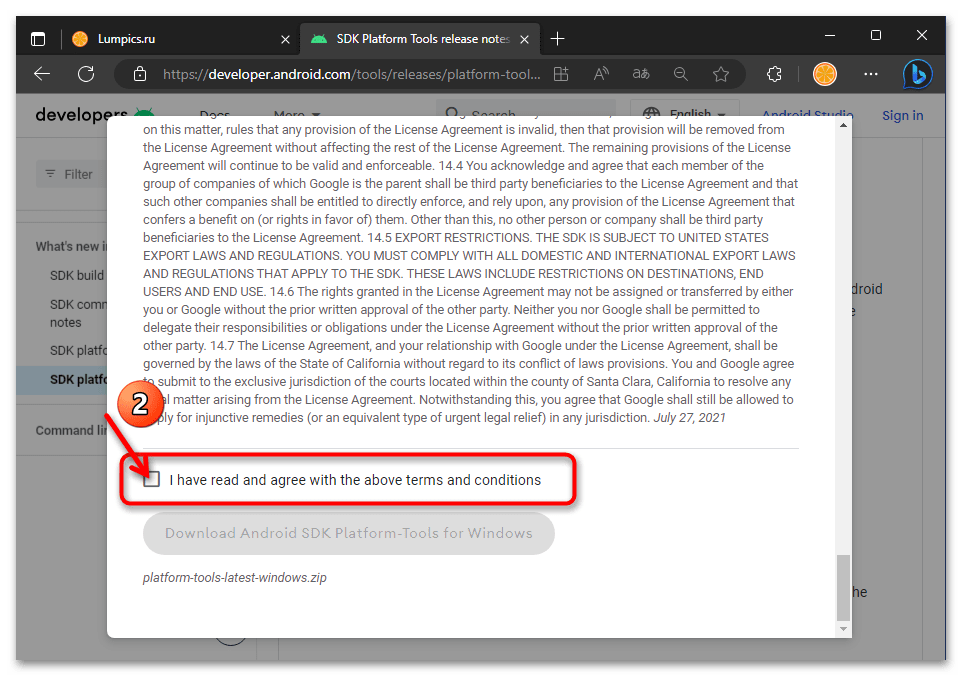
- Прокрутите информацию в отобразившемся поверх веб-страницы окне до конца,
установите отметку в чекбоксе «I have read and agree with the above terms and conditions».
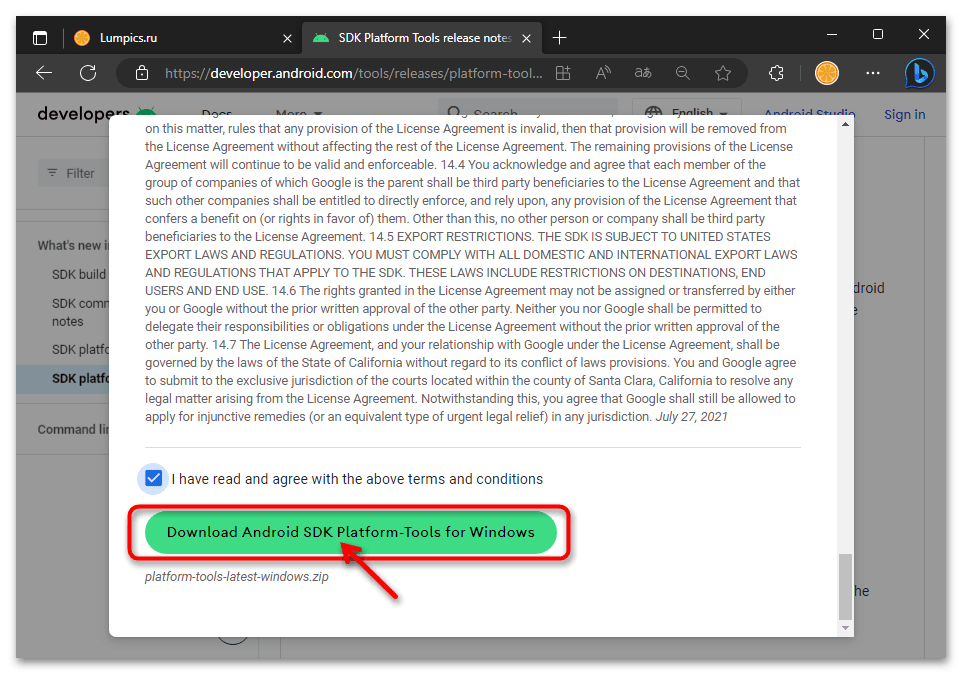
- Нажмите на ставшую активной после выполнения предыдущего шага кнопку «Download Android SDK Platform-Tools for Windows».
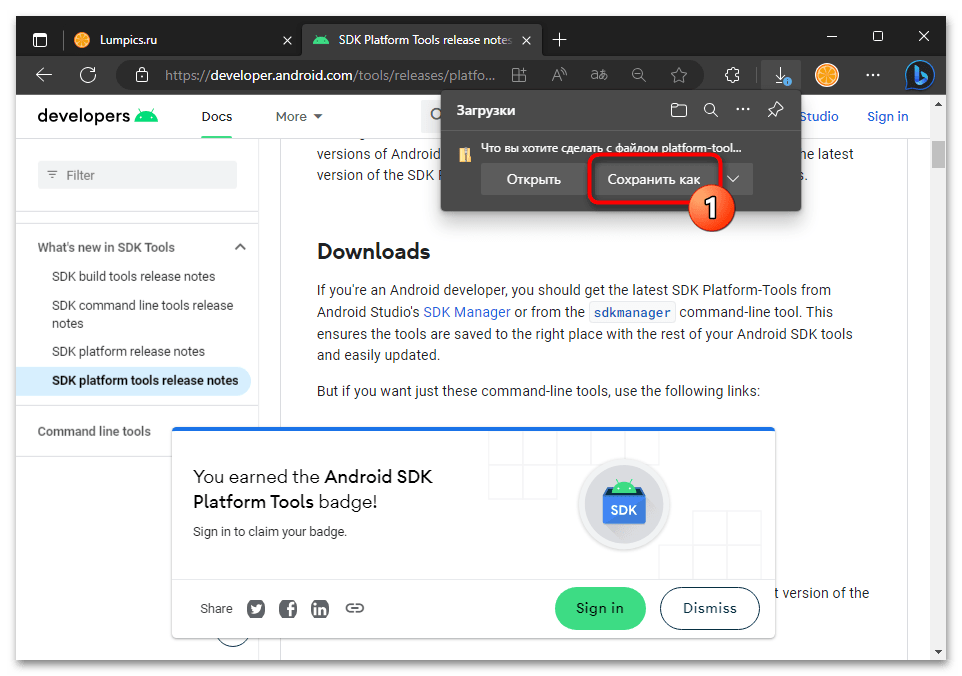
- Если это предполагают настройки браузера, укажите (и запомните) путь сохранения предоставляемого сайтом ZIP-архива на диске компьютера
(по умолчанию будет скачан в системную библиотеку Win 10 «Загрузки»). Подтвердите инициацию получения пакета
и дождитесь окончания этого процесса.
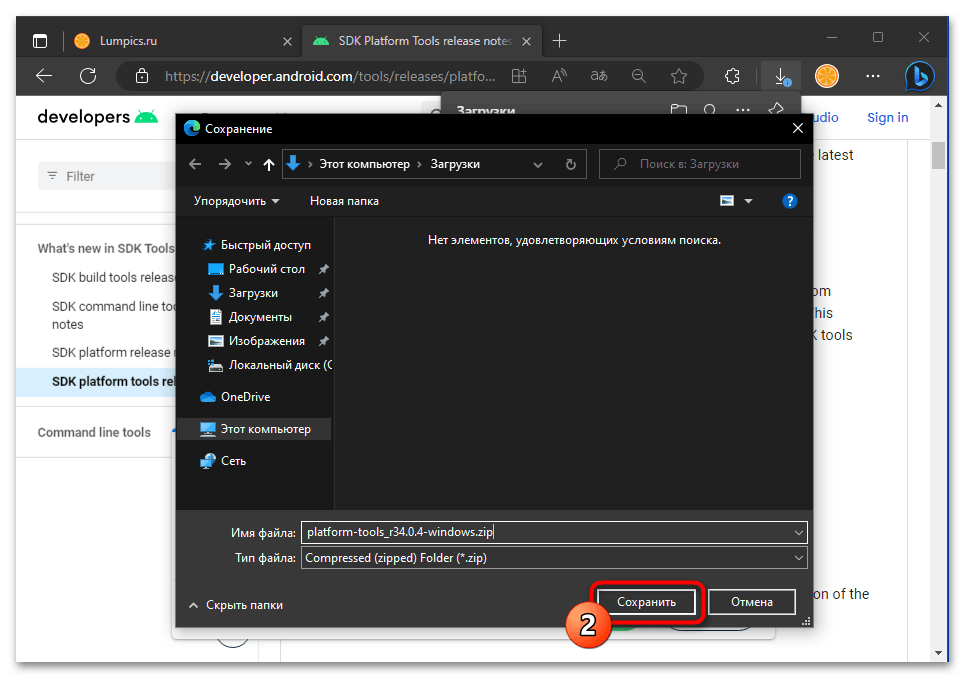
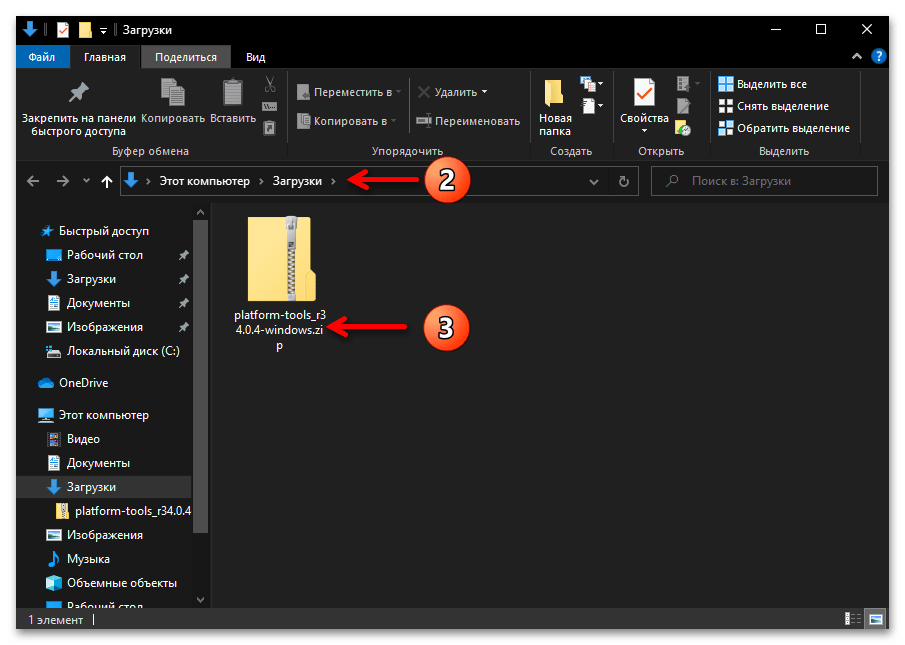
- По завершении скачивания файла platform-tools_rВЕРСИЯ-windows.zip откройте содержащую его папку
в Проводнике Windows.
Читайте также: Запуск «Проводника» в ОС Windows 10
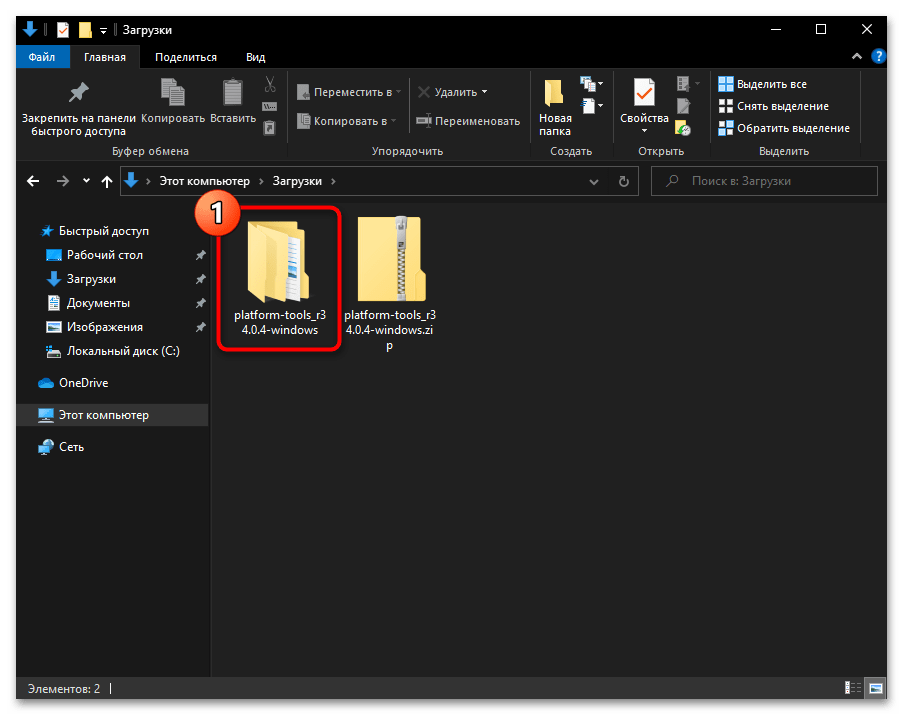
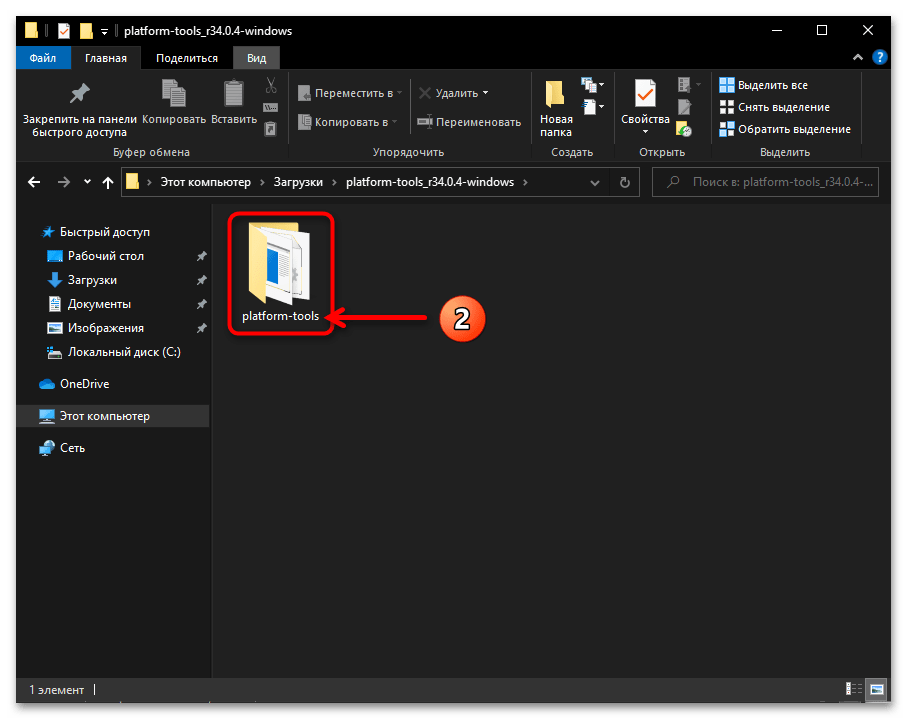
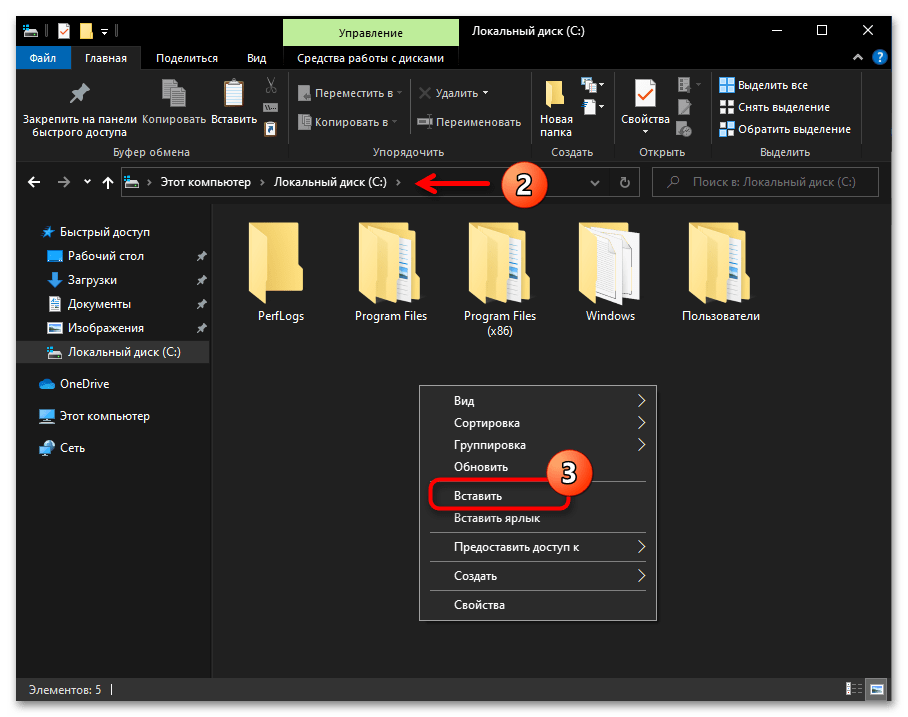
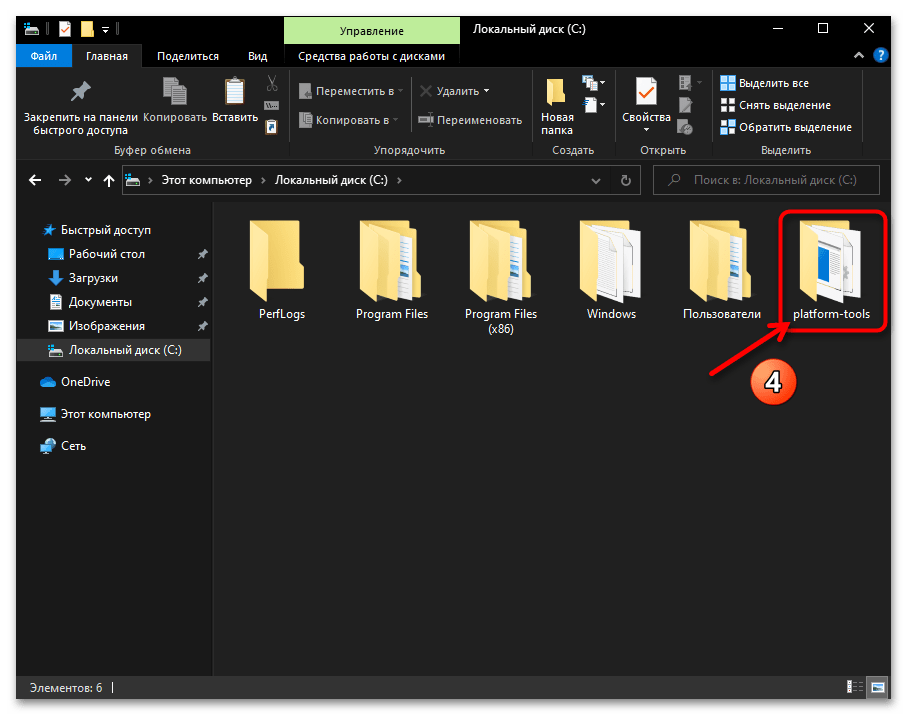
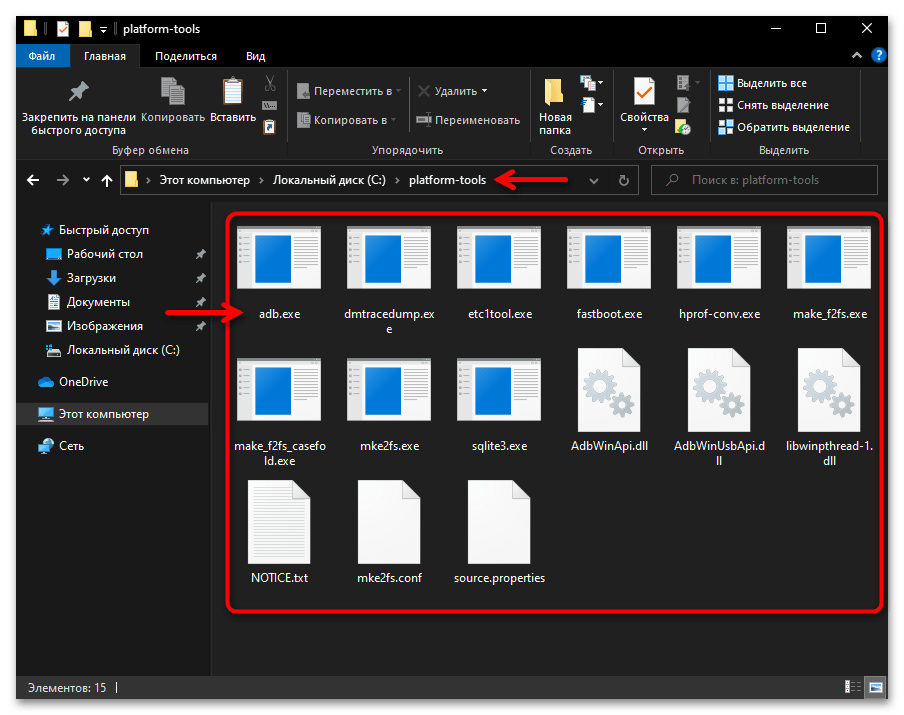
- В результате разархивации пакета SDK Platform Tools образуется директория, которая содержит вложенную папку «platform-tools» –
именно она и является целевой в нашем случае.
По сути, на этом получение утилиты ADB можно считать завершённым, её уже можно запускать из указанной папки средствами консоли Windows 10 одним из предложенных далее в этой статье способов. При этом, для удобства в дальнейшем, а также полного соответствия рекомендациям разработчиков Android Debug Bridge необходимо скопировать или переместить каталог «platform-tools»
в корень
системного диска ПК (С:).
Кроме прочего, каталог с утилитой ADB можно переименовать по собственному усмотрению (например, сократить наименование или как-то иначе, но не применяя кириллических символов). При таком подходе запомните присвоенное каталогу с утилитой ADB имя, и точно вводите его вместо
platform-toolsпри выполнении дальнейших инструкций из этого материала.
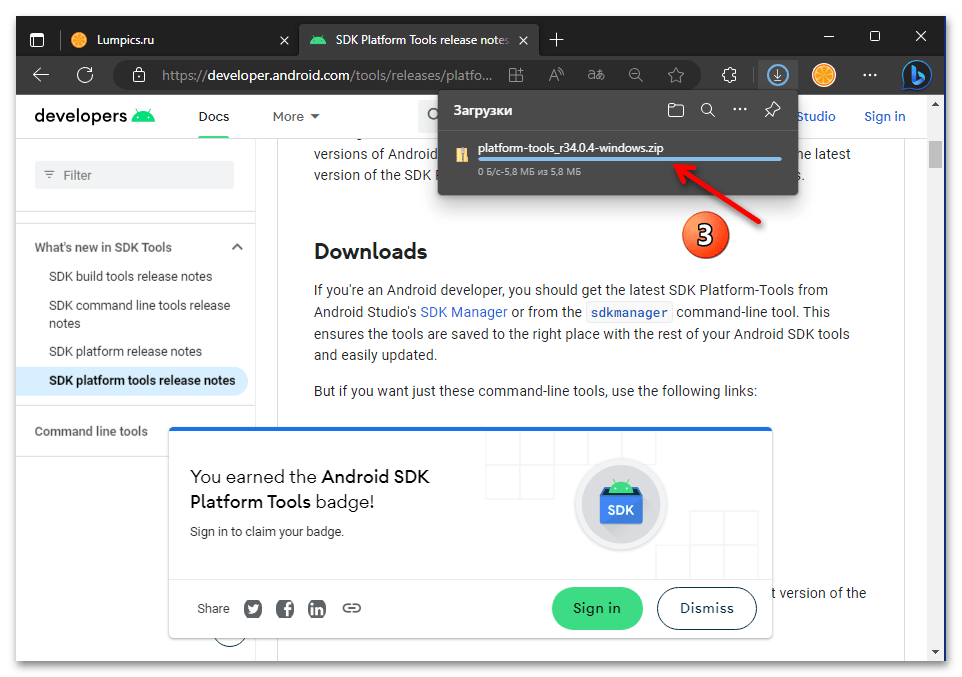
Далее извлеките всё содержимое архива в отдельный каталог. (С этой целью кликните правой кнопкой мыши по наименованию пакета, выберите «Извлечь всё» в открывшемся контекстном меню, подтвердите действие).
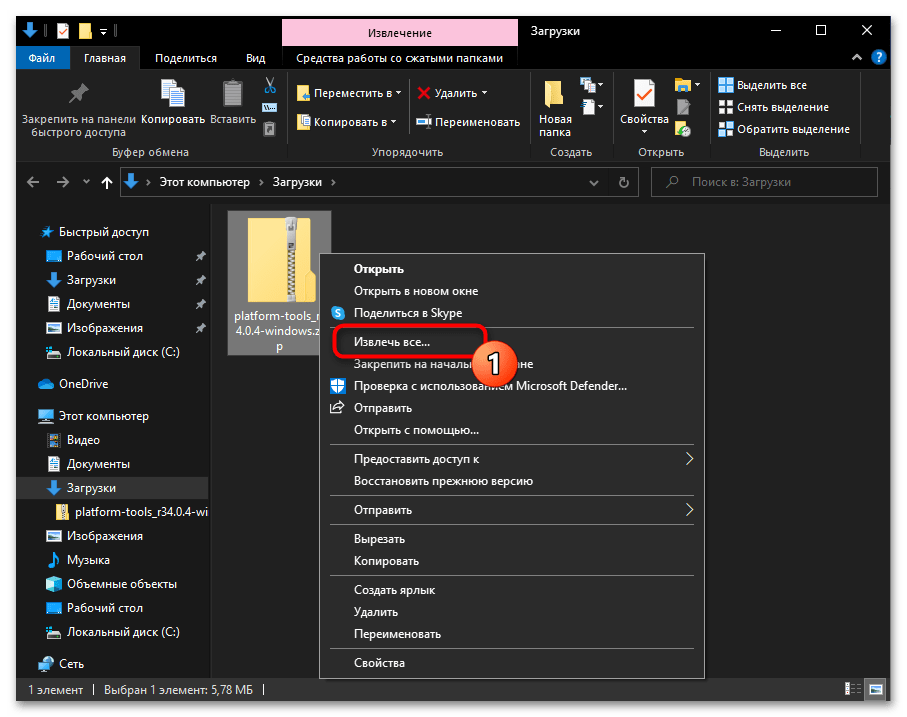
Подробнее: Распаковка ZIP-архивов в ОС Windows 10
Входящие в комплект SDK Platform Tools утилиты (не только рассматриваемая в этой статье ADB, но также Fastboot) в случае с Windows 10 могут быть запущены и эффективно эксплуатироваться в классической «Командной строке», а также её более современном аналоге – консольной оболочке «PowerShell». Далее рассмотрим подробно, как используются оба указанных инструмента для решения нашей задачи.
Способ 1: «Командная строка» Windows
По сути, чтобы получить доступ к функциям утилиты ADB через «Командную строку» Windows, достаточно открыть во второй содержащий компоненты первой каталог («platform-tools»). Практически это реализуемо минимум двумя путями, вы можете использовать тот, который кажется более удобным.
Вариант 1: Консольная команда «cd»
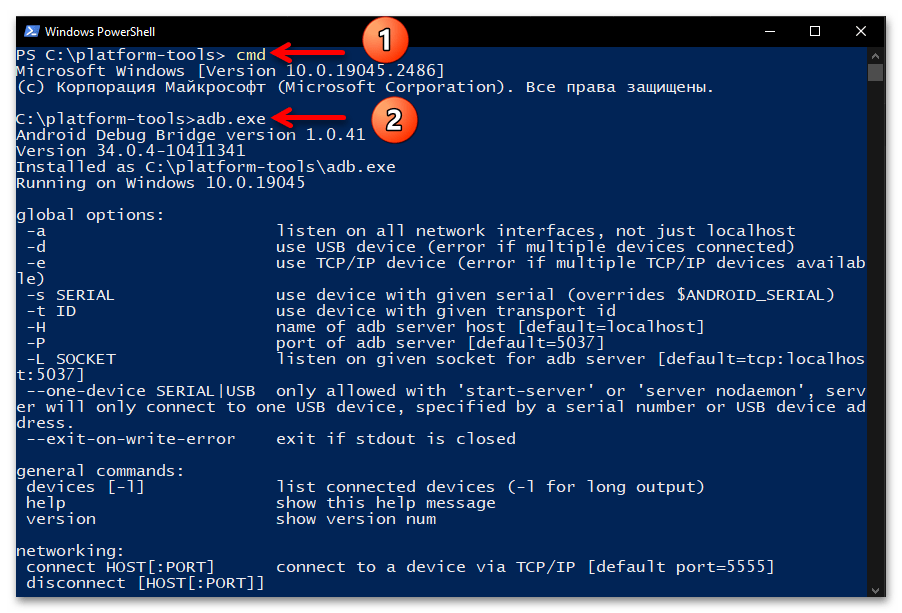
Самый распространённый и привычный большинству метод запуска консольной утилиты ADB заключается в открытии приложения «Командная строка» и переходе через неё в папку с целевым софтом с помощью специализированной текстовой команды:
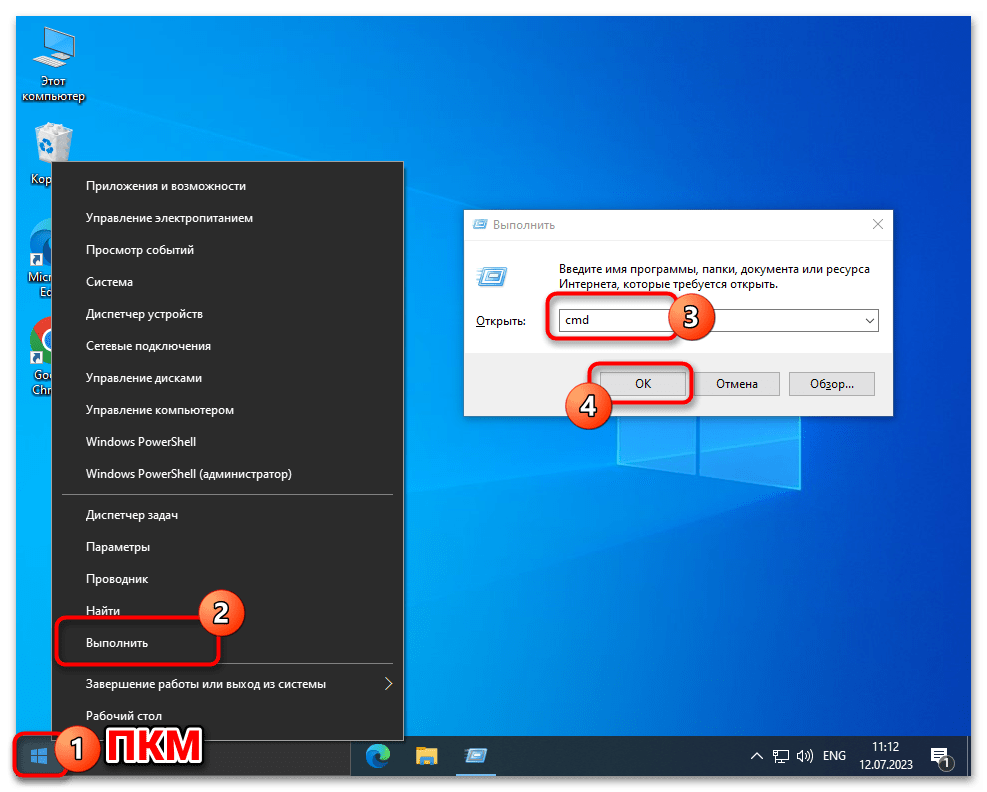
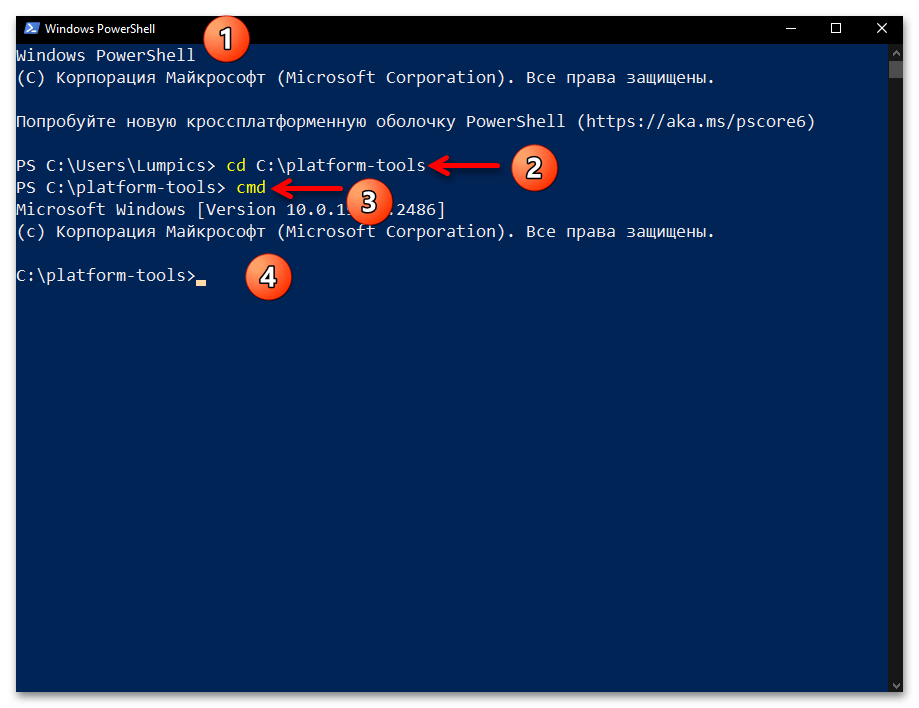
- Любым способом запустите «Командную строку» Виндовс 10. К примеру, и быстрее всего с этой целью можно задействовать оснастку «Выполнить»: нажмите «Windows» + «R» на клавиатуре, введите в поле «Открыть» отобразившегося окошка следующий текст:
cmdЩёлкните по кнопке «ОK» мышкой или нажмите «Enter».
Подробнее: Открытие «Командной строки» в Windows 10
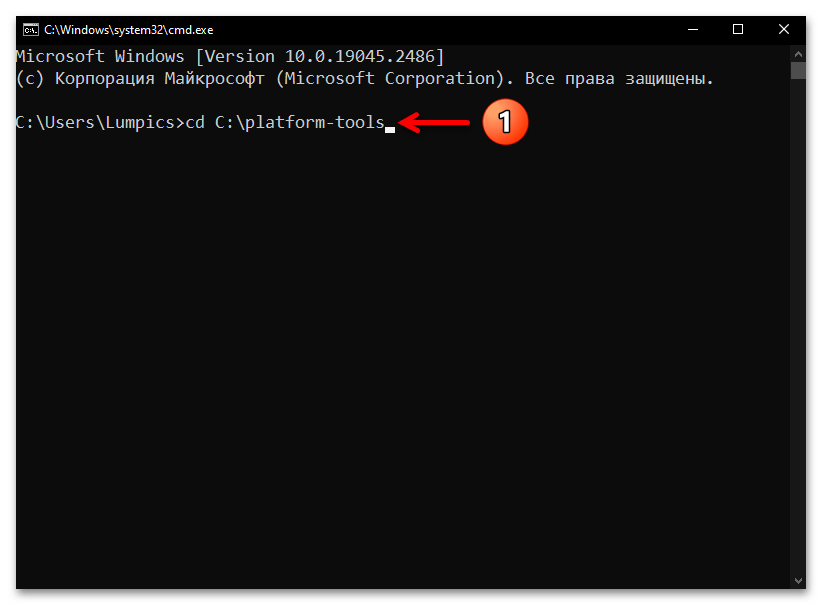
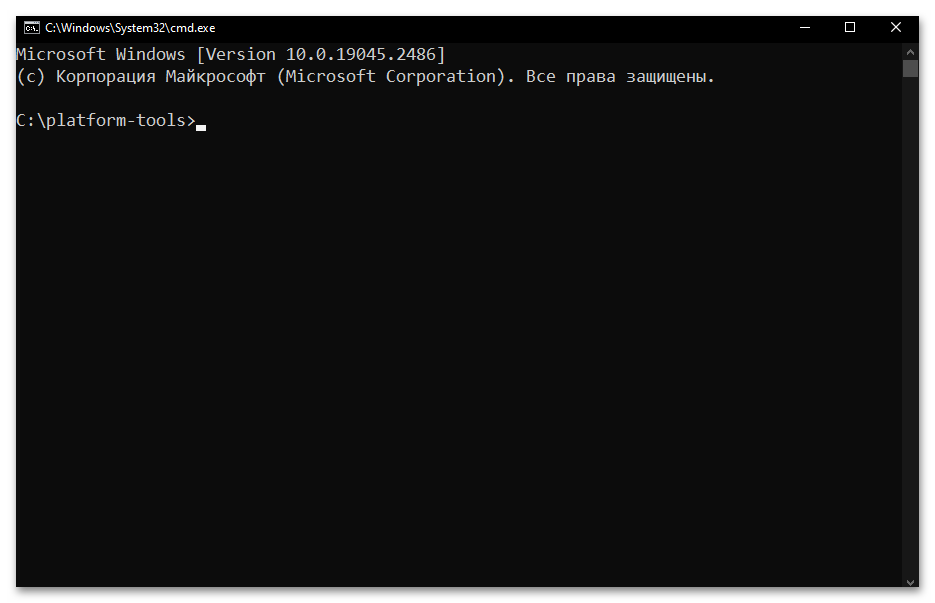
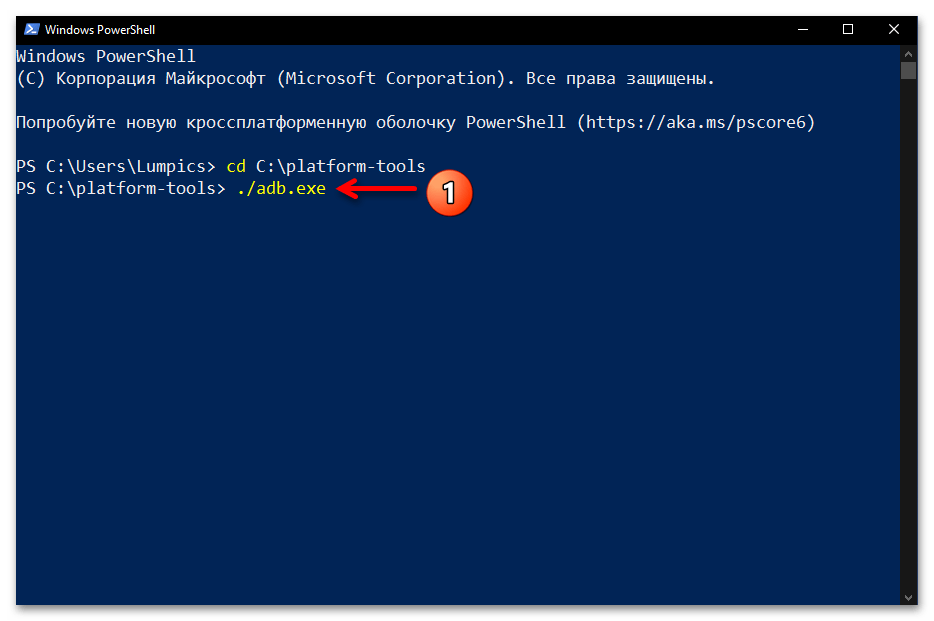
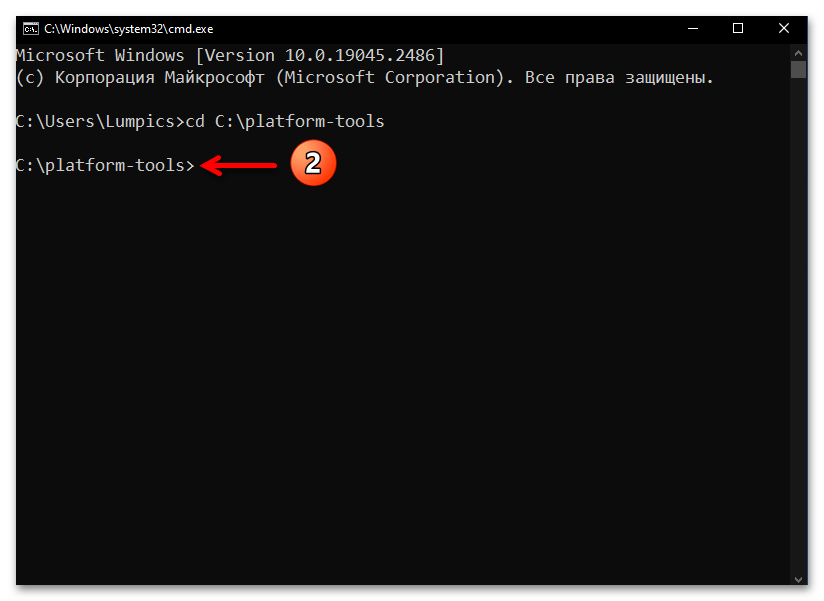
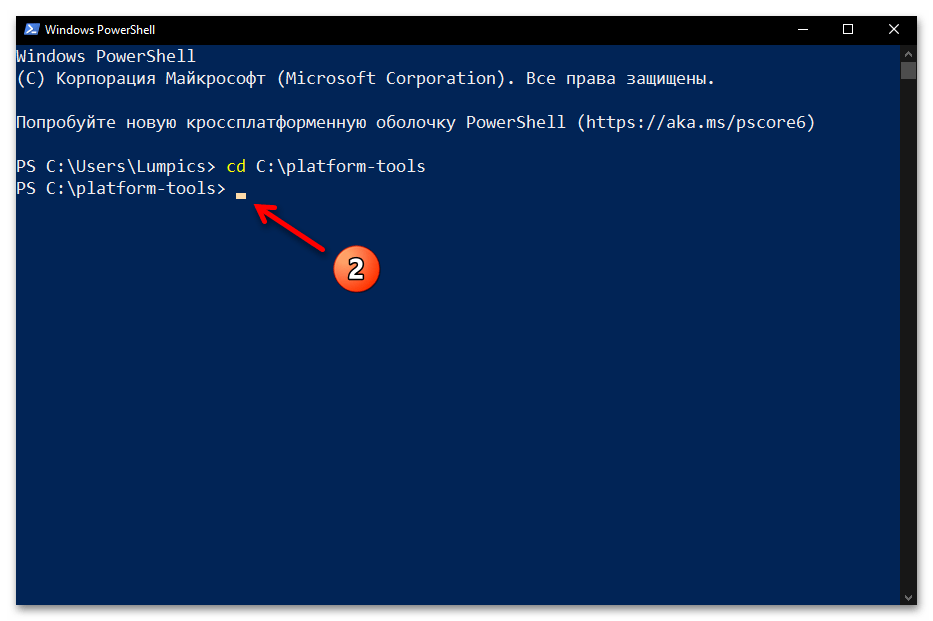
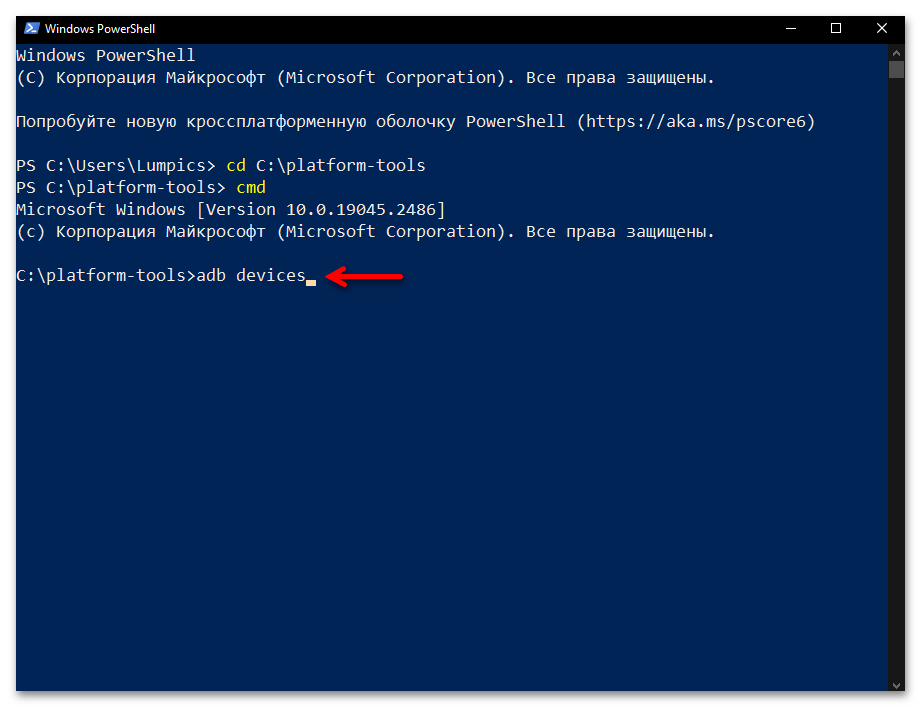
- Введите команду перехода в каталог утилиты ADB – она состоит из указания
cdи затем полного пути к целевой директории на диске компьютера. То есть, если вы точно следовали рекомендациям выше в статье, команда будет следующей:cd C:\platform-toolsНаписав команду, отправьте её на выполнение — для этого нажмите «Ввод» на клавиатуре.
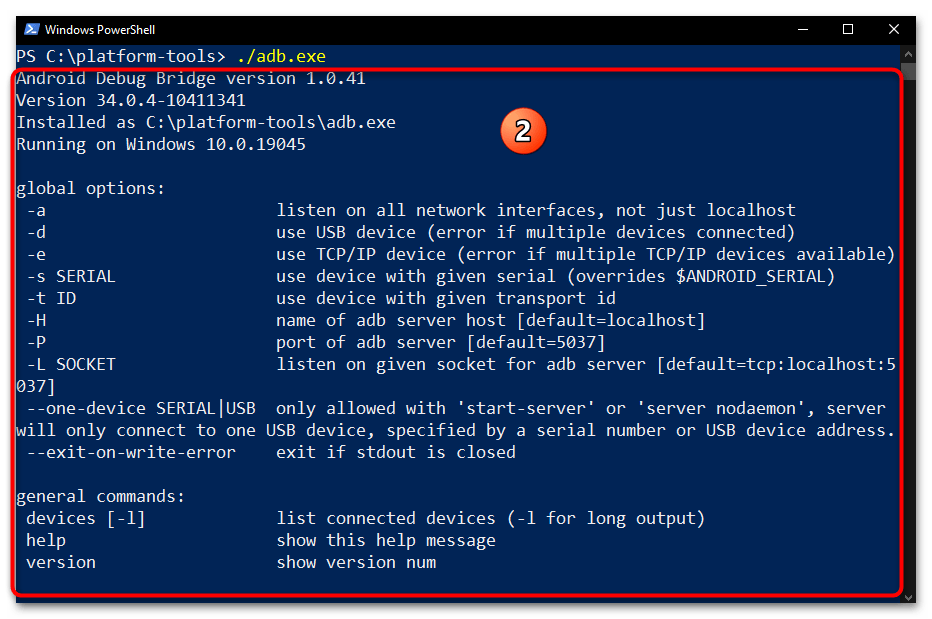
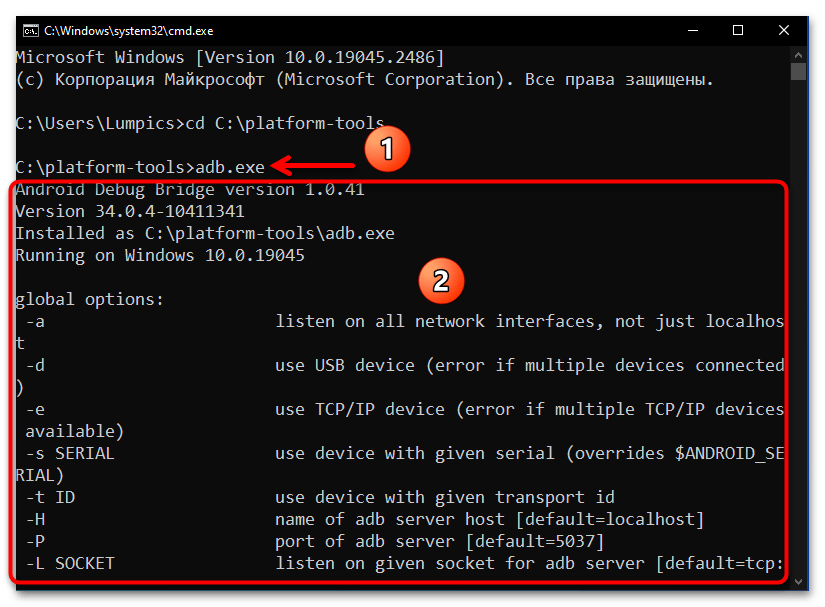
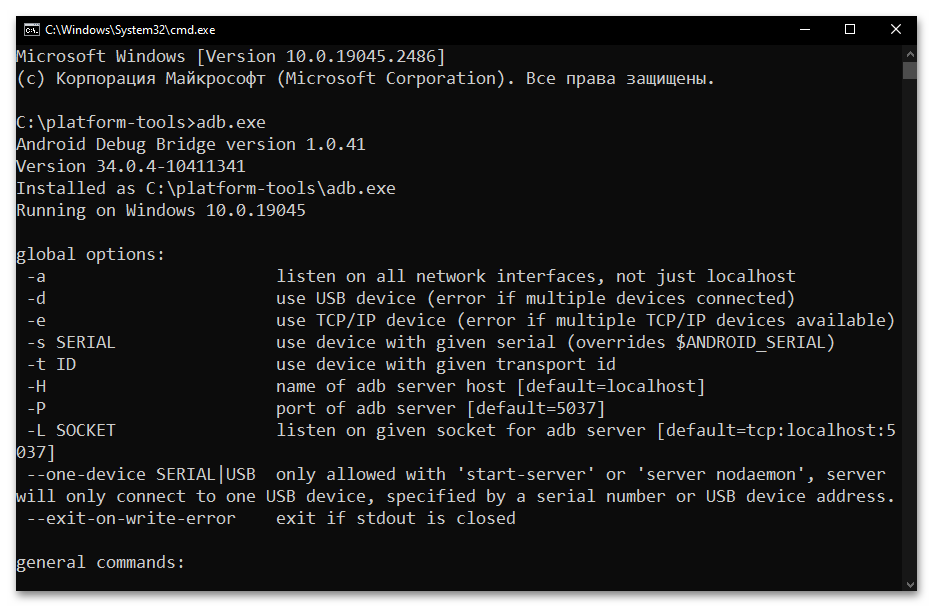
- Фактически всё, далее можно приступать к отправке текстовых команд ADB, — утилита готова к их приёму и обработке. Чтобы удостовериться в том, что отладочный мост введён в эксплуатацию, а также для получения списка основных команд ADB, можно ввести в консоли и отправить на выполнение следующее указание:
adb.exe
Вариант 2: Средства Проводника Windows
Более удобный и часто выполнимый быстрее, нежели вышеописанный, подход к запуску утилиты АДБ в классической «Командной строке» эксплуатирует возможности системного файлового менеджера Виндовс 10:
- Откройте Проводник Windows 10, перейдите в каталог ADB («platform-tools»).
- Кликните левой кнопкой мыши в (важно!) свободной от надписей области поля, которое расположено в верхней части окна Проводника и отображает путь
к текущей открытой вами папке.
- С клавиатуры введите следующий текст:
cmd - Нажмите «Enter» — в результате запустится «Командная строка» Windows c уже открытой в ней папкой «platform-tools».
На этом наша задача считается решённой, вы можете приступать к вводу в «Командную строку» и отправке на выполнение команд Android Debug Bridge.
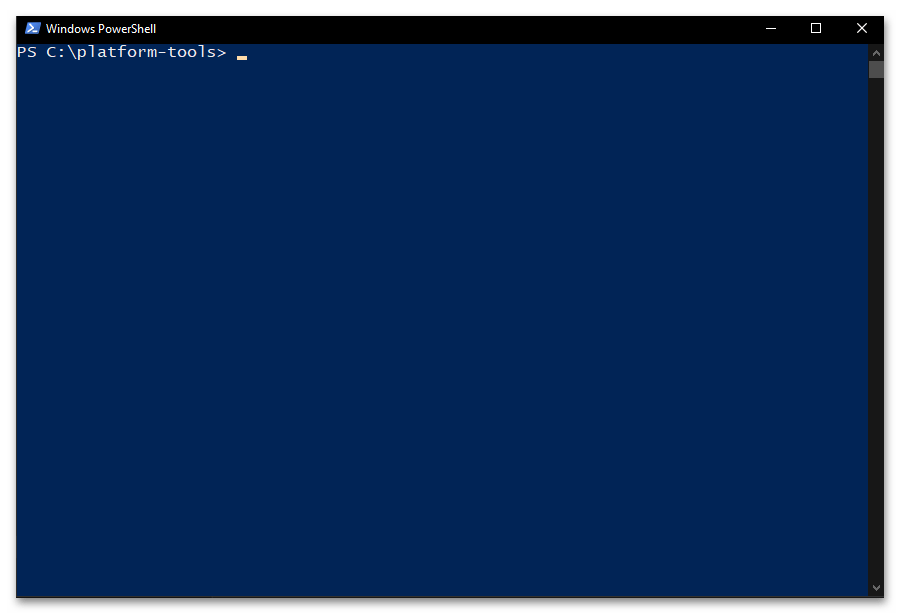
Способ 2: Windows PowerShell
Запуск ADB через поставляемое в комплекте ОС Windows 10 средство PowerShell выполняется не намного сложнее, нежели при использовании классической «Командной строки», а практически реализуется одним из двух нижеописанных путей.
Вариант 1: Консольная команда «cd»
Основной вариант запуска Android Debug Bridge средствами PowerShell фактически повторяет таковой в «Командной строке», — необходимо запустить консоль, а затем с помощью специальной команды открыть в ней каталог с утилитой ADB и сопровождающими её файлами.
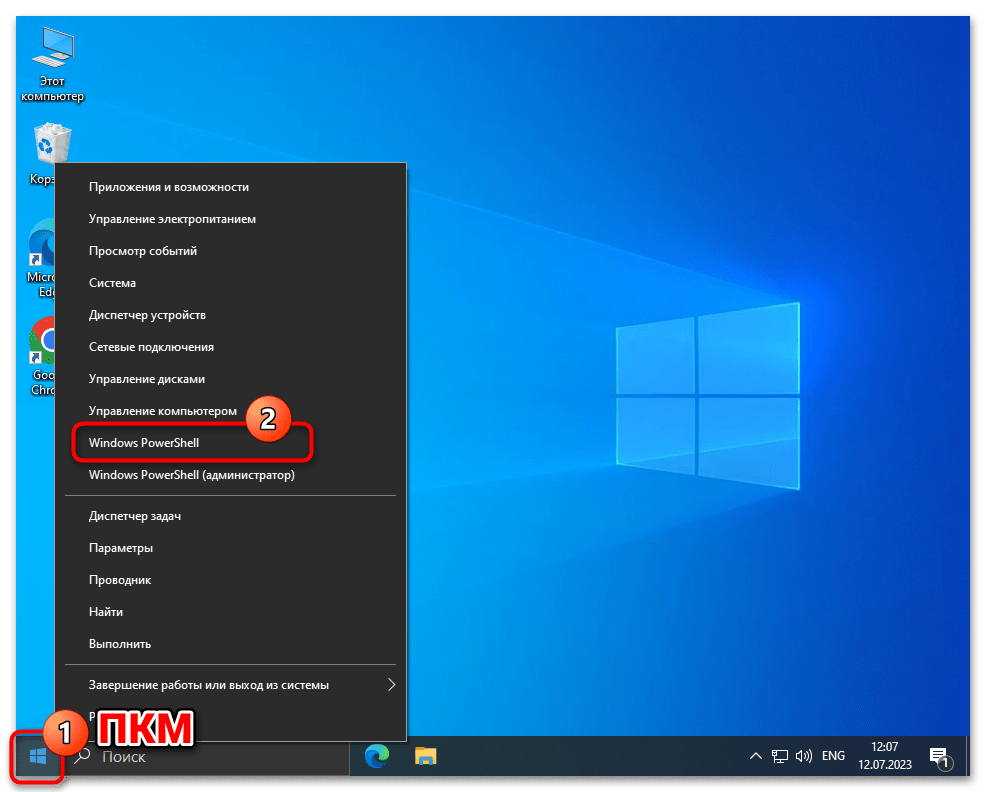
- Откройте консольную оболочку PowerShell. Как и классическую «Командную строку» в Windows 10 это средство можно запустить большим числом способов, а быстрее всего — из меню дополнительных действий кнопки «Пуск» на «Панели задач» операционки: кликните по последней правой кнопкой манипулятора и выберите «Windows PowerShell» в отобразившемся перечне.
Подробнее: Запуск «PowerShell» в ОС Windows 10
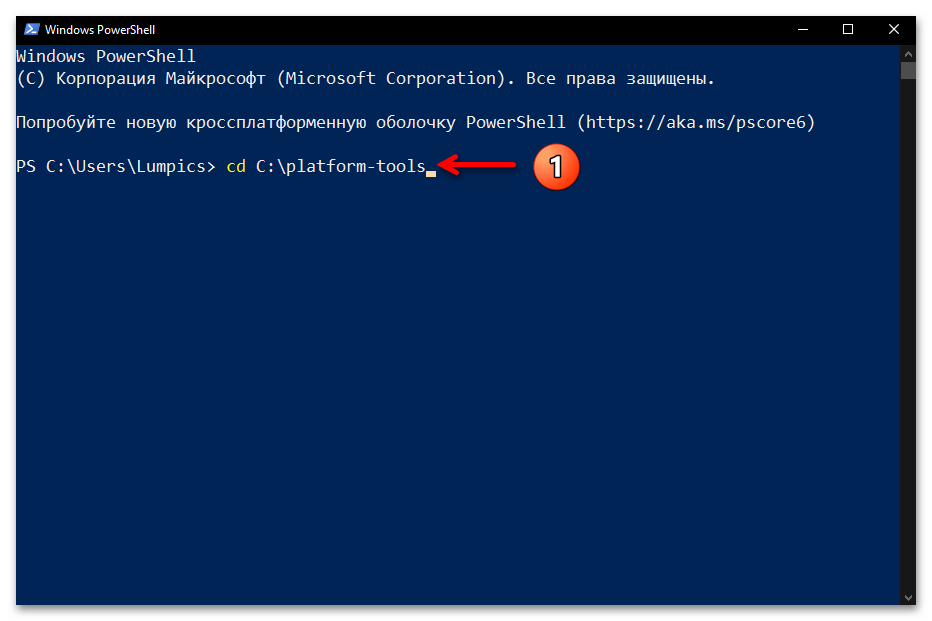
- Введите команду перехода в папку утилиты ADB, — её синтаксис аналогичен рассмотренному выше в этом материале указанию для классической «Командной строки»:
cd C:\platform-toolsНажав «Ввод» на клавиатуре, отправьте указание на выполнение консолью.
- Собственно, всё — средство ADB готово к выполнению своего предназначения. Дальнейшие ваши действия двухвариантные:
- При запуске ADB-команд в Windows PowerShell по умолчанию перед ними необходимо прописывать префикс
./. То есть, к примеру, чтобы вывести в консоли список основных команд ADB в текущем случае, необходимо отправить на выполнение следующее текстовое указание:./adb.exeПосле написания команды и нажатия «Enter» получаем следующий результат:
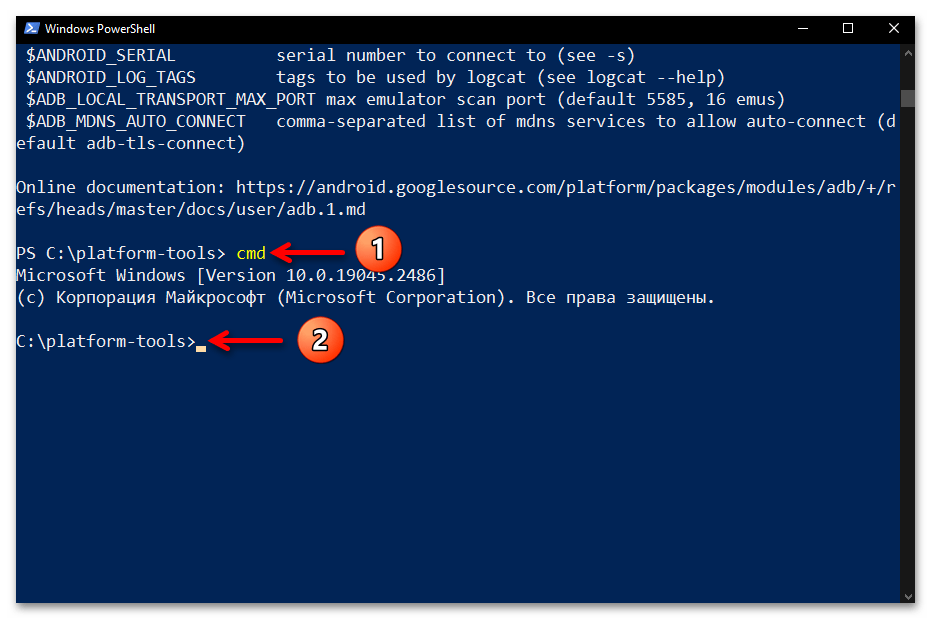
- Если подставлять
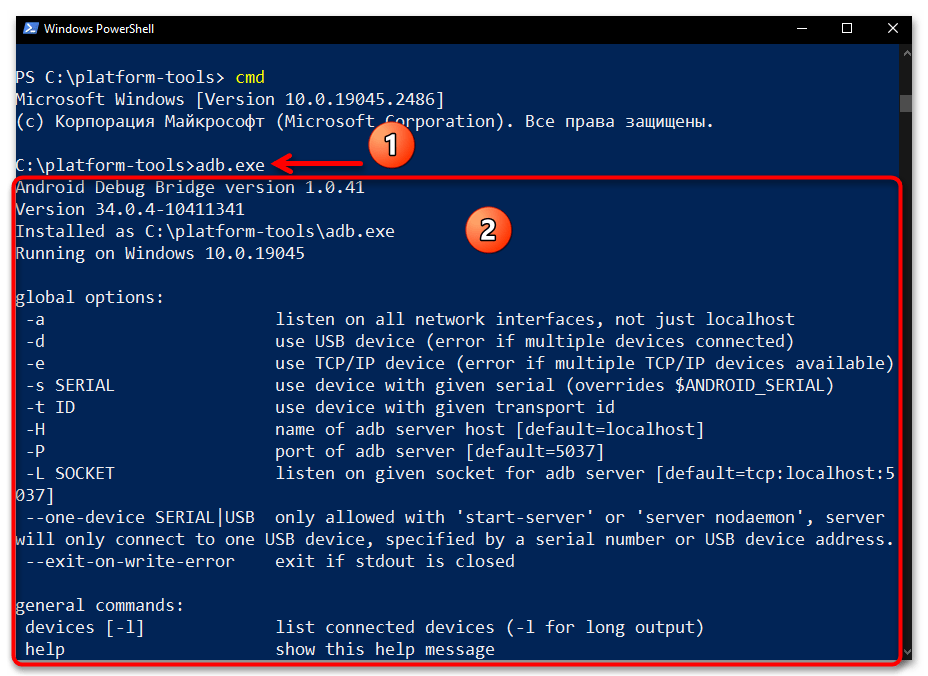
./перед каждой передаваемой средствами ПоверШелл через Андроид Дебаг Бридж командой вы не желаете, то можете перед началом работы открыть себе доступ к «классической» командной строке в современной консольной оболочке. Для этого запустите в PowerShell команду:cmdДалее отправляйте указания ADB мобильному девайсу c ОС Android без префикса:
- При запуске ADB-команд в Windows PowerShell по умолчанию перед ними необходимо прописывать префикс
Вариант 2: Расширенное контекстное меню папки
Ещё один метод запуска ADB в консольной оболочке PowerShell реализуется средствами Проводника Windows 10, а его использование часто оказывается более удобным, нежели описанный выше подход.
- Перейдите в папку с утилитой ADB через Проводник Win 10.
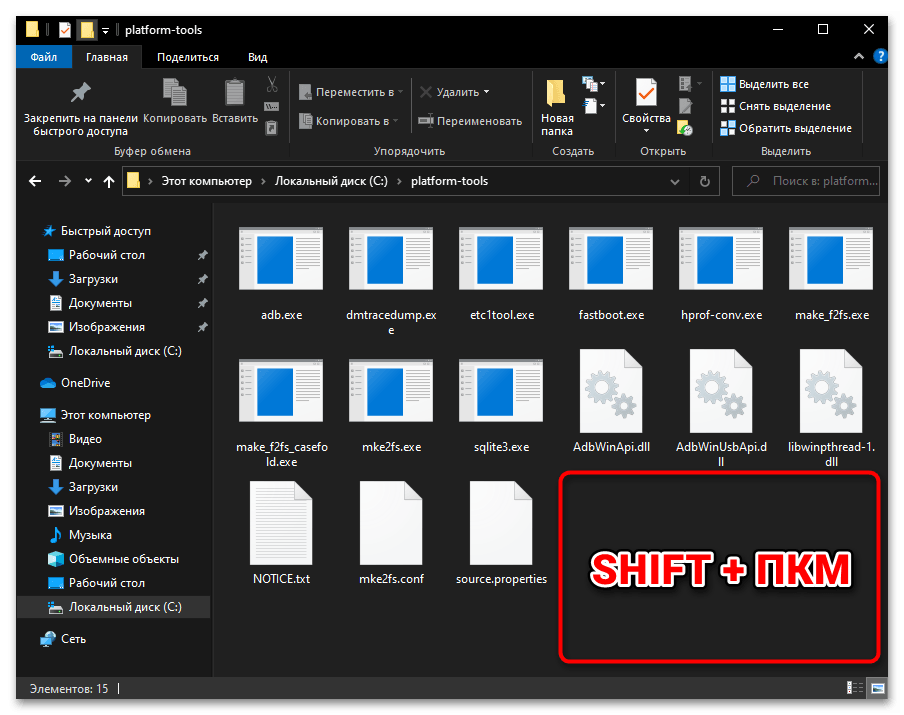
- Нажмите «Shift» на клавиатуре компьютера и, удерживая эту клавишу, щёлкните правой кнопкой манипулятора по свободному от элементов (значков файлов) месту в демонстрирующей содержимое каталога «platform-tools» области окна Проводника.
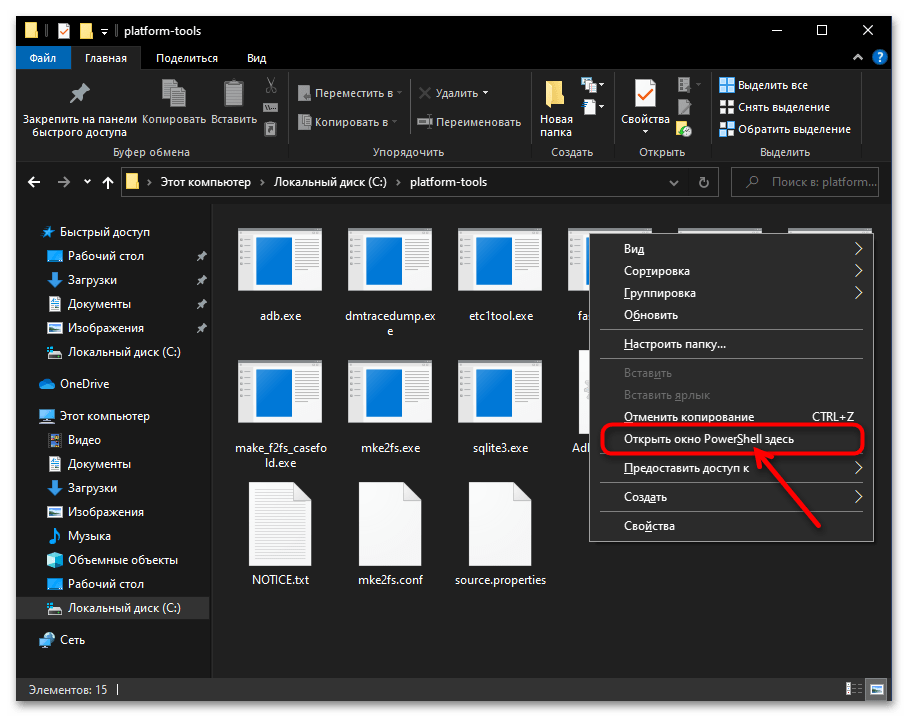
- По результату вышеописанной манипуляции откроется расширенное контекстное меню папки (после этого можно прекратить воздействие на кнопку «Shift» клавиатуры). В меню выберите пункт «Открыть окно Power Shell здесь».
- Итогом манипуляций станет запуск приложения Windows Power Shell c уже открытым в нём каталогом «platform-tools». На этом наша задача считается решённой, приступайте к вводу и отправке на выполнение команд Android Debug Bridge.
(Принцип здесь тот же, что и при рассмотренном выше варианте запуска утилиты: либо предварительно запустите команду
cmd, а затем отправляйте ADB-команды в их «стандартном» виде; либо подставляйте префикс./перед каждым указанием).
Дополнительно. Подключение Android-устройства к ADB на ПК
Чтобы скачивание, развёртывание и запуск ADB в среде Windows 10 позволили достичь конечных целей своего осуществления, то есть вы получили возможность производить вмешательство в работу системного ПО управляемого ОС Android мобильного девайса с компьютера, чрезвычайно важно правильно подключить смартфон или планшет к консольной утилите. Полный алгоритм выполнения данной операции изложен ниже.
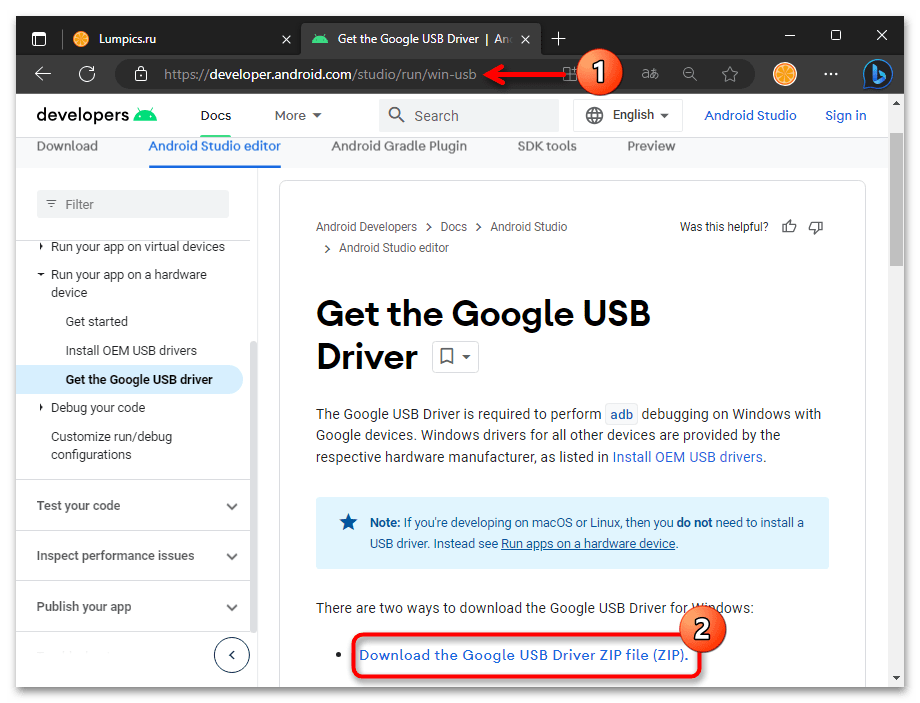
Скачать универсальные драйверы от Google для работы с Android-девайсами через ADB
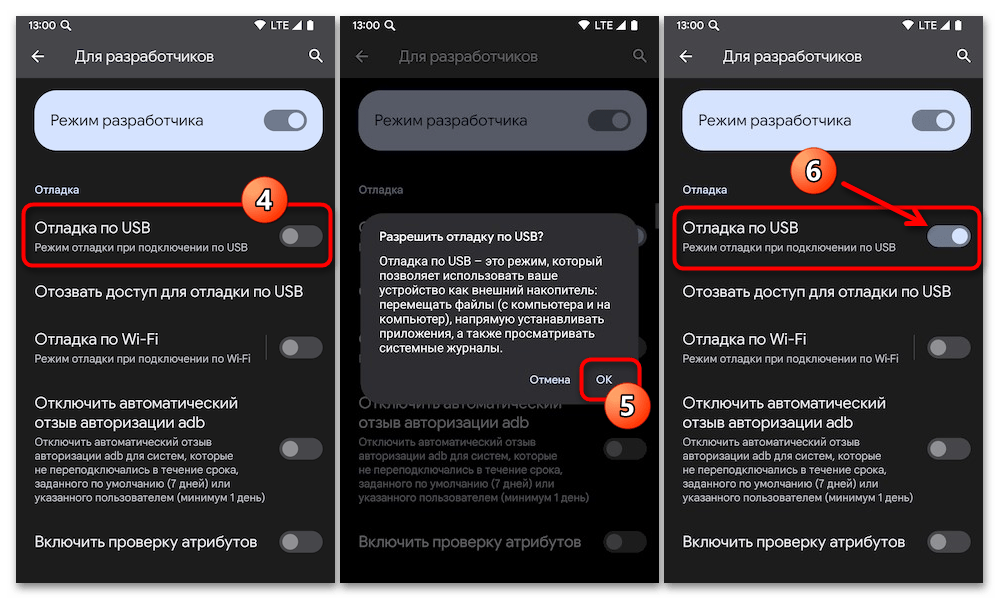
- Прежде чем приступать к выполнению вмешательства в работу системного ПО смартфона или планшета под управлением ОС Android с компьютера через ADB, на мобильном устройстве необходимо активировать особый режим функционирования – «Отладка через USB».
Сделайте это в первую очередь, а подробные инструкции по решению данного вопроса, если они необходимы, вы обнаружите в статьях по следующим ссылкам:
Подробнее:
Как включить «Отладку по USB» на Android-девайсе
Активация режима «Отладка по USB» на смартфонах Xiaomi (Mi, Redmi, POCO) - Подсоедините Андроид-девайс с активированной «Отладкой по ЮСБ» к USB-порту компьютера кабелем.
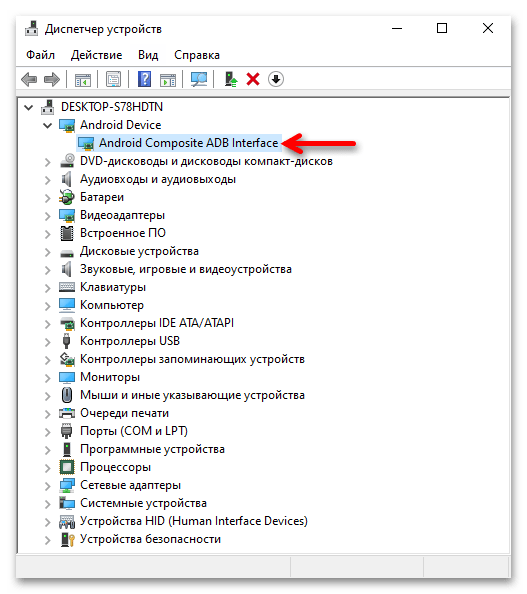
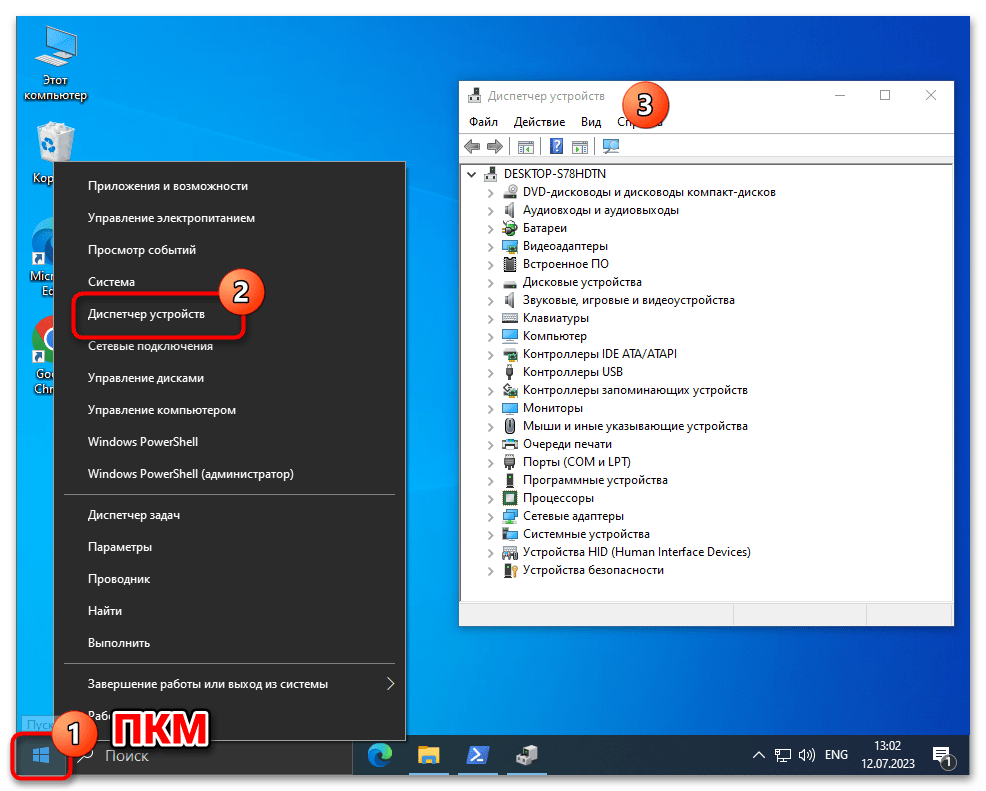
- Далее, например из контекстного меню кнопки «Пуск» на «Панели задач» операционки, откройте «Диспетчер устройств» Windows 10.
- Убедитесь, что мобильное устройство определилось операционной системой правильно и для него загружен необходимый драйвер. В таком варианте «Диспетчер устройств» отображает категорию «Android Phone», и в ней — запись «Android Composite ADB Interface» (последняя не должна сопровождаться какими-либо отметками, типа восклицательного знака на жёлтом фоне).
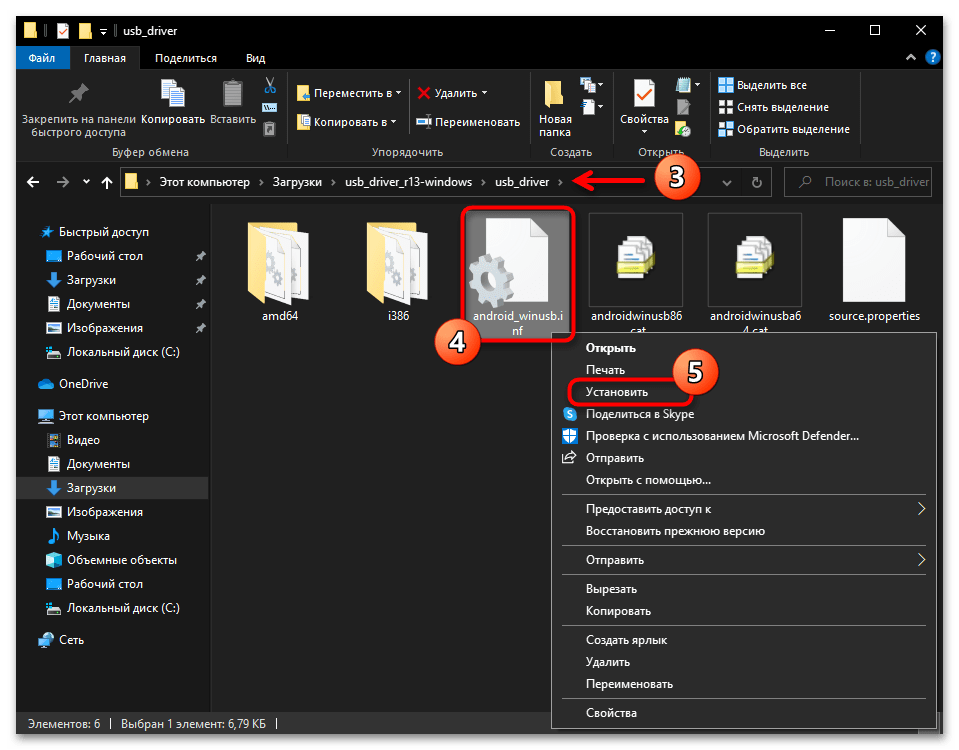
Если с определением Android-девайса в «Диспетчере устройств» Windows 10 наблюдаются какие-либо проблемы, чаще всего их следует решать путём установки/переустановки ADB-драйвера.
Читайте также: Инсталляция драйверов для работы с Android-девайсами с ПК
Опять же, в большинстве случаев, самым правильным выбором драйвера для обеспечения сопряжения ПК и Андроид-устройства через АДБ будет универсальный компонент, доступный для скачивания на интернет-ресурсе «Android Developers»
(ссылка доступна перед настоящей инструкцией).
- Запустите утилиту ADB любым из предложенных выше в этом материале способом.
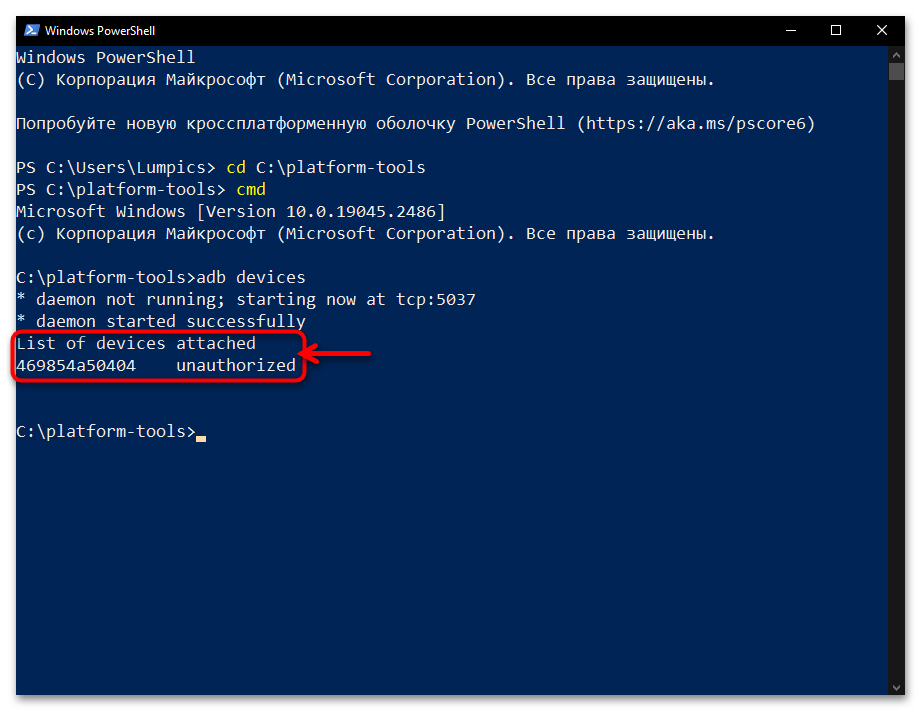
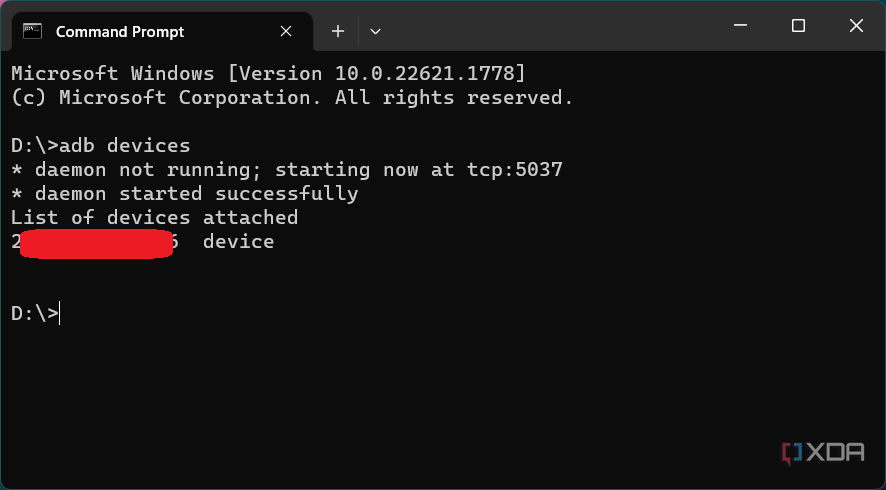
Напишите и отправьте на выполнение консолью Windows 10 следующую команду:
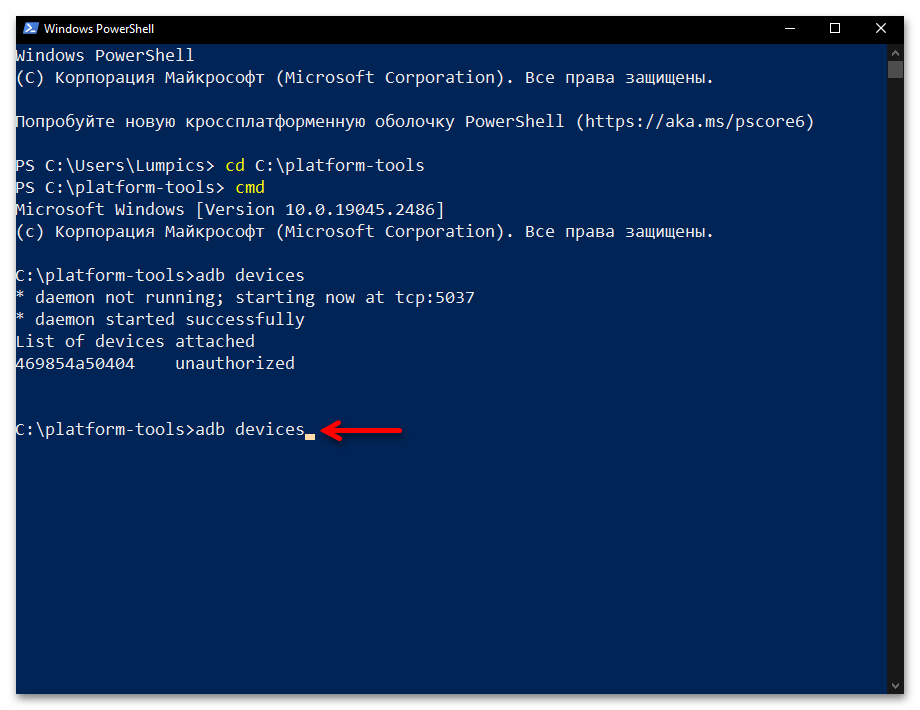
аdb devices - Если сопряжение ПК и мобильного устройства через Android Debug Bridge осуществляется впервые, «Командная строка»/«PowerShell» в ответ на указание из предыдущего пункта инструкции выдаст следующее:
List of devices attached
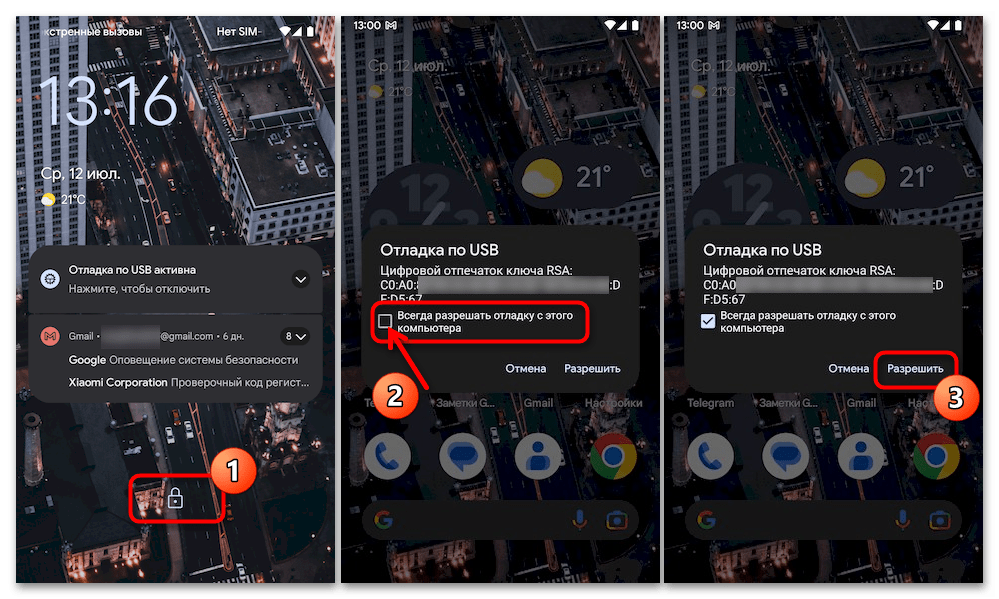
ID_Android-устройства unauthorizedВ таком случае, возьмите (не отсоединяя от компьютера) смартфон или планшет, разблокируйте его. Поставьте отметку «Всегда разрешать отладку с этого компьютера» в отображаемом на экране Android-девайса окне «Отладка по USB», а после этого коснитесь кнопки «Разрешить».
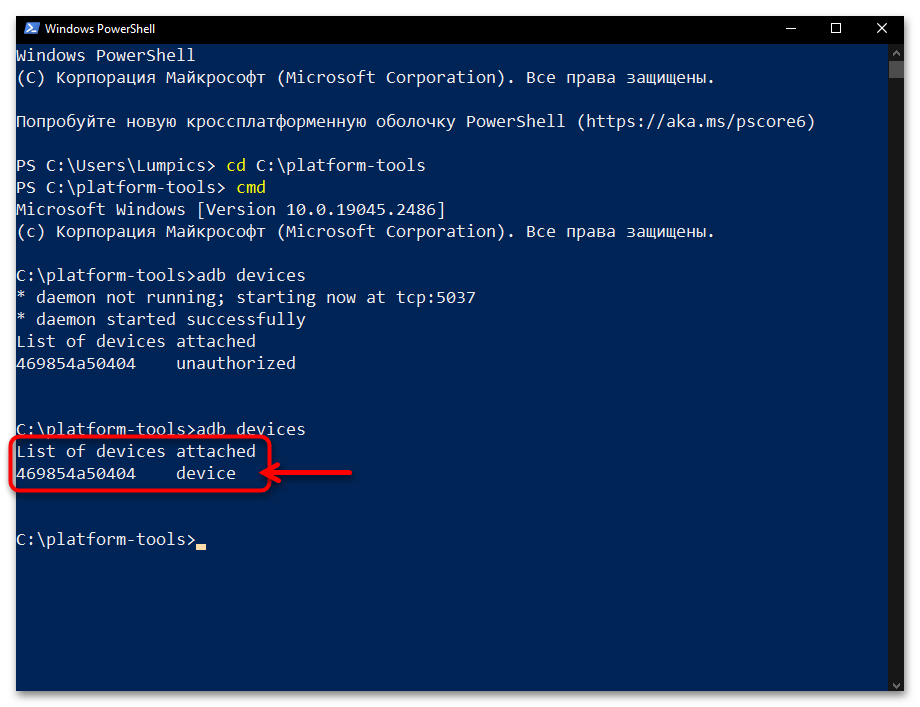
Далее перейдите к окну консоли с запущенной утилитой ADB на компьютере, повторите запуск команды
аdb devices. - Получив в «Командной строке» или «PowerShell» ответ в виде строчки
ID_Android-устройства device, вы можете переходить к непосредственному решению возлагаемых на ADB задач, — смартфон/планшет теперь подключён к утилите правильно и готов к выполнению её (а по сути – ваших) указаний.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
Sign in to your XDA account
Quick Links
-
What is the Android Debug Bridge (ADB)?
-
How to set up ADB on your phone
-
How to set up ADB on your computer
-
Add ADB to your Path environment variables
-
WSL, ADB over Wi-Fi, and using your browser
-
What else can I do with ADB?
Most of the best phones on the market run Android, and it’s preferred by many for being a more open operating system than Apple’s iOS. However, there are many things on Android that are also hidden from the average user. Thankfully, many of these capabilities can be accessed by using the Android Debug Bridge (ADB). If you’re wondering how to set it up, we’re here to help with that.
Related
These are 5 features I want Android 15 to bring, because Android updates are getting boring
Android 15 is a few months out, but there are still some features we could see, especially Pixel-exclusive features.
What is the Android Debug Bridge (ADB)?
And how does it work?
ADB is a tool provided by Google for developers to debug and test their software on Android phones. It provides access to certain features that aren’t available to regular users, and since anyone can technically use ADB, you have a way to use these advanced features even if you’re not a developer.
The internal structure of ADB is based on the classic client-server architecture. There are three components that make up the entire process.
- The client, i.e. the PC/Mac/Chromebook you have connected to your Android device. We are sending commands to our device from the computer through the USB cable or wirelessly.
- A daemon (known as «adbd») that runs commands on an Android phone. The daemon runs as a background process on each device.
- A server that manages communication between the client and the daemon. The server runs as a background process on the computer.
Because there are three pieces that make up ADB (the client, the daemon, and the server), certain pieces need to be up and running in the first place. If you have freshly booted the computer (and you don’t have it set up to start the daemon on boot), then you will need it to be running before any communication can be sent to the target Android device.
How to set up ADB on your phone
Preparing to communicate with your computer
Setting up ADB requires some preparation on both the Android phone and the PC you want to use. For starters, follow these steps on your phone:
- Launch the Settings application on your phone.
-
Tap the About phone option generally near the bottom of the list.
Depending on the OEM skin, the About phone page may be called something else or buried somewhere else in the Settings app on your device.
- Then tap the Build number option seven times to enable Developer Mode. You will see a toast message when it is done.
-
Now go back to the main Settings screen, and you should see a new Developer options menu you can access.
On Google Pixel phones and some other devices, you might need to navigate to Settings > System to find the Developer options menu.
- Go in there and enable the USB debugging option.
For now, you’re done with the process on the phone. Next up, you will need to scroll below and follow the rest of the instructions for your particular operating system.
How to set up ADB on your computer
How to set up ADB on Microsoft Windows
- Download the Android SDK Platform Tools ZIP file for Windows.
- Extract the contents of this ZIP file into an easily accessible folder (such as C:\platform-tools).
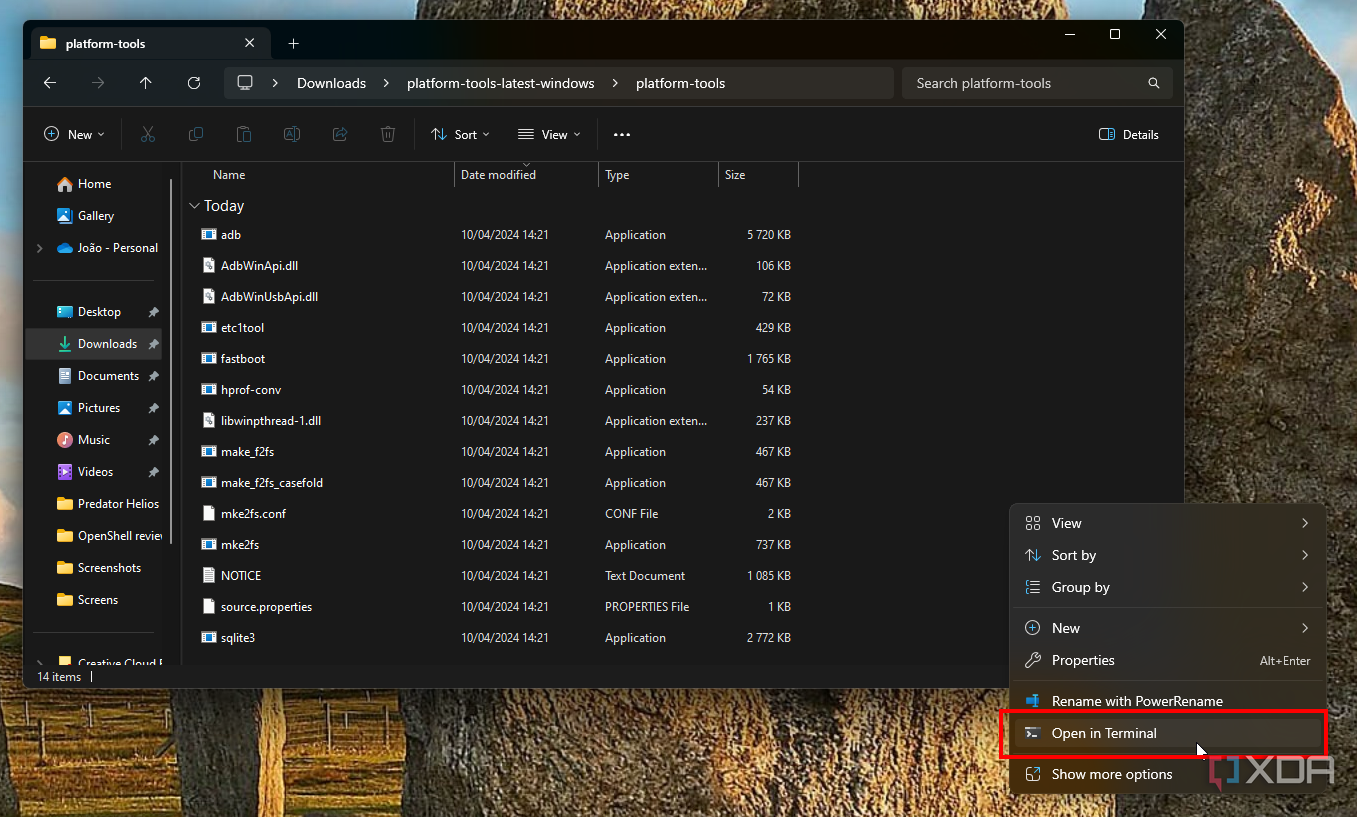
- Open File Explorer and browse to where you extracted the contents of this ZIP file.
-
Right-click an empty area of the File Explorer window and choose Open in Terminal. If you have an older version of Windows without Windows Terminal, you need to hold Shift on the keyboard while right-clicking, then choose Open PowerShell window here.
- Connect your smartphone or tablet to your computer with a USB cable. Change the USB mode to “file transfer (MTP)” mode. Some OEMs may or may not require this, but it’s best to just leave it in this mode for general compatibility.
-
In the PowerShell/Terminal window, enter the following command to launch the ADB daemon.
./adb devices
-
On your phone’s screen, you should see a prompt to allow or deny USB Debugging access. Tap Allow.
-
Finally, re-enter the command from step 6. If everything was successful, you should now see your device’s serial number in the command prompt/Terminal window.
You can now run any ADB command on your device! As a side note, you can also isntall adb using a package manager like winget, which makes it easier to keep adb updated.
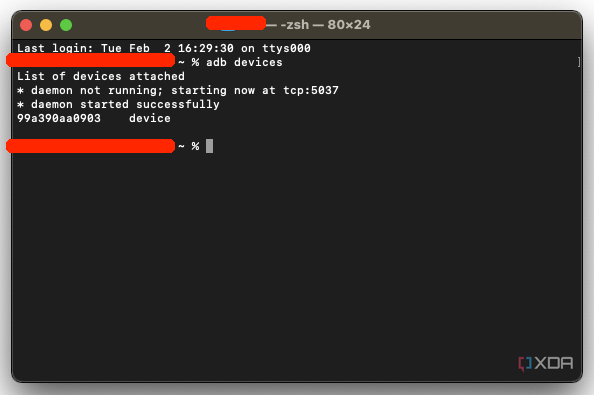
How to set up ADB on macOS
- Download the Android SDK Platform Tools ZIP file for macOS.
- Extract the ZIP to an easily accessible location (like the Desktop, for example).
- Open Terminal.
-
To browse to the folder you extracted ADB into, enter the following command, where path/to/extracted/folder represents the folder where you extracted the ZIP file to.:
cd /path/to/extracted/folder/
For example, if you extracted them to your desktop, the command would look like this:
cd /Users/XDA/Desktop/platform-tools/
- Connect your device to your Mac with a compatible USB cable. Change the USB connection mode to “file transfer (MTP)” mode. This is not always required for every device, but it’s best to just leave it in this mode, so you don’t run into any issues.
-
Once the Terminal is in the same folder your ADB tools are in, you can execute the following command to launch the ADB daemon:
./adb devices
-
On your phone, you’ll see an Allow USB debugging prompt. Allow the connection.
-
Finally, re-enter the command from step 7. If everything was successful, you should now see your device’s serial number in macOS’s Terminal window.
Congratulations! You can now run any ADB command on your device!
While the guide above will certainly work, veteran macOS users can also opt to install ADB on their Macs using an unofficial package manager such as Homebrew or MacPorts. That way, you don’t have to manually update the binaries.
How to set up ADB on Linux
- Download the Android SDK Platform Tools ZIP file for Linux.
- Extract the ZIP to an easily accessible location (like the Desktop, for example).
- Open a Terminal window.
-
Browse to the extracted folder using the following command, replacing path/to/extracted/folder with the folder where you extracted the ZIP file to:
cd /path/to/extracted/folder/
For example:
cd /home/XDA/Desktop/platform-tools/
- Connect your device to your Linux machine with your USB cable. Change the connection mode to file transfer (MTP) mode. This is not always necessary for every device, but it’s recommended, so you don’t run into any issues.
-
Once the Terminal is in the same folder your ADB tools are in, you can execute the following command to launch the ADB daemon:
./adb devices
-
Back on your Android device, you’ll see a prompt asking you to allow USB debugging. Go ahead and grant it.
-
Finally, re-enter the command from step 8. If everything was successful, you should now see your device’s serial number in the Terminal window output.
Congrats! You can now run any ADB command on your device!
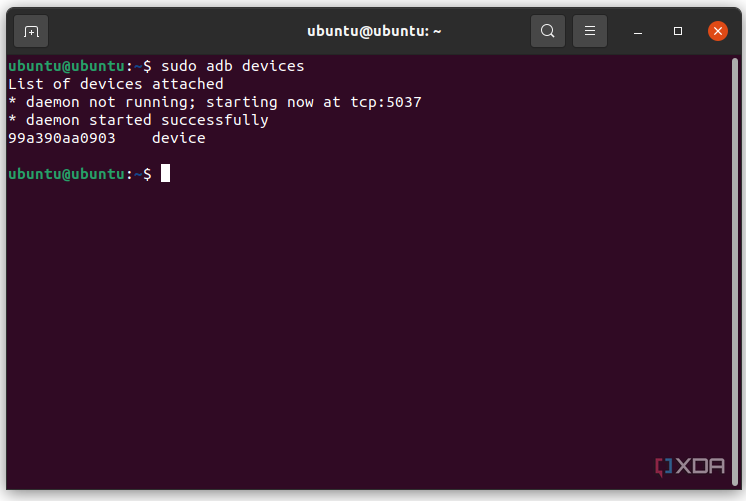
Linux users should know that there is an easier way to install ADB on their computers. The guide above will certainly work for you, but those who own a mainstream Debian/Ubuntu or Fedora/SUSE-based distro of Linux can skip steps 1 and 2 of the guide above and use one of the following commands:
-
Debian/Ubuntu-based Linux users can type the following command to install ADB:
sudo apt-get install android-sdk-platform-tools
-
Fedora/SUSE-based Linux users can type the following command to install ADB:
sudo dnf install android-tools
However, it is always better to opt for the latest binary from the Android SDK Platform Tools release since the distro-specific packages often contain outdated builds.
Add ADB to your Path environment variables
You can use ADB just fine through the steps above, but if you’re doing this frequently, adding ADB to the PATH environment variable is a huge time saver. All major operating systems have a PATH variable, and it allows you to specify the location of important programs that are also trusted by the user, so the computer can automatically access it without ahving to open the program’s location first. For instance, you can type «calc» in the Run prompt of Windows to launch calculator, but not «chrome» to start Google Chrome — simply because the location of the latter isn’t included in the PATH variable.
Adding ADB to the PATH environment variable allows you to run ADB by running the terminal normally, and it also makes it so you don’t need to precede ADB commands with ./ . Here’s how to do it.
Windows
-
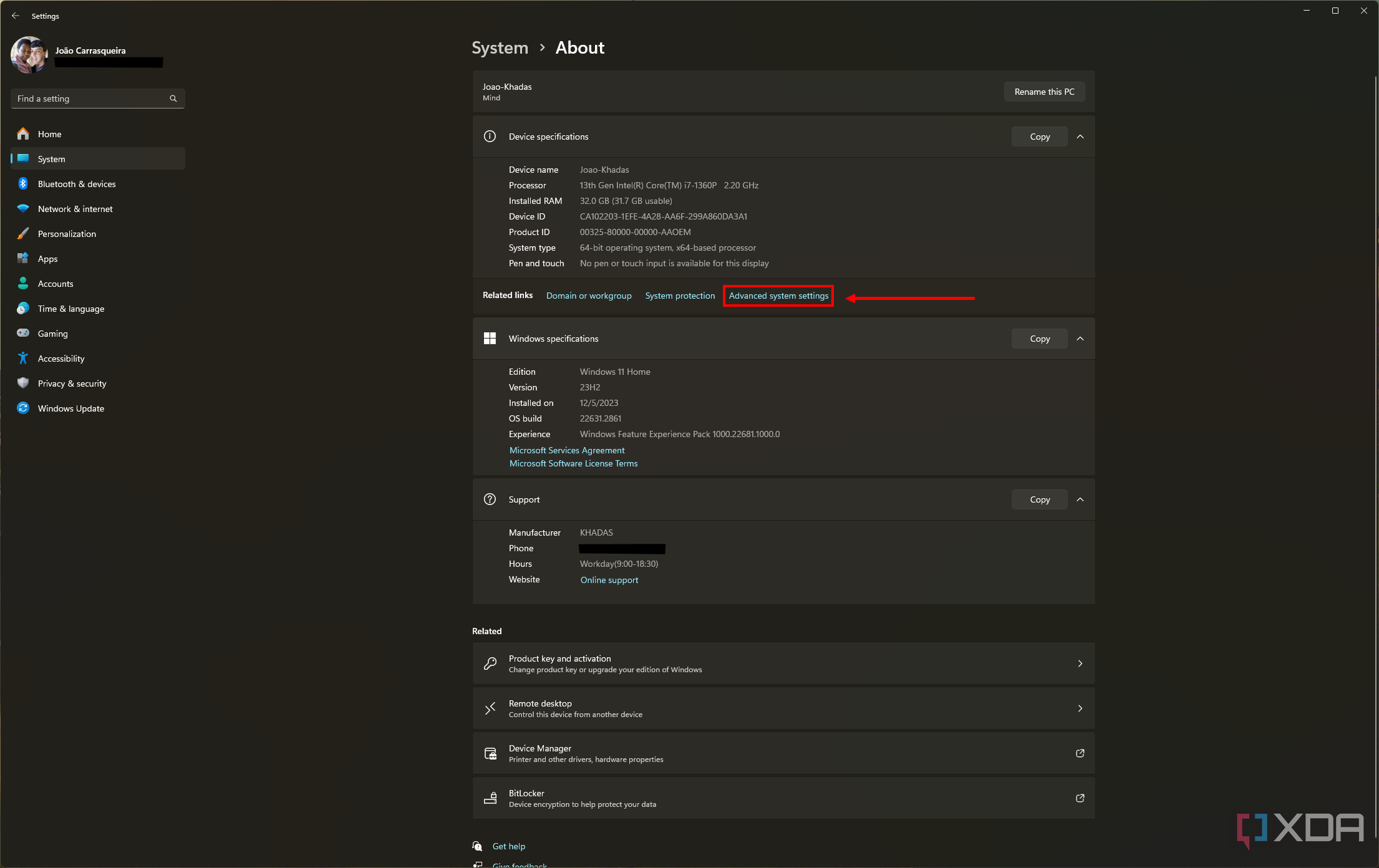
Right-click on the Start button (or use the Windows + X keyboard shortcut) and select the System option. You will be greeted with a screen showing some system information.
-
Select Advanced system settings from the Related links section under Device specifications.
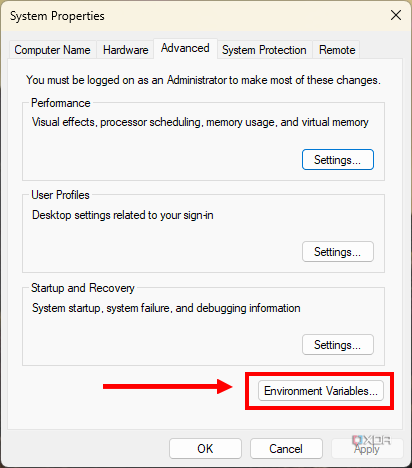
-
Click on the Environment Variables button.
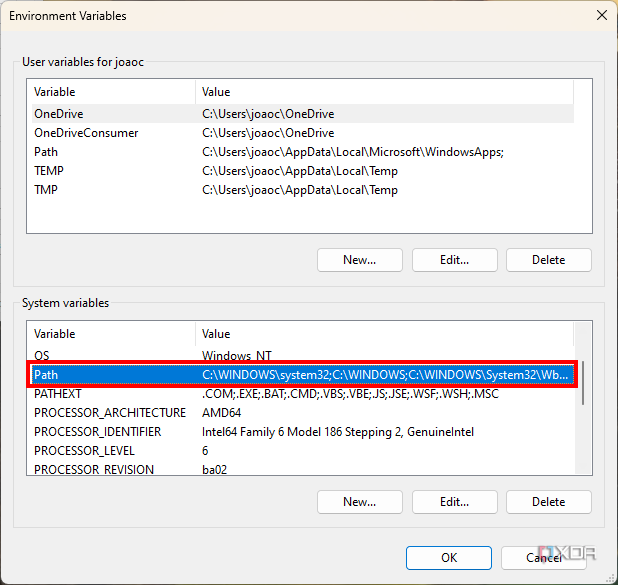
-
Look for the variable named Path under System variables and double-click it.
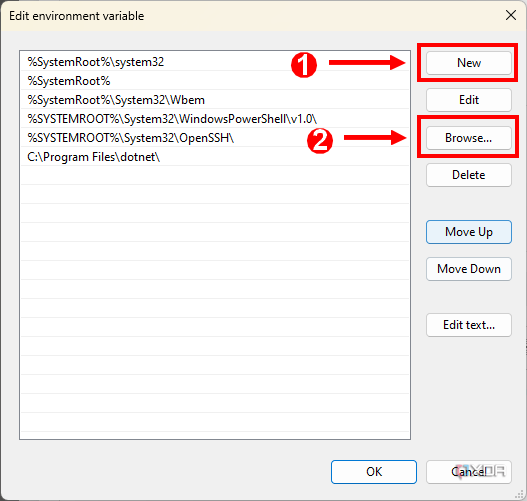
-
Click New, then Browse and navigate to the folder where you extracted the ADB files (e.g. C:\platform-tools).
- When you see the folder location is properly listed, click the OK button out of all the Windows you have opened to confirm.
- Sometimes, the graphical shell needs a restart to make the changes take effect. You can simply sign out and sign in again or reboot your PC to force Windows to use the updated PATH settings.
Now start a new terminal or command prompt instance and type adb to verify the location has been added.
In case you use a package manager like Chocolatey to install ADB, it should take care of the PATH variable editing portion as well. As a result, you can skip the above process.
macOS
You can use the following steps to set up the PATH environment variable in macOS, but if you installed ADB using a package manager like Homebrew, this is unnecessary. Here’s how it works:
- Note down the location where you extracted the ADB tools.
-
Open the Terminal app and make sure to be in the Home directory.
cd ~
-
In case you’re running any macOS version older than Catalina, the default shell should be Bash. For macOS Catalina and newer, the default changed to the Z shell (Zsh). Hence, you need to determine the current shell before changing the PATH variable. Type the following command and press Enter to see the shell your Mac is using:
echo $0
-
Depending on the output, create a shell configuration file. For Bash:
touch .bash_profile
For Zsh:
touch .zshrc
People who are already using custom shell configurations can skip this step.
-
Open the shell configuration file with TextEdit: For Bash:
open -e .bash_profile
For Zsh:
open -e .zshrc
If you prefer to use nano/pico/vi or any other CLI text editor, you can instead.
-
Adjust the location according to the first step in the following command and add it to the shell configuration file you just opened:
export PATH=$PATH:/path/to/extracted/folder/
For example:
export PATH=$PATH:/Users/XDA/Desktop/platform-tools/
-
Save the file and close the TextEdit app. Next, go back to the Terminal app and reload your shell settings. For Bash:
source .bash_profile
For Zsh:
source .zshrc
-
You’re done. Optionally, verify the PATH variable assertions using the following command:
echo $PATH
To test if the process was successful, start a new Terminal instance and type adb. You can also install adb with Homebrew, which will automatically add it to your PATH!
Linux
- Note down the location where you extracted the ADB tools.
-
Open the Terminal app and make sure to be in the Home directory.
cd ~
- Due to the fact that most common Linux distributions ship with Bash as their default shell, the next steps will be Bash-specific. You can, of course, consult the documentation of your preferred shell and modify the commands to suit your needs.
-
Open the shell configuration file with a text editor:
sudo nano .bashrc
You can also use other editors like vi or gedit.
-
Add the following line to the end of the .bashrc file. Remember to adjust the location according to the first step beforehand.
export PATH=$PATH:/path/to/extracted/folder/
For example:
export PATH=$PATH:/home/xda/platform-tools/
Be careful editing this file; do not add anything else or change anything else.
-
Save the file. Next, go back to the Terminal app and reload your shell settings:
source ~/.bashrc
-
Optionally, verify the PATH variable assertions using the following command:
echo $PATH
Now you can call ADB from anywhere under Linux. To check if it’s working, spawn a new Terminal window and type adb.
It is worth mentioning that you don’t need to perform these steps if you prefer to install (and update) ADB using the distro-specific packages.
WSL, ADB over Wi-Fi, and using your browser
How to set up ADB on Windows Subsystem for Linux and ChromeOS
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) offers Windows users a seamless way to run Linux apps. However, the environment has yet to offer full-fledged USB hardware access. As a consequence, ADB under WSL can’t access your Android device, even if you install it using the aforementioned way. Nonetheless, there exists an official workaround, which utilizes the open-source usbipd-win project. To know more, take a look at our tutorial on how to set up USB passthrough in WSL.
For ChromeOS, you need to turn on the built-in Linux development environment first. By default, it offers you a Debian instance. You can then easily set up ADB using the Linux-oriented steps mentioned earlier.
Just to cover all of our bases here, users may need to put a ./ in front of any ADB commands you use in the future, especially when they are using the extracted binaries directly from the Google-provided Platform Tools ZIP. This is something any *nix user (or Windows user running PowerShell/Terminal) will likely know, but it’s important to remember.
How to set up ADB on your browser
The ADB protocol can be implemented using the WebUSB API in order to control Android phones directly from web browsers. Tango (formerly known as Yet Another WebADB) is one such project that allows users to perform most of the functionality provided by ADB right from the web browser without installing any binary. All you need is a web browser that supports the WebUSB API (such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, or Firefox) and you are good to go. It’s worth noting that some browsers, such as Vivaldi, don’t properly display the popup for USB device connections, so they may not work for this.
How to use ADB over Wi-Fi
Android 11 and higher editions natively support ADB connection over Wi-Fi. This eliminates the need to deal with common USB connection issues and additional steps, such as Android OEM driver installation on Windows.
In order to set up wireless debugging, do the following:
- Make sure that your PC/Mac and the phone are connected to the same wireless network.
-
On your phone, go to Developer options under Settings and enable Wireless debugging. On the Allow wireless debugging on this network? popup, select Allow.
-
Tap on the Wireless debugging option and select Pair device with pairing code.
-
Take note of the pairing code, IP address, and port number displayed on the phone screen.
-
On your PC/Mac, run the following command:
adb pair IP_Address:PortUse the IP address and port number from step 4.
- When prompted, enter the pairing code that you received in step 4. A message should indicate that your device has been successfully paired.
-
Next, run the following command on the PC/Mac’s terminal window:
adb connect IP_Address:PortLook at the IP address & Port section under Wireless debugging in step 3 for the IP address and port.
-
If everything goes right, then you should see a message like the following:
connected to 192.168.68.100:37173 - Now you’re ready to type whatever ADB shell command you want.
Examples of ADB commands
To check if you have successfully installed ADB, connect your device to your PC/Mac with your USB cable, and run the adb devices command as described above. It should display your device listed in the Command Prompt/PowerShell/Terminal window. If you get a different output, we recommend starting over with the steps.
As mentioned above, you can use ADB to do all sorts of things on an Android device. Some of these commands are built directly into the ADB binary and should work on all devices. You can also open up what is referred to as an ADB Shell that will let you run commands directly on the device. The commands which are run directly on the device can vary from device to device (since OEMs can remove access to certain ones, and also modify ADB behavior) and can vary from one version of Android to the next as well.
Below, you’ll find a list of example commands which you can do on your device:
-
Print a list of connected devices:
adb devices
-
Kill the ADB server:
adb kill-server
-
Install an application:
adb install
-
Set up port forwarding:
adb forward tcp:6100 tcp:7100
-
Copy a file/directory from the device:
adb pull
-
Copy a file/directory to the device:
adb push
-
Initiate an ADB shell:
adb shell
What else can I do with ADB?
Below is a list of XDA tutorials for various devices that detail many applications of ADB commands in order to modify hidden settings, customize OEM features or user interfaces, and much more!

Related
How to boot into recovery mode using button combos, ADB, and root apps
If you have an Android or iOS device and are wondering how to boot into recovery to clear cache or reset your device, this is how to do it!

Related
How to uninstall carrier/OEM bloatware without root access
If you want to get rid of carrier/OEM apps from your phone, here’s how you can uninstall bloatware from your device without root access!
Related
How to debloat your phone (and more) without connecting to a PC
LADB is an app that lets you run ADB shell commands from your phone, no root and no PC needed! Use it to debloat your phone and more!

Related
How to sideload apps on Android TV: APK Install and ADB Sideload methods explained in easy-to-follow steps!
Not sure how to sideload apps on Android TV? We explain two easy ways to sideload APKs or Android app bundles on Android TV devices.
Related
Control your Android Smartphone from your PC for free with scrcpy
A new tool called «scrcpy» allows you to display your phone screen on your computer with just a USB connection and ADB. No root required.

Related
ADB tips and tricks: Commands that every power user should know about
There’s a lot to the Android Debug Bridge that you may not know about. Click here for some useful tips and tricks for using ADB!
The Android Debug Bridge (ADB) is a versatile command-line tool that allows you to communicate with an Android device. It serves as a bridge between your device and development environment, enabling you to run shell commands, debug apps, install applications, and transfer files, among other tasks. In this article, we will guide you through the process of setting up ADB on Windows 11, ensuring that you have all the tools you need to maximize the use of your Android devices.
Understanding ADB and its Importance
ADB is part of the Android Software Development Kit (SDK), which provides developers and advanced users with powerful controls to debug and manage their devices. ADB lets you perform a variety of tasks, including but not limited to:
- Installing and Uninstalling Applications: You can install APK files directly from your computer.
- Debugging Applications: Developers can track app behavior in real time using various commands.
- File Transfers: Sending files directly to your Android device or pulling files to your computer is a breeze with ADB.
- Running Shell Commands: You can execute commands on your Android device shell.
Setting up ADB on Windows 11 will empower you to control your Android devices effectively, whether you’re a developer or just an enthusiastic user looking to explore beneath the surface.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the setup of ADB, ensure that you have the following:
- Windows 11 Installed: Make sure your system is running Windows 11.
- Android Device: You will need an Android device for testing.
- USB Cable: A good quality USB cable compatible with your Android device.
- Basic Command Line Knowledge: Familiarity with command-line operations will help you navigate the installation process smoothly.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up ADB on Windows 11
Step 1: Download the ADB Toolkit
-
Visit the Official Site:
Go to the official Android developer website to download the ADB and Fastboot tools. This is part of the SDK Platform Tools package.SDK Platform Tools
-
Choose the Windows Version:
On the download page, locate the download link for Windows. This will typically be a zip file. -
Extract the Files:
Once the zip file is downloaded, extract it to a location on your computer where you’ll easily find it, likeC:adb.
Step 2: Enable USB Debugging on Your Android Device
To connect your Android device to ADB, you need to enable USB Debugging.
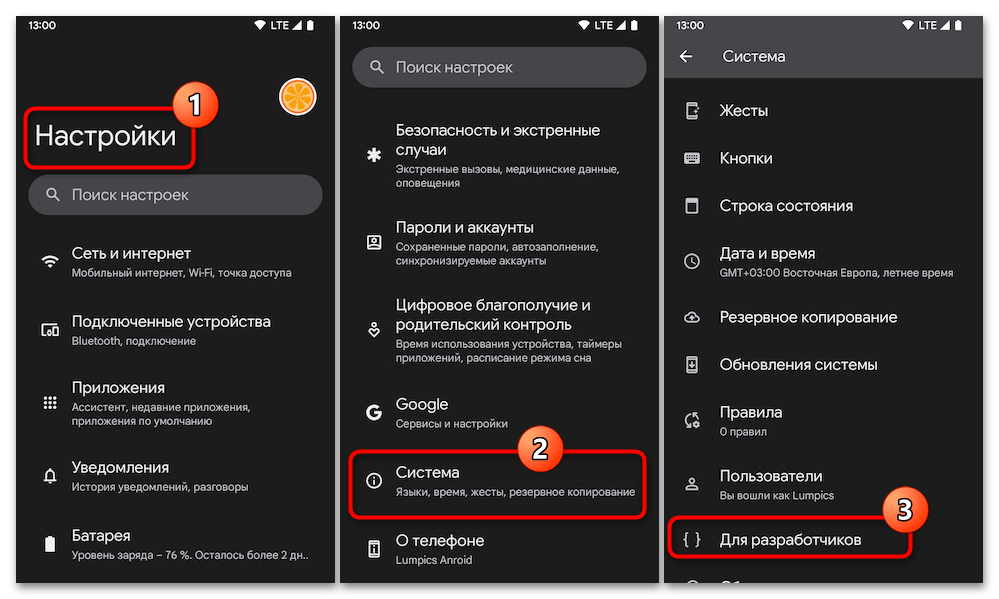
- Open Settings: On your Android device, go to Settings.
- About Phone: Scroll down and find the About Phone option.
- Build Number: Tap the Build Number option seven times until you see a message that says “You are now a developer!”
- Back to Settings: Go back to the main settings menu and look for Developer Options.
- USB Debugging: In Developer Options, turn on USB Debugging. Confirm any prompts that may pop up.
Step 3: Connect Your Device to the Computer
Using a USB cable, connect your Android device to your Windows 11 computer. When prompted on your device, select the option to allow USB debugging. A message should appear asking you if you want to allow USB debugging from your computer; make sure to check the box to allow and tap OK.
Step 4: Set Up System Environment Variables
Setting up system environment variables makes it easier to run ADB commands from any command prompt on your computer.
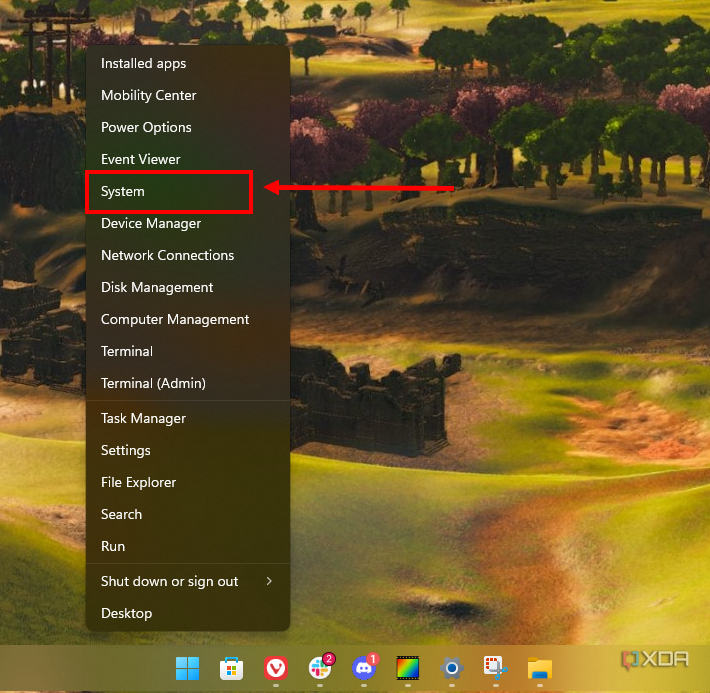
- Open System Properties: Right-click on the Start menu and select System. Then click on Advanced system settings.
- Environment Variables: In the System Properties window, click on the Environment Variables button.
- Edit Path:
- Under the System variables section, scroll and find the Path variable, then click on Edit.
- Click New and enter the path where you extracted ADB (for example,
C:adb).
- Confirm: Click OK on all dialog boxes to close them and apply the changes.
Step 5: Verify ADB Installation
To confirm that ADB is correctly installed and configured, you can run a simple command.
-
Open Command Prompt:
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type
cmdand hit Enter.
-
Check ADB Version:
Type the following command and hit Enter:adb versionIf ADB is set up correctly, you should see the version number of the ADB installed.
Step 6: Testing ADB Connection
Now it’s time to check if your Android device is recognized by ADB.
-
List Connected Devices:
In the command prompt, type the following command:adb devices -
Check the output: If everything is set up correctly, you should see your device’s serial number listed in the command output. If it’s not listed, troubleshoot your connections and ensure USB debugging is enabled.
Common ADB Commands
Now that you have ADB set up, you can use it to perform various operations. Here are some common commands that you might find useful:
- Install an APK:
adb install path/to/app.apk - Uninstall an App:
adb uninstall package.name - Copy Files to Device:
adb push path/to/local/file /sdcard/ - Copy Files from Device:
adb pull /sdcard/file /path/on/local/machine - Reboot the Device:
adb reboot
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter issues during the setup or usage of ADB, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
-
Device Not Recognized: Ensure that USB debugging is enabled and that the drivers for your Android device are installed. You can install manufacturer-specific drivers or use the Google USB Driver.
-
ADB Not Recognized: Make sure that the ADB path is correctly added to your system environment variables.
-
Firewall or Anti-Virus Interference: Sometimes, security software can interfere with ADB connections. Disable them temporarily while testing.
Conclusion
Setting up ADB on Windows 11 is a straightforward process that involves downloading the necessary files, enabling USB Debugging on your Android device, and configuring your computer to communicate with it effectively. With ADB at your fingertips, you can unlock an array of capabilities that greatly enhance your interaction with Android devices.
Whether you’re a developer testing applications, an enthusiast tinkering with your device, or someone in need of quick file transfers, ADB is an invaluable tool. By following the steps outlined above, you should be well-equipped to utilize ADB effectively. As you continue exploring its features, you’ll discover even more ways to leverage the power of ADB in your Android experience. Happy debugging and experimenting!
Android is the most feature-rich platform. It has all the options you’ll ever need to control and configure the device however you want. However, some advanced settings are buried deep down. To access them you have to install ADB shell and use it. Today, I will show you how to install ADB on Windows 10.
What is ADB
Android Debug Bridge or more widely knows as ADB shell is a command line tool that helps developers access advanced settings and debug Android apps and system settings. Besides from debugging, you can use ADB shell to back up the android device, install apps on your SD card by default, disable specific features of an app, transfer files, etc. In fact, you can even use ADB to make system level changes.
Generally, ADB is bundled with Android SDK (Software Development Kit). So, if you’ve installed Android SDK then you already have access to the ADB shell on Windows 10 with several other essential tools like Fastboot. However, if you are not a developer and don’t want to install the complete Android SDK package for just one tool that is only used occasionally then you can install ADB on Windows separately. i.e, without installing Android SDK.
Related: How to Run Android Apps on Ubuntu [Natively]
Enable USB Debugging Mode
Before installing ADB on Windows 10, you need to configure your Android device to accept the ADB commands. To do that, you have to enable USB debugging mode. Thankfully, it is very easy to do. Just follow the below instructions.
- Launch apps menu and tap on the “Settings” icon.
- Here, scroll down and tap on the option “About“.
- Now, scroll down again and repeatedly tap on the option “Build number” 7 times.
- Go back to the main Settings screen, scroll down and tap on the new option “Developer Options“.
- Here, toggle the button next to USB Debugging option. Tap on the option “Ok” in the confirmation pop-up to enable USB debugging mode.
That’s it, you’ve configured the Android device to receive ADB shell commands. You can now install ADB on Windows 10.
Related: 10 Best Secret Texting Apps for Android (Private Texting Apps for Android)
Note: the same procedure is applicable for older versions of Windows like 7 and 8.
1. To start off, download ADB for Windows from the official Google website.
2. Create a new folder with the name “ADB” in the root of the C drive. Now, extract all the files in the downloaded ZIP file to the folder you just created. This is how it looks like when you are done extracting.
3. Grab a USB data cable and connect your android device to the Windows computer. If prompted, select “file transfer (MTP)” mode.
4. Now, search for “Command Prompt” in the start menu and open it.
5. In the command prompt, use the below command to navigate the ADB installation folder. If you’ve installed ADB folder in some other place then change the command accordingly.
cd c:\ADB
6. Once you are here, execute the following command ADB Daemon.
adb devices
7. As soon as you execute the command, you will see “Allow USB debugging” prompt on your android device screen. Tap on the “Ok” button. Now, your device will be listed in the command prompt.
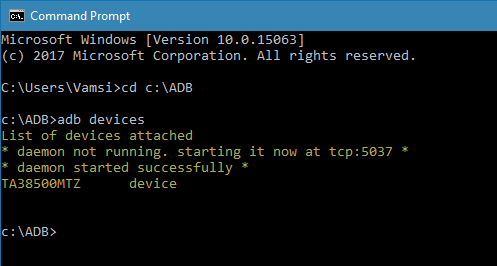
If you see your device listed then you’ve successfully installed ADB on Windows 10. If not, make sure that the device is properly connected and you have installed android drives on Windows. Generally, you can download android drivers specific to your device on the manufacturer website.
Related: How to Use Multiple Facebook Accounts on Android
Optional: Access ADB from Any Folder
As you can see, with the above method, you have to first navigate to the ADB installation folder if you want to use the ADB shell. This is not so much a problem but an inconvenience. To deal with that, you can add ADB to Windows Path. This allows you to access ADB from any folder or directory.
1. To add ADB to Windows path, search for “View advanced system settings” in the start menu and open it.
2. In this window, click on the button “Environment Variables“.
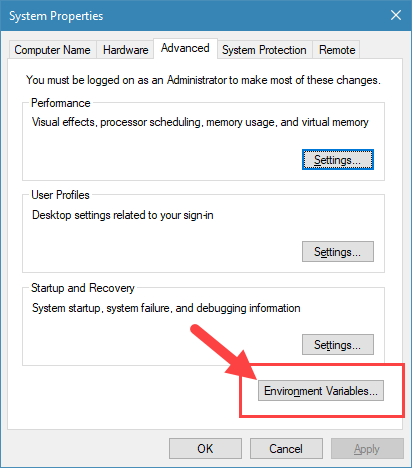
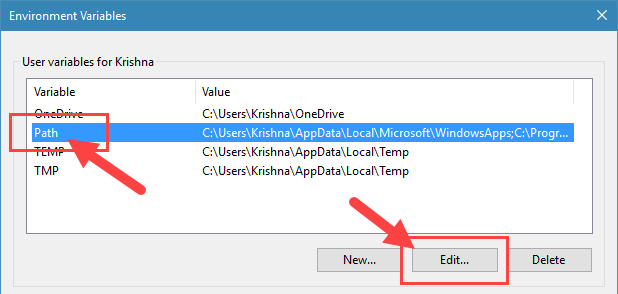
3. Here select the Path variable under “User variables for Username” and click on the button “Edit“.
Related: How To Disable Auto Media Download Feature In WhatsApp [Android]
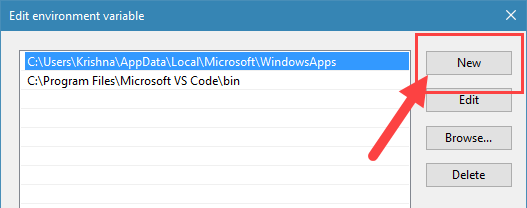
4. Now, click on the “New” button.
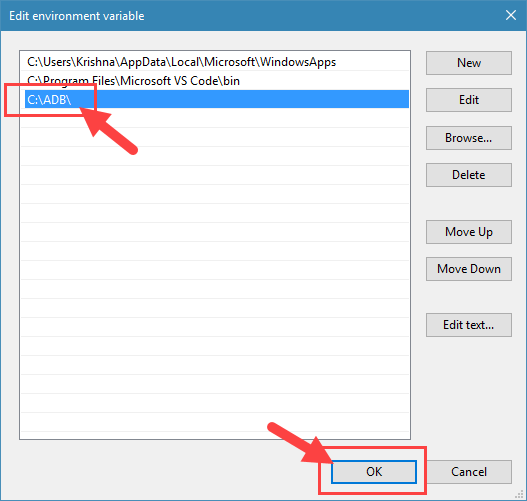
5. Enter the path to the ADB folder and click on the button “Ok” to save the changes. In my case, the folder path is C:\ADB.
6. Click on the “Ok” on other main windows to save the changes.
From this point forward, you can access ABD from any folder. As you can see from the below image, I’m starting the ADB daemon from a folder in my E drive.
That’s all there is to do and it is that simple to install ADB on Windows 10 and add ADB to Windows path. If you find this article useful then do read how to disable volume buttons in android and how to hide audiobooks from music players in android.
Comment below sharing your thoughts and experiences about using the above method to install ADB on Windows.
Related: How to Download Android Apps to PC without Installing Any Software [Quick Tip]
What is ADB? ADB is short for Android Debug Bridge, a versatile command-line tool that lets you communicate with a device. It was mainly for developers to debug apps, but now basic users can also use it to perform many useful activities between computer and their Android smartphones. In this article, we are going to show you how to install ADB in Windows computer and how to use ADB to do something interesting to Android mobile phone.
It is quite easy to install and set up ADB in Windows computer. Actually, the size of the tool is merely 4.51MB, so it won’t take up much space on your computer. Here we Windows 10 as example.
- Step 1. Download Platform Tools for Windows. Confirm to download on the new window and save the zip file to a folder on your PC.
- Step 2. Extract the zip file after download.
- Step 3. Press Shift key and right click within the extracted folder, then choose Open PowerShell window here (or Open command window here on some computers)
- Step 4. A command prompt should appear.
This means that ADB is set up on your Windows computer. In order to communicate with your Android phone, however, you also need to enable USB debugging on your handset.
Part 2. Enable USB Debugging on Your Mobile Phone
USB debugging must be turned on in order to use ADB. The steps to turn on USB debugging are varied on different versions of Android OS, but the instruction below should work for most Android smartphones used nowadays.
- Step 1. Go to Settings > About phone.
- Step 2. Scroll down to find and tap Build number for 7 times.
- Step 3. Back to Settings, then find and tap Developer options.
- Step 4. Within Developer options, enable USB debugging. Confirm your choice.
- Step 5. Connect your phone to PC.
- Step 6. Choose Allow when “Allow USB debugging?” window pops up on your phone screen.
Note: It is suggested that tick Always allow this computer if you are using a trusted computer in order to get smooth experience with ADB and in case of accidents when you need to rescue data but unable to operate on the phone, like Android broken screen data recovery.
Part 3. Test ADB
Once you have finished the above preparing work, you can test if ADB works.
- Step 1. Run ADB command window as described on Part 1.
- Step 2. Connect your phone to PC, and type adb devices in command window and hit Enter.
If everything goes right, a result will return as above (with different series code). If nothing appears, then you should check if the driver for your phone is properly installed. A straight indication of functional driver is that your phone should be recognized by the computer.
Part 4. Useful Things You Can Do with ADB
Once ADB is correctly installed on your Windows computer, you can do many useful things with ADB. The following is just a small portion of all the things it can do. You will find that lots of tools can do the same thing in normal environment, but ADB can do it easily and may play important role on some occasions.
USB debugging must be turned on!
Option 1. Backup and Restore Android with ADB
Backup is not necessarily the most frequently used function for Android users, but it should be the very first thing whenever we try anything new or danger. In case of accidents, a backup of mobile phone will work like a saver to our life. ADB can help you make backups for your Android smartphone with no need of root or custom recovery.
adb backup -all -f <path/filename.ab>
adb restore <path/filename.ab>
The path should be a location on your computer system drive. For example,
adb backup -all -f /Backup/backup1.ab
Notes:
- The backups are saved to computer instead of phone memory or SD card.
- You’ll need to unlock your phone to allow the backup to start.
- The backup mainly contains documents and media files on your phone. For a literarily full backup of phone data and whole system, refer how to make a Nandroid backup in custom recovery.
Option 2. Install APK for Android from Computer
There are already lots of methods to install apps to Android phone, including installing apk files on mobile phone, but occasionally you may need to install APK to Android phone from computer. This is especially useful if you know that the installation is completely silent with no need of operation on phone screen.
adb install <path to the apk on your computer>
The path should be a location on your computer system drive. Please move the apk file to the system drive if it is not. For example,
adb install /MyDownloads/TitaniumBackup.apk
Notes:
- No need to operate on phone screen.
- No prompt of permissions from the app.
- No need to enable Unknown source on mobile phone.
- Be care of apk files containing malware.
This function may work magically when you want to install an app to your phone but unable to control the device, like due to broken or black screen.
Option 3. Reboot Phone to Recovery Mode and Bootloader
In recovery mode, people can clear cache and data, factory reset or backup mobile phone. In bootloader (or Download mode for Samsung), people can flash ROMs to handset. If you don’t know anything about recovery mode and bootloader, please make sure you know it clearly and need it first.
adb reboot recovery
adb reboot bootloader
Notes:
- No need to press key/button groups on phone body.
- Occasionally, you may need to reboot manually or even remove battery when the command fails.
- After every reboot, you’ll need to reconnect the phone in order to let ADB work
Option 4. Convert SD Card as Internal Storage with ADB
Since Android Marshmallow, users can format SD card as internal storage, which effectively reduces insufficient storage problem. The conversion is easy to do on Settings > Storage if your phone is supported for the feature. However, some manufacturers intentionally hide this function from users even if their smartphones have upgraded to Android 6.0 or newer. With ADB, we can convert SD card as internal storage when the option is invisible.
Warning: Please move or back up SD files card first. After the conversion, the SD card won’t be recognized by other mobile phones or computers. Once your phone is reset or dead, you may find the SD card inaccessible by any device.
- Step 1. Launch ADB command window.
- Step 2. Connect the phone inserted with SD card to computer.
- Step 3. Type the following commands and hit enter after each:
adb shell
sm list-disks
sm partition disk:179,64 private - Step 4. Go to Settings > Storage to check your storage status.
Note: If there is no change in phone storage, then you may reboot it and check the storage again.
The above are 4 useful things that Android users may like or need to do with ADB. If you have more ideas or questions about what we can do with ADB, please kindly share with us.