Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Lua is a lightweight programming language that has gained popularity in the world of game development and scripting. Its simplicity and versatility make it an ideal choice for creating interactive stories, simulations, and games. With Lua, developers can easily automate repetitive tasks, create custom game scripts, and even build their own applications. Its flexibility also allows it to be used in a wide range of industries, from education to business, making it a valuable tool for anyone looking to create engaging and interactive experiences.
Installing Lua on Windows is a crucial step for developers and gamers who want to tap into its vast potential. By having Lua on your PC, you can access a vast community of developers, plugins, and resources, allowing you to create complex projects and scripts with ease. With Lua, you can access the Lua community, which is known for its extensive documentation, tutorials, and example code. This community support makes it easier for developers to learn and experiment with Lua, and to create high-quality projects quickly and efficiently.
In this tutorial, we’ll guide you through the process of installing or downloading Lua Windows, so they can start exploring its capabilities and creating their own projects.
Installing Lua on Windows
To install lua on Windows, just follow the steps given below.
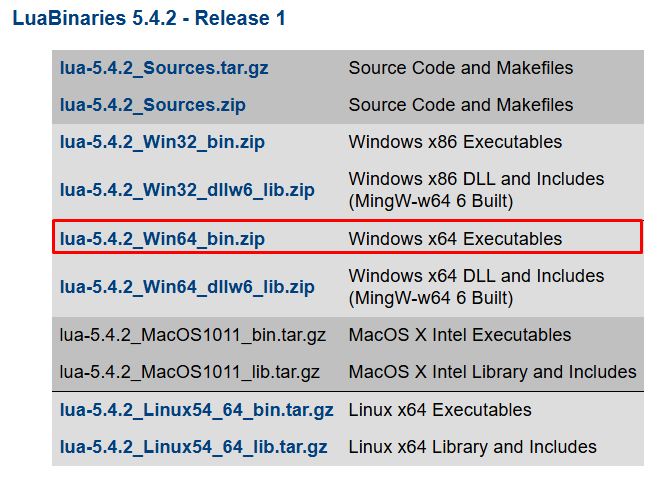
Step 1: Downloading Lua Binaries
To start, you’ll need to download the Lua binaries from the official LuaBinaries download page. LuaBinaries is the official distribution of Lua binary files, and it’s available for both 32-bit and 64-bit Windows systems.
For this tutorial, we’ll be downloading the 64-bit version of the Windows x64 executables, which is suitable for 64-bit Windows systems.
Step 2: Extracting the Archive
Once you’ve downloaded the Lua Windows installer, you’ll need to extract the archive using a tool like 7-Zip or rar. Right-click on the downloaded archive and either select “Extract Here” or provide a different path.
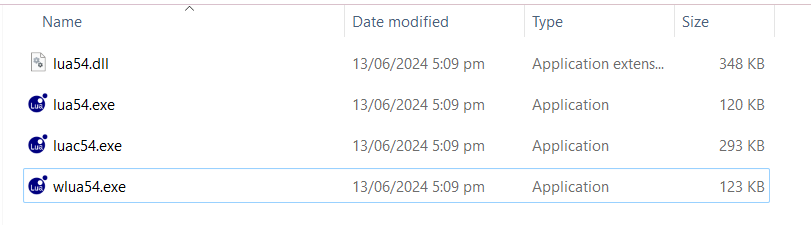
After extracting the archive, you should see four different files:
- lua54.dll: This is the Lua runtime library, which contains the Lua interpreter and is used by Lua scripts.
- lua54.exe: This is the Lua executable, which is used to run Lua scripts and is equivalent to the lua command.
- luac54.exe: This is the Lua compiler, which is used to compile Lua scripts into bytecode.
- wlua54.exe: This is the Lua wrapper, which is used to provide a Windows-specific interface to Lua.
These files are the core components of the Lua installation and are used to run Lua scripts, compile Lua code, and provide access to Lua’s functionality.
Explore the Blazing Fast Speed of Windows VPS!
With Ultahost, hosting a Windows VPS is simpler and faster than ever. Enjoy ultra-fast SSD NVMe speeds without any dropouts or slowdowns.
Step 3: Setting Up Environment Variables
Environment variables are important because they allow you to specify the location of the Lua executable and libraries. Here’s how to add Lua to the PATH environment variable:
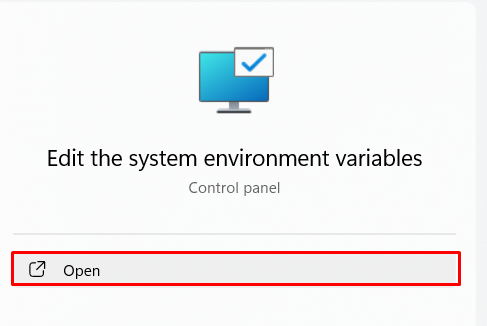
- Open Environment Variables Settings: Search for “environment variables” in the Windows search bar and select “Edit the system environment variables”.
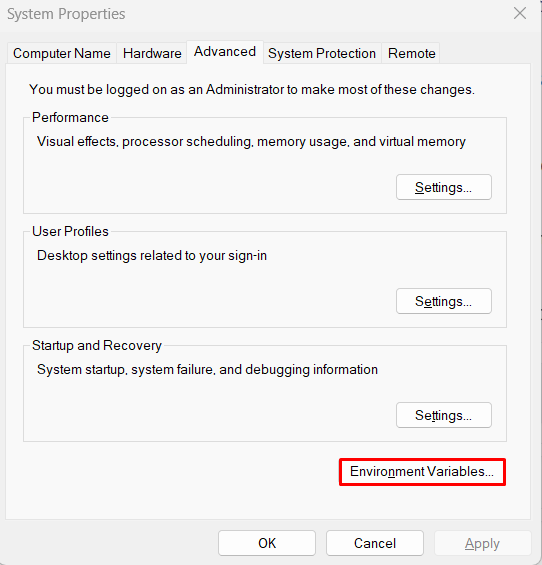
- Launch Environment Variables:In the “System Properties” window, click the “Environment Variables…” button:
- Add Lua to PATH: Now open the path, Click on “New” button and then add the full path to the bin folder inside the directory where you extracted Lua.
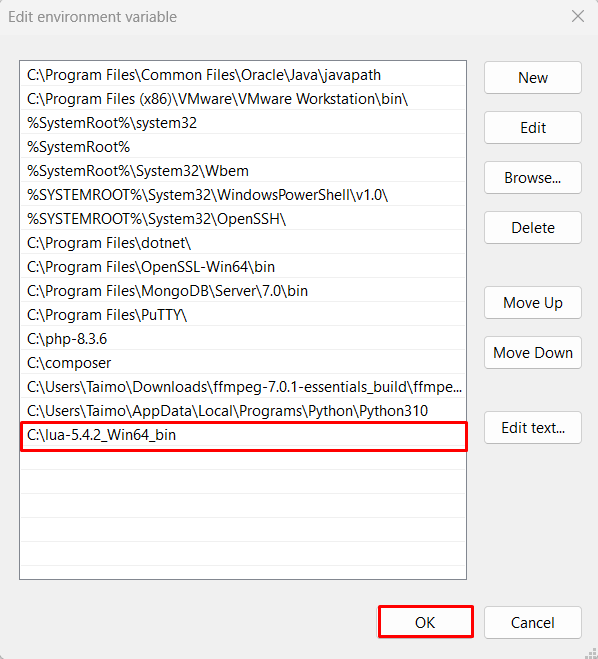
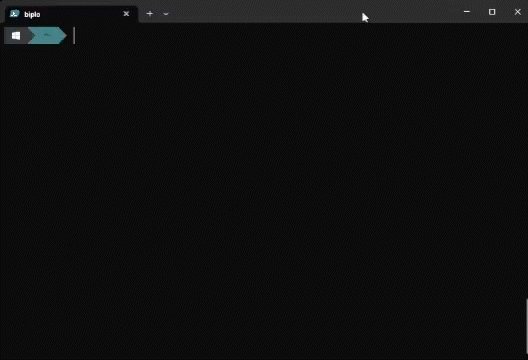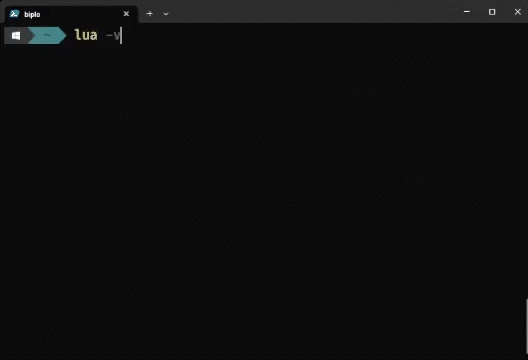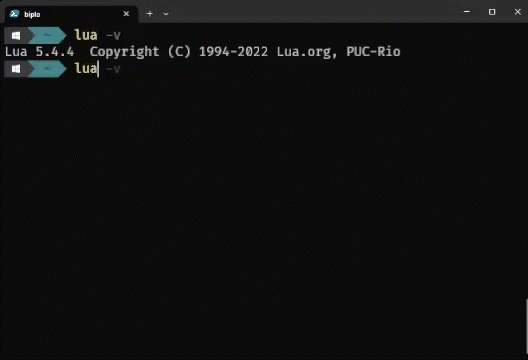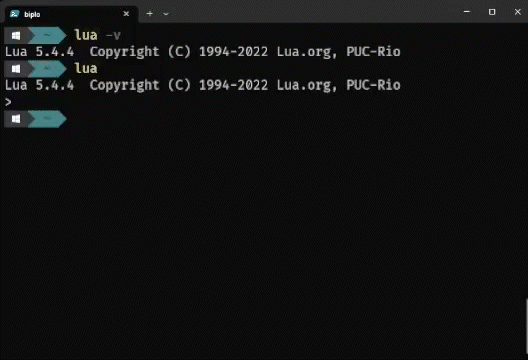
Step 4: Verifying the Lua Installation
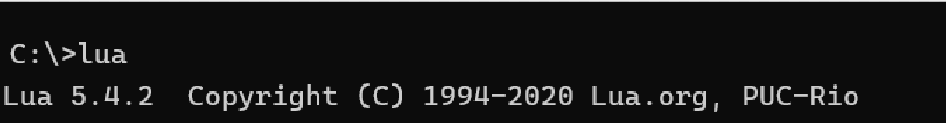
To verify that the Lua is installed correctly, follow these steps., open the Command Prompt and run the following command:
lua -v
Install Lua Windows provides access to a vast community of developers, plugins, and resources, allowing you to create complex projects and scripts with ease. With Lua, you can tap into the extensive documentation, tutorials, and example code provided by the Lua community, making it easier to learn and experiment with Lua.
Additionally, having Lua on Windows allows you to:
- Automate repetitive tasks and workflows
- Create custom game scripts and mods
- Build your own applications and games
- Access a vast library of plugins and resources
- Join a community of developers and learn from their experiences
Features of Lua
Lua is a powerful and versatile language that offers a range of features that make it an ideal choice for game development and scripting. Some of its key features include:
- Lightweight: Lua is a small and lightweight language that can be easily embedded into applications, making it perfect for games and simulations.
- Flexible: Lua is a dynamically-typed language that allows for flexible coding styles and rapid prototyping.
- Easy to Learn: Lua has a simple syntax and is easy to learn, even for developers without prior programming experience.
- Cross-Platform: Lua can run on a wide range of platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Advantages of Lua
Lua offers a range of advantages that make it a popular choice among developers and gamers. Some of its key advantages include:
- Fast Execution: Lua is a highly optimized language that executes code quickly and efficiently, making it perfect for games and simulations.
- Low Memory Footprint: Lua has a low memory footprint, making it ideal for applications that require minimal system resources.
- Extensive Libraries: Lua has a vast collection of libraries and frameworks that provide additional functionality and make it easier to develop complex applications.
- Dynamic Typing: Lua’s dynamic typing system allows for flexible coding styles and rapid prototyping, making it easier to experiment with new ideas and concepts.
- Coroutines: Lua’s coroutine system allows for efficient and lightweight cooperative multitasking, making it ideal for applications that require concurrent execution of tasks.
Conclusion
Lua, a lightweight programming language, has become a staple in game development and scripting due to its simplicity and adaptability. It allows developers to efficiently automate tasks, craft custom game logic, and build applications. Lua’s installation on Windows involves downloading the Lua binaries from LuaBinaries, extracting the archive, and setting up environment variables to ensure the system can locate Lua executables and libraries. This process grants access to a community of developers, a wealth of plugins, and a plethora of resources, enabling users to create sophisticated projects and scripts with ease.
Lua’s technical features include a lightweight design that facilitates embedding in applications, a flexible dynamically-typed syntax that supports rapid development, and an easy-to-learn structure accessible to new programmers. Lua’s advantages extend to its fast execution speed, minimal memory usage, and a comprehensive collection of libraries that enhance functionality. Its dynamic typing system and support for coroutines promote flexible coding and efficient multitasking, making it a preferred choice for complex applications and simulations.
Staying updated with new releases, features, best practices, and industry trends is crucial. Conduct thorough research to select a trusted platform that meets your technical needs. With Ultahost’s VDS hosting, you can effortlessly upgrade your resources as your requirements grow, all with just a few clicks.
FAQ
What is Lua?
Lua is a powerful, efficient, lightweight, embeddable scripting language. It is used for various purposes, including embedded systems, game development, and web applications.
What are prerequisites for installing Lua on Windows?
To install Lua on Windows, you will need:
- A Windows operating system (Windows 7, 8, 10, or later).
- Administrator privileges to install software.
- A command-line interface (CLI) like Command Prompt or PowerShell.
Where can I download Lua for Windows?
You can download Lua from the official Lua website: lua.org. Look for the latest Windows binaries provided in the download section.
How do I update Lua on Windows?
To update Lua, follow the same steps as the installation process. Download the latest version from the official website or use the package manager to update Lua.
Where can I find Lua documentation and resources?
- The official Lua website: lua.org
- Lua Reference Manual: Lua 5.4 Reference Manual
- Lua User’s Wiki: lua-users.org
To install Lua on Windows, download the LuaBinaries package from the official Lua website, extract it, and add the Lua folder to your system’s PATH environment variable for easy access to the command line interface.
Here’s a code snippet to check your Lua installation:
print("Hello, World!")
What You Need to Know Before Installing Lua
Understanding Lua Versions
Before diving into the installation process, it’s essential to understand the different versions of Lua. The latest stable release is generally recommended for beginners and most applications. While the development versions can offer additional features, they often contain bugs and are not recommended for production environments. For most users learning how to install Lua on Windows, sticking with the stable version is the best choice.
System Requirements
Lua is known for its lightweight nature, but it’s still wise to be aware of the system requirements.
- Minimum system requirements: Lua runs on almost any modern Windows system, including Windows 7 and later. Generally, if your machine runs Windows, it can run Lua.
- Recommended specifications: For optimal performance and to handle larger scripts efficiently, a system with at least 2GB of RAM and a dual-core processor is suggested.

How to Install Lua: A Simple Step-By-Step Guide
Option 1: Installing Lua Manually
Downloading Lua
To manually install Lua, you’ll first need to download the necessary binaries. Follow these steps:
- Navigate to the official Lua website at [lua.org](https://www.lua.org/download.html).
- Locate the section for the latest binary releases for Windows.
- Download the appropriate zip file that corresponds to your system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
After downloading the zip file, extract it to a directory of your choice, preferably `C:\Lua`.
Setting Up the Environment Variables
Setting up environment variables allows you to run Lua from any command prompt without needing to specify the full path to the Lua executable files. Here’s how to do it:
- Right-click on the This PC or Computer icon and select Properties.
- Click on Advanced System Settings and then the Environment Variables button.
- In the System variables section, find the variable named `Path`, select it, and click Edit.
- Click New and add the path to the directory where you extracted Lua (for example, `C:\Lua\bin`).
- Click OK to close all dialog boxes.
After this, you can verify the setup by opening Command Prompt and typing:
lua -v
This command should return the version number of Lua, confirming that the installation was successful.
Testing the Installation
To test if Lua was installed correctly, open a Command Prompt window and execute a simple Lua script. Type in and run:
print("Hello, Lua!")
If everything is set up correctly, you should see the output: Hello, Lua!
Option 2: Using a Package Manager (e.g., Chocolatey)
What is Chocolatey?
Chocolatey is a popular package manager for Windows that simplifies the installation and management of software. It offers a quick way to install Lua along with its dependencies, making it perfect for users seeking a streamlined experience.
Installing Chocolatey
Installing Chocolatey is a straightforward process. Open an Administrator Command Prompt and run the following command:
@"%SystemRoot%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))" && SET "PATH=%PATH%;%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\chocolatey\bin"
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Installing Lua with Chocolatey
Once Chocolatey is set up, installing Lua is as easy as typing a single command in the same Administrator Command Prompt:
choco install lua
After the installation completes, verify the installation as shown previously with the command:
lua -v
Option 3: Using LuaRocks
What is LuaRocks?
LuaRocks is a package manager for Lua modules, but it also assists in installing Lua itself, along with many useful libraries and dependencies. This can be a great option if you plan to work with various Lua modules.
Installing LuaRocks
To install LuaRocks on Windows, you should first have the basic Lua installed. The recommended way is to use the installer from the LuaRocks website. Once you’ve downloaded the installer, you need to follow these steps:
- Open Command Prompt as an Administrator.
- Navigate to the directory where the installer was downloaded using the `cd` command (for example, `cd Downloads`).
- Run the installer by typing:
luarocks-<version>.bat install
Replace `<version>` with the actual version number you downloaded.
Installing Lua through LuaRocks
After installing LuaRocks, you can install Lua simply by executing the following command:
luarocks install lua
This command takes care of everything required to set up Lua with LuaRocks on your system.

Install Lua on Ubuntu: A Simple Step-by-Step Guide
Common Installation Issues and Troubleshooting
Common Errors
Even with clear instructions, users may still encounter issues. Here are a few common errors and their solutions:
-
Error: ‘lua’ is not recognized as an internal or external command: This typically indicates that the environment variables haven’t been set properly. Retrace your steps to ensure the Lua path is included in the `Path` environment variable.
-
Error during Chocolatey installation: Ensure that you run the Command Prompt as an Administrator, as Chocolatey requires elevated privileges for installation.
Finding Help
If you encounter any issues beyond these common errors, ample resources are available. The official Lua documentation is a great starting point. You can also visit community forums such as the Lua mailing list or Stack Overflow for troubleshooting assistance.

lua Editor Windows: A Quick Start Guide
Conclusion
Now that you have explored multiple methods for how to install Lua on Windows, you can confidently choose the one that best fits your needs. Each method has its benefits and nuances, so feel free to experiment with them. With Lua successfully installed, you are well on your way to beginning an exciting journey in programming!

How to Learn Lua for Roblox: A Quick Guide
Additional Resources
For further reading, don’t hesitate to consult the official Lua documentation, which is rich with examples and explanations. Additionally, consider looking into recommended books and online courses that can enhance your understanding of Lua programming, as well as community support forums where you can connect with fellow learners.
Last Updated :
26 Mar, 2025
Lua is a lightweight and flexible scripting language that is easy to integrate into applications. It is commonly used in game development, web applications, and embedded systems. Lua can be extended with C or C++, making it a powerful tool for developers.
To start writing and executing Lua scripts, it’s important to understand how to set up the Lua environment. In this article, we’ll show you how to set it up, explain how it works, and help you get started with Lua development.
Setting Up the Lua Environment
You can install Lua in multiple ways depending on your platform:
Installing Lua on Windows
To install Lua on Windows:
- Download Lua: Go to Lua for Windows and download the installer.
- Install Lua: Run the installer and follow the steps.
- Add to Path: Make sure the path to lua.exe (the Lua interpreter) is added to your system’s PATH. This allows you to run Lua from the command line.
After installation, you can verify by running:
lua -v
Installing Lua on macOS
- Install using Homebrew:
brew install lua
- Verify by running:
lua -v
Installing Lua on Linux
- Use the package manager to install Lua:
sudo apt install lua5.4 # For Ubuntu/Debian
sudo yum install lua # For CentOS/RHEL
- Verify by running:
lua -v
Running Lua Code
There are two main ways to run Lua code: Interactive Mode (REPL) and Script Mode.
1. Interactive Mode (REPL)
The REPL (Read-Eval-Print Loop) mode allows you to execute Lua code line-by-line interactively:
- Open the command line and type:
lua
- This will open a Lua prompt where you can type and execute Lua code one line at a time.
print("Hello, Lua!")
2. Script Mode
In script mode, you create a Lua script file (e.g., hello.lua) and run it from the command line.
- Create a Lua file: Open any text editor and write a simple Lua script:
print("Hello from Lua!")
- Run the script: In the terminal, execute the script by running:
lua hello.lua
Lua Libraries
Lua includes several built-in libraries that are very helpful for development:
- math: Provides functions like sqrt(), sin(), cos(), etc.
- string: Offers functions to manipulate strings (e.g., string.sub()).
- table: Contains functions for working with tables (arrays, dictionaries).
- io: Used for reading and writing files.
- os: Interacts with the operating system (e.g., to get the current time).
Installing Lua Modules with LuaRocks
To extend Lua’s functionality, you can use LuaRocks, which is the package manager for Lua. Here’s how you can install it and use it to add Lua modules:
1. Install LuaRocks:
- On macOS:
brew install luarocks
- On Ubuntu:
sudo apt install luarocks
- For Windows: Download and install LuaRocks from the official LuaRocks website.
2. Install a Lua Module
To install a Lua module using LuaRocks, such as luasocket (a module for networking), run:
luarocks install luasocket
Lua Compiler and Interpreter
While Lua is generally interpreted (i.e., it runs line-by-line), there is also a Lua compiler that can compile Lua code into bytecode for faster execution. This is useful for optimizing performance in certain applications.
- Interpreter: Executes Lua code directly, making it great for testing small scripts.
- Compiler: You can use the luac command to compile Lua code into bytecode, which runs faster than interpreted code.
Compiling Lua Code:
You can compile Lua code into bytecode by running the following command:
luac -o output.luac hello.lua
To execute the compiled bytecode:
lua output.luac
Lua IDEs
Using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) or a text editor makes writing and debugging Lua code easier. Some popular options for Lua development include:
- ZeroBrane Studio: A lightweight Lua IDE with debugging support.
- IntelliJ IDEA (with Lua Plugin): A popular Java IDE that supports Lua through plugins.
- SciTE: A simple, lightweight text editor that supports Lua syntax highlighting and allows you to run Lua scripts directly.
Using SciTE for Lua
SciTE is a simple and effective text editor for Lua development. It allows you to write, run, and debug Lua code efficiently.
1. Steps to Set Up SciTE for Lua:
Download and Install SciTE: Download SciTE from the SciTE website and install it.
2. Configure SciTE for Lua:
- Open SciTE and go to Tools > Open User Options File.
- Add the following lines to associate .lua files with the Lua interpreter:
command.go.$lua="lua.exe $(FileName)"
command.save.$lua=SaveAll
3. Run Lua Code:
- Open a .lua file in SciTE.
- Press F5 or go to Tools > Go to run the Lua code..
Simple Lua Program Example
Here is a basic example of a Lua program that defines a function and performs a simple operation:
XML
function add(a, b) return a + b end local num1 = 10 local num2 = 20 local result = add(num1, num2) print("The sum of " .. num1 .. " and " .. num2 .. " is: " .. result)
Output
In this code
- Function Definition: The add(a, b) function takes two parameters, a and b, and returns their sum.
- Variable Declaration: num1 is assigned the value 10, and num2 is assigned the value 20.
- Function Call: The function add(num1, num2) is called, passing num1 and num2 as arguments, and the result is stored in the result variable.
- Lua? Why?
- Prerequisites
- Cygwin
- Install Lua
- Building Lua from source
- Download & Extract Lua Source Code
- Generate a build script
- Finishing up
Lua? Why?
It’s been a while since I transitioned back to Windows (w11 specifically.) Since I possess only a single computer right now, I needed it to be able to do everything, which is mainly coding and music production. Since Windows has become a good all-rounder of an OS right now, making the switch back seems a no-brainer. Bonus points for increased battery life.
Having moved to windows, I missed Vim. I installed NeoVim to work with, but to write custom config files Lua was necessary.
Unfortunately, there is no direct binary to install. We need to build Lua from source.
Fortunately, there is good documentation available for that.
Prerequisites
- 7zip (or any other equivalent)
- C/C++ Compiler (eg: gcc)
- Make (eg: GNUMake, mingw32-make)
Cygwin
Cygwin has a large collection of GNU and Open Source tools which provide functionality similar to a Linux distribution on Windows.
Naturally, we can install gcc and make in Cygwin easily.
Download and Run the setup program, and add packages by searching and installing them.
Install Lua
There is not binary for windows, so Lua needs to be built from source.
Building Lua from source
In the official documentation for building Lua on Windows they’re using the TDM-GCC compiler.
Cygwin is already installed with gcc and make so there is no need for TDM-GCC.
Download source from the official website and extract it at C:\lua directory. Use 7zip.
Generate a build script
Using the official build script as the base, let’s modify the paths for gcc and make to the paths inside the Cygwin packages.
@echo off
:: ========================
:: file build.cmd
:: ========================
setlocal
:: you may change the following variable's value
:: to suit the downloaded version
set lua_version=5.4.4
set work_dir=%~dp0
:: Removes trailing backslash
:: to enhance readability in the following steps
set work_dir=%work_dir:~0,-1%
set lua_install_dir=%work_dir%\lua
set compiler_bin_dir=C:\cygwin64\bin\gcc.exe
set lua_build_dir=%work_dir%\lua-%lua_version%
set path=%compiler_bin_dir%;%path%
cd /D %lua_build_dir%
C:\cygwin64\bin\make.exe PLAT=mingw
echo.
echo **** COMPILATION TERMINATED ****
echo.
echo **** BUILDING BINARY DISTRIBUTION ****
echo.
:: create a clean "binary" installation
mkdir %lua_install_dir%
mkdir %lua_install_dir%\doc
mkdir %lua_install_dir%\bin
mkdir %lua_install_dir%\include
copy %lua_build_dir%\doc\*.* %lua_install_dir%\doc\*.*
copy %lua_build_dir%\src\*.exe %lua_install_dir%\bin\*.*
copy %lua_build_dir%\src\*.dll %lua_install_dir%\bin\*.*
copy %lua_build_dir%\src\luaconf.h %lua_install_dir%\include\*.*
copy %lua_build_dir%\src\lua.h %lua_install_dir%\include\*.*
copy %lua_build_dir%\src\lualib.h %lua_install_dir%\include\*.*
copy %lua_build_dir%\src\lauxlib.h %lua_install_dir%\include\*.*
copy %lua_build_dir%\src\lua.hpp %lua_install_dir%\include\*.*
echo.
echo **** BINARY DISTRIBUTION BUILT ****
echo.
%lua_install_dir%\bin\lua.exe -e"print [[Hello!]];print[[Simple Lua test successful!!!]]"
echo.
pause
Take care to put the correct Cygwin paths for gcc and make in the above lines:
set compiler_bin_dir=C:\cygwin64\bin\gcc.exe
C:\cygwin64\bin\make.exe PLAT=mingw
Save as build.cmd inside C:\lua and run. This will build Lua.
Finishing up
The build should be complete without any issues. After the build is done, add C:\lua\bin to the path.
Logout & Login for the env variables to take effect.
Test if lua is working.
Next is to setup NeoVim to my taste.
